A Brief Narrative Review of the Underlying Mechanisms Whereby Omega-3 Fatty Acids May Influence Skeletal Muscle: From Cell Culture to Human Interventions
Abstract
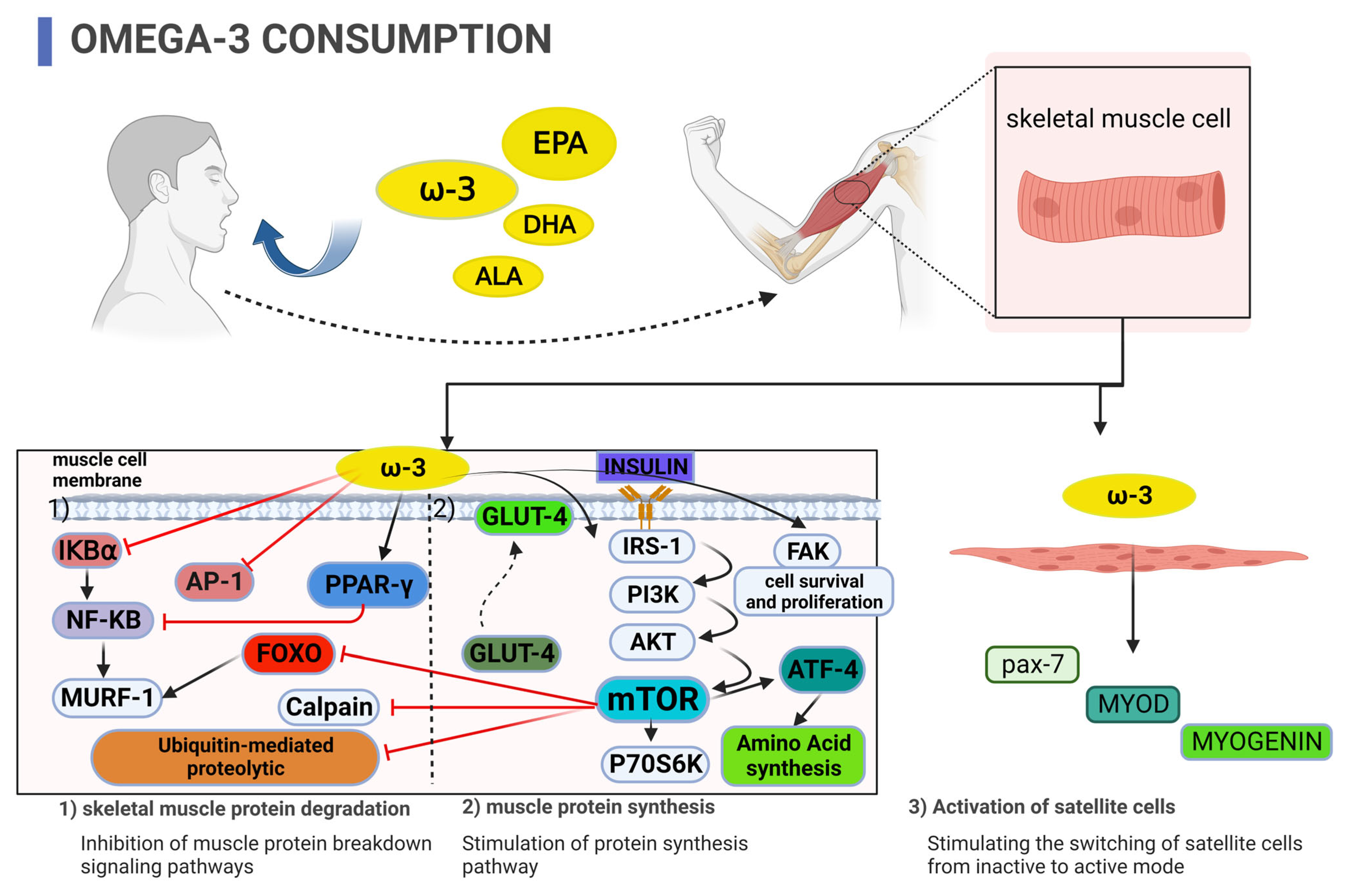
:1. Introduction
2. Cell Culture Studies
3. Animal Studies
4. Human Studies
5. Future Directions for Research
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dent, E.; Daly, R.M.; Hoogendijk, E.O.; Scott, D. Exercise to Prevent and Manage Frailty and Fragility Fractures. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2023, 21, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuck, A.K.; Tsai, L.-T.; Freystaetter, G.; Vellas, B.; Kanis, J.A.; Rizzoli, R.; Kressig, K.S.; Armbrecht, G.; Da Silva, J.A.P.; Dawson-Hughes, B.; et al. Comparing Prevalence of Sarcopenia Using Twelve Sarcopenia Definitions in a Large Multinational European Population of Community-Dwelling Older Adults. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2023, 27, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, H.E.; Michie, K.L.; Gries, K.J.; Zhang, X.; Ryan, Z.C.; Lanza, I.R. A Randomized Trial of the Effects of Dietary N3-PUFAs on Skeletal Muscle Function and Acute Exercise Response in Healthy Older Adults. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simopoulos, A.P. An Increase in the Omega-6/Omega-3 Fatty Acid Ratio Increases the Risk for Obesity. Nutrients 2016, 8, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liput, K.P.; Lepczyński, A.; Ogłuszka, M.; Nawrocka, A.; Poławska, E.; Grzesiak, A.; Ślaska, B.; Pareek, C.S.; Czarnik, U.; Pierzchała, M. Effects of Dietary N-3 and n-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Inflammation and Cancerogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Li, M.; Chang, M.; Liu, R.; Qiu, J.; Wang, K.; Deng, C.; Shen, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wang, W.; et al. Inflammation: Roles in Skeletal Muscle Atrophy. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateș, L.; Popa, D.-S.; Rusu, M.E.; Fizeșan, I.; Leucuța, D. Walnut Intake Interventions Targeting Biomarkers of Metabolic Syndrome and Inflammation in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jannas-Vela, S.; Espinosa, A.; Candia, A.A.; Flores-Opazo, M.; Peñailillo, L.; Valenzuela, R. The Role of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Their Lipid Mediators on Skeletal Muscle Regeneration: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Seoane, J.; Jiménez, S.L.; Del Coso, J.; Pareja-Galeano, H. Muscle Hypertrophy Induced by N-3 PUFA Supplementation in Absence of Exercise: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGlory, C.; Calder, P.C.; Nunes, E.A. The Influence of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Skeletal Muscle Protein Turnover in Health, Disuse, and Disease. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tachtsis, B.; Camera, D.; Lacham-Kaplan, O. Potential Roles of N-3 PUFAs during Skeletal Muscle Growth and Regeneration. Nutrients 2018, 10, E309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhullar, A.S.; Putman, C.T.; Mazurak, V.C. Potential Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on the Myogenic Program of Satellite Cells. Nutr. Metab. Insights 2016, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.-W.; Yu, K.; Shyh-Chang, N.; Li, G.-X.; Jiang, L.-J.; Yu, S.-L.; Xu, L.-Y.; Liu, R.-J.; Guo, Z.-J.; Xie, H.-Y.; et al. Circulating Factors Associated with Sarcopenia during Ageing and after Intensive Lifestyle Intervention. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019, 10, 586–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, Q.; Zheng, P.; Zhang, J.; Huang, F. DHA Inhibits Protein Degradation More Efficiently than EPA by Regulating the PPARγ/NFκB Pathway in C2C12 Myotubes. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 318981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, F.; Wei, H.; Luo, H.; Jiang, S.; Peng, J. EPA Inhibits the Inhibitor of ΚBα (IκBα)/NF-ΚB/Muscle RING Finger 1 Pathway in C2C12 Myotubes in a PPARγ-Dependent Manner. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 105, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Magee, P.; Pearson, S.; Allen, J. The Omega-3 Fatty Acid, Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA), Prevents the Damaging Effects of Tumour Necrosis Factor (TNF)-Alpha during Murine Skeletal Muscle Cell Differentiation. Lipids Health Dis. 2008, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magee, P.; Pearson, S.; Whittingham-Dowd, J.; Allen, J. PPARγ as a Molecular Target of EPA Anti-Inflammatory Activity during TNF-α-Impaired Skeletal Muscle Cell Differentiation. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 1440–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmagid, S.A.; Clarke, S.E.; Nielsen, D.E.; Badawi, A.; El-Sohemy, A.; Mutch, D.M.; Ma, D.W.L. Comprehensive Profiling of Plasma Fatty Acid Concentrations in Young Healthy Canadian Adults. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chevalier, L.; Plourde, M. Comparison of Pharmacokinetics of Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplements in Monoacylglycerol or Ethyl Ester in Humans: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 75, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfour, H.A.; Allouh, M.Z.; Said, R.S. Myogenic Regulatory Factors: The Orchestrators of Myogenesis after 30 Years of Discovery. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 243, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Hernández, J.M.; García-González, E.G.; Brun, C.E.; Rudnicki, M.A. The Myogenic Regulatory Factors, Determinants of Muscle Development, Cell Identity and Regeneration. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 72, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, A.; Sharples, A.P.; Al-Shanti, N.; Stewart, C.E. Omega-3 Fatty Acid EPA Improves Regenerative Capacity of Mouse Skeletal Muscle Cells Exposed to Saturated Fat and Inflammation. Biogerontology 2017, 18, 109–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bryner, R.W.; Woodworth-Hobbs, M.E.; Williamson, D.L.; Alway, S.E. Docosahexaenoic Acid Protects Muscle Cells from Palmitate-Induced Atrophy. ISRN Obes. 2012, 2012, 647348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kadri, L.; Bacle, A.; Khoury, S.; Vandebrouck, C.; Bescond, J.; Faivre, J.-F.; Ferreira, T.; Sebille, S. Polyunsaturated Phospholipids Increase Cell Resilience to Mechanical Constraints. Cells 2021, 10, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.-K.; Deng, Z.; Jiang, S.-Z.; Song, T.-X.; Zhou, Y.-F.; Peng, J.; Tao, Y.-X. Eicosapentaenoic Acid Abolishes Inhibition of Insulin-Induced MTOR Phosphorylation by LPS via PTP1B Downregulation in Skeletal Muscle. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2017, 439, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodworth-Hobbs, M.E.; Hudson, M.B.; Rahnert, J.A.; Zheng, B.; Franch, H.A.; Price, S.R. Docosahexaenoic Acid Prevents Palmitate-Induced Activation of Proteolytic Systems in C2C12 Myotubes. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kamolrat, T.; Gray, S.R. The Effect of Eicosapentaenoic and Docosahexaenoic Acid on Protein Synthesis and Breakdown in Murine C2C12 Myotubes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 432, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- JafariNasabian, P.; Inglis, J.E.; Reilly, W.; Kelly, O.J.; Ilich, J.Z. Aging Human Body: Changes in Bone, Muscle and Body Fat with Consequent Changes in Nutrient Intake. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 234, R37–R51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fonte-Faria, T.; Citelli, M.; Atella, G.C.; Raposo, H.F.; Zago, L.; de Souza, T.; da Silva, S.V.; Barja-Fidalgo, C. Chia Oil Supplementation Changes Body Composition and Activates Insulin Signaling Cascade in Skeletal Muscle Tissue of Obese Animals. Nutrition 2019, 58, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, M.-S. The Role of Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (MTOR) in Insulin Signaling. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, V.; Marinho, R.; Vitorino, D.; Santos, G.A.; Moraes, J.C.; Dragano, N.; Sartori-Cintra, A.; Pereira, L.; Catharino, R.R.; da Silva, A.S.R.; et al. Diets Containing α-Linolenic (Ω3) or Oleic (Ω9) Fatty Acids Rescues Obese Mice From Insulin Resistance. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 4033–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaco, C.M.F.; Proudfoot, R.; Miotto, P.M.; Herbst, E.A.F.; MacPherson, R.E.K.; Holloway, G.P. α-Linolenic Acid Supplementation Prevents Exercise-Induced Improvements in White Adipose Tissue Mitochondrial Bioenergetics and Whole-Body Glucose Homeostasis in Obese Zucker Rats. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antuña, E.; Cachán-Vega, C.; Bermejo-Millo, J.C.; Potes, Y.; Caballero, B.; Vega-Naredo, I.; Coto-Montes, A.; Garcia-Gonzalez, C. Inflammaging: Implications in Sarcopenia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamolrat, T.; Gray, S.R.; Thivierge, M.C. Fish Oil Positively Regulates Anabolic Signalling alongside an Increase in Whole-Body Gluconeogenesis in Ageing Skeletal Muscle. Eur. J. Nutr. 2013, 52, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voulgaridou, G.; Papadopoulou, S.D.; Spanoudaki, M.; Kondyli, F.S.; Alexandropoulou, I.; Michailidou, S.; Zarogoulidis, P.; Matthaios, D.; Giannakidis, D.; Romanidou, M.; et al. Increasing Muscle Mass in Elders through Diet and Exercise: A Literature Review of Recent RCTs. Foods 2023, 12, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gortan Cappellari, G.; Semolic, A.; Ruozi, G.; Barbetta, D.; Bortolotti, F.; Vinci, P.; Zanetti, M.; Mak, R.H.; Garibotto, G.; Giacca, M.; et al. N-3 PUFA Dietary Lipid Replacement Normalizes Muscle Mitochondrial Function and Oxidative Stress through Enhanced Tissue Mitophagy and Protects from Muscle Wasting in Experimental Kidney Disease. Metabolism 2022, 133, 155242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhedhairi, S.A.; Aba Alkhayl, F.F.; Ismail, A.D.; Rozendaal, A.; German, M.; MacLean, B.; Johnston, L.; Miller, A.A.; Hunter, A.M.; Macgregor, L.J.; et al. The Effect of Krill Oil Supplementation on Skeletal Muscle Function and Size in Older Adults: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 1228–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolland, Y.; de Souto Barreto, P.; Maltais, M.; Guyonnet, S.; Cantet, C.; Andrieu, S.; Vellas, B. Effect of Long-Term Omega 3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation with or without Multidomain Lifestyle Intervention on Muscle Strength in Older Adults: Secondary Analysis of the Multidomain Alzheimer Preventive Trial (MAPT). Nutrients 2019, 11, 1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bostock, E.L.; Morse, C.I.; Winwood, K.; McEwan, I.M.; Onambélé, G.L. Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Vitamin D in Immobilisation: Part A- Modulation of Appendicular Mass Content, Composition and Structure. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2017, 21, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krzymińska-Siemaszko, R.; Czepulis, N.; Lewandowicz, M.; Zasadzka, E.; Suwalska, A.; Witowski, J.; Wieczorowska-Tobis, K. The Effect of a 12-Week Omega-3 Supplementation on Body Composition, Muscle Strength and Physical Performance in Elderly Individuals with Decreased Muscle Mass. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 10558–10574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Logan, S.L.; Spriet, L.L. Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation for 12 Weeks Increases Resting and Exercise Metabolic Rate in Healthy Community-Dwelling Older Females. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, G.I.; Julliand, S.; Reeds, D.N.; Sinacore, D.R.; Klein, S.; Mittendorfer, B. Fish Oil–Derived N−3 PUFA Therapy Increases Muscle Mass and Function in Healthy Older Adults1. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hutchins-Wiese, H.L.; Kleppinger, A.; Annis, K.; Liva, E.; Lammi-Keefe, C.J.; Durham, H.A.; Kenny, A.M. The impact of supplemental n-3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids and dietary antioxidants on physical performance in postmenopausal women. J. Nutr. 2013, 17, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noreen, E.E.; Sass, M.J.; Crowe, M.L.; Pabon, V.A.; Brandauer, J.; Averill, L.K. Effects of Supplemental Fish Oil on Resting Metabolic Rate, Body Composition, and Salivary Cortisol in Healthy Adults. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2010, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cornish, S.M.; Myrie, S.B.; Bugera, E.M.; Chase, J.E.; Turczyn, D.; Pinder, M. Omega-3 Supplementation with Resistance Training Does Not Improve Body Composition or Lower Biomarkers of Inflammation More so than Resistance Training Alone in Older Men. Nutr. Res. 2018, 60, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornish, S.M.; Chilibeck, P.D. Alpha-Linolenic Acid Supplementation and Resistance Training in Older Adults. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. Physiol. Appl. Nutr. Metab. 2009, 34, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriakidou, Y.; Wood, C.; Ferrier, C.; Dolci, A.; Elliott, B. The Effect of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation on Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2021, 18, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haß, U.; Kochlik, B.; Herpich, C.; Rudloff, S.; Norman, K. Effects of an Omega-3 Supplemented, High-Protein Diet in Combination with Vibration and Resistance Exercise on Muscle Power and Inflammation in Old Adults: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Marco Castro, E.; Kampschulte, N.; Murphy, C.H.; Schebb, N.H.; Roche, H.M. Oxylipin Status, before and after LC n-3 PUFA Supplementation, Has Little Relationship with Skeletal Muscle Biology in Older Adults at Risk of Sarcopenia. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 2023, 189, 102531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGlory, C.; Gorissen, S.H.M.; Kamal, M.; Bahniwal, R.; Hector, A.J.; Baker, S.K.; Chabowski, A.; Phillips, S.M. Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation Attenuates Skeletal Muscle Disuse Atrophy during Two Weeks of Unilateral Leg Immobilization in Healthy Young Women. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2019, 33, 4586–4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, J.; Smith, G.I.; Kelly, S.C.; Julliand, S.; Reeds, D.N.; Mittendorfer, B. Effect of Dietary N-3 PUFA Supplementation on the Muscle Transcriptome in Older Adults. Physiol. Rep. 2016, 4, e12785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGlory, C.; Galloway, S.D.R.; Hamilton, D.L.; McClintock, C.; Breen, L.; Dick, J.R.; Bell, J.G.; Tipton, K.D. Temporal Changes in Human Skeletal Muscle and Blood Lipid Composition with Fish Oil Supplementation. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 2014, 90, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.I.; Atherton, P.; Reeds, D.N.; Mohammed, B.S.; Rankin, D.; Rennie, M.J.; Mittendorfer, B. Dietary Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation Increases the Rate of Muscle Protein Synthesis in Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial123. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, G.I.; Atherton, P.; Reeds, D.N.; Mohammed, B.S.; Rankin, D.; Rennie, M.J.; Mittendorfer, B. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Augment the Muscle Protein Anabolic Response to Hyperinsulinaemia-Hyperaminoacidaemia in Healthy Young and Middle-Aged Men and Women. Clin. Sci. 2011, 121, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heileson, J.L.; Machek, S.B.; Harris, D.R.; Tomek, S.; de Souza, L.C.; Kieffer, A.J.; Barringer, N.D.; Gallucci, A.; Forsse, J.S.; Funderburk, L.K. The Effect of Fish Oil Supplementation on Resistance Training-Induced Adaptations. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2023, 20, 2174704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, Y.; Ueda, H.; Yanagimoto, K.; Kato, A.; Ochi, E. 4-Week Eicosapentaenoic Acid-Rich Fish Oil Supplementation Partially Protects Muscular Damage Following Eccentric Contractions. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2021, 18, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barquilha, G.; Dos Santos, C.M.M.; Caçula, K.G.; Santos, V.C.; Polotow, T.G.; Vasconcellos, C.V.; Gomes-Santos, J.A.F.; Rodrigues, L.E.; Lambertucci, R.H.; Serdan, T.D.A.; et al. Fish Oil Supplementation Improves the Repeated-Bout Effect and Redox Balance in 20-30-Year-Old Men Submitted to Strength Training. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, Y.; Chang, E. Increased Intake of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Is Associated with Reduced Odds of Low Hand Grip Strength in Korean Adults. Nutrients 2023, 15, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, P.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jiao, J. Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Intake, Omega-6/Omega-3 Ratio and Mortality: Findings from Two Independent Nationwide Cohorts. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brook, M.S.; Din, U.; Tarum, J.; Selby, A.; Quinlan, J.; Bass, J.J.; Gharahdaghi, N.; Boereboom, C.; Abdulla, H.; Franchi, M.V.; et al. Omega-3 Supplementation during Unilateral Resistance Exercise Training in Older Women: A within Subject and Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 46, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Boit, M.; Sibson, R.; Sivasubramaniam, S.; Meakin, J.R.; Greig, C.A.; Aspden, R.M.; Thies, F.; Jeromson, S.; Hamilton, D.L.; Speakman, J.R.; et al. Sex Differences in the Effect of Fish-Oil Supplementation on the Adaptive Response to Resistance Exercise Training in Older People: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Daďová, K.; Petr, M.; Šteffl, M.; Sontáková, L.; Chlumský, M.; Matouš, M.; Štich, V.; Štěpán, M.; Šiklová, M. Effect of Calanus Oil Supplementation and 16 Week Exercise Program on Selected Fitness Parameters in Older Women. Nutrients 2020, 12, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalle, S.; Van Roie, E.; Hiroux, C.; Vanmunster, M.; Coudyzer, W.; Suhr, F.; Bogaerts, S.; Van Thienen, R.; Koppo, K. Omega-3 Supplementation Improves Isometric Strength But Not Muscle Anabolic and Catabolic Signaling in Response to Resistance Exercise in Healthy Older Adults. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2021, 76, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Félix-Soriano, E.; Martínez-Gayo, A.; Cobo, M.J.; Pérez-Chávez, A.; Ibáñez-Santos, J.; Palacios Samper, N.; Goikoetxea Galarza, I.; Cuervo, M.; García-Unciti, M.; González-Muniesa, P.; et al. Effects of DHA-Rich n-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation and/or Resistance Training on Body Composition and Cardiometabolic Biomarkers in Overweight and Obese Post-Menopausal Women. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-R.; Jo, E.; Khamoui, A.V. Chronic Fish Oil Consumption with Resistance Training Improves Grip Strength, Physical Function, and Blood Pressure in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. Sports 2019, 7, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodacki, C.L.; Rodacki, A.L.; Pereira, G.; Naliwaiko, K.; Coelho, I.; Pequito, D.; Fernandes, L.C. Fish-Oil Supplementation Enhances the Effects of Strength Training in Elderly Women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Štěpán, M.; Daďová, K.; Matouš, M.; Krauzová, E.; Sontáková, L.; Koc, M.; Larsen, T.; Kuda, O.; Štich, V.; Rossmeislová, L.; et al. Exercise Training Combined with Calanus Oil Supplementation Improves the Central Cardiodynamic Function in Older Women. Nutrients 2021, 14, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Chiu, W.-C.; Hsu, Y.-P.; Lo, Y.-L.; Wang, Y.-H. Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Muscle Mass, Muscle Strength and Muscle Performance among the Elderly: A Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornish, S.M.; Cordingley, D.M.; Shaw, K.A.; Forbes, S.C.; Leonhardt, T.; Bristol, A.; Candow, D.G.; Chilibeck, P.D. Effects of Omega-3 Supplementation Alone and Combined with Resistance Exercise on Skeletal Muscle in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santo André, H.C.; Esteves, G.P.; Barreto, G.H.C.; Longhini, F.; Dolan, E.; Benatti, F.B. The Influence of N-3PUFA Supplementation on Muscle Strength, Mass, and Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Adv. Nutr. 2023, 14, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossato, L.T.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; de Oliveira, E.P. Is There Sufficient Evidence to Supplement Omega-3 Fatty Acids to Increase Muscle Mass and Strength in Young and Older Adults? Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupont, J.; Dedeyne, L.; Dalle, S.; Koppo, K.; Gielen, E. The Role of Omega-3 in the Prevention and Treatment of Sarcopenia. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 31, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gray, S.R.; Mittendorfer, B. Fish Oil-Derived n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids for the Prevention and Treatment of Sarcopenia. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2018, 21, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaput, J.-P.; Janssen, I.; Sampasa-Kanyinga, H.; Tomkinson, G.; Lang, J.J. Economic Burden of Low Muscle Strength in Canadian Adults. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. Physiol. Appl. Nutr. Metab. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taheri, M.; Chilibeck, P.D.; Cornish, S.M. A Brief Narrative Review of the Underlying Mechanisms Whereby Omega-3 Fatty Acids May Influence Skeletal Muscle: From Cell Culture to Human Interventions. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2926. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15132926
Taheri M, Chilibeck PD, Cornish SM. A Brief Narrative Review of the Underlying Mechanisms Whereby Omega-3 Fatty Acids May Influence Skeletal Muscle: From Cell Culture to Human Interventions. Nutrients. 2023; 15(13):2926. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15132926
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaheri, Maryam, Philip D. Chilibeck, and Stephen M. Cornish. 2023. "A Brief Narrative Review of the Underlying Mechanisms Whereby Omega-3 Fatty Acids May Influence Skeletal Muscle: From Cell Culture to Human Interventions" Nutrients 15, no. 13: 2926. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15132926
APA StyleTaheri, M., Chilibeck, P. D., & Cornish, S. M. (2023). A Brief Narrative Review of the Underlying Mechanisms Whereby Omega-3 Fatty Acids May Influence Skeletal Muscle: From Cell Culture to Human Interventions. Nutrients, 15(13), 2926. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15132926






