An Evaluation of Food and Nutrient Intake among Pregnant Women in The Netherlands: A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Screening and Extraction
2.3. Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Dietary Pattern
3.1.1. Fruits and Vegetables
3.1.2. Fish
3.1.3. Alcohol
3.1.4. Legumes, Caffeine, Fats and Oils, and Sugary Drinks
3.1.5. Nuts, Wholemeal Products, and Meat
3.2. Nutrient Intake, Status, and Food Supplement Use
3.2.1. Protein intake
3.2.2. Folic Acid
3.2.3. Vitamin B12
3.2.4. Calcium
3.2.5. Vitamin A, Riboflavin, Niacin, and Vitamin B6
3.2.6. Vitamin D
3.2.7. Iron
3.2.8. Vitamin C, Iron, and Magnesium
3.2.9. Vitamin K1, Iodine, Potassium, Copper, or Zinc
3.2.10. Multivitamin Supplements
4. Discussion
4.1. Previous Research
4.2. Supplement Use
4.3. Quality of the Data
4.4. Strengths and Limitations
4.5. Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| No. | Query |
|---|---|
| #41 | #40 AND (‘article’/it OR ‘article in press’/it OR ‘editorial’/it OR ‘letter’/it OR ‘note’/it OR ‘review’/it) |
| #40 | #39 AND [humans]/lim AND (2008–2017)/py |
| #39 | #6 AND #30 AND #38 |
| #38 | #31 OR #32 OR #33 OR #34 OR #35 OR #36 OR #37 |
| #37 | ‘food frequency questionnaire’/exp |
| #36 | ‘nutritional assessment’/exp |
| #35 | ‘nutritional deficiency’/exp |
| #34 | ‘nutritional status’/exp |
| #33 | ‘maternal nutrition’/exp |
| #32 | ‘dietary intake’/exp |
| #31 | ‘child nutrition’/exp |
| #30 | #20 NOT #29 |
| #29 | #24 OR #28 |
| #28 | #25 OR #26 OR #27 |
| #27 | hospitalized:ti,ab |
| #26 | ‘patient*’:ti,ab |
| #25 | ‘patient’/exp |
| #24 | #21 OR #22 OR #23 |
| #23 | preterm:ti,ab |
| #22 | ‘premature labor’/exp |
| #21 | ‘prematurity’/exp |
| #20 | #11 OR #16 OR #19 |
| #19 | #17 OR #18 |
| #18 | ‘pregnancy’/exp |
| #17 | ‘pregnant woman’/exp |
| #16 | #12 OR #13 OR #14 OR #15 |
| #15 | ‘fetus’/exp |
| #14 | ‘embryo’/exp |
| #13 | ‘perinatal period’/exp |
| #12 | ‘prenatal period’/exp |
| #11 | #7 OR #8 OR #9 OR #10 |
| #10 | ‘child care’/exp |
| #9 | ‘preschool child’/exp |
| #8 | ‘toddler’/exp |
| #7 | ‘infant’/exp |
| #6 | #1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4 OR #5 |
| #5 | dutch:ti,ab |
| #4 | ‘dutchman’/exp |
| #3 | ‘netherlands’:ca |
| #2 | ‘netherlands’:ti,ab |
| #1 | ‘netherlands’/exp |
| No. | Query |
|---|---|
| #29 | #28 AND ([adult]/lim OR [young adult]/lim) |
| #28 | #23 NOT #27 |
| #27 | #24 OR #25 OR #26 |
| #26 | ‘older individual*’:ti,ab |
| #25 | ‘elderly’:ti,ab |
| #24 | ‘older adult*’:ti,ab |
| #23 | #22 AND (‘article’/it OR ‘article in press’/it OR ‘editorial’/it OR ‘letter’/it OR ‘note’/it OR ‘review’/it) |
| #22 | #21 AND [humans]/lim AND [2008–2017]/py |
| #21 | #6 AND #14 AND #20 |
| #20 | #15 NOT #19 |
| #19 | #16 OR #17 OR #18 |
| #18 | hospitalized:ti,ab |
| #17 | ‘patient*’:ti,ab |
| #16 | ‘patient’/exp |
| #15 | ‘female’/exp |
| #14 | #7 OR #8 OR #9 OR #10 OR #11 OR #12 OR #13 |
| #13 | ‘folate status’:ti,ab |
| #12 | ‘folic acid status’:ti,ab |
| #11 | ‘vitamin d status’:ti,ab |
| #10 | ‘folic acid’/exp |
| #9 | ‘folic acid deficiency’/exp |
| #8 | ‘vitamin d’/exp |
| #7 | ‘vitamin d deficiency’/exp |
| #6 | #1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4 OR #5 |
| #5 | dutch:ti,ab |
| #4 | ‘dutchman’/exp |
| #3 | ‘netherlands’:ca |
| #2 | ‘netherlands’:ti,ab |
| #1 | ‘netherlands’/exp |
Appendix B
| Study Name and References | Study Design | Year(s) of Data Collection | Number of Participants 1 | Participant Characteristics | Parameters Assessed 2 | Method | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food Consumption | Nutrient Intake 3 | Nutrient Supplement Intake | Biochemical Nutrient Status | Dietary Assessment | Biochemical Nutrient Status | |||||
| ABCD [20,52,65,78,89,93,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132,133,134,135,136,137,138,139,140] | Longitudinal cohort study | 2003–2004 | 235–8267 | 15–44 years T1 Amsterdam | (Fatty) fish, alcohol, and caffeine | Folic acid, vitamin B12, vitamin D, and iron | Folate, vitamin B12, vitamin D, ferritin, and iron | FFQ and questionnaire | Serum | |
| APROPOS-II [31] | Cross-sectional study | 2019–2021 | 1077 | 29–33 years T1 The Netherlands | Vegetables, fruit, Alcohol, and caffeine | Folic acid | Questionnaire | |||
| DACE [141,142] | Longitudinal cohort study | 1998–2002 | 101 | Age n.s. T1–T3 Northern Netherlands | Alcohol | Questionnaire | ||||
| DELIVER [66,143,144,145] | Cross-sectional study | 2009–2011 | 1097–6107 | 16–48 years T1–T3 Across The Netherlands | Vegetables, fruit, and alcohol | Folic acid | Questionnaire | |||
| Dutch Monitor on Substance Use and Pregnancy [67] | Cross-sectional study | 2016 | 1858 | >18 years T1–T3 Across The Netherlands | Alcohol | Folic acid | Questionnaire | |||
| EUROCAT 4 [68,146] | Case-control study | 1996–2005 | 448–3012 | 15–50 years Trimester n.s. Northern Netherlands | Alcohol | Folic acid | Questionnaire | |||
| EuroPrevall Birth Cohort [69] | Cohort study | 2005–2010 | 976 | Age range n.s. T3–4 weeks after birth Amsterdam | Folic acid, vitamin D, and multivitamin | Questionnaire administered by trained interviewer | ||||
| Expert study I [83,102] | Cohort study | 2013–2015 | 2477 | >18 years T1 Southeastern Netherlands | Calcium | Calcium | Questionnaire | |||
| Generation R [20,21,26,39,41,44,51,53,54,55,70,82,84,92,94,96,98,116,124,147,148,149,150,151,152,153,154,155,156,157,158,159,160,161,162,163,164,165,166,167,168,169,170,171,172,173,174,175,176,177,178,179,180,181,182,183,184,185,186,187,188,189,190,191,192,193,194,195,196,197,198,199,200,201,202,203,204,205,206,207,208,209,210,211,212,213,214,215,216,217,218,219,220,221,222,223,224,225,226,227,228,229,230,231,232,233,234,235,236,237,238,239,240,241,242] | Longitudinal cohort study | 2001–2005 | 59–8742 | 20–40 years T1 Rotterdam | Vegetables, fruit, nuts, bread, (breakfast) cereal, pasta, rice, legumes, vegetable oil, margarine, butter, meat, fresh meat, processed meat, sugar-containing drinks, (fatty) fish, alcohol, caffeine, and salt | Protein, calcium, iron, and magnesium | Folic acid, multivitamin, and iron | Folate, vitamin B12, vitamin D, iodine, ferritin, and iron | FFQ 5 and questionnaire | Plasma, serum, and urine |
| GLIMP2 [50] | Cohort study | 2015–2017 | 53–67 | Age range n.s. T0, T1, or T2 Eastern Netherlands | Alcohol | Protein, vitamin B6, folate, vitamin B12, vitamin D, and iron | Folic acid, vitamin B12, vitamin D, and iron | Vitamin B6, folate, vitamin B12, vitamin D, and ferritin | FFQ 5 | Whole blood, plasma, and serum |
| HAPPY [87] | Longitudinal, cohort study | 2013–2014 | 2041 | Age range n.s. T1 Southeastern Netherlands | Alcohol | Vitamin D and multivitamin | Copper and zinc | Questionnaire | Plasma | |
| HAVEN [43,71,243] | Case-control study | 2003–2006 | 251–324 | 25–40 years FFQ assessment 16 months after pregnancy; alcohol and supplement use 4 weeks prior to 8 weeks post conception. Rotterdam, Leiden, and Amsterdam | Alcohol | DHA, EPA, riboflavin, niacin, and folate | Folic acid and multivitamin | FFQ 6 and questionnaire | ||
| Healthy pregnant [72] | Case-control study | 2004–2009 | 529 | Age range n.s. Trimester n.s. Veendam, Groningen | Alcohol | Folic acid | Questionnaire | |||
| HERNIA [56] | Case-control study | 2006–2009 | 46 | Age range n.s. T2 Rotterdam | Protein | Folic acid and multivitamin | FFQ 5 and questionnaire | Serum | ||
| IROSTAT [95] | Case-control study | 2011–2012 | 313 | Age range n.s. T1–T3 Den Haag, Rotterdam | Iron | Questionnaire | ||||
| JOZO [99] | Cohort study | 2018–2019 | 292 | 21–43 years T1–T3 Northern Netherlands | Iodine | Iodine | n.s. | Urine | ||
| KOALA [20,32,42,81,89,91,124,244] | Cohort study | 2000–2002 | 913–2834 | Age range n.s. T3 Central and South Netherlands | Vegetables, fruit, bread, (breakfast) cereals, legumes, meat, processed meat and poultry, and alcohol | DHA, vitamin B12 | Fish oil, vitamin B12, vitamin D, and multivitamin | Vitamin B12 and vitamin D | Questionnaire | Plasma |
| Lifelines [73] | Cohort study | Children born in 1993–2013 | 5602 | 15–>40 years Trimester n.s. Northern Netherlands | Alcohol | Folic acid | Questionnaire | |||
| LINC [245] | Cohort study | 2011–2013 | 59 | 23–40 years Trimester n.s. Region of Zwolle | Alcohol | Questionnaire | ||||
| LucKi [20] | Cohort study | 2006-n.s. | 543 | Age range n.s. Trimester n.s. The Netherlands | (Fatty) fish | Questionnaire | ||||
| Maastricht cohort and intervention study about pregnancy-related girdle pain [74] | Cohort study | 2000–2002 | 7526 | Age range n.s. Trimester n.s. Control group in positional plagiocephaly cohort Southeastern area of The Netherlands | Folic acid and multivitamin | Questionnaire | ||||
| MEFAB [246,247] | Cohort study | 1989–1995 | 242–292 | Age range n.s. Assessed at follow-up visit outpatient clinic in Maastricht, which is south of The Netherlands | Alcohol | Questionnaire | Plasma | |||
| MINDS-Leiden [248] | Longitudinal study | n.s. | 150 | 17–25 years T3 Leiden | Alcohol | Questionnaire | ||||
| Parents to Be [75] | RCT | 2000–2003 | 422 | 18–40 years 2 months after birth Leiden | Alcohol | Folic acid | Questionnaire | |||
| ‘Peiling melkvoeding van zuigelingen’ [249] | National survey | 2015 | 1678 | 17–48 years Until 7 months after pregnancy The Netherlands | Alcohol (use before conception) | Questionnaire | ||||
| PIAMA [20,36,37,76,124] | Cohort study | 1996–1997 | 3335–3963 | Age range n.s. T1–T3 The Netherlands | Vegetables, fruit, nuts, and fish | Folic acid and multivitamins | FFQ and questionnaire | |||
| Pregnancy Anxiety and Depression [46,250] | Cohort study | 2011–2013 | 1340 | Age range n.s. T2 The Netherlands | Alcohol | Questionnaire | ||||
| RESPECT study [38] | Cohort study | 2012–2014 | 3684 | Age range n.s. T1 Central region of The Netherlands | Fruit | Folic acid | Questionnaire | |||
| Rotterdam Predict Study [35,77,79,80,100,251,252,253,254,255,256,257,258] | Cohort study | 2009–2016 | 74–638 | 22–45 years T1, women who conceived naturally or via IVF/ICSI treatment Rotterdam | Vegetables, fruit, and alcohol | Folic acid and multivitamin | Folate and vitamin B12, | Questionnaire | RBC and serum | |
| TRAILS [48,259] | Cohort study | 2001 | 1667 | Age range n.s. T1–T3 Northern part of The Netherlands | Alcohol | Questionnaire | ||||
| ZOOG [88,101] | Intervention study | 2014–2015 | 36 | 21–38 years T2 Northern part of The Netherlands | Vitamin D and multivitamin | Vitamin D | Questionnaire | |||
| Belderbos et al. [86] | Cohort study | 2006–2009 | 156 | Age range n.s. T1–T3 Utrecht | Vitamin D | Questionnaire | ||||
| Bliek et al. [58] | Case-control study | 1998–2003 | 258 | Age range n.s. 15 months after birth The Netherlands | Folic acid and multivitamin | Questionnaire | ||||
| Cooijmans et al. [260] | RCT | 2016–2018 | 60 | Age range n.s. T3 Nijmegen | Alcohol | Questionnaire | ||||
| de Smit et al. [59] | Controlled trial | 2007–2008 | 21 | Age range n.s. 11 months after birth Eastern part of The Netherlands | Folic acid | Questionnaire | ||||
| Diepeveen et al. [261] | Case-control study | n.s. | 253 | Age range n.s. 10 days after birth The Netherlands | Alcohol | Questionnaire | ||||
| Dirix et al. [49] | Case-control study | n.s. | 90 | Age range n.s. T3 Southern Limburg region | Alcohol | Questionnaire | ||||
| Doornbos et al. [40] | RCT | n.s. | 36 | Age range n.s. T1, T2 and 3 months after birth Region n.s. | (Fatty) fish | FFQ | ||||
| Groen in ’t Woud et al. [60] | Case-control study | delivery date 1990–2013 | 2601 | Age range n.s. Trimester n.s., Netherlands | Folic acid | Questionnaire | ||||
| Hogeveen et al. [61] | Cross-sectional study | 2002–2004 | 366 | Age range n.s. T3 Nijmegen | Folic acid | Folate | Questionnaire | Plasma | ||
| Lamb et al. [262] | Cohort study | 2008 | 410 | Age range n.s. At birth Nijmegen | Alcohol | Questionnaire | ||||
| Meulenbroeks et al. [121] | Survey | 2019–2019 | 121 midwives and 179 obstetricians | Age range and trimester n.a. The Netherlands | Plant-based diet | Questionnaire | ||||
| Merkx et al. [33] | Cross-sectional study | 2012 | 455 | Age range n.s. Trimester n.s. Southern part of The Netherlands | Vegetables, fruit, and fish | FFQ 4 | ||||
| Obermann-Borst et al. [62] | Cohort study | 2003–2007 | 120 | Age range n.s. 17 months after birth Rotterdam | Folic acid | Questionnaire | ||||
| Poels et al. [47] | Case-control study | 2015–2016 | 283 | 16–>35 years Within 1 year after birth Zeist | Alcohol | Folic acid | Questionnaire | |||
| Pop et al. [263] | Cohort study | 2013–2014 | 1903 | 19–43 years T1 Southeastern part of The Netherlands | Alcohol | Questionnaire | ||||
| Schoorl et al. [97] | Case-control study | n.s. | 145 | Age range n.s. T3 Region n.s. | Hemoglobin | Blood | ||||
| Stern et al. [264] | Longitudinal study | n.s. | 187 | 21–43 years During pregnancy up to 12 months after birth The Netherlands | Alcohol | Questionnaire | ||||
| TNO et al. [63] | Controlled trial | 2006–2007 | 333 | Age range n.s. Trimester n.s. The Netherlands | Folic acid | Questionnaire | ||||
| van Dijk et al. [34] | RCT | 2014–2017 | 109 | 18–45 years Non-pregnant and T1 beginning T2 Rotterdam | Vegetables and fruit | Folic acid | Questionnaire | |||
| Voortman et al. [57] | FFQ validation study | 2010 | 83 | Age range n.s. T2 Rotterdam | Protein, thiamine, riboflavin, vitamin B6, folate, vitamin B12, vitamin C, calcium, iron, and retinol | Folic acid | Folate and vitamin B12 | FFQ, 3 non-consecutive 24 h-recalls, and questionnaire | RBC and plasma | |
| Vujkovic et al. [45] | Case-control study | 1999–2001 | 81 | Age range n.s. 14 months after birth The Netherlands | Folic acid | Questionnaire | ||||
| Weernink et al. [90] | Case-control study | 2009–2010 | 548 | Age range n.s. 2–4 months after birth The Netherlands | Vitamin D | Questionnaire | ||||
| Zetstra-van der Woude et al. [64] | Cross-sectional study | 2009 | 486 | Age range n.s. T1–T3 Northern part of The Netherlands | Folic acid | Questionnaire | ||||
References
- Tuncalp, Ö.; Rogers, L.M.; Lawrie, T.A.; Barreix, M.; Peña-Rosas, J.P.; Bucagu, M.; Neilson, J.; Oladapo, O.T. WHO recommendations on antenatal nutrition: An update on multiple micronutrient supplements. BMJ Glob. Health 2020, 5, e003375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jouanne, M.; Oddoux, S.; Noël, A.; Voisin-Chiret, A.S. Nutrient Requirements during Pregnancy and Lactation. Nutrients 2021, 13, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Good Maternal Nutrition. The Best Start in Life; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Raghavan, R.; Dreibelbis, C.; Kingshipp, B.L.; Wong, Y.P.; Abrams, B.; Gernand, A.D.; Rasmussen, K.M.; Siega-Riz, A.M.; Stang, J.; Casavale, K.O.; et al. Dietary patterns before and during pregnancy and birth outcomes: A systematic review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 729S–756S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, R.L.; Pac, S.G.; Fulgoni, V.L., 3rd; Reidy, K.C.; Catalano, P.M. Estimation of Total Usual Dietary Intakes of Pregnant Women in the United States. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e195967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Health Council of The Netherlands. Dietary Recommendations for Pregnant Women; Health Council of The Netherlands: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2021.
- Nordic Council of Ministers. Nordic Nutrition Recommendations 2012. Integrating Nutrition and Physical Activity; Nordic Council of Ministers: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA); U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020–2025, 9th ed.; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2020.
- Health Council of The Netherlands. Dietary Reference Values for Vitamins and Minerals for Pregnant Women; Health Council of The Netherlands: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2021.
- Health Council of The Netherlands. Dietary Reference Values for Proteins; Health Council of The Netherlands: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2021.
- Health Council of The Netherlands. An Evaluation of Dietary Reference Values for Vitamins and Minerals for Pregnant Women. No. 2021/27A/02; Health Council of The Netherlands: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2021.
- Health Council of The Netherlands. An Evaluation of the EFSA’s Dietary Reference Values (DRVs), Part 1. Dietary Reference Values for Vitamins and Minerals for Adults. No. 2018/19A; Health Council of The Netherlands: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2018.
- CBS. Birth. Available online: https://www.cbs.nl/nl-nl/visualisaties/dashboard-bevolking/bevolkingsgroei/geboren-kinderen#:~:text=Hoeveel%20kinderen%20worden%20er%20per,in%201946%20zelfs%20284%20duizend (accessed on 22 June 2022).
- ter Borg, S.; Koopman, N.; Verkaik-Kloosterman, J. Food Consumption, Nutrient Intake and Status during the First 1000 days of Life in The Netherlands: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Health Council of The Netherlands. Towards an Adequate Intake of Vitamin D. Publication no. 2008/15; Health Council of The Netherlands: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2008.
- Health Council of The Netherlands. Towards an Optimal Use of Folic Acid. Publication no. 2008/02; Health Council of The Netherlands: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2008.
- Health Council of The Netherlands. Towards an Adequate Intake of Vitamin A. Publication no. 2008/26; Health Council of The Netherlands: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2008.
- Health Council of The Netherlands. Towards Maintaining an Optimum Iodine Intake. Publication no. 2008/14; Health Council of The Netherlands: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2008.
- Stratakis, N.; Roumeliotaki, T.; Oken, E.; Ballester, F.; Barros, H.; Basterrechea, M.; Cordier, S.; de Groot, R.; den Dekker, H.T.; Duijts, L.; et al. Fish and seafood consumption during pregnancy and the risk of asthma and allergic rhinitis in childhood: A pooled analysis of 18 European and US birth cohorts. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 1465–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwland-Both, M.I.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M.; Vujkovic, M.; Lesaffre, E.M.E.H.; Mook-Kanamori, D.O.; Hofman, A.; Lindemans, J.; Russcher, H.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Steegers, E.A.P. A periconceptional energy-rich dietary pattern is associated with early fetal growth: The Generation R study. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2013, 120, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Scientific Opinion on principles for deriving and applying Dietary Reference Values. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Optimal Serum and Red Blood Cell Folate Concentrations in women of Reproductive Age for Prevention of Neural Tube Defects; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Guideline on Use of Ferritin Concentrations to Assess Iron Status in Individuals and Populations; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO); UNICEF; ICCIDD. Assessment of Iodine Deficiency Disorders and Monitoring Their Elimination. A Guide for Programme Managers, 3rd ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Dineva, M.; Rayman, M.P.; Levie, D.; Guxens, M.; Peeters, R.P.; Vioque, J.; Gonzalez, L.; Espada, M.; Ibarluzea, J.; Sunyer, J.; et al. Similarities and differences of dietary and other determinants of iodine status in pregnant women from three European birth cohorts. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 59, 371–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohner, F.; Zimmermann, M.; Jooste, P.; Pandav, C.; Caldwell, K.; Raghavan, R.; Raiten, D.J. Biomarkers of nutrition for development—Iodine review. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 1322S–1342S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nederlandse Vereniging Voor Klinische Chemie en Laboratoriumgeneeskunde (NVKC). General Overview Reference Values. Available online: https://www.nvkc.nl/algemeen-overzicht-referentiewaarden (accessed on 7 September 2022).
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for copper. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for zinc. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maas, V.Y.F.; Poels, M.; de Kievit, M.H.; Hartog, A.P.; Franx, A.; Koster, M.P.H. Planning is not equivalent to preparing, how Dutch women perceive their pregnancy planning in relation to preconceptional lifestyle behaviour change—A cross-sectional study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2022, 22, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoes-Wust, A.P.; Molto-Puigmarti, C.; van Dongen, M.C.; Dagnelie, P.C.; Thijs, C. Organic food consumption during pregnancy is associated with different consumer profiles, food patterns and intake: The KOALA Birth Cohort Study. Public Health Nutr. 2017, 20, 2134–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merkx, A.; Ausems, M.; Budé, L.; de Vries, R.; Nieuwenhuijze, M.J. Weight gain in healthy pregnant women in relation to pre-pregnancy BMI, diet and physical activity. Midwifery 2015, 31, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijk, M.R.; Koster, M.P.H.; Oostingh, E.C.; Willemsen, S.P.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M. A Mobile App Lifestyle Intervention to Improve Healthy Nutrition in Women Before and During Early Pregnancy: Single-Center Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e15773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gootjes, D.V.; Koster, M.P.H.; Willemsen, S.P.; Koning, A.H.J.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M. The Impact of Neighbourhood Deprivation on Embryonic Growth Trajectories: Rotterdam Periconception Cohort. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van den Berg, S.W.; Wijga, A.H.; van Rossem, L.; Gehring, U.; Koppelman, G.H.; Smit, H.A.; Boer, J.M.A. Maternal fish consumption during pregnancy and BMI in children from birth up to age 14 years: The PIAMA cohort study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 55, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willers, S.M.; Wijga, A.H.; Brunekreef, B.; Kerkhof, M.; Gerritsen, J.; Hoekstra, M.O.; De Jongste, J.C.; Smit, H.A. Maternal food consumption during pregnancy and the longitudinal development of childhood asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 178, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, V.Y.F.; Poels, M.; Lamain-de Ruiter, M.; Kwee, A.; Bekker, M.N.; Franx, A.; Koster, M.P.H. Associations between periconceptional lifestyle behaviours and adverse pregnancy outcomes. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2021, 21, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmermans, S.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.; Vujkovic, M.; Den Breeijen, H.; Russcher, H.; Lindemans, J.; MacKenbach, J.; Hofman, A.; Lesaffre, E.E.; Jaddoe, V.V.; et al. The Mediterranean diet and fetal size parameters: The Generation R Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, 1399–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doornbos, B.; van Goor, S.A.; Dijck-Brouwer, D.A.J.; Schaafsma, A.; Korf, J.; Muskiet, F.A.J. Supplementation of a low dose of DHA or DHA + AA does not prevent peripartum depressive symptoms in a small population based sample. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 33, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefte-de Jong, J.C.; De Vries, J.H.; Franco, O.H.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Hofman, A.; Raat, H.; De Jongste, J.C.; Moll, H.A. Fish consumption in infancy and asthma-like symptoms at preschool age. Pediatrics 2012, 130, 1060–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molto´-Puigmart´i, C.; van Dongen, M.C.J.M.; Dagnelie, P.C.; Plat, J.; Mensink, R.P.; Tan, F.E.S.; Heinrich, J.; Thijs, C. Maternal but not fetal FADS gene variants modify the association between maternal long-chain PUFA intake in pregnancy and birth weight. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 1430–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smedts, H.P.M.; Rakhshandehroo, M.; Verkleij-Hagoort, A.C.; De Vries, J.H.M.; Ottenkamp, J.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M. Maternal intake of fat, riboflavin and nicotinamide and the risk of having offspring with congenital heart defects. Eur. J. Nutr. 2008, 47, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gootjes, D.V.; Posthumus, A.G.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Steegers, E.A.P. Association between neighbourhood deprivation, fetal growth, small-for-gestational age and preterm birth: A population-based prospective cohort study. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e049075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vujkovic, M.; Steegers, E.A.; Looman, C.W.; Ocké, M.C.; Van Der Spek, P.J.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P. The maternal Mediterranean dietary pattern is associated with a reduced risk of spina bifida in the offspring. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2009, 116, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beijers, C.; Ormel, J.; Meijer, J.L.; Verbeek, T.; Bockting, C.L.H.; Burger, H. Stressful events and continued smoking and continued alcohol consumption during mid-pregnancy. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poels, M.; van Stel, H.F.; Franx, A.; Koster, M.P.H. The effect of a local promotional campaign on preconceptional lifestyle changes and the use of preconception care. Eur. J. Contracept. Reprod. Health Care 2018, 23, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brinksma, D.M.; Hoekstra, P.J.; van den Hoofdakker, B.; de Bildt, A.; Buitelaar, J.K.; Hartman, C.A.; Dietrich, A. Age-dependent role of pre- and perinatal factors in interaction with genes on ADHD symptoms across adolescence. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2017, 90, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirix, C.E.H.; Hornstra, G.; Nijhuis, J.G. Fetal learning and memory: Weak associations with the early essential polyunsaturated fatty acid status. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2009, 80, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Looman, M.; Geelen, A.; Samlal, R.A.K.; Heijligenberg, R.; Klein Gunnewiek, J.M.T.; Balvers, M.G.J.; Wijnberger, L.D.E.; Brouwer-Brolsma, E.M.; Feskens, E.J.M. Changes in Micronutrient Intake and Status, Diet Quality and Glucose Tolerance from Preconception to the Second Trimester of Pregnancy. Nutrients 2019, 11, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haan, E.; Sallis, H.M.; Zuccolo, L.; Labrecque, J.; Ystrom, E.; Reichborn-Kjennerud, T.; Andreassen, O.; Havdahl, A.; Munafo, M.R. Prenatal smoking, alcohol and caffeine exposure and maternal-reported attention deficit hyperactivity disorder symptoms in childhood: Triangulation of evidence using negative control and polygenic risk score analyses. Addiction 2022, 117, 1458–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, G.; van Eijsden, M.; Galindo-Garre, F.; Vrijkotte, T.G.M.; Gemke, R.J.B.J. Smoking overrules many other risk factors for small for gestational age birth in less educated mothers. Early Hum. Dev. 2013, 89, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jen, V.; Erler, N.S.; Tielemans, M.J.; Braun, K.V.E.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Franco, O.H.; Voortman, T. Mothers’ intake of sugar-containing beverages during pregnancy and body composition of their children during childhood: The Generation R Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouthoorn, S.H.; Gaillard, R.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Hofman, A.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Van Lenthe, F.J.; Raat, H. Ethnic differences in blood pressure and hypertensive complications during pregnancy the generation R study. Hypertension 2012, 60, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakker, R.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Obradov, A.; Raat, H.; Hofman, A.; Jaddoe, V.W.V. Maternal caffeine intake from coffee and tea, fetal growth, and the risks of adverse birth outcomes: The Generation R Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 1691–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beurskens, L.W.J.E.; Schrijver, L.H.; Tibboel, D.; Wildhagen, M.F.; Knapen, M.F.C.M.; Lindemans, J.; De Vries, J.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M. Dietary vitamin A intake below the recommended daily intake during pregnancy and the risk of congenital diaphragmatic hernia in the offspring. Birth Defects Res. Part A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2013, 97, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voortman, T.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M.; Bergen, N.E.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Looman, C.W.N.; Kiefte-de Jong, J.C.; Schalekamp-Timmermans, S. Validation of a Semi-Quantitative Food-Frequency Questionnaire for Dutch Pregnant Women from the General Population Using the Method or Triads. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bliek, B.J.B.; Van Schaik, R.H.N.; Van Der Heiden, I.P.; Sayed-Tabatabaei, F.A.; Van Duijn, C.M.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M. Maternal medication use, carriership of the ABCB1 3435C>T polymorphism and the risk of a child with cleft lip with or without cleft palate. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2009, 149, 2088–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Smit, D.J.; Weinreich, S.S.; Cornel, M.C. Effects of a simple educational intervention in well-baby clinics on women’s knowledge about and intake of folic acid supplements in the periconceptional period: A controlled trial. Public Health Nutr. 2015, 18, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Groen In’t Woud, S.; Renkema, K.Y.; Schreuder, M.F.; Wijers, C.H.W.; van der Zanden, L.F.M.; Knoers, N.V.A.M.; Feitz, W.F.J.; Bongers, E.M.H.F.; Roeleveld, N.; van Rooij, I.A.L.M. Maternal risk factors involved in specific congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract: A case-control study. Birth Defects Res. Part A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2016, 106, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogeveen, M.; Blom, H.J.; van der Heijden, E.H.; Semmekrot, B.A.; Sporken, J.M.; Ueland, P.M.; den Heijer, M. Maternal homocysteine and related B vitamins as risk factors for low birthweight. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 202, 572.e1–572.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obermann-Borst, S.A.; Eilers, P.H.C.; Tobi, E.W.; De Jong, F.H.; Slagboom, P.E.; Heijmans, B.T.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M. Duration of breastfeeding and gender are associated with methylation of The LEPTIN gene in very young children. Pediatr. Res. 2013, 74, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- TNO; de Jong, A.; Mohangoo, A.D.; Korfker, D.G.; Schonbeck, Y.; van der Pal, S.M.; Detmar, S.B. Effect Van Stimuleringsbeleid Preconceptioneel Foliumzuurgebruik Op Kennis En Gebruik Van Foliumzuur Door Allochtone Vrouwen; TNO: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zetstra-van der Woude, P.A.; de Walle, H.E.; de Jong-van den Berg, L.T. Periconceptional folic acid use: Still room to improve. Birth Defects Res. Part A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2012, 94, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholing, J.M.; Olthof, M.R.; Jonker, F.A.; Vrijkotte, T.G. Association between pre-pregnancy weight status and maternal micronutrient status in early pregnancy. Public Health Nutr. 2018, 21, 2046–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baron, R.; Manniën, J.; de Jonge, A.; Heymans, M.W.; Klomp, T.; Hutton, E.K.; Brug, J. Socio-Demographic and Lifestyle-Related Characteristics Associated with Self-Reported Any, Daily and Occasional Smoking during Pregnancy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheffers-van Schayck, T.; Tuithof, M.; Otten, R.; Engels, R.; Kleinjan, M. Smoking Behavior of Women Before, During, and after Pregnancy: Indicators of Smoking, Quitting, and Relapse. Eur. Addict. Res. 2019, 25, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Beynum, I.M.; Kapusta, L.; Bakker, M.K.; Den Heijer, M.; Blom, H.J.; De Walle, H.E.K. Protective effect of periconceptional folic acid supplements on the risk of congenital heart defects: A registry-based case-control study in the northern Netherlands. Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliver, E.M.; Grimshaw, K.E.; Schoemaker, A.A.; Keil, T.; McBride, D.; Sprikkelman, A.B.; Ragnarsdottir, H.S.; Trendelenburg, V.; Emmanouil, E.; Reche, M.; et al. Dietary habits and supplement use in relation to national pregnancy recommendations: Data from the EuroPrevall birth cohort. Matern. Child Health J. 2014, 18, 2408–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefte-de Jong, J.C.; Timmermans, S.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Hofman, A.; Tiemeier, H.; Steegers, E.A.; de Jongste, J.C.; Moll, H.A. High circulating folate and vitamin B-12 concentrations in women during pregnancy are associated with increased prevalence of atopic dermatitis in their offspring. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aoulad Fares, D.; Wiegel, R.E.; Eggink, A.J.; Willemsen, S.P.; van Meurs, J.B.J.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M. Shorter periconception maternal telomere length and the risk of congenital cardiac outflow defects in the offspring. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 52, e13784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jentink, J.; Zetstra-van der Woude, A.P.; Bos, J.; de Jong-van den Berg, L.T.W. Evaluation of the representativeness of a Dutch non-malformed control group for the general pregnant population: Are these controls useful for EUROCAT? Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2011, 20, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinder, N.; Bergman, J.E.; Kromhout, H.; Vermeulen, R.; Corsten-Janssen, N.; Boezen, H.M.; du Marchie Sarvaas, G.J.; de Walle, H.E. Maternal occupational exposure and congenital heart defects in offspring. Scand. J. Work Environ. Health 2020, 46, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michels, A.; Bakkali, N.E.; Bastiaenen, C.H.; De Bie, R.A.; Colla, C.G.; Van Der Hulst, R.R. Periconceptional folic acid use and the prevalence of positional plagiocephaly. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2008, 19, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsinga, J.; de Jong-Potjer, L.C.; van der Pal-de Bruin, K.M.; le Cessie, S.; Assendelft, W.J.J.; Buitendijk, S.E. The Effect of Preconception Counselling on Lifestyle and Other Behaviour Before and During Pregnancy. Women’s Health Issues 2008, 18, S117–S125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekkers, M.B.M.; Elstgeest, L.E.M.; Scholtens, S.; Haveman-Nies, A.; De Jongste, J.C.; Kerkhof, M.; Koppelman, G.H.; Gehring, U.; Smit, H.A.; Wijga, A.H. Maternal use of folic acid supplements during pregnancy, and childhood respiratory health and atopy. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 39, 1468–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Duijn, L.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M.; Baart, E.B.; Willemsen, S.P.; Laven, J.S.E.; Rousian, M. The impact of IVF culture medium on post-implantation embryonic growth and development with emphasis on sex specificity: The Rotterdam Periconceptional Cohort. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2022, 45, 1085–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikkens, J.J.; van Eijsden, M.; Bonsel, G.J.; Cornel, M.C. Validation of self-reported folic acid use in a multiethnic population: Results of the Amsterdam Born Children and their Development study. Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 2022–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parisi, F.; Rousian, M.; Koning, A.H.J.; Willemsen, S.P.; Cetin, I.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M. Periconceptional maternal one-carbon biomarkers are associated with embryonic development according to the Carnegie stages. Hum. Reprod. 2017, 32, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parisi, F.; Rousian, M.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M.; Koning, A.H.J.; Willemsen, S.P.; de Vries, J.H.M.; Cetin, I.; Steegers, E.A.P. Early first trimester maternal ‘high fish and olive oil and low meat’ dietary pattern is associated with accelerated human embryonic development. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 1655–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denissen, K.F.M.; Heil, S.G.; Eussen, S.; Heeskens, J.P.J.; Thijs, C.; Mommers, M.; Smits, L.J.M.; van Dongen, M.; Dagnelie, P.C. Intakes of Vitamin B-12 from Dairy Food, Meat, and Fish and Shellfish Are Independently and Positively Associated with Vitamin B-12 Biomarker Status in Pregnant Dutch Women. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monasso, G.S.; Santos, S.; Geurtsen, M.L.; Heil, S.G.; Felix, J.F.; Jaddoe, V.W.V. Associations of Early Pregnancy and Neonatal Circulating Folate, Vitamin B-12, and Homocysteine Concentrations with Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Children at 10 y of Age. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 1628–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willemse, J.; Smits, L.J.M.; Braat, M.M.E.; Meertens, L.J.E.; van Montfort, P.; van Dongen, M.C.; Ellerbrock, J.; van Dooren, I.M.A.; Duvekot, E.J.; Zwaan, I.M.; et al. Counseling pregnant women on calcium: Effects on calcium intake. J. Perinat. Med. 2022, 51, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miliku, K.; Felix, J.F.; Voortman, T.; Tiemeier, H.; Eyles, D.W.; Burne, T.H.; McGrath, J.J.; Jaddoe, V.W.V. Associations of maternal and fetal vitamin D status with childhood body composition and cardiovascular risk factors. Matern. Child Nutr. 2019, 15, e12672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for niacin. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belderbos, M.E.; Houben, M.L.; Wilbrink, B.; Lentjes, E.; Bloemen, E.M.; Kimpen, J.L.L.; Rovers, M.; Bont, L. Cord blood vitamin D deficiency is associated with respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. Pediatrics 2011, 127, e1513–e1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, V.; Krabbe, J.; Maret, W.; Rayman, M. Plasma mineral (selenium, zinc or copper) concentrations in the general pregnant population, adjusted for supplement intake, in relation to thyroid function. Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 125, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoutjesdijk, E.; Schaafsma, A.; Kema, I.P.; van der Molen, J.; Dijck-Brouwer, D.A.J.; Muskiet, F.A.J. Influence of daily 10–85 mug vitamin D supplements during pregnancy and lactation on maternal vitamin D status and mature milk antirachitic activity. Br. J. Nutr. 2019, 121, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Weert, B.; van den Berg, D.; Hrudey, E.J.; Oostvogels, A.J.; de Miranda, E.; Vrijkotte, T.G. Is first trimester vitamin D status in nulliparous women associated with pregnancy related hypertensive disorders? Midwifery 2016, 34, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weernink, M.G.M.; van Wijk, R.M.; Groothuis-Oudshoorn, C.G.M.; Lanting, C.I.; Grant, C.C.; van Vlimmeren, L.A.; Boere-Boonekamp, M.M. Insufficient vitamin D supplement use during pregnancy and early childhood: A risk factor for positional skull deformation. Matern. Child Nutr. 2016, 12, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremers, E.; Thijs, C.; Penders, J.; Jansen, E.; Mommers, M. Maternal and child’s vitamin D supplement use and vitamin D level in relation to childhood lung function: The KOALA birth cohort study. Thorax 2011, 66, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miliku, K.; Vinkhuyzen, A.; Blanken, L.M.E.; McGrath, J.J.; Eyles, D.W.; Burne, T.H.; Hofman, A.; Tiemeier, H.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Gaillard, R.; et al. Maternal Vitamin D concentrations during pregnancy, fetal growth patterns, and risks of adverse birth outcomes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 1514–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brandenbarg, J.; Vrijkotte, T.G.M.; Goedhart, G.; Van Eijsden, M. Maternal early-pregnancy vitamin d status is associated with maternal depressive symptoms in the amsterdam born children and their development cohort. Psychosom. Med. 2012, 74, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quezada-Pinedo, H.G.; Cassel, F.; Muckenthaler, M.U.; Gassmann, M.; Huicho, L.; Reiss, I.K.; Duijts, L.; Gaillard, R.; Vermeulen, M.J. Ethnic differences in adverse iron status in early pregnancy: A cross-sectional population-based study. J. Nutr. Sci. 2022, 11, e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uijterschout, L.; Vloemans, J.; Rövekamp-Abels, L.; Feitsma, H.; Van Goudoever, J.B.; Brus, F. The influences of factors associated with decreased iron supply to the fetus during pregnancy on iron status in healthy children aged 0.5 to 3 years. J. Perinatol. 2014, 34, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taeubert, M.J.; Wiertsema, C.J.; Vermeulen, M.J.; Quezada-Pinedo, H.G.; Reiss, I.K.; Muckenthaler, M.U.; Gaillard, R. Maternal Iron Status in Early Pregnancy and Blood Pressure Throughout Pregnancy, Placental Hemodynamics, and the Risk of Gestational Hypertensive Disorders. J. Nutr. 2022, 152, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoorl, M.; Schoorl, M. Effects of iron supplementation on microcytic and hypochromic red blood cells during the third trimester of pregnancy. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2022, 44, 1060–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heppe, D.H.M.; Medina-Gomez, C.; Hofman, A.; Franco, O.H.; Rivadeneira, F.; Jaddoe, V.W.V. Maternal first-trimester diet and childhood bone mass: The Generation R Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 98, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayunga, K.C.; Lim, A.P.M.; Lubberts, J.; Stoutjesdijk, E.; Touw, D.J.; Muskiet, F.A.J.; Dijck-Brouwer, D.A.J. Pregnant Dutch Women Have Inadequate Iodine Status and Selenium Intake. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oostingh, E.C.; de Vos, I.; Ham, A.C.; Brouwer-Brolsma, E.M.; Willemsen, S.P.; Eggink, A.J.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M. No independent associations between preconception paternal dietary patterns and embryonic growth; the Predict Study. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 38, 2333–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoutjesdijk, E.; Schaafsma, A.; Dijck-Brouwer, D.A.J.; Muskiet, F.A.J. Iodine status during pregnancy and lactation: A pilot study in The Netherlands. Neth. J. Med. 2018, 76, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Willemse, J.; Meertens, L.J.E.; Scheepers, H.C.J.; Achten, N.M.J.; Eussen, S.J.; van Dongen, M.C.; Smits, L.J.M. Calcium intake from diet and supplement use during early pregnancy: The Expect study I. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 59, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blumfield, M.L.; Hure, A.J.; Macdonald-Wicks, L.; Smith, R.; Collins, C.E. A systematic review and meta-analysis of micronutrient intakes during pregnancy in developed countries. Nutr. Rev. 2013, 71, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rossum, C.T.M.; Buurma-Rethans, E.J.M.; Dinnissen, C.S.; Beukers, M.H.; Brants, H.A.M.; Dekkers, A.L.M.; Ocké, M.C. The Diet of the Dutch. Results of the Dutch National Food Consumption Survey 2012–2016; National Institute for Public Health and the Environment: Bilthoven, The Netherlands, 2020.
- National Institute of Public Health and the Environment. Wat eet Nederland. Resultaten. Voedingsmiddelen. Verandering. Available online: https://www.wateetnederland.nl/resultaten/voedingsmiddelen/verandering (accessed on 8 September 2022).
- Dinnissen, C.S.; Hendriksen, M. Salt and Potassium Intake 2020/2021 in Adults from the North of The Netherlands. Monitoring the Nutritional Status in the Lifelines Cohort; National Institute for Public Health and the Environment: Bilthoven, The Netherlands, 2022.
- Health Council of The Netherlands. Natrium. Achtergronddocument bij Richtlijnen Goede Voeding 2015. Publicatienr. A15/15; Health Council of The Netherlands: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2015.
- Duley, L.; Henderson-Smart, D.; Meher, S. Altered dietary salt for preventing pre-eclampsia, and its complications. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2005, 4, CD005548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dinnissen, C.S.; de Jong, M.H.; Verkaik-Kloosterman, J.; Hendriksen, M. Adult iodine intake in the North of The Netherlands in 2020–2021 and the Development of this Since 2006–2007 Nutritional Status Study among the Lifelines Cohort; National Institute for Public Health and the Environment: Bilthoven, The Netherlands, 2022.
- Hendriksen, M.A.; van Raaij, J.M.; Geleijnse, J.M.; Wilson-van den Hooven, C.; Ocké, M.C.; van der, A.D. Monitoring salt and iodine intakes in Dutch adults between 2006 and 2010 using 24 h urinary sodium and iodine excretions. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 1431–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- National Institute of Public Health and the Environment. Jodium in Zwangere Vrouwen Onderzoek (JOZO). Available online: https://www.rivm.nl/voedselconsumptiepeiling/voedingsstatusonderzoek/JOZO (accessed on 17 April 2023).
- Passier, A.; Woestenberg, P.; Vorstenbosch, S. Onderzoek Moeders van Morgen: Gebruik foliumzuur volgens voorschrift rondom zwangerschap blijft een aandachtspunt. NPFO 2021, 6, a1742. [Google Scholar]
- Health Council of The Netherlands. Evaluation of the Dietary Reference Values for Vitamin D. Nr. 2012/15E; Health Council of The Netherlands: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2012.
- Henriquez-Sanchez, P.; Sanchez-Villegas, A.; Doreste-Alonso, J.; Ortiz-Andrellucchi, A.; Pfrimer, K.; Serra-Majem, L. Dietary assessment methods for micronutrient intake: A systematic review on vitamins. Br. J. Nutr. 2009, 102 (Suppl. 1), S10–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Illner, A.K.; Freisling, H.; Boeing, H.; Huybrechts, I.; Crispim, S.P.; Slimani, N. Review and evaluation of innovative technologies for measuring diet in nutritional epidemiology. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 41, 1187–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Den Hil, L.C.L.; Taal, H.R.; De Jonge, L.L.; Heppe, D.H.M.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Hofman, A.; Van Der Heijden, A.J.; Jaddoe, V.W.V. Maternal first-trimester dietary intake and childhood blood pressure: The Generation R Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 1454–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allen, L.H.; Miller, J.W.; de Groot, L.; Rosenberg, I.H.; Smith, A.D.; Refsum, H.; Raiten, D.J. Biomarkers of Nutrition for Development (BOND): Vitamin B-12 Review. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 1995S–2027S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Lonkhuijzen, R.M.; Cremers, S.; de Vries, J.H.M.; Feskens, E.J.M.; Wagemakers, A. Evaluating ‘Power 4 a Healthy Pregnancy’ (P4HP)-protocol for a cluster randomized controlled trial and process evaluation to empower pregnant women towards improved diet quality. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Medicine; Committee on Nutritional Status During Pregnancy and Lactation. Assessment of Nutrient Needs. In Nutrition During Pregnancy: Part I Weight Gain: Part II Nutrient Supplements; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1990; Volume 12, pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- National Institute of Public Health and the Environment. Wat eet Nederland. Peiling van de Voedselconsumptie 2019–2021. Onderwerpen. Dieten en Leefregels. Available online: https://www.wateetnederland.nl/ (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Meulenbroeks, D.; Versmissen, I.; Prins, N.; Jonkers, D.; Gubbels, J.; Scheepers, H. Care by Midwives, Obstetricians, and Dietitians for Pregnant Women Following a Strict Plant-Based Diet: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rossum, C.; ter Borg, S.; Nawijn, E.; Oliveira, A.; Carvalho, C.; Ocké, M. Literature review on methodologies and tools for national dietary surveys; results of ERA EU-menu-project. EFSA Support. Publ. 2022, 19, 7725E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eijsden, M.; Hornstra, G.; Van Der Wal, M.F.; Bonsel, G.J. Ethnic differences in early pregnancy maternal n-3 and n-6 fatty acid concentrations: An explorative analysis. Br. J. Nutr. 2009, 101, 1761–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stratakis, N.; Roumeliotaki, T.; Oken, E.; Barros, H.; Basterrechea, M.; Charles, M.A.; Eggesbo, M.; Forastiere, F.; Gaillard, R.; Gehring, U.; et al. Fish intake in pregnancy and child growth: A pooled analysis of 15 European and US birth cohorts. JAMA Pediatr. 2016, 170, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer-Brolsma, E.M.; Vrijkotte, T.G.M.; Feskens, E.J.M. Maternal vitamin D concentrations are associated with faster childhood reaction time and response speed, but not with motor fluency and flexibility, at the age of 5–6 years: The Amsterdam Born Children and their Development (ABCD) Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 120, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Beer, M.; Vrijkotte, T.G.M.; Fall, C.H.D.; Van Eijsden, M.; Osmond, C.; Gemke, R.J.B.J. Associations of infant feeding and timing of weight gain and linear growth during early life with childhood blood pressure: Findings from a prospective population based cohort study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e166281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dieberger, A.M.; de Rooij, S.R.; Korosi, A.; Vrijkotte, T.G.M. Maternal Lipid Concentrations during Early Pregnancy and Eating Behaviour and Energy Intake in the Offspring. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goedhart, G.; Van Eijsden, M.; Van Der Wal, M.F.; Bonsel, G.J. Ethnic differences in term birthweight: The role of constitutional and environmental factors. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2008, 22, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harskamp-van Ginkel, M.W.; Kool, R.E.; van Houtum, L.; Belmon, L.S.; Huss, A.; Chinapaw, M.J.M.; Vrijkotte, T.G.M. Potential determinants during ‘the first 1000 days of life’ of sleep problems in school-aged children. Sleep Med. 2020, 69, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horjus, D.L.; Bokslag, A.; Hutten, B.A.; van den Born, B.H.; Middeldorp, S.; Vrijkotte, T.G.M. Creatine kinase is associated with blood pressure during pregnancy. J. Hypertens. 2019, 37, 1467–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krikke, G.G.; Grooten, I.J.; Vrijkotte, T.G.M.; Van Eijsden, M.; Roseboom, T.J.; Painter, R.C. Vitamin B12 and folate status in early pregnancy and cardiometabolic risk factors in the offspring at age 5–6 years: Findings from the ABCD multi-ethnic birth cohort. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2016, 123, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loomans, E.M.; Hofland, L.; Van Der Stelt, O.; Van Der Wal, M.F.; Koot, H.M.; Van Den Bergh, B.R.H.; Vrijkotte, T.G.M. Caffeine intake during pregnancy and risk of problem behavior in 5- to 6-year-old children. Pediatrics 2012, 130, e305–e313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schreuder, Y.J.; Hutten, B.A.; Van Eijsden, M.; Jansen, E.H.; Vissers, M.N.; Twickler, M.T.; Vrijkotte, T.G.M. Ethnic differences in maternal total cholesterol and triglyceride levels during pregnancy: The contribution of demographics, behavioural factors and clinical characteristics. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 65, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, A.E.; Van Eijsden, M.; Stronks, K.; Gemke, R.J.B.J.; Vrijkotte, T.G.M. Maternal depressive symptoms, serum folate status, and pregnancy outcome: Results of the Amsterdam Born Children and their Development study. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 203, 563.e1–563.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedhart, G.; van der Wal, M.F.; van Eijsden, M.; Bonsel, G.J. Maternal vitamin B-12 and folate status during pregnancy and excessive infant crying. Early Hum. Dev. 2011, 87, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eijsden, M.; Smits, L.J.M.; Van Der Wal, M.F.; Bonsel, G.J. Association between short interpregnancy intervals and term birth weight: The role of folate depletion. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 88, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hrudey, E.J.; Reynolds, R.M.; Oostvogels, A.J.J.M.; Brouwer, I.A.; Vrijkotte, T.G.M. The association between maternal 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration during gestation and early childhood cardiometabolic outcomes: Is there interaction with pre-pregnancy BMI? PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e133313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leffelaar, E.R.; Vrijkotte, T.G.M.; Van Eijsden, M. Maternal early pregnancy vitamin D status in relation to fetal and neonatal growth: Results of the multi-ethnic Amsterdam Born Children and their Development cohort. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Den Berg, G.; Van Eijsden, M.; Vrijkotte, T.G.M.; Gemke, R.J.B.J. Suboptimal maternal vitamin D status and low education level as determinants of small-for-gestational-age birth weight. Eur. J. Nutr. 2013, 52, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Eijsden, M.; Snijder, M.B.; Brouwer, I.; Vrijkotte, T.G.M. Maternal early-pregnancy vitamin D status in relation to linear growth at the age of 5–6 years: Results of the ABCD cohort. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 67, 972–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berghuis, S.A.; Van Braeckel, K.; Sauer, P.J.J.; Bos, A.F. Prenatal exposure to persistent organic pollutants and cognition and motor performance in adolescence. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berghuis, S.A.; Bos, A.F.; Sauer, P.J.J.; Bocca, G. Prenatal Environmental Exposure to Persistent Organic Pollutants and Indices of Overweight and Cardiovascular Risk in Dutch Adolescents. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, R.; Manniën, J.; te Velde, S.J.; Klomp, T.; Hutton, E.K.; Brug, J. Socio-demographic inequalities across a range of health status indicators and health behaviours among pregnant women in prenatal primary care: A cross-sectional study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2015, 15, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manniën, J.; de Jonge, A.; Cornel, M.C.; Spelten, E.; Hutton, E.K. Factors associated with not using folic acid supplements preconceptionally. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 2344–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereboom, M.T.R.; Manniën, J.; Spelten, E.R.; Schellevis, F.G.; Hutton, E.K. Observational study to assess pregnant women’s knowledge and behaviour to prevent toxoplasmosis, listeriosis and cytomegalovirus. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2013, 13, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Walle, H.E.K.; De Jong-Van Den Berg, L.T.W. Ten years after the Dutch public health campaign on folic acid: The continuing challenge. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 64, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ars, C.L.; Nijs, I.M.; Marroun, H.E.; Muetzel, R.; Schmidt, M.; Steenweg-de Graaff, J.; van der Lugt, A.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Hofman, A.; Steegers, E.A.; et al. Prenatal folate, homocysteine and vitamin B12 levels and child brain volumes, cognitive development and psychological functioning: The Generation R Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2019, 122, S1–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aubert, A.M.; Chen, L.W.; Shivappa, N.; Cooper, C.; Crozier, S.R.; Duijts, L.; Forhan, A.; Hanke, W.; Harvey, N.C.; Jankowska, A.; et al. Predictors of maternal dietary quality and dietary inflammation during pregnancy: An individual participant data meta-analysis of seven European cohorts from the ALPHABET consortium. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 1991–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadoer, S.; Gaillard, R.; Felix, J.F.; Raat, H.; Renders, C.M.; Hofman, A.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Jaddoe, V.W.V. Ethnic disparities in maternal obesity and weight gain during pregnancy. The Generation R Study. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2015, 193, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bai, G.; Korfage, I.J.; Hafkamp-De Groen, E.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Mautner, E.; Raat, H. Associations between nausea, vomiting, fatigue and health-related quality of life of women in early pregnancy: The generation r study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakker, R.; Pluimgraaff, L.E.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Raat, H.; Tiemeier, H.; Hofman, A.; Jaddoe, V.W.V. Associations of light and moderate maternal alcohol consumption with fetal growth characteristics in different periods of pregnancy: The generation R study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 39, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakker, R.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Biharie, A.A.; MacKenbach, J.P.; Hofman, A.; Jaddoe, V.W.V. Explaining differences in birth outcomes in relation to maternal age: The generation R study. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2011, 118, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, R.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Raat, H.; Hofman, A.; Jaddoe, V.W.V. Maternal caffeine intake, blood pressure, and the risk of hypertensive complications during pregnancy. the generation R study. Am. J. Hypertens. 2011, 24, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, R.; Timmermans, S.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Hofman, A.; Jaddoe, V.W.V. Folic acid supplements modify the adverse effects of maternal smoking on fetal growth and neonatal complications. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 2172–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barjaktarovic, M.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; de Rijke, Y.B.; Visser, T.J.; Korevaar, T.I.M.; Peeters, R.P. The Association of Thyroid Function With Maternal and Neonatal Homocysteine Concentrations. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 4548–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bautista Niño, P.K.; Tielemans, M.J.; Schalekamp-Timmermans, S.; Steenweg-De Graaff, J.; Hofman, A.; Tiemeier, H.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Felix, J.F.; Franco, O.H. Maternal fish consumption, fatty acid levels and angiogenic factors: The Generation R Study. Placenta 2015, 36, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergen, N.E.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Timmermans, S.; Hofman, A.; Lindemans, J.; Russcher, H.; Raat, H.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M.; Steegers, E.A.P. Homocysteine and folate concentrations in early pregnancy and the risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes: The generation R study. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2012, 119, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergen, N.E.; Schalekamp-Timmermans, S.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Hofman, A.; Lindemans, J.; Russcher, H.; Tiemeier, H.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M.; Steegers, E.A.P. Maternal and Neonatal Markers of the Homocysteine Pathway and Fetal Growth: The Generation R Study. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2016, 30, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biyik, K.Z.; Tideman, J.W.L.; Polling, J.R.; Buitendijk, G.H.S.; Jaddoe, V.V.W.; Larsen, M.; Klaver, C.C.W. Subfoveal choroidal thickness at age 9 years in relation to clinical and perinatal characteristics in the population-based Generation R Study. Acta Ophthalmol. 2020, 98, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaauwendraad, S.M.; Gaillard, R.; Santos, S.; Sol, C.M.; Kannan, K.; Trasande, L.; Jaddoe, V.W.V. Maternal Phthalate and Bisphenol Urine Concentrations during Pregnancy and Early Markers of Arterial Health in Children. Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 047007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaauwendraad, S.M.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Santos, S.; Kannan, K.; Dohle, G.R.; Trasande, L.; Gaillard, R. Associations of maternal urinary bisphenol and phthalate concentrations with offspring reproductive development. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 309, 119745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cajachagua-Torres, K.N.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; de Rijke, Y.B.; van den Akker, E.L.T.; Reiss, I.K.M.; van Rossum, E.F.C.; El Marroun, H. Parental cannabis and tobacco use during pregnancy and childhood hair cortisol concentrations. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2021, 225, 108751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jonge, L.L.; van Osch-Gevers, L.; Geelhoed, J.J.M.; Hofman, A.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Helbing, W.A.; Jaddoe, V.W.V. Breastfeeding is not associated with left cardiac structures and blood pressure during the first two years of life. The Generation R Study. Early Hum. Dev. 2010, 86, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Dekker, H.T.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Reiss, I.K.; de Jongste, J.C.; Duijts, L. Maternal folic acid use during pregnancy, methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene polymorphism, and child’s lung function and asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2018, 48, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhamo, B.; Miliku, K.; Voortman, T.; Tiemeier, H.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Wolvius, E.B.; Ongkosuwito, E.M. The Associations of Maternal and Neonatal Vitamin D with Dental Development in Childhood. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2019, 3, nzy100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Durmu, B.; Ay, L.; Duijts, L.; Moll, H.A.; Hokken-Koelega, A.C.S.; Raat, H.; Hofman, A.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Jaddoe, V.W.V. Infant diet and subcutaneous fat mass in early childhood: The Generation R Study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 66, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Marroun, H.; Bolhuis, K.; Franken, I.H.A.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Hillegers, M.H.; Lahey, B.B.; Tiemeier, H. Preconception and prenatal cannabis use and the risk of behavioural and emotional problems in the offspring; a multi-informant prospective longitudinal study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 48, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- el Marroun, H.; Tiemeier, H.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Hofman, A.; Mackenbach, J.P.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Verhulst, F.C.; van den Brink, W.; Huizink, A.C. Demographic, emotional and social determinants of cannabis use in early pregnancy: The Generation R study. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2008, 98, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfrink, M.E.C.; Moll, H.A.; Kiefte-de Jong, J.C.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Hofman, A.; Ten Cate, J.M.; Veerkamp, J.S.J. Pre- and postnatal determinants of deciduous molar hypomineralisation in 6-year-old children. The generation R study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferguson, K.K.; van den Dries, M.A.; Gaillard, R.; Pronk, A.; Spaan, S.; Tiemeier, H.; Jaddoe, V.W.V. Organophosphate Pesticide Exposure in Pregnancy in Association with Ultrasound and Delivery Measures of Fetal Growth. Environ. Health Perspect. 2019, 127, 087005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garcia, A.H.; Erler, N.S.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Tiemeier, H.; van den Hooven, E.H.; Franco, O.H.; Rivadeneira, F.; Voortman, T. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D concentrations during fetal life and bone health in children aged 6 years: A population-based prospective cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazibara, T.; den Dekker, H.T.; de Jongste, J.C.; McGrath, J.J.; Eyles, D.W.; Burne, T.H.; Reiss, I.K.; Franco, O.H.; Tiemeier, H.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; et al. Associations of maternal and fetal 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels with childhood lung function and asthma: The Generation R Study. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2016, 46, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gazibara, T.; Elbert, N.J.; den Dekker, H.T.; de Jongste, J.C.; Reiss, I.; McGrath, J.J.; Eyles, D.W.; Burne, T.H.; Tiemeier, H.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; et al. Associations of maternal and fetal 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels with childhood eczema: The Generation R Study. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 27, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geurtsen, M.L.; van Soest, E.E.L.; Voerman, E.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Gaillard, R. High maternal early-pregnancy blood glucose levels are associated with altered fetal growth and increased risk of adverse birth outcomes. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 1880–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghassabian, A.; Steenweg-de Graaff, J.; Peeters, R.P.; Ross, H.A.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Hofman, A.; Verhulst, F.C.; White, T.; Tiemeier, H. Maternal urinary iodine concentration in pregnancy and children’s cognition: Results from a population-based birth cohort in an iodine-sufficient area. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e005520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gishti, O.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Duijts, L.; Franco, O.H.; Hofman, A.; Ikram, M.K.; Gaillard, R. Influence of breastfeeding on retinal vessel calibers in school-age children. The Generation R Study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 70, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, R.; Wiertsema, C.J.; Silva, C.C.V.; Monasso, G.S.; Gaillard, R.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Santos, S.; Jaddoe, V.W.V. Associations of Fetal and Infant Growth Patterns With Early Markers of Arterial Health in School-Aged Children. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2219225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heppe, D.H.M.; Kiefte-De Jong, J.C.; Durmuş, B.; Moll, H.A.; Raat, H.; Hofman, A.; Jaddoe, V.W.V. Parental, fetal, and infant risk factors for preschool overweight: The Generation R Study. Pediatr. Res. 2013, 73, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heppe, D.H.M.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Timmermans, S.; Breeijen, H.D.; Tiemeier, H.; Hofman, A.; Jaddoe, V.W.V. Maternal fish consumption, fetal growth and the risks of neonatal complications: The Generation R Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 105, 938–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heppe, D.H.M.; Van Dam, R.M.; Willemsen, S.P.; Den Breeijen, H.; Raat, H.; Hofman, A.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Jaddoe, V.W.V. Maternal milk consumption, fetal growth, and the risks of neonatal complications: The Generation R Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herba, C.M.; Roza, S.; Govaert, P.; Hofman, A.; Jaddoe, V.; Verhulst, F.C.; Tiemeier, H. Breastfeeding and early brain development: The Generation R study. Matern. Child Nutr. 2013, 9, 332–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiefte-De Jong, J.C.; De Vries, J.H.; Bleeker, S.E.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Hofman, A.; Raat, H.; Moll, H.A. Socio-demographic and lifestyle determinants of ‘Western-like’ and ‘Health conscious’ dietary patterns in toddlers. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 109, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiefte-de Jong, J.C.; de Vries, J.H.; Escher, J.C.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Hofman, A.; Raat, H.; Moll, H.A. Role of dietary patterns, sedentary behaviour and overweight on the longitudinal development of childhood constipation: The Generation R study. Matern. Child Nutr. 2013, 9, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leermakers, E.T.M.; Kiefte-de Jong, J.C.; Hofman, A.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Franco, O.H. Lutein intake at the age of 1 year and cardiometabolic health at the age of 6 years: The Generation R Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leermakers, E.T.M.; Sonnenschein-Van Der Voort, A.M.M.; Heppe, D.H.M.; De Jongste, J.C.; Moll, H.A.; Franco, O.H.; Hofman, A.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Duijts, L. Maternal fish consumption during pregnancy and risks of wheezing and eczema in childhood: The Generation R Study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 67, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leermakers, E.T.M.; Tielemans, M.J.; van den Broek, M.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Franco, O.H.; Kiefte-de Jong, J.C. Maternal dietary patterns during pregnancy and offspring cardiometabolic health at age 6 years: The generation R study. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leermakers, E.T.M.; van den Hooven, E.H.; Franco, O.H.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Moll, H.A.; Kiefte-de Jong, J.C.; Voortman, T. A priori and a posteriori derived dietary patterns in infancy and cardiometabolic health in childhood: The role of body composition. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 37, 1589–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levie, D.; Bath, S.C.; Guxens, M.; Korevaar, T.I.M.; Dineva, M.; Fano, E.; Ibarluzea, J.M.; Llop, S.; Murcia, M.; Rayman, M.P.; et al. Maternal Iodine Status During Pregnancy Is Not Consistently Associated with Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder or Autistic Traits in Children. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 1516–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levie, D.; Korevaar, T.I.M.; Bath, S.C.; Murcia, M.; Dineva, M.; Llop, S.; Espada, M.; van Herwaarden, A.E.; de Rijke, Y.B.; Ibarluzea, J.M.; et al. Association of maternal iodine status with child IQ: A meta-analysis of individual-participant data. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 5957–5967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lubczynska, M.J.; Muetzel, R.L.; El Marroun, H.; Basagana, X.; Strak, M.; Denault, W.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Hillegers, M.; Vernooij, M.W.; Hoek, G.; et al. Exposure to Air Pollution during Pregnancy and Childhood, and White Matter Microstructure in Preadolescents. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 027005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mensink-Bout, S.M.; van Meel, E.R.; de Jongste, J.C.; Voortman, T.; Reiss, I.K.; De Jong, N.W.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Duijts, L. Maternal and neonatal 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations and school-age lung function, asthma and allergy. The Generation R Study. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2019, 49, 900–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miliku, K.; Mesu, A.; Franco, O.H.; Hofman, A.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Jaddoe, V.W.V. Maternal and Fetal Folate, Vitamin B12, and Homocysteine Concentrations and Childhood Kidney Outcomes. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 69, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miliku, K.; Voortman, T.; Bakker, H.; Hofman, A.; Franco, O.H.; Jaddoe, V.W.V. Infant Breastfeeding and Kidney Function in School-Aged Children. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 66, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miliku, K.; Voortman, T.; Franco, O.H.; McGrath, J.J.; Eyles, D.W.; Burne, T.H.; Hofman, A.; Tiemeier, H.; Jaddoe, V.W.V. Vitamin D status during fetal life and childhood kidney outcomes. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 70, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miliku, K.; Voortman, T.; Van Den Hooven, E.H.; Hofman, A.; Franco, O.H.; Jaddoe, V.W.V. First-trimester maternal protein intake and childhood kidney outcomes: The generation R study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monasso, G.S.; Felix, J.F.; Heil, S.G.; de Rijke, Y.B.; Gaillard, R.; Jaddoe, V.W.V. Vitamin B12, folate and homocysteine concentrations during pregnancy and early signs of atherosclerosis at school-age. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 5133–5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monasso, G.S.; Küpers, L.K.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Heil, S.G.; Felix, J.F. Associations of circulating folate, vitamin B12 and homocysteine concentrations in early pregnancy and cord blood with epigenetic gestational age: The Generation R Study. Clin. Epigenet. 2021, 13, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, T.A.; Korevaar, T.I.M.; Peeters, R.P.; van Herwaarden, A.E.; de Rijke, Y.B.; White, T.; Tiemeier, H. Urinary Iodine Concentrations in Pregnant Women and Offspring Brain Morphology. Thyroid 2021, 31, 964–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, C.L.A.; Grgic, O.; Trajanoska, K.; van der Tas, J.T.; Rivadeneira, F.; Wolvius, E.B.; Voortman, T.; Kragt, L. Associations Between Prenatal, Perinatal, and Early Childhood Vitamin D Status and Risk of Dental Caries at 6 Years. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 1993–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, A.N.; Elbert, N.J.; Pasmans, S.G.M.A.; Kiefte-de Jong, J.C.; De Jong, N.W.; Moll, H.A.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; de Jongste, J.C.; Franco, O.H.; Duijts, L.; et al. Diet quality throughout early life in relation to allergic sensitization and atopic diseases in childhood. Nutrients 2017, 9, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Philips, E.M.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Asimakopoulos, A.G.; Kannan, K.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Santos, S.; Trasande, L. Bisphenol and phthalate concentrations and its determinants among pregnant women in a population-based cohort in The Netherlands, 2004–5. Environ. Res. 2018, 161, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Philips, E.M.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Deierlein, A.; Asimakopoulos, A.G.; Kannan, K.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Trasande, L. Exposures to phthalates and bisphenols in pregnancy and postpartum weight gain in a population-based longitudinal birth cohort. Environ. Int 2020, 144, 106002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roza, S.J.; Van Batenburg-Eddes, T.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; MacKenbach, J.P.; Hofman, A.; Verhulst, F.C.; Tiemeier, H. Maternal folic acid supplement use in early pregnancy and child behavioural problems: The Generation R Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 103, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sammallahti, S.; Tiemeier, H.; Reiss, I.K.M.; Muckenthaler, M.U.; El Marroun, H.; Vermeulen, M. Maternal early-pregnancy ferritin and offspring neurodevelopment: A prospective cohort study from gestation to school age. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2022, 36, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.C.V.; Vehmeijer, F.O.L.; El Marroun, H.; Felix, J.F.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Santos, S. Maternal psychological distress during pregnancy and childhood cardio-metabolic risk factors. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 29, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, L.M.; Coolman, M.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Moll, H.A.; Hofman, A.; Mackenbach, J.P.; Raat, H. Maternal educational level and risk of gestational hypertension: The Generation R Study. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2008, 22, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steenweg-de Graaff, J.; Roza, S.J.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Hofman, A.; Verhulst, F.C.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Tiemeier, H. Maternal folate status in early pregnancy and child emotional and behavioral problems: The generation R study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 1413–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steenweg-de Graaff, J.; Roza, S.J.; Walstra, A.N.; El Marroun, H.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Hofman, A.; Verhulst, F.C.; Tiemeier, H.; White, T. Associations of maternal folic acid supplementation and folate concentrations during pregnancy with foetal and child head growth: The Generation R Study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steenweg-De Graaff, J.; Tiemeier, H.; Ghassabian, A.; Rijlaarsdam, J.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Verhulst, F.C.; Roza, S.J. Maternal Fatty Acid Status during Pregnancy and Child Autistic Traits: The Generation R Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 183, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steenweg-de Graaff, J.; Tiemeier, H.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M.; Hofman, A.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Verhulst, F.C.; Roza, S.J. Maternal dietary patterns during pregnancy and child internalising and externalising problems. The Generation R Study. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stroobant, W.; Braun, K.V.; Kiefte-de Jong, J.C.; Moll, H.A.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Brouwer, I.A.; Franco, O.H.; Voortman, T. Intake of Different Types of Fatty Acids in Infancy Is Not Associated with Growth, Adiposity, or Cardiometabolic Health up to 6 Years of Age. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tielemans, M.J.; Erler, N.S.; Franco, O.H.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Kiefte-de jong, J.C. Dietary acid load and blood pressure development in pregnancy: The Generation R Study. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 37, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tielemans, M.J.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Voortman, T.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Rivadeneira, F.; Franco, O.H.; Kiefte-de Jong, J.C. Protein intake during pregnancy and offspring body composition at 6 years: The Generation R Study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 56, 2151–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Timmermans, S.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Hofman, A.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M.; Steegers, E.A.P. Periconception folic acid supplementation, fetal growth and the risks of low birth weight and preterm birth: The Generation R Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2009, 102, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Timmermans, S.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Mackenbach, J.P.; Hofman, A.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M.; Steegers, E.A.P. Determinants of folic acid use in early pregnancy in a multi-ethnic urban population in The Netherlands: The Generation R study. Prev. Med. 2008, 47, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmermans, S.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Silva, L.M.; Hofman, A.; Raat, H.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M.; Steegers, E.A.P. Folic acid is positively associated with uteroplacental vascular resistance: The Generation R Study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2011, 21, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmermans, S.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M.; Vujkovic, M.; Bakker, R.; Den Breeijen, H.; Raat, H.; Russcher, H.; Lindemans, J.; Hofman, A.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; et al. Major dietary patterns and blood pressure patterns during pregnancy: The Generation R Study. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 205, 337.e1–337.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Troe, E.J.; Raat, H.; Jaddoe, V.; Hofman, A.; Steegers, E.; Verhulst, F.; Witteman, J.; Mackenbach, J. Smoking during pregnancy in ethnic populations: The Generation R study. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2008, 10, 1373–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tromp, I.; Jong, J.K.D.; Raat, H.; Jaddoe, V.; Franco, O.; Hofman, A.; De Jongste, J.; Moll, H. Breastfeeding and the risk of respiratory tract infections after infancy: The Generation R Study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e172763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tromp, I.I.M.; Briedé, S.; Kiefte-De Jong, J.C.; Renders, C.M.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Franco, O.H.; Hofman, A.; Raat, H.; Moll, H.A. Factors associated with the timing of introduction of complementary feeding: The Generation R Study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 67, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Broek, M.; Leermakers, E.T.M.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Rivadeneira, F.; Raat, H.; Hofman, A.; Franco, O.H.; Kiefte-De Jong, J.C. Maternal dietary patterns during pregnancy and body composition of the child at age 6 y: The Generation R Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van den Dries, M.A.; Guxens, M.; Spaan, S.; Ferguson, K.K.; Philips, E.; Santos, S.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Ghassabian, A.; Trasande, L.; Tiemeier, H.; et al. Phthalate and Bisphenol Exposure during Pregnancy and Offspring Nonverbal IQ. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 077009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Dries, M.A.; Keil, A.P.; Tiemeier, H.; Pronk, A.; Spaan, S.; Santos, S.; Asimakopoulos, A.G.; Kannan, K.; Gaillard, R.; Guxens, M.; et al. Prenatal Exposure to Nonpersistent Chemical Mixtures and Fetal Growth: A Population-Based Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2021, 129, 117008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Tas, J.T.; Elfrink, M.E.C.; Heijboer, A.C.; Rivadeneira, F.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Tiemeier, H.; Schoufour, J.D.; Moll, H.A.; Ongkosuwito, E.M.; Wolvius, E.B.; et al. Foetal, neonatal and child vitamin D status and enamel hypomineralization. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 2018, 46, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Gijssel, R.M.A.; Braun, K.V.E.; Kiefte-de Jong, J.C.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Franco, O.H.; Voortman, T. Associations between dietary fiber intake in infancy and cardiometabolic health at school age: The generation R study. Nutrients 2016, 8, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Mil, N.H.; Bouwl-Both, M.I.; Stolk, L.; Verbiest, M.M.P.J.; Hofman, A.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Verhulst, F.C.; Eilers, P.H.C.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; Steegers, E.A.P.; et al. Determinants of maternal pregnancy one-carbon metabolism and newborn human DNA methylation profiles. Reproduction 2014, 148, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Mil, N.H.; Tiemeier, H.; Bongers-Schokking, J.J.; Ghassabian, A.; Hofman, A.; Hooijkaas, H.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; de Muinck Keizer-Schrama, S.M.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Visser, T.J.; et al. Low urinary iodine excretion during early pregnancy is associated with alterations in executive functioning in children. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 2167–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Zwol-Janssens, C.; Trasande, L.; Asimakopoulos, A.G.; Martinez-Moral, M.P.; Kannan, K.; Philips, E.M.; Rivadeneira, F.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Santos, S. Fetal exposure to bisphenols and phthalates and childhood bone mass: A population-based prospective cohort study. Environ. Res. 2020, 186, 109602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdejo-Roman, J.; Bjornholm, L.; Muetzel, R.L.; Torres-Espinola, F.J.; Lieslehto, J.; Jaddoe, V.; Campos, D.; Veijola, J.; White, T.; Catena, A.; et al. Maternal prepregnancy body mass index and offspring white matter microstructure: Results from three birth cohorts. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 43, 1995–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vidakovic, A.J.; Gishti, O.; Voortman, T.; Felix, J.F.; Williams, M.A.; Hofman, A.; Demmelmair, H.; Koletzko, B.; Tiemeier, H.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; et al. Maternal plasma PUFA concentrations during pregnancy and childhood adiposity: The Generation R Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vidakovic, A.J.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Gishti, O.; Felix, J.F.; Williams, M.A.; Hofman, A.; Demmelmair, H.; Koletzko, B.; Tiemeier, H.; Gaillard, R. Body mass index, gestational weight gain and fatty acid concentrations during pregnancy: The Generation R Study. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 30, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vinkhuyzen, A.A.E.; Eyles, D.W.; Burne, T.H.; Blanken, L.M.E.; Kruithof, C.J.; Verhulst, F.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Tiemeier, H.; McGrath, J.J. Prevalence and predictors of vitamin D deficiency based on maternal mid-gestation and neonatal cord bloods: The Generation R Study. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 164, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voerman, E.; Gaillard, R.; Geurtsen, M.L.; Jaddoe, V.W.V. Maternal First-Trimester Cow-Milk Intake Is Positively Associated with Childhood General and Abdominal Visceral Fat Mass and Lean Mass but Not with Other Cardiometabolic Risk Factors at the Age of 10 Years. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 1965–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voerman, E.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Hulst, M.E.; Oei, E.H.; Gaillard, R. Associations of maternal caffeine intake during pregnancy with abdominal and liver fat deposition in childhood. Pediatr. Obes. 2020, 15, e12607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voerman, E.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Gishti, O.; Hofman, A.; Franco, O.H.; Gaillard, R. Maternal caffeine intake during pregnancy, early growth, and body fat distribution at school age. Obesity 2016, 24, 1170–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voortman, T.; Bakker, H.; Sedaghat, S.; Kiefte–de Jong, J.C.; Hofman, A.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Franco, O.H.; van den Hooven, E.H. Protein intake in infancy and kidney size and function at the age of 6 years: The Generation R Study. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2015, 30, 1825–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voortman, T.; Leermakers, E.T.M.; Franco, O.H.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Moll, H.A.; Hofman, A.; van den Hooven, E.H.; Kiefte-de Jong, J.C. A priori and a posteriori dietary patterns at the age of 1 year and body composition at the age of 6 years: The Generation R Study. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 31, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wahab, R.J.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Gaillard, R. Associations of maternal early-pregnancy dietary glycemic index with childhood general, abdominal and ectopic fat accumulation. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 1628–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahab, R.J.; Scholing, J.M.; Gaillard, R. Maternal early pregnancy dietary glycemic index and load, fetal growth, and the risk of adverse birth outcomes. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 60, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiertsema, C.J.; Mensink-Bout, S.M.; Duijts, L.; Mulders, A.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Gaillard, R. Associations of DASH Diet in Pregnancy With Blood Pressure Patterns, Placental Hemodynamics, and Gestational Hypertensive Disorders. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e017503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiertsema, C.J.; Wahab, R.J.; Mulders, A.; Gaillard, R. Associations of dietary glycemic index and load during pregnancy with blood pressure, placental hemodynamic parameters and the risk of gestational hypertensive disorders. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, R.; El Marroun, H.; Cecil, C.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Hillegers, M.; Tiemeier, H.; White, T. Maternal folate levels during pregnancy and offspring brain development in late childhood. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 40, 3391–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Driel, L.M.J.W.; Verkleij-Hagoort, A.C.; De Jonge, R.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Van Duijn, C.M.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M. Two MTHFR polymorphisms, maternal B-vitamin intake, and CHDs. Birth Defects Res. Part A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2008, 82, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talsness, C.E.; Penders, J.; Jansen, E.H.J.M.; Damoiseaux, J.; Thijs, C.; Mommers, M. Influence of vitamin D on key bacterial taxa in infant microbiota in the KOALA Birth Cohort Study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e188011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaak, I.; de Cock, M.; de Boer, M.; Lamoree, M.; Leonards, P.; van de Bor, M. Prenatal exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances and Behavioral development in children. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brouwer-Brolsma, E.M.; van de Rest, O.; Godschalk, R.; Zeegers, M.P.A.; Gielen, M.; de Groot, R.H.M. Associations between maternal long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid concentrations and child cognition at 7 years of age: The MEFAB birth cohort. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2017, 126, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jochems, S.H.J.; Gielen, M.; Rump, P.; Hornstra, G.; Zeegers, M.P. Potential programming of selected cardiometabolic risk factors at childhood by maternal polyunsaturated fatty acid availability in the MEFAB cohort. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2015, 100, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Adrichem, D.S.; Huijbregts, S.C.J.; Van Der Heijden, K.B.; Van Goozen, S.H.M.; Swaab, H. Aggressive behavior during toddlerhood: Interrelated effects of prenatal risk factors, negative affect, and cognition. Child Neuropsychol. 2020, 26, 982–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TNO; Peeters, D.; Lanting, C.I.; Van Wouwe, J.P. Peiling Melkvoeding van Zuigelingen 2015. TNO/CH 2015 R10385; TNO: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Beijers, C.; Burger, H.; Verbeek, T.; Bockting, C.L.H.; Ormel, J. Continued smoking and continued alcohol consumption during early pregnancy distinctively associated with personality. Addict. Behav. 2014, 39, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husen, S.C.; Kemper, N.; Go, A.; Willemsen, S.P.; Rousian, M.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M. Periconceptional maternal folate status and the impact on embryonic head and brain structures: The Rotterdam Periconceptional Cohort. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2022, 44, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, J.; Schoenmakers, S.; Ringelberg, B.; Reijnders, I.F.; Willemsen, S.P.; De Rijke, Y.B.; Mulders, A.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M. Periconceptional maternal and paternal homocysteine levels and early utero-placental (vascular) growth trajectories: The Rotterdam periconception cohort. Placenta 2021, 115, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smit, A.J.P.; Hojeij, B.; Rousian, M.; Schoenmakers, S.; Willemsen, S.P.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M.; van Rossem, L. A high periconceptional maternal ultra-processed food consumption impairs embryonic growth: The Rotterdam periconceptional cohort. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 1667–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, F.; Rousian, M.; Huijgen, N.A.; Koning, A.H.J.; Willemsen, S.P.; de Vries, J.H.M.; Cetin, I.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M. Periconceptional maternal ‘high fish and olive oil, low meat’ dietary pattern is associated with increased embryonic growth: The Rotterdam Periconceptional Cohort (Predict) Study. Ultrasound Obs. Gynecol. 2017, 50, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parisi, F.; Rousian, M.; Koning, I.V.; Willemsen, S.P.; de Vries, J.H.M.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M. Periconceptional maternal dairy-rich dietary pattern is associated with prenatal cerebellar growth. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Dijk, M.R.; Borggreven, N.V.; Willemsen, S.P.; Koning, A.H.J.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M.; Koster, M.P.H. Maternal Lifestyle Impairs Embryonic Growth: The Rotterdam Periconception Cohort. Reprod. Sci. 2018, 25, 916–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Uitert, E.M.; Van Ginkel, S.; Willemsen, S.P.; Lindemans, J.; Koning, A.H.J.; Eilers, P.H.C.; Exalto, N.; Laven, J.S.E.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M. An optimal periconception maternal folate status for embryonic size: The Rotterdam Predict study. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2014, 121, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijnands, K.P.J.; Van Uitert, E.M.; Roeters Van Lennep, J.E.; Koning, A.H.J.; Mulders, A.G.M.G.J.; Laven, J.S.E.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M. The periconception maternal cardiovascular risk profile influences human embryonic growth trajectories in IVF/ICSI pregnancies. Hum. Reprod. 2016, 31, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaspers, M.; de Meer, G.; Verhulst, F.C.; Ormel, J.; Reijneveld, S.A. Limited validity of parental recall on pregnancy, birth, and early childhood at child age 10 years. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2010, 63, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooijmans, K.H.M.; Beijers, R.; Brett, B.E.; de Weerth, C. Daily skin-to-skin contact in full-term infants and breastfeeding: Secondary outcomes from a randomized controlled trial. Matern. Child Nutr. 2022, 18, e13241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diepeveen, F.B.; van Dommelen, P.; Oudesluys-Murphy, A.M.; Verkerk, P.H. Specific language impairment is associated with maternal and family factors. Child Care Health Dev. 2017, 43, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, D.J.; Middeldorp, C.M.; van Beijsterveldt, C.E.M.; Vink, J.M.; Haak, M.C.; Boomsma, D.I. Birth weight in a large series of triplets. BMC Pediatr. 2011, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pop, V.; van Son, M.; Wijnen, H.; Spek, V.; Denollet, J.; Bergink, V. Increase of depressive symptomatology during pregnancy over 25 years’ time in four population based cohorts. J. Affect. Disord. 2019, 259, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, J.A.; Beijers, R.; Ehrlich, K.B.; Cassidy, J.; de Weerth, C. Beyond Early Adversity: The Role of Parenting in Infant Physical Health. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 2020, 41, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


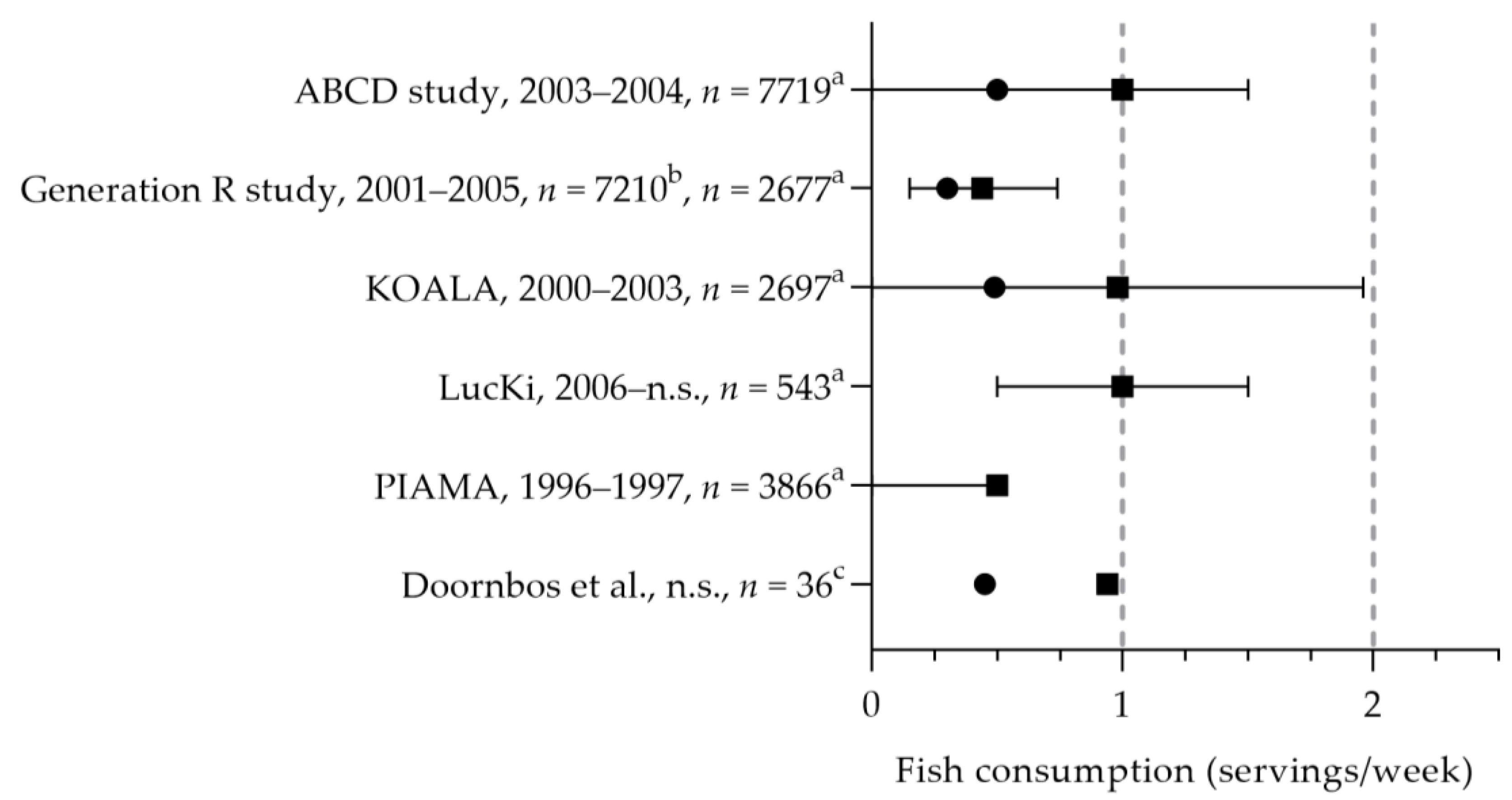



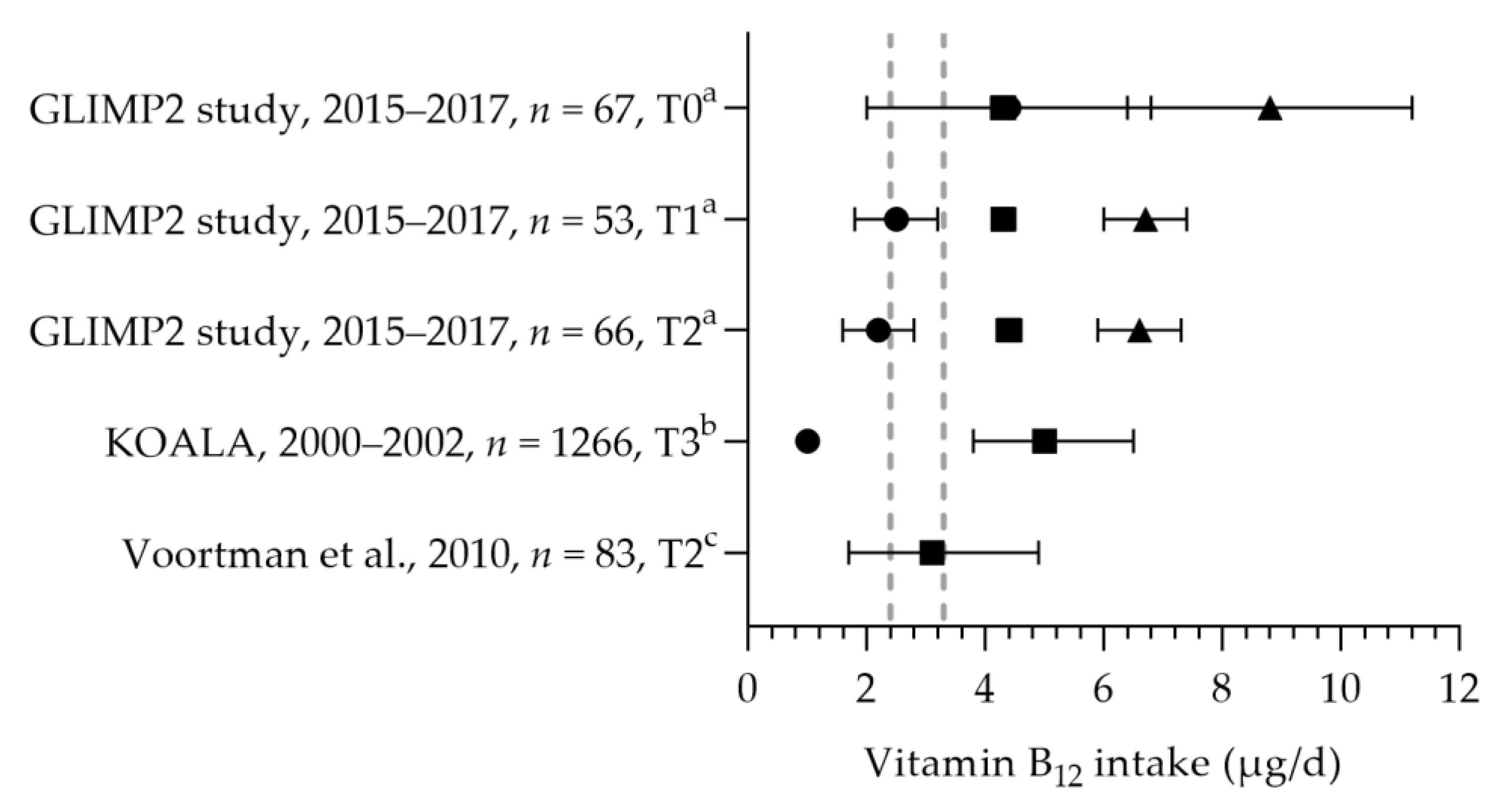



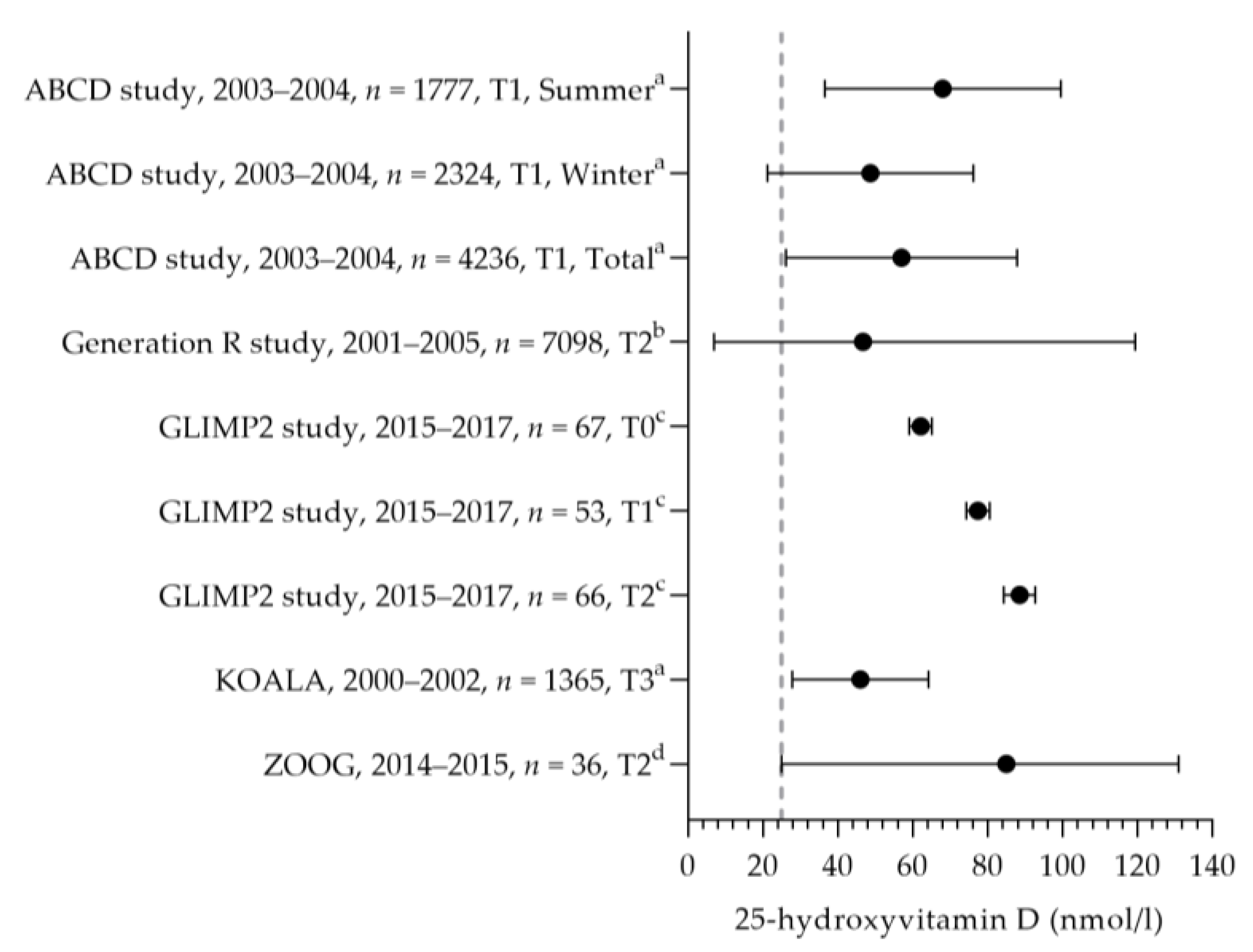

| Dietary Recommendations |
|---|
Healthy and varied food
|
| Nutrient | EAR | RDA | AI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protein (g/kg) | 0.66 + First trimester: 0.5 g Second: 7.2 g Third: 32 g | 0.83 + First trimester: 1 g Second: 9 g Third: 28 g | |
| Vitamin A (μg RAE) 1 | 580 | 750 | |
| Thiamin (B1 and mg/MJ) | 0.072 | 0.1 (1.0 mg/d) First trimester: 0.9 mg/d Second: 1.0 mg/d Third: 1.1 mg/d | |
| Riboflavin (B2 and mg) | 1.5 | 1.9 | |
| Niacin (B3, mg, and NE/MJ) | 1.3 | 1.6 (16 mg NE/d) First trimester: 15 mg NE/d Second: 16 mg NE/d Third: 17 mg NE/d | |
| Vitamin B6 (mg) | 1.3 | 1.8 | |
| Folate (μg DFE) 2 | 400 | ||
| Vitamin B12 (μg) | 2.4 | 3.3 | |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 85 | ||
| Vitamin D (μg) | 10 | ||
| Vitamin K1 (μg) | 70 | ||
| Calcium (mg) | <20 weeks gestation: 18–24 year: 860 ≥25 year: 750 | <20 weeks gestation: 18–24 year: 1.000 ≥25 year: 950 | ≥20 weeks gestation: 1.000 |
| Iron (mg) | 7 | 16 | |
| Iodine (μg) | 200 | ||
| Potassium (g) | 3.5 | ||
| Copper (mg) | 0.8 | 1.0 | |
| Magnesium (mg) | 300 | ||
| Zinc (mg) | 7.0 | 9.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
ter Borg, S.; Koopman, N.; Verkaik-Kloosterman, J. An Evaluation of Food and Nutrient Intake among Pregnant Women in The Netherlands: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3071. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15133071
ter Borg S, Koopman N, Verkaik-Kloosterman J. An Evaluation of Food and Nutrient Intake among Pregnant Women in The Netherlands: A Systematic Review. Nutrients. 2023; 15(13):3071. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15133071
Chicago/Turabian Styleter Borg, Sovianne, Nynke Koopman, and Janneke Verkaik-Kloosterman. 2023. "An Evaluation of Food and Nutrient Intake among Pregnant Women in The Netherlands: A Systematic Review" Nutrients 15, no. 13: 3071. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15133071
APA Styleter Borg, S., Koopman, N., & Verkaik-Kloosterman, J. (2023). An Evaluation of Food and Nutrient Intake among Pregnant Women in The Netherlands: A Systematic Review. Nutrients, 15(13), 3071. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15133071





