Construction of a QSAR Model Based on Flavonoids and Screening of Natural Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
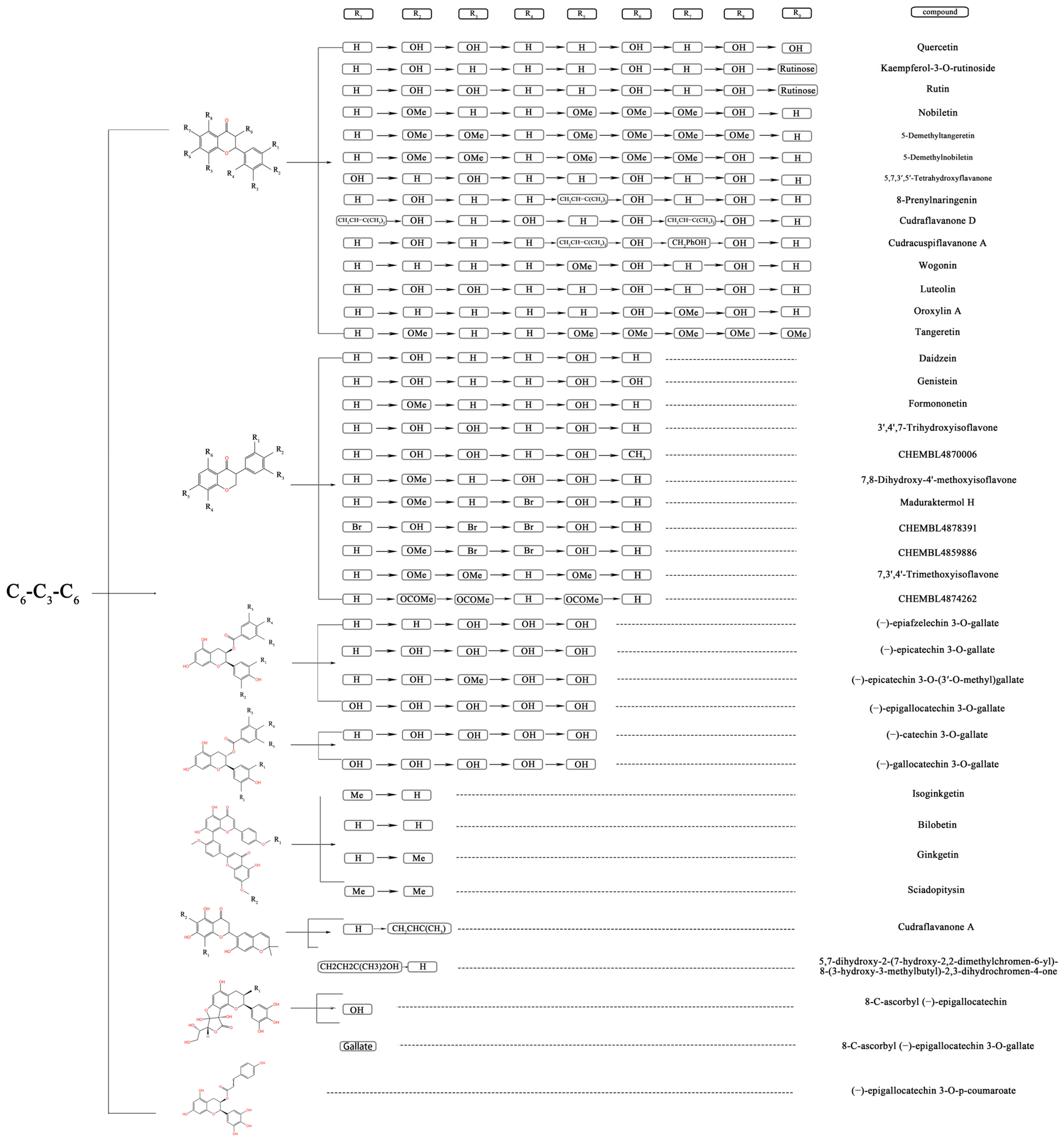
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Molecular Descriptors
2.3. Model Construction and Prediction of pIC50 Values
2.4. Validation of Models and Selection of the Optimal One for Prediction
2.5. Natural Product Screening Based on the MCS Algorithm and ADMET
2.6. Molecular Docking
2.7. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
2.8. Combined Free Energy Calculation by MMGBSA
3. Results and Discussion
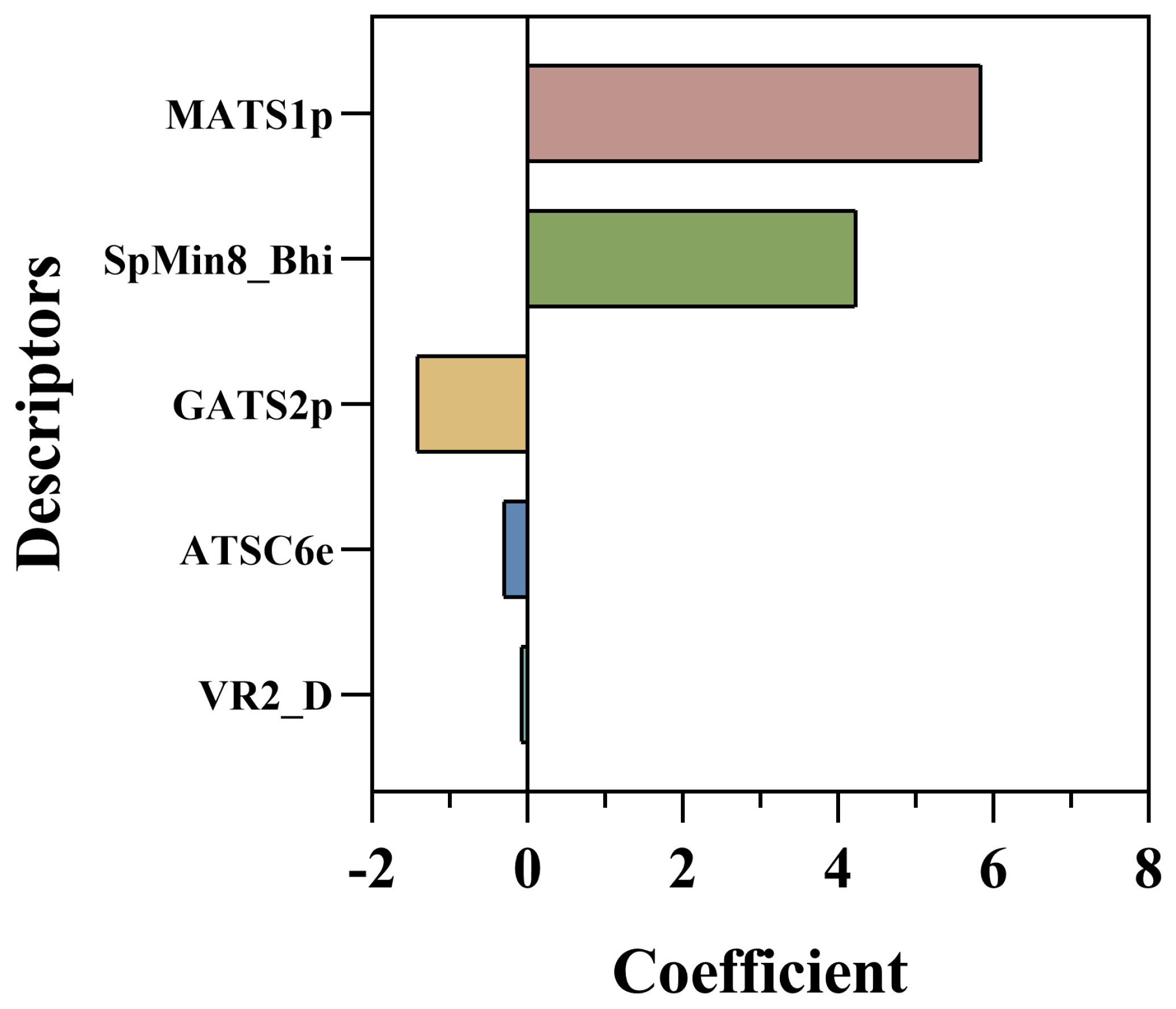
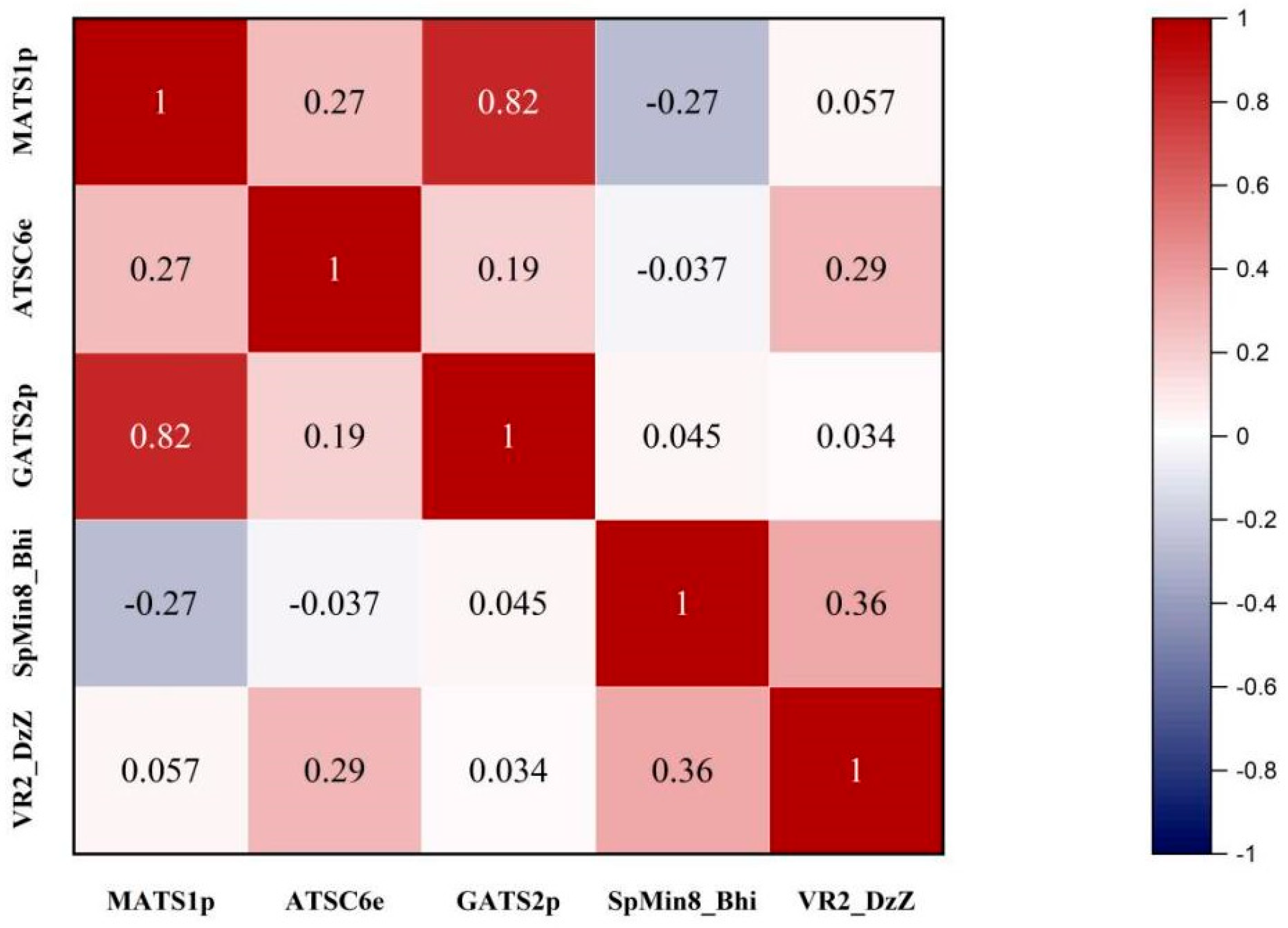
3.1. QSAR Analysis
3.2. Discovery of Natural PL Inhibitors and ADMET Analysis
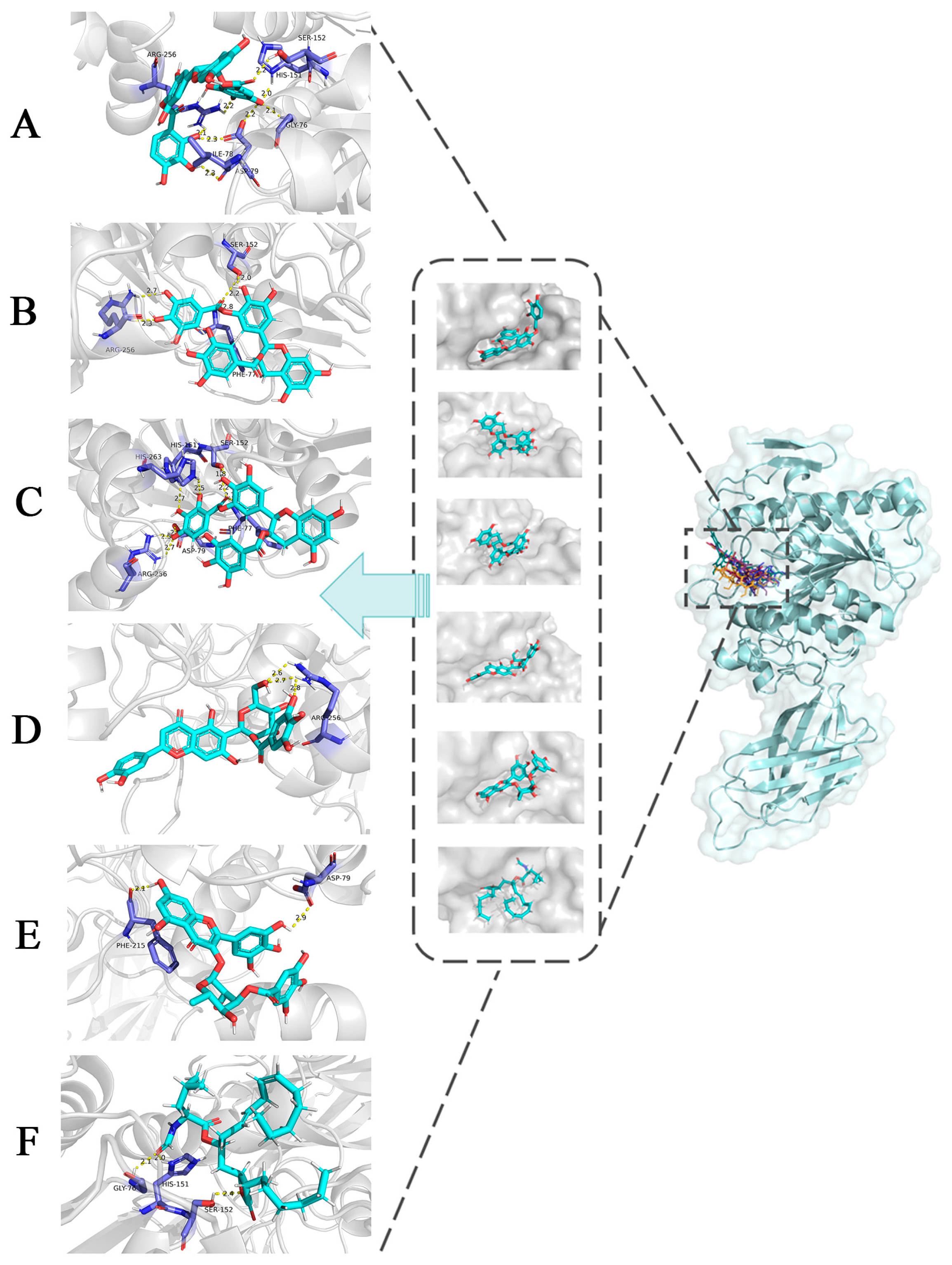
3.3. Molecular Docking Analysis
3.4. Molecular Dynamics Simulation Analysis
3.5. Combining Free Energy Calculations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ardissino, M.; Vincent, M.; Hines, O.; Amin, R.; Eichhorn, C.; Tang, A.R.; Collins, P.; Moussa, O.; Purkayastha, S. Long-term cardiovascular outcomes after orlistat therapy in patients with obesity: A nationwide, propensity-score matched cohort study. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2022, 8, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.-T.; Liu, X.-T.; Chen, Q.-X.; Shi, Y. Lipase Inhibitors for Obesity: A Review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 128, 110314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Chauhan, S. Pancreatic lipase inhibitors: The road voyaged and successes. Life Sci. 2021, 271, 119115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, A.M.; Yanovski, J.A.; Calis, K.A. Orlistat, a New Lipase Inhibitor for the Management of Obesity. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2000, 20, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Yang, C.; Yu, Z.; Li, X.; Mu, Q.; Liao, G.; Yu, B. Natural products as LSD1 inhibitors for cancer therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, A.J.; McNulty, J. Polyphenolic natural products and natural product–inspired steroidal mimics as aromatase inhibitors. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 1274–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Maldonado, P.; Alvarenga, N.; Burgos-Edwards, A.; Flores-Giubi, M.E.; Barúa, J.E.; Romero-Rodríguez, M.C.; Soto-Rifo, R.; Valiente-Echeverría, F.; Langjahr, P.; Cantero-González, G.; et al. Screening of Natural Products Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Entry. Molecules 2022, 27, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavi, S.M.; Šamec, D.; Tomczyk, M.; Milella, L.; Russo, D.; Habtemariam, S.; Suntar, I.; Rastrelli, L.; Daglia, M.; Xiao, J.; et al. Flavonoid biosynthetic pathways in plants: Versatile targets for metabolic engineering. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 38, 107316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yang, M.; Xu, J.; Hu, Y.; Gao, R.; Huang, K.; He, X. Coreopsis tinctoria and Its Flavonoids Ameliorate Hyperglycemia in Obese Mice Induced by High-Fat Diet. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Zhou, F.; Dong, J.; Wang, Y.; Lang, Z.; Li, S.; Li, S. Study on the role of flavonoids derived extract from seed residues of hippophae rhamnoides on high-fat diet induced obese mice. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2020, 32, 1597–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-M.; Chen, Y.-T.; Ruan, J.-C.; Wang, W.-J.; Chen, J.-G.; Zhang, Q.-F. Structure-activity relationship of dietary flavonoids on pancreatic lipase. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 6, 100424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hu, X.; Pan, J.; Gong, D.; Zhang, G. Mechanistic insights into the inhibition of pancreatic lipase by apigenin: Inhibitory interaction, conformational change and molecular docking studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 335, 116505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardullo, N.; Muccilli, V.; Pulvirenti, L.; Tringali, C. Natural Isoflavones and Semisynthetic Derivatives as Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitors. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 84, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Majumder, T.; Sarkar, A.; Mukherjee, P.; Basu, S. Flavonoids as BACE1 inhibitors: QSAR modelling, screening and in vitro evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ning, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Sun, C.; Huo, X.; Yu, Z.; Feng, L.; Zhang, B.; Tian, X.; et al. Drug interaction study of flavonoids toward CYP3A4 and their quantitative structure activity relationship (QSAR) analysis for predicting potential effects. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 294, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercader, A.G.; Pomilio, A.B. QSAR study of flavonoids and biflavonoids as influenza H1N1 virus neuraminidase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 1724–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakai, M.; Fukui, Y.; Asami, S.; Toyoda-Ono, Y.; Iwashita, T.; Shibata, H.; Mitsunaga, T.; Hashimoto, F.; Kiso, Y. Inhibitory Effects of Oolong Tea Polyphenols on Pancreatic Lipase in Vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 4593–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.; Tan, S.; Xu, T.; Liu, H.; Huang, J.; Yao, X. MolAICal: A soft tool for 3D drug design of protein targets by artificial intelligence and classical algorithm. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbaa161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-Y.; Han, L.-T. Study on the molecular mechanism of anti-liver cancer effect of Evodiae fructus by network pharmacology and QSAR model. Front. Chem. 2023, 10, 1060500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanwell, M.D.; Curtis, D.E.; Lonie, D.C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Zurek, E.; Hutchison, G.R. Avogadro: An advanced semantic chemical editor, visualization, and analysis platform. J. Cheminform. 2012, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halgren, T.A. MMFF VII. Characterization of MMFF94, MMFF94s, and Other Widely Available Force Fields for Conforma-tional Energies and for Intermolecular-Interaction Energies and Geometries. J. Comput. Chem. 1999, 20, 730–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriwaki, H.; Tian, Y.-S.; Kawashita, N.; Takagi, T. Mordred: A molecular descriptor calculator. J. Cheminform. 2018, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, C.W. PaDEL-descriptor: An open source software to calculate molecular descriptors and fingerprints. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 1466–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratov, E.N.; Bajorath, J.; Sheridan, R.P.; Tetko, I.V.; Filimonov, D.; Poroikov, V.; Oprea, T.I.; Baskin, I.I.; Varnek, A.; Roitberg, A.; et al. QSAR without borders. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 3525–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajalsiddig, T.T.H.; Osman, A.B.M.; Saeed, A.E.M. 2D-QSAR Modeling and Molecular Docking Studies on 1H-Pyrazole-1-carbothioamide Derivatives as EGFR Kinase Inhibitors. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 18662–18674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gackowski, M.; Szewczyk-Golec, K.; Pluskota, R.; Koba, M.; Mądra-Gackowska, K.; Woźniak, A. Application of Multivariate Adaptive Regression Splines (MARSplines) for Predicting Antitumor Activity of Anthrapyrazole Derivatives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, D.; Hahn, M. Extended-Connectivity Fingerprints. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2010, 50, 742–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhu, J.; Wang, L.; Jing, H.; Ma, C.; Kou, X.; Wang, H. Inhibitory mechanisms and interaction of tangeretin, 5-demethyltangeretin, nobiletin, and 5-demethylnobiletin from citrus peels on pancreatic lipase: Kinetics, spectroscopies, and molecular dynamics simulation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 1927–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pan, F.; Yang, Z.; Gao, F.; Li, J.; Zhang, F.; Wang, T. Construction of QSAR model based on cysteine-containing dipeptides and screening of natural tyrosinase inhibitors. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Li, J.; Zhao, L.; Tuersuntuoheti, T.; Mehmood, A.; Zhou, N.; Hao, S.; Wang, C.; Guo, Y.; Lin, W. A molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation study on the interaction between cyanidin -3-O-glucoside and major proteins in cow’s milk. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, J.A.; Martinez, C.; Kasavajhala, K.; Wickstrom, L.; Hauser, K.E.; Simmerling, C. ff14SB: Improving the accuracy of protein side chain and backbone parameters from ff99SB. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 3696–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genheden, S.; Ryde, U. The MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA methods to estimate ligand-binding affinities. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2015, 10, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.K.; Pilania, P.; Singh, P.; Sharma, S.; Prabhakar, Y.S. CP-MLR directed QSAR study of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: Sulfonamide and sulfamate inhibitors. Open Chem. 2009, 7, 909–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciubotariu, D.; Medeleanu, M.; Vlaia, V.; Olariu, T.; Ciubotariu, C.; Dragos, D.; Corina, S. Molecular van der Waals Space and Topological Indices from the Distance Matrix. Molecules 2004, 9, 1053–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Jia, Y.; Ma, Y.; Cheng, G.; Cai, S. Phenolic Composition, Antioxidant Properties, and Inhibition toward Digestive Enzymes with Molecular Docking Analysis of Different Fractions from Prinsepia utilis Royle Fruits. Molecules 2018, 23, 3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, R.K.; Verma, V.V.; Kumar, A.; Tandon, S.; Das, B.C.; Hedau, S.T. In silico prediction and interaction of resveratrol on methyl-CpG binding proteins by molecular docking and MD simulations study. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 11493–11504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shojapour, M.; Farahmand, S. Point mutation consideration in CcO protein of the electron transfer chain by MD simulation. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2022, 117, 108309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollingsworth, S.A.; Dror, R.O. Molecular Dynamics Simulation for All. Neuron 2018, 99, 1129–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.-H.; Jiang, X.-L.; Liu, Y.-M.; Hu, J.-J.; Liang, J.; Liao, X. Screening of Lipase Inhibitors from Scutellaria Baicalensis Extract Using Lipase Immobilized on Magnetic Nanoparticles and Study on the Inhibitory Mechanism. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 2275–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.-K.; Weng, Z.-M.; Ge, G.-B.; Li, H.-L.; Ding, L.-L.; Dai, Z.-R.; Hou, X.-D.; Leng, Y.-H.; Yu, Y.; Hou, J. Biflavones from Ginkgo Biloba as Novel Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitors: Inhibition Potentials and Mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 2216–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, Y.H.; Kim, S.B.; Liu, Q.; Lee, J.W.; Hwang, B.Y.; Lee, M.K. Benzylated and Prenylated Flavonoids from the Root Barks of Cudrania Tricuspidata with Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitory Activity. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 3455–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habtemariam, S. Antihyperlipidemic Components of Cassia Auriculata Aerial Parts: Identification Through In Vitro Studies: Antihyperlipidemic Components of Cassia auriculata Aerial Parts. Phytother. Res. 2013, 27, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Train | Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.9444 | R2 | 0.8962 |
| R2adj | 0.9323 | R2adj | 0.8847 |
| MAE | 0.1754 | MAE | 0.2515 |
| RSS | 1.3710 | RSS | 1.0134 |
| SDEC | 0.2174 | SDEC | 0.3035 |
| pIC50pre = 3.83259 + (5.84689) × MATS1p + (−0.30375) × ATSC6e + (−1.41739) × GATS2p + (4.23423) × SpMin8_Bhi + (−0.07596) × VR2_D | |||
| Flavonoid | pIC50 a | pIC50pre b | Residual |
|---|---|---|---|
| Daidzein | 4.081 | 4.037 | 0.044 |
| Genistein | 4.222 | 4.050 | 0.172 |
| 3′,4′,7-Trihydroxyisoflavone | 4.155 | 3.957 | 0.198 |
| CHEMBL4870006 | 4.036 | 4.051 | 0.015 |
| Maduraktermol H | 4.201 | 3.977 | 0.224 |
| CHEMBL4878391 | 4.060 | 4.072 | 0.011 |
| 7,3′,4′-Trimethoxyisoflavone | 3.444 | 3.838 | 0.394 |
| CHEMBL4874262 | 3.914 | 3.707 | 0.207 |
| Wogonin | 3.813 | 3.765 | 0.049 |
| Oroxylin A | 4.251 | 4.007 | 0.244 |
| (−)-Epiafzelechin 3-O-gallate | 5.588 | 5.912 | 0.323 |
| (−)-Epicatechin 3-O-gallate | 6.345 | 6.070 | 0.275 |
| (−)-Epigallocatechin 3-O-gallate | 6.457 | 6.181 | 0.276 |
| (−)-Epigallocatechin 3-O-p-coumaroate | 6.053 | 6.256 | 0.203 |
| (−)-Gallocatechin 3-O-gallate | 6.360 | 6.181 | 0.178 |
| 8-C-ascorbyl (−)-epigallocatechin | 6.190 | 6.268 | 0.079 |
| Tangeretin | 4.833 | 4.763 | 0.070 |
| Nobiletin | 4.880 | 4.876 | 0.004 |
| 5-Demethylnobiletin | 5.379 | 5.294 | 0.085 |
| Quercetin | 3.836 | 4.134 | 0.298 |
| Bilobetin | 5.447 | 5.133 | 0.315 |
| Ginkgetin | 5.161 | 5.706 | 0.545 |
| 5,7,3′,5′-Tetrahydroxyflavanone | 4.087 | 4.182 | 0.094 |
| 8-Prenylnaringenin | 4.114 | 4.190 | 0.076 |
| Cudraflavanone A | 5.187 | 5.229 | 0.041 |
| 2′,5,7-Trihydroxy-4,5′-(2,2-dimethylchromeno)-8-(3-hydroxy-3-methylbuthyl)flavanone | 4.073 | 4.330 | 0.257 |
| Luteolin | 3.573 | 3.755 | 0.182 |
| Kaempferol-3-Orutinoside | 5.538 | 5.335 | 0.203 |
| Rutin | 3.827 | 3.850 | 0.023 |
| Formononetin * | 3.921 | 3.765 | 0.156 |
| 7,8-Dihydroxy-4′-methoxyisoflavone * | 4.032 | 4.128 | 0.097 |
| CHEMBL4859886 * | 4.000 | 3.998 | 0.002 |
| (−)-Epicatechin 3-O-(3′-O-methyl)gallate * | 6.167 | 5.755 | 0.413 |
| (−)-Catechin 3-O-gallate * | 6.265 | 6.039 | 0.226 |
| 8-C-ascorbyl (−)-epigallocatechin 3-O-gallate * | 6.102 | 6.696 | 0.594 |
| 5-Demethyltangeretin * | 5.444 | 5.793 | 0.349 |
| Isoginkgetin * | 5.538 | 5.421 | 0.117 |
| Sciadopitysin * | 4.893 | 4.674 | 0.219 |
| Cudraflavanone D * | 5.046 | 5.493 | 0.448 |
| Cudracuspiflavanone A * | 4.261 | 4.115 | 0.146 |
| Compounds | Molecular Structure | IC50pre (μM) | Water Solubility | BS | GI Absorption | Pgp Substrate | log Kp (cm/s) | Carcino_Mouse | Carcino_Rat |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
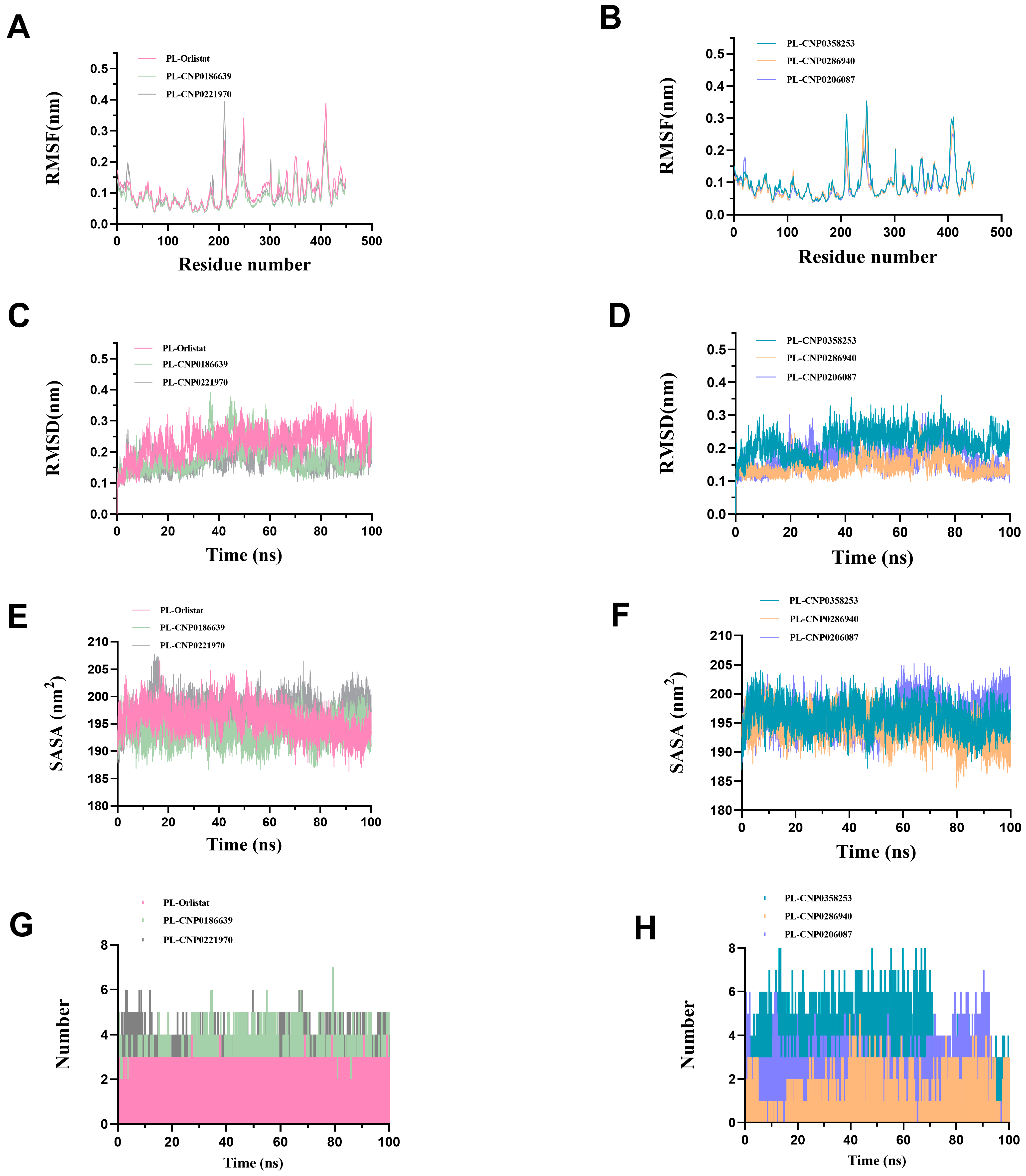
| CNP0186639 | 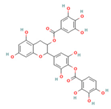 | 0.49 | Moderately soluble | 0.17 | Low | No | −7.55 | negative | positive |
| CNP0221970 |  | 0.61 | Moderately soluble | 0.17 | Low | No | −7.94 | negative | positive |
| CNP0358253 | 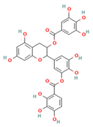 | 0.73 | Moderately soluble | 0.17 | Low | No | −7.55 | negative | positive |
| CNP0286940 | 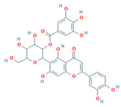 | 0.85 | Moderately soluble | 0.17 | Low | No | −9.24 | negative | negative |
| CNP0206087 | 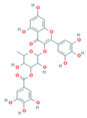 | 1.27 | Moderately soluble | 0.17 | Low | No | −8.87 | negative | positive |
| Active Compound | Protein (PDBID) | Docking Energy (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| Orlistat | pancreatic lipase (1LPB) | −6.7 |
| CNP0186639 | pancreatic lipase (1LPB) | −9.6 |
| CNP0221970 | pancreatic lipase (1LPB) | −9.2 |
| CNP0358253 | pancreatic lipase (1LPB) | −9.5 |
| CNP0286940 | pancreatic lipase (1LPB) | −9.3 |
| CNP0206087 | pancreatic lipase (1LPB) | −8.4 |
| Energy (kJ/mol) | ΔEvdw | ∆Eele | ∆Gpol | ∆Gnon-pol | ∆Ggas | ∆Gsol | ∆Gbind |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orlistat | −37.56 | −33.32 | 40.95 | −5.75 | −70.88 | 35.2 | −35.68 |
| CNP0186639 | −42.87 | −31.17 | 46.74 | −5.92 | −74.04 | 40.82 | −33.22 |
| CNP0221970 | −36.33 | −53.92 | 63.46 | −5.51 | −90.26 | 57.96 | −32.3 |
| CNP0358253 | −36.66 | −71.72 | 70.01 | −5.99 | −108.38 | 64.03 | −44.35 |
| CNP0286940 | −45.42 | −19.41 | 39.72 | −5.67 | −64.83 | 34.06 | −30.77 |
| CNP0206087 | −38.78 | −40.53 | 61.83 | −5.41 | −79.31 | 56.42 | −22.89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, Y.; Pan, F.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wang, O.; Li, Q.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, L. Construction of a QSAR Model Based on Flavonoids and Screening of Natural Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitors. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3489. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153489
Yuan Y, Pan F, Zhu Z, Yang Z, Wang O, Li Q, Zhao L, Zhao L. Construction of a QSAR Model Based on Flavonoids and Screening of Natural Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitors. Nutrients. 2023; 15(15):3489. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153489
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Yutong, Fei Pan, Zehui Zhu, Zichen Yang, Ou Wang, Qing Li, Liang Zhao, and Lei Zhao. 2023. "Construction of a QSAR Model Based on Flavonoids and Screening of Natural Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitors" Nutrients 15, no. 15: 3489. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153489
APA StyleYuan, Y., Pan, F., Zhu, Z., Yang, Z., Wang, O., Li, Q., Zhao, L., & Zhao, L. (2023). Construction of a QSAR Model Based on Flavonoids and Screening of Natural Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitors. Nutrients, 15(15), 3489. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153489









