The Pivotal Role of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor-Regulated Tight Junction Proteins and Innate Immunity on the Synergistic Effects of Postbiotic Butyrate and Active Vitamin D3 to Defense against Microbial Invasion in Salmonella Colitis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. Reagents
2.3. Postbiotics Preparation
2.4. AHR Inhibitor Solution Preparation
2.5. Animal Experiments
2.6. Analysis of Salmonella Loads in Spleen and Liver
2.7. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Staining Procedures
2.8. Immunohistochemistry Staining Analysis
2.9. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis of Cecum or Cultured Cells RNA
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
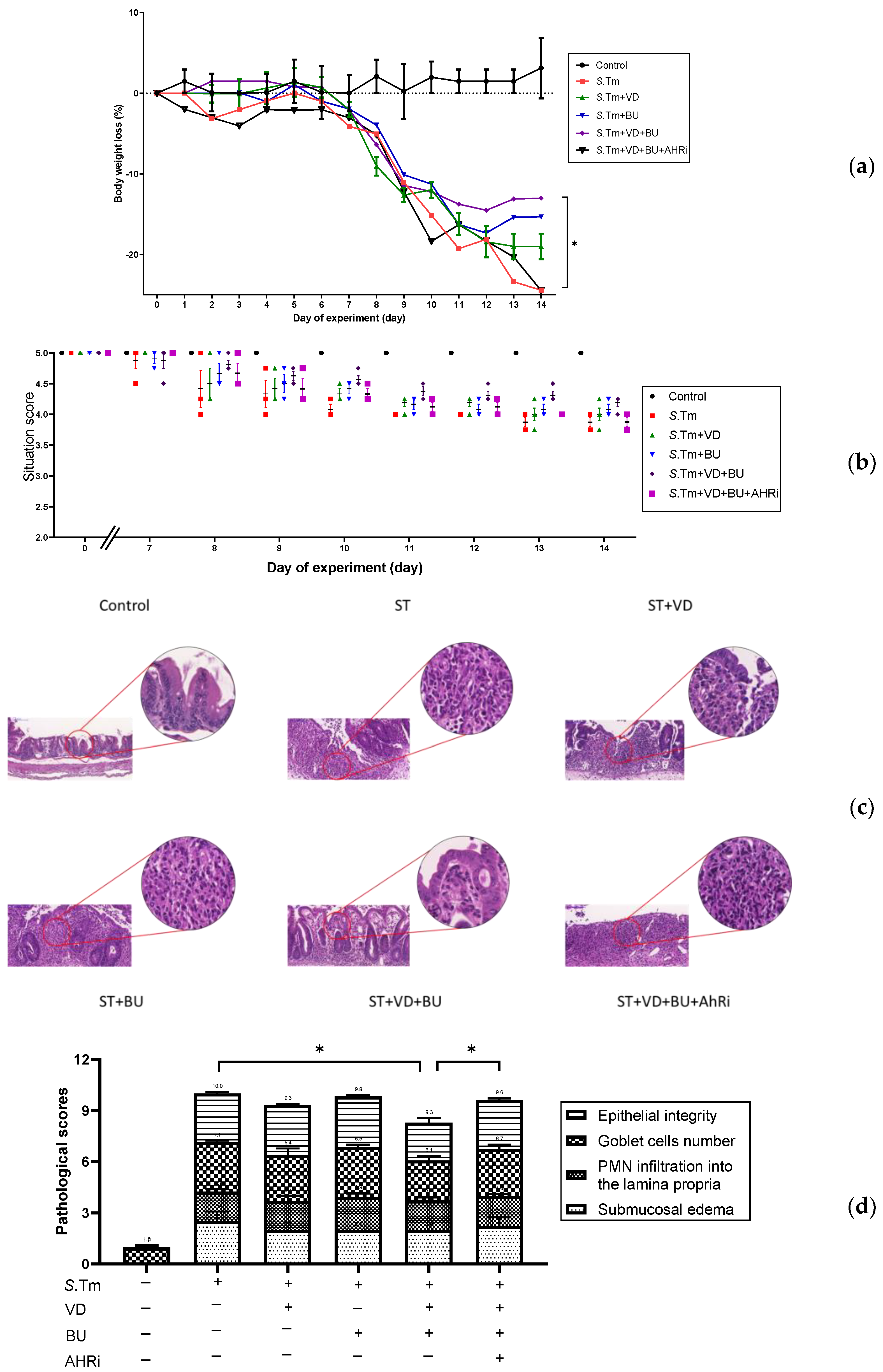
3.1. The Involvement of AhR in the Synergistic Effects of Admixture of VD3 and Butyrate on the Severity of Salmonella Colitis
3.2. The Involvement of AhR in the Synergistic Effects of Admixture of VD3 and Butyrate on the Cecal Cytokines and Antimicrobial Peptides in Salmonella Colitis Mice
3.3. Admixture of VD3 and Butyrate Exerted Reduction of Bacterial Translocation in Salmonella-Infected Mice
3.4. Admixture of VD3 and Butyrate Exerted Synergistic Effect on Tight Junction Proteins Expression in Cecal Mucosa of Mice with Salmonella Colitis
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Glynn, M.K.; Bopp, C.; Dewitt, W.; Dabney, P.; Mokhtar, M.; Angulo, F.J. Emergence of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serotype typhimurium DT104 infections in the United States. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 1333–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lauderdale, T.L.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Chen, P.C.; Lai, J.F.; Wang, H.Y.; Shiau, Y.R.; Huang, I.W.; Hung, C.L.; TSAR Hospitals. Multidrug resistance among different serotypes of clinical Salmonella isolates in Taiwan. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2006, 55, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helms, M.; Vastrup, P.; Gerner-Smidt, P.; Molbak, K. Excess mortality associated with antimicrobial drug-resistant Salmonella typhimurium. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasai, S.; Ishigaki, T.; Takumi, R.; Kamimura, T.; Kikuchi, H. Beta-catenin signaling induces CYP1A1 expression by disrupting adherens junctions in Caco-2 human colon carcinoma cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 2509–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Wang, Q.; Ma, Y.; Li, L.; Yu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, G.; Li, X.; Xiao, W.; Xu, P.; et al. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Activation Modulates Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Function by Maintaining Tight Junction Integrity. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yu, K.; Fan, X.; Xiao, W.; Cai, Y.; Xu, P.; Yu, M.; Yang, H. 6-Formylindolo(3,2-b)carbazole induced aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation prevents intestinal barrier dysfunction through regulation of claudin-2 expression. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 288, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, S.A.; Fu, J.; Chang, P.V. Microbial tryptophan metabolites regulate gut barrier function via the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 19376–19387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metidji, A.; Omenetti, S.; Crotta, S.; Li, Y.; Nye, E.; Ross, E.; Li, V.; Maradana, M.R.; Schiering, C.; Stockinger, B. The Environmental Sensor AHR Protects from Inflammatory Damage by Maintaining Intestinal Stem Cell Homeostasis and Barrier Integrity. Immunity 2018, 49, 353–362.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schiering, C.; Wincent, E.; Metidji, A.; Iseppon, A.; Li, Y.; Potocnik, A.J.; Omenetti, S.; Henderson, C.J.; Wolf, C.R.; Nebert, D.W.; et al. Feedback control of AHR signalling regulates intestinal immunity. Nature 2017, 542, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiss, E.A.; Vonarbourg, C.; Kopfmann, S.; Hobeika, E.; Finke, D.; Esser, C.; Diefenbach, A. Natural aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands control organogenesis of intestinal lymphoid follicles. Science 2011, 334, 1561–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Guo, X.; Chen, Z.M.; He, L.; Sonnenberg, G.F.; Artis, D.; Fu, Y.X.; Zhou, L. Group 3 innate lymphoid cells inhibit T-cell-mediated intestinal inflammation through aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling and regulation of microflora. Immunity 2013, 39, 386–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collins, J.W.; Keeney, K.M.; Crepin, V.F.; Rathinam, V.A.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Finlay, B.B.; Frankel, G. Citrobacter rodentium: Infection, inflammation and the microbiota. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Huang, Y.; Wang, F. Short-Chain Fatty Acids Manifest Stimulative and Protective Effects on Intestinal Barrier Function Through the Inhibition of NLRP3 Inflammasome and Autophagy. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 49, 190–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Reytor, D.; Puebla, C.; Karahanian, E.; Garcia, K. Use of Short-Chain Fatty Acids for the Recovery of the Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Affected by Bacterial Toxins. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 650313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twardowska, A.; Makaro, A.; Binienda, A.; Fichna, J.; Salaga, M. Preventing Bacterial Translocation in Patients with Leaky Gut Syndrome: Nutrition and Pharmacological Treatment Options. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.C.; Huang, S.C. The Combined Beneficial Effects of Postbiotic Butyrate on Active Vitamin D3-Orchestrated Innate Immunity to Salmonella Colitis. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.C.; Huang, S.C. The Cooperation of Bifidobacterium longum and Active Vitamin D3 on Innate Immunity in Salmonella Colitis Mice via Vitamin D Receptor. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthel, M.; Hapfelmeier, S.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Kremer, M.; Rohde, M.; Hogardt, M.; Pfeffer, K.; Russmann, H.; Hardt, W.D. Pretreatment of mice with streptomycin provides a Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium colitis model that allows analysis of both pathogen and host. Infect Immun 2003, 71, 2839–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crowe, A.R.; Yue, W. Semi-quantitative Determination of Protein Expression using Immunohistochemistry Staining and Analysis: An Integrated Protocol. Bio Protoc 2019, 9, e3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.C.; Huang, S.C. Active vitamin D3 attenuates the severity of Salmonella colitis in mice by orchestrating innate immunity. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2021, 9, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE guidelines: Minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masuda, K.; Kimura, A.; Hanieh, H.; Nguyen, N.T.; Nakahama, T.; Chinen, I.; Otoyo, Y.; Murotani, T.; Yamatodani, A.; Kishimoto, T. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor negatively regulates LPS-induced IL-6 production through suppression of histamine production in macrophages. Int. Immunol. 2011, 23, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pernomian, L.; Duarte-Silva, M.; de Barros Cardoso, C.R. The Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AHR) as a Potential Target for the Control of Intestinal Inflammation: Insights from an Immune and Bacteria Sensor Receptor. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 59, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khailova, L.; Frank, D.N.; Dominguez, J.A.; Wischmeyer, P.E. Probiotic administration reduces mortality and improves intestinal epithelial homeostasis in experimental sepsis. Anesthesiology 2013, 119, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Asmar, R.; Panigrahi, P.; Bamford, P.; Berti, I.; Not, T.; Coppa, G.V.; Catassi, C.; Fasano, A. Host-dependent zonulin secretion causes the impairment of the small intestine barrier function after bacterial exposure. Gastroenterology 2002, 123, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenberg, G.F.; Fouser, L.A.; Artis, D. Border patrol: Regulation of immunity, inflammation and tissue homeostasis at barrier surfaces by IL-22. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolk, K.; Kunz, S.; Witte, E.; Friedrich, M.; Asadullah, K.; Sabat, R. IL-22 increases the innate immunity of tissues. Immunity 2004, 21, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Hong, W.; Jin, X.; Li, G.; Zhou, G.; Fan, L. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor is a novel negative regulator of interleukin-17-mediated signaling and inflammation in vitro. FEBS Lett. 2019, 593, 952–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Xie, Y.; Mei, X.; Sun, Y.; Shi, W.; Wu, Z. Reciprocal regulation of interleukin-17A and interleukin-22 secretion through aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation in CD4(+) T cells of patients with vitiligo. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ktsoyan, Z.; Ghazaryan, K.; Manukyan, G.; Martirosyan, A.; Mnatsakanyan, A.; Arakelova, K.; Gevorgyan, Z.; Sedrakyan, A.; Asoyan, A.; Boyajyan, A.; et al. Inflammatory Responses to Salmonella Infections Are Serotype-Specific. Int. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 2013, 168179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayuzumi, H.; Inagaki-Ohara, K.; Uyttenhove, C.; Okamoto, Y.; Matsuzaki, G. Interleukin-17A is required to suppress invasion of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium to enteric mucosa. Immunology 2010, 131, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, K.; Ogawa, A.; Mizoguchi, E.; Shimomura, Y.; Andoh, A.; Bhan, A.K.; Blumberg, R.S.; Xavier, R.J.; Mizoguchi, A. IL-22 ameliorates intestinal inflammation in a mouse model of ulcerative colitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siegemund, S.; Schutze, N.; Schulz, S.; Wolk, K.; Nasilowska, K.; Straubinger, R.K.; Sabat, R.; Alber, G. Differential IL-23 requirement for IL-22 and IL-17A production during innate immunity against Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis. Int. Immunol. 2009, 21, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.S.; Tato, C.M.; Joyce-Shaikh, B.; Gulen, M.F.; Cayatte, C.; Chen, Y.; Blumenschein, W.M.; Judo, M.; Ayanoglu, G.; McClanahan, T.K.; et al. Interleukin-23-Independent IL-17 Production Regulates Intestinal Epithelial Permeability. Immunity 2015, 43, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, J.; Yang, K.; Zhou, C.; Xu, P.; Xiao, W.; Yang, H. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation alleviates dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis through enhancing the differentiation of goblet cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 514, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Pang, Z.; Shu, W.; Wu, W.; Sun, M.; Cong, Y.; Liu, Z. Anti-TNF Therapy Induces CD4+ T-Cell Production of IL-22 and Promotes Epithelial Repairs in Patients With Crohn’s Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2018, 24, 1733–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshbin, K.; Camilleri, M. Effects of dietary components on intestinal permeability in health and disease. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2020, 319, G589–G608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenza, G.L. Oxygen sensing, homeostasis, and disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, J.; Zhang, Z.; Musch, M.W.; Ning, G.; Sun, J.; Hart, J.; Bissonnette, M.; Li, Y.C. Novel role of the vitamin D receptor in maintaining the integrity of the intestinal mucosal barrier. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 294, G208–G216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, H.; Wu, H.; Li, H.; Liu, L.; Guo, J.; Li, C.; Shih, D.Q.; Zhang, X. Protective role of 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D3 in the mucosal injury and epithelial barrier disruption in DSS-induced acute colitis in mice. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012, 12, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Robles, H.; Castro-Ochoa, K.F.; Citalan-Madrid, A.F.; Schnoor, M. Beneficial effects of nutritional supplements on intestinal epithelial barrier functions in experimental colitis models in vivo. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 4181–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauber, J.; Svanholm, C.; Termen, S.; Iffland, K.; Menzel, T.; Scheppach, W.; Melcher, R.; Agerberth, B.; Luhrs, H.; Gudmundsson, G.H. Expression of the cathelicidin LL-37 is modulated by short chain fatty acids in colonocytes: Relevance of signalling pathways. Gut 2003, 52, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwab, M.; Reynders, V.; Shastri, Y.; Loitsch, S.; Stein, J.; Schroder, O. Role of nuclear hormone receptors in butyrate-mediated up-regulation of the antimicrobial peptide cathelicidin in epithelial colorectal cells. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 2107–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raqib, R.; Sarker, P.; Bergman, P.; Ara, G.; Lindh, M.; Sack, D.A.; Islam, K.M.N.; Gudmundsson, G.H.; Andersson, J.; Agerberth, B. Improved outcome in shigellosis associated with butyrate induction of an endogenous peptide antibiotic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 9178–9183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeng, X.; Sunkara, L.T.; Jiang, W.; Bible, M.; Carter, S.; Ma, X.; Qiao, S.; Zhang, G. Induction of porcine host defense peptide gene expression by short-chain fatty acids and their analogs. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiong, H.; Guo, B.; Gan, Z.; Song, D.; Lu, Z.; Yi, H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Du, H. Butyrate upregulates endogenous host defense peptides to enhance disease resistance in piglets via histone deacetylase inhibition. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steinmann, J.; Halldorsson, S.; Agerberth, B.; Gudmundsson, G.H. Phenylbutyrate induces antimicrobial peptide expression. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 5127–5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, F.; Wu, W.; Sun, M.; Bilotta, A.J.; Yao, S.; Xiao, Y.; Huang, X.; Eaves-Pyles, T.D.; Golovko, G.; et al. GPR43 mediates microbiota metabolite SCFA regulation of antimicrobial peptide expression in intestinal epithelial cells via activation of mTOR and STAT3. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sani, N.A.; Hasani, M.; Kianmehr, A.; Mohammadi, S.; Arabi, M.S.; Yazdani, Y. Enhanced nuclear translocation and activation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) in THP-1 monocytic cell line by a novel niosomal formulation of indole-3-carbinol. J. Liposome Res. 2020, 30, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Hu, X.; Bao, L.; Wu, K.; Feng, L.; Qiu, M.; Hao, H.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, N. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation by Lactobacillus reuteri tryptophan metabolism alleviates Escherichia coli-induced mastitis in mice. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoseph, B.P.; Klingensmith, N.J.; Liang, Z.; Breed, E.R.; Burd, E.M.; Mittal, R.; Dominguez, J.A.; Petrie, B.; Ford, M.L.; Coopersmith, C.M. Mechanisms of Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction in Sepsis. Shock 2016, 46, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturgeon, C.; Lan, J.; Fasano, A. Zonulin transgenic mice show altered gut permeability and increased morbidity/mortality in the DSS colitis model. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2017, 1397, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaus, D.A.; Motal, M.C.; Burger-Klepp, U.; Marschalek, C.; Schmidt, E.M.; Lebherz-Eichinger, D.; Krenn, C.G.; Roth, G.A. Increased plasma zonulin in patients with sepsis. Biochem. Med. 2013, 23, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslamian, G.; Ardehali, S.H.; Hajimohammadebrahim-Ketabforoush, M.; Shariatpanahi, Z.V. Association of intestinal permeability with admission vitamin D deficiency in patients who are critically ill. J. Investig. Med. 2020, 68, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, M.C.; Madsen, K.; Doyle, J.; Meddings, J. Reducing small intestinal permeability attenuates colitis in the IL10 gene-deficient mouse. Gut 2009, 58, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luettig, J.; Rosenthal, R.; Barmeyer, C.; Schulzke, J.D. Claudin-2 as a mediator of leaky gut barrier during intestinal inflammation. Tissue Barriers 2015, 3, e977176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.G.; Lu, R.; Xia, Y.; Zhou, D.; Petrof, E.; Claud, E.C.; Sun, J. Lack of Vitamin D Receptor Leads to Hyperfunction of Claudin-2 in Intestinal Inflammatory Responses. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2019, 25, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.G.; Wu, S.; Lu, R.; Zhou, D.; Zhou, J.; Carmeliet, G.; Petrof, E.; Claud, E.C.; Sun, J. Tight junction CLDN2 gene is a direct target of the vitamin D receptor. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stio, M.; Retico, L.; Annese, V.; Bonanomi, A.G. Vitamin D regulates the tight-junction protein expression in active ulcerative colitis. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Kelly, C.J.; Battista, K.D.; Schaefer, R.; Lanis, J.M.; Alexeev, E.E.; Wang, R.X.; Onyiah, J.C.; Kominsky, D.J.; Colgan, S.P. Microbial-Derived Butyrate Promotes Epithelial Barrier Function through IL-10 Receptor-Dependent Repression of Claudin-2. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 2976–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankertz, J.; Amasheh, M.; Krug, S.M.; Fromm, A.; Amasheh, S.; Hillenbrand, B.; Tavalali, S.; Fromm, M.; Schulzke, J.D. TNFalpha up-regulates claudin-2 expression in epithelial HT-29/B6 cells via phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase signaling. Cell Tissue Res. 2009, 336, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Yoshinaga, N.; Tanabe, S. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) regulates claudin-2 expression and tight junction permeability in intestinal epithelium. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 31263–31271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsai, P.Y.; Zhang, B.; He, W.Q.; Zha, J.M.; Odenwald, M.A.; Singh, G.; Tamura, A.; Shen, L.; Sailer, A.; Yeruva, S.; et al. IL-22 Upregulates Epithelial Claudin-2 to Drive Diarrhea and Enteric Pathogen Clearance. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 21, 671–681.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kinugasa, T.; Sakaguchi, T.; Gu, X.; Reinecker, H.C. Claudins regulate the intestinal barrier in response to immune mediators. Gastroenterology 2000, 118, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roxas, J.L.; Koutsouris, A.; Bellmeyer, A.; Tesfay, S.; Royan, S.; Falzari, K.; Harris, A.; Cheng, H.; Rhee, K.J.; Hecht, G. Enterohemorrhagic E. coli alters murine intestinal epithelial tight junction protein expression and barrier function in a Shiga toxin independent manner. Lab. Investig. 2010, 90, 1152–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capaldo, C.T.; Nusrat, A. Cytokine regulation of tight junctions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2009, 1788, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, F.-C.; Huang, S.-C. The Pivotal Role of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor-Regulated Tight Junction Proteins and Innate Immunity on the Synergistic Effects of Postbiotic Butyrate and Active Vitamin D3 to Defense against Microbial Invasion in Salmonella Colitis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020305
Huang F-C, Huang S-C. The Pivotal Role of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor-Regulated Tight Junction Proteins and Innate Immunity on the Synergistic Effects of Postbiotic Butyrate and Active Vitamin D3 to Defense against Microbial Invasion in Salmonella Colitis. Nutrients. 2023; 15(2):305. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020305
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Fu-Chen, and Shun-Chen Huang. 2023. "The Pivotal Role of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor-Regulated Tight Junction Proteins and Innate Immunity on the Synergistic Effects of Postbiotic Butyrate and Active Vitamin D3 to Defense against Microbial Invasion in Salmonella Colitis" Nutrients 15, no. 2: 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020305
APA StyleHuang, F. -C., & Huang, S. -C. (2023). The Pivotal Role of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor-Regulated Tight Junction Proteins and Innate Immunity on the Synergistic Effects of Postbiotic Butyrate and Active Vitamin D3 to Defense against Microbial Invasion in Salmonella Colitis. Nutrients, 15(2), 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020305






