Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum and Weissella viridescens on the Gut Microbiota and Serum Metabolites of Mice with Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture
2.2. Animals and Experimental Design
2.3. DNA Isolation and Bioinformatics Analysis
2.4. RT-qPCR
2.5. Pathological Analysis of Colon
2.6. Serum Metabolomics
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physiological Effects of Intragastric Administration of Lincomycin Hydrochloride
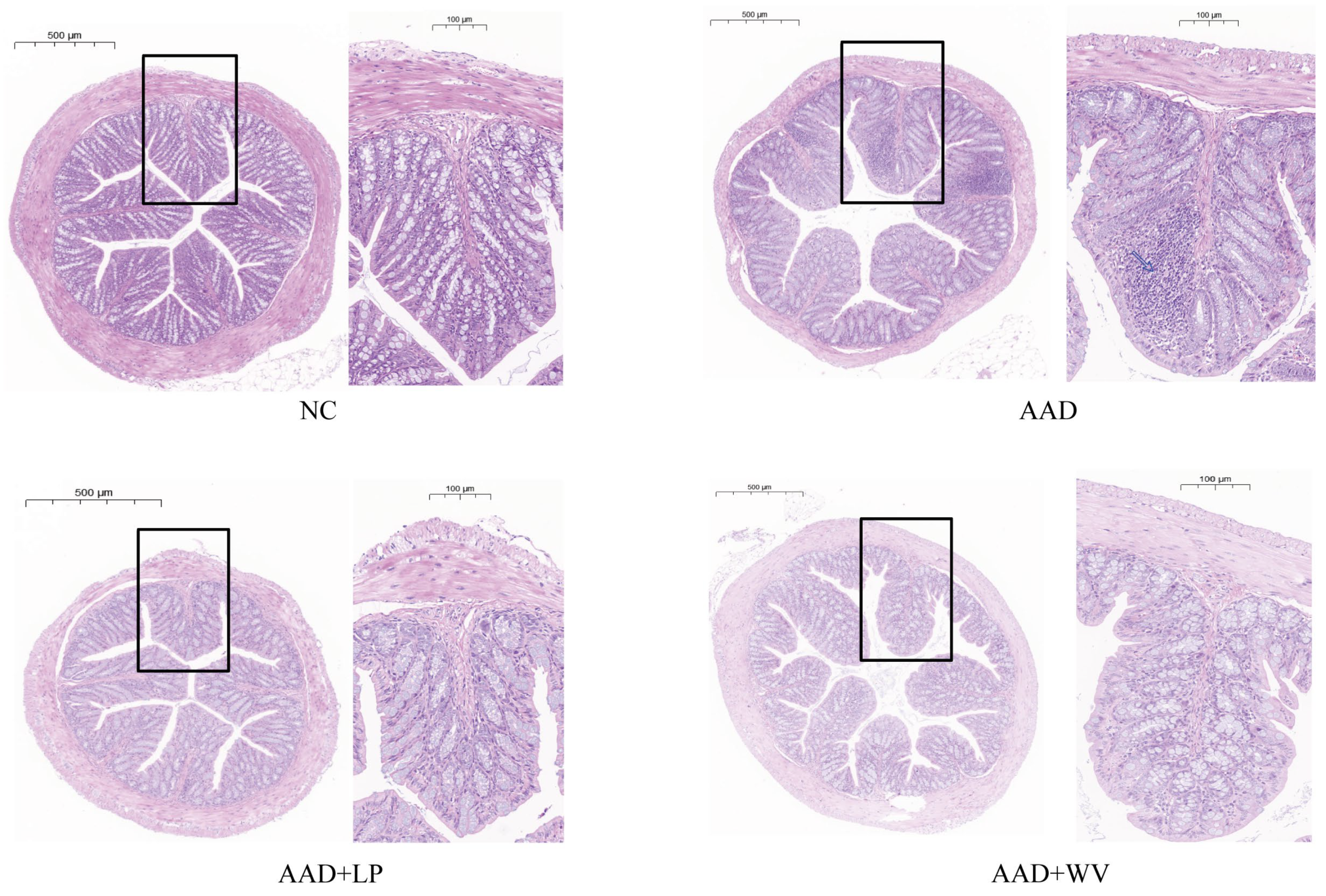
3.2. L. plantarum H-6 and W. viridescens J-1 Attenuate Intestinal Injury Induced by Lincomycin Hydrochloride
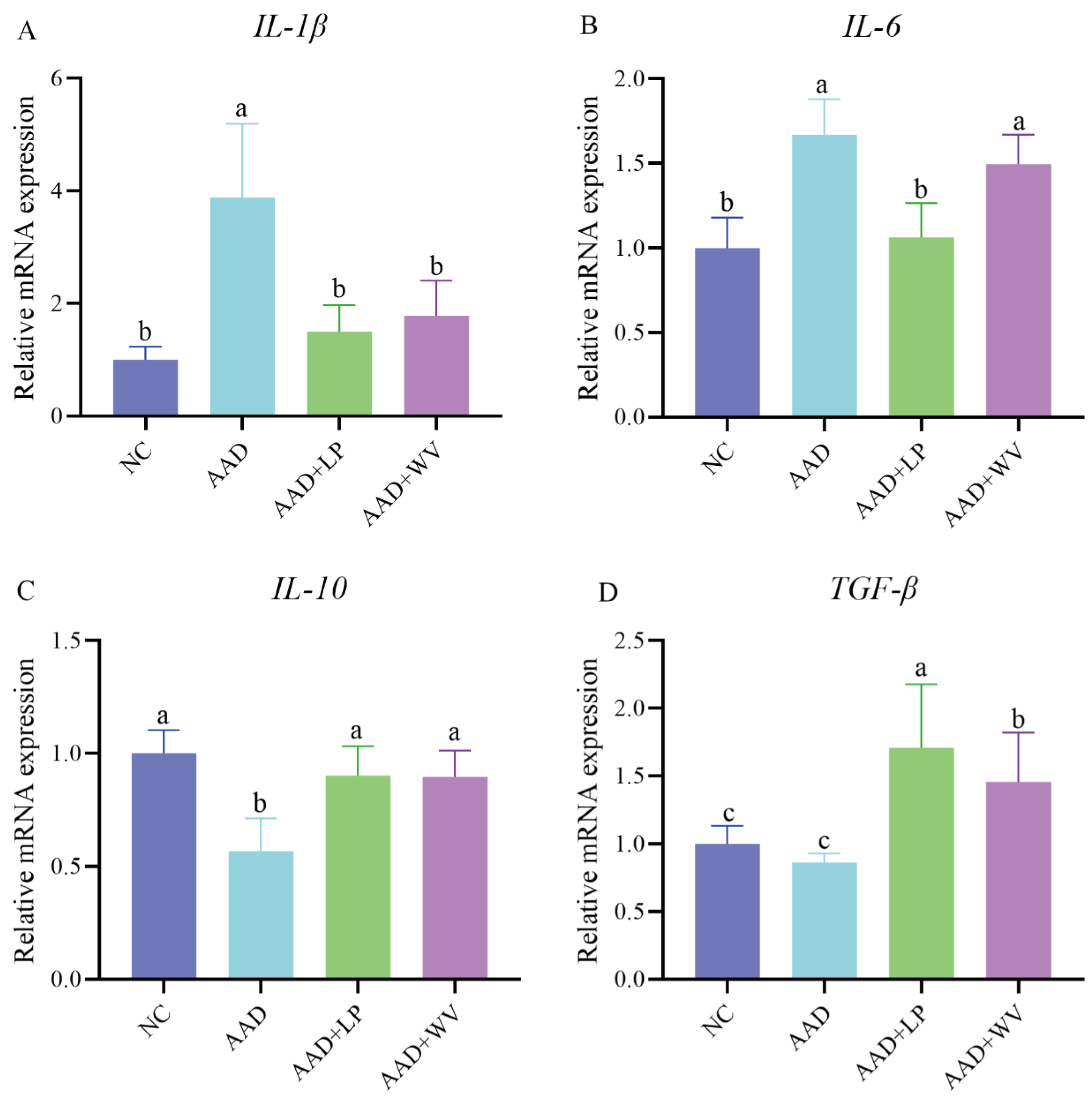
3.3. Effects of L. plantarum H-6 and W. viridescens J-1 on Inflammatory Factors in Colon Tissue
3.4. Effects of L. plantarum H-6 and W. viridescens J-1 on Serum Metabolomics in Mice
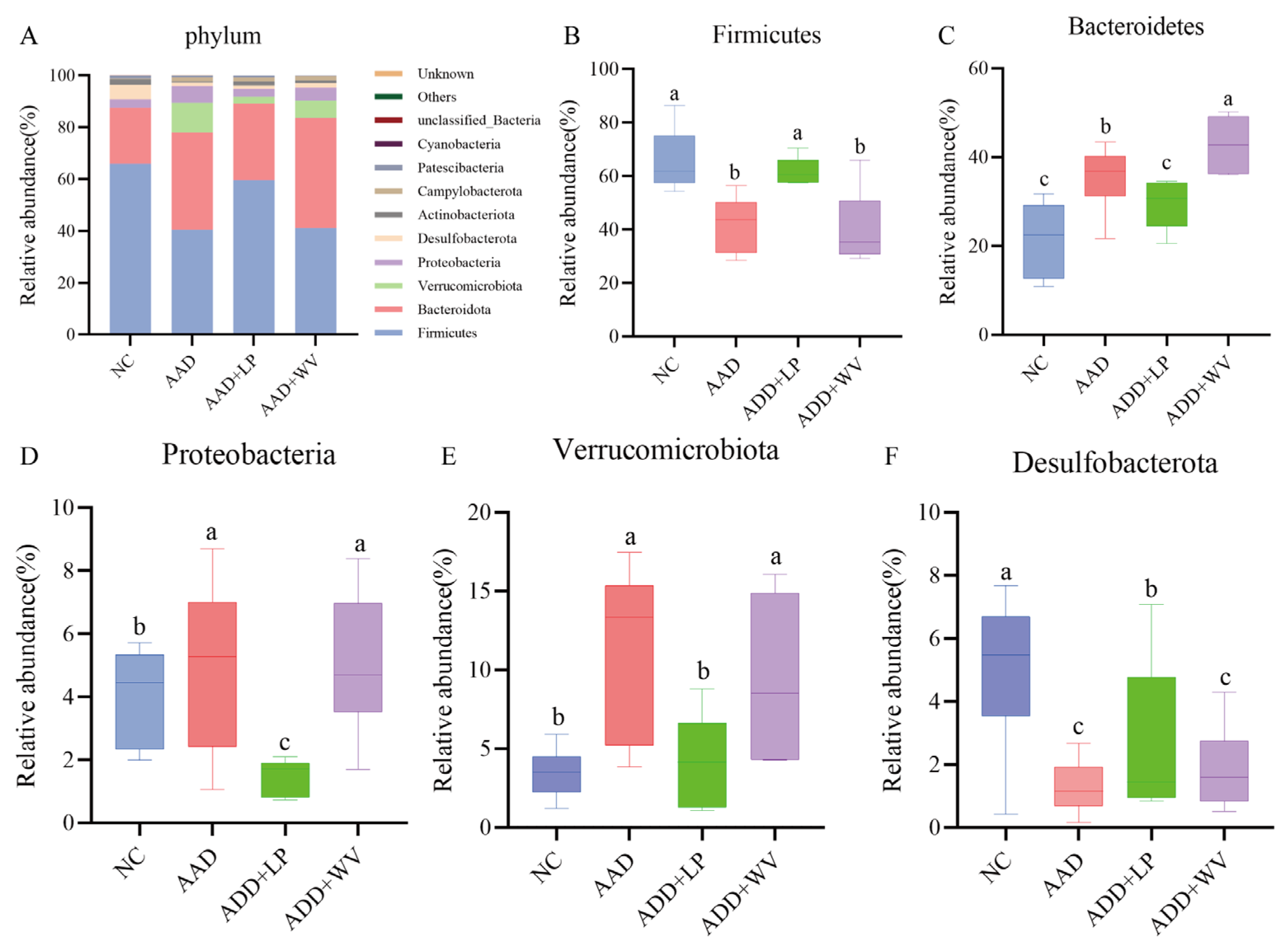
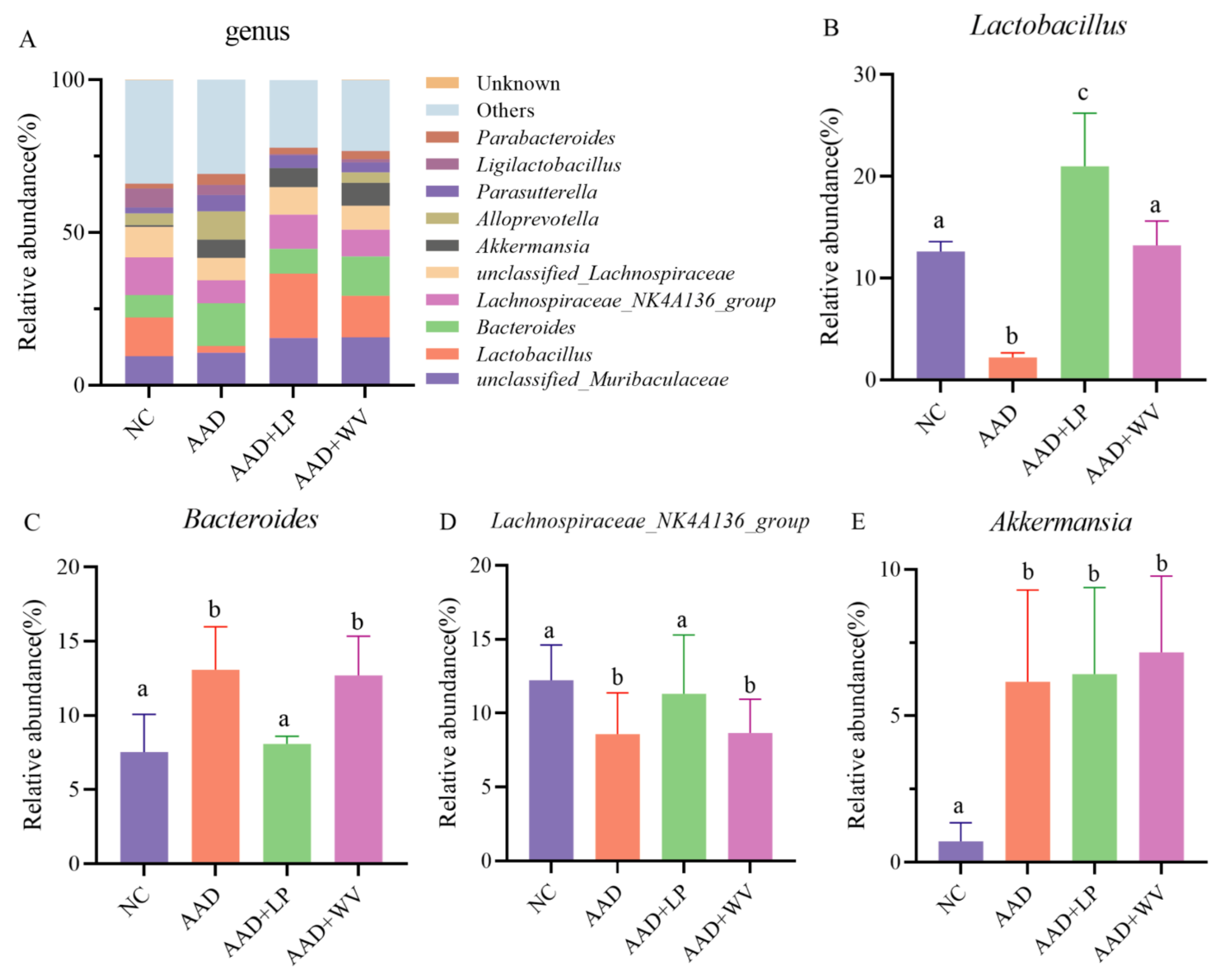
3.5. The Influence of L. plantarum H-6 and W. viridescens J-1 on the Composition and Diversity of Gut Flora
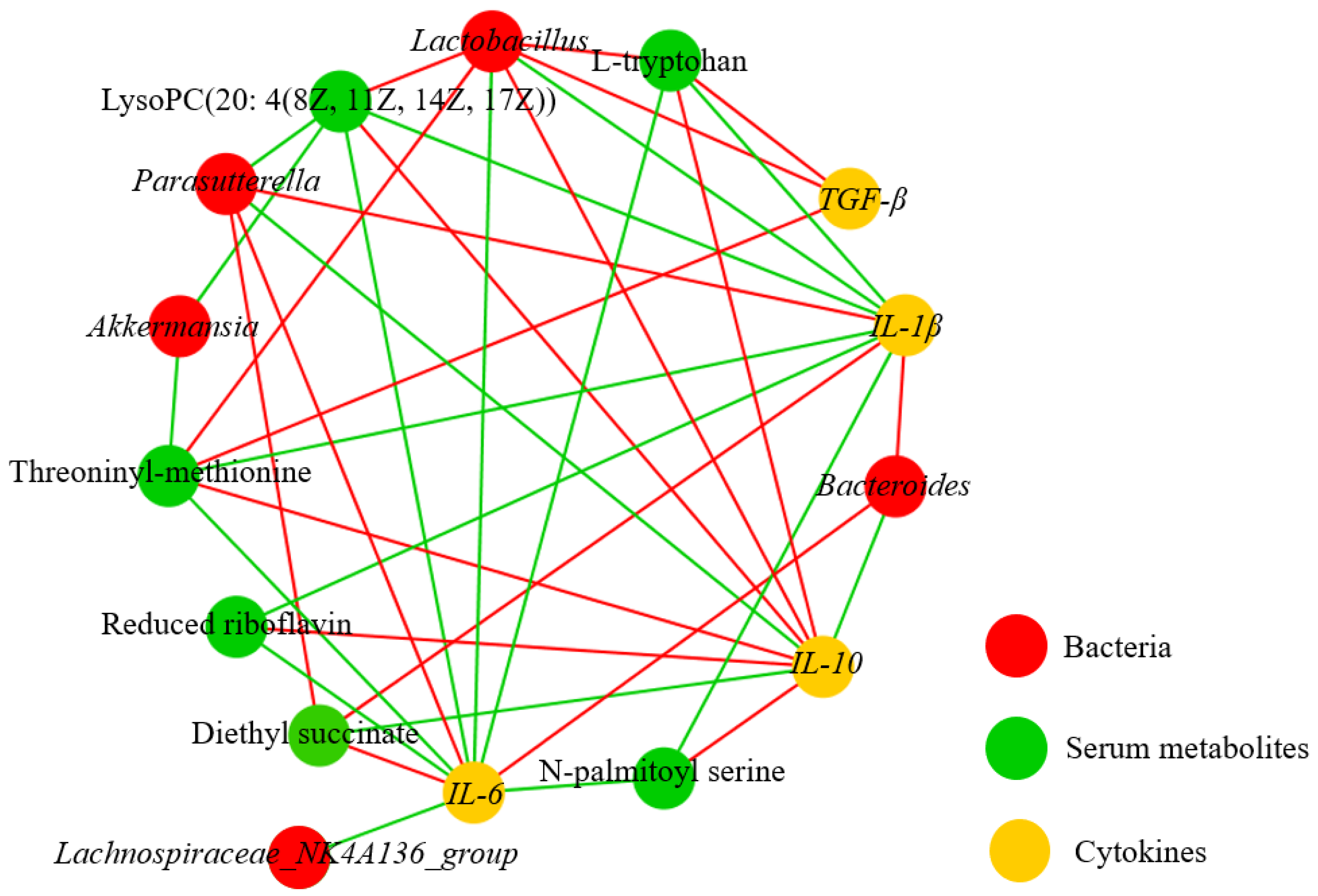
3.6. Correlation Analysis on Metabolites, Bacterium, and Immune Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mekonnen, S.A.; Merenstein, D.; Fraser, C.M.; Marco, M.L. Molecular mechanisms of probiotic prevention of antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2020, 61, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, N.; Tan, Z. Gut microbiota characteristics in mice with antibiotic-associated diarrhea. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Goldenberg, J.Z.; Humphrey, C.; El Dib, R.; Johnston, B.C. Probiotics for the prevention of pediatric antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 4, Cd004827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Högenauer, C.; Hammer, H.F.; Krejs, G.J.; Reisinger, E.C. Mechanisms and management of antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1998, 27, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullish, B.H.; Williams, H.R. Clostridium difficile infection and antibiotic-associated diarrhoea. Clin. Med. 2018, 18, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, I.; Moucari, R. Probiotics for antibiotic-associated diarrhea: Do we have a verdict? World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 17788–17795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Buch, H.; Shan, Y.; Chang, L.; Bai, Y.; Shen, C.; Zhang, X.; Huo, Y.; et al. Rescue fecal microbiota transplantation for antibiotic-associated diarrhea in critically ill patients. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; He, Y.; Guo, L. Combined administration of antibiotics increases the incidence of antibiotic-associated diarrhea in critically ill patients. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Sim, J.X.Y.; Lee, W.L.; Cui, L.; Chan, Y.F.Z.; Chang, E.D.; Teh, Y.E.; Zhang, A.N.; Armas, F.; Chandra, F.; et al. Gut Ruminococcaceae levels at baseline correlate with risk of antibiotic-associated diarrhea. iScience 2022, 25, 103644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarland, L.V. Antibiotic-associated diarrhea: Epidemiology, trends and treatment. Future Microbiol. 2008, 3, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, R.L.; Suda, K.J.; Evans, C.T. Antibiotic treatment for Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhoea in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 3, Cd004610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopacz, K.; Phadtare, S. Probiotics for the Prevention of Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Yu, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X.; Wei, H.; Shah, N.P.; Xu, F. Enhancing flora balance in the gastrointestinal tract of mice by lactic acid bacteria from Chinese sourdough and enzyme activities indicative of metabolism of protein, fat, and carbohydrate by the flora. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 7809–7820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.L.; Wang, B.Z.; Li, Z.P.; Li, Y.L.; Liang, J.J. Alterations of intestinal flora and the effects of probiotics in children with recurrent respiratory tract infection. World J. Pediatr. 2019, 15, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surendran Nair, M.; Amalaradjou, M.A.; Venkitanarayanan, K. Antivirulence Properties of Probiotics in Combating Microbial Pathogenesis. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 98, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuo, Y.; Song, X.; Song, Y.; Liu, W.; Tang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, S.; Qian, F.; Mu, G. Screening probiotics from Lactobacillus strains according to their abilities to inhibit pathogen adhesion and induction of pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-8. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4822–4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, T.; Asasaka, T.; Sato, E.; Mori, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Ohori, H. Inhibition of binding of Helicobacter pylori to the glycolipid receptors by probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2002, 32, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, N.; Li, P.; Gu, Q. Probiotic therapy in Helicobacter pylori infection: A potential strategy against a serious pathogen? Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 1573–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukasik, J.; Dierikx, T.; Besseling-van der Vaart, I.; de Meij, T.; Szajewska, H. Multispecies Probiotic for the Prevention of Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea in Children: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Pediatr. 2022, 176, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Chen, C.; Wen, T.; Zhao, Q. Probiotics for the Prevention of Antibiotic-associated Diarrhea in Adults: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trials. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2021, 55, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zeng, X.; Guo, D.; Zou, Y.; Gan, H.; Huang, X. Early use of probiotics might prevent antibiotic-associated diarrhea in elderly (>65 years): A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, M.; Zhou, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, K.; Ma, C. Beneficial effects of sulfated polysaccharides from the red seaweed Gelidium pacificum Okamura on mice with antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 4625–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Qi, Y.; Chen, L.; Qu, D.; Li, Z.; Gao, K.; Chen, J.; Sun, Y. Effects of Panax ginseng polysaccharides on the gut microbiota in mice with antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Yan, W.; Fang, J.; Jiang, H.; Liu, G. Potential role of Lactobacillus plantarum in colitis induced by dextran sulfate sodium through altering gut microbiota and host metabolism in murine model. Sci. China Life Sci. 2021, 64, 1906–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ding, S.; Liu, G.; Fang, J.; Yan, W.; Duraipandiyan, V.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Esmail, G.A.; Jiang, H. Egg Protein Transferrin-Derived Peptides IRW and IQW Regulate Citrobacter rodentium-Induced, Inflammation-Related Microbial and Metabolomic Profiles. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Al Naggar, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Xue, X.; Wu, L.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Wang, K. Acaricide flumethrin-induced sublethal risks in honeybees are associated with gut symbiotic bacterium Gilliamella apicola through microbe-host metabolic interactions. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 136030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Chen, G.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, W.; Qi, S.; Xue, X.; Wang, K.; Wu, L. Effects of dietary phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin on DSS-induced colitis by regulating metabolism and gut microbiota in mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2022, 105, 109004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Liang, S.; Zhao, J.; Li, X.; Guo, J.; Xin, B.; Li, B.; Huo, G.; Ma, W. Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis XLTG11 improves antibiotic-related diarrhea by alleviating inflammation, enhancing intestinal barrier function and regulating intestinal flora. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 6404–6418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkins, T.; Sequoia, J. Probiotics for Gastrointestinal Conditions: A Summary of the Evidence. Am. Fam. Physician 2017, 96, 170–178. [Google Scholar]
- Mantegazza, C.; Molinari, P.; D’Auria, E.; Sonnino, M.; Morelli, L.; Zuccotti, G.V. Probiotics and antibiotic-associated diarrhea in children: A review and new evidence on Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG during and after antibiotic treatment. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 128, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; He, Y.; Yu, J.; Liu, M.; Yang, X.; Ta, N.; Zhang, E.; Liang, C. Regulatory Effect of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 2-33 on Intestinal Microbiota of Mice with Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 921875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.S.; Huang, Y.Y.; Kuang, J.H.; Yu, J.J.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Liu, D.M. Streptococcus thermophiles DMST-H2 Promotes Recovery in Mice with Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Chen, L.; Gao, K.; Shao, Z.; Huo, X.; Hua, M.; Liu, S.; Sun, Y.; Li, S. Effects of Schisandra chinensis polysaccharides on rats with antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagnini, C.; Saeed, R.; Bamias, G.; Arseneau, K.O.; Pizarro, T.T.; Cominelli, F. Probiotics promote gut health through stimulation of epithelial innate immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Park, D.H.; Lee, M.J.; Jeon, C.Y.; Kang, K.S.; Choi, Y.K. Beneficial Effect of Paeonol on Antibiotic-Associated Inflammatory Response in Mice with Diarrhea. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, T.; Gao, L.; Yang, Z.J.; Wang, F.F.; Shang, H.W.; Hua, R.; Xu, J.D. Biological characteristics of IL-6 and related intestinal diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 204–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminsky, L.W.; Al-Sadi, R.; Ma, T.Y. IL-1β and the Intestinal Epithelial Tight Junction Barrier. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 767456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.; Fan, Y.; Long, X.; Pan, Y.; Mu, J.; Tan, F.; Zhao, X. Protective effect of Lactobacillus plantarum YS3 on dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in C57BL/6J mice. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Ding, S.; Ma, Y.; Fang, J.; Jiang, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, G. Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus brevis Alleviate Intestinal Inflammation and Microbial Disorder Induced by ETEC in a Murine Model. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6867962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Xu, K.; Liu, H.; Liu, G.; Bai, M.; Peng, C.; Li, T.; Yin, Y. Impact of the Gut Microbiota on Intestinal Immunity Mediated by Tryptophan Metabolism. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, T.A.; Nguyen, J.C.; Polglaze, K.E.; Bertrand, P.P. Influence of Tryptophan and Serotonin on Mood and Cognition with a Possible Role of the Gut-Brain Axis. Nutrients 2016, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etienne-Mesmin, L.; Chassaing, B.; Gewirtz, A.T. Tryptophan: A gut microbiota-derived metabolites regulating inflammation. World J. Gastrointest. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 8, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desbonnet, L.; Garrett, L.; Clarke, G.; Bienenstock, J.; Dinan, T.G. The probiotic Bifidobacteria infantis: An assessment of potential antidepressant properties in the rat. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2008, 43, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsland, B.J. Regulating inflammation with microbial metabolites. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adak, A.; Khan, M.R. An insight into gut microbiota and its functionalities. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 473–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Guo, C.; Li, X.; Li, G.; Xiong, W.; Zeng, Z. Intestinal Flora and Disease Mutually Shape the Regional Immune System in the Intestinal Tract. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Żółkiewicz, J.; Marzec, A.; Ruszczyński, M.; Feleszko, W. Postbiotics—A Step Beyond Pre- and Probiotics. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, B.; Delgado, S.; Blanco-Míguez, A.; Lourenço, A.; Gueimonde, M.; Margolles, A. Probiotics, gut microbiota, and their influence on host health and disease. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Deng, X.; Huang, J.; Lu, S.; Li, P.; Du, B. Supplementation of Bacillus sp. DU-106 Alleviates Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea in Association with the Regulation of Intestinal Microbiota in Mice. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2022, 14, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bäumler, A.J.; Sperandio, V. Interactions between the microbiota and pathogenic bacteria in the gut. Nature 2016, 535, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhya, I.; Hansen, R.; El-Omar, E.M.; Hold, G.L. IBD-what role do Proteobacteria play? Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Xie, S.; Miao, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, M.; Yu, Q. Lactobacillus reuteri maintains intestinal epithelial regeneration and repairs damaged intestinal mucosa. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 997–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Chen, Y.; Fei, S.; Xie, C.; Xia, Y.; Ai, L. Colonisation with endogenous Lactobacillus reuteri R28 and exogenous Lactobacillus plantarum AR17-1 and the effects on intestinal inflammation in mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 2481–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Liu, Y.; Song, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, F.; Luo, Y.; Qian, F.; Mu, G.; Tuo, Y. The ameliorative effect of Lactobacillus plantarum-12 on DSS-induced murine colitis. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 5205–5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancheri, P.; Watson, A.J.M. The Relative Contributions of the Gut Microbiome, Host Genetics, and Environment to Cytokine Responses to Microbial Stimulation. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 2068–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhi, S.C.; Baranwal, A. Probiotic use in the critically ill. Indian J. Pediatr. 2008, 75, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García Trallero, O.; Herrera Serrano, L.; Bibián Inglés, M.; Roche Vallés, D.; Rodríguez, A.M. Effect of the administration of a probiotic with a combination of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains on antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Rev. Esp. Quimioter. 2019, 32, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Lu, S.; Ye, Z.; Cai, X.; Wu, S.; Li, P.; Du, B. New compound probiotic beverage protects against antibiotic-associated diarrhea in mice by modulating the microbiota. Future Microbiol. 2022, 17, 943–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, W.; Liu, C.; Ye, C.; Sun, J.; Tan, X.; Zhang, C.; Qu, Q.; Shi, D.; Guo, S. Structural modulation of gut microbiota during alleviation of antibiotic-associated diarrhea with herbal formula. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 1622–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, S.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, J.; Chen, L.; Ding, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, L.; Chen, X. Poria cocos Polysaccharide Ameliorated Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea in Mice via Regulating the Homeostasis of the Gut Microbiota and Intestinal Mucosal Barrier. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
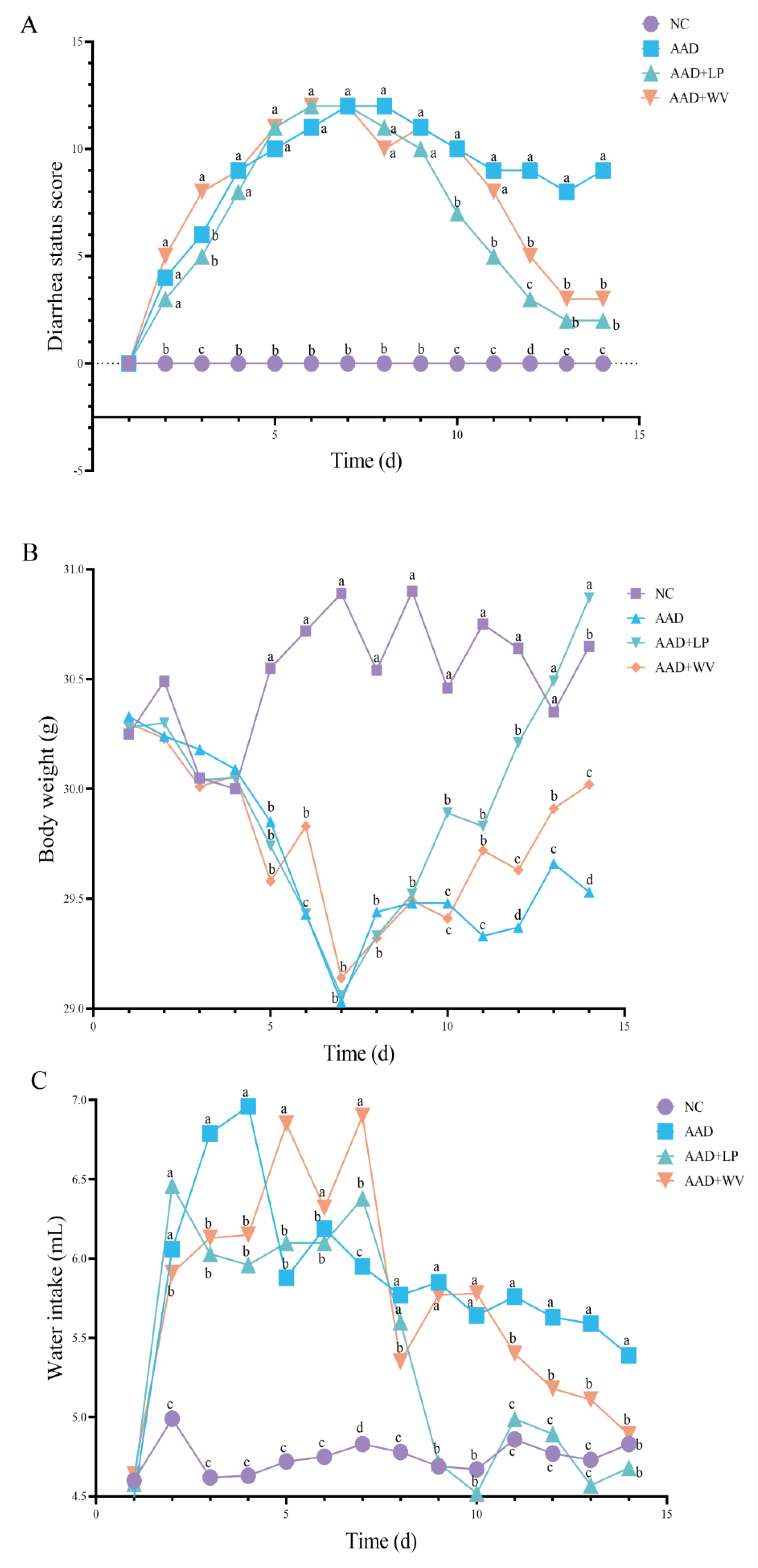


| Scores | Diarrhea Status |
|---|---|
| 0 | Mental state was normal, no diarrhea |
| 1 | Loose and non-stick perianal stools, average mental state |
| 2 | Severe diarrhea, loss of appetite, weight loss, mental malaise |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, Z.; Liu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Z.; Liu, G.; Fang, J. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum and Weissella viridescens on the Gut Microbiota and Serum Metabolites of Mice with Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4603. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15214603
Yan Z, Liu Z, Ma Y, Yang Z, Liu G, Fang J. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum and Weissella viridescens on the Gut Microbiota and Serum Metabolites of Mice with Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea. Nutrients. 2023; 15(21):4603. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15214603
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Zhiwei, Zhuangzhuang Liu, Yong Ma, Zhao Yang, Gang Liu, and Jun Fang. 2023. "Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum and Weissella viridescens on the Gut Microbiota and Serum Metabolites of Mice with Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea" Nutrients 15, no. 21: 4603. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15214603
APA StyleYan, Z., Liu, Z., Ma, Y., Yang, Z., Liu, G., & Fang, J. (2023). Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum and Weissella viridescens on the Gut Microbiota and Serum Metabolites of Mice with Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea. Nutrients, 15(21), 4603. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15214603







