Novel Multi-Strain E3 Probiotic Formulation Improved Mental Health Symptoms and Sleep Quality in Hong Kong Chinese
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subject Recruitment and Study Design
2.2. Library Preparation and 16S rRNA Sequencing
2.3. Probiotic Mixture
2.4. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Cohort
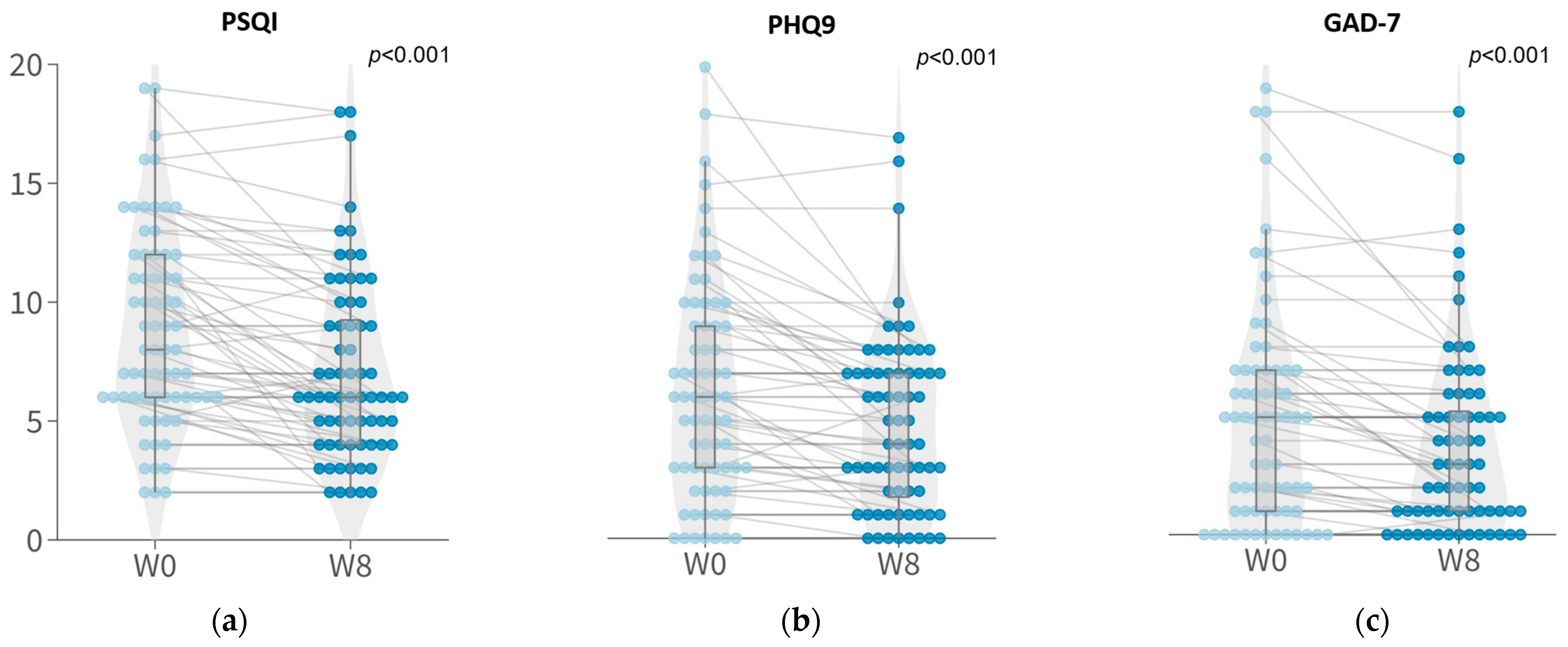
3.2. Symptomatic Improvements in Sleep Quality and Depressive and Anxious Symptoms with 8-Week Probiotic Intervention
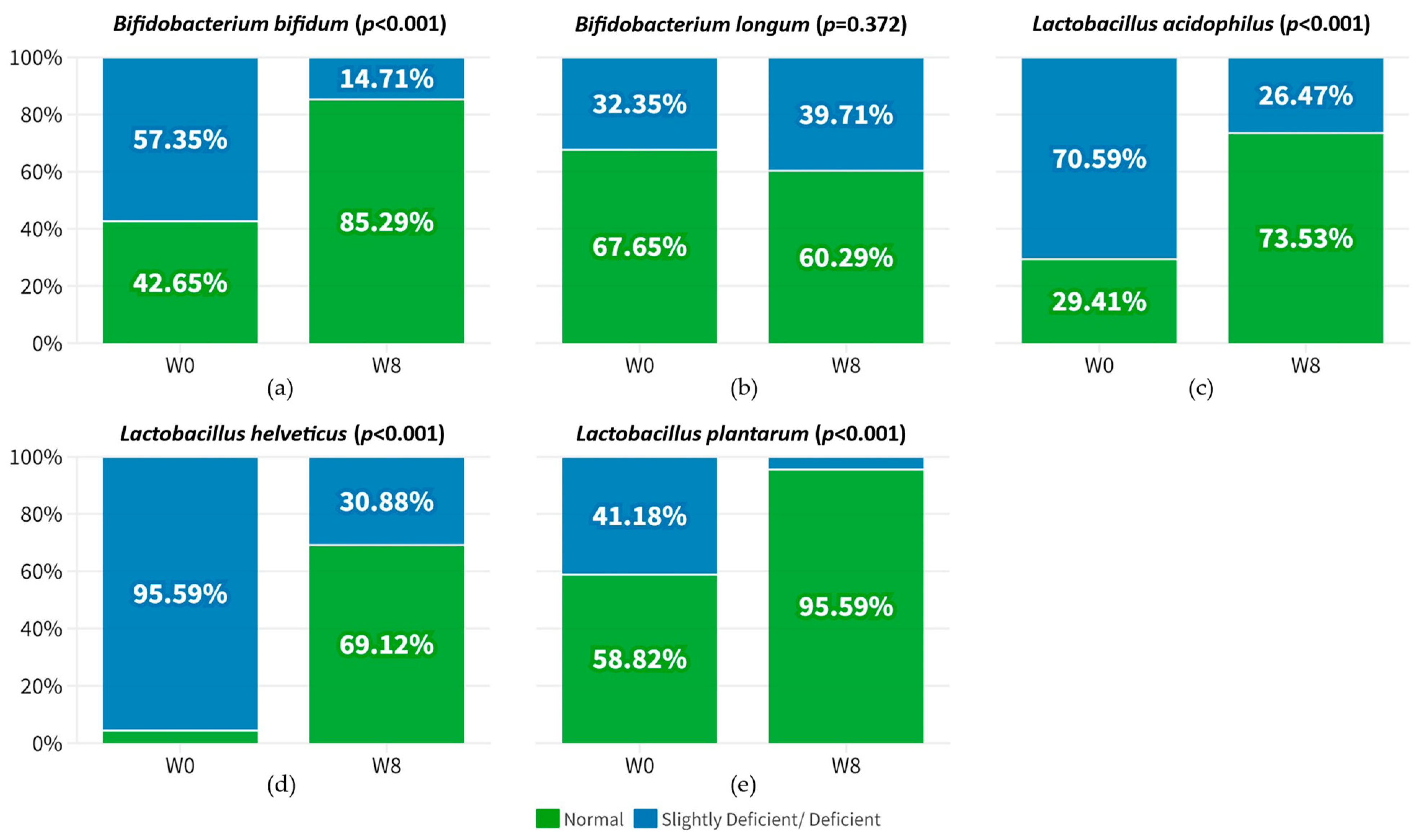
3.3. Improvement in the Relative Abundance of Probiotic Species after 8-Week Probiotic Intake
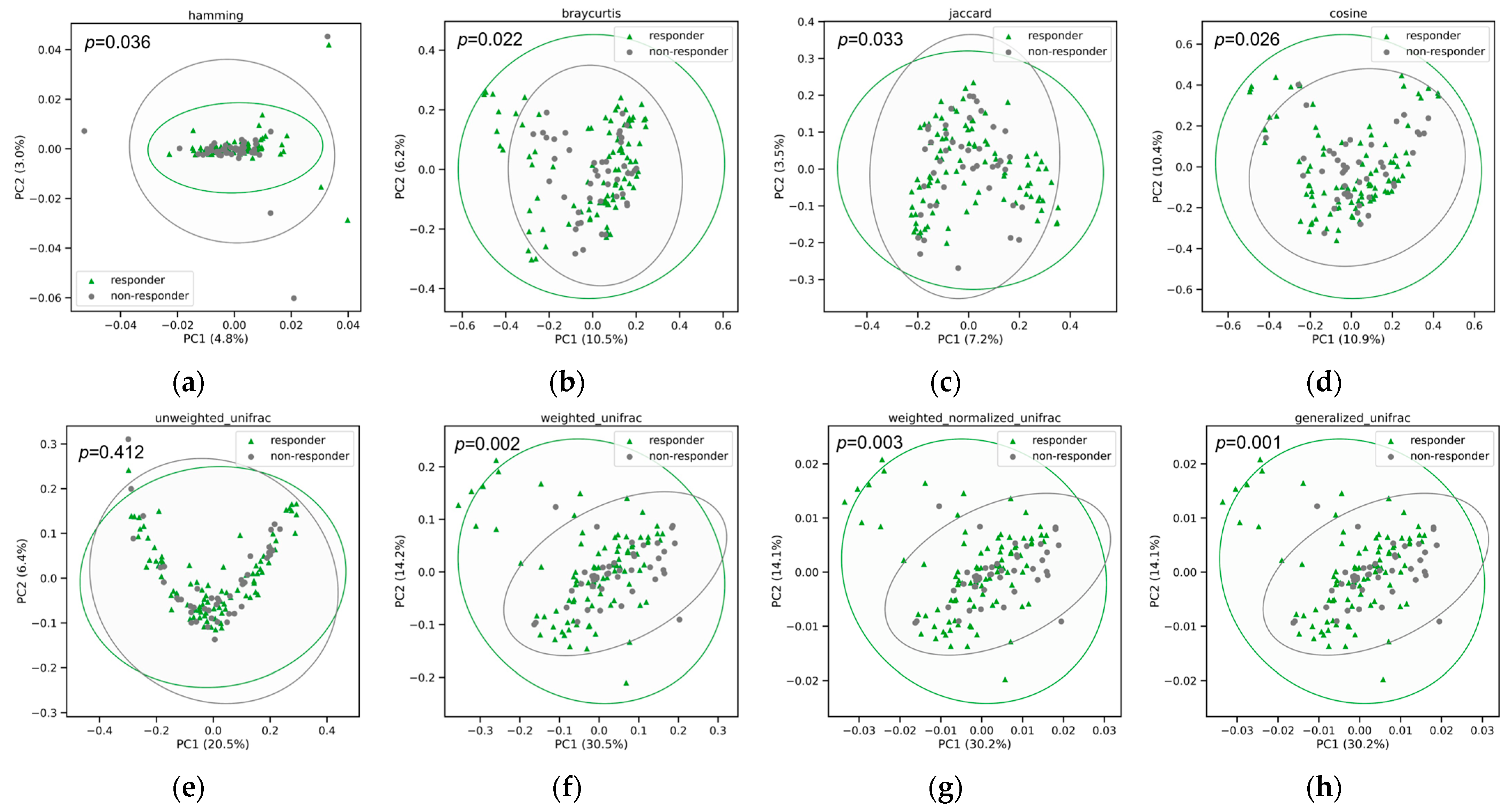
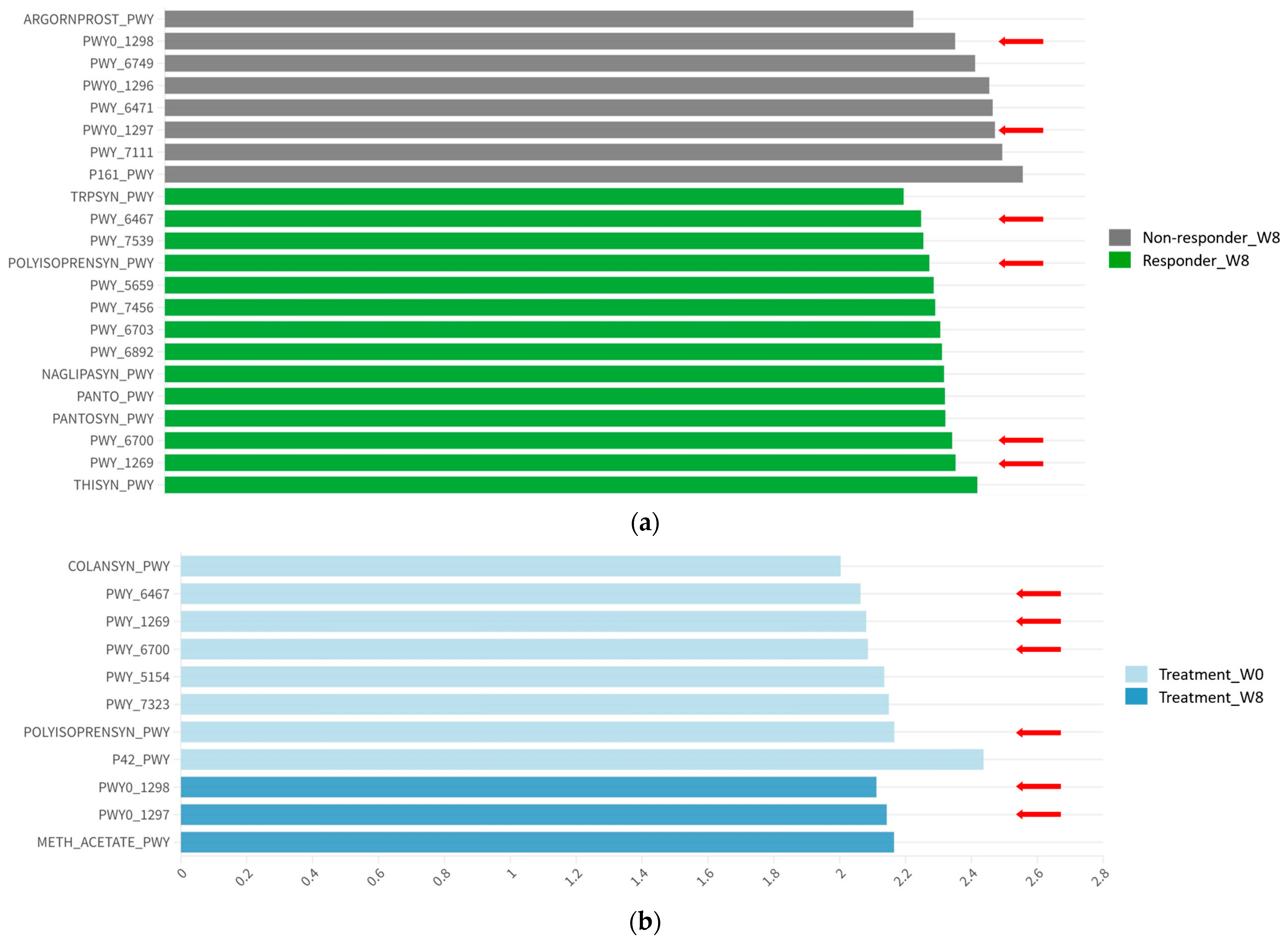
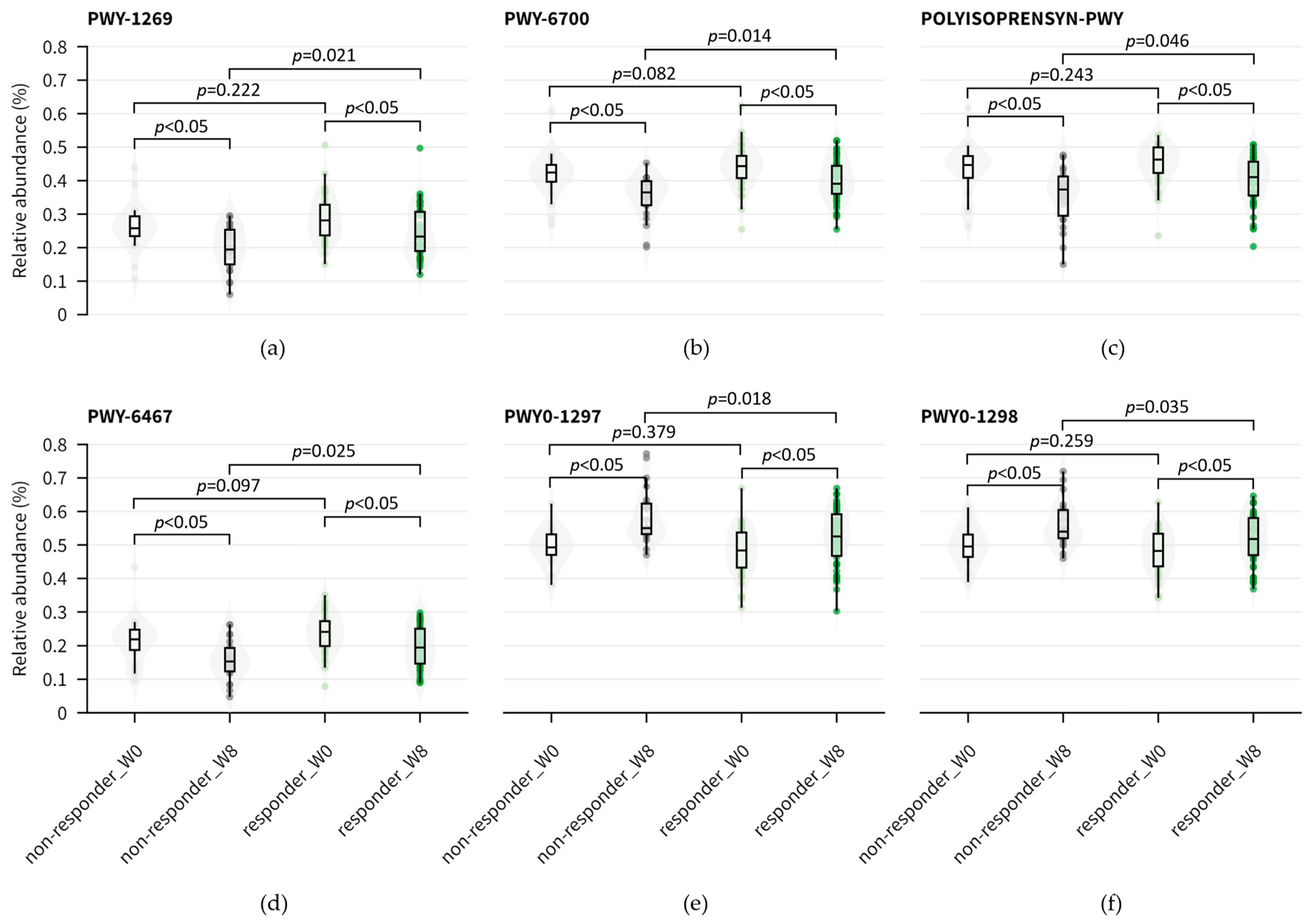
3.4. Functional Abundance and Pathways
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, E.P.H.; Hui, B.P.H.; Wan, E.Y.F. Depression and Anxiety in Hong Kong during COVID-19. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, L.C.; Wong, C.S.; Wang, M.J.; Chan, W.C.; Chen, E.Y.; Ng, R.M.; Hung, S.F.; Cheung, E.F.; Sham, P.C.; Chiu, H.F.; et al. Prevalence, psychosocial correlates and service utilization of depressive and anxiety disorders in Hong Kong: The Hong Kong Mental Morbidity Survey (HKMMS). Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2015, 50, 1379–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, S.M.Y.; Chen, E.Y.H.; Suen, Y.N.; Wong, C.S.M.; Chang, W.C.; Chan, S.K.W.; McGorry, P.D.; Morgan, C.; van Os, J.; McDaid, D.; et al. Prevalence, time trends, and correlates of major depressive episode and other psychiatric conditions among young people amid major social unrest and COVID-19 in Hong Kong: A representative epidemiological study from 2019 to 2022. Lancet Reg. Health West. Pac. 2023, 40, 100881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorboni, S.G.; Moghaddam, H.S.; Jafarzadeh-Esfehani, R.; Soleimanpour, S. A Comprehensive Review on the Role of the Gut Microbiome in Human Neurological Disorders. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2022, 35, e0033820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bercik, P.; Denou, E.; Collins, J.; Jackson, W.; Lu, J.; Jury, J.; Deng, Y.; Blennerhassett, P.; Macri, J.; McCoy, K.D.; et al. The intestinal microbiota affect central levels of brain-derived neurotropic factor and behavior in mice. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 599–609.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Yan, Q.; Ma, Y.; Fang, J.; Yang, Y. Recognizing the role of the vagus nerve in depression from microbiota-gut brain axis. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 1015175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, L.; Chang, L.; Pu, Y.; Qu, Y.; Hashimoto, K. A key role of the subdiaphragmatic vagus nerve in the depression-like phenotype and abnormal composition of gut microbiota in mice after lipopolysaccharide administration. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabotti, M.; Scirocco, A.; Maselli, M.A.; Severi, C. The gut-brain axis: Interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 203–209. [Google Scholar]
- Helton, S.G.; Lohoff, F.W. Serotonin pathway polymorphisms and the treatment of major depressive disorder and anxiety disorders. Pharmacogenomics 2015, 16, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belujon, P.; Grace, A.A. Dopamine System Dysregulation in Major Depressive Disorders. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017, 20, 1036–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuss, P. Anxiety disorders and GABA neurotransmission: A disturbance of modulation. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2015, 11, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, B.M.; Phan, K.L. The role of glutamate in anxiety and related disorders. CNS Spectr. 2005, 10, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, C.J.; Lydic, R.; Baghdoyan, H.A. Sleep duration varies as a function of glutamate and GABA in rat pontine reticular formation. J. Neurochem. 2011, 118, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, J.M.; Yu, K.; Donaldson, G.P.; Shastri, G.G.; Ann, P.; Ma, L.; Nagler, C.R.; Ismagilov, R.F.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Hsiao, E.Y. Indigenous bacteria from the gut microbiota regulate host serotonin biosynthesis. Cell 2015, 161, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, J.M. Serotonin control of sleep-wake behavior. Sleep. Med. Rev. 2011, 15, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desbonnet, L.; Garrett, L.; Clarke, G.; Bienenstock, J.; Dinan, T.G. The probiotic Bifidobacteria infantis: An assessment of potential antidepressant properties in the rat. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2008, 43, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, J.A.; Forsythe, P.; Chew, M.V.; Escaravage, E.; Savignac, H.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Bienenstock, J.; Cryan, J.F. Ingestion of Lactobacillus strain regulates emotional behavior and central GABA receptor expression in a mouse via the vagus nerve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16050–16055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoban, A.E.; Moloney, R.D.; Golubeva, A.V.; McVey Neufeld, K.A.; O'Sullivan, O.; Patterson, E.; Stanton, C.; Dinan, T.G.; Clarke, G.; Cryan, J.F. Behavioural and neurochemical consequences of chronic gut microbiota depletion during adulthood in the rat. Neuroscience 2016, 339, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, G.; Grenham, S.; Scully, P.; Fitzgerald, P.; Moloney, R.D.; Shanahan, F.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. The microbiome-gut-brain axis during early life regulates the hippocampal serotonergic system in a sex-dependent manner. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 18, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz Heijtz, R.; Wang, S.; Anuar, F.; Qian, Y.; Björkholm, B.; Samuelsson, A.; Hibberd, M.L.; Forssberg, H.; Pettersson, S. Normal gut microbiota modulates brain development and behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3047–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinan, T.G.; Stanton, C.; Cryan, J.F. Psychobiotics: A novel class of psychotropic. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 74, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, K.K.; Liu, Y.W.; Kuo, P.H.; Chung, Y.E.; Lu, M.L.; Chen, C.H. Effect of probiotics on depressive symptoms: A meta-analysis of human studies. Psychiatry Res. 2019, 282, 112568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morkl, S.; Butler, M.I.; Holl, A.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Probiotics and the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis: Focus on Psychiatry. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2020, 9, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burokas, A.; Arboleya, S.; Moloney, R.D.; Peterson, V.L.; Murphy, K.; Clarke, G.; Stanton, C.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Targeting the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis: Prebiotics Have Anxiolytic and Antidepressant-like Effects and Reverse the Impact of Chronic Stress in Mice. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 82, 472–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Kong, Z.; Song, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, X. The validity and reliability of the PHQ-9 on screening of depression in neurology: A cross sectional study. BMC Psychiatry 2022, 22, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Huntley, J.; Fierer, N.; Owens, S.M.; Betley, J.; Fraser, L.; Bauer, M.; et al. Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Peddada, S.D. Analysis of compositions of microbiomes with bias correction. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Ding, H.; Chen, H.; Ye, X.; Li, H.; Lin, X.; Ke, Z. Thiamine nutritional status and depressive symptoms are inversely associated among older Chinese adults. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges-Vieira, J.G.; Cardoso, C.K.S. Efficacy of B-vitamins and vitamin D therapy in improving depressive and anxiety disorders: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Neurosci. 2023, 26, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, L.; Lan, X.; Cohen, D.; Zhang, Y.; Ravindran, A.V.; Yuan, S.; Zheng, P.; Coghill, D.; Yang, L.; et al. Polyunsaturated fatty acids metabolism, purine metabolism and inosine as potential independent diagnostic biomarkers for major depressive disorder in children and adolescents. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.I.; Dournes, C.; Sillaber, I.; Uhr, M.; Asara, J.M.; Gassen, N.C.; Rein, T.; Ising, M.; Webhofer, C.; Filiou, M.D.; et al. Purine and pyrimidine metabolism: Convergent evidence on chronic antidepressant treatment response in mice and humans. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doke, M.; McLaughlin, J.P.; Baniasadi, H.; Samikkannu, T. Sleep Disorder and Cocaine Abuse Impact Purine and Pyrimidine Nucleotide Metabolic Signatures. Metabolites 2022, 12, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messaoudi, M.; Violle, N.; Bisson, J.F.; Desor, D.; Javelot, H.; Rougeot, C. Beneficial psychological effects of a probiotic formulation (Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium longum R0175) in healthy human volunteers. Gut Microbes 2011, 2, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenbergen, L.; Sellaro, R.; van Hemert, S.; Bosch, J.A.; Colzato, L.S. A randomized controlled trial to test the effect of multispecies probiotics on cognitive reactivity to sad mood. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 48, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutoh, N.; Kakiuchi, I.; Hiraku, A.; Iwabuchi, N.; Kiyosawa, K.; Igarashi, K.; Tanaka, M.; Nakamura, M.; Miyasaka, M. Heat-killed Lactobacillus helveticus improves mood states: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Benef. Microbes 2023, 14, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, H.X.; Yusoff, N.A.A.; Hor, Y.Y.; Lew, L.C.; Jaafar, M.H.; Choi, S.B.; Yusoff, M.S.B.; Wahid, N.; Abdullah, M.; Zakaria, N.; et al. Lactobacillus plantarum DR7 alleviates stress and anxiety in adults: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Benef. Microbes 2019, 10, 355–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janik, R.; Thomason, L.A.M.; Stanisz, A.M.; Forsythe, P.; Bienenstock, J.; Stanisz, G.J. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy reveals oral Lactobacillus promotion of increases in brain GABA, N-acetyl aspartate and glutamate. NeuroImage 2016, 125, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carney, M.W.; Williams, D.G.; Sheffield, B.F. Thiamine and pyridoxine lack newly-admitted psychiatric patients. Br. J. Psychiatry 1979, 135, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savignac, H.M.; Corona, G.; Mills, H.; Chen, L.; Spencer, J.P.; Tzortzis, G.; Burnet, P.W. Prebiotic feeding elevates central brain derived neurotrophic factor, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunits and D-serine. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 63, 756–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, K.; Cowen, P.J.; Harmer, C.J.; Tzortzis, G.; Errington, S.; Burnet, P.W. Prebiotic intake reduces the waking cortisol response and alters emotional bias in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology 2015, 232, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ironside, M.; O'Shea, J.; Cowen, P.J.; Harmer, C.J. Frontal Cortex Stimulation Reduces Vigilance to Threat: Implications for the Treatment of Depression and Anxiety. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 79, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Patients (No.) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Responder 5 (n = 46) | Non-Responder (n = 22) | p Value |
| Characteristics | |||
| Sex, No. (%) | |||
| Male | 17 (37.0) | 9 (40.9) | 0.7940 |
| Female | 29 (63.0) | 13 (59.1) | |
| Age, median [range], y | 52.0 [21–79] | 52.5 [22–67] | 0.5027 |
| BMI 1, mean (SD) | 22.6 (4.1) | 22.8 (3.5) | 0.7188 |
| Allergy ever, No. (%) | 18 (39.1) | 5 (22.7) | 0.2735 |
| ΔGAD7, mean (SD) 2 | −1.7 (2.4) | 0.1 (0.3) | <0.001 |
| Minimal or No anxiety, No. (%) | 40 (87.0) | 19 (86.4) | |
| Anxiety Symptoms, No. (%) | 6 (13.0) | 3 (13.6) | |
| ΔPHQ9, mean (SD) 3 | −2.1 (2.6) | 0.05 (0.4) | <0.001 |
| Minimal or No Depressive, No. (%) | 33 (71.7) | 19 (86.4) | |
| Depressive Symptoms, No. (%) | 13 (28.3) | 3 (13.6) | |
| ΔPSQI, mean (SD) 4 | −2.4 (2.3) | −0.1 (1.2) | <0.001 |
| Normal Sleeper, No. (%) | 10 (21.7) | 3 (13.6) | |
| Poor Sleeper, No. (%) | 36 (78.3) | 19 (86.4) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chan, H.H.Y.; Siu, P.L.K.; Choy, C.T.; Chan, U.K.; Zhou, J.; Wong, C.H.; Lee, Y.W.; Chan, H.W.; Tsui, J.C.C.; Loo, S.K.F.; et al. Novel Multi-Strain E3 Probiotic Formulation Improved Mental Health Symptoms and Sleep Quality in Hong Kong Chinese. Nutrients 2023, 15, 5037. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15245037
Chan HHY, Siu PLK, Choy CT, Chan UK, Zhou J, Wong CH, Lee YW, Chan HW, Tsui JCC, Loo SKF, et al. Novel Multi-Strain E3 Probiotic Formulation Improved Mental Health Symptoms and Sleep Quality in Hong Kong Chinese. Nutrients. 2023; 15(24):5037. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15245037
Chicago/Turabian StyleChan, Helen Hoi Yin, Pui Ling Kella Siu, Chi Tung Choy, Un Kei Chan, Junwei Zhou, Chi Ho Wong, Yuk Wai Lee, Ho Wang Chan, Joseph Chi Ching Tsui, Steven King Fan Loo, and et al. 2023. "Novel Multi-Strain E3 Probiotic Formulation Improved Mental Health Symptoms and Sleep Quality in Hong Kong Chinese" Nutrients 15, no. 24: 5037. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15245037
APA StyleChan, H. H. Y., Siu, P. L. K., Choy, C. T., Chan, U. K., Zhou, J., Wong, C. H., Lee, Y. W., Chan, H. W., Tsui, J. C. C., Loo, S. K. F., & Tsui, S. K. W. (2023). Novel Multi-Strain E3 Probiotic Formulation Improved Mental Health Symptoms and Sleep Quality in Hong Kong Chinese. Nutrients, 15(24), 5037. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15245037







