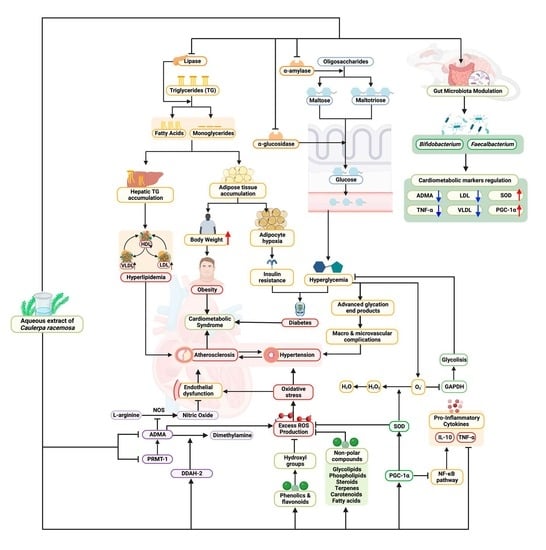
Dietary Supplementation of Caulerpa racemosa Ameliorates Cardiometabolic Syndrome via Regulation of PRMT-1/DDAH/ADMA Pathway and Gut Microbiome in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection and Preparation of Caulerpa Racemosa
2.2. Preparation of the Aqueous Extract of Caulerpa Racemosa (AEC)
2.3. In Vitro Studies
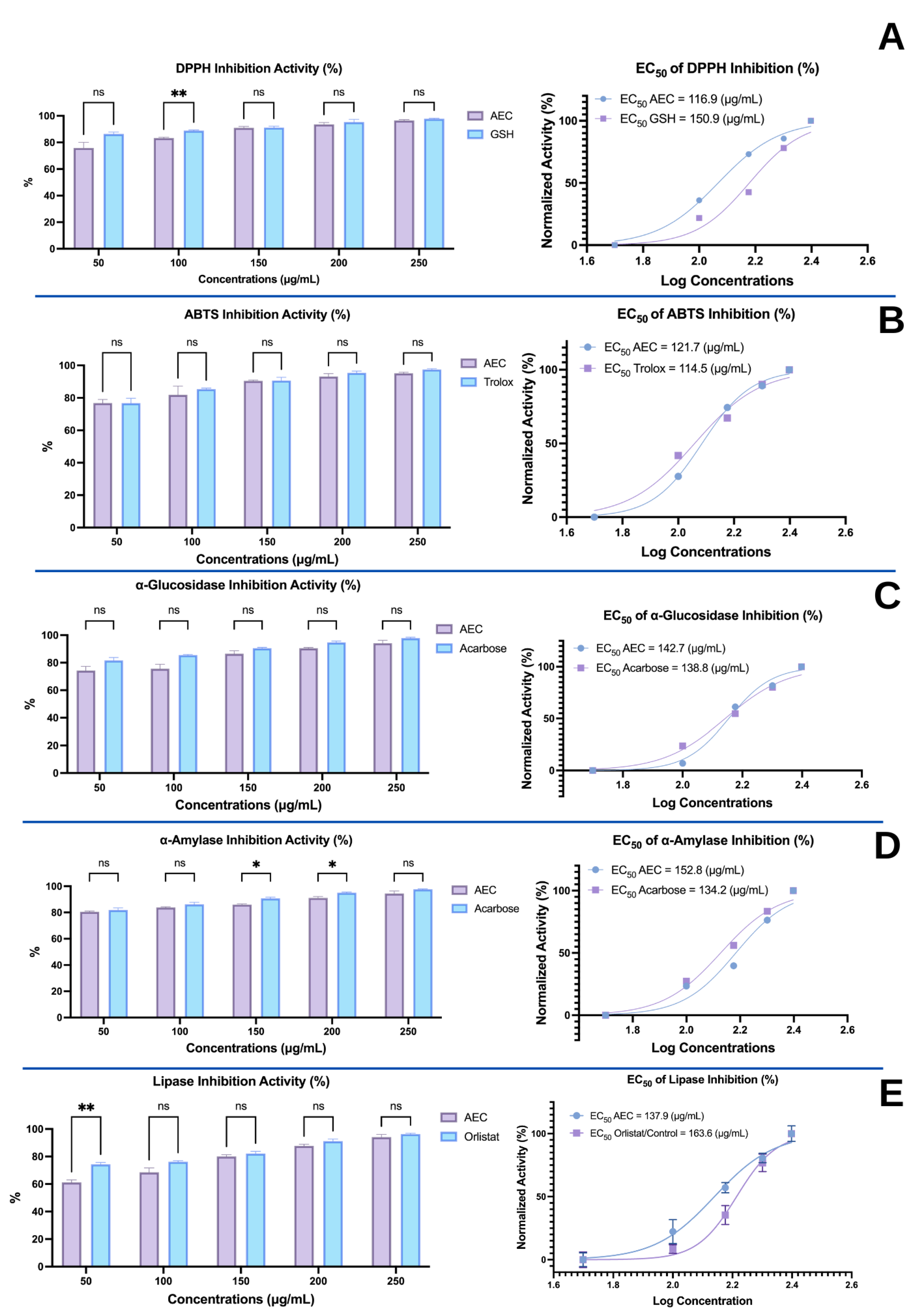
2.3.1. Antioxidant Activity by ABTS and DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity Assays (ABTS and DPPH Inhibition, %)
2.3.2. α-Glucosidase Inhibition Assay
2.3.3. α-Amylase Inhibition Assay (%)
2.3.4. Lipase Inhibition Assay (%)
2.4. In Vivo Study Design
2.4.1. Animal Handling and Ethical Approval
2.4.2. Study Design of Treatments
2.4.3. Feed or Pellet Composition and CFED Production
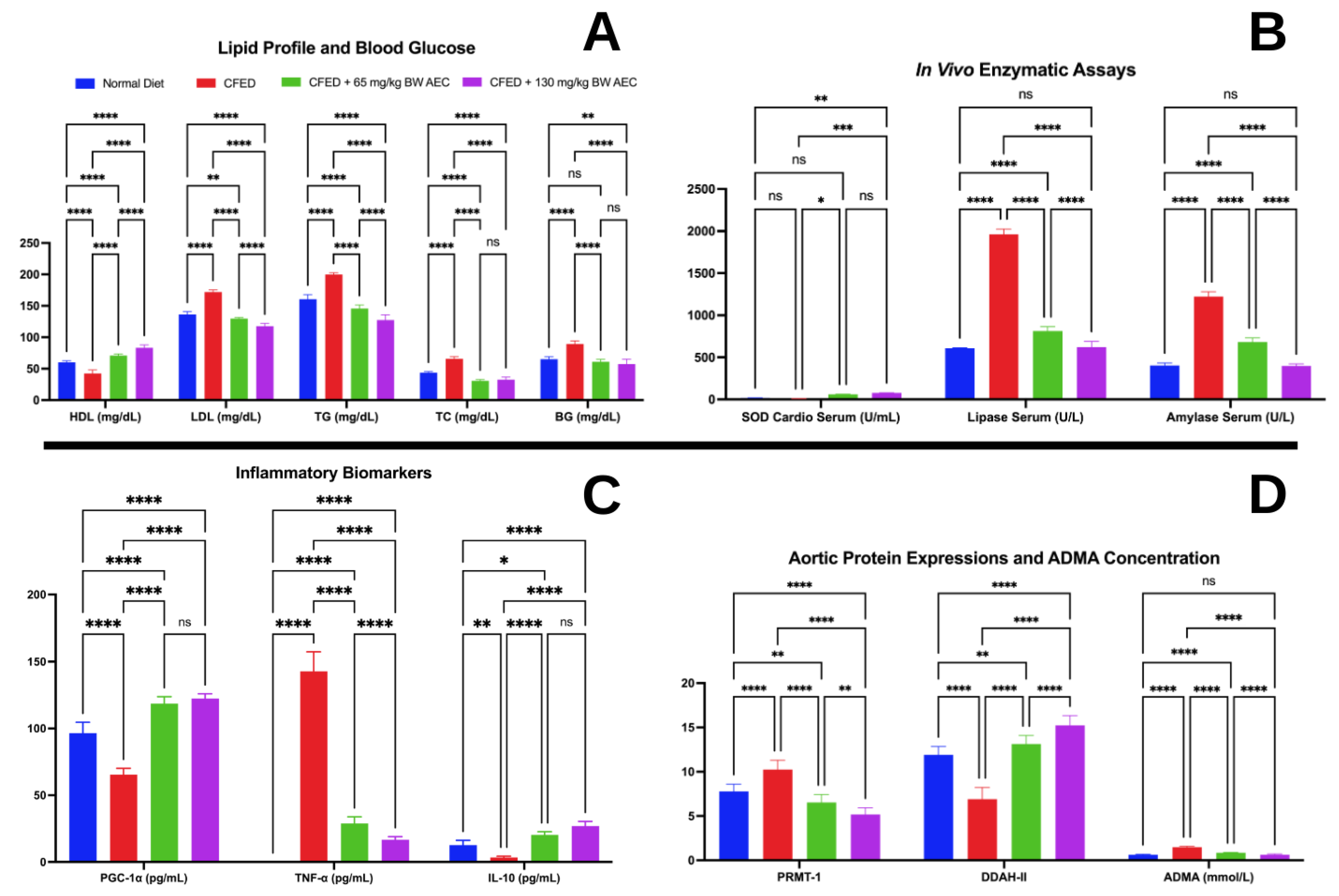
2.4.4. Biomedical Analysis of Collected Blood Samples
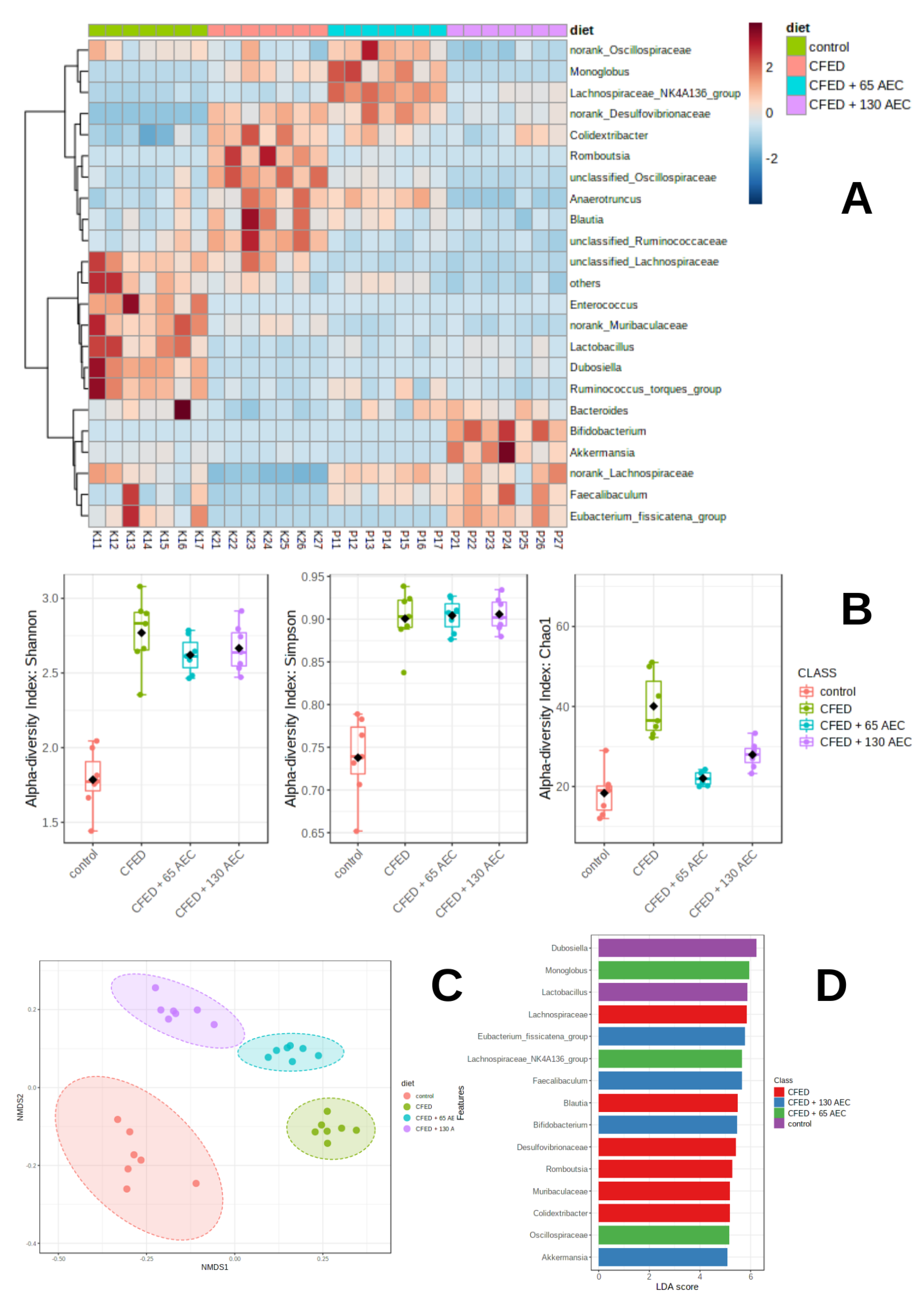
2.5. Gut Microbiota Sequencing and Analysis of the 16S rRNA Gene in Mice Feces
2.6. Data Analysis and Management
3. Results
3.1. In Vitro Activities of the Aqueous Extract of Caulerpa racemosa (AEC)
3.2. Effects of the Extract of Caulerpa Racemosa (AEC) on the Cardiometabolic Markers in Mice
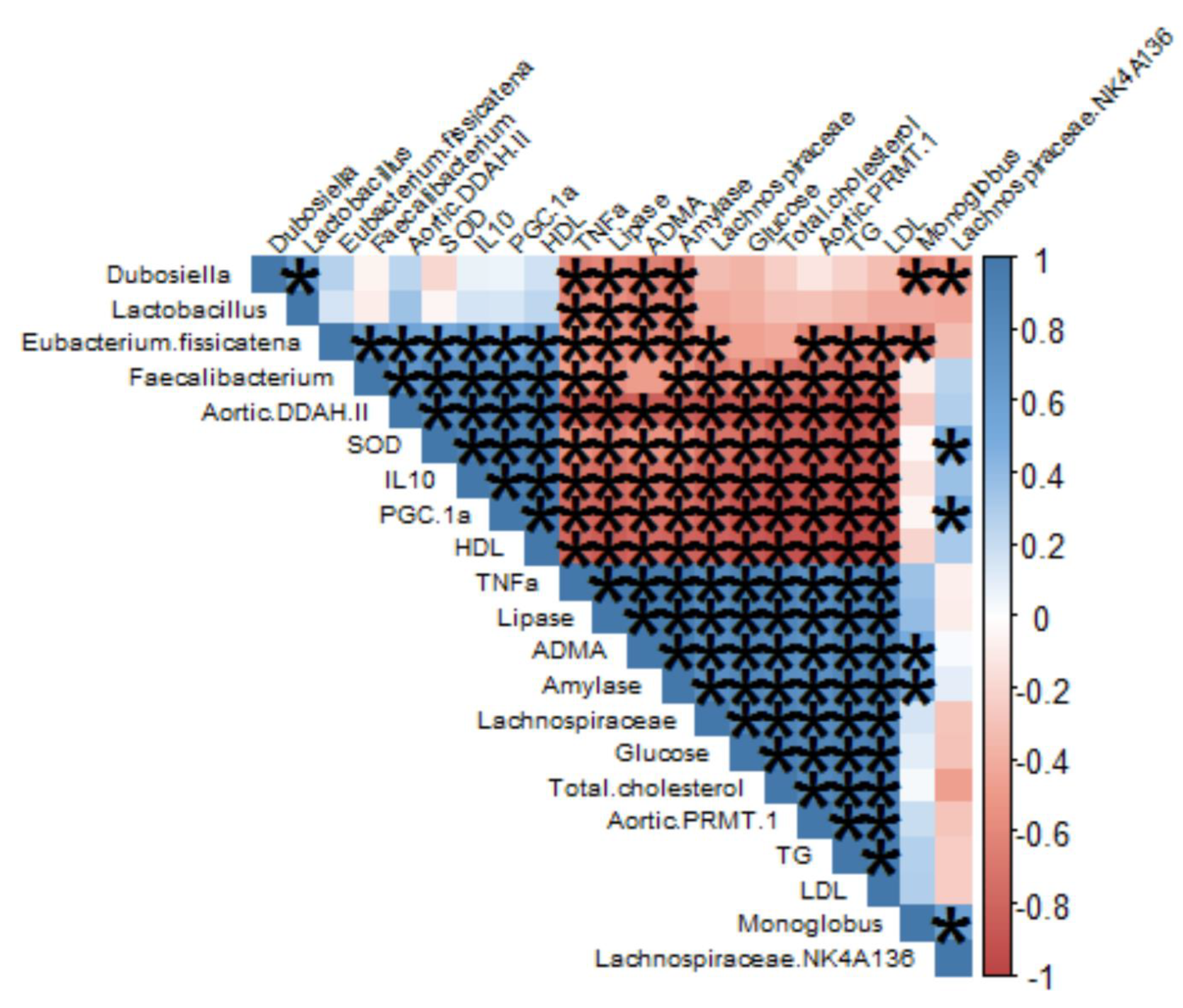
3.3. Gut Microbiome Modulation in Mice Administered a Cholesterol- and Fat-Enriched Diet Supplemented with AEC
3.3.1. Effect of AEC on Gut Microbiota Composition
3.3.2. Effect of AEC on Gut Microbiota Diversity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kirk, E.P.; Klein, S. Pathogenesis and pathophysiology of the cardiometabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2009, 11, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magon, N.; Chauhan, M. Pregnancy and the Formative Fifteen of Diabetes. J. Obstet. Gynecol. India 2014, 64, 440–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, S.; Chawla, R.; Madhu, S. The dirty dozen of diabetes. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 17, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacco, F.; Brownlee, M. Oxidative stress and diabetic complications. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 1058–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association, A.D. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2022 Abridged for Primary Care Providers. Clin. Diabetes 2022, 40, 10–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flood, D.; Seiglie, J.A.; Dunn, M.; Tschida, S.; Theilmann, M.; Marcus, M.E.; Brian, G.; Norov, B.; Mayige, M.T.; Gurung, M.S.; et al. The state of diabetes treatment coverage in 55 low-income and middle-income countries: A cross-sectional study of nationally representative, individual-level data in 680 102 adults. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2021, 2, e340–e351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifah, S.; Hartini, K.S.; Sadeli, A. Yuandani Identification of medicinal plants used by the community for indigenous poultry health management. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1122, 012045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandlik, R.V.; Naik, S.R.; Zine, S.; Ved, H.; Doshi, G. Antidiabetic Activity of Caulerpa racemosa: Role of Proinflammatory Mediators, Oxidative Stress, and Other Biomarkers. Planta Medica Int. Open 2022, 9, e60–e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Liu, D.Q.; Liang, T.J.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.Y.; Liu, A.H.; Guo, Y.W.; Mao, S.C. Bioactive constituents from the green alga Caulerpa racemosa. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Li, Y.; Famurewa, A.C.; Olatunji, O.J. Antidiabetic and nephroprotective effects of polysaccharide extract from the seaweed caulerpa racemosa in high fructose-streptozotocin induced diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2021, 14, 2121–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juturu, V. Polyphenols and Cardiometabolic Syndrome. In Polyphenols in Human Health and Disease; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; Volume 2, pp. 1067–1076. ISBN 9780123984562. [Google Scholar]
- Permatasari, H.K.; Nurkolis, F.; Hardinsyah, H.; Taslim, N.A.; Sabrina, N.; Ibrahim, F.M.; Visnu, J.; Kumalawati, D.A.; Febriana, S.A.; Sudargo, T.; et al. Metabolomic Assay, Computational Screening, and Pharmacological Evaluation of Caulerpa racemosa as an Anti-obesity With Anti-aging by Altering Lipid Profile and Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-γ Coactivator 1-α Levels. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permatasari, H.K.; Kuswari, M.; Nurkolis, F.; Mayulu, N.; Ibrahim, F.M.; Taslim, N.A.; Wewengkang, D.S.; Sabrina, N.; Arifin, G.R.; Mantik, K.E.K.; et al. Sea grapes extract improves blood glucose, total cholesterol, and PGC-1α in rats fed on cholesterol- and fat-enriched diet. F1000Research 2021, 10, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permatasari, H.K.; Nurkolis, F.; Mayulu, N.; Vivo, C.D.; Noor, S.L.; Rahmawati, R.; Radu, S.; Hardinsyah, H.; Taslim, N.A.; Wewengkang, D.S.; et al. Sea grapes powder with the addition of tempe rich in collagen: An anti-aging functional food. F1000Research 2022, 10, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahawatta, D.P.; Asanka Sanjeewa, K.K.; Jayawardena, T.U.; Kim, H.S.; Yang, H.W.; Jiang, Y.; Je, J.G.; Lee, T.K.; Jeon, Y.J. Drying seaweeds using hybrid hot water Goodle dryer (HHGD): Comparison with freeze-dryer in chemical composition and antioxidant activity. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2021, 24, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premarathna, A.D.; Ranahewa, T.H.; Wijesekera, S.K.; Harishchandra, D.L.; Karunathilake, K.J.K.; Waduge, R.N.; Wijesundara, R.R.M.K.K.; Jayasooriya, A.P.; Wijewardana, V.; Rajapakse, R.P.V.J. Preliminary screening of the aqueous extracts of twenty-three different seaweed species in Sri Lanka with in-vitro and in-vivo assays. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Bai, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, L.; Wei, C.; Jin, W. Effects of the Cistanche tubulosa Aqueous Extract on the Gut Microbiota of Mice with Intestinal Disorders. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 4936970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabrina, N.; Rizal, M.; Nurkolis, F.; Hardinsyah, H.; Tanner, M.J.; Gunawan, W.B.; Handoko, M.N.; Mayulu, N.; Taslim, N.A.; Puspaningtyas, D.S.; et al. Bioactive peptides identification and nutritional status ameliorating properties on malnourished rats of combined eel and soy-based tempe flour. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permatasari, H.K.; Nurkolis, F.; Gunawan, W.B.; Yusuf, V.M.; Yusuf, M.; Kusuma, R.J.; Sabrina, N.; Muharram, F.R.; Taslim, N.A.; Mayulu, N.; et al. Modulation of gut microbiota and markers of metabolic syndrome in mice on cholesterol and fat enriched diet by butterfly pea flower kombucha. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 1251–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Permatasari, H.K.; Firani, N.K.; Prijadi, B.; Irnandi, D.F.; Riawan, W.; Yusuf, M.; Amar, N.; Chandra, L.A.; Yusuf, V.M.; Subali, A.D.; et al. Kombucha drink enriched with sea grapes (Caulerpa racemosa) as potential functional beverage to contrast obesity: An in vivo and in vitro approach. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2022, 49, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapotubun, A.M.; Matrutty, T.E.A.A.; Riry, J.; Tapotubun, E.J.; Fransina, E.G.; Mailoa, M.N.; Riry, W.A.; Setha, B.; Rieuwpassa, F. Seaweed Caulerpa sp. position as functional food. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; Volume 517, p. 012021. [Google Scholar]
- Forman, H.J.; Zhang, H.; Rinna, A. Glutathione: Overview of its protective roles, measurement, and biosynthesis. Mol. Asp. Med. 2009, 30, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Belkacemi, L.; Belalia, M.; Djendara, A.; Bouhadda, Y. Antioxidant and antibacterial activities and identification of bioactive compounds of various extracts of Caulerpa racemosa from Algerian coast. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2020, 10, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, W.F.; Tay, V.; Tan, S.H.; Yow, Y.Y.; Chew, J. Decoding antioxidant and antibacterial potentials of Malaysian green seaweeds: Caulerpa racemosa and Caulerpa lentillifera. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Alencar, D.B.; de Carvalho, F.C.T.; Rebouças, R.H.; dos Santos, D.R.; dos Santos Pires-Cavalcante, K.M.; de Lima, R.L.; Baracho, B.M.; Bezerra, R.M.; Viana, F.A.; dos Fernandes Vieira, R.H.S.; et al. Bioactive extracts of red seaweeds Pterocladiella capillacea and Osmundaria obtusiloba (Floridophyceae: Rhodophyta) with antioxidant and bacterial agglutination potential. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2016, 9, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chielle, E.O.; Gens, F.; Rossi, E.M. Oxidative, inflammatory and cardiometabolic biomarkers of clinical relevance in patients with metabolic syndrome. J. Bras. Patol. Med. Lab. 2018, 54, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, B.K. Ultrasound: A clean, green extraction technology. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 71, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spínola, V.; Llorent-Martínez, E.; Lwt, P.C. Inhibition of α-amylase, α-glucosidase and pancreatic lipase by phenolic compounds of Rumex maderensis (Madeira sorrel). Influence of simulated gastrointestinal digestion on hyperglycaemia-related damage linked with aldose reductase activity and protein glycation. LWT 2020, 118, 108727. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Xu, G.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Ying, H. Purification of an α-amylase inhibitor in a polyethylene glycol/fructose-1,6-bisphosphate trisodium salt aqueous two-phase system. Process Biochem. 2008, 43, 765–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves Filho, G.P.; de Paula Oliveira, R.; de Medeiros, S.R.B.; Rocha, H.A.O.; Moreira, S.M.G. Sulfated polysaccharides from green seaweed Caulerpa prolifera suppress fat accumulation. J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 32, 4299–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoppo, J.I.C.; Nurkolis, F.; Pramono, A.; Ardiaria, M.; Murbawani, E.A.; Yusuf, M.; Qhabibi, F.R.; Yusuf, V.M.; Amar, N.; Karim, M.R.A.; et al. Amelioration of obesity-related metabolic disorders via supplementation of Caulerpa lentillifera in rats fed with a high-fat and high-cholesterol diet. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakers, A.; De Siqueira, M.K.; Seale, P.; Villanueva, C.J. Adipose-tissue plasticity in health and disease. Cell 2022, 185, 419–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulman, G.I. Ectopic Fat in Insulin Resistance, Dyslipidemia, and Cardiometabolic Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1131–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, L.; Feng, D.; Wang, T.; Ren, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J. Inhibitors of α-amylase and α-glucosidase: Potential linkage for whole cereal foods on prevention of hyperglycemia. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 6320–6337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.M.; Wonnerth, A.; Huber, K.; Wojta, J. Cardiovascular disease risk reduction by raising HDL cholesterol—Current therapies and future opportunities. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 167, 1177–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistrosch, F.; Natali, A.; Hanefeld, M. Is hyperglycemia a cardiovascular risk factor? Diabetes Care 2011, 34 (Suppl. S2), S128–S131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley Schwartz, S. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and the cardiometabolic syndrome: Impact of incretin-based therapies. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2010, 2010, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, A.C.; Corsi, D.; Cavi, N.; Bruni, N.; Dosio, F. Superoxide dismutase administration: A review of proposed human uses. Molecules 2021, 26, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younus, H. Therapeutic potentials of superoxide dismutase. Int. J. Health Sci. 2018, 12, 88–93. [Google Scholar]
- Akhigbe, R.; Ajayi, A. The impact of reactive oxygen species in the development of cardiometabolic disorders: A review. Lipids Health Dis. 2021, 20, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Qin, Y.; Liu, B.; Gao, M.; Li, A.; Li, X.; Gong, G. PGC-1α-Mediated Mitochondrial Quality Control: Molecular Mechanisms and Implications for Heart Failure. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 871357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rius-Pérez, S.; Torres-Cuevas, I.; Millán, I.; Ortega, Á.L.; Pérez, S.; Sandhu, M.A. PGC-1 α, Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress: An Integrative View in Metabolism. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 1452696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, N.; Paquot, N.; Scheen, A.J. Inflammatory markers and cardiometabolic diseases. Acta Clin. Belgica Int. J. Clin. Lab. Med. 2015, 70, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, D.R.; Arora, P.; Garcia-Bailo, B. The Relationship between Metabolic Syndrome and Markers of Cardiometabolic Disease among Canadian Adults. J. Diabetes Metab. 2011, S2, 003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Sheng, M.; Zhang, X.; Gu, Q.; Zheng, Z. PRMT-1 and DDAHs-induced ADMA upregulation is involved in ROS- and RAS-mediated diabetic retinopathy. Exp. Eye Res. 2009, 89, 1028–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, A.J.; Karuppiah, K.; Cardounel, A.J. Role of the PRMT-DDAH-ADMA axis in the regulation of endothelial nitric oxide production. Pharmacol. Res. 2009, 60, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, M.D.; Brown, T.; George Zheng, Y. The biological axis of protein arginine methylation and asymmetric dimethylarginine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Mu, J.J.; Fang, Y.; Yuan, Z.Y.; Liu, F.Q. Impact of high salt independent of blood pressure on PRMT/ADMA/DDAH pathway in the aorta of dahl salt-sensitive rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 8062–8072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayers, E.W.; Barrett, T.; Benson, D.A.; Bolton, E.; Bryant, S.H.; Canese, K.; Chetvernin, V.; Church, D.M.; Dicuccio, M.; Federhen, S.; et al. Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, D5–D16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacca, M.; Celano, G.; Calabrese, F.M.; Portincasa, P.; Gobbetti, M.; De Angelis, M. The controversial role of human gut lachnospiraceae. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameyama, K.; Itoh, K. Intestinal colonization by a lachnospiraceae bacterium contributes to the development of diabetes in obese mice. Microbes Environ. 2014, 29, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, F.; Zheng, R.D.; Sun, X.Q.; Ding, W.J.; Wang, X.Y.; Fan, J.G. Gut microbiota dysbiosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2017, 16, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, B.; Zhang, C.; Sheng, Y.; Zhao, C.; He, X.; Xu, W.; Huang, K.; Luo, Y. Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effect of S-allyl-cysteine sulfoxide (alliin) in DIO mice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraj, S.R.; Osborne, J.W. Bioactive compounds from Caulerpa racemosa as a potent larvicidal and antibacterial agent. Front. Biol. 2014, 9, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, N.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Bindels, L.B.; Druart, C.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Cani, P.D.; de los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G.; Delzenne, N.M. Functional effects of EPS-producing bifidobacterium administration on energy metabolic alterations of diet-induced obese mice. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zheng, A.; Ni, L.; Wu, L.; Hu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, Z.; Ni, Y. Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis lkm512 Attenuates Obesity-Associated Inflammation and Insulin Resistance through the Modification of Gut Microbiota in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2022, 66, 2100639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maioli, T.U.; Borras-Nogues, E.; Torres, L.; Barbosa, S.C.; Martins, V.D.; Langella, P.; Azevedo, V.A.; Chatel, J.M. Possible Benefits of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii for Obesity-Associated Gut Disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 740636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurkolis, F.; Taslim, N.A.; Qhabibi, F.R.; Kang, S.; Moon, M.; Choi, J.; Choi, M.; Park, M.N.; Mayulu, N.; Kim, B. Ulvophyte Green Algae Caulerpa lentillifera: Metabolites Profile and Antioxidant, Anticancer, Anti-Obesity, and In Vitro Cytotoxicity Properties. Molecules 2023, 28, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Groups | Normal | CFED | C | D | p b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial body weight (g) | 22.55 ± 1.717 | 22.05 ± 2.203 | 22.03 ± 1.033 | 22.42 ± 2.908 | 0.9231 |
| Final body weight (g) | 65.59 ± 3.606 | 82.27 ± 4.206 | 48.66 ± 5.509 | 43.18 ± 4.481 | <0.0001 |
| p a | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| Weight gain (g/day) | 0.9357 ± 0.08751 | 1.309 ± 0.07279 | 0.5789 ± 0.1116 | 0.4513 ± 0.1338 | <0.0001 |
| Food intake (g) | 5.204 ± 0.6179 | 5.116 ± 0.8741 | 5.037 ± 1.168 | 5.009 ± 0.6075 | 0.9556 |
| Water intake (mL) | 5.758 ± 0.6237 | 5.752 ± 0.8913 | 5.349 ± 1.001 | 5.208 ± 0.5297 | 0.2954 |
| FER (%) | 18.18 ± 2.413 | 26.32 ± 5.064 | 12.00 ± 3.480 | 9.011 ± 2.496 | <0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nurkolis, F.; Taslim, N.A.; Subali, D.; Kurniawan, R.; Hardinsyah, H.; Gunawan, W.B.; Kusuma, R.J.; Yusuf, V.M.; Pramono, A.; Kang, S.; et al. Dietary Supplementation of Caulerpa racemosa Ameliorates Cardiometabolic Syndrome via Regulation of PRMT-1/DDAH/ADMA Pathway and Gut Microbiome in Mice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15040909
Nurkolis F, Taslim NA, Subali D, Kurniawan R, Hardinsyah H, Gunawan WB, Kusuma RJ, Yusuf VM, Pramono A, Kang S, et al. Dietary Supplementation of Caulerpa racemosa Ameliorates Cardiometabolic Syndrome via Regulation of PRMT-1/DDAH/ADMA Pathway and Gut Microbiome in Mice. Nutrients. 2023; 15(4):909. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15040909
Chicago/Turabian StyleNurkolis, Fahrul, Nurpudji Astuti Taslim, Dionysius Subali, Rudy Kurniawan, Hardinsyah Hardinsyah, William Ben Gunawan, Rio Jati Kusuma, Vincentius Mario Yusuf, Adriyan Pramono, Sojin Kang, and et al. 2023. "Dietary Supplementation of Caulerpa racemosa Ameliorates Cardiometabolic Syndrome via Regulation of PRMT-1/DDAH/ADMA Pathway and Gut Microbiome in Mice" Nutrients 15, no. 4: 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15040909
APA StyleNurkolis, F., Taslim, N. A., Subali, D., Kurniawan, R., Hardinsyah, H., Gunawan, W. B., Kusuma, R. J., Yusuf, V. M., Pramono, A., Kang, S., Mayulu, N., Syauki, A. Y., Tallei, T. E., Tsopmo, A., & Kim, B. (2023). Dietary Supplementation of Caulerpa racemosa Ameliorates Cardiometabolic Syndrome via Regulation of PRMT-1/DDAH/ADMA Pathway and Gut Microbiome in Mice. Nutrients, 15(4), 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15040909