Effect of a Single Multi-Vitamin and Mineral Supplement on Nutritional Intake in Korean Elderly: Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2018–2020
Abstract
:1. Introduction
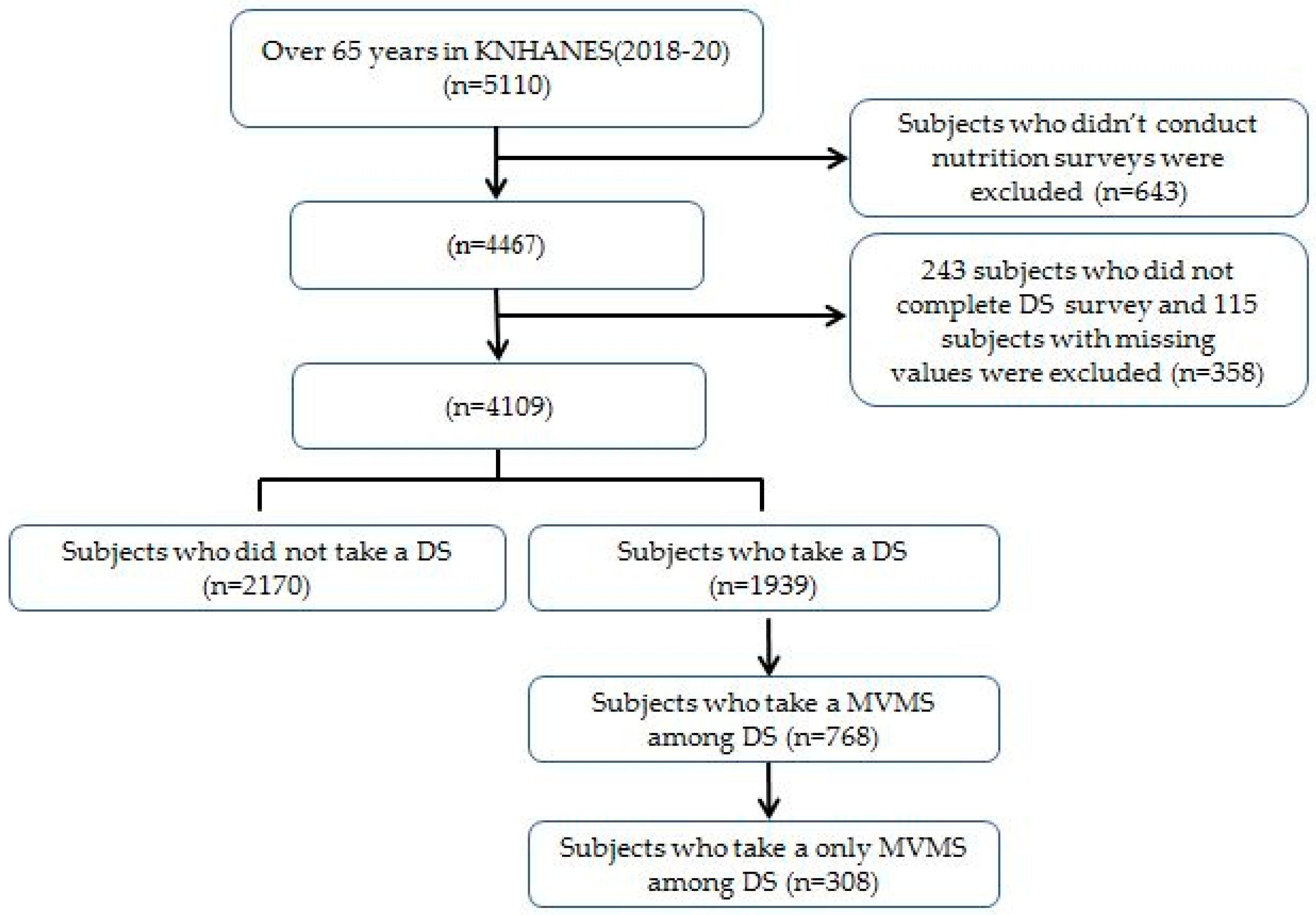
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Baseline Characteristics
2.3. Definition of MVMS Users
2.4. Vitamin and Mineral Intake from Foods and Supplements
2.5. Statistical Analysis
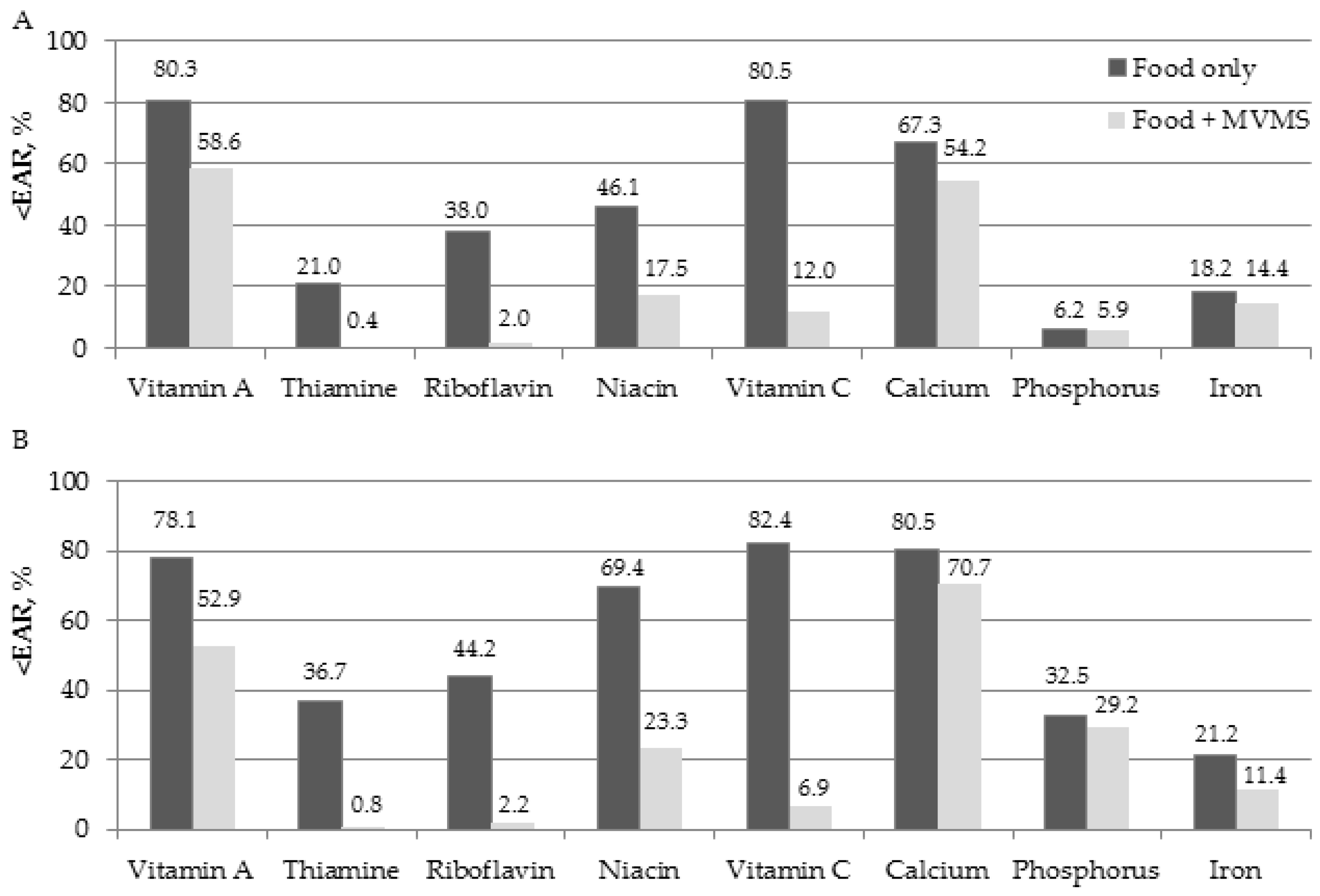
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cereda, E. Mini nutritional assessment. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2012, 15, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verlaan, S.; Ligthart-Melis, G.C.; Wijers, S.L.; Cederholm, T.; Maier, A.B.; de van der Schueren, M.A. High prevalence of physical frailty among community-dwelling malnourished older adults—A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2017, 18, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Lee, Y.; Won, C.W.; Lee, K.E.; Chon, D. Nutritional Status and Frailty in Community-Dwelling Older Korean Adults: The Korean Frailty and Aging Cohort Study. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2018, 22, 774–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ter Borg, S.; Verlaan, S.; Hemsworth, J.; Mijnarends, D.M.; Schols, J.M.; Luiking, Y.C.; de Groot, L.C. Micronutrient intakes and potential inadequacies of community-dwelling older adults: A systematic review. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, 1195–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, E.; Miller, M.; Yaxley, A.; Isenring, E. Malnutrition in the elderly: A narrative review. Maturitas 2013, 76, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gahche, J.J.; Bailey, R.L.; Potischman, N.; Dwyer, J.T. Dietary supplement use was very high among older adults in the United States in 2011–2014. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 1968–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blumberg, J.B.; Frei, B.; Fulgoni Iii, V.L.; Weaver, C.M.; Zeisel, S.H. Contribution of dietary supplements to nutritional adequacy in various adult age groups. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maggini, S.; Pierre, A.; Calder, P.C. Immune function and micronutrient requirements change over the life course. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sinopoli, A.; Caminada, S.; Isonne, C.; Santoro, M.M.; Baccolini, V. What Are the Effects of Vitamin a Oral Supplementation in the Prevention and Management of Viral Infections? A Systematic Review of Randomized Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semba, R.D.; Bartali, B.; Zhou, J.; Blaum, C.; Ko, C.-W.; Fried, L.P. Low serum micronutrient concentrations predict frailty among older women living in the community. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2006, 61, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S. Vitamin supplementation in the elderly. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2015, 31, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inzitari, M.; Doets, E.; Bartali, B.; Benetou, V.; Di Bari, M.; Visser, M.; Volpato, S.; Gambassi, G.; Topinkova, E.; De Groot, L. Nutrition in the age-related disablement process. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2011, 15, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Man, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, J. Dietary micronutrients intake status among Chinese elderly people living at home: Data from CNNHS 2010–2012. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, R.R.; Singh, L.; Thakur, A.; Singh, S.; Kumar, B. Role of Vitamins in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Review. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2022, 21, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, R.S.; Cleveland, L.E.; Goldman, J.D.; Moshfegh, A.J. Older adults who use vitamin/mineral supplements differ from nonusers in nutrient intake adequacy and dietary attitudes. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2007, 107, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeden, A.; Remig, V.; Holcomb, C.A.; Herald, T.J.; Baybutt, R.C. Vitamin and mineral supplements have a nutritionally significant impact on micronutrient intakes of older adults attending senior centers. J. Nutr. Elder. 2010, 29, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kang, M.; Kim, D.; Baek, Y.; Moon, S.; Jung, H.; Song, Y.; Paik, H. Dietary supplement use and its effect on nutrient intake in Korean adult population in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey IV (2007–2009) data. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 68, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Lee, Y.; Park, K. Vitamin and mineral supplement use among Korean adults: Baseline data from the trace element study of Korean adults in Yeungnam area. Nutrients 2018, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blumberg, J.B.; Frei, B.B.; Fulgoni Iii, V.L.; Weaver, C.M.; Zeisel, S.H. Impact of frequency of multi-vitamin/multi-mineral supplement intake on nutritional adequacy and nutrient deficiencies in US adults. Nutrients 2017, 9, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bailey, R.L.; Fulgoni III, V.L.; Keast, D.R.; Dwyer, J.T. Examination of vitamin intakes among US adults by dietary supplement use. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 112, 657–663.e654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murphy, S.P.; White, K.K.; Park, S.-Y.; Sharma, S. Multivitamin-multimineral supplements’ effect on total nutrient intake. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 280S–284S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.; Kim, D.W.; Jung, H.J.; Shim, J.E.; Song, Y.; Kim, K.; Paik, H.-Y. Dietary supplement use and nutrient intake among children in South Korea. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 116, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, J.G.; Hwang, H.R.; Jeong, D.W.; Cho, Y.H.; Choi, E.J.; Yi, Y.H.; Tak, Y.J. Vitamin-Mineral Supplement Use Patterns in Elderly Koreans: Data from the 2007–2008 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Korean J. Fam. Med. 2016, 37, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ministry of Health and Welfare (KR); The Korean Nutrition Society. Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans 2020; Ministry of Health and Welfare: Sejong, Republic of Korea, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Shakur, Y.A.; Tarasuk, V.; Corey, P.; O’Connor, D.L. A comparison of micronutrient inadequacy and risk of high micronutrient intakes among vitamin and mineral supplement users and nonusers in Canada. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Angeles-Agdeppa, I.; Sun, Y.; Denney, L.; Tanda, K.V.; Octavio, R.A.D.; Carriquiry, A.; Capanzana, M.V. Food sources, energy and nutrient intakes of adults: 2013 Philippines National Nutrition Survey. Nutr. J. 2019, 18, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, C.; No, J.-K.; Kim, H.-S. Dietary pattern classifications with nutrient intake and body composition changes in Korean elderly. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2014, 8, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kwon, Y.-S.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Park, Y.; Park, Y.-K.; Kim, S. Dietary assessment and factors according to fruits and vegetables intake in Korean elderly people: Analysis of data from the Korea national health and nutrition examination survey, 2013–2018. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanis, J.A.; Cooper, C.; Rizzoli, R.; Reginster, J.Y.; on behalf of the Scientific Advisory Board of the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis (ESCEO); Committees of Scientific Advisors; National Societies of the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF). European guidance for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Osteoporos. Int. 2019, 30, 3–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soares, M.M.; Silva, M.A.; Garcia, P.P.C.; Silva, L.S.d.; Costa, G.D.d.; Araújo, R.M.A.; Cotta, R.M.M. Efect of vitamin A suplementation: A systematic review. Cienc. Saude Coletiva 2019, 24, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, M.M.F.; Chin, K.-Y.; Ima-Nirwana, S.; Wong, S.K. Vitamin A and bone health: A review on current evidence. Molecules 2021, 26, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Food-Only (n = 2170) | Food + MVMS (n = 308) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age group | |||
| 65–74 years | 53.5 (1.4) | 61.2 (3.4) | 0.046 |
| 75 years | 46.5 (1.4) | 38.8 (3.4) | |
| Sex, men | 48.8 (1.1) | 44.9 (3.2) | 0.259 |
| Education level | |||
| Elementary school or lower | 57.5 (1.5) | 52.1 (3.7) | 0.053 |
| Graduation from middle school | 16.9 (1.0) | 15.6 (2.4) | |
| Graduation from high school | 19.1 (1.0) | 21.3 (2.7) | |
| University or more | 6.5 (0.7) | 11.1 (2.1) | |
| Household income quartile | |||
| Low | 49.6 (1.6) | 40.2 (3.8) | 0.048 |
| Middle low | 26.5 (1.4) | 33.8 (3.5) | |
| Middle high | 15.8 (1.1) | 19.4 (2.8) | |
| High | 8.0 (0.9) | 6.6 (1.7) | |
| Smoking status | |||
| Ex-smoker or non-smoker | 89.3 (0.9) | 95.2 (1.4) | 0.003 |
| Smoker | 10.7 (0.9) | 4.8 (1.4) | |
| Frequency of alcohol drinking | |||
| None | 51.9 (1.3) | 50.7 (3.2) | 0.471 |
| 1 time/week or less | 30.9 (1.2) | 34.1 (2.9) | |
| 2–3 time/week | 9.1 (0.7) | 9.7 (2.0) | |
| 4 time/week or more | 8.1 (0.6) | 5.5 (1.5) | |
| Physical activity | |||
| lesser than mild | 71.4 (1.4) | 63.0 (3.3) | 0.012 |
| more than moderate | 28.6 (1.4) | 37.0 (3.3) | |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | |||
| Underweight (BMI < 18.5) | 3.1 (0.5) | 5.3 (1.3) | 0.071 |
| Normal (18.5 ≤ BMI < 23) | 33.2 (1.2) | 26.3 (3.0) | |
| Overweight (23 ≤ BMI < 25) | 25.0 (1.1) | 28.4 (2.9) | |
| Obesity (25 ≤ BMI) | 38.7 (1.3) | 40.1 (3.2) | |
| Have a disease | 70.2 (1.1) | 68.7 (2.9) | 0.621 |
| Have a cancer | 9.1 (0.8) | 6.7 (1.6) | 0.210 |
| Nutrients | EAR | Food-Only (n = 991) | Food + MVMS (n = 139) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food Alone | Food Alone | p-Value * | Food Include MVMS | p-Value † | ||
| Total calories (kcal/day) | NA | 1750.85 ± 21.81 | 1886.62 ± 55.00 | 0.021 | NA | NA |
| Carbohydrate (g/day) | NA | 289.47 ± 3.36 | 302.19 ± 9.85 | 0.227 | NA | NA |
| Protein (g/day) | NA | 59.55 ± 0.91 | 63.72 ± 2.76 | 0.152 | NA | NA |
| Fat (g/day) | NA | 29.77 ± 0.77 | 34.49 ± 2.29 | 0.047 | NA | NA |
| Fiber (g/day) | NA | 25.95 ± 0.51 | 27.06 ± 1.22 | 0.401 | NA | NA |
| Vitamin A (μg/day) | 510 (65–74 years) 500 (≥75 years) | 309.90 ± 10.08 | 420.87 ± 104.06 | 0.294 | 702.73 ± 111.49 | <0.001 |
| Thiamine (mg/day) | 0.9 | 1.23 ± 0.02 | 1.26 ± 0.04 | 0.400 | 34.28 ± 2.56 | <0.001 |
| Riboflavin (mg/day) | 1.2 (65–74 years) 1.1 (≥75 years) | 1.27 ± 0.02 | 1.45 ± 0.07 | 0.031 | 20.21 ± 2.71 | <0.001 |
| Niacin (mg/day) | 11 (65–74 years) 10 (≥75 years) | 11.22 ± 0.20 | 12.23 ± 0.65 | 0.142 | 36.53 ± 2.80 | <0.001 |
| Vitamin C (mg/day) | 75 | 53.73 ± 2.03 | 60.44 ± 6.74 | 0.336 | 200.72 ± 18.77 | <0.001 |
| Calcium (mg/day) | 600 | 477.15 ± 11.39 | 557.31 ± 37.28 | 0.038 | 630.38 ± 39.27 | <0.001 |
| Phosphorus (mg/day) | 580 | 957.35 ± 14.40 | 1039.02 ± 41.16 | 0.065 | 1050.12 ± 41.05 | 0.036 |
| Iron (mg/day) | 7 | 11.68 ± 0.26 | 12.60 ± 0.67 | 0.200 | 14.95 ± 0.90 | <0.001 |
| Nutrients | EAR | Food-Only (n = 1179) | Food + MVMS (n = 169) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food Alone | Food Alone | p-Value * | Food Include MVMS | p-Value † | ||
| Total calories (kcal/day) | NA | 1346.96 ± 20.46 | 1342.32 ± 44.19 | 0.926 | NA | NA |
| Carbohydrate (g/day) | NA | 241.01 ± 3.63 | 227.32 ± 7.46 | 0.109 | NA | NA |
| Protein (g/day) | NA | 44.02 ± 0.87 | 46.85 ± 1.95 | 0.205 | NA | NA |
| Fat (g/day) | NA | 21.43 ± 0.70 | 25.91 ± 1.91 | 0.025 | NA | NA |
| Fiber (g/day) | NA | 21.32 ± 0.43 | 20.76 ± 1.04 | 0.624 | NA | NA |
| Vitamin A (μg/day) | 410 | 260.91 ± 14.99 | 259.96 ± 25.35 | 0.973 | 621.69 ± 62.20 | <0.001 |
| Thiamine (mg/day) | 0.8 (65–74 years) 0.7 (≥75 years) | 0.97 ± 0.02 | 0.90 ± 0.03 | 0.080 | 31.89 ± 2.40 | <0.001 |
| Riboflavin (mg/day) | 0.9 (65–74 years) 0.8 (≥75 years) | 0.95 ± 0.02 | 1.02 ± 0.05 | 0.170 | 19.44 ± 2.36 | <0.001 |
| Niacin (mg/day) | 10 (65–74 years) 9 (≥75 years) | 8.16 ± 0.17 | 8.04 ± 0.36 | 0.778 | 31.05 ± 2.25 | <0.001 |
| Vitamin C (mg/day) | 75 | 50.82 ± 2.26 | 46.96 ± 4.97 | 0.486 | 197.92 ± 13.06 | <0.001 |
| Calcium (mg/day) | 600 | 372.77 ± 8.83 | 382.28 ± 20.99 | 0.673 | 464.67 ± 25.52 | <0.001 |
| Phosphorus (mg/day) | 580 | 725.31 ± 13.06 | 753.78 ± 30.54 | 0.401 | 762.76 ± 30.45 | 0.268 |
| Iron (mg/day) | 6 (65–74 years) 5 (≥75 years) | 8.65 ± 0.17 | 8.77 ± 0.34 | 0.760 | 13.15 ± 0.92 | <0.001 |
| Nutrients | Male | Female | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food-Only | Food + MVMS | Change (%) | Food-Only | Food + MVMS | Change (%) | |
| Vitamin A | 1.0 (1.0) | 1.5 (1.1) | 0.5 | 0 | 1.4 (1.0) | 1.4 |
| Vitamin C | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Calcium | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Phosphorus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Iron | 1.0 (1.0) | 2.1 (1.5) | 1.1 | 0 | 1.2 (1.2) | 1.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.; Park, S.G. Effect of a Single Multi-Vitamin and Mineral Supplement on Nutritional Intake in Korean Elderly: Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2018–2020. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15071561
Kim H, Park SG. Effect of a Single Multi-Vitamin and Mineral Supplement on Nutritional Intake in Korean Elderly: Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2018–2020. Nutrients. 2023; 15(7):1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15071561
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hyoeun, and Seung Guk Park. 2023. "Effect of a Single Multi-Vitamin and Mineral Supplement on Nutritional Intake in Korean Elderly: Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2018–2020" Nutrients 15, no. 7: 1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15071561
APA StyleKim, H., & Park, S. G. (2023). Effect of a Single Multi-Vitamin and Mineral Supplement on Nutritional Intake in Korean Elderly: Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2018–2020. Nutrients, 15(7), 1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15071561




