Analysis of Human Milk Microbiota in Northern Greece by Comparative 16S rRNA Sequencing vs. Local Dairy Animals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Milk Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction, Library Preparation, and 16S RNA Ion Torrent Sequencing
2.3. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characteristics and 16S rRNA Sequencing Data Description
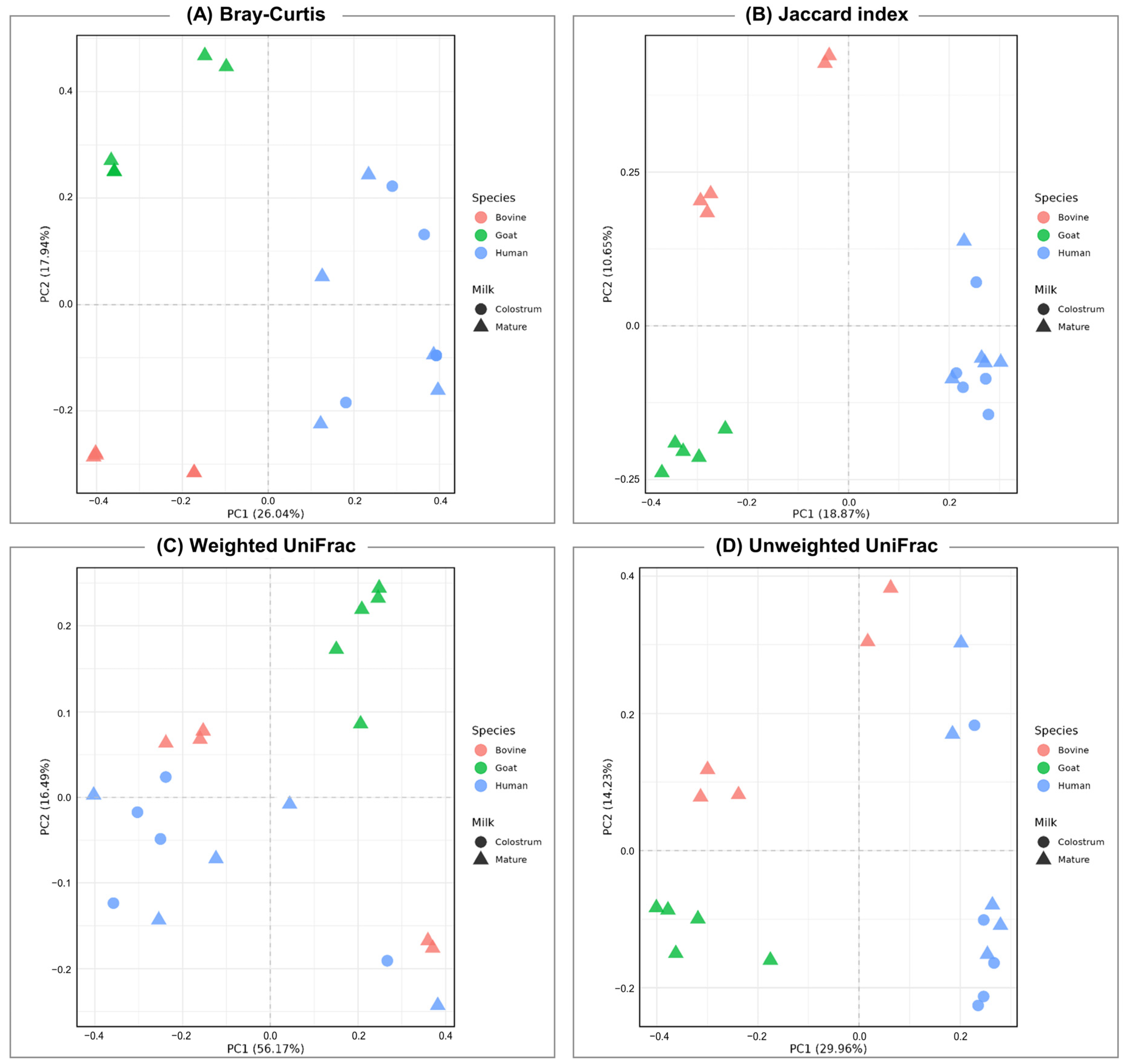
3.2. Diversity of Bacterial Communities
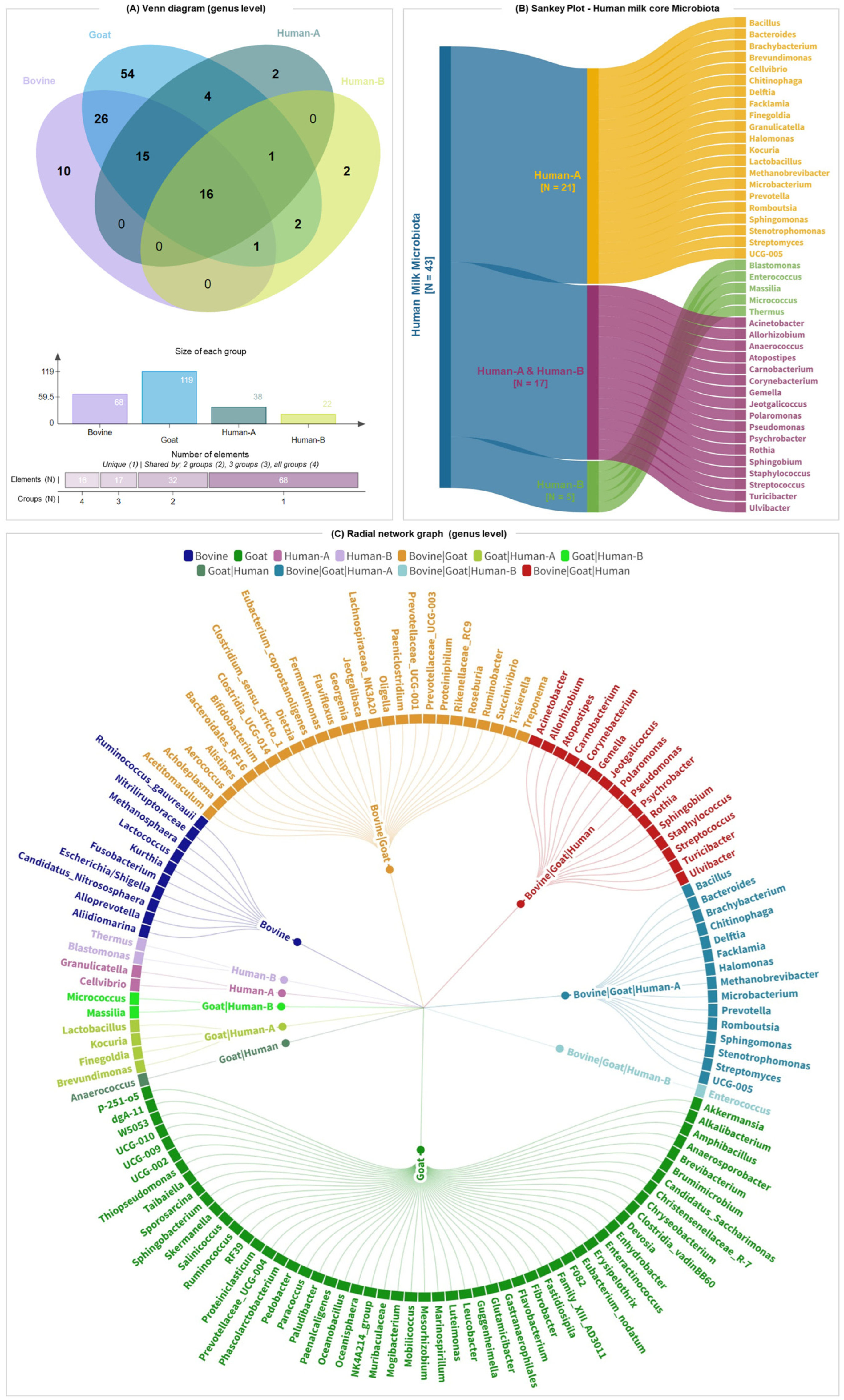
3.3. Microbial Community Composition in Milk Samples
3.4. Core Milk Microbiome of Bovine, Goat, and Human Milk
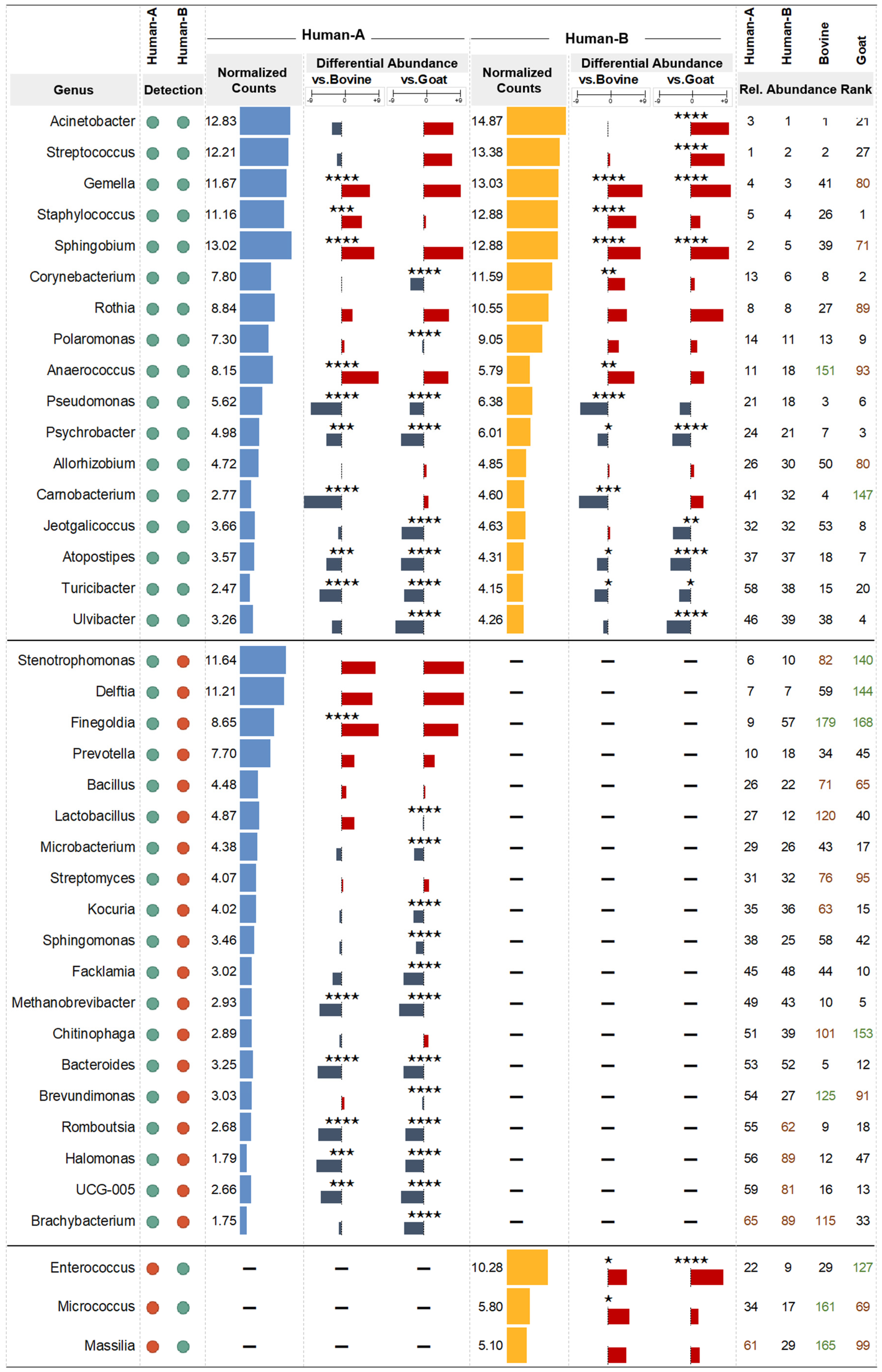
3.5. Differential Abundance Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McGuire, M.K.; McGuire, M.A. Got Bacteria? The Astounding, yet Not-so-Surprising, Microbiome of Human Milk. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 44, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreas, N.J.; Kampmann, B.; Mehring Le-Doare, K. Human Breast Milk: A Review on Its Composition and Bioactivity. Early Hum. Dev. 2015, 91, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Shen, X.; Johnson, J.S.; Spakowicz, D.J.; Agnello, M.; Zhou, W.; Avina, M.; Honkala, A.; Chleilat, F.; Chen, S.J.; et al. Longitudinal Profiling of the Microbiome at Four Body Sites Reveals Core Stability and Individualized Dynamics during Health and Disease. Cell Host Microbe 2024, 32, 506–526.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Togo, A.; Dufour, J.C.; Lagier, J.C.; Dubourg, G.; Raoult, D.; Million, M. Repertoire of Human Breast and Milk Microbiota: A Systematic Review. Future Microbiol. 2019, 14, 623–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinleyici, M.; Pérez-Brocal, V.; Arslanoglu, S.; Aydemir, O.; Sevuk Ozumut, S.; Tekin, N.; Vandenplas, Y.; Moya, A.; Dinleyici, E.C. Composition of Microbiota in Transient and Mature Human Milk: Significant Changes in Large for Gestational Age Group. Nutrients 2024, 16, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moossavi, S.; Sepehri, S.; Robertson, B.; Bode, L.; Goruk, S.; Field, C.J.; Lix, L.M.; de Souza, R.J.; Becker, A.B.; Mandhane, P.J.; et al. Composition and Variation of the Human Milk Microbiota Are Influenced by Maternal and Early-Life Factors. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 25, 324–335.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chernikova, D.A.; Koestler, D.C.; Hoen, A.G.; Housman, M.L.; Hibberd, P.L.; Moore, J.H.; Morrison, H.G.; Sogin, M.L.; Zain-Ul-Abideen, M.; Madan, J.C. Fetal Exposures and Perinatal Influences on the Stool Microbiota of Premature Infants. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016, 29, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pannaraj, P.S.; Li, F.; Cerini, C.; Bender, J.M.; Yang, S.; Rollie, A.; Adisetiyo, H.; Zabih, S.; Lincez, P.J.; Bittinger, K.; et al. Association Between Breast Milk Bacterial Communities and Establishment and Development of the Infant Gut Microbiome. JAMA Pediatr. 2017, 171, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagi, E.; Aceti, A.; Quercia, S.; Beghetti, I.; Rampelli, S.; Turroni, S.; Soverini, M.; Zambrini, A.V.; Faldella, G.; Candela, M.; et al. Microbial Community Dynamics in Mother’s Milk and Infant’s Mouth and Gut in Moderately Preterm Infants. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stinson, L.F.; Sindi, A.S.M.; Cheema, A.S.; Lai, C.T.; Mühlhaüsler, B.S.; Wlodek, M.E.; Payne, M.S.; Geddes, D.T. The Human Milk Microbiome: Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How? Nutr. Rev. 2021, 79, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogaert, D.; van Beveren, G.J.; de Koff, E.M.; Lusarreta Parga, P.; Balcazar Lopez, C.E.; Koppensteiner, L.; Clerc, M.; Hasrat, R.; Arp, K.; Chu, M.L.J.N.; et al. Mother-to-Infant Microbiota Transmission and Infant Microbiota Development across Multiple Body Sites. Cell Host Microbe 2023, 31, 447–460.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jost, T.; Lacroix, C.; Braegger, C.P.; Rochat, F.; Chassard, C. Vertical Mother-Neonate Transfer of Maternal Gut Bacteria via Breastfeeding. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 2891–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, J.M. The Origin of Human Milk Bacteria: Is There a Bacterial Entero-Mammary Pathway during Late Pregnancy and Lactation? Adv. Nutr. 2014, 5, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pärnänen, K.; Karkman, A.; Hultman, J.; Lyra, C.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Larsson, D.G.J.; Rautava, S.; Isolauri, E.; Salminen, S.; Kumar, H.; et al. Maternal Gut and Breast Milk Microbiota Affect Infant Gut Antibiotic Resistome and Mobile Genetic Elements. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodayar-Pardo, P.; Mira-Pascual, L.; Collado, M.C.; Martínez-Costa, C. Impact of Lactation Stage, Gestational Age and Mode of Delivery on Breast Milk Microbiota. J. Perinatol. 2014, 34, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, K.E.; Ryan, C.A.; Dempsey, E.M.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C. Breast Milk, a Source of Beneficial Microbes and Associated Benefits for Infant Health. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damaceno, Q.S.; Souza, J.P.; Nicoli, J.R.; Paula, R.L.; Assis, G.B.; Figueiredo, H.C.; Azevedo, V.; Martins, F.S. Evaluation of Potential Probiotics Isolated from Human Milk and Colostrum. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2017, 9, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago, L.; Toscano, M.; De Grandi, R.; Grossi, E.; Padovani, E.M.; Peroni, D.G. Microbiota Network and Mathematic Microbe Mutualism in Colostrum and Mature Milk Collected in Two Different Geographic Areas: Italy versus Burundi. ISME J. 2017, 11, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.W.; Watanabe, K.; Hsu, C.C.; Chao, S.H.; Yang, Z.H.; Lin, Y.J.; Chen, C.C.; Cao, Y.M.; Huang, H.C.; Chang, C.H.; et al. Bacterial Composition and Diversity in Breast Milk Samples from Mothers Living in Taiwan and Mainland China. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemu, B.K.; Azeze, G.G.; Wu, L.; Lau, S.L.; Wang, C.C.; Wang, Y. Effects of Maternal Probiotic Supplementation on Breast Milk Microbiome and Infant Gut Microbiome and Health: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. MFM 2023, 5, 101148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, E.; De Andrés, J.; Manrique, M.; Pareja-Tobes, P.; Tobes, R.; Martínez-Blanch, J.F.; Codoñer, F.M.; Ramón, D.; Fernández, L.; Rodríguez, J.M. Metagenomic Analysis of Milk of Healthy and Mastitis-Suffering Women. J. Hum. Lact. 2015, 31, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solís, G.; de los Reyes-Gavilan, C.G.; Fernández, N.; Margolles, A.; Gueimonde, M. Establishment and Development of Lactic Acid Bacteria and Bifidobacteria Microbiota in Breast-Milk and the Infant Gut. Anaerobe 2010, 16, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermansson, H.; Kumar, H.; Collado, M.C.; Salminen, S.; Isolauri, E.; Rautava, S. Breast Milk Microbiota Is Shaped by Mode of Delivery and Intrapartum Antibiotic Exposure. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, S.; Friedberg, I.; Ivanov, I.V.; Davidson, L.A.; Goldsby, J.S.; Dahl, D.B.; Herman, D.; Wang, M.; Donovan, S.M.; Chapkin, R.S. A Metagenomic Study of Diet-Dependent Interaction between Gut Microbiota and Host in Infants Reveals Differences in Immune Response. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, r32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billington, C.; Kingsbury, J.M.; Rivas, L. Metagenomics Approaches for Improving Food Safety: A Review. J. Food Prot. 2022, 85, 448–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, S.; Fursova, K.; Shulcheva, I.; Nikanova, D.; Artyemieva, O.; Kolodina, E.; Sorokin, A.; Dzhelyadin, T.; Shchannikova, M.; Shepelyakovskaya, A.; et al. Comparative Analysis of Milk Microbiomes and Their Association with Bovine Mastitis in Two Farms in Central Russia. Animals 2021, 11, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnis, E.A.; Kalanetra, K.M.; Mills, D.A.; Maga, E.A. Analysis of Raw Goat Milk Microbiota: Impact of Stage of Lactation and Lysozyme on Microbial Diversity. Food Microbiol. 2015, 46, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keefe, C.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Gehret, E.; Herman, C.; Jewell, M.; Wood, C.V.; Bolyen, E.; Gregory Caporaso, J. Facilitating Bioinformatics Reproducibility with QIIME 2 Provenance Replay. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2023, 19, e1011676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt Removes Adapter Sequences from High-Throughput Sequencing Reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Xiao, L.; Zuo, Z.; Zhao, F. MAMI: A Comprehensive Database of Mother–Infant Microbiome and Probiotic Resources. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D738–D746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoufos, G.; Kardaras, F.S.; Alexiou, A.; Kavakiotis, I.; Lambropoulou, A.; Kotsira, V.; Tastsoglou, S.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. Peryton: A Manual Collection of Experimentally Supported Microbe-Disease Associations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1328–D1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, L.; Langa, S.; Martín, V.; Maldonado, A.; Jiménez, E.; Martín, R.; Rodríguez, J.M. The Human Milk Microbiota: Origin and Potential Roles in Health and Disease. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 69, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, F.; Eshaghi, M.; Razavi, S.; Sarokhalil, D.D.; Talebi, M.; Pourshafie, M.R. Characterization of Bacteriocin Production in Lactobacillus Spp. Isolated from Mother’s Milk. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 118, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consales, A.; Cerasani, J.; Sorrentino, G.; Morniroli, D.; Colombo, L.; Mosca, F.; Giannì, M.L. The Hidden Universe of Human Milk Microbiome: Origin, Composition, Determinants, Role, and Future Perspectives. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2022, 181, 1811–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kordy, K.; Gaufin, T.; Mwangi, M.; Li, F.; Cerini, C.; Lee, D.J.; Adisetiyo, H.; Woodward, C.; Pannaraj, P.S.; Tobin, N.H.; et al. Contributions to Human Breast Milk Microbiome and Enteromammary Transfer of Bifidobacterium Breve. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0219633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, C.J.; Gleeson, D.; O’Toole, P.W.; Cotter, P.D. Impacts of Seasonal Housing and Teat Preparation on Raw Milk Microbiota: A High-Throughput Sequencing Study. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 83, e02694-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dombrowska-Pali, A.; Wiktorczyk-Kapischke, N.; Chrustek, A.; Olszewska-Słonina, D.; Gospodarek-Komkowska, E.; Socha, M.W. Human Milk Microbiome-A Review of Scientific Reports. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.; Curley, D.; O’callaghan, T.F.; O’shea, C.A.; Dempsey, E.M.; O’toole, P.W.; Ross, R.P.; Ryan, C.A.; Stanton, C. The Composition of Human Milk and Infant Faecal Microbiota Over the First Three Months of Life: A Pilot Study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojo-Okunola, A.; Nicol, M.; du Toit, E. Human Breast Milk Bacteriome in Health and Disease. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, M.R.; Avershina, E.; Storrø, O.; Johnsen, R.; Rudi, K.; Øien, T. Breastfeeding-Associated Microbiota in Human Milk Following Supplementation with Lactobacillus Rhamnosus GG, Lactobacillus Acidophilus La-5, and Bifidobacterium Animalis Ssp. Lactis Bb-12. J. Dairy. Sci. 2018, 101, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.H.; Vaidya, Y.H.; Patel, R.J.; Pandit, R.J.; Joshi, C.G.; Kunjadiya, A.P. Culture Independent Assessment of Human Milk Microbial Community in Lactational Mastitis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Jiang, J.; Lu, M.; Tong, W.; Zhou, R.; Li, J.; Yuan, J.; Wang, F.; Li, D. Human Milk Microbiota Development during Lactation and Its Relation to Maternal Geographic Location and Gestational Hypertensive Status. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 1438–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Weber, D.; Xu, W.; Durbin-Johnson, B.P.; Phinney, B.S.; Lönnerdal, B. Absolute Quantification of Human Milk Caseins and the Whey/Casein Ratio during the First Year of Lactation. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 4113–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudry, G.; Charton, E.; Le Huerou-Luron, I.; Ferret-Bernard, S.; Le Gall, S.; Even, S.; Blat, S. The Relationship Between Breast Milk Components and the Infant Gut Microbiota. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 629740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, M.K.; McGuire, M.A. Human Milk: Mother Nature’s Prototypical Probiotic Food? Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catlett, J.L.; Carr, S.; Cashman, M.; Smith, M.D.; Walter, M.; Sakkaff, Z.; Kelley, C.; Pierobon, M.; Cohen, M.B.; Buan, N.R. Metabolic Synergy between Human Symbionts Bacteroides and Methanobrevibacter. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e01067-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Yi, D.Y. Components of Human Breast Milk: From Macronutrient to Microbiome and MicroRNA. Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 2020, 63, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poonia, A. Shiva Bioactive Compounds, Nutritional Profile and Health Benefits of Colostrum: A Review. Food Prod. Process. Nutr. 2022, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvorov, A. What Is Wrong with Enterococcal Probiotics? Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 12, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardanzellu, F.; Fanos, V.; Reali, A. “Omics” in Human Colostrum and Mature Milk: Looking to Old Data with New Eyes. Nutrients 2017, 9, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamczyk, I.; Kaliszczak, K.; Skowron, K.; Grudlewska-Buda, K.; Twarużek, M.; Sinkiewicz-Darol, E. Microbiological Status of Donor Human Milk—A Single Center Study from Poland. Food Microbiol. 2024, 122, 104528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, R.; Petersen, F.C.; Shekhar, S. Commensal Bacteria: An Emerging Player in Defense Against Respiratory Pathogens. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baty, J.J.; Stoner, S.N.; Scoffield, J.A. Oral Commensal Streptococci: Gatekeepers of the Oral Cavity. J. Bacteriol. 2022, 204, e00257-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negari, I.P.; Keshari, S.; Huang, C.M. Probiotic Activity of Staphylococcus Epidermidis Induces Collagen Type I Production through FFaR2/p-ERK Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Liu, S.; Khan, M.Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, T.; Alugongo, G.M.; Li, S.; Cao, Z. Bovine Milk Microbiota: Key Players, Origins, and Potential Contributions to Early-Life Gut Development. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 59, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvamani, S.; Dailin, D.J.; Gupta, V.K.; Wahid, M.; Keat, H.C.; Natasya, K.H.; Malek, R.A.; Haque, S.; Sayyed, R.Z.; Abomoelak, B.; et al. An Insight into Probiotics Bio-Route: Translocation from the Mother’s Gut to the Mammary Gland. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Individual ID | Sample ID | Day of Collection | Stage of Lactation | Species | Living Area | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (A) Human Breast Milk Samples | ||||||
| H1 | H1-A | 3 | Colostrum | Human | Thrace | |
| H1 | H1-B | 30–40 | Mature | Human | Thrace | |
| H2 | H2-A | 3 | Colostrum | Human | Thrace | |
| H2 | H2-B | 30–40 | Mature | Human | Thrace | |
| H3 | H3-A | 3 | Colostrum | Human | Thrace | |
| H3 | H3-B | 30–40 | Mature | Human | Thrace | |
| H4 | H4-A | 3 | Colostrum | Human | Thrace | |
| H4 | H4-B | 30–40 | Mature | Human | Thrace | |
| H5 | H5-A | 3 | Colostrum | Human | Thrace | |
| H5 | H5-B | 30–40 | Mature | Human | Thrace | |
| (B) Animal Milk Samples | ||||||
| C1 | C1 | 50–70 | Mature | Bovine | Dairy Industry | |
| C2 | C2 | 50–70 | Mature | Bovine | Dairy Industry | |
| C3 | C3 | 50–70 | Mature | Bovine | Dairy Industry | |
| C4 | C4 | 50–70 | Mature | Bovine | Dairy Industry | |
| C5 | C5 | 50–70 | Mature | Bovine | Dairy Industry | |
| G1 | G1 | 50–70 | Mature | Goat | Dairy Industry | |
| G2 | G2 | 50–70 | Mature | Goat | Dairy Industry | |
| G3 | G3 | 50–70 | Mature | Goat | Dairy Industry | |
| G4 | G4 | 50–70 | Mature | Goat | Dairy Industry | |
| G5 | G5 | 50–70 | Mature | Goat | Dairy Industry | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsifintaris, M.; Sitmalidis, M.; Tokamani, M.; Anastasiadi, C.; Georganta, M.; Tsochantaridis, I.; Vlachakis, D.; Tsikouras, P.; Nikolettos, N.; Chrousos, G.P.; et al. Analysis of Human Milk Microbiota in Northern Greece by Comparative 16S rRNA Sequencing vs. Local Dairy Animals. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2175. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142175
Tsifintaris M, Sitmalidis M, Tokamani M, Anastasiadi C, Georganta M, Tsochantaridis I, Vlachakis D, Tsikouras P, Nikolettos N, Chrousos GP, et al. Analysis of Human Milk Microbiota in Northern Greece by Comparative 16S rRNA Sequencing vs. Local Dairy Animals. Nutrients. 2024; 16(14):2175. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142175
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsifintaris, Margaritis, Michail Sitmalidis, Maria Tokamani, Christina Anastasiadi, Maria Georganta, Ilias Tsochantaridis, Dimitrios Vlachakis, Panagiotis Tsikouras, Nikolaos Nikolettos, George P. Chrousos, and et al. 2024. "Analysis of Human Milk Microbiota in Northern Greece by Comparative 16S rRNA Sequencing vs. Local Dairy Animals" Nutrients 16, no. 14: 2175. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142175
APA StyleTsifintaris, M., Sitmalidis, M., Tokamani, M., Anastasiadi, C., Georganta, M., Tsochantaridis, I., Vlachakis, D., Tsikouras, P., Nikolettos, N., Chrousos, G. P., Sandaltzopoulos, R., & Giannakakis, A. (2024). Analysis of Human Milk Microbiota in Northern Greece by Comparative 16S rRNA Sequencing vs. Local Dairy Animals. Nutrients, 16(14), 2175. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142175











