Supplementation of Vitamin D3 and Fructooligosaccharides Downregulates Intestinal Defensins and Reduces the Species Abundance of Romboutsia ilealis in C57BL/6J Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Real-Time PCR
2.3. DNA Stool Extraction and 16s rRNA Sequencing
2.4. 16s rDNA PCR Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
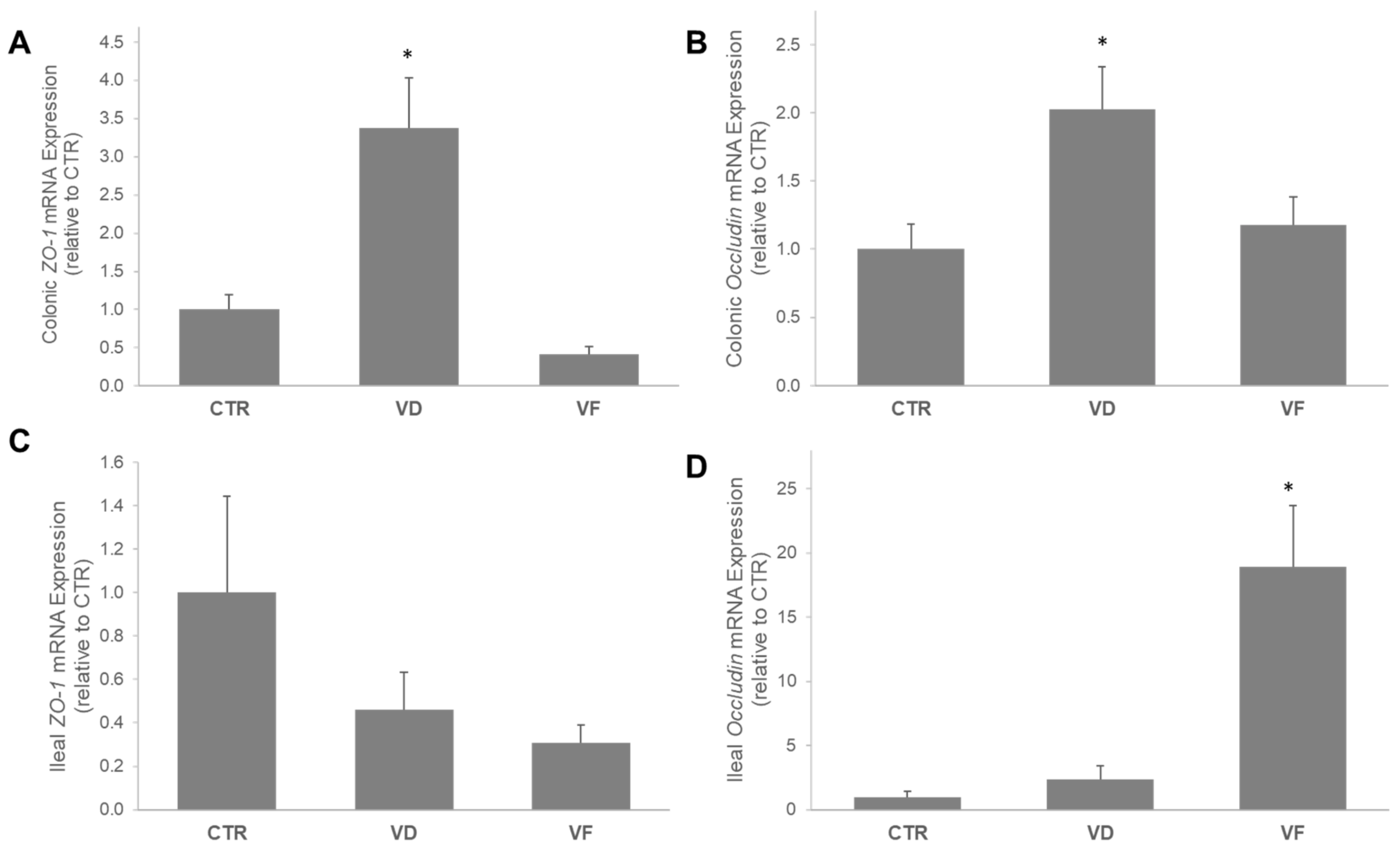
3.1. VD and VF Differentially Regulate the mRNA Expressions of Tight Junction Proteins in the Colon and Ileum
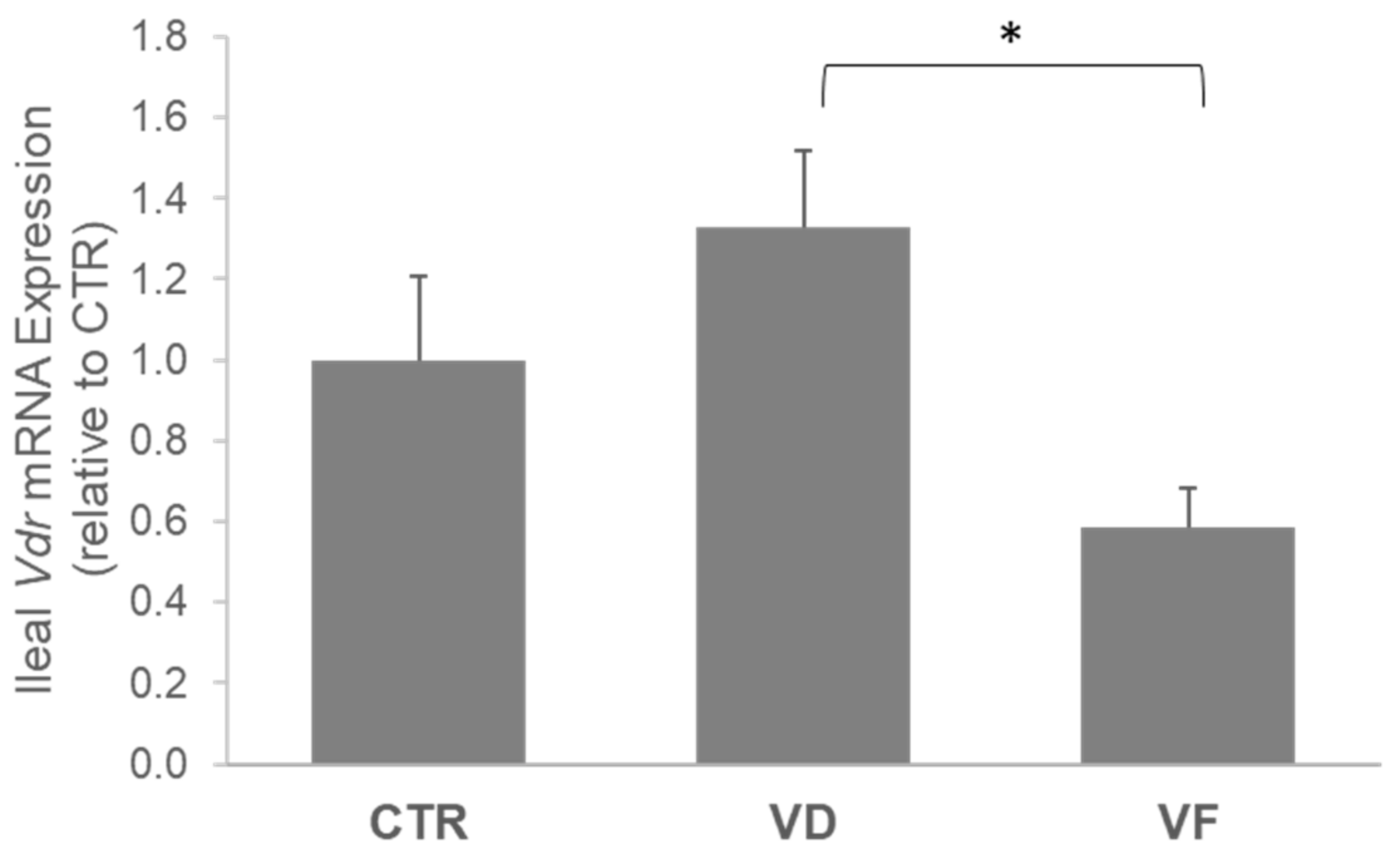
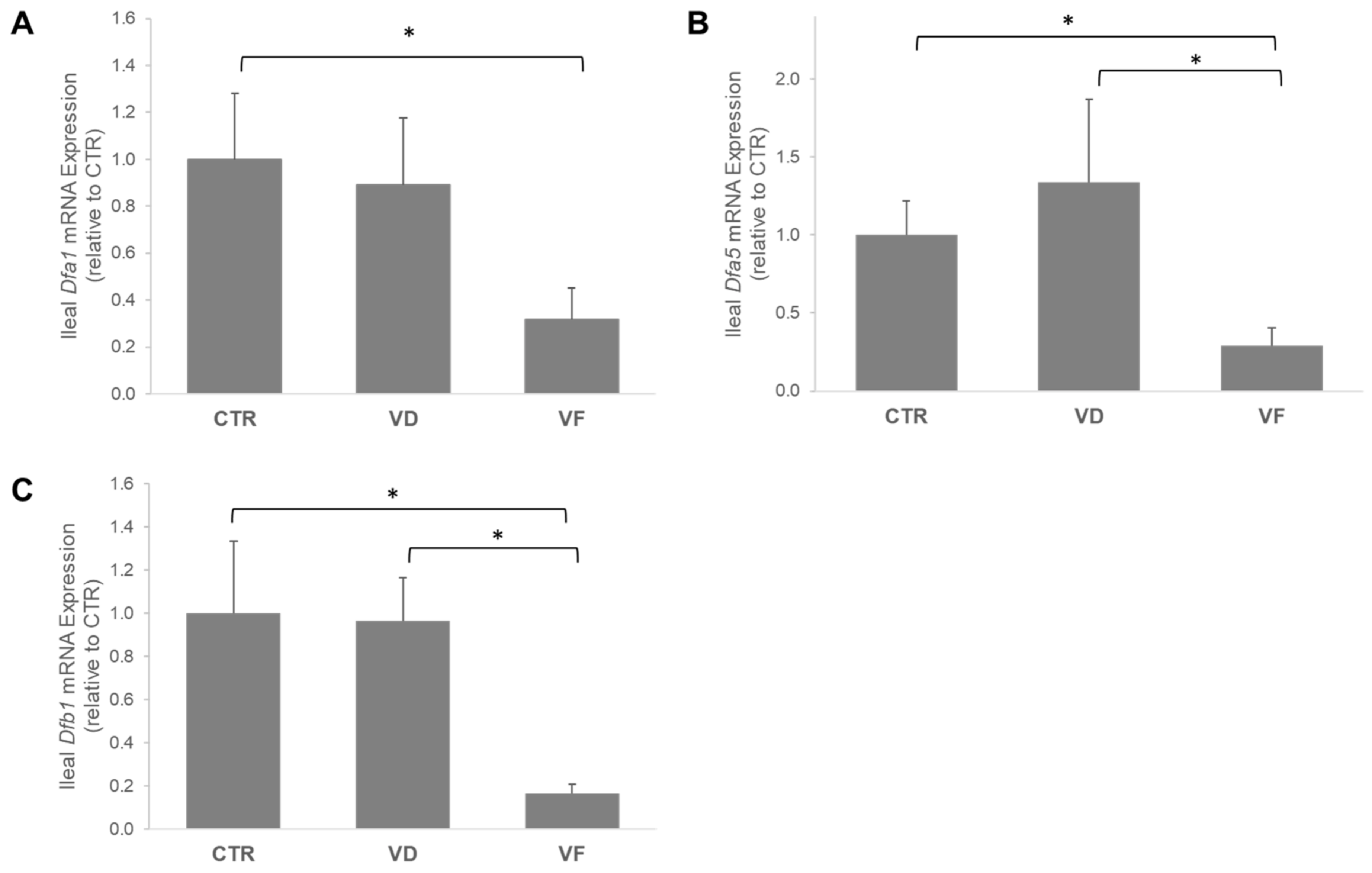
3.2. Combination of VD and FOSs Suppressed Vitamin D Signaling and Production of Defensins in the Ileum
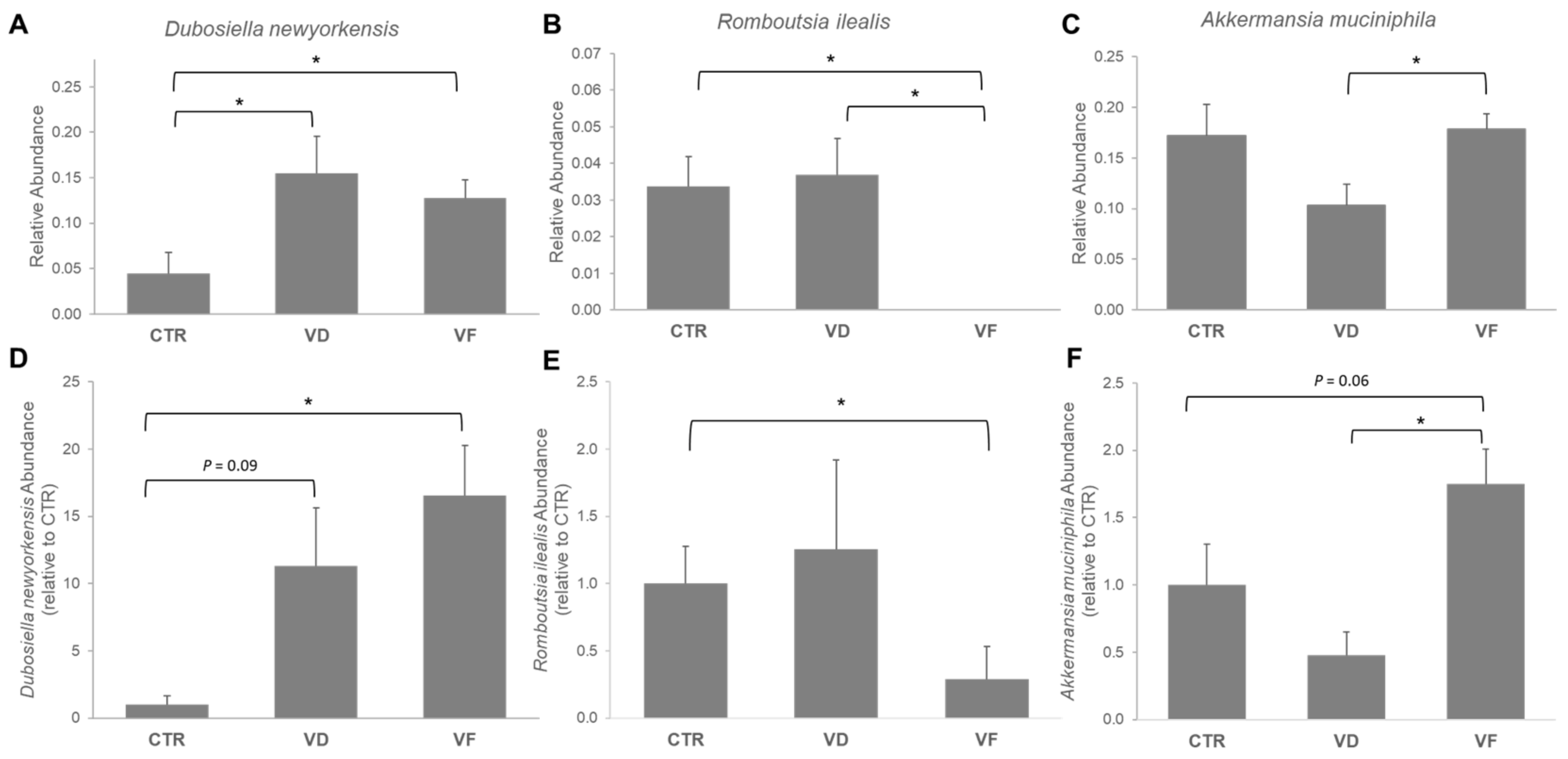
3.3. Combination of VD and FOS Shifted the Gut Microbial Diversity and Altered Selected Gut Bacteria Species in Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holick, M.F. Sunlight and vitamin D for bone health and prevention of autoimmune diseases, cancers, and cardiovascular disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 1678S–1688S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charoenngam, N.; Shirvani, A.; Kalajian, T.A.; Song, A.; Holick, M.F. The Effect of Various Doses of Oral Vitamin D(3) Supplementation on Gut Microbiota in Healthy Adults: A Randomized, Double-blinded, Dose-response Study. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Pinto, R.; Ferri, C.; Cominelli, F. Vitamin D Axis in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Role, Current Uses and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, D.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Y.G.; Lu, R.; Xia, Y.; Dong, H.; Sun, J. Lack of Vitamin D Receptor Causes Dysbiosis and Changes the Functions of the Murine Intestinal Microbiome. Clin. Ther. 2015, 37, 996–1009.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.; Nie, Y.; Zhu, A.; Chen, Z.; Wu, P.; Zhang, L.; Luo, M.; Sun, Q.; Cai, L.; Lai, Y.; et al. Vitamin D Signaling through Induction of Paneth Cell Defensins Maintains Gut Microbiota and Improves Metabolic Disorders and Hepatic Steatosis in Animal Models. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.; Silwal, P.; Kim, I.; Modlin, R.L.; Jo, E.K. Vitamin D-Cathelicidin Axis: At the Crossroads between Protective Immunity and Pathological Inflammation during Infection. Immune Netw. 2020, 20, e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, E.L.; Ismailova, A.; Dimeloe, S.; Hewison, M.; White, J.H. Vitamin D and Immune Regulation: Antibacterial, Antiviral, Anti-Inflammatory. JBMR Plus 2021, 5, e10405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrov, V.; White, J.H. Species-specific regulation of innate immunity by vitamin D signaling. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 164, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Sinnott, B.; Niu, B.; Lowry, M.B.; Fantacone, M.L.; Gombart, A.F. Synergistic induction of human cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide gene expression by vitamin D and stilbenoids. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, Y.; Kong, Q.; Mou, H.; Yi, H. Antimicrobial Peptides: Classification, Design, Application and Research Progress in Multiple Fields. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 582779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevins, C.L.; Salzman, N.H. Paneth cells, antimicrobial peptides and maintenance of intestinal homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.T.; Nestel, F.P.; Bourdeau, V.; Nagai, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liao, J.; Tavera-Mendoza, L.; Lin, R.; Hanrahan, J.W.; Mader, S.; et al. Cutting edge: 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 is a direct inducer of antimicrobial peptide gene expression. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 2909–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Yu, J.; Yuan, W.; Li, L. Vitamin D(3) eradicates Helicobacter pylori by inducing VDR-CAMP signaling. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1033201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfora, E.E.; Meex, R.C.R.; Venema, K.; Blaak, E.E. Gut microbial metabolites in obesity, NAFLD and T2DM. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, T.; Kubota, T.; Nakanishi, Y.; Tsugawa, H.; Suda, W.; Kwon, A.T.; Yazaki, J.; Ikeda, K.; Nemoto, S.; Mochizuki, Y.; et al. Gut microbial carbohydrate metabolism contributes to insulin resistance. Nature 2023, 621, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Kang, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, Q.; Tian, H.; Xue, Y.; Ren, P.; Kuang, X.; et al. Lactobacillus acidophilus ameliorates obesity in mice through modulation of gut microbiota dysbiosis and intestinal permeability. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 175, 106020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthold, R.V.; Fernandes, G.R.; Franco-de-Moraes, A.C.; Folchetti, L.G.; Ferreira, S.R. Gut microbiota interactions with the immunomodulatory role of vitamin D in normal individuals. Metabolism 2017, 69, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Rawat, A.; Alwakeel, M.; Sharif, E.; Al Khodor, S. The potential role of vitamin D supplementation as a gut microbiota modifier in healthy individuals. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, J.; Zhang, Z.; Musch, M.W.; Ning, G.; Sun, J.; Hart, J.; Bissonnette, M.; Li, Y.C. Novel role of the vitamin D receptor in maintaining the integrity of the intestinal mucosal barrier. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 294, G208–G216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J. VDR/vitamin D receptor regulates autophagic activity through ATG16L1. Autophagy 2016, 12, 1057–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Yan, J.; Zhi, C.; Zhou, Q.; Yuan, X. 1,25(OH)2D3 deficiency-induced gut microbial dysbiosis degrades the colonic mucus barrier in Cyp27b1 knockout mouse model. Gut Pathog. 2019, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.G. Vitamin D Receptor Influences Intestinal Barriers in Health and Disease. Cells 2022, 11, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokhale, S.; Bhaduri, A. Provitamin D3 modulation through prebiotics supplementation: Simulation based assessment. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabater-Molina, M.; Larque, E.; Torrella, F.; Zamora, S. Dietary fructooligosaccharides and potential benefits on health. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 65, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.W.; Cephas, K.D.; Holscher, H.D.; Kerr, K.R.; Mangian, H.F.; Tappenden, K.A.; Swanson, K.S. Nondigestible Fructans Alter Gastrointestinal Barrier Function, Gene Expression, Histomorphology, and the Microbiota Profiles of Diet-Induced Obese C57BL/6J Mice. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, K.; Ichimura, M.; Tsuneyama, K.; Moritoki, Y.; Tsunashima, H.; Omagari, K.; Hara, M.; Yasuda, I.; Miyakawa, H.; Kikuchi, K. Fructo-oligosaccharides and intestinal barrier function in a methionine-choline-deficient mouse model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renteria, K.M.; Constantine, E.; Teoh, C.M.; Cooper, A.; Lozano, N.; Bauer, S.; Koh, G.Y. Combination of vitamin D(3) and fructooligosaccharides upregulates colonic vitamin D receptor in C57BL/6J mice and affects anxiety-related behavior in a sex-specific manner. Nutr. Res. 2024, 125, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Yan, J.; Bak, J.; Park, J.; Lee, H.; Kim, H. Sargassum thunbergii Extract Attenuates High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice by Modulating AMPK Activation and the Gut Microbiota. Foods 2022, 11, 2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaishnava, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Severson, K.M.; Ruhn, K.A.; Yu, X.; Koren, O.; Ley, R.; Wakeland, E.K.; Hooper, L.V. The antibacterial lectin RegIIIgamma promotes the spatial segregation of microbiota and host in the intestine. Science 2011, 334, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, V.K.; Aggarwal, M. Factors influencing the absorption of vitamin D in GIT: An overview. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 3753–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, Y.G.; Lu, R.; Xia, Y.; Zhou, D.; Petrof, E.O.; Claud, E.C.; Chen, D.; Chang, E.B.; Carmeliet, G.; et al. Intestinal epithelial vitamin D receptor deletion leads to defective autophagy in colitis. Gut 2015, 64, 1082–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, C.; Schroder, O.; Zahn, N.; Gaschott, T.; Steinhilber, D.; Stein, J.M. The TGFbeta/Smad 3-signaling pathway is involved in butyrate-mediated vitamin D receptor (VDR)-expression. J. Cell Biochem. 2007, 102, 1420–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Torres, M.; Guzmán, C.; Petrov, P.D.; Jover, R. Valproate and Short-Chain Fatty Acids Activate Transcription of the Human Vitamin D Receptor Gene through a Proximal GC-Rich DNA Region Containing Two Putative Sp1 Binding Sites. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, G.R.; Spector, S.A. Toll-like receptor 8 ligands activate a vitamin D mediated autophagic response that inhibits human immunodeficiency virus type 1. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1003017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongkrasant, P.; Pongkorpsakol, P.; Ariyadamrongkwan, J.; Meesomboon, R.; Satitsri, S.; Pichyangkura, R.; Barrett, K.E.; Muanprasat, C. A prebiotic fructo-oligosaccharide promotes tight junction assembly in intestinal epithelial cells via an AMPK-dependent pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Bruggencate, S.J.; Bovee-Oudenhoven, I.M.; Lettink-Wissink, M.L.; Katan, M.B.; van der Meer, R. Dietary fructooligosaccharides affect intestinal barrier function in healthy men. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, K. Long-term oral administration of burdock fructooligosaccharide alleviates DSS-induced colitis in mice by mediating anti-inflammatory effects and protection of intestinal barrier function. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2023, 11, e1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geesala, R.; Recharla, N.; Zhang, K.; Johnson, J.C.; Golovko, G.; Khanipov, K.; Brining, D.L.; Shi, X.-Z. Exclusive Enteral Nutrition Beneficially Modulates Gut Microbiome in a Preclinical Model of Crohn’s-like Colitis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Daza, M.C.; Roquim, M.; Dudonné, S.; Pilon, G.; Levy, E.; Marette, A.; Roy, D.; Desjardins, Y. Berry Polyphenols and Fibers Modulate Distinct Microbial Metabolic Functions and Gut Microbiota Enterotype-Like Clustering in Obese Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tu, S.; Ji, X.; Wu, J.; Meng, J.; Gao, J.; Shao, X.; Shi, S.; Wang, G.; Qiu, J.; et al. Dubosiella newyorkensis modulates immune tolerance in colitis via the L-lysine-activated AhR-IDO1-Kyn pathway. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiantera, V.; Laganà, A.S.; Basciani, S.; Nordio, M.; Bizzarri, M. A Critical Perspective on the Supplementation of Akkermansia muciniphila: Benefits and Harms. Life 2023, 13, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, R.R.; Gurung, M.; Li, Z.; García-Jaramillo, M.; Greer, R.; Gaulke, C.; Bauchinger, F.; You, H.; Pederson, J.W.; Vasquez-Perez, S.; et al. Transkingdom interactions between Lactobacilli and hepatic mitochondria attenuate western diet-induced diabetes. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morissette, A.; André, D.M.; Agrinier, A.L.; Varin, T.V.; Pilon, G.; Flamand, N.; Houde, V.P.; Marette, A. The metabolic benefits of substituting sucrose for maple syrup are associated with a shift in carbohydrate digestion and gut microbiota composition in high-fat high-sucrose diet-fed mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 325, E661–E671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.H.; Li, Y.X.; Xu, Y.C.; Wang, N.N.; Yan, Q.J.; Jiang, Z.Q. Tamarind Xyloglucan Oligosaccharides Attenuate Metabolic Disorders via the Gut-Liver Axis in Mice with High-Fat-Diet-Induced Obesity. Foods 2023, 12, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
 , control; VD
, control; VD  , vitamin D3; VF
, vitamin D3; VF  , vitamin D3 + fructooligosaccharides. ◆, Mean of Chao 1 index.
, vitamin D3 + fructooligosaccharides. ◆, Mean of Chao 1 index.
 , control; VD
, control; VD  , vitamin D3; VF
, vitamin D3; VF  , vitamin D3 + fructooligosaccharides. ◆, Mean of Chao 1 index.
, vitamin D3 + fructooligosaccharides. ◆, Mean of Chao 1 index.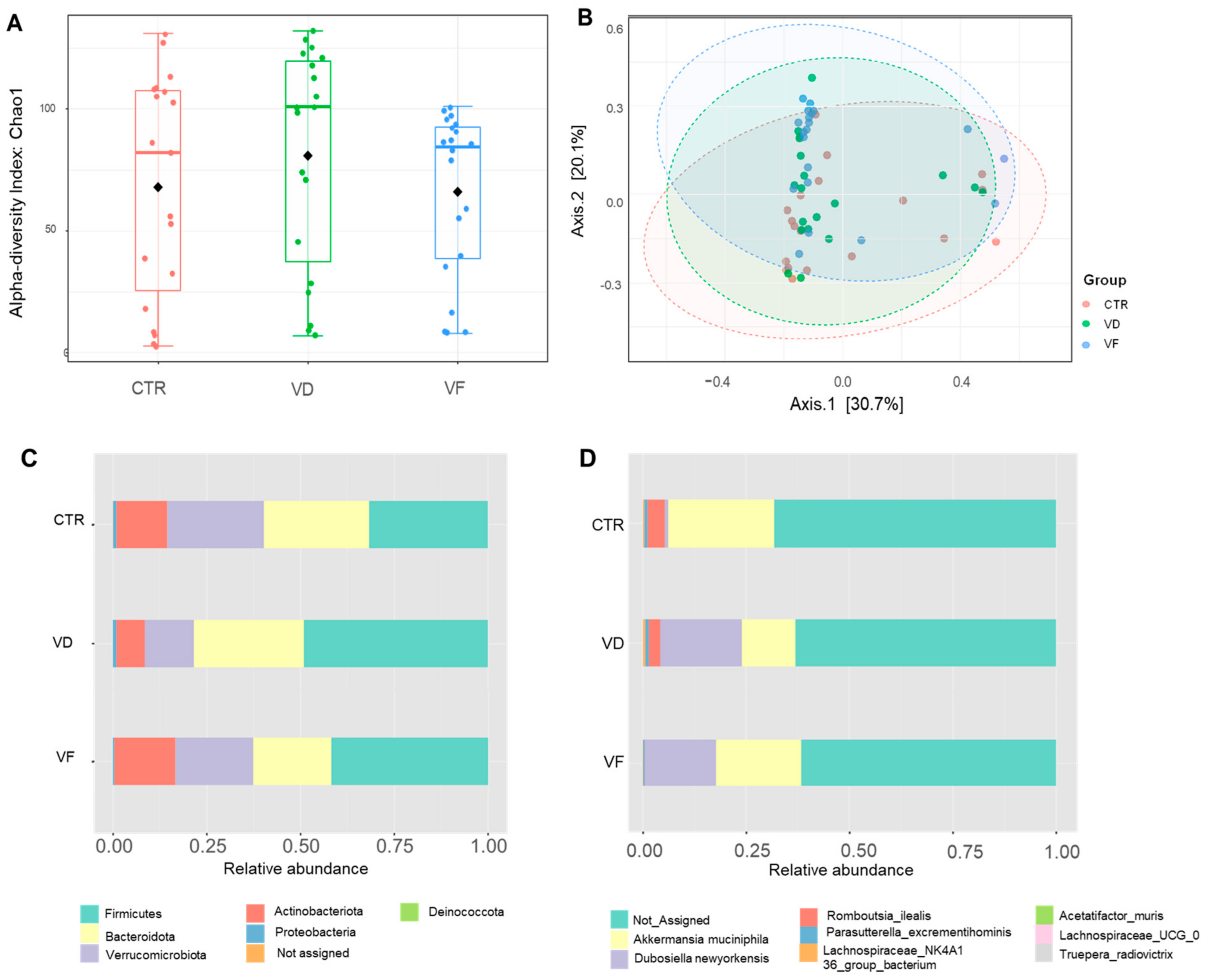
| Primer | Forward (5′–3′) | Reverse (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Gapdh | GGAGAAACCTGCCAAGTA | AAGAGTGGGAGTTGCTGTTG |
| Vdr | ATGGAGGCAATGGCAGCCAGCACCTC | GAAACCCTTGCAGCCTTCACAGGTCA |
| ZO-1 | GCC GCT AAG AGC ACA GCA A | GCC CTC CTT TTA ACA CAT CAG A |
| Occludin | GTG AAT GGG TCA CCG AGG G | AGA TAA GCG AAC CTG CCG AG |
| Dfa1 | GGCTCCTGCTCACCAATTCT | GCCTCAGAGCTGATGGTTGT |
| Dfa5 | GCTCCTGCTCAACAATTCTCC | CAGCTGCAGCAGAATACGA |
| Dfb1 | ACACCCCATCTGCAACCTTA | TGTCCAAGTCCCAACACAGA |
| Akkermansia muciniphila [5] | CAGCACGTGAAGGTGGGGAC | CCTTGCGGTTGGCTTCAGAT |
| Dubosiella newyorkensis | CGAGGAAGGTCTTCGGATCG | AGGACTCACTGCGTTGACTG |
| Romboutsia ilealis [28] | GGGGCTAGCGTTATTCCGAA | CACCTGTCACTTCTGTCCCC |
| Eubacteria (Universal) [29] | ACT CCT ACG GGA GGC AGC AGT | ATT ACC GCG GCT GCT GGC |
| Ileal mRNA Expressions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| DFa5 | DFa1 | DFb1 | |
| Pearson’s correlation coefficient (r) with ileal VDR | 0.561 | 0.519 | −0.028 |
| p-value | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.87 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hanson, T.; Constantine, E.; Nobles, Z.; Butler, E.; Renteria, K.M.; Teoh, C.M.; Koh, G.Y. Supplementation of Vitamin D3 and Fructooligosaccharides Downregulates Intestinal Defensins and Reduces the Species Abundance of Romboutsia ilealis in C57BL/6J Mice. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2236. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142236
Hanson T, Constantine E, Nobles Z, Butler E, Renteria KM, Teoh CM, Koh GY. Supplementation of Vitamin D3 and Fructooligosaccharides Downregulates Intestinal Defensins and Reduces the Species Abundance of Romboutsia ilealis in C57BL/6J Mice. Nutrients. 2024; 16(14):2236. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142236
Chicago/Turabian StyleHanson, Tyler, Ethan Constantine, Zack Nobles, Emily Butler, Karisa M. Renteria, Chin May Teoh, and Gar Yee Koh. 2024. "Supplementation of Vitamin D3 and Fructooligosaccharides Downregulates Intestinal Defensins and Reduces the Species Abundance of Romboutsia ilealis in C57BL/6J Mice" Nutrients 16, no. 14: 2236. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142236
APA StyleHanson, T., Constantine, E., Nobles, Z., Butler, E., Renteria, K. M., Teoh, C. M., & Koh, G. Y. (2024). Supplementation of Vitamin D3 and Fructooligosaccharides Downregulates Intestinal Defensins and Reduces the Species Abundance of Romboutsia ilealis in C57BL/6J Mice. Nutrients, 16(14), 2236. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142236







