Advances in the Synthesis and Physiological Metabolic Regulation of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide
Abstract
1. Introduction
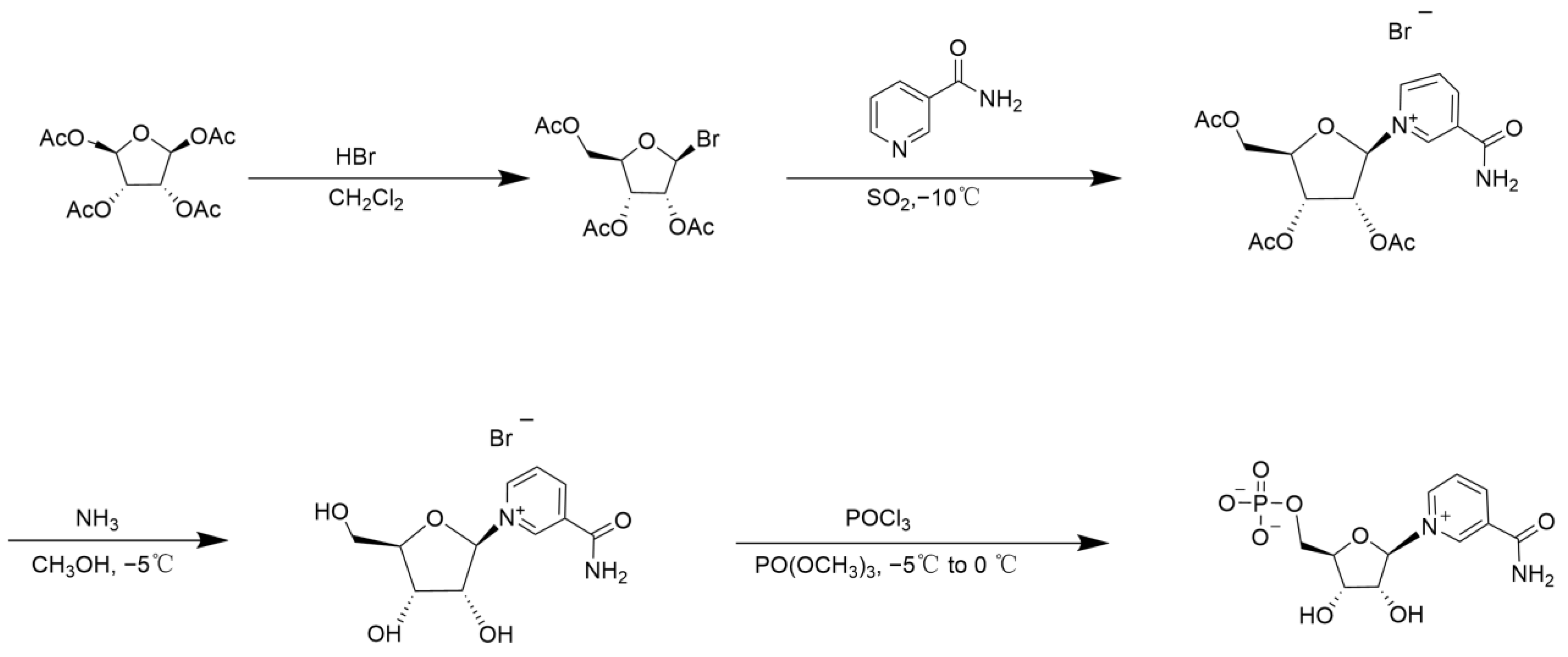
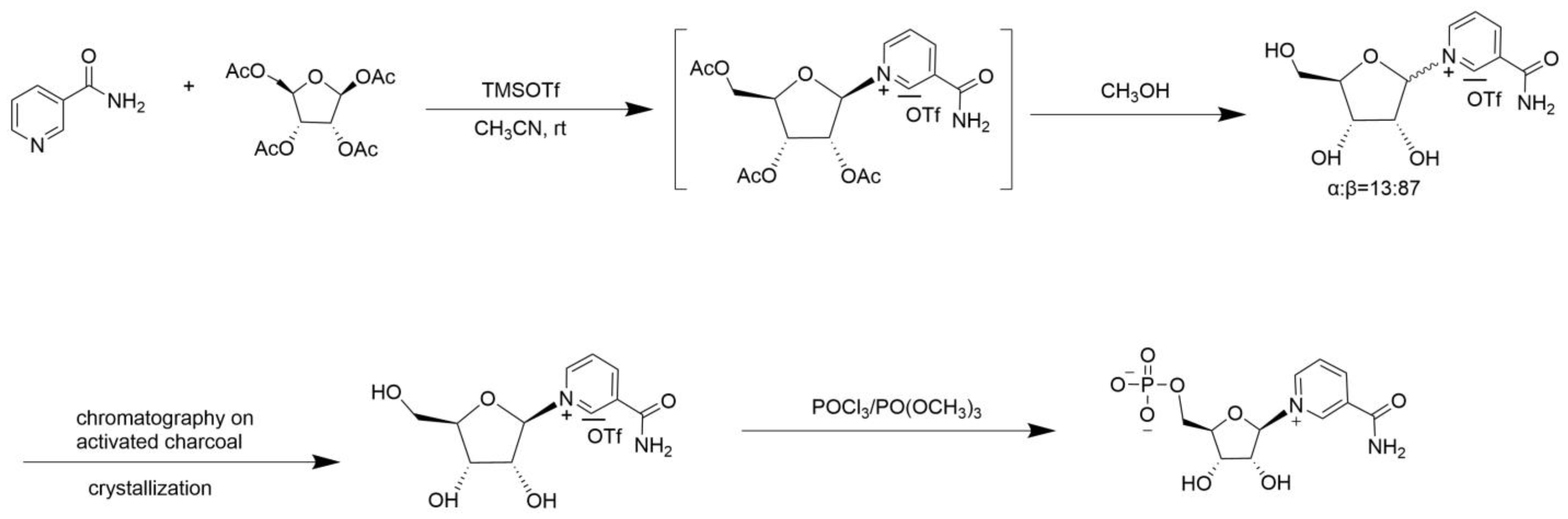
2. Chemical Catalytic Synthesis of NMN
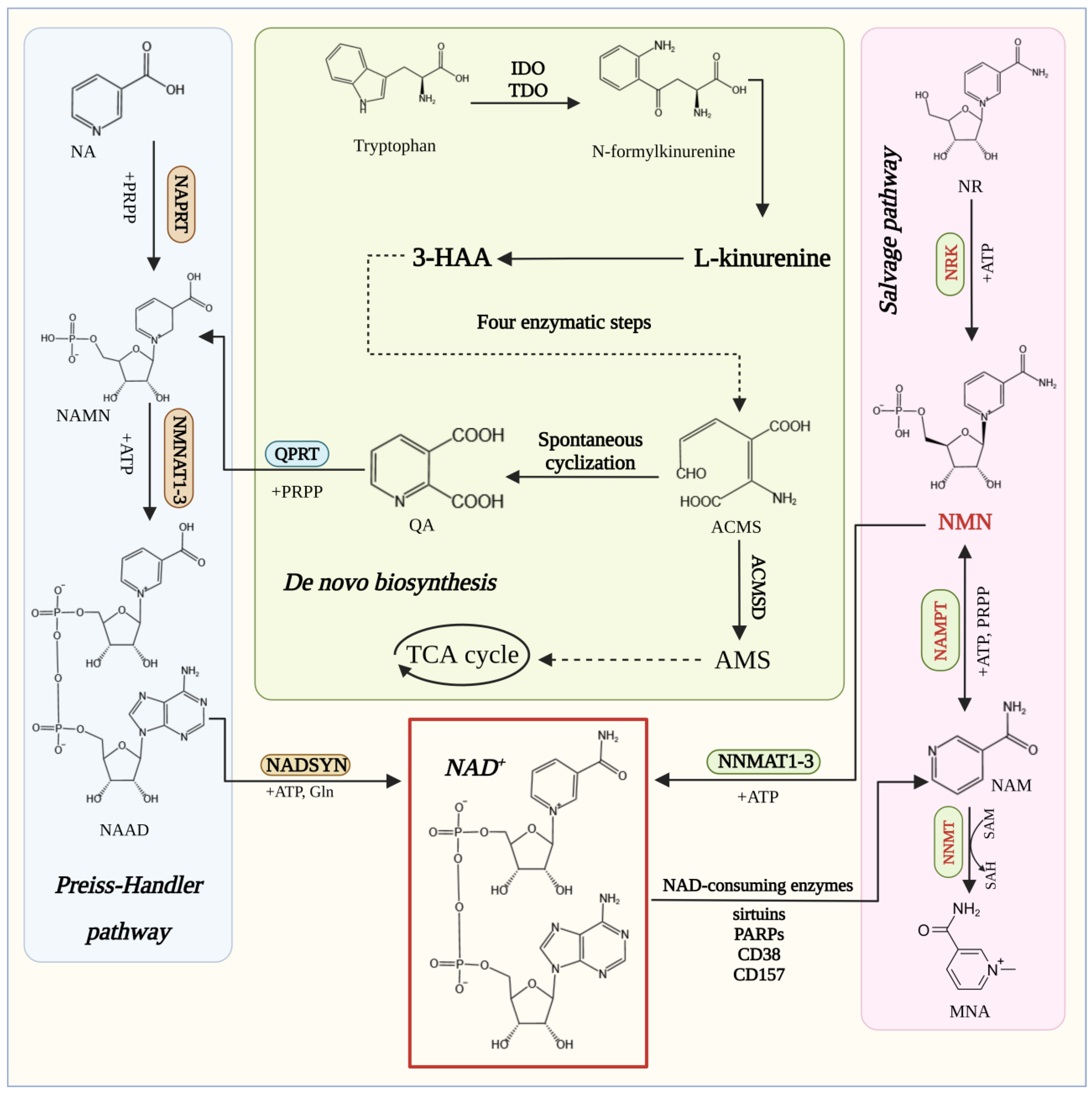
3. Biosynthesis of NMN
3.1. Enzymes Catalyzing the Synthesis of NMN
3.2. Metabolic Engineering for NMN Synthesis
3.2.1. Metabolic Engineering of the NAMPT Pathway
3.2.2. Metabolic Engineering of the NRK Pathway
3.3. Protein Engineering of NMN Synthase
3.4. Selection of NMN Synthesis Hosts
3.5. ATP Regeneration Systems
4. NMN Regulates Physiological Metabolism
4.1. Anti-Aging
4.2. Treatment of Metabolic Diseases
4.3. Regulation of Immune Cell Function
4.4. Effects on Neurodegeneration
4.5. Other Diseases
5. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
References
- Guan, Y.; Wang, S.R.; Huang, X.Z.; Xie, Q.H.; Xu, Y.Y.; Shang, D.; Hao, C.M. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide, an NAD(+) Precursor, Rescues Age-Associated Susceptibility to AKI in a Sirtuin 1-Dependent Manner. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 2337–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.X.; Zhou, C.R.; Huang, J.Z.; Tao, Y.; Ke, C.R.; Yang, X.W. Advances in physiological activities and synthesis of β-nicotinamide mononucleotide. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2023, 39, 516–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formentini, L.; Moroni, F.; Chiarugi, A. Detection and Pharmacological Modulation of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) in Vitro and in Vivo. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 77, 1612–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, S.; Alexander, N.; Vlachakis, N.D.; Maronde, R.F. Role of Conjugation and Red Blood Cells for Inactivation of Circulating Normetanephrine. Am. J. Physiol. 1984, 247, R208–R211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Mo, F.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, M.; Wei, X. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide: A Promising Molecule for Therapy of Diverse Diseases by Targeting NAD+ Metabolism. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poltronieri, P.; Mezzolla, V.; Farooqi, A.A.; Di Girolamo, M. NAD Precursors, Mitochondria Targeting Compounds and ADP-Ribosylation Inhibitors in Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases and Cancer. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 8453–8479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, J.; Baur, J.A.; Imai, S. NAD+ Intermediates: The Biology and Therapeutic Potential of NMN and NR. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, J.; Mills, K.F.; Yoon, M.J.; Imai, S. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide, a Key NAD+ Intermediate, Treats the Pathophysiology of Diet- and Age-Induced Diabetes in Mice. Cell Metab. 2011, 14, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.F.; Yoshida, S.; Stein, L.R.; Grozio, A.; Kubota, S.; Sasaki, Y.; Redpath, P.; Migaud, M.E.; Apte, R.S.; Uchida, K.; et al. Long-Term Administration of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Mitigates Age-Associated Physiological Decline in Mice. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belenky, P.; Bogan, K.L.; Brenner, C. NAD+ Metabolism in Health and Disease. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2007, 32, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Feng, J.; Wang, J.; Hao, N.; Wang, X.; Chen, K. Design of an in Vitro Multienzyme Cascade System for the Biosynthesis of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2022, 12, 1080–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Li, N.; Yu, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, J. Systematic Engineering of Escherichia Coli for Efficient Production of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide from Nicotinamide. ACS Synth. Biol. 2022, 11, 2979–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houry, D.; Raasakka, A.; Ferrario, E.; Niere, M.; Bifulco, E.; Kursula, P.; Ziegler, M. Identification of Structural Determinants of Nicotinamide Phosphoribosyl Transferase (NAMPT) Activity and Substrate Selectivity. J. Struct. Biol. 2023, 215, 108004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos, E.S. NAMPT in Regulated NAD Biosynthesis and Its Pivotal Role in Human Metabolism. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 1947–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Martin, N.I.; van Haren, M.J. Nicotinamide N-Methyl Transferase (NNMT): An Emerging Therapeutic Target. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 2699–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campagna, R.; Vignini, A. NAD+ Homeostasis and NAD+-Consuming Enzymes: Implications for Vascular Health. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zapata-Perez, R.; Tammaro, A.; Schomakers, B.V.; Scantlebery, A.M.L.; Denis, S.; Elfrink, H.L.; Giroud-Gerbetant, J.; Canto, C.; Lopez-Leonardo, C.; McIntyre, R.L.; et al. Reduced Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Is a New and Potent NAD(+) Precursor in Mammalian Cells and Mice. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, T.; Nyul-Toth, A.; Balasubramanian, P.; Tarantini, S.; Ahire, C.; Yabluchanskiy, A.; Csipo, T.; Farkas, E.; Wren, J.D.; Garman, L.; et al. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) Supplementation Promotes Neurovascular Rejuvenation in Aged Mice: Transcriptional Footprint of SIRT1 Activation, Mitochondrial Protection, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Apoptotic Effects. Geroscience 2020, 42, 527–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantini, S.; Valcarcel-Ares, M.N.; Toth, P.; Yabluchanskiy, A.; Tucsek, Z.; Kiss, T.; Hertelendy, P.; Kinter, M.; Ballabh, P.; Sule, Z.; et al. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) Supplementation Rescues Cerebromicrovascular Endothelial Function and Neurovascular Coupling Responses and Improves Cognitive Function in Aged Mice. Redox Biol. 2019, 24, 101192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailopulo, I.A.; Pricota, T.I.; Timoshchuk, V.A.; Akhrem, A.A. Synthesis of Glycosides of Nicotinamide and Nicotinamide Mononucleotide. Synthesis 1981, 1981, 388–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Churchil, H.; Choi, W.-B.; Lynch, J.E.; Roberts, F.E.; Volante, R.P.; Reider, P.J. A Chemical Synthesis of Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD + ). Chem. Commun. 1999, 729–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanimori, S.; Ohta, T.; Kirihata, M. An Efficient Chemical Synthesis of Nicotinamide Riboside (NAR) and Analogues. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2002, 12, 1135–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franchetti, P.; Pasqualini, M.; Petrelli, R.; Ricciutelli, M.; Vita, P.; Cappellacci, L. Stereoselective Synthesis of Nicotinamide β-Riboside and Nucleoside Analogs. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 4655–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeck, R.; Woenckhaus, C. [9] Simple Methods for Preparing Nicotinamide Mononucleotide and Related Analogs. In Methods in Enzymology; Vitamins and Coenzymes Part E; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1980; Volume 66, pp. 62–70. [Google Scholar]
- Walt, D.R.; Findeis, M.A.; Rios-Mercadillo, V.M.; Auge, J.; Whitesides, G.M. An Efficient Chemical and Enzymic Synthesis of Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984, 106, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walt, D.R.; Rios-Mercadillo, V.M.; Auge, J.; Whitesides, G.M. Synthesis of Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD) from Adenosine Monophosphate (AMP). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 7805–7806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.; Zhang, L.; Gao, W.; Huang, C.; Huber, P.E.; Zhou, X.; Li, C.; Shen, G.; Zou, B. NAD+ Metabolism: Pathophysiologic Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. Signal Transduct. Targeted Ther. 2020, 5, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revollo, J.R.; Grimm, A.A.; Imai, S. The Regulation of Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Biosynthesis by Nampt/PBEF/Visfatin in Mammals. Curr. Opin. Gastroen. 2007, 23, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinescu, G.C.; Popescu, R.-G.; Stoian, G.; Dinischiotu, A. β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) Production in Escherichia Coli. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoji, S.; Yamaji, T.; Makino, H.; Ishii, J.; Kondo, A. Metabolic Design for Selective Production of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide from Glucose and Nicotinamide. Metab. Eng. 2021, 65, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, S.; Szumlanski, C.L.; Weinshilboum, R.M. Human Liver Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase. cDNA Cloning, Expression, and Biochemical Characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 14835–14840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loring, H.S.; Thompson, P.R. Kinetic Mechanism of Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 5524–5532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neelakantan, H.; Vance, V.; Wetzel, M.D.; Wang, H.-Y.L.; McHardy, S.F.; Finnerty, C.C.; Hommel, J.D.; Watowich, S.J. Selective and Membrane-Permeable Small Molecule Inhibitors of Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase Reverse High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 147, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pissios, P. Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase: More than a Vitamin B3 Clearance Enzyme. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 340–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberti, A.; Fernández, A.F.; Fraga, M.F. Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase: At the Crossroads between Cellular Metabolism and Epigenetic Regulation. Mol. Metab. 2021, 45, 101165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-Y.; Pi, Y.-N.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Xia, B.-R. Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase: A Promising Biomarker and Target for Human Cancer Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 894744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Yang, C.; Wang, T.; Deng, H. Complex Roles of Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase in Cancer Progression. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.-D.; Zhu, X.-J.; Li, J.-J.; Mei, Y.-Z.; Li, W.-S.; Li, J.-H. Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase (NNMT): A Novel Therapeutic Target for Metabolic Syndrome. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1410479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmeisser, K.; Parker, J.A. Nicotinamide-N-Methyltransferase Controls Behavior, Neurodegeneration and Lifespan by Regulating Neuronal Autophagy. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; van Haren, M.J.; Buijs, N.; Innocenti, P.; Zhang, Y.; Sartini, D.; Campagna, R.; Emanuelli, M.; Parsons, R.B.; Jespers, W.; et al. Potent Inhibition of Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase by Alkene-Linked Bisubstrate Mimics Bearing Electron Deficient Aromatics. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 12938–12963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; van Haren, M.J.; Moret, E.E.; Rood, J.J.M.; Sartini, D.; Salvucci, A.; Emanuelli, M.; Craveur, P.; Babault, N.; Jin, J.; et al. Bisubstrate Inhibitors of Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase (NNMT) with Enhanced Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 6597–6614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyamu, I.D.; Vilseck, J.Z.; Yadav, R.; Noinaj, N.; Huang, R. Exploring Unconventional SAM Analogues to Build Cell-Potent Bisubstrate Inhibitors for Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202114813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyamu, I.D.; Zhao, T.; Huang, R. Structure–Activity Relationship Studies on Cell-Potent Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase Bisubstrate Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 10510–10527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Haren, M.J.; Gao, Y.; Buijs, N.; Campagna, R.; Sartini, D.; Emanuelli, M.; Mateuszuk, L.; Kij, A.; Chlopicki, S.; Escudé Martinez de Castilla, P.; et al. Esterase-Sensitive Prodrugs of a Potent Bisubstrate Inhibitor of Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase (NNMT) Display Cellular Activity. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Haren, M.J.; Zhang, Y.; Thijssen, V.; Buijs, N.; Gao, Y.; Mateuszuk, L.; Fedak, F.A.; Kij, A.; Campagna, R.; Sartini, D.; et al. Macrocyclic Peptides as Allosteric Inhibitors of Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase (NNMT). RSC Chem. Biol. 2021, 2, 1546–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyamu, I.D.; Huang, R. Mechanisms and Inhibitors of Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase. RSC Med. Chem. 2021, 12, 1254–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.H.; Fu, M.J.; Liang, X.L. A Method of Enzymatic Preparation β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide. CN106755209A, 29 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, X.-L.; Dai, Y.-S.; Li, C.-X.; Pan, J.; Xu, J.-H.; Mu, B. Enzymatic Synthesis of High-Titer Nicotinamide Mononucleotide with a New Nicotinamide Riboside Kinase and an Efficient ATP Regeneration System. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2022, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.A.; Xiang, S.; Tong, L. Crystal Structure of Human Nicotinamide Riboside Kinase. Structure 2007, 15, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajczak, J.; Joffraud, M.; Trammell, S.A.J.; Ras, R.; Canela, N.; Boutant, M.; Kulkarni, S.S.; Rodrigues, M.; Redpath, P.; Migaud, M.E.; et al. NRK1 Controls Nicotinamide Mononucleotide and Nicotinamide Riboside Metabolism in Mammalian Cells. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Wu, X.-H.; Li, H.; Li, K.-X.; Guo, Q.; Shen, Q.; Xue, Y.-P.; Zheng, Y.-G. Streamlining Design, Engineering, and Applications of Nicotinamide Riboside Kinase for Sustainable Biosynthesis of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide in Flow. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 15218–15227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Tsai, A.; Dattmore, D.A.; Stives, D.P.; Chitrakar, I.; D’alessandro, A.M.; Patil, S.; Hicks, K.A.; French, J.B. Crystal Structure of E. coli PRPP Synthetase. BMC Struct. Biol. 2019, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharjan, A.; Singhvi, M.; Kim, B.S. Biosynthesis of a Therapeutically Important Nicotinamide Mononucleotide through a Phosphoribosyl Pyrophosphate Synthetase 1 and 2 Engineered Strain of Escherichia Coli. ACS Synth. Biol. 2021, 10, 3055–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, W.B.; Aspacio, D.; Bever, D.; King, E.; Zhang, L.; Li, H. Metabolic Engineering of Escherichia Coli for Optimized Biosynthesis of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide, a Noncanonical Redox Cofactor. Microb. Cell Fact. 2020, 19, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, W.; Jiang, N.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Chen, K.; Wang, X. Synthesis of NMN by Cascade Catalysis of Intracellular Multiple Enzymes. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 28131–28138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yasawong, M.; Yu, B. Metabolic Engineering of Escherichia Coli for Biosynthesis of β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide from Nicotinamide. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 2581–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.E.; Sinclair, D.A. The Elusive NMN Transporter Is Found. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 8–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasiak, K.; Saunders, P.P. Purification and Properties of a Human Nicotinamide Ribonucleoside Kinase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1996, 333, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.-J.; Liu, X.-X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shi, H.-L.; Kan, Y.-C.; Yao, L.-G.; Tang, C.-D. High Level Expression of Nicotinamide Nucleoside Kinase from Saccharomyces Cerevisiae and Its Purification and Immobilization by One-Step Method. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1134152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Yang, X.; Tian, X.; Li, L.; Liu, M. Yeast Cell Surface Engineering of a Nicotinamide Riboside Kinase for the Production of β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide via Whole-Cell Catalysis. ACS Synth. Biol. 2022, 11, 3451–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhao, S.M.; Zhou, J.H.; Zeng, H.Y.; Xu, G. A Method for Synthesis of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Based on Enzymatic Method. CN112877386A, 28 January 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, T.M.; Lin, L.F.; Ling, R.M.; Qing, G.F.; He, X.X.; Tan, W.J.; Pan, J.F.; Liu, J. An Enzyme Catalyzed Synthesis Method of β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide. CN112795606A, 14 April 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, P.-S.; Boyken, S.E.; Baker, D. The Coming of Age of de Novo Protein Design. Nature 2016, 537, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currin, A.; Parker, S.; Robinson, C.J.; Takano, E.; Scrutton, N.S.; Breitling, R. The evolving art of creating genetic diversity: From directed evolution to synthetic biology. Biotechnol. Adv. 2021, 50, 107762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Hong, J.; Cui, J.; An, Y.-N.; Guo, Q.; Shen, Q.; Cheng, F.; Xue, Y.-P.; Zheng, Y.-G. Improvement of an Enzymatic Cascade Synthesis of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide via Protein Engineering and Reaction-Process Reinforcement. Biotechnol. J. 2024, 19, 2300748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobas, M.A.; Tao, R.; Nagai, J.; Kronschläger, M.T.; Borden, P.M.; Marvin, J.S.; Looger, L.L.; Khakh, B.S. A Genetically Encoded Single-Wavelength Sensor for Imaging Cytosolic and Cell Surface ATP. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, C.; Dang, M.; Ming, D.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, X.; Ren, L. Structure-Guided Mining and Engineering of Nicotinamide Riboside Kinase for Efficient Synthesis of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide. Mol. Catal. 2024, 559, 114058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortemme, T. De Novo Protein Design—From New Structures to Programmable Functions. Cell 2024, 187, 526–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.L.; Juergens, D.; Bennett, N.R.; Trippe, B.L.; Yim, J.; Eisenach, H.E.; Ahern, W.; Borst, A.J.; Ragotte, R.J.; Milles, L.F.; et al. De Novo Design of Protein Structure and Function with RFdiffusion. Nature 2023, 620, 1089–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiyama, K.; Iijima, K.; Yoshino, M.; Dohra, H.; Tokimoto, Y.; Nishikawa, K.; Idogaki, H.; Yoshida, N. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Production by Fructophilic Lactic Acid Bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Liu, T.; Yao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W.; Qin, J. Enhancing the Biosynthesis of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide in Lactococcus Lactis by Heterologous Expression of FtnadE*. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Yu, L.; Deng, J.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, K.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wen, W.; Yu, S.; Pan, Y.; et al. Sulfur Vacancy-Rich MoS2 as a Catalyst for the Hydrogenation of CO2 to Methanol. Nat. Catal. 2021, 4, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, F.; Zhang, T.M. Method for Secretory Expression of Pichia Pastoris Endogenous Nicotinamide Ribokinase and Application Thereof. CN113980929A, 28 January 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Shi, L.; Cai, M.H.; Ren, Y.N. Construction and Application of Genetic Engineering Bacteria for Producing NMN (N-methyl-N) by Utilizing Nicotinamide Fermentation. CN114836495A, 02 August 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, X.; Rong, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, T.; Zeng, Y.; Hong, K.; Jiang, L.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Microbial Creation of β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide and Its Regulation of Lipid Metabolism in the Liver of High-Fat Diet Mice. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2024, 42, e4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, T. Method for Producing Nicotinamide Mononucleotide and Transformant Used in Said Method. U.S. Patent Application 16/832,347, 22 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Andexer, J.N.; Richter, M. Emerging Enzymes for ATP Regeneration in Biocatalytic Processes. ChemBioChem 2015, 16, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Meng, D.; You, C. An Artificial Multi-Enzyme Cascade Biocatalysis for Biomanufacturing of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide from Starch and Nicotinamide in One-Pot. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2023, 162, 110122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-W.; Ryoo, G.-H.; Jang, H.-Y.; Rah, S.-Y.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, D.-K.; Bae, E.J.; Park, B.-H. NAD-Boosting Molecules Suppress Mast Cell Degranulation and Anaphylactic Responses in Mice. Theranostics 2022, 12, 3316–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgos, E.S.; Schramm, V.L. Weak Coupling of ATP Hydrolysis to the Chemical Equilibrium of Human Nicotinamide Phosphoribosyltransferase. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 11086–11096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsyuba, E.; Romani, M.; Hofer, D.; Auwerx, J. NAD(+) Homeostasis in Health and Disease. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 9–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulton, S.; Kyle, S.; Durkacz, B.W. Low Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Adenylyltransferase Activity in a Tiazofurin-Resistant Cell Line: Effects on NAD Metabolism and DNA Repair. Br. J. Cancer 1997, 76, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Irie, J.; Itoh, H. Aging and Homeostasis. Age-Associated Diseases and Clinical Application of NMN(Nicotinamide Mononucleotide). Clin. Calcium 2017, 27, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chini, C.C.S.; Peclat, T.R.; Warner, G.M.; Kashyap, S.; Espindola-Netto, J.M.; de Oliveira, G.C.; Gomez, L.S.; Hogan, K.A.; Tarrago, M.G.; Puranik, A.S.; et al. CD38 Ecto-Enzyme in Immune Cells Is Induced during Aging and Regulates NAD(+) and NMN Levels. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 1284–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasek, N.S.; Kuchel, G.A.; Kirkland, J.L.; Xu, M. Strategies for Targeting Senescent Cells in Human Disease. Nat. Aging 2021, 1, 870–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Tian, X.; Luo, J.; Bao, T.; Wang, S.; Wu, X. Molecular Mechanisms of Aging and Anti-Aging Strategies. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Luo, J.; Tian, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, X. Progress in Understanding Oxidative Stress, Aging, and Aging-Related Diseases. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Cui, Z.; Gao, Q.; Rui, R.; Xiong, B. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Supplementation Reverses the Declining Quality of Maternally Aged Oocytes. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 107987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajo, T.; Kitajima, N.; Katayoshi, T.; Tsuji-Naito, K. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Inhibits Oxidative Stress-Induced Damage in a SIRT1/NQO-1-Dependent Manner. Toxicol. Vitro 2023, 93, 105683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiss, T.; Balasubramanian, P.; Valcarcel-Ares, M.N.; Tarantini, S.; Yabluchanskiy, A.; Csipo, T.; Lipecz, A.; Reglodi, D.; Zhang, X.A.; Bari, F.; et al. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) Treatment Attenuates Oxidative Stress and Rescues Angiogenic Capacity in Aged Cerebromicrovascular Endothelial Cells: A Potential Mechanism for the Prevention of Vascular Cognitive Impairment. Geroscience 2019, 41, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajman, L.; Chwalek, K.; Sinclair, D.A. Therapeutic Potential of NAD-Boosting Molecules: The in Vivo Evidence. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 529–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Liang, Y.; Wu, P.; Shi, X.; Zhang, G.; Cai, Z. Continuous Dermal Exposure to Triclocarban Perturbs the Homeostasis of Liver-Gut Axis in Mice: Insights from Metabolic Interactions and Microbiome Shifts. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 5117–5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, M.; Nakagawa-Nagahama, Y.; Miura, M.; Kashiwabara, K.; Yaku, K.; Sawada, M.; Sekine, R.; Fukamizu, Y.; Sato, T.; Sakurai, T.; et al. Chronic Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Supplementation Elevates Blood Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Levels and Alters Muscle Function in Healthy Older Men. npj Aging 2022, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, B.J.; Rosenberg, M.A.; Jeganathan, K.B.; Hafner, A.V.; Michan, S.; Dai, J.; Baker, D.J.; Cen, Y.; Wu, L.E.; Sauve, A.A.; et al. SIRT2 Induces the Checkpoint Kinase BubR1 to Increase Lifespan. EMBO J. 2014, 33, 1438–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagi, M.; Do, Y.; Hirai, H.; Miki, K.; Toshima, T.; Fukahori, Y.; Setoyama, D.; Abe, C.; Nabeshima, Y.I.; Kang, D.; et al. Improving Lysosomal Ferroptosis with NMN Administration Protects against Heart Failure. Life Sci. Alliance 2023, 6, e202302116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, C.A.; Guan, Y.; Mukherjee, S.; Singh, K.; Botolin, P.; Davila, A.; Baur, J.A. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Preserves Mitochondrial Function and Increases Survival in Hemorrhagic Shock. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e120182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, G.M.; Youngson, N.A.; Sinclair, D.A.; Morris, M.J. Head to Head Comparison of Short-Term Treatment with the NAD(+) Precursor Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) and 6 Weeks of Exercise in Obese Female Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.F.; Chavez, J.D.; Garcia-Menendez, L.; Choi, Y.; Roe, N.D.; Chiao, Y.A.; Edgar, J.S.; Goo, Y.A.; Goodlett, D.R.; Bruce, J.E.; et al. Normalization of NAD+ Redox Balance as a Therapy for Heart Failure. Circulation 2016, 134, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, A.S.; Abraham, D.M.; Hershberger, K.A.; Bhatt, D.P.; Mao, L.; Cui, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Muehlbauer, M.J.; Grimsrud, P.A.; et al. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Requires SIRT3 to Improve Cardiac Function and Bioenergetics in a Friedreich’s Ataxia Cardiomyopathy Model. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e93885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.M.; Sun, M.Z.; Liu, Y.P.; Liang, J.J.; Wang, T.X.; Zhang, Z.S. Gymnemic Acid Alleviates Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Suppresses Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Vivo and in Vitro. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2019, 67, 3662–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, E.J. The Influence of Obesity and Metabolic Health on Vascular Health. Endocrinol Metab. 2022, 37, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.N. Current Challenges of Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders in China. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasilewska, N.; Lebensztejn, D.M. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Lipotoxicity. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2021, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yu, J.; Bai, J.; Huang, H.; Ying, S.; Wang, A.; Wang, P. Interaction between Obesity and Hypertension on Arteriosclerosis in Chinese Urban Adults: A Population-Based Cross-Sectional Study. Clin. Nurs. Res. 2023, 32, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.L.; Sinha, S. Obesity and Aging: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Approaches. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 67, 101268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerner, R.R.; Klepsch, V.; Macheiner, S.; Arnhard, K.; Adolph, T.E.; Grander, C.; Wieser, V.; Pfister, A.; Moser, P.; Hermann-Kleiter, N.; et al. NAD Metabolism Fuels Human and Mouse Intestinal Inflammation. Gut 2018, 67, 1813–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoldo, M.J.; Listijono, D.R.; Ho, W.-H.J.; Riepsamen, A.H.; Goss, D.M.; Richani, D.; Jin, X.L.; Mahbub, S.; Campbell, J.M.; Habibalahi, A.; et al. NAD+ Repletion Rescues Female Fertility during Reproductive Aging. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 1670–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covarrubias, A.J.; Perrone, R.; Grozio, A.; Verdin, E. NAD(+) Metabolism and Its Roles in Cellular Processes during Ageing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 119–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, T.; Guarente, L. SnapShot: Sirtuins, NAD, and Aging. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 192–192.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateuszuk, Ł.; Campagna, R.; Kutryb-Zając, B.; Kuś, K.; Słominska, E.M.; Smolenski, R.T.; Chlopicki, S. Reversal of Endothelial Dysfunction by Nicotinamide Mononucleotide via Extracellular Conversion to Nicotinamide Riboside. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 178, 114019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeberg, K.A.; Udovich, C.C.; Martens, C.R.; Seals, D.R.; Craighead, D.H. Dietary Supplementation with NAD+-Boosting Compounds in Humans: Current Knowledge and Future Directions. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2023, 78, 2435–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zong, C.; Feng, C.; Zhang, C.; Smirnov, A.; Sun, G.; Shao, C.; Zhang, L.; Hou, X.; Liu, W.; et al. Hippo Pathway Activation in Aged Mesenchymal Stem Cells Contributes to the Dysregulation of Hepatic Inflammation in Aged Mice. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2300424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.Y.; Meng, X.F.; Han, Y.P.; Yan, J.L.; Xiao, C.; Qian, L.B. Profile of Crosstalk between Glucose and Lipid Metabolic Disturbance and Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 983713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, B.-S. Chronic Low-Grade Inflammation and Aging. Int. J. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2021, 15, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeler, M.; Ellero-Simatos, S.; Birkner, T.; Mayneris-Perxachs, J.; Olsson, L.; Brolin, H.; Loeber, U.; Kraft, J.D.; Polizzi, A.; Marti-Navas, M.; et al. The Interplay between Dietary Fatty Acids and Gut Microbiota Influences Host Metabolism and Hepatic Steatosis. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhu, R.; Wang, H.; Tao, Q.; Lin, X.; Ge, S.; Zhai, Z. Nicotinamide Phosphate Transferase (NAMPT) Increases in Plasma in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndromes, and Promotes Macrophages to M2 Polarization. Int. Heart J. 2018, 59, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Sasso, G.; Menzies, K.J.; Mottis, A.; Piersigilli, A.; Perino, A.; Yamamoto, H.; Schoonjans, K.; Auwerx, J. SIRT2 Deficiency Modulates Macrophage Polarization and Susceptibility to Experimental Colitis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.Y.; Yu, J. The Role of NAD plus Metabolism in Macrophages in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2023, 209, 111755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Wang, M.; Chen, Y.; Song, H.; Wen, D.; Tu, J.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Z. NAMPT Inhibition Reduces Macrophage Inflammation through the NAD+/PARP1 Pathway to Attenuate Liver Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2023, 369, 110294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Dai, J.; Niu, M.; Li, B.; Chen, C.; Jiang, M.; Wu, Z.; Bao, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; et al. Inhibition of Nicotinamide Phosphoribosyltransferase Protects against Acute Pancreatitis via Modulating Macrophage Polarization and Its Related Metabolites. Pancreatology 2021, 21, 870–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Macedo, L.H.; Souza, C.O.S.; Gardinassi, L.G.; Faccioli, L.H. CD14 Regulates the Metabolomic Profiles of Distinct Macrophage Subsets under Steady and Activated States. Immunobiology 2022, 227, 152191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.F.; Pu, Q.; Dai, S.Y.; Ma, Q.; Li, X.; Zhu, W. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Alleviates Hyperosmolarity-Induced IL-17a Secretion and Macrophage Activation in Corneal Epithelial Cells/Macrophage Co-Culture System. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortell, R.; Moss, J.; McKenna, R.C.; Rigby, M.R.; Niedzwiecki, D.; Stevens, L.A.; Patton, W.A.; Mordes, J.P.; Greiner, D.L.; Rossini, A.A. Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD) and Its Metabolites Inhibit T Lymphocyte Proliferation: Role of Cell Surface NAD Glycohydrolase and Pyrophosphatase Activities. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 2049–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarugi, A. Glaucoma: Neuroprotection with NAD-Based Therapeutic Interventions. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 44, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.E.; Casado, B.L. Knowledge of Alzheimer’s Disease among Vietnamese Americans and Correlates of Their Knowledge about Alzheimer’s Disease. Dement.-Int. J. Soc. Res. Pract. 2019, 18, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zago, E.; Dal Molin, A.; Dimitri, G.M.; Xumerle, L.; Pirazzini, C.; Bacalini, M.G.; Maturo, M.G.; Azevedo, T.; Spasov, S.; Gomez-Garre, P.; et al. Early Downregulation of Hsa-miR-144-3p in Serum from Drug-Naive Parkinson’s Disease Patients. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanby, M.F.; Scott, K.M.; Scotton, W.; Wijesekera, L.; Mole, T.; Ellis, C.E.; Leigh, P.N.; Shaw, C.E.; Al-Chalabi, A. The Risk to Relatives of Patients with Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Brain 2011, 134, 3454–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaur, P.; Brugg, B.; Mericskay, M.; Li, Z.; Schmidt, M.S.; Vivien, D.; Orset, C.; Jacotot, E.; Brenner, C.; Duplus, E. Nicotinamide Riboside, a Form of Vitamin B(3), Protects against Excitotoxicity-Induced Axonal Degeneration. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 5440–5452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henricksen, L.A.; Federoff, H.J. Redefining Neuroprotective Gene Therapeutic Strategies:: Lessons Learned from Caloric Restriction and NAD(+) Metabolism. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2004, 6, S43–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Han, T.; Nijhawan, D.; Theodoropoulos, P.; Naidoo, J.; Yadavalli, S.; Mirzaei, H.; Pieper, A.A.; Ready, J.M.; McKnight, S.L. P7C3 Neuroprotective Chemicals Function by Activating the Rate-Limiting Enzyme in NAD Salvage. Cell 2014, 158, 1324–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moursi, M.M.; D’Alecy, L.G. Depressor Response during Experimental Portal Hypertension in Dog. Am. J. Physiol. 1986, 251, H1188–H1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Niou, Z.-X.; Enriquez, A.; LaMar, J.; Huang, J.-Y.; Ling, K.; Jafar-Nejad, P.; Gilley, J.; Coleman, M.P.; Tennessen, J.M.; et al. NMNAT2 Supports Vesicular Glycolysis via NAD Homeostasis to Fuel Fast Axonal Transport. Mol. Neurodegener. 2024, 19, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdts, J.; Brace, E.J.; Sasaki, Y.; DiAntonio, A.; Milbrandt, J. SARM1 Activation Triggers Axon Degeneration Locally via NAD(+) Destruction. Science 2015, 348, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilley, J.; Coleman, M.P. Endogenous Nmnat2 Is an Essential Survival Factor for Maintenance of Healthy Axons. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xing, S.; Chen, C.; Shen, D.; Chen, J. Abeta Promotes CD38 Expression in Senescent Microglia in Alzheimer’s Disease. Biol. Res. 2022, 55, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covarrubias, A.J.; Kale, A.; Perrone, R.; Lopez-Dominguez, J.A.; Pisco, A.O.; Kasler, H.G.; Schmidt, M.S.; Heckenbach, I.; Kwok, R.; Wiley, C.D.; et al. Senescent Cells Promote Tissue NAD(+) Decline during Ageing via the Activation of CD38(+) Macrophages. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 1265–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandir, A.S.; Przedborski, S.; Jackson-Lewis, V.; Wang, Z.Q.; Simbulan-Rosenthal, C.M.; Smulson, M.E.; Hoffman, B.E.; Guastella, D.B.; Dawson, V.L.; Dawson, T.M. Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase Activation Mediates 1-Methyl-4-Phenyl-1, 2,3,6-Tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-Induced Parkinsonism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 5774–5779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrakdar, E.T.; Uyanikgil, Y.; Kanit, L.; Koylu, E.; Yalcin, A. Nicotinamide Treatment Reduces the Levels of Oxidative Stress, Apoptosis, and PARP-1 Activity in Aβ (1-42)-Induced Rat Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Free Radical Res. 2014, 48, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmina, A.; Ai, I.; Morgun, A.; Okuneva, O.; Na, M.; Lopatina, O.; Petrova, M.; Taranushenko, T.E.; Fursov, A.A.; Kuvacheva, N.V. [NAD+-Converting Enzymes in Neuronal and Glial Cells: CD38 as a Novel Target for Neuroprotection]. Ann. Russ. Acad. Med. Sci. 2012, 67, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmina, A.B.; Okuneva, O.S.; Malinovskaya, N.A.; Taranushenko, T.E.; Morgun, A.V.; Mantorova, N.S.; Mikhutkina, S.V. NAD -Dependent Mechanisms of Disturbances of Viability of Brain Cells during the Acute Period of Hypoxic-Ischemic Perinatal Injury. Neurochem. J. 2008, 2, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poddar, S.K.; Sifat, A.E.; Haque, S.; Nahid, N.A.; Chowdhury, S.; Mehedi, I. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide: Exploration of Diverse Therapeutic Applications of a Potential Molecule. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Kong, M.; Wang, Y.; Mao, Y.; Xu, H.; He, W.; He, Y.; Gu, J. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Improves the Alzheimer’s Disease by Regulating Intestinal Microbiota. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 670, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Tomita, Y.; Miwa, Y.; Shinojima, A.; Ban, N.; Yamaguchi, S.; Nishioka, K.; Negishi, K.; Yoshino, J.; Kurihara, T. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Prevents Retinal Dysfunction in a Mouse Model of Retinal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, C.; Hu, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, T.; Zou, A.; Yu, D.; Shen, T.; Cai, W.; Yu, J. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Ameliorates Cellular Senescence and Inflammation Caused by Sodium Iodate in RPE. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 5961123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.-L.; Kitada, N.; Yasuhara, M.; Hori, R. Quantitative Estimation of Renal Clearance of N-Acetylprocainamide in Rats with Various Experimental Acute Renal Failure. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 13, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, M.; Wang, W.; Zhai, Z.; Wang, R.; Li, Y.; Liang, J.; Kothari, D.; Niu, K.; Wu, X. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Supplementation Protects the Intestinal Function in Aging Mice and D-Galactose Induced Senescent Cells. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 7507–7519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, N.; Yang, C.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Deng, H. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Inhibits Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation to Prevent Liver Fibrosis via Promoting PGE(2) Degradation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 162, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, K.-M.; Bao, T.; Gao, L.; Ru, M.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L.; Ye, C.; Wang, S.; Wu, X. The Impacts of Short-Term NMN Supplementation on Serum Metabolism, Fecal Microbiota, and Telomere Length in Pre-Aging Phase. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 756243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, F.; Kang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Dai, L.; Shao, Q.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, J.; Cui, L. Effect of β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide on Tumor Formation and Growth in a Lung Cancer Mouse Model. Mater. Chem. Front. 2021, 5, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, C. Comment on “Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Increases Muscle Insulin Sensitivity in Prediabetic Women”. Science 2021, 373, eabj1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loreto, A.; Di Stefano, M.; Gering, M.; Conforti, L. Wallerian Degeneration Is Executed by an NMN-SARM1-Dependent Late Ca2+ Influx but Only Modestly Influenced by Mitochondria. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 2539–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadeeshani, H.; Li, J.; Ying, T.; Zhang, B.; Lu, J. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) as an Anti-Aging Health Product–Promises and Safety Concerns. J. Adv. Res. 2022, 37, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakabayashi-Nakao, K.; Maruyama, K.; Ishii, H.; Muramatsu, K.; Hatakeyama, K.; Ohshima, K.; Ogura, S.-I.; Nakajima, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Mochizuki, T. Investigation of proNT/NMN Secretion from Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Cells Using a Mouse Xenograft Model. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 28, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, K.H.; Tang, J.J.; Rashid, M.A.; Cho, C.H.; Corujo-Ramirez, A.; Choi, J.; Bae, M.G.; Brogren, D.; Hawse, J.R.; Hou, X.; et al. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Prevents Cisplatin-Induced Cognitive Impairments. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 3727–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Li, J.; Yang, F.; Ning, G.; Zhen, L.; Wu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, D.; Xie, C.; et al. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Promotes Osteogenesis and Reduces Adipogenesis by Regulating Mesenchymal Stromal Cells via the SIRT1 Pathway in Aged Bone Marrow. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Picciotto, N.E.; Gano, L.B.; Johnson, L.C.; Martens, C.R.; Sindler, A.L.; Mills, K.F.; Imai, S.; Seals, D.R. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Supplementation Reverses Vascular Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress with Aging in Mice. Aging Cell 2016, 15, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Amorim, J.A.; Moustafa, G.A.; Lee, J.-J.; Yu, Z.; Ishihara, K.; Iesato, Y.; Barbisan, P.; Ueta, T.; Togka, K.A.; et al. Neuroprotective Effects and Mechanisms of Action of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) in a Photoreceptor Degenerative Model of Retinal Detachment. Aging 2020, 12, 24504–24521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, K.; Okumura, K. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Augments the Cytotoxic Activity of Natural Killer Cells in Young and Elderly Mice. Biomed. Res. 2021, 42, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hu, X.; Yang, Y.; Takata, T.; Sakurai, T. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Protects against β-Amyloid Oligomer-Induced Cognitive Impairment and Neuronal Death. Brain Res. 2016, 1643, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Han, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; An, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhai, Y.; Dai, X.; Tang, B.; et al. β-nicotinamide mononucleotide rescues the quality of aged oocyte and improves subsequent embryo development in pigs. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0291640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habibalahi, A.; Campbell, J.M.; Bertoldo, M.J.; Mahbub, S.B.; Goss, D.M.; Ledger, W.L.; Gilchrist, R.B.; Wu, L.E.; Goldys, E.M. Unique Deep Radiomic Signature Shows NMN Treatment Reverses Morphology of Oocytes from Aged Mice. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Ding, W.; Yang, C.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Deng, H. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Administration Restores Redox Homeostasis via the Sirt3–Nrf2 Axis and Protects Aged Mice from Oxidative Stress-Induced Liver Injury. J. Proteome Res. 2022, 21, 1759–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Jiang, A.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, W.; Ren, C.; Qian, X.; Zhou, Z.; Gong, A. NMN Maintains Intestinal Homeostasis by Regulating the Gut Microbiota. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 714604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okabe, K.; Nawaz, A.; Nishida, Y.; Yaku, K.; Usui, I.; Tobe, K.; Nakagawa, T. NAD+ Metabolism Regulates Preadipocyte Differentiation by Enhancing Alpha-Ketoglutarate-Mediated Histone H3K9 Demethylation at the PPARgamma Promoter. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 586179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tian, X.; Yu, Q.; Bao, T.; Dai, C.; Jiang, L.; Niu, K.; Yang, J.; Wang, S.; Wu, X. Alleviation of Hepatic Insulin Resistance and Steatosis with NMN via Improving Endoplasmic Reticulum–Mitochondria Miscommunication in the Liver of HFD Mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 175, 116682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Human Clinical Trials Focusing on Ageing | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | Study Design | Dose and Duration | NcT/uMiN No. |
| NMN | Healthy volunteers aged from 40 to 65 years | Oral administration Long-term NMN administration 300 mg daily for 60 days | NCT04228640 |
| Healthy male volunteers aged from 40 to 60 years | Oral administration Long-term NMN administration for 8 weeks Dose is not described | UMIN000030609 | |
| Double-blind study in postmenopausal and prediabetic women aged 55–75 years | Oral administration Long-term NMN administration: 250 mg daily for 8 weeks | NCT03151239 | |
| Healthy male volunteers aged from 40 to 60 years | Oral administration Single administration of 100, 250, or 500 mg NMN | UMIN000021309 | |
| Healthy volunteers aged from 50 to 70 years | Oral administration Long-term NMN administration: 100 mg or 200 mg for 24 weeks | UMIN000025739 | |
| Mouse models focusing on metabolism | |||
| Compound | Model | Results | References |
| NMN | Tg (SIRT2) and Bubr1H/+ mice | Increased NAD+ contents and restored BubR1 levels | [94] |
| Male C57BL/6N mice | Inhibited age-induced weight gain, increased insulin sensitivity, plasma lipid levels, physical activity, and energy expenditure, while also improving mitochondrial function in muscles | [1,9] | |
| p32cKO mice | Enhanced skeletal muscle mitochondrial oxidative metabolism in aged mice | [95] | |
| Male Long–Evans rats, ischemia–reperfusion or cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in Sirt1+/− mice, C57BL/6 mice, and 129S2/Sv mice | Improved mitochondrial function, decreased inflammation, improved physiological reserve, and decreased mortality, despite having no major effects on blood pressure or oxidative damage. Protected renal function from cisplatin-induced injury in wild-type but not Sirt1+/− mice | [1,96] | |
| High-fat diet-induced obese female mice | Improved glucose tolerance and increased liver citrate synthase activity, and triglyceride accumulation | [97] | |
| Transverse aortic constriction-stressed mice, male conditional knockout mice, male cardiac-specific Fxn-knockout mice (Friedreich ataxia cardiomyopathy model), and male Sirt3-knockout/Fkn-knockout mice | Improved mitochondrial function and protection from heart failure. Improved cardiac function, reduced energy waste, and improved energy utilization in Fxn-knockout mice but not in Sirt3/Fkn double-knockout mice | [98,99] | |
| Research Field | Research Progress | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| DNA repair | NMN increased the telomere length of liver cells in fibrotic mice. NMN activated DNA repair proteins, such as PARP1, in aged mice. | [148] [149] |
| Metabolism | NMN increased insulin sensitivity in mice and humans. NMN increased the number of mitochondria in the liver of obese mice. NMN enhanced the efficiency of energy production in mouse mitochondria. | [150] [151] [152] |
| Cancer | NMN enhanced the efficacy of PD-1-mediated immunotherapy. NMN improved the cognitive function of mice after chemotherapy. | [153] [154] |
| Bone repair | NMN doubled the number of new bone-forming cells in mice. | [155] |
| Cardiovascular | NMN reversed the decline of vascular elasticity in aged mice. | [156] |
| Eye function | NMN reduced photoreceptor cell death after retinal detachment in mice. | [157] |
| Immunity | NMN enhanced the action of immune T cells and stimulated the production of immunoglobulins. | [158] |
| Lifespan | NMN prolonged the lifespan of mice. | [9] [146] |
| Nervous system | NMN improved cognition and memory in a rodent model of Alzheimer’s disease. NMN ameliorated depressive behavior in model mice. | [142] [159] |
| Reproductive system | NMN improved the reproductive ability of female mice. NMN protected porcine oocytes from cell death due to exposure to environmental toxins. | [160] |
| Skin and muscles | NMN promoted muscle remodeling in older individuals. | [161] |
| Organ health | NMN reduced liver damage in chronic alcohol intake model mice, reduced renal cell death, and protected the kidneys from ischemic damage. NMN promoted the development and differentiation of intestinal stem cells in mice. | [162] [163] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, C.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Gao, L.; Chen, X. Advances in the Synthesis and Physiological Metabolic Regulation of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2354. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142354
Zheng C, Li Y, Wu X, Gao L, Chen X. Advances in the Synthesis and Physiological Metabolic Regulation of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide. Nutrients. 2024; 16(14):2354. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142354
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Chuxiong, Yumeng Li, Xin Wu, Le Gao, and Xiaoyi Chen. 2024. "Advances in the Synthesis and Physiological Metabolic Regulation of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide" Nutrients 16, no. 14: 2354. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142354
APA StyleZheng, C., Li, Y., Wu, X., Gao, L., & Chen, X. (2024). Advances in the Synthesis and Physiological Metabolic Regulation of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide. Nutrients, 16(14), 2354. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142354






