Progress in the Study of Animal Models of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
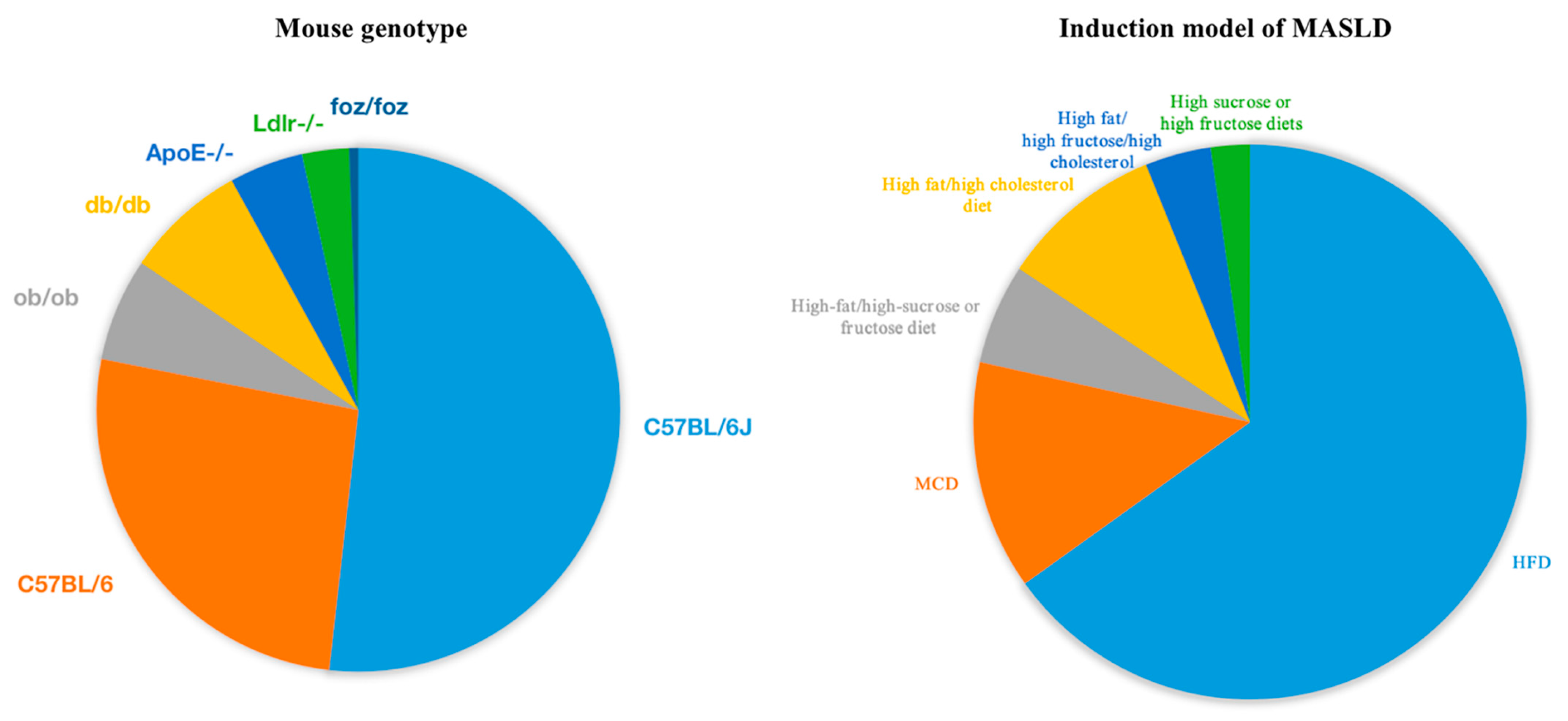
2. Commonly Used Rodent and Non-Human Primate Models
2.1. Rodents
| Genus | Models | Gene Description | Features | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mouse | ob/ob | Leptin deficiency | Obesity, insulin resistance, steatosis | [43] |
| db/db | Leptin receptor deficiency | Obesity, insulin resistance, steatosis | [44] | |
| foz/foz | Deficient in the Alstrom syndrome 1 gene | Obesity, steatosis, insulin resistance, high cholesterol levels | [45] | |
| LIR-/- | Liver-specific insulin receptor knockout | Hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, high cholesterol levels | [46] | |
| LDLR-/- | LDL receptor-deficient | High cholesterol levels | [47,48] | |
| ApoE-/- | Apolipoprotein E deficient | High cholesterol levels | [49,50,51] | |
| FXR-/- | Farnesoid X receptor deficient | Decreased lipid and cholesterol metabolism | [52] | |
| CD36-/- | Fatty acid translocase CD36 deficient | High plasma fatty acid and triglyceride levels | [53] | |
| SREBP1c-/- | Sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c deficient | Steatosis, insulin resistance, high triglyceride levels | [54] | |
| PPARa-/- | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor deficient | Severe fatty liver | [55] | |
| IL6-/- | Interleukin-6 deficient | Obesity, steatosis, insulin resistance | [56] | |
| rat | fa/fa | Zucker obese rat | Obesity, insulin resistance, hyperglycemia | [34] |
2.2. Non-Human Primates
3. Common Diet-Induced Models of MASLD
3.1. High-Fat Diet
3.2. Methionine- and Choline-Deficient (MCD) Diet
3.3. Choline-Deficient L-Amino Acid (CDAA) Diet
3.4. High Fat/Cholesterol Diet
3.5. High-Fat/Fructose Diet
| Models | Mechanisms | Obesity | Insulin Resistance | Inflammation | Liver Fibrosis | Duration of MASLD Induction | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HFD | Metabolic abnormalities, oxidative stress and inflammation, insulin resistance | Y | Y | Y | N | 8–24 weeks | [67,68,69,70,71] |
| MCD | Metabolic abnormalities, oxidative stress and inflammation, fibrosis | N | N | Y | Y | 4–9 weeks | [76,78,94] |
| CDAA | Metabolic abnormalities, oxidative stress and inflammation, fibrosis | Y | N | Y | Y | 4–9 weeks | [81,95] |
| HFD + Fructose | Metabolic abnormalities, oxidative stress and inflammation, mild fibrosis, insulin resistance | Y | Y | Y | Y | 12–16 weeks | [86,87,88,89,90] |
| HFD + Cholesterol | Metabolic abnormalities, oxidative stress and inflammation, insulin resistance | Y | Y | Y | N | 12–16 weeks | [96] |
| HFD + Fructose + Cholesterol | Metabolic abnormalities, oxidative stress and inflammation, fibrosis, insulin resistance | Y | Y | Y | Y | 12–16 weeks | [82,97] |
4. Chemical Substance Induction Model
4.1. Streptozotocin
4.2. Carbon Tetrachloride
4.3. Diethylnitrosamine
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Estes, C.; Razavi, H.; Loomba, R.; Younossi, Z.; Sanyal, A.J. Modeling the epidemic of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease demonstrates an exponential increase in burden of disease. Hepatology 2018, 67, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, L.; Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Cao, Y.Y.; Zheng, M.H. Current status and future trends of the global burden of MASLD. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 35, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loomba, R.; Sanyal, A.J. The global NAFLD epidemic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinella, M.E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Ratziu, V.; Francque, S.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kanwal, F.; Romero, D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arab, J.P.; et al. A multisociety Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. Hepatology 2023, 78, 1966–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, L.; Ding, Y. Transitioning from NAFLD to MAFLD and MASLD: Consistent prevalence and risk factors in a Chinese cohort. J. Hepatol. 2024, 80, e154–e155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tao, X.; Zeng, M.; Mi, Y.; Xu, L. Clinical and histological features under different nomenclatures of fatty liver disease: NAFLD, MAFLD, MASLD and MetALD. J. Hepatol. 2024, 80, e64–e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunt, E.M.; Janney, C.G.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Bacon, B.R. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A proposal for grading and staging the histological lesions. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 94, 2467–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grander, C.; Grabherr, F.; Tilg, H. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Pathophysiological concepts and treatment options. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 119, 1787–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauchi-Sato, K.; Ozeki, S.; Houjou, T.; Taguchi, R.; Fujimoto, T. The surface of lipid droplets is a phospholipid monolayer with a unique Fatty Acid composition. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 44507–44512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonardo, A.; Lombardini, S.; Ricchi, M.; Scaglioni, F.; Loria, P. Review article: Hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 22 (Suppl. S2), 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; So, J.S.; Park, J.G.; Lee, A.H. Transcriptional control of hepatic lipid metabolism by SREBP and ChREBP. Semin. Liver Dis. 2013, 33, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashek, D.G. Hepatic fatty acid trafficking: Multiple forks in the road. Adv. Nutr. 2013, 4, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seebacher, F.; Zeigerer, A.; Kory, N.; Krahmer, N. Hepatic lipid droplet homeostasis and fatty liver disease. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 108, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, C.P.; James, O.F. Steatohepatitis: A tale of two “hits”? Gastroenterology 1998, 114, 842–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, P.; Kleiner, D.E.; Dam-Larsen, S.; Adams, L.A.; Bjornsson, E.S.; Charatcharoenwitthaya, P.; Mills, P.R.; Keach, J.C.; Lafferty, H.D.; Stahler, A.; et al. Liver Fibrosis, but No Other Histologic Features, Is Associated with Long-term Outcomes of Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 389–397.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Evolution of inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: The multiple parallel hits hypothesis. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1836–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, N.; Jia, L.; Cheng, A.; Ren, H.; Fu, Y.; Ding, X.; Haq, I.U.; Liu, E. Global research trends on gut microbiota and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis: Insights from bibliometric and scientometric analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1390483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhekadur, P.K.; Kumar, D.P.; Sanyal, A.J. Preclinical models of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelleymounter, M.A.; Cullen, M.J.; Baker, M.B.; Hecht, R.; Winters, D.; Boone, T.; Collins, F. Effects of the obese gene product on body weight regulation in ob/ob mice. Science 1995, 269, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recena Aydos, L.; Aparecida do Amaral, L.; Serafim de Souza, R.; Jacobowski, A.C.; Freitas Dos Santos, E.; Rodrigues Macedo, M.L. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Induced by High-Fat Diet in C57bl/6 Models. Nutrients 2019, 11, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanaspa, M.A.; Sanchez-Lozada, L.G.; Choi, Y.J.; Cicerchi, C.; Kanbay, M.; Roncal-Jimenez, C.A.; Ishimoto, T.; Li, N.; Marek, G.; Duranay, M.; et al. Uric acid induces hepatic steatosis by generation of mitochondrial oxidative stress: Potential role in fructose-dependent and -independent fatty liver. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 40732–40744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackerman, Z.; Oron-Herman, M.; Grozovski, M.; Rosenthal, T.; Pappo, O.; Link, G.; Sela, B.A. Fructose-induced fatty liver disease: Hepatic effects of blood pressure and plasma triglyceride reduction. Hypertension 2005, 45, 1012–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collison, K.S.; Maqbool, Z.M.; Inglis, A.L.; Makhoul, N.J.; Saleh, S.M.; Bakheet, R.H.; Al-Johi, M.A.; Al-Rabiah, R.K.; Zaidi, M.Z.; Al-Mohanna, F.A. Effect of dietary monosodium glutamate on HFCS-induced hepatic steatosis: Expression profiles in the liver and visceral fat. Obesity 2010, 18, 1122–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Lozada, L.G.; Mu, W.; Roncal, C.; Sautin, Y.Y.; Abdelmalek, M.; Reungjui, S.; Le, M.; Nakagawa, T.; Lan, H.Y.; Yu, X.; et al. Comparison of free fructose and glucose to sucrose in the ability to cause fatty liver. Eur. J. Nutr. 2010, 49, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, A.; Tumer, N.; Gao, Y.; Cheng, K.Y.; Scarpace, P.J. Prevention and reversal of diet-induced leptin resistance with a sugar-free diet despite high fat content. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 106, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsch, R.; Clarkson, V.; Shephard, E.G.; Marais, D.A.; Jaffer, M.A.; Woodburne, V.E.; Kirsch, R.E.; Hall Pde, L. Rodent nutritional model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Species, strain and sex difference studies. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2003, 18, 1272–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoppeler, S.; Palmes, D.; Fehr, M.; Holzen, J.P.; Zibert, A.; Siaj, R.; Schmidt, H.H.; Spiegel, H.U.; Bahde, R. Gender and strain-specific differences in the development of steatosis in rats. Lab. Anim. 2013, 47, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriano, F.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Falony, G.; Roumain, M.; Paquot, A.; Pelicaen, R.; Regnier, M.; Delzenne, N.M.; Raes, J.; Muccioli, G.G.; et al. Novel insights into the genetically obese (ob/ob) and diabetic (db/db) mice: Two sides of the same coin. Microbiome 2021, 9, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Jia, X.; Bai, X.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, W.; Shu, M.; Zhu, Y.; Jin, S. Leptin gene-targeted editing in ob/ob mouse adipose tissue based on the CRISPR/Cas9 system. J. Genet. Genom. 2021, 48, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.W.; Cannon, B.; Nedergaard, J. Leptin: Is It Thermogenic? Endocr. Rev. 2020, 41, 232–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, M.L. Consumption of O2 and early detection of fa/fa genotype in rats. Metabolism 1979, 28, 1147–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahl, E.P.; Dhindsa, D.S.; Lee, S.K.; Sandesara, P.B.; Chalasani, N.P.; Sperling, L.S. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and the Heart: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 948–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Fujita, S.; Yamagishi, A.; Shirai, T.; Maeda, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Kobayashi, K.I.; Inoue, J.; Yamamoto, Y. Brown Rice Inhibits Development of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Obese Zucker (fa/fa) Rats by Increasing Lipid Oxidation Via Activation of Retinoic Acid Synthesis. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 2705–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonardo, A.; Nascimbeni, F.; Mantovani, A.; Targher, G. Hypertension, diabetes, atherosclerosis and NASH: Cause or consequence? J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowicz, A.; Wisniewska, A.; Kus, K.; Bialas, M.; Lomnicka, M.; Toton-Zuranska, J.; Kiepura, A.; Stachyra, K.; Suski, M.; Bujak-Gizycka, B.; et al. Diminazene Aceturate Stabilizes Atherosclerotic Plaque and Attenuates Hepatic Steatosis in apoE-Knockout Mice by Influencing Macrophages Polarization and Taurine Biosynthesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, A.; Tripodi, G.L.; Kareinen, I.; Berg, M.; Forteza, M.J.; Gistera, A.; Griepke, S.; Casagrande, F.B.; Martins, J.O.; Abdalla, D.S.P.; et al. Genetic Deficiency of Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase Aggravates Vascular but Not Liver Disease in a Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Atherosclerosis Comorbidity Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowicz, A.; Wisniewska, A.; Kus, K.; Kiepura, A.; Gebska, A.; Gajda, M.; Bialas, M.; Toton-Zuranska, J.; Stachyra, K.; Suski, M.; et al. The Influence of Trehalose on Atherosclerosis and Hepatic Steatosis in Apolipoprotein E Knockout Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoemaker, M.H.; Kleemann, R.; Morrison, M.C.; Verheij, J.; Salic, K.; van Tol, E.A.F.; Kooistra, T.; Wielinga, P.Y. A casein hydrolysate based formulation attenuates obesity and associated non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and atherosclerosis in LDLr-/-.Leiden mice. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Li, Y.; Syn, W.K.; Wang, Z.; Lopes-Virella, M.F.; Lyons, T.J.; Huang, Y. Amitriptyline inhibits nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and atherosclerosis induced by high-fat diet and LPS through modulation of sphingolipid metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 318, E131–E144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staels, B.; Rubenstrunk, A.; Noel, B.; Rigou, G.; Delataille, P.; Millatt, L.J.; Baron, M.; Lucas, A.; Tailleux, A.; Hum, D.W.; et al. Hepatoprotective effects of the dual peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha/delta agonist, GFT505, in rodent models of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2013, 58, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Nakade, Y.; Yamauchi, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ishii, N.; Ohashi, T.; Ito, K.; Sato, K.; Fukuzawa, Y.; Yoneda, M. Glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue prevents nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in non-obese mice. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 2512–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Proenca, R.; Maffei, M.; Barone, M.; Leopold, L.; Friedman, J.M. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 1994, 372, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, K.P.; Dickie, M.M.; Coleman, D.L. Diabetes, a new mutation in the mouse. Science 1966, 153, 1127–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, S.B.; Liu, X.; Ganguly, S.; Dhar, D.; Pasillas, M.P.; Ricciardelli, E.; Li, R.Z.; Troutman, T.D.; Kisseleva, T.; Glass, C.K.; et al. Heterogeneity of HSCs in a Mouse Model of NASH. Hepatology 2021, 74, 667–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jesus, D.F.; Orime, K.; Kaminska, D.; Kimura, T.; Basile, G.; Wang, C.H.; Haertle, L.; Riemens, R.; Brown, N.K.; Hu, J.; et al. Parental metabolic syndrome epigenetically reprograms offspring hepatic lipid metabolism in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 2391–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, S.; Goodspeed, L.; Wang, S.; Kim, J.; Zeng, L.; Ioannou, G.N.; Haigh, W.G.; Yeh, M.M.; Kowdley, K.V.; O’Brien, K.D.; et al. Dietary cholesterol exacerbates hepatic steatosis and inflammation in obese LDL receptor-deficient mice. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 1626–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieghs, V.; Van Gorp, P.J.; Wouters, K.; Hendrikx, T.; Gijbels, M.J.; van Bilsen, M.; Bakker, J.; Binder, C.J.; Lütjohann, D.; Staels, B.; et al. LDL receptor knock-out mice are a physiological model particularly vulnerable to study the onset of inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri-Ansari, N.; Nikolopoulou, C.; Papoutsi, K.; Kyrou, I.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Kyriakopoulos, G.; Chatzigeorgiou, A.; Kalotychou, V.; Randeva, M.S.; Chatha, K.; et al. Empagliflozin Attenuates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) in High Fat Diet Fed ApoE((-/-)) Mice by Activating Autophagy and Reducing ER Stress and Apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.C.; Xu, J.W.; Li, S.; Ng, X.E.; Tung, Y.T. Effects of exercise on high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and lipid metabolism in ApoE knockout mice. Nutr. Metab. 2022, 19, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniewska, A.; Stachowicz, A.; Kuś, K.; Ulatowska-Białas, M.; Totoń-Żurańska, J.; Kiepura, A.; Stachyra, K.; Suski, M.; Gajda, M.; Jawień, J.; et al. Inhibition of Atherosclerosis and Liver Steatosis by Agmatine in Western Diet-Fed apoE-Knockout Mice Is Associated with Decrease in Hepatic De Novo Lipogenesis and Reduction in Plasma Triglyceride/High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Ratio. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifford, B.L.; Sedgeman, L.R.; Williams, K.J.; Morand, P.; Cheng, A.; Jarrett, K.E.; Chan, A.P.; Brearley-Sholto, M.C.; Wahlstrom, A.; Ashby, J.W.; et al. FXR activation protects against NAFLD via bile-acid-dependent reductions in lipid absorption. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 1671–1684.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, C.; Luo, X.; Wang, P.; Zhou, W.; Zhong, S.; Xie, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, P.; Tang, R.; et al. CD36 palmitoylation disrupts free fatty acid metabolism and promotes tissue inflammation in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.P.; Kim, D.Y.; Lee, Y.G.; Lee, Y.S.; Truong, X.T.; Lee, J.H.; Song, D.K.; Kwon, T.K.; Park, S.H.; Jung, C.H.; et al. SREBP-1c impairs ULK1 sulfhydration-mediated autophagic flux to promote hepatic steatosis in high-fat-diet-fed mice. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 3820–3832.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocker, C.N.; Patel, D.P.; Velenosi, T.J.; Kim, D.; Yan, T.; Yue, J.; Li, G.; Krausz, K.W.; Gonzalez, F.J. Extrahepatic PPARalpha modulates fatty acid oxidation and attenuates fasting-induced hepatosteatosis in mice. J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 2140–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Yin, S.; Ren, R.; Liu, S.; Yong, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zheng, M.H.; Kunos, G.; Gao, B.; et al. Myeloid-Cell-Specific IL-6 Signaling Promotes MicroRNA-223-Enriched Exosome Production to Attenuate NAFLD-Associated Fibrosis. Hepatology 2021, 74, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhesus Macaque Genome, S.; Analysis, C.; Gibbs, R.A.; Rogers, J.; Katze, M.G.; Bumgarner, R.; Weinstock, G.M.; Mardis, E.R.; Remington, K.A.; Strausberg, R.L.; et al. Evolutionary and biomedical insights from the rhesus macaque genome. Science 2007, 316, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, R.; Li, Y.; Liao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, W.; Liang, B. Plasma lipidomic signatures of spontaneous obese rhesus monkeys. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, P.; Venkatesan, R.; Kumar, M.; Usmani, A.; Majumdar, S.S. Macaca radiata (bonnet monkey): A spontaneous model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2008, 28, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Raab, S.; Zheng, W.; Wang, J.; Liu, N.; Zhu, T.; Xue, L.; Song, Z.; Mao, J.; et al. Rhesus macaques develop metabolic syndrome with reversible vascular dysfunction responsive to pioglitazone. Circulation 2011, 124, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Liu, Y.; Shang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, D.; Hou, N.; Wang, J.; Sun, X.; Peng, Y.; Pan, L.; et al. Characterization of spontaneously-developed non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in aged rhesus monkeys. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2018, 10, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, P.; Rom, O.; Li, K.; Jia, L.; Gao, X.; Liu, Z.; Ding, S.; Zhao, M.; Wang, H.; Chen, S.; et al. DT-109 ameliorates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in nonhuman primates. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 742–757.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asgharpour, A.; Cazanave, S.C.; Pacana, T.; Seneshaw, M.; Vincent, R.; Banini, B.A.; Kumar, D.P.; Daita, K.; Min, H.K.; Mirshahi, F.; et al. A diet-induced animal model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular cancer. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clapper, J.R.; Hendricks, M.D.; Gu, G.; Wittmer, C.; Dolman, C.S.; Herich, J.; Athanacio, J.; Villescaz, C.; Ghosh, S.S.; Heilig, J.S.; et al. Diet-induced mouse model of fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis reflecting clinical disease progression and methods of assessment. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2013, 305, G483–G495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.H.; Hirsova, P.; Malhi, H.; Gores, G.J. Animal Models of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: Eat, Delete, and Inflame. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 1325–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreres, L.; Jilkova, Z.M.; Vial, G.; Marche, P.N.; Decaens, T.; Lerat, H. Modeling Diet-Induced NAFLD and NASH in Rats: A Comprehensive Review. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surwit, R.S.; Kuhn, C.M.; Cochrane, C.; McCubbin, J.A.; Feinglos, M.N. Diet-induced type II diabetes in C57BL/6J mice. Diabetes 1988, 37, 1163–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schemmel, R.; Mickelsen, O.; Gill, J.L. Dietary obesity in rats: Body weight and body fat accretion in seven strains of rats. J. Nutr. 1970, 100, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieber, C.S.; Leo, M.A.; Mak, K.M.; Xu, Y.; Cao, Q.; Ren, C.; Ponomarenko, A.; DeCarli, L.M. Model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, L.; Asrih, M.; Repond, C.; Sempoux, C.; Stehle, J.C.; Leloup, C.; Jornayvaz, F.R.; Pellerin, L. AMPK activation caused by reduced liver lactate metabolism protects against hepatic steatosis in MCT1 haploinsufficient mice. Mol. Metab. 2017, 6, 1625–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roy, T.; Llopis, M.; Lepage, P.; Bruneau, A.; Rabot, S.; Bevilacqua, C.; Martin, P.; Philippe, C.; Walker, F.; Bado, A.; et al. Intestinal microbiota determines development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Gut 2013, 62, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.N.; Zhang, P.; Gong, J.; Zhang, X.J.; Wang, P.X.; Yin, M.; Jiang, Z.; Shen, L.J.; Ji, Y.X.; Tong, J.; et al. Tmbim1 is a multivesicular body regulator that protects against non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice and monkeys by targeting the lysosomal degradation of Tlr4. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 742–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, A.; Li, J.; Ji, S.; Ma, F.; Wang, G.; Xue, Y.; Liu, Z.; Gao, J.; Han, J.; Tai, P.; et al. The Effects of B1344, a Novel Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Analog, on Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Nonhuman Primates. Diabetes 2020, 69, 1611–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Fan, L.; Wu, J.; Xu, H.; Leung, W.Y.; Fu, K.; Wu, J.; Liu, K.; Man, K.; Yang, X.; et al. Macrophage p38alpha promotes nutritional steatohepatitis through M1 polarization. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbin, K.D.; Zeisel, S.H. Choline metabolism provides novel insights into nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and its progression. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2012, 28, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinella, M.E.; Elias, M.S.; Smolak, R.R.; Fu, T.; Borensztajn, J.; Green, R.M. Mechanisms of hepatic steatosis in mice fed a lipogenic methionine choline-deficient diet. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinella, M.E.; Green, R.M. The methionine-choline deficient dietary model of steatohepatitis does not exhibit insulin resistance. J. Hepatol. 2004, 40, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arman, T.; Lynch, K.D.; Montonye, M.L.; Goedken, M.; Clarke, J.D. Sub-Chronic Microcystin-LR Liver Toxicity in Preexisting Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Rats. Toxins 2019, 11, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.; Pera, N.; Phung, N.; Leclercq, I.; Yun Hou, J.; Farrell, G. Lipid peroxidation, stellate cell activation and hepatic fibrogenesis in a rat model of chronic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2003, 39, 756–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; An, P.; Vaid, K.A.; Nasser, I.; Huang, P.; Tan, L.; Zhao, S.; Schuppan, D.; Popov, Y.V. Comparison of murine steatohepatitis models identifies a dietary intervention with robust fibrosis, ductular reaction, and rapid progression to cirrhosis and cancer. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2020, 318, G174–G188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Minicis, S.; Agostinelli, L.; Rychlicki, C.; Sorice, G.P.; Saccomanno, S.; Candelaresi, C.; Giaccari, A.; Trozzi, L.; Pierantonelli, I.; Mingarelli, E.; et al. HCC development is associated to peripheral insulin resistance in a mouse model of NASH. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savard, C.; Tartaglione, E.V.; Kuver, R.; Haigh, W.G.; Farrell, G.C.; Subramanian, S.; Chait, A.; Yeh, M.M.; Quinn, L.S.; Ioannou, G.N. Synergistic interaction of dietary cholesterol and dietary fat in inducing experimental steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2013, 57, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, T.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Sullivan, S.; Nadeau, K.J.; Green, M.; Roncal, C.; Nakagawa, T.; Kuwabara, M.; Sato, Y.; Kang, D.H.; et al. Fructose and sugar: A major mediator of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 1063–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelmalek, M.F.; Suzuki, A.; Guy, C.; Unalp-Arida, A.; Colvin, R.; Johnson, R.J.; Diehl, A.M.; Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Clinical Research, N. Increased fructose consumption is associated with fibrosis severity in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1961–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronati, M.; Baratta, F.; Pastori, D.; Ferro, D.; Angelico, F.; Del Ben, M. Added Fructose in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and in Metabolic Syndrome: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetri, L.H.; Basaranoglu, M.; Brunt, E.M.; Yerian, L.M.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A. Severe NAFLD with hepatic necroinflammatory changes in mice fed trans fats and a high-fructose corn syrup equivalent. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 295, G987–G995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.; Duan, N.N.; Liu, C.; Niu, C.; Liu, X.P.; Wu, J. Characterization of a murine nonalcoholic steatohepatitis model induced by high fat high calorie diet plus fructose and glucose in drinking water. Lab. Investig. 2018, 98, 1184–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Ye, J.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, N.P.; Zhao, Y.M.; Fan, J.; Liu, X.P.; Wu, J. Activation of pluripotent genes in hepatic progenitor cells in the transition of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis to pre-malignant lesions. Lab. Investig. 2017, 97, 1201–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, R.; Kirby, M.; Xanthakos, S.A.; Softic, S.; Feldstein, A.E.; Saxena, V.; Tang, P.H.; Miles, L.; Miles, M.V.; Balistreri, W.F.; et al. High-fructose, medium chain trans fat diet induces liver fibrosis and elevates plasma coenzyme Q9 in a novel murine model of obesity and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2010, 52, 934–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alisi, A.; Manco, M.; Pezzullo, M.; Nobili, V. Fructose at the center of necroinflammation and fibrosis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2011, 53, 372–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cydylo, M.A.; Davis, A.T.; Kavanagh, K. Fatty liver promotes fibrosis in monkeys consuming high fructose. Obesity 2017, 25, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goedeke, L.; Peng, L.; Montalvo-Romeral, V.; Butrico, G.M.; Dufour, S.; Zhang, X.M.; Perry, R.J.; Cline, G.W.; Kievit, P.; Chng, K.; et al. Controlled-release mitochondrial protonophore (CRMP) reverses dyslipidemia and hepatic steatosis in dysmetabolic nonhuman primates. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaay0284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bremer, A.A.; Stanhope, K.L.; Graham, J.L.; Cummings, B.P.; Wang, W.; Saville, B.R.; Havel, P.J. Fructose-fed rhesus monkeys: A nonhuman primate model of insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2011, 4, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefi, F.; Shahim, S.; Razavieh, A.; Mehryar, A.H.; Hosseini, A.A.; Alborzi, S. Some normative data on the Bender Gestalt test performance of Iranian children. Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 1992, 62 Pt 3, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denda, A.; Kitayama, W.; Kishida, H.; Murata, N.; Tsutsumi, M.; Tsujiuchi, T.; Nakae, D.; Konishi, Y. Development of hepatocellular adenomas and carcinomas associated with fibrosis in C57BL/6J male mice given a choline-deficient, L-amino acid-defined diet. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 2002, 93, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, G.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Leclercq, I.; Yeh, M.M.; Goldin, R.; Teoh, N.; Schuppan, D. Mouse Models of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: Toward Optimization of Their Relevance to Human Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2019, 69, 2241–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Poulsen, K.L.; Sanz-Garcia, C.; Huang, E.; McMullen, M.R.; Roychowdhury, S.; Dasarathy, S.; Nagy, L.E. MLKL-dependent signaling regulates autophagic flux in a murine model of non-alcohol-associated fatty liver and steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, M.; Shibazaki, Y.; Wakamatsu, K.; Honda, Y.; Kawauchi, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Arumugam, S.; Watanabe, K.; Ichida, T.; Asakura, H.; et al. A murine model for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis showing evidence of association between diabetes and hepatocellular carcinoma. Med. Mol. Morphol. 2013, 46, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, L.; McLennan, S.V.; Williams, P.F.; Bonner, J.; Chowdhury, S.; McCaughan, G.W.; Gorrell, M.D.; Yue, D.K.; Twigg, S.M. Diabetes is a progression factor for hepatic fibrosis in a high fat fed mouse obesity model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owada, Y.; Tamura, T.; Tanoi, T.; Ozawa, Y.; Shimizu, Y.; Hisakura, K.; Matsuzaka, T.; Shimano, H.; Nakano, N.; Sakashita, S.; et al. Novel non-alcoholic steatohepatitis model with histopathological and insulin-resistant features. Pathol. Int. 2018, 68, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, C.Y.; Liu, Z.; Ma, X.S.; He, Y.H.; Chen, S.S.; Bai, X.Y. Hydroxysafflor yellow A suppresses liver fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride with high-fat diet by regulating PPAR-γ/p38 MAPK signaling. Pharm. Biol. 2014, 52, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, N.; Kado, S.; Kano, M.; Masuoka, N.; Nagata, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Miyazaki, K.; Ishikawa, F. A high-fat diet and multiple administration of carbon tetrachloride induces liver injury and pathological features associated with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2013, 40, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.H.; Shin, J.W.; Park, S.K.; Seo, J.N.; Li, L.; Jang, J.J.; Lee, M.J. Diethylnitrosamine (DEN) induces irreversible hepatocellular carcinogenesis through overexpression of G1/S-phase regulatory proteins in rat. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 191, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, K.J.; Swan, R.Z.; Walling, T.L.; Iannitti, D.A.; McKillop, I.H.; Sindram, D. Obesity, but not ethanol, promotes tumor incidence and progression in a mouse model of hepatocellular carcinoma in vivo. Surg. Endosc. 2013, 27, 2782–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toriguchi, K.; Hatano, E.; Tanabe, K.; Takemoto, K.; Nakamura, K.; Koyama, Y.; Seo, S.; Taura, K.; Uemoto, S. Attenuation of steatohepatitis, fibrosis, and carcinogenesis in mice fed a methionine-choline deficient diet by CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein homologous protein deficiency. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 29, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, Y.; Hua, Y.; Alam, N.; Liu, E. Progress in the Study of Animal Models of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3120. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183120
Fu Y, Hua Y, Alam N, Liu E. Progress in the Study of Animal Models of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Nutrients. 2024; 16(18):3120. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183120
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Yu, Yuxin Hua, Naqash Alam, and Enqi Liu. 2024. "Progress in the Study of Animal Models of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease" Nutrients 16, no. 18: 3120. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183120
APA StyleFu, Y., Hua, Y., Alam, N., & Liu, E. (2024). Progress in the Study of Animal Models of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Nutrients, 16(18), 3120. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183120







