The Effect of Dietary Types on Gut Microbiota Composition and Development of Non-Communicable Diseases: A Narrative Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Gut Microbiota Composition in the Gastrointestinal Tract
4. Function of Gut Microbiota
5. Factors Influencing the Gut Microbiota
6. Diseases Related to Gut Microbiota
7. The Effect of Diets on Gut Microbiota Composition
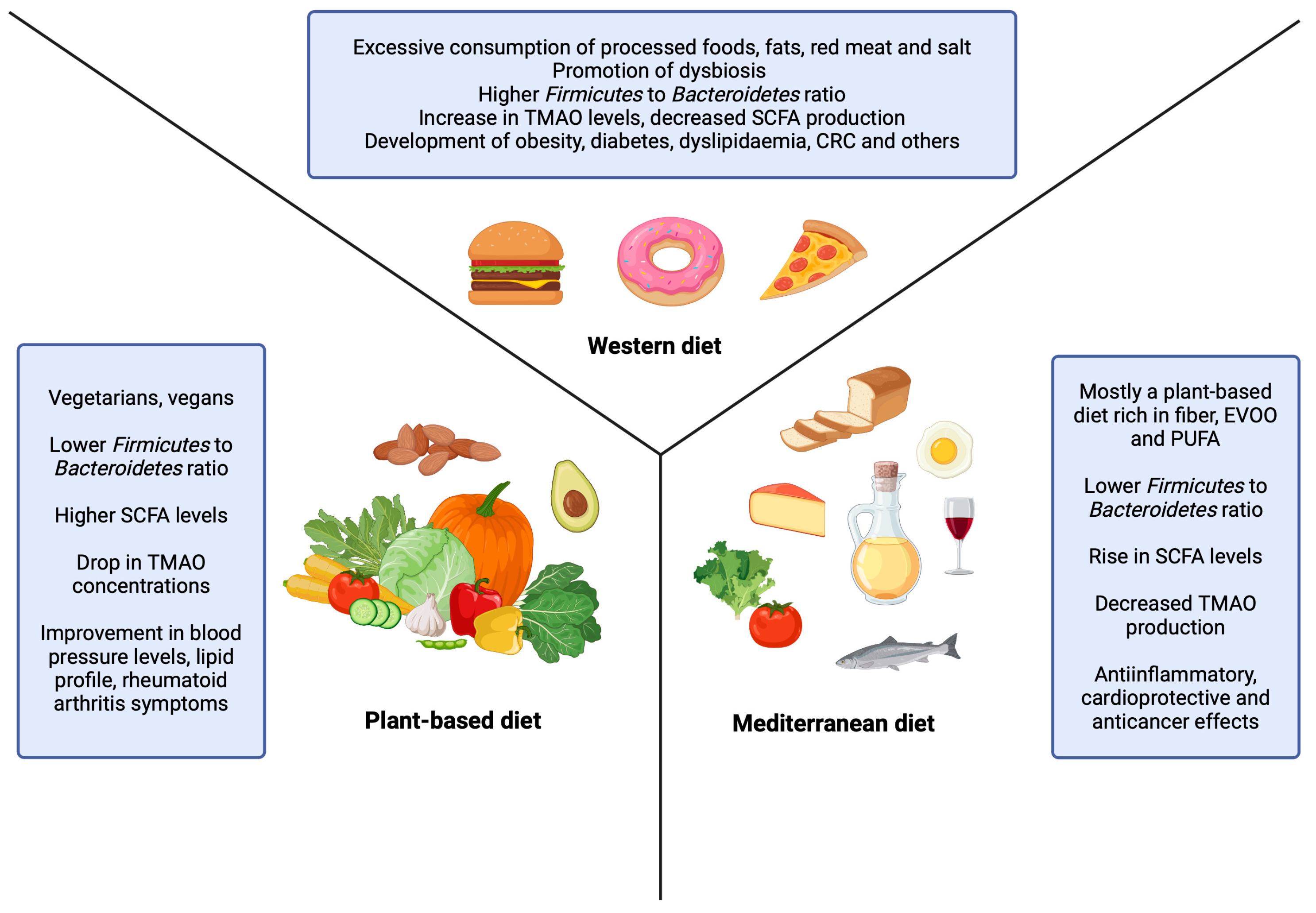
7.1. Plant-Based Diet
7.2. Mediterranean Diet
7.3. Western Diet
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thursby, E.; Juge, N. Introduction to the human gut microbiota. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 1823–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, E.; Zilber-Rosenberg, I. Microbes Drive Evolution of Animals and Plants: The Hologenome Concept. mBio 2016, 7, e01395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anhê, F.F.; Barra, N.G.; Schertzer, J.D. Glucose alters the symbiotic relationships between gut microbiota and host physiology. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 318, E111–E116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Li, R.; Raes, J.; Arumugam, M.; Burgdorf, K.S.; Manichanh, C.; Nielsen, T.; Pons, N.; Levenez, F.; Yamada, T.; et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 2010, 464, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvucci, E. The human-microbiome superorganism and its modulation to restore health. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 70, 781–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hugon, P.; Dufour, J.C.; Colson, P.; Fournier, P.E.; Sallah, K.; Raoult, D. A comprehensive repertoire of prokaryotic species identified in human beings. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Montero, C.; Fraile-Martínez, O.; Gómez-Lahoz, A.M.; Pekarek, L.; Castellanos, A.J.; Noguerales-Fraguas, F.; Coca, S.; Guijarro, L.G.; García-Honduvilla, N.; Asúnsolo, A.; et al. Nutritional Components in Western Diet Versus Mediterranean Diet at the Gut Microbiota-Immune System Interplay. Implications for Health and Disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hills, R.D., Jr.; Pontefract, B.A.; Mishcon, H.R.; Black, C.A.; Sutton, S.C.; Theberge, C.R. Gut Microbiome: Profound Implications for Diet and Disease. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cena, H.; Calder, P.C. Defining a Healthy Diet: Evidence for The Role of Contemporary Dietary Patterns in Health and Disease. Nutrients 2020, 12, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beam, A.; Clinger, E.; Hao, L. Effect of Diet and Dietary Components on the Composition of the Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berding, K.; Vlckova, K.; Marx, W.; Schellekens, H.; Stanton, C.; Clarke, G.; Jacka, F.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Diet and the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis: Sowing the Seeds of Good Mental Health. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 1239–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wastyk, H.C.; Fragiadakis, G.K.; Perelman, D.; Dahan, D.; Merrill, B.D.; Yu, F.B.; Topf, M.; Gonzalez, C.G.; Van Treuren, W.; Han, S.; et al. Gut-microbiota-targeted diets modulate human immune status. Cell 2021, 184, 4137–4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, D.R.; Tapsell, L.C.; Temple, N.J. Food Synergy: The Key to Balancing the Nutrition Research Effort. Public Health Rev. 2011, 33, 507–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapsell, L.C.; Neale, E.P.; Satija, A.; Hu, F.B. Foods, Nutrients, and Dietary Patterns: Interconnections and Implications for Dietary Guidelines. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, J.; Ley, R. The human gut microbiome: Ecology and recent evolutionary changes. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 65, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, H.J.; Scott, K.P.; Louis, P.; Duncan, S.H. The role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arweiler, N.B.; Netuschil, L. The Oral Microbiota. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 902, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Ni, C.; Du, Z.; Yan, F. Human oral microbiota and its modulation for oral health. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 99, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Lu, X.; Nossa, C.W.; Francois, F.; Peek, R.M.; Pei, Z. Inflammation and intestinal metaplasia of the distal esophagus are associated with alterations in the microbiome. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardone, G.; Compare, D. The human gastric microbiota: Is it time to rethink the pathogenesis of stomach diseases? United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2015, 3, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bik, E.M.; Eckburg, P.B.; Gill, S.R.; Nelson, K.E.; Purdom, E.A.; Francois, F.; Perez-Perez, G.; Blaser, M.J.; Relman, D.A. Molecular analysis of the bacterial microbiota in the human stomach. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Aidy, S.; van den Bogert, B.; Kleerebezem, M. The small intestine microbiota, nutritional modulation and relevance for health. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 32, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Guryn, K.; Hubert, N.; Frazier, K.; Urlass, S.; Musch, M.W.; Ojeda, P.; Pierre, J.F.; Miyoshi, J.; Sontag, T.J.; Cham, C.M.; et al. Small Intestine Microbiota Regulate Host Digestive and Absorptive Adaptive Responses to Dietary Lipids. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckburg, P.B.; Bik, E.M.; Bernstein, C.N.; Purdom, E.; Dethlefsen, L.; Sargent, M.; Gill, S.R.; Nelson, K.E.; Relman, D.A. Diversity of the human intestinal microbial flora. Science 2005, 308, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arumugam, M.; Raes, J.; Pelletier, E.; Le Paslier, D.; Yamada, T.; Mende, D.R.; Fernandes, G.R.; Tap, J.; Bruls, T.; Batto, J.M.; et al. Enterotypes of the human gut microbiome. Nature 2011, 473, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariat, D.; Firmesse, O.; Levenez, F.; Guimarăes, V.; Sokol, H.; Doré, J.; Corthier, G.; Furet, J.P. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio of the human microbiota changes with age. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollister, E.B.; Gao, C.; Versalovic, J. Compositional and functional features of the gastrointestinal microbiome and their effects on human health. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.W.; Baird, P.; Davis, R.H., Jr.; Ferreri, S.; Knudtson, M.; Koraym, A.; Waters, V.; Williams, C.L. Health benefits of dietary fiber. Nutr. Rev. 2009, 67, 188–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, P.; Flint, H.J. Formation of propionate and butyrate by the human colonic microbiota. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, S.H.; Belenguer, A.; Holtrop, G.; Johnstone, A.M.; Flint, H.J.; Lobley, G.E. Reduced dietary intake of carbohydrates by obese subjects results in decreased concentrations of butyrate and butyrate-producing bacteria in feces. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa-Oliveira, R.; Fachi, J.L.; Vieira, A.; Sato, F.T.; Vinolo, M.A. Regulation of immune cell function by short-chain fatty acids. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2016, 5, e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, D.J.; Preston, T. Formation of short chain fatty acids by the gut microbiota and their impact on human metabolism. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, E.S.; Morrison, D.J.; Frost, G. Control of appetite and energy intake by SCFA: What are the potential underlying mechanisms? Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2015, 74, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Sun, M.; Chen, F.; Cao, A.T.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Yao, S.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Microbiota metabolite short-chain fatty acid acetate promotes intestinal IgA response to microbiota which is mediated by GPR43. Mucosal Immunol. 2017, 10, 946–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeler, M.; Caesar, R. Dietary lipids, gut microbiota, and lipid metabolism. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2019, 20, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canyelles, M.; Borràs, C.; Rotllan, N.; Tondo, M.; Escolà-Gil, J.C.; Blanco-Vaca, F. Gut Microbiota-Derived TMAO: A Causal Factor Promoting Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, J.G.; Milani, C.; de Giori, G.S.; Sesma, F.; van Sinderen, D.; Ventura, M. Bacteria as vitamin suppliers to their host: A gut microbiota perspective. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pompei, A.; Cordisco, L.; Amaretti, A.; Zanoni, S.; Matteuzzi, D.; Rossi, M. Folate Production by Bifidobacteria as a Potential Probiotic Property. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Kinross, J.; Burcelin, R.; Gibson, G.; Jia, W.; Pettersson, S. Host-gut microbiota metabolic interactions. Science 2012, 336, 1262–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín, L.; Miguélez, E.M.; Villar, C.J.; Lombó, F. Bioavailability of dietary polyphenols and gut microbiota metabolism: Antimicrobial properties. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 905215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Cowan, C.S.M.; Sandhu, K.V.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S.; Boehme, M.; Codagnone, M.G.; Cussotto, S.; Fulling, C.; Golubeva, A.V.; et al. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1877–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carabotti, M.; Scirocco, A.; Maselli, M.A.; Severi, C. The gut-brain axis: Interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Góralczyk-Bińkowska, A.; Szmajda-Krygier, D.; Kozłowska, E. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Psychiatric Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurilshikov, A.; Wijmenga, C.; Fu, J.; Zhernakova, A. Host Genetics and Gut Microbiome: Challenges and Perspectives. Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 633–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voreades, N.; Kozil, A.; Weir, T.L. Diet and the development of the human intestinal microbiome. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, J.E.; Spor, A.; Scalfone, N.; Fricker, A.D.; Stombaugh, J.; Knight, R.; Angenent, L.T.; Ley, R.E. Succession of microbial consortia in the developing infant gut microbiome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4578–4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizumi, T.; Battaglia, T.; Ruiz, V.; Perez Perez, G.I. Gut Microbiome and Antibiotics. Arch. Med. Res. 2017, 48, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandhyala, S.M.; Talukdar, R.; Subramanyam, C.; Vuyyuru, H.; Sasikala, M.; Nageshwar Reddy, D. Role of the normal gut microbiota. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8787–8803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, N.; Valdés-Varela, L.; González, S.; Gueimonde, M.; de Los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G. Nutrition and the gut microbiome in the elderly. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, K.; Moodley, P.; Dhanda, A.D. Alcohol’s Impact on the Gut and Liver. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litwinowicz, K.; Choroszy, M.; Waszczuk, E. Changes in the composition of the human intestinal microbiome in alcohol use disorder: A systematic review. Am. J. Drug Alcohol. Abuse. 2020, 46, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Shi, G. Smoking and microbiome in oral, airway, gut and some systemic diseases. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, R.L. A Review of the Role of the Gut Microbiome in Personalized Sports Nutrition. Front. Nutr. 2020, 6, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estaki, M.; Pither, J.; Baumeister, P.; Little, J.P.; Gill, S.K.; Ghosh, S.; Ahmadi-Vand, Z.; Marsden, K.R.; Gibson, D.L. Cardiorespiratory fitness as a predictor of intestinal microbial diversity and distinct metagenomic functions. Microbiome 2016, 4, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, E.Z. Human gut microbiota/microbiome in health and diseases: A review. Antonie Van. Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 2019–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, A.E.; Jäger, R.; Carpenter, K.C.; Kerksick, C.M.; Purpura, M.; Townsend, J.R.; West, N.P.; Black, K.; Gleeson, M.; Pyne, D.B.; et al. The athletic gut microbiota. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2020, 17, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syromyatnikov, M.; Nesterova, E.; Gladkikh, M.; Smirnova, Y.; Gryaznova, M.; Popov, V. Characteristics of the Gut Bacterial Composition in People of Different Nationalities and Religions. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costea, P.I.; Hildebrand, F.; Arumugam, M.; Bäckhed, F.; Blaser, M.J.; Bushman, F.D.; de Vos, W.M.; Ehrlich, S.D.; Fraser, C.M.; Hattori, M.; et al. Enterotypes in the landscape of gut microbial community composition. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adak, A.; Maity, C.; Ghosh, K.; Pati, B.R.; Mondal, K.C. Dynamics of predominant microbiota in the human gastrointestinal tract and change in luminal enzymes and immunoglobulin profile during high-altitude adaptation. Folia Microbiol. 2013, 58, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, C.; Stojanović, O.; Colin, D.J.; Suarez-Zamorano, N.; Tarallo, V.; Veyrat-Durebex, C.; Rigo, D.; Fabbiano, S.; Stevanović, A.; Hagemann, S.; et al. Gut Microbiota Orchestrates Energy Homeostasis during Cold. Cell 2015, 163, 1360–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shreiner, A.B.; Kao, J.Y.; Young, V.B. The gut microbiome in health and disease. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2015, 31, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, Y.; Muniz Pedrogo, D.A.; Kashyap, P.C. Irritable bowel syndrome: A gut microbiota-related disorder? Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2017, 312, G52–G62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittayanon, R.; Lau, J.T.; Yuan, Y.; Leontiadis, G.I.; Tse, F.; Surette, M.; Moayyedi, P. Gut Microbiota in Patients With Irritable Bowel Syndrome—A Systematic Review. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabián, O.; Kamaradová, K. Morphology of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD). Morfologie zánětlivých střevních onemocnění (IBD). Cesk Patol. 2022, 58, 27–37. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, E.R.; Zisman, T.L.; Suskind, D.L. The microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease: Current and therapeutic insights. J. Inflamm. Res. 2017, 10, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittayanon, R.; Lau, J.T.; Leontiadis, G.I.; Tse, F.; Yuan, Y.; Surette, M.; Moayyedi, P. Differences in Gut Microbiota in Patients With vs Without Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Systematic Review. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 930–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaglio, A.E.V.; Grillo, T.G.; De Oliveira, E.C.S.; Di Stasi, L.C.; Sassaki, L.Y. Gut microbiota, inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 4053–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, A.W.; Hoyles, L. Human microbiome myths and misconceptions. Nat. Microbiol. 2023, 8, 1392–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeGruttola, A.K.; Low, D.; Mizoguchi, A.; Mizoguchi, E. Current Understanding of Dysbiosis in Disease in Human and Animal Models. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 1137–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhao, X.; Sun, L.; Liu, Y.; Lv, Y.; Gang, X.; Wang, G. Gut Microbiota Profile in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Based on 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing: A Systematic Review. Dis. Markers 2020, 2020, 3936247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Chen, H.; Tao, S.; Zhang, Z. Implication of the gut microbiome composition of type 2 diabetic patients from northern China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, L. Role and Mechanism of Gut Microbiota in Human Disease. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 625913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, F.; Liang, S.; Zhang, W.; Guan, Y.; Shen, D.; et al. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 2012, 490, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurung, M.; Li, Z.; You, H.; Rodrigues, R.; Jump, D.B.; Morgan, A.; Shulzhenko, N. Role of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes pathophysiology. eBioMedicine 2020, 51, 102590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Sun, B.; Yu, D.; Zhu, C. Gut Microbiota: An Important Player in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 834485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westfall, S.; Lomis, N.; Kahouli, I.; Dia, S.Y.; Singh, S.P.; Prakash, S. Microbiome, probiotics, and neurodegenerative diseases: Deciphering the gut-brain axis. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 3769–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megur, A.; Baltriukienė, D.; Bukelskienė, V.; Burokas, A. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis and Alzheimer’s Disease: Neuroinflammation Is to Blame? Nutrients 2020, 13, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattorusso, A.; Di Genova, L.; Dell’Isola, G.B.; Mencaroni, E.; Esposito, S. Autism Spectrum Disorders and the Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2019, 11, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, M.; Weeks, T.L.; Hazen, S.L. Gut Microbiota and Cardiovascular Disease. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 553–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostfeld, R.J. Definition of a plant-based diet and overview of this special issue. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, S.M.; Raposo, A.; Saraiva, A.; Zandonadi, R.P. Vegetarian Diet: An Overview through the Perspective of Quality of Life Domains. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimble, R.; Gouinguenet, P.; Ashor, A.; Stewart, C.; Deighton, K.; Matu, J.; Griffiths, A.; Malcomson, F.C.; Joel, A.; Houghton, D.; et al. Effects of a Mediterranean diet on the gut microbiota and microbial metabolites: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials and observational studies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 8698–8719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merra, G.; Noce, A.; Marrone, G.; Cintoni, M.; Tarsitano, M.G.; Capacci, A.; De Lorenzo, A. Influence of Mediterranean Diet on Human Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2020, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baliou, S.; Ioannou, P.; Apetroaei, M.-M.; Vakonaki, E.; Fragkiadaki, P.; Kirithras, E.; Tzatzarakis, M.N.; Arsene, A.L.; Docea, A.O.; Tsatsakis, A. The Impact of the Mediterranean Diet on Telomere Biology: Implications for Disease Management—A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrera-Bastos, P.; Fontes-Villalba, M.; O’Keefe, J.H.; Lindeberg, S.; Cordain, L. The Western diet and lifestyle and diseases of civilization. Res. Rep. Clin. Cardiol. 2011, 2, 15–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varlamov, O. Western-style diet, sex steroids, and metabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malesza, I.J.; Malesza, M.; Walkowiak, J.; Mussin, N.; Walkowiak, D.; Aringazina, R.; Bartkowiak-Wieczorek, J.; Mądry, E. High-Fat, Western-Style Diet, Systemic Inflammation, and Gut Microbiota: A Narrative Review. Cells 2021, 10, 3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, S.R.K.; Kok, C.W.; Kunasegaran, T.; Ramadas, A. Effect of Plant-Based Diets on Gut Microbiota: A Systematic Review of Interventional Studies. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, L.A.; Maurice, C.F.; Carmody, R.N.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Button, J.E.; Wolfe, B.E.; Ling, A.V.; Devlin, A.S.; Varma, Y.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature 2014, 505, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crimarco, A.; Springfield, S.; Petlura, C.; Streaty, T.; Cunanan, K.; Lee, J.; Fielding-Singh, P.; Carter, M.M.; Topf, M.A.; Wastyk, H.C.; et al. A randomized crossover trial on the effect of plant-based compared with animal-based meat on trimethylamine-N-oxide and cardiovascular disease risk factors in generally healthy adults: Study With Appetizing Plantfood-Meat Eating Alternative Trial (SWAP-MEAT). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 1188–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djekic, D.; Shi, L.; Brolin, H.; Carlsson, F.; Särnqvist, C.; Savolainen, O.; Cao, Y.; Bäckhed, F.; Tremaroli, V.; Landberg, R.; et al. Effects of a Vegetarian Diet on Cardiometabolic Risk Factors, Gut Microbiota, and Plasma Metabolome in Subjects With Ischemic Heart Disease: A Randomized, Crossover Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, 016518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahleova, H.; Rembert, E.; Alwarith, J.; Yonas, W.N.; Tura, A.; Holubkov, R.; Agnello, M.; Chutkan, R.; Barnard, N.D. Effects of a Low-Fat Vegan Diet on Gut Microbiota in Overweight Individuals and Relationships with Body Weight, Body Composition, and Insulin Sensitivity. A Randomized Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, H.L.; Gomez-Arango, L.F.; Wilkinson, S.A.; McIntyre, H.D.; Callaway, L.K.; Morrison, M.; Dekker Nitert, M. A Vegetarian Diet Is a Major Determinant of Gut Microbiota Composition in Early Pregnancy. Nutrients 2018, 10, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, M.; Vishnubhotla, R.; Ramay, H.R.; Gonçalves, M.C.B.; Shin, A.S.; Pawale, D.; Subramaniam, B.; Sadhasivam, S. Isha yoga practices, vegan diet, and participation in Samyama meditation retreat: Impact on the gut microbiome & metabolome—A non-randomized trial. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2023, 23, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisanu, S.; Palmas, V.; Madau, V.; Casula, E.; Deledda, A.; Cusano, R.; Uva, P.; Vascellari, S.; Boi, F.; Loviselli, A.; et al. Impact of a Moderately Hypocaloric Mediterranean Diet on the Gut Microbiota Composition of Italian Obese Patients. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meslier, V.; Laiola, M.; Roager, H.M.; De Filippis, F.; Roume, H.; Quinquis, B.; Giacco, R.; Mennella, I.; Ferracane, R.; Pons, N.; et al. Mediterranean diet intervention in overweight and obese subjects lowers plasma cholesterol and causes changes in the gut microbiome and metabolome independently of energy intake. Gut 2020, 69, 1258–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinott, E.; Meir, A.Y.; Tsaban, G.; Zelicha, H.; Kaplan, A.; Knights, D.; Tuohy, K.; Scholz, M.U.; Koren, O.; Stampfer, M.J.; et al. The effects of the Green-Mediterranean diet on cardiometabolic health are linked to gut microbiome modifications: A randomized controlled trial. Genome Med. 2022, 14, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picchianti Diamanti, A.; Panebianco, C.; Salerno, G.; Di Rosa, R.; Salemi, S.; Sorgi, M.L.; Meneguzzi, G.; Mariani, M.B.; Rai, A.; Iacono, D.; et al. Impact of Mediterranean Diet on Disease Activity and Gut Microbiota Composition of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Wang, F.; Yuan, J.; Li, J.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Wang, R.; Tang, J.; Huang, T. Effects of dietary fat on gut microbiota and faecal metabolites, and their relationship with cardiometabolic risk factors: A 6-month randomized controlled-feeding trial. Gut 2019, 68, 1417–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanegas, S.M.; Meydani, M.; Barnett, J.B.; Goldin, B.; Kane, A.; Rasmussen, H.; Brown, C.; Vangay, P.; Knights, D.; Jonnalagadda, S. Substituting whole grains for refined grains in a 6-wk randomized trial has a modest effect on gut microbiota and immune and inflammatory markers of healthy adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 635–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Guo, X.; Wei, W.; Li, R.; Hu, K.; Liu, X.; Jiang, W.; Liu, S.; Wang, W.; Sun, H.; et al. The Association of Fried Meat Consumption With the Gut Microbiota and Fecal Metabolites and Its Impact on Glucose Homoeostasis, Intestinal Endotoxin Levels, and Systemic Inflammation: A Randomized Controlled-Feeding Trial. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 1970–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramne, S.; Brunkwall, L.; Ericson, U.; Gray, N.; Kuhnle, G.G.C.; Nilsson, P.M.; Orho-Melander, M.; Sonestedt, E. Gut microbiota composition in relation to intake of added sugar, sugar-sweetened beverages and artificially sweetened beverages in the Malmö Offspring Study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 2087–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Hwang, S.S.; Park, E.J.; Bae, J.W. Strict vegetarian diet improves the risk factors associated with metabolic diseases by modulating gut microbiota and reducing intestinal inflammation. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Mantrana, I.; Selma-Royo, M.; Alcantara, C.; Collado, M.C. Shifts on Gut Microbiota Associated to Mediterranean Diet Adherence and Specific Dietary Intakes on General Adult Population. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, J.; Yamamoto, A.; Palermo-Conde, L.A.; Higashi, K.; Sonomoto, K.; Tan, J.; Lee, Y.K. Impact of Westernized Diet on Gut Microbiota in Children on Leyte Island. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seethaler, B.; Nguyen, N.K.; Basrai, M.; Kiechle, M.; Walter, J.; Delzenne, N.M.; Bischoff, S.C. Short-chain fatty acids are key mediators of the favorable effects of the Mediterranean diet on intestinal barrier integrity: Data from the randomized controlled LIBRE trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 116, 928–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brignardello, J.; Fountana, S.; Posma, J.M.; Chambers, E.S.; Nicholson, J.K.; Wist, J.; Frost, G.; Garcia-Perez, I.; Holmes, E. Characterization of diet-dependent temporal changes in circulating short-chain fatty acid concentrations: A randomized crossover dietary trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 116, 1368–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Filippis, F.; Pellegrini, N.; Vannini, L.; Jeffery, I.B.; La Storia, A.; Laghi, L.; Serrazanetti, D.I.; Di Cagno, R.; Ferrocino, I.; Lazzi, C.; et al. High-level adherence to a Mediterranean diet beneficially impacts the gut microbiota and associated metabolome. Gut 2016, 65, 1812–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bergeron, N.; Levison, B.S.; Li, X.S.; Chiu, S.; Jia, X.; Koeth, R.A.; Li, L.; Wu, Y.; Tang, W.H.W.; et al. Impact of chronic dietary red meat, white meat, or non-meat protein on trimethylamine N-oxide metabolism and renal excretion in healthy men and women. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trefflich, I.; Jabakhanji, A.; Menzel, J.; Blaut, M.; Michalsen, A.; Lampen, A.; Abraham, K.; Weikert, C. Is a vegan or a vegetarian diet associated with the microbiota composition in the gut? Results of a new cross-sectional study and systematic review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2990–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losno, E.A.; Sieferle, K.; Perez-Cueto, F.J.A.; Ritz, C. Vegan Diet and the Gut Microbiota Composition in Healthy Adults. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luisi, M.L.E.; Lucarini, L.; Biffi, B.; Rafanelli, E.; Pietramellara, G.; Durante, M.; Vidali, S.; Provensi, G.; Madiai, S.; Gheri, C.F.; et al. Effect of Mediterranean Diet Enriched in High Quality Extra Virgin Olive Oil on Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Gut Microbiota in Obese and Normal Weight Adult Subjects. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, L.; Molinari, R.; Farinon, B.; Merendino, N. Impact of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on the Gut Microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, D. Health Benefits of Mediterranean Diet. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, D.; Whelan, K.; Rossi, M.; Morrison, M.; Holtmann, G.; Kelly, J.T.; Shanahan, E.R.; Staudacher, H.M.; Campbell, K.L. Dietary fiber intervention on gut microbiota composition in healthy adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 107, 965–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, T.M.; Kabisch, S.; Pfeiffer, A.F.H.; Weickert, M.O. The Effects of the Mediterranean Diet on Health and Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Ming, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Lin, Z.; Gao, F.; Zhu, Y. Effect of Fibre-Rich Diet and Rope Skipping on Memory, Executive Function, nad Gut Microbiota in Young Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2024, 68, e2300673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinöcker, M.K.; Lindseth, I.A. The Western Diet-Microbiome-Host Interaction and Its Role in Metabolic Disease. Nutrients 2018, 10, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolters, M.; Ahrens, J.; Romaní-Pérez, M.; Watkins, C.; Sanz, Y.; Benítez-Páez, A.; Stanton, C.; Günther, K. Dietary fat, the gut microbiota, and metabolic health—A systematic review conducted within the MyNewGut project. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 2504–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Ghazaleh, N.; Chua, W.J.; Gopalan, V. Intestinal microbiota and its association with colon cancer and red/processed meat consumption. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 36, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Dietary Type | Sample | Study Groups | Main Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant-based | 31 participants, with ischemic heart disease | 16 individuals followed a vegetarian diet (94% men, median age of 67 years), 15 followed a meat diet (93% men, median age of 68 years) | ↑ Ruminococcaceae, Akkermansiaceae, and Lachnospiraceae in individuals following a vegetarian diet | [91] |
| Plant-based | 168 overweight participants | 84 individuals followed a vegan diet (82% women, mean age of 52.9 years), 84 were in the control group (88% women, mean age of 57.5 years) | ↑ Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, and ↓ Bacteroides fragilis in individuals following a vegan diet | [92] |
| Plant-based | 27 pregnant women | 9 women followed a vegetarian diet (mean age of 33 years), 18 were omnivorous (mean age of 34 years) | ↑ Roseburia and Lachnospiraceae ↓ Collinsella and Holdemania in vegetarian women | [93] |
| Plant-based | 288 participants | 265 individuals followed a vegan diet and meditation (139 women, mean age of 40.9 years), 23 were in the control group (13 men, mean age of 42 years) | ↑ Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus, Streptococcus, Collinsella, and Ruminococcaceae in individuals following a vegan diet | [94] |
| Mediterranean | 69 participants | 23 obese individuals followed a hypocaloric MD (20 women, mean age of 53 years), 46 were normal-weight individuals (40 women, mean age of 49 years) | ↓ Firmicutes ↑ Bacteroidetes and Proteobacteria in obese individuals following hypocaloric MD | [95] |
| Mediterranean | 82 overweight and obese participants | 43 individuals followed MD, 39 followed a regular diet (43 women, 39 men, mean age of 43 years) | ↑ Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, Lachnospiraceae, and Roseburia in individuals following MD | [96] |
| Mediterranean | 294 participants with dyslipidemia or abdominal obesity | 96 individuals followed healthy dietary guidelines (88% men, mean age of 51.34 years), 95 MD (87.5% men, mean age of 51.74 years), 95 Green MD (89.5% men, mean age 50.68 years) | ↑ Prevotella and ↓ Bifidobacterium in individuals following MD and Green MD | [97] |
| Mediterranean | 60 participants with rheumatoid arthritis | 20 individuals adhered highly to an MD (100% women, mean age 66 years), 40 had low or moderate adherence to an MD (75% women, mean age of 59.5 years) | ↓ Lactobacillaceae and Prevotella copri in individuals with higher adherence to an MD | [98] |
| Western | 307 healthy participants | Individuals were divided into 3 groups based on fat intake, a 1:1:1 ratio (age between 18 and 35 years, 52% were women) | ↓ Faecalibacterium, ↑ Bacteroides and Alistipes in individuals following a high-fat diet | [99] |
| Western | 81 participants | 40 individuals consumed refined grains (25 men, mean age of 54 years), 41 consumed whole grains (24 men, mean age of 55 years) | ↑ Lachnospira and ↓ Enterobacteriaceae in individuals consuming whole grains instead of refined grains | [100] |
| Western | 117 overweight participants | 59 individuals ate fried meat 4 times/week (55.9% women, mean age of 21.1 years) 58 had limited intake of fried meat (53.5% women, mean age of 21.7 years) | ↑ Veillonella, Dorea, and Dialister ↓ Flavonifractor and Lachnospiraceae in individuals, who consumed fried meat | [101] |
| Western | 1371 participants | 1371 individuals consumed added sugars (577 with urinary sugar biomarker), 1086 sugar-sweetened beverages (SSBs), 1085 artificially sweetened beverages (ASBs), aged between 18 and 70 years | ↓ Lachnobacterium, increased Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio in individuals consuming sugar-sweetened beverages | [102] |
| Plant-Based Diet | Mediterranean Diet | Western Diet | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio | ↓ [103] | ↓ [104] | ↑ [105] |
| SCFA production | ↑ [89] | ↑ [106] | ↓ [107] |
| TMAO production | ↓ [90] | ↓ [108] | ↑ [109] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soldán, M.; Argalášová, Ľ.; Hadvinová, L.; Galileo, B.; Babjaková, J. The Effect of Dietary Types on Gut Microbiota Composition and Development of Non-Communicable Diseases: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3134. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183134
Soldán M, Argalášová Ľ, Hadvinová L, Galileo B, Babjaková J. The Effect of Dietary Types on Gut Microbiota Composition and Development of Non-Communicable Diseases: A Narrative Review. Nutrients. 2024; 16(18):3134. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183134
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoldán, Martin, Ľubica Argalášová, Lucia Hadvinová, Bonzel Galileo, and Jana Babjaková. 2024. "The Effect of Dietary Types on Gut Microbiota Composition and Development of Non-Communicable Diseases: A Narrative Review" Nutrients 16, no. 18: 3134. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183134
APA StyleSoldán, M., Argalášová, Ľ., Hadvinová, L., Galileo, B., & Babjaková, J. (2024). The Effect of Dietary Types on Gut Microbiota Composition and Development of Non-Communicable Diseases: A Narrative Review. Nutrients, 16(18), 3134. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183134







