Interdependence of Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Myopia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Myopia and Its Consequences
4. Myopia Correction Methods and Their Impact on the Defect Progression
5. Effect of Diet on the Progression of Myopia
5.1. Macronutrients
5.2. Micronutrients
6. Lifestyle and the Progression of Myopia
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, Q.; Verhoeven, V.J.M.; Wojciechowski, R.; Barathi, V.A.; Hysi, P.G.; Guggenheim, J.A.; Höhn, R.; Vitart, V.; Khawaja, A.P.; Yamashiro, K.; et al. Meta-Analysis of Gene-Environment-Wide Association Scans Accounting for Education Level Identifies Additional Loci for Refractive Error. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holden, B.A.; Fricke, T.R.; Wilson, D.A.; Jong, M.; Naidoo, K.S.; Sankaridurg, P.; Wong, T.Y.; Naduvilath, T.; Resnikoff, S. Global Prevalence of Myopia and High Myopia and Temporal Trends from 2000 through 2050. Ophthalmology 2016, 123, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harb, E.N.; Wildsoet, C.F. Nutritional Factors and Myopia: An Analysis of National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2021, 98, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojciechowski, R.; Hysi, P.G. Focusing in on the Complex Genetics of Myopia. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.M.; Chang, D.S.T.; Wu, P.C. The Association between Near Work Activities and Myopia in Children—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.K.; Lee, J.H.; Kakizaki, H.; Jee, D. Prevalence of myopia and its association with body stature and educational level in 19-year-old male conscripts in Seoul, South Korea. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 5579–5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, I.; Rose, K. How genetic is school myopia? Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2005, 24, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.chinanews.com.cn/sh/2019/04-29/8823606.shtml (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- Williams, K.M.; Verhoeven, V.J.M.; Cumberland, P.; Bertelsen, G.; Wolfram, C.; Buitendijk, G.H.S.; Hofman, A.; van Duijn, C.M.; Vingerling, J.R.; Kuijpers, R.W.A.M.; et al. Prevalence of refractive error in Europe: The European Eye Epidemiology (E(3)) Consortium. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 30, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Group* TEDPR. The prevalence of refractive errors among adults in the United States, Western Europe, and Australia. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2004, 122, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Sheng, Y.; Wang, G.; Liu, J. Association Between Physical Indicators and Myopia in American Adolescents: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999–2008. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 260, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidoo, K.S.; Fricke, T.R.; Frick, K.D.; Jong, M.; Naduvilath, T.J.; Resnikoff, S.; Sankaridurg, P. Potential Lost Productivity Resulting from the Global Burden of Myopia: Systematic Review, Meta-analysis, and Modeling. Ophthalmology 2019, 126, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfield, M. COVID-19 and myopia. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2022, 42, 255–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Musch, D.C.; Wei, N.; Qi, X.; Ding, G.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Song, L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Progression of Myopia in School-Aged Children after COVID-19 Home Confinement. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2021, 139, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, K.L.; Lu, Q.; Tan, D.; Chia, A. Risk factors for progressive myopia in the atropine therapy for myopia study. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 159, 945–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, A.; Chua, W.H.; Cheung, Y.B.; Wong, W.L.; Lingham, A.; Fong, A.; Tan, D. Atropine for the treatment of childhood myopia: Safety and efficacy of 0.5%, 0.1%, and 0.01% doses (Atropine for the Treatment of Myopia 2). Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojciechowski, R.; Cheng, C.Y. Involvement of multiple molecular pathways in the genetics of ocular refraction and myopia. Retina 2018, 38, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malinowski, A.; Mrugacz, M.; Stopa, M.; Filipek, E.; Moniuszko-Malinowska, A.; Czupryna, P. A Clinical Study of the Impact of Soft Contact Lenses on the Progression of Myopia in Young Patients. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2022, 16, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walline, J.J.; Greiner, K.L.; McVey, M.E.; Jones-Jordan, L.A. Multifocal contact lens myopia control. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2013, 90, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varnas, S.; Gu, X.; Metcalfe, A. Bayesian meta-analysis of myopia control with multifocal lenses. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedir, J.; Girma, A. Prevalence of refractive error and visual impairment among rural school-age children of Goro District, Gurage Zone, Ethiopia. Ethiop. J. Health Sci. 2014, 24, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, K.; Yang, D.Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.R.; Jing, X.X.; Guo, Y.Y.; Zhu, D.; You, Q.S.; Tao, Y.; Jonas, J.B. Prevalence of myopia in schoolchildren in Ejina: The Gobi Desert Children Eye Study. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 1769–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.J.; You, Q.S.; Duan, J.L.; Luo, Y.X.; Liu, L.J.; Li, X.; Gao, Q.; Zhu, H.P.; He, Y.; Xu, L.; et al. Prevalence and associated factors of myopia in high-school students in Beijing. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Yokoi, T.; Nagaoka, N.; Shinohara, K.; Onishi, Y.; Ishida, T.; Yoshida, T.; Xu, X.; Jonas, J.B.; Ohno-Matsui, K. Progression of Myopic Maculopathy during 18-Year Follow-up. Ophthalmology 2018, 125, 863–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.N.; Wang, Y.X.; Yang, Y.; Xu, L.; Xu, J.; Wang, Q.; Yang, J.Y.; Yang, X.; Zhou, W.J. Ten-Year Progression of Myopic Maculopathy: The Beijing Eye Study 2001–2011. Ophthalmology 2018, 125, 1253–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Guo, Z.; Song, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, C. Gender Difference of the Association Between Sleep Duration and Myopia Among Children and Adolescents. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2024, 16, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, D.; Sun, B.; Wu, M.; Liu, H.; Zhou, L.; Guo, L. Prevalence and associated factors of myopia among school students in Shenyang, China: A cross-sectional study. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1239158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pan, C.W.; Ramamurthy, D.; Saw, S.M. Worldwide prevalence and risk factors for myopia. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2012, 32, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, S.K.; Dannoue, M.; Kawakami, K.; Uemura, A.; Kameyama, A.T.; Hori, Y. Prevalence of Myopia and Its Associated Factors Among Japanese Preschool Children. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 901480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, K.M.; Bentham, G.C.G.; Young, I.S.; McGinty, A.; McKay, G.J.; Hogg, R.; Hammond, C.J.; Chakravarthy, U.; Rahu, M.; Seland, J.; et al. Association Between Myopia, Ultraviolet B Radiation Exposure, Serum Vitamin D Concentrations, and Genetic Polymorphisms in Vitamin D Metabolic Pathways in a Multicountry European Study. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2017, 135, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, S.Y.L.; Ikram, M.K.; Tan, C.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Ni, Y.; Shirong, C.; Gluckman, P.D.; Chong, Y.-S.; Yap, F.; Wong, T.-Y.; et al. Growing Up in Singapore Towards Healthy Outcomes Study Group. Relative Contribution of Risk Factors for Early-Onset Myopia in Young Asian Children. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 8101–8107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkicharla, P.K.; Kammari, P.; Das, A.V. Myopia progression varies with age and severity of myopia. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosner, M.; Laor, A.; Belkin, M. Myopia and Stature: Findings in a Population of 106,926 Males. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 1995, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonas, J.B.; Ang, M.; Cho, P.; Guggenheim, J.A.; He, M.G.; Jong, M.; Logan, N.S.; Liu, M.; Morgan, I.; Ohno-Matsui, K.; et al. Prevention of Myopia and Its Progression. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2021, 62, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryl, A.; Mrugacz, M.; Mariak, Z.; Krajewska, M. Blood flow in vessels supplying the eye in persons with degenerative myopia. Part I. Blood flow in the ophthalmic artery. KlinOczna 2013, 115, 217–221. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Bryl, A.; Mrugacz, M.; Mariak, Z. Blood flow in vessels supplying the eye in persons with degenerative myopia. Part II. Blood flow in the central retinal artery. KlinOczna 2013, 115, 222–225. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Mrugacz, M.; Bryl, A. Evaluation of the arterial blood flow parameters in the eye of myopic patients. Pol. MerkurLekarski 2013, 34, 205–209. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Santodomingo-Rubido, J.; Villa-Collar, C.; Gilmartin, B.; Gutiérrez-Ortega, R. Myopia control with orthokeratology contact lenses in Spain: Refractive and biometric changes. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 5060–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haarman, A.E.G.; Enthoven, C.A.; Tideman, J.W.L.; Tedja, M.S.; Verhoeven, V.J.M.; Klaver, C.C.W. The Complications of Myopia: A Review and Meta-Analysis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.H.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.X.; Wang, S.; You, Q.S.; Jonas, J.B. Prevalence and progression of myopic retinopathy in Chinese adults: The Beijing Eye Study. Ophthalmology 2010, 117, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.Q.; Liu, W.; Liang, Y.B.; Zhang, F.; Wang, J.J.; Peng, Y.; Wong, T.Y.; Wang, N.L.; Mitchell, P.; Friedman, D.S. Prevalence and characteristics of myopic retinopathy in a rural Chinese adult population: The Handan Eye Study. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2011, 129, 1199–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asakuma, T.; Yasuda, M.; Ninomiya, T.; Noda, Y.; Arakawa, S.; Hashimoto, S.; Ohno-Matsui, K.; Kiyohara, Y.; Ishibashi, T. Prevalence and risk factors for myopic retinopathy in a Japanese population: The Hisayama Study. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 1760–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doshi, A.; Kreidl, K.O.; Lombardi, L.; Sakamoto, D.K.; Singh, K. Nonprogressive glaucomatous cupping and visual field abnormalities in young Chinese males. Ophthalmology 2007, 114, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fledelius, H.C. Myopia and Diabetes Mellitus with Special Reference to Adult-Onset Myopia. Acta Ophthalmol. 1986, 64, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjolie, A.K.; Goldschmidt, E. Myopia in Insulin Treated Diabetes. Acta Ophthalmol. 1985, 63, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrugacz, M.; Pony-Uram, M.; Bryl, A.; Zorena, K. Current Approach to the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Cataracts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Jin, N.; Zhu, X.; Lu, D.; Jin, C.; Li, Z.; Han, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lai, D.; Liu, K.; et al. A prospective study of serum metabolomic and lipidomic changes in myopic children and adolescents. Exp. Eye Res. 2020, 199, 108182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdinest, N.; London, N.; Ovadia, H.; Levinger, N. Nitric Oxide Interaction with the Eye. Vision 2021, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vutipongsatorn, K.; Yokoi, T.; Ohno-Matsui, K. Current and emerging pharmaceutical interventions for myopia. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 103, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacher, P.; Beckman, J.S.; Liaudet, L. Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 315–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Han, X.; Guo, S.B.; Li, H.H. Gallic Acid Attenuates Angiotensin II-Induced Hypertension and Vascular Dysfunction by Inhibiting the Degradation of Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lai, J.Y.; Luo, L.J. Antioxidant Gallic Acid-Functionalized Biodegradable in Situ Gelling Copolymers for Cytoprotective Antiglaucoma Drug Delivery Systems. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 2950–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujikado, T.; Kawasaki, Y.; Fujii, J.; Taniguchi, N.; Okada, M.; Suzuki, A.; Ohmi, G.; Tano, Y. The effect of nitric oxide synthase inhibitor on form-deprivation myopia. Curr. Eye Res. 1997, 16, 992–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorena, K.; Gładysiak, A.; Ślęzak, D. Early Intervention and Nonpharmacological Therapy of Myopia in Young Adults. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 2018, 4680603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiti, R.; Shyangbo, R.; Sharma, I.P.; Dahal, M. Review on current concepts of myopia and its control strategies. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 14, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holden, B.A.; Sankaridurg, P.R.; de la Jara, P.L.; Naduvilath, T.; Ho, A.; Sweeney, D.F.; Markoulli, M.; Smith, E.L., III; Ge, J. Decreasing peripheral hyperopia with distance centre relatively plus powered periphery contact lenses reduced the rate of progress of myopia: A 5 year Vision CRC study. Investig. Ophthal Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 6300. [Google Scholar]
- Correction of Myopia Evaluation Trial Study Group for the Pediatric Eye Disease Investigator Group. Progressive-addition lenses versus single-vision lenses for slowing progression of myopia in children with high accommodative lag and near esophoria. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 2749–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, C.S.Y.; Tang, W.C.; Tse, D.Y.-Y.; Lee, R.P.K.; Chun, R.K.M.; Hasegawa, K.; Qi, H.; Hatanaka, T.; To, C.H. Defocus Incorporated Multiple Segments (DIMS) spectacle lenses slow myopia progression: A 2-year randomised clinical trial. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 104, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, P.; Cheung, S.W. Retardation of myopia in Orthokeratology (ROMIO) study: A 2-year randomized clinical trial. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 7077–7085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xu, F.; Zhang, T.; Liu, M.; Wang, D.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Q. Orthokeratology to control myopia progression: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124535. [Google Scholar]
- Kakita, T.; Hiraoka, T.; Oshika, T. Influence of overnight orthokeratology on axial elongation in childhood myopia. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 2170–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, P.; Tan, Q. Myopia and orthokeratology for myopia control. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2019, 102, 364–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walline, J.J.; Jones, L.A.; Sinnott, L.T. Corneal reshaping and myopia progression. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 93, 1181–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yip, B.H.K.; Tang, S.M.; Kam, K.W.; Young, A.L.; Chen, L.J.; Tham, C.C.; Pang, C.P.; et al. Age Effect on Treatment Responses to 0.05%, 0.025%, and 0.01% Atropine: Low-Concentration Atropine for Myopia Progression Study. Ophthalmology 2021, 128, 1180–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, M.Y.; Liu, J.H.; Kao, S.C.; Shiao, C.H. Comparison of the effect of atropine and cyclopentolate on myopia. Ann. Ophthalmol. 1989, 21, 180–182, 187. [Google Scholar]
- Chua, W.-H.; Balakrishnan, V.; Chan, Y.-H.; Tong, L.; Ling, Y.; Quah, B.-L.; Tan, D. Atropine for the treatment of childhood myopia. Ophthalmology 2006, 113, 2285–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Huang, Y.; Yu, S.Z.; Chen, X.J.; Yi, H.; Zeng, X.L. Therapeutic effect of atropine 1% in children with low myopia. J. AAPOS 2015, 19, 426–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.R.; Bian, H.L.; Wang, Q. Atropine 0.5% eyedrops for the treatment of children with low myopia: A randomized controlled trial. Medicine 2017, 96, e7371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, G.C. Review: Effects of nitric oxide on eye diseases and their treatment. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 17, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, A.; Chua, W.H.; Wen, L.; Fong, A.; Goon, Y.Y.; Tan, D. Atropine for the treatment of childhood myopia: Changes after stopping atropine 0.01%, 0.1% and 0.5%. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 157, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, A.; Lu, Q.S.; Tan, D. Five-year clinical trial on atropine for the treatment of myopia 2: Myopia control with atropine 0.01% eye drops. Ophthalmology 2016, 123, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walline, J.J.; Lindsley, K.; Vedula, S.S.; Cotter, S.A.; Mutti, D.O.; Twelker, J.D. Interventions to slow progression of myopia in children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 1, CD004916. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Logan, N.S.; Wolffsohn, J.S. Role of un-correction, under-correction and over-correction of myopia as a strategy for slowing myopic progression. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2020, 103, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, C.; Gan, Q.; Xu, P.; Yang, T.; Xu, J.; Cao, W.; Wang, H.; Pan, H.; Ren, Z.; Xiao, H.; et al. Dietary Patterns and Associations with Myopia in Chinese Children. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Noh, Y.H.; Jung, K.I. The Relationship between Myopia and Obesity in Adults. Korean J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 38, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Qu, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhang, H. Association between body mass index and myopia in the United States population in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys 1999 to 2008: A cross-sectional study. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lee, S.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, K.G.; Kim, J. Obesity and high myopia in children and adolescents: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0265317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, S.C.; Stack, J.; O’Dwyer, V. Risk factors associated with myopia in schoolchildren in Ireland. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 103, 1803–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tideman, J.W.L.; Polling, J.R.; Hofman, A.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Mackenbach, J.P.; Klaver, C.C. Environmental factors explain socioeconomic prevalence differences in myopia in 6-year-old children. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 102, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.; Fisch, G.; Teague, B.; Tamborlane, W.V.; Banyas, B.; Allen, K.; Savoye, M.; Rieger, V.; Taksali, S.; Barbetta, G.; et al. Prevalence of impaired glucose tolerance among children and adolescents with marked obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordain, L.; Eaton, S.B.; Brand Miller, J.; Lindeberg, S.; Jensen, C. An evolutionary analysis of the aetiology and pathogenesis of juvenile-onset myopia. Acta Ophthalmol. Scand. 2002, 80, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Wu, M.; Yi, X.; Shi, J.; Ouyang, Y.; Dong, N.; Gong, G.; Guo, L.; Zhou, L. Correlation analysis of myopia and dietary factors among primary and secondary school students in Shenyang, China. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Galvis, V.; López-Jaramillo, P.; Tello, A.; Castellanos-Castellanos, Y.A.; Camacho, P.A.; Cohen, D.D.; Gómez-Arbeláez, D.; Merayo-Lloves, J. Is myopia another clinical manifestation of insulin resistance? Med. Hypotheses 2016, 90, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furushima, M.; Imaizumi, M.; Nakatsuka, K. Changes in refraction caused by induction of acute hyperglycemia in healthy volunteers. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 1999, 43, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.B. Myopia, Sodium Chloride, and Vitreous Fluid Imbalance: A Nutritional Epidemiology Perspective. Epidemiologia 2024, 5, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kim, J.M.; Choi, Y.J. Myopia and Nutrient Associations with Age-Related Eye Diseases in Korean Adults: A Cross-Sectional KNHANES Study. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Edwards, M.H. Do variations in normal nutrition play a role in the development of myopia? Optom. Vis. Sci. 1996, 73, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.S.; Gazzard, G.; Low, Y.-L.; Choo, R.; Tan, D.T.; Tong, L.; Wong, T.Y.; Saw, S.-M. Dietary Factors, Myopia, and Axial Dimensions in Children. Ophthalmology 2010, 117, 993–997.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berticat, C.; Mamouni, S.; Ciais, A.; Villain, M.; Raymond, M.; Daien, V. Probability of myopia in children with high refined carbohydrates consumption in France. BMC Ophthalmol. 2020, 20, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, P.A. Dietary treatment of myopia in children. Lancet 1958, 1, 1152–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Choi, Y.J. Nutritional intake, environmental factors, and their impact on myopia prevalence in Korean children aged 5–12 years. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2024, 43, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, M.; Tan, C.; Foo, L.; Sugianto, R.; Toh, J.Y.; Sun, C.; Yap, F.; Sabanayagam, C.; Chong, F.M.; Saw, S. Dietary intake and associations with myopia in Singapore children. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2022, 42, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Gao, F.; Jin, N.; Wang, D.; Wang, B.; Du, B.; Wei, R. Association between whole-grain intake and myopia in chinese children: A cross-sectional epidemiological study. BMC Ophthalmol. 2023, 23, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pan, M.; Zhao, F.; Xie, B.; Wu, H.; Zhang, S.; Ye, C.; Guan, Z.; Kang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; et al. Dietary ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids are protective for myopia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2104689118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limbu, R.; Cottrell, G.S.; McNeish, A.J. Characterisation of the vasodilation effects of DHA and EPA, n-3 PUFAs (fish oils), in rat aorta and mesenteric resistance arteries. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehr, K.R.; Walker, M.K. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids improve endothelial function in humans at risk for atherosclerosis: A review. Prostaglandins Other Lipid. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2018, 134, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, S.; Yang, Q.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Hao, K.; Xu, S.; Zhao, N.; Zheng, P. Association of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid intakes with juvenile myopia: A cross-sectional study based on the NHANES database. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1122773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, S.; Ye, S.; Wang, Q.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, X. Breastfeeding and myopia: A cross-sectional study of children aged 6–12 years in Tianjin, China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomi, Y.; Iwasaki-Kurashige, K.; Matsumoto, H. Therapeutic Effects of Anthocyanins for Vision and Eye Health. Molecules 2019, 24, 3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryl, A.; Falkowski, M.; Zorena, K.; Mrugacz, M. The Role of Resveratrol in Eye Diseases—A Review of the Literature. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.-N.; Zhang, X.-J.; Ling, X.-T.; Bui, C.H.-T.; Wang, Y.-M.; Ip, P.; Chu, W.-K.; Chen, L.-J.; Tham, C.C.; Yam, J.C.; et al. Vitamin D and Ocular Diseases: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, S.; Sankaridurg, P.; Naduvilath, T.; Zang, J.; Zou, H.; Zhu, J.; Lv, M.; He, X.; Xu, X. Time spent in outdoor activities in relation to myopia prevention and control: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Acta Ophthalmol. 2017, 95, 551–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Yang, J.; Yuan, J.; Du, B.; Li, T.; Wu, Q.; Yan, J.; Zhu, Y.; Meng, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. The Myopia Prevalence and Association with Physical Activity among Primary School Students Aged 6–12 Years: A Cross-Sectional Study in Tianjin, China. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2024, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nakaishi, H.H.; Matsumoto, S.T.; Hirayama, M. Effects of black current anthocyanoside intake on dark adap-tation and VDT work-induced transient refractive alteration in healthy humans. Altern. Med. Rev. 2000, 5, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nwachukwu, I.D.; Udenigwe, C.C.; Aluko, R.E. Lutein and zeaxanthin: Production technology, bioavailability, mechanisms of action, visual function, and health claim status. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 49, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.-A.; Chen, C.-S.; Wang, Y.-C.; Lin, E.-S.; Chang, C.-Y.; Chen, J.J.-Y.; Wu, M.-Y.; Lin, H.-J.; Wan, L. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Resveratrol on Human Retinal Pigment Cells and a Myopia Animal Model. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2021, 43, 716–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamarty, S.; Gupta, S.K.; Dhakal, R.; Verkicharla, P.K. Is There Any Association between Nutrition and Myopia? A Systematic Review. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2023, 100, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.C.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, Y.C. An epidemiological study of the risk factors associated with myopia in young adult men in Korea. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, S.Y.; Sabanayagam, C.; Tan, C.; Lim, L.S.; Toh, J.; Chong, Y.; Gluckman, P.D.; Yap, F.; Cheng, C.; Ngo, C.S.; et al. Diet and risk of myopia in three-year-old Singapore children: The GUSTO cohort. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2018, 101, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Kurihara, T.; Miyauchi, M.; Ishida, A.; Jiang, X.; Ikeda, S.-I.; Torii, H.; Tsubota, K. Oral crocetin administration suppressed refractive shift and axial elongation in a murine model of lens-induced myopia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Torii, H.; Fujimoto, S.; Jiang, X.; Ikeda, S.-I.; Yotsukura, E.; Koh, S.; Kurihara, T.; Nishida, K.; Tsubota, K. The Effect of Dietary Supplementation of Crocetin for Myopia Control in Children: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.M.; Choi, Y.J. Association between dietary nutrient intake and prevalence of myopia in Korean adolescents: Evidence from the 7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Front. Pediatr. 2024, 11, 1285465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Choi, J.A.; Han, K.; Park, Y.M.; La, T.Y. Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D is associated with myopia in Korean adolescents. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 2041–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutti, D.O.; Marks, A.R. Blood levels of vitamin D in teens and young adults with myopia. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2011, 88, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tideman, J.W.L.; Polling, J.R.; Voortman, T.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; Hofman, A.; Vingerling, J.R.; Franco, O.H.; Klaver, C.C.W. Low serum vitamin D is associated with axial length and risk of myopia in young children. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 31, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazar, S.; Hewitt, A.W.; Black, L.J.; McKnight, C.M.; Mountain, J.A.; Sherwin, J.C.; Oddy, W.H.; Coroneo, M.T.; Lucas, R.M.; Mackey, D.A. Myopia is associated with lower vitamin D status in young adults. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 4552–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.B.; Jang, J.; Yang, H.K.; Hwang, J.M.; Park, S.K. Prevalence and risk factors of myopia in adult Korean population: Korea national health and nutrition examination survey 2013–2014 (KNHANES VI). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Li, P.; Liu, Y.Q.; Chen, Y. Association study of the serum 25(OH)D concentration and myopia in Chinese children. Medicine 2021, 100, e26570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahyudi, D.; Reiki, W.; Hardhono, S. The Effect of Vitamin-D and Sunlight to Progressive Myopia in Students with Glasses Correction. Pak. J. Med. Health Sci. 2020, 14, 1588–1591. [Google Scholar]
- Lingham, G.; Yazar, S.; Lucas, R.M.; Walsh, J.P.; Zhu, K.; Hunter, M.; Lim, E.M.; Cooke, B.R.; Mackey, D.A. Low 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentration Is Not Associated With Refractive Error in Middle-Aged and Older Western Australian Adults. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2019, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lin, H.; Jiang, L.; Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Lu, F. Low Serum Vitamin D Is Not Correlated with Myopia in Chinese Children and Adolescents. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 809787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imdad, A.; Mayo-Wilson, E.; Herzer, K.; Bhutta, Z.A. Vitamin A supplementation for preventing morbidity and mortality in children from six months to five years of age. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 3, CD008524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, C.; Foster, A. Childhood blindness in the context of VISION 2020–the right to sight. Bull. World Health Organ. 2001, 79, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mayo-Wilson, E.; Imdad, A.; Herzer, K.; Yakoob, M.Y.; Bhutta, Z.A. Vitamin A supplements for preventing mortality, illness, and blindness in children aged under 5: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2011, 343, d5094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, F.J.; Mackey, D.A.; O’Sullivan, T.A.; Oddy, W.H.; Yazar, S. Is Dietary Vitamin A Associated with Myopia from Adolescence to Young Adulthood? Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedor, M.; Socha, K.; Urban, B.; Soroczyńska, J.; Matyskiela, M.; Borawska, M.H.; Bakunowicz-Łazarczyk, A. Serum Concentration of Zinc, Copper, Selenium, Manganese, and Cu/Zn Ratio in Children and Adolescents with Myopia. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2017, 176, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. Variation analysis of six kinds of common micro-elements contents of blood in myopic primary school students in Dongguan district. Cent. Chin. Med. 2009, 1, 20–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X. Clinical significance of serum trace elements in juvenile patients with myopia. J. Huaihai Med. 2003, 4, 279–280. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, M.; Liu, H.C.J. The relationship between serum zinc, copper, selenium and the visions of middle school students. Chin. J. Sch. Health 2006, 4, 318–319. [Google Scholar]
- Burke, N.; Butler, J.S.; Flitcroft, I.; Loughman, J. The relationship between serum zinc levels and myopia. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2021, 104, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, M.; Chu, A.; Petocz, P.; Samman, S. Effect of vegetarian diets on zinc status: A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies in humans. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 2362–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sood, R.S. The prevalence of myopia Vis-à-Vis the type of diet in young adults. IJBAMS 2012, 2, 205–209. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y. Determination of select trace elements in hair of college students in Jinzhou, China. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2011, 144, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, K.A.; Morgan, I.G.; Ip, J.; Kifley, A.; Huynh, S.; Smith, W.; Mitchell, P. Outdoor activity reduces the prevalence of myopia in children. Ophthalmology 2008, 115, 1279–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Xiang, F.; Zeng, Y.; Mai, J.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, J.; Smith, W.; Rose, K.; Morgan, I.G. Effect of Time Spent Outdoors at School on the Development of Myopia Among Children in China: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2015, 314, 1142–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvis, V.; Tello, A.; Gómez, L.M.; Camacho, P.A.; Ortiz, R.G. Re: Wu et al.: Myopia prevention and outdoor light intensity in a school-based cluster randomized trial (Ophthalmology. 2018;125:1239-1250). Ophthalmology 2018, 125, e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwin, J.C.; Reacher, M.H.; Keogh, R.H.; Khawaja, A.P.; Mackey, D.A.; Foster, P.J. The association between time spent outdoors and myopia in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 2141–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, S.Y.; Weng, T.H.; Lin, C.M.; Lin, S.M. Ethnic disparity in prevalence and associated risk factors of myopia in adolescents. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2020, 119 Pt 1, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torii, H.; Kurihara, T.; Seko, Y.; Negishi, K.; Ohnuma, K.; Inaba, T.; Kawashima, M.; Jiang, X.; Kondo, S.; Miyauchi, M.; et al. Violet Light Exposure Can Be a Preventive Strategy Against Myopia Progression. eBioMedicine 2017, 15, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lan, W.; Zhang, D. Network meta-analysis of the efficacy of physical exercise interventions on vision health in children and adolescents. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1393909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chua, S.Y.; Ikram, M.K.; Tan, C.S.; Stone, R.A.; Cai, S.; Gluckman, P.D.; Yap, S.C.; Yap, F.; Wong, T.-Y.; Ngo, C.S.; et al. GUSTO Study Group. Is there a link between passive smoke exposure and early-onset myopia in preschool Asian children? Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2016, 36, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stafford-Bell, N.; McVeigh, J.; Lingham, G.; Straker, L.; Eastwood, P.R.; Yazar, S.; Mackey, D.A.; Lee, S.S. Associations of 12-year sleep behaviour trajectories from childhood to adolescence with myopia and ocular biometry during young adulthood. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2022, 42, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Chen, X.; Lin, J.; Fan, X.; Chen, T.; Yu, Y.; Chen, J.; Hu, J. Association between sleep duration and myopia among Chinese children during the COVID-19 pandemic: A cross-sectional study. Front. Public Health 2023, 10, 1015138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sensaki, S.; Sabanayagam, C.; Chua, S.; Htoon, H.M.; Broekman, B.F.P.; Thiam, D.G.Y.; Ngo, C.; Saw, S.M. Sleep duration in infants was not associated with myopia at 3 years. Asia Pac. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 7, 102–108. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.-F.; Li, S.-M.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Kang, M.-T.; Sun, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y.-P.; Yang, X.-Y.; Wang, N. Sleep duration, bedtime, and myopia progression in a 4-year follow-up of Chinese children: The anyang childhood eye study. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayaki, M.; Torii, H.; Tsubota, K.; Negishi, K. Decreased sleep quality in high myopia children. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, D.; Xiao, G.; Yu, K.; Gong, Y. Sleep less, myopia more. Theory Clin. PractPediatr. 2017, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

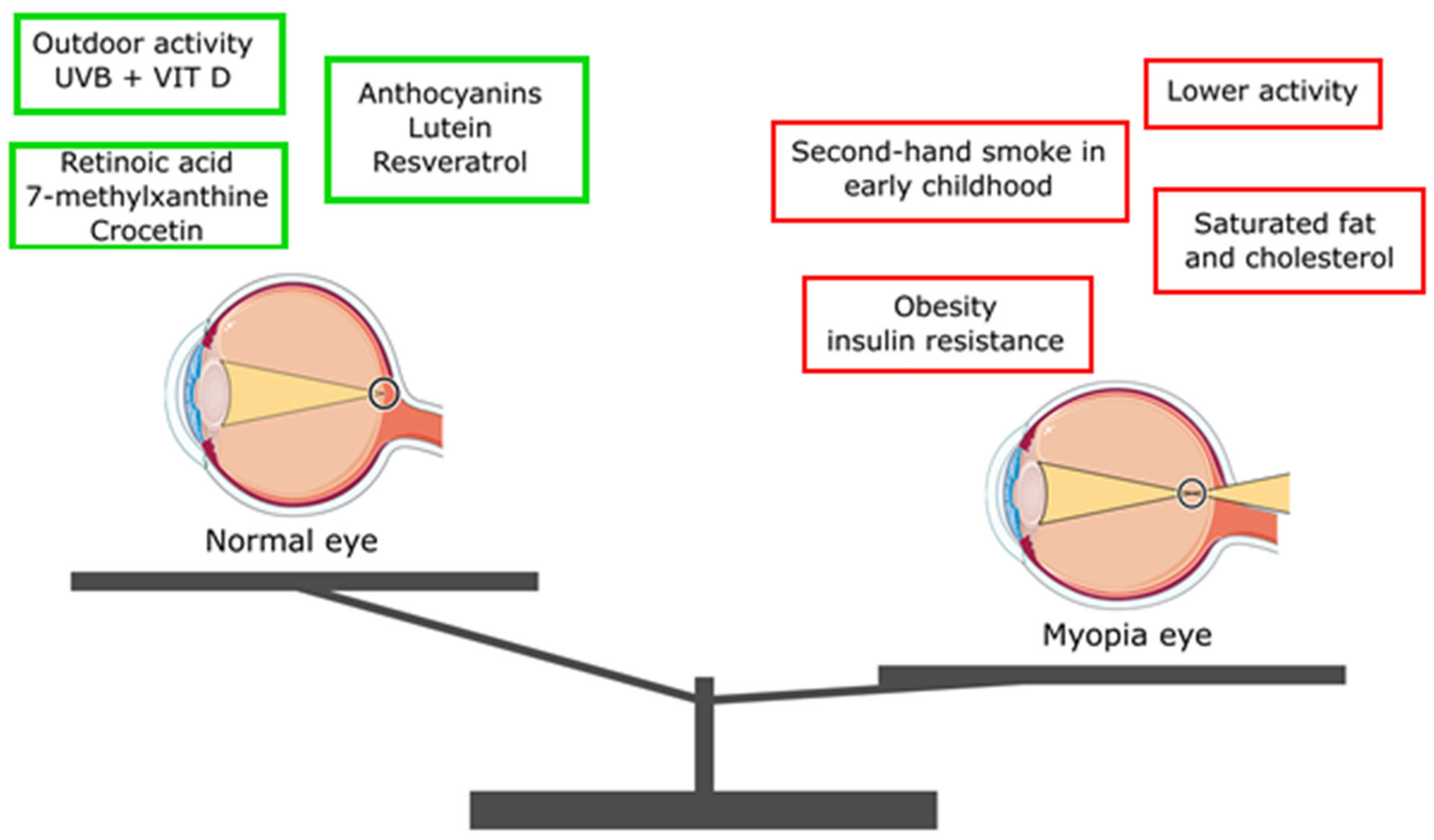
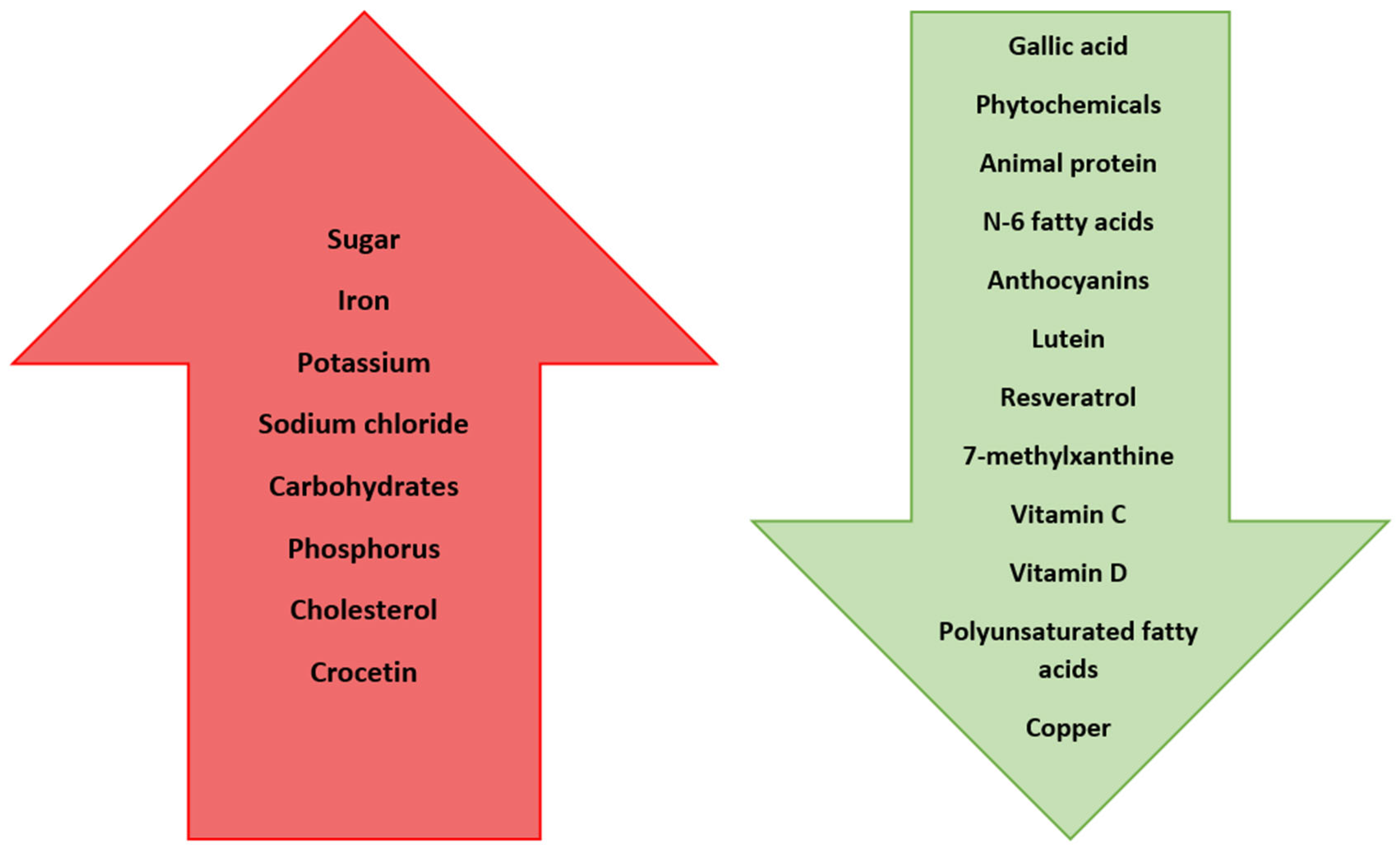
| Nutrient | Effect on Myopia Progression/Development |
|---|---|
| Gallic acid | Reduces the development of myopia by lowering oxidative stress |
| Sugar | Triggers the secretion of IGF-1, which influences cell growth and differentiation, leading to the development of myopia |
| Phytochemicals (e.g., carotenoids) | Prevent myopia development |
| Sodium chloride | Triggers fluid retention in the vitreous of the eye, which leads to myopia development |
| Iron | Elevated intake increases the risk of myopia |
| Potassium | Elevated intake increases the risk of myopia |
| Carbohydrates | Elevated intake increases the risk of myopia |
| Protein | Increasing the intake of animal protein slows down the progression of myopia; conclusions remain contradictory |
| Phosphorus | Elevated intake increases the risk of myopia |
| N-6 fatty acids | Greater intake reduces the risk of myopia |
| Cholesterol | Increased consumption increases the chance of developing myopia |
| Anthocyanins | Reduce apparent myopia |
| Lutein | Reduces the risk of myopia development by 40% |
| Resveratrol | Reduces the risk of myopia development by decreasing expression of TGF-β, MMP2, TNFα, IL-6, and IL-1β |
| 7-methylxanthine | Helps to control myopia progression |
| Crocetin | Prevents myopia development by improving choroidal circulation |
| Vitamin A | No significant associations of its effect on myopia |
| Vitamin C | Reduces the development by 38% |
| Vitamin D | Reduces myopia incidence and progression |
| Polyunsaturated fatty acids | Have protective effect against the development of myopia |
| Copper | Deficiency predisposes patients to develop myopia |
| Zinc | Inconsistent results regarding its influence on myopia development |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mrugacz, M.; Zorena, K.; Pony-Uram, M.; Lendzioszek, M.; Pieńczykowska, K.; Bryl, A. Interdependence of Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Myopia. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3331. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16193331
Mrugacz M, Zorena K, Pony-Uram M, Lendzioszek M, Pieńczykowska K, Bryl A. Interdependence of Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Myopia. Nutrients. 2024; 16(19):3331. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16193331
Chicago/Turabian StyleMrugacz, Małgorzata, Katarzyna Zorena, Magdalena Pony-Uram, Maja Lendzioszek, Kamila Pieńczykowska, and Anna Bryl. 2024. "Interdependence of Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Myopia" Nutrients 16, no. 19: 3331. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16193331
APA StyleMrugacz, M., Zorena, K., Pony-Uram, M., Lendzioszek, M., Pieńczykowska, K., & Bryl, A. (2024). Interdependence of Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Myopia. Nutrients, 16(19), 3331. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16193331







