Effects of a Carbohydrate Meal on Lipolysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Study Subjects
2.2. Intervention
2.3. Measurements
2.4. Outcomes
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Weight Loss During Carbohydrate Restriction
3.2. U-Shaped Ketosis Profile in Non-Diabetic Adults
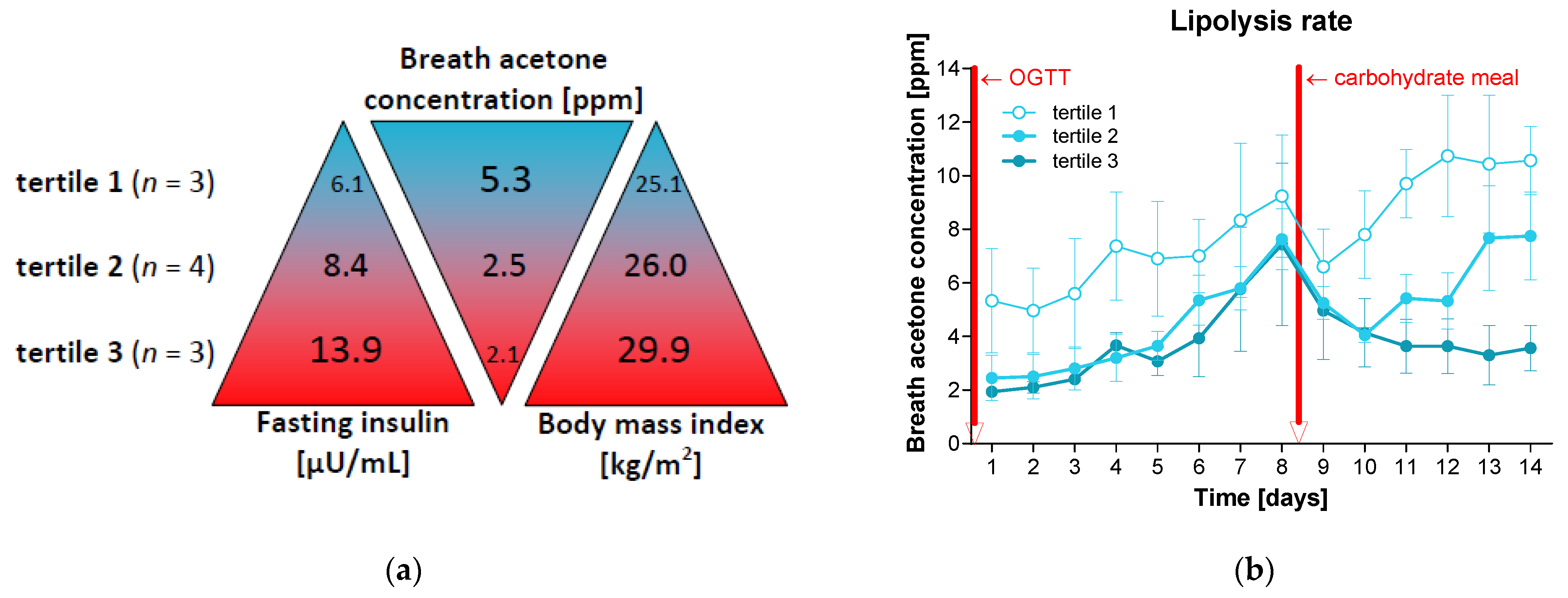
3.3. A Single Carbohydrate Meal Disturbed Lipolysis for Several Days
3.4. Increased Insulin Levels Decelerate Ketosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alman, K.L.; Lister, N.B.; Garnett, S.P.; Gow, M.L.; Aldwell, K.; Jebeile, H. Dietetic management of obesity and severe obesity in children and adolescents: A scoping review of guidelines. Obes. Rev. 2021, 1, e13132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wing, R.R. Long-term effects of a lifestyle intervention on weight and cardiovascular risk factors in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Four-year results of the Look AHEAD trial. Arch. Intern. Med. 2010, 170, 1566–1575. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lean, M.E.; Leslie, W.S.; Barnes, A.C.; Brosnahan, N.; Thom, G.; McCombie, L.; Peters, C.; Zhyzhneuskaya, S.; Al-Mrabeh, A.; Hollingsworth, K.G.; et al. Primary care-led weight management for remission of type 2 diabetes (DiRECT): An open-label, cluster-randomised trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, T.I.A.; Martinez, A.R.; Jørgensen, T.S.H. Epidemiology of Obesity. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2022, 274, 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/healthy-diet (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Razquin, C.; Sanchez-Tainta, A.; Salas-Salvado, J.; Buil-Cosiales, P.; Corella, D.; Fito, M.; Ros, E.; Estruch, R.; Aros, F.; Gomez-Gracia, E.; et al. Dietary energy density and body weight changes after 3 years in the PREDIMED study. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 68, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas-Salvado, J.; Bullo, M.; Babio, N.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Ibarrola-Jurado, N.; Basora, J.; Estruch, R.; Covas, M.I.; Corella, D.; Aros, F.; et al. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with the Mediterranean diet: Results of the PREDIMED-Reus nutrition intervention randomized trial. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estruch, R.; Ros, E.; Salas-Salvado, J.; Covas, M.I.; Corella, D.; Aros, F.; Gomez-Gracia, E.; Ruiz-Gutierrez, V.; Fiol, M.; Lapetra, J.; et al. Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease with a Mediterranean Diet Supplemented with Extra-Virgin Olive Oil or Nuts. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, M.; Mente, A.; Zhang, X.; Swaminathan, S.; Li, W.; Mohan, V.; Iqbal, R.; Kumar, R.; Wentzel-Viljoen, E.; Rosengren, A.; et al. Associations of fats and carbohydrate intake with cardiovascular disease and mortality in 18 countries from five continents (PURE): A prospective cohort study. Lancet 2017, 390, 2050–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zuuren, E.J.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Kuijpers, T.; Pijl, H. Effects of low-carbohydrate-compared with low-fat-diet interventions on metabolic control in people with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review including GRADE assessments. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 108, 300–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, S.; Hauer, B.; Becker, R.; Artzner, S.; Grauer, P.; Loblein, K.; Nielsen, M.; Renn, W.; Rett, K.; Wahl, H.G.; et al. Lipolysis in skeletal muscle is rapidly regulated by low physiological doses of insulin. Diabetologia 1999, 42, 1171–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiPilato, L.M.; Ahmad, F.; Harms, M.; Seale, P.; Manganiello, V.; Birnbaum, M.J. The Role of PDE3B Phosphorylation in the Inhibition of Lipolysis by Insulin. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 35, 2752–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrabarti, P.; Kim, J.Y.; Singh, M.; Shin, Y.K.; Kim, J.; Kumbrink, J.; Wu, Y.; Lee, M.J.; Kirsch, K.H.; Fried, S.K.; et al. Insulin inhibits lipolysis in adipocytes via the evolutionarily conserved mTORC1-Egr1-ATGL-mediated pathway. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 33, 3659–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumvoll, M.; Jacob, S.; Wahl, H.G.; Hauer, B.; Loblein, K.; Grauer, P.; Becker, R.; Nielsen, M.; Renn, W.; Häring, H. Suppression of systemic, intramuscular, and subcutaneous adipose tissue lipolysis by insulin in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 3740–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fain, J.N.; Kovacev, V.P.; Scow, R.O. Antilipolytic effect of insulin in isolated fat cells of the rat. Endocrinology 1966, 78, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergouignan, A.; Antoun, E.; Momken, I.; Schoeller, D.A.; Gauquelin-Koch, G.; Simon, C.; Blanc, S. Effect of contrasted levels of habitual physical activity on metabolic flexibility. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 114, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freese, J.; Klement, R.J.; Ruiz-Nunez, B.; Schwarz, S.; Lotzerich, H. The sedentary (r)evolution: Have we lost our metabolic flexibility? F1000Res 2017, 6, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Gerspach, A.C.; Cajacob, L.; Riva, D.; Herzog, R.; Drewe, J.; Beglinger, C.; Wolnerhanssen, B.K. Mechanisms Regulating Insulin Response to Intragastric Glucose in Lean and Non-Diabetic Obese Subjects: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Parallel-Group Trial. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, H.; Stumvoll, M.; Kramer, W.; Kempf, K.; Martin, S. Insulin translates unfavourable lifestyle into obesity. BMC Med. 2018, 16, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempf, K.; Röhling, M.; Banzer, W.; Braumann, K.M.; Halle, M.; McCarthy, D.; Predel, H.G.; Schenkenberger, I.; Tan, S.; Toplak, H.; et al. High-Protein, Low-Glycaemic Meal Replacement Decreases Fasting Insulin and Inflammation Markers-A 12-Month Subanalysis of the ACOORH Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röhling, M.; Kempf, K.; Martin, S. Kontinuierliches Glukosemonitoring nach Verzehr alltäglicher Lebensmittel und ihre Wirkung auf den postprandialen Glukose- und Insulinspiegel. Aktuelle Ernährungsmedizin 2021, 46, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempf, K.; Röhling, M.; Kolb, H.; Martin, S. Impact of a Low-Insulin-Stimulating Bread on Weight Development-A Real Life Randomised Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röhling, M.; Martin, K.; Ellinger, S.; Schreiber, M.; Martin, S.; Kempf, K. Weight Reduction by the Low-Insulin-Method-A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amatruda, T.T.; Chase, J.W.; Engel, F.L. The role of the endocrine glands in ketosis II. Ketonemia following insulin hypoglycemia. J. Clin. Investig. 1962, 41, 758–769. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dhillon, K.K.; Gupta, S. Biochemistry, Ketogenesis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.C. Measuring breath acetone for monitoring fat loss. Obesity 2015, 23, 2327–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 15197:2013; In Vitro Diagnostic Test Systems — Requirements for Blood-Glucose Monitoring Systems for Self-Testing in Managing Diabetes Mellitus. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- Aberer, F.; Hajnsek, M.; Rumpler, M.; Zenz, S.; Baumann, P.M.; Elsayed, H.; Puffing, A.; Treiber, G.; Pieber, T.R.; Sourij, H.; et al. Evaluation of subcutaneous glucose monitoring systems under routine environmental conditions in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 1051–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheniser, K.; Saxon, D.R.; Kashyap, S.R. Long-Term Weight Loss Strategies for Obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 1854–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goletzke, J.; Atkinson, F.S.; Ek, K.L.; Bell, K.; Brand-Miller, J.C.; Buyken, A.E. Glycaemic and insulin index of four common German breads. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 70, 808–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatruda, T.T.; Engel, F.L. The role of the endocrine glands in ketosis. I. The ketosis of fasting. Yale J. Biol. Med. 1959, 31, 303–323. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, D.W. Studies in the ketosis of fasting. J. Clin. Investig. 1967, 46, 1283–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fain, J.N.; Scom, R.O.; Urgoiti, E.J.; Chernick, S.S. Effect of insulin on fatty acid synthesis in vivo and in vitro in pancreatectomized rats. Endocrinology 1965, 77, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempf, K.; Tankova, T.; Martin, S. ROSSO-in-praxi-international: Long-term effects of self-monitoring of blood glucose on glucometabolic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus not treated with insulin. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2013, 15, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 7. Diabetes Technology: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2024. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, S126–S144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, K.F. A Review of Excessive Sugar Metabolism on Oral and General Health. Chin. J. Dent. Res. 2017, 20, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shokrekhodaei, M.; Quinones, S. Review of Non-invasive Glucose Sensing Techniques: Optical, Electrical and Breath Acetone. Sensors 2020, 20, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, O.E.; Felig, P.; Morgan, A.P.; Wahren, J.; Cahill, G.F., Jr. Liver and kidney metabolism during prolonged starvation. J. Clin. Investig. 1969, 48, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.L.; Soeters, M.R.; Wust, R.C.I.; Houtkooper, R.H. Metabolic Flexibility as an Adaptation to Energy Resources and Requirements in Health and Disease. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 489–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, A.B.; Queathem, E.D.; Puchalska, P.; Crawford, P.A. Metabolic Messengers: Ketone bodies. Nat. Metab. 2023, 5, 2062–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, A.; Seimon, R.; Lee, C.; Ayre, J.; Franklin, J.; Markovic, T.; Caterson, I.; Sainsbury, A. Do ketogenic diets really suppress appetite? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyńka, D.; Kowalcze, K.; Ambrozkiewicz, F.; Paziewska, A. Effect of the Ketogenic Diet on the Prophylaxis and Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus: A Review of the Meta-Analyses and Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2023, 15, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuttall, F.Q.; Almokayyad, R.M.; Gannon, M.C. Comparison of a carbohydrate-free diet vs. fasting on plasma glucose, insulin and glucagon in type 2 diabetes. Metabolism 2015, 64, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Day 1 | Day 14 | Difference After 14 Days | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (women/men) [n] | 7/3 | |||
| Age [years] | 48.4 ± 14.3 | |||
| Weight [kg] | 79.1 ± 18.8 | 76.2 ± 17.3 | −3.0 ± 1.9 | 0.002 |
| Body mass index [kg/m2] | 26.9 ± 3.9 | 25.9 ± 3.4 | −1.0 ± 0.6 | 0.002 |
| Waist circumference [cm] | 90.4 ± 12.7 | 86.0 ± 12.0 | −4.4 ± 3.3 | 0.016 |
| Hip circumference [cm] | 100.4 ± 9.0 | 98.1 ± 8.4 | −2.3 ± 1.0 | 0.008 |
| Fat mass [kg] | 28.7 ± 9.4 | 27.1 ± 9.2 | −1.6 ± 1.0 | 0.004 |
| Fat mass [%] | 36.1 ± 1.0 | 35.3 ± 6.8 | −0.8 ± 1.1 | 0.059 |
| Visceral fat [L] | 2.2 ± 1.4 | 1.8 ± 1.4 | −0.4 ± 0.5 | 0.014 |
| Fat-free mass [kg] | 50.4 ± 12.6 | 49.0 ± 11.5 | −1.4 ± 1.6 | 0.027 |
| Fat-free mass [%] | 63.9 ± 6.5 | 64.7 ± 6.8 | 0.8 ± 1.1 | 0.059 |
| Skeletal muscle mass [kg] | 23.8 ± 7.2 | 23.0 ± 6.8 | −0.8 ± 0.7 | 0.006 |
| Total water mass [L] | 37.4 ± 9.0 | 36.4 ± 8.3 | −1.1 ± 1.3 | 0.025 |
| Resting energy expenditure [kcal/day] | 1562 ± 298 | 1531 ± 279 | −31 ± 26 | 0.002 |
| Total energy expenditure [kcal/day] | 2689 ± 532 | 2586 ± 460 | −103 ± 111 | 0.002 |
| Fasting insulin [µU/mL] | 9.4 ± 3.8 | 6.9 ± 3.7 | −2.5 ± 1.9 | 0.006 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kempf, K.; Martin, S. Effects of a Carbohydrate Meal on Lipolysis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3531. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16203531
Kempf K, Martin S. Effects of a Carbohydrate Meal on Lipolysis. Nutrients. 2024; 16(20):3531. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16203531
Chicago/Turabian StyleKempf, Kerstin, and Stephan Martin. 2024. "Effects of a Carbohydrate Meal on Lipolysis" Nutrients 16, no. 20: 3531. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16203531
APA StyleKempf, K., & Martin, S. (2024). Effects of a Carbohydrate Meal on Lipolysis. Nutrients, 16(20), 3531. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16203531






