Gender-Specific Malnutrition and Muscle Depletion in Gastric and Colorectal Cancer: Role of Dietary Intake in a Jordanian Cohort
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Ethical Approval
2.3. Anthropometric Measurements and Muscle Depletion
2.4. Malnutrition Risk Assessment
2.5. Assessment of Quality of Life
2.6. Assessment of Dietary Intake
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of the Study Subjects
3.2. Malnutrition Risk, Muscle Depletion, Adequacy of Dietary Intake, and Quality of Life Scales
3.3. Malnutrition Risk, Muscle Depletion, and Quality of Life Scales According to Cancer Stage and Time Since Diagnosis
3.4. Dietary Intake
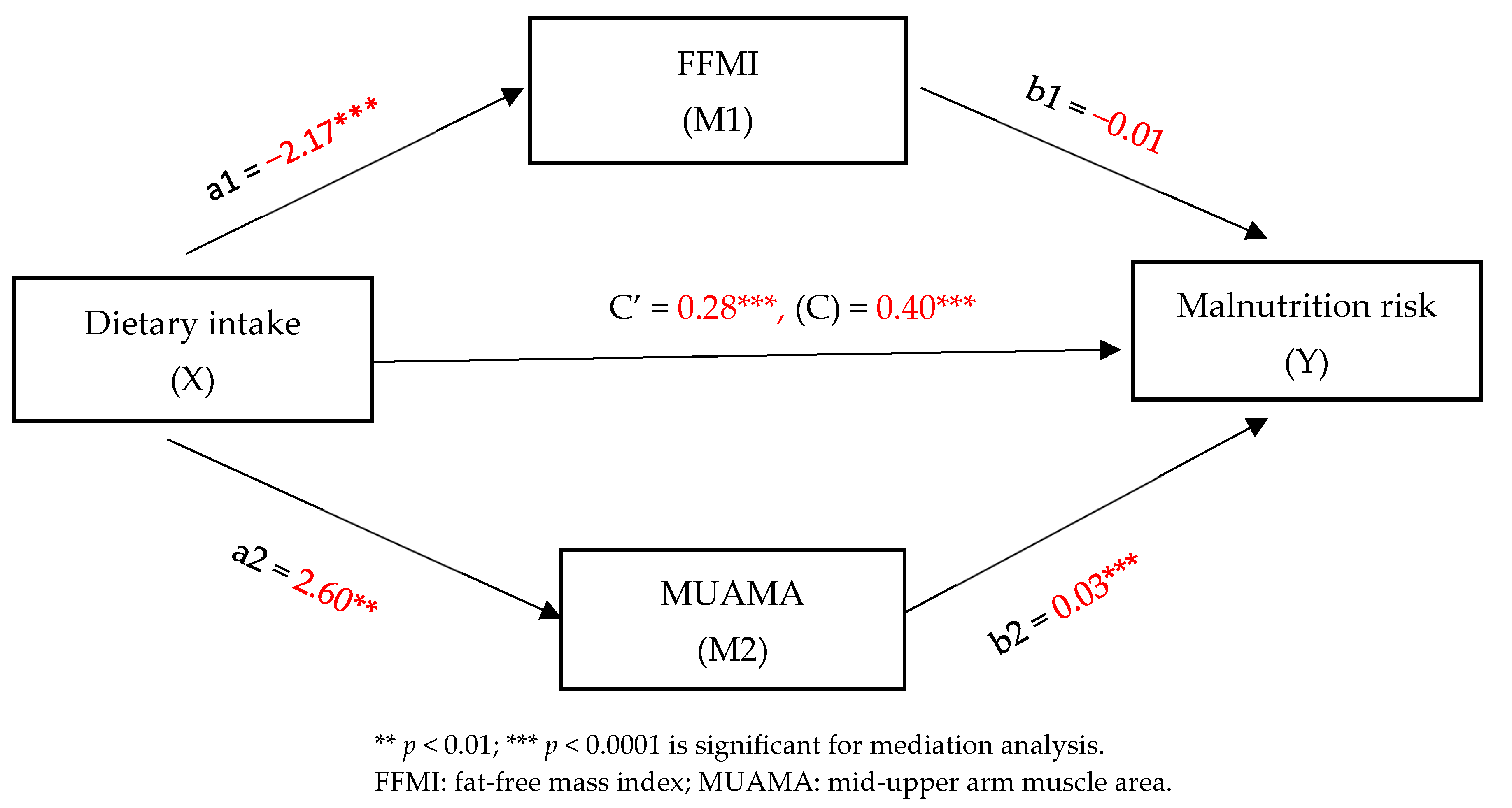
3.5. Mediation Analysis
3.6. Predictors of Malnutrition Risk
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arends, J. Ernährung von Tumorpatienten. Aktuel Ernahrungsmed 2012, 37, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arends, J.; Bachmann, P.; Baracos, V.; Barthelemy, N.; Bertz, H.; Bozzetti, F.; Fearon, K.; Hütterer, E.; Isenring, E.; Kaasa, S.; et al. ESPEN guidelines on nutrition in cancer patients. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 11–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, K.M.; Loeliger, J.; Nolte, L.; Kelaart, A.; Kiss, N.K. Prevalence of malnutrition and impact on clinical outcomes in cancer services: A comparison of two time points. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.; Birdsell, L.; Macdonald, N.; Reiman, T.; Clandinin, M.T.; McCargar, L.J.; Murphy, R.; Ghosh, S.; Sawyer, M.B.; Baracos, V.E. Cancer cachexia in the age of obesity: Skeletal muscle depletion is a powerful prognostic factor, independent of body mass index. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1539–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederholm, T.; Barazzoni, R.; Austin, P.; Ballmer, P.; Biolo, G.; Bischoff, S.C.; Compher, C.; Correia, I.; Higashiguchi, T.; Holst, M.; et al. ESPEN guidelines on definitions and terminology of clinical nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deftereos, I.; Djordjevic, A.; Carter, V.M.; McNamara, J.; Yeung, J.M.; Kiss, N. Malnutrition screening tools in gastrointestinal cancer: A systematic review of concurrent validity. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 38, 101627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.J.; Ji, Y.B.; Ma, B.W.; Huang, D.D.; Chen, W.Z.; Pan, Z.Y.; Shen, X.; Zhuang, C.L.; Yu, Z. Comparison of three common nutritional screening tools with the new European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism (ESPEN) criteria for malnutrition among patients with geriatric gastrointestinal cancer: A prospective study in China. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e019750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seron-Arbeloa, C.; Labarta-Monzon, L.; Puzo-Foncillas, J.; Mallor-Bonet, T.; Lafita-Lopez, A.; Bueno-Vidales, N.; Montoro-Huguet, M. Malnutrition screening and assessment. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Aguilar, R.; Malih, N.; Abbate, M.; Fresneda, S.; Yañez, A.; Bennasar-Veny, M. Validity of nutrition screening tools for risk of malnutrition among hospitalized adult patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 43, 1094–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ager-Wittenaar, H.; Ottery, F.D. Assessing nutritional status in cancer: Role of the Patient-Generated Subjective Global Assessment. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2017, 20, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gills, C.; Richer, L.; Fenton, T.R.; Gramlich, L.; Keller, H.; Culos- Reed, S.N.; Sajobi, T.T.; Awasthi, R.; Carli, F. Colorectal cancer patients with malnutrition suffer poor physical and mental health before surgery. Surgery 2021, 170, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, C.Y.; Majid, H.A.; Jamhuri, N.; Ahmad, A.F.; Selvarajoo, T.A. Lower ileostomy output among patients with postoperative colorectal cancer after being supplemented with partially hydrolyzed guar gum: Outcome of a pilot study. Nutrition 2022, 103–104, 111758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobo, D.N.; Gianotti, L.; Adiamah, A.; Barazzoni, R.; Deutz, N.E.P.; Dhatariya, K.; Greenhaff, P.L.; Hiesmayr, M.; Hjort Jakobsen, D.; Klek, S.; et al. Perioperative nutrition: Recommendations from the ESPEN expert group. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 3211–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Shahethi, A.H.; Mahdi, F.A.; Al-Shameri, E.A.; Abol Gaith, F.M. Factors associated with malnutrition in hospitalized cancer patients in a National Oncology Center in conflict-affected settings in Sana’a, Yemen: An institution-based cross-sectional study. Cureus 2023, 15, e45411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bye, A.; Sjøblom, B.; Wentzel-Larsen, T.; Grønberg, B.H.; Baracos, V.E.; Hjermstad, M.J.; Aass, N.; Bremnes, R.M.; Fløtten, Ø.; Jordhøy, M. Muscle mass and association to quality of life in non-small cell lung cancer patients. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2017, 8, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.C.; Hong, B.Z. High Prevalence of malnutrition and associated factors in newly diagnosed upper gastrointestinal cancer patients: A cross-sectional study. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Care 2024, 9, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.Y.; Ibrahim, Z.; Abu Zaid, Z.; Mat Daud, Z.’A.; Md Yusop, N.B. Clinical malnutrition predictive model among gynecologic cancer patients prior to elective operation: A cross-sectional study. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 4373–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán Poveda, M.; Suárez-de-la-Rica, A.; Cancer Minchot, E.; Ocón Bretón, J.; Sánchez Pernaute, A.; Rodríguez Caravaca, G.; PREMAS Study Group. The prevalence and impact of nutritional risk and malnutrition in gastrointestinal surgical oncology patients: A prospective, observational, multicenter, and exploratory Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.D.; Nieman, D.C. Nutrational Assessment, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 170–233. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.X.; Tighiouart, H.; Beddhu, S.; Cheung, A.K.; Dwyer, J.T.; Eknoyan, G.; Beck, G.J.; Levey, A.S.; Sarnak, M.J. Both low muscle mass and low fat are associated with higher all-cause mortality in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2010, 77, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratton, R.J.; Hackston, A.; Longmore, D.; Dixon, R.; Price, S.; Stroud, M.; King, C.; Elia, M. Malnutrition in hospital outpatients and inpatients: Prevalence, concurrent validity and ease of use of the ‘malnutrition universal screening tool’ (‘MUST’) for adults. Br. J. Nutr. 2004, 92, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Questionnaires. EORTC Quality of Life. Available online: https://qol.eortc.org/questionnaire/eortc-qlq-c30/ (accessed on 8 August 2023).
- Parsa, N. Environmental factors inducing human cancers. Iran. J. Public. Health 2012, 41, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ravasco, P. Nutrition in cancer patients. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cushen, S.J.; Power, D.G.; Ryan, A.M. Nutrition assessment in oncology. Top. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 30, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inciong, J.F.B.; Chaudhary, A.; Hsu, H.S.; Joshi, R.; Seo, J.M.; Trung, L.V.; Ungpinitpong, W.; Usman, N. Hospital malnutrition in northeast and southeast Asia: A systematic literature review. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2020, 39, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deftereos, I.; Yeung, J.M.C.; Arslan, J.; Carter, V.M.; Isenring, E.; Kiss, N. Assessment of nutritional status and nutrition impact symptoms in patients undergoing resection for upper gastrointestinal cancer: Results from the multi-centre NOURISH point prevalence study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscaritoli, M.; Arends, J.; Bachmann, P.; Baracos, V.; Barthelemy, N.; Bertz, H.; Bozzetti, F.; Hütterer, E.; Isenring, E.; Kaasa, S.; et al. ESPEN practical guideline: Clinical nutrition in cancer. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 2898–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reber, E.; Schönenberger, K.A.; Vasiloglou, M.F.; Stanga, Z. Nutritional risk screening in cancer patients: The first step toward better clinical outcome. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 603936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Cajas-Monson, L.C.; Eisenstein, S.; Parry, L.; Cosman, B.; Ramamoorthy, S. Preoperative malnutrition assessments as predictors of postoperative mortality and morbidity in colorectal cancer: An analysis of ACS-NSQIP. Nutr. J. 2015, 14, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arends, J. Malnutrition in cancer patients: Causes, consequences and treatment options. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2024, 50, 107074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cereda, E.; Pedrazzoli, P.; Lobascio, F.; Masi, S.; Crotti, S.; Klersy, C.; Turri, A.; Stobäus, N.; Tank, M.; Franz, K.; et al. The prognostic impact of BIA-derived fat-free mass index in patients with cancer. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 3901–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casirati, A.; Vandoni, G.; Della Valle, S.; Greco, G.; Platania, M.; Colatruglio, S.; Lalli, L.; Gavazzi, C. Nutritional status and body composition assessment in patients with a new diagnosis of advanced solid tumour: Exploratory comparison of computed tomography and bioelectrical impedance analysis. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 1268–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourtzakis, M.; Prado, C.M.M.; Lieffers, J.R.; Reiman, T.; McCargar, L.J.; Baracos, V.E. practical and precise approach to quantification of body composition in cancer patients using computed tomography images acquired during routine care. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2008, 33, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gascón-Ruiz, M.; Casas-Deza, D.; Torres-Ramón, I.; Zapata-García, M.; Alonso, N.; Sesma, A.; Lambea, J.; Álvarez-Alejandro, M.; Quílez, E.; Isla, D.; et al. GLIM vs. ESPEN criteria for the diagnosis of early malnutrition in oncological outpatients. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 3741–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiss, N.; Prado, C.M.; Daly, R.M.; Denehy, L.; Edbrooke, L.; Baguley, B.J.; Fraser, S.F.; Khosravi, A.; Abbott, G. Low muscle mass, malnutrition, sarcopenia, and associations with survival in adults with cancer in the UK Biobank cohort. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2023, 14, 1775–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abaza, H.; Taqash, A.; Shattal, M.A.; Abuhijla, F.; Abdel-Khaleq, H.; Awadallah, O.; Al-Jafari, K.; Al-Jafari, Z.; Al-Omari, A. Association between muscle mass and overall survival among colorectal cancer patients at tertiary cancer center in the Middle East. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cencioni, C.; Trestini, I.; Piro, G.; Bria, E.; Tortora, G.; Carbone, C.; Spallotta, F. Gastrointestinal cancer patient nutritional management: From specific needs to novel epigenetic dietary approaches. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Shoda, K.; Konishi, H.; Okamoto, K.; Otsuji, E. Nutrition update in gastric cancer surgery. Ann. Gastroenterol. Surg. 2020, 4, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeyer, P.E.; Carli, F.; Evans, D.C.; Guilbert, S.; Kozar, R.; Pryor, A.; Thiele, R.H.; Everett, S.; Grocott, M.; Gan, T.J.; et al. American Society for Enhanced Recovery and Perioperative Quality Initiative Joint Consensus Statement on Nutrition Screening and Therapy Within a Surgical Enhanced Recovery Pathway. Anesth. Analg. 2018, 126, 1883–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Type of Cancer | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All (N = 100) | Gastric (n = 41) | Colorectal (n = 59) | ||
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | ||
| Sex | ||||
| 60 (60.0) | 23 (56.1) | 37 (62.7) | 0.323 |
| 40 (40.0) | 18 (43.9) | 22 (37.3) | ||
| BMI score (kg/m2) | ||||
| 51 (51.0) | 17 (41.5) | 34 (57.6) | 0.216 |
| 35 (35.0) | 16 (39.0) | 19 (32.2) | ||
| 14 (14.0) | 8 (19.5) | 6 (10.2) | ||
| Weight loss score (%) | ||||
| 9 (9.0) | 1 (2.4) | 8 (13.6) | 0.103 |
| 15 (15.0) | 5 (12.2) | 10 (16.9) | ||
| 76 (76.0) | 35 (85.4) | 41 (69.5) | ||
| Acute disease score | ||||
| 46 (46.0) | 17 (41.5) | 29 (49.2) | 0.659 |
| 20 (20.0) | 8 (19.5) | 12 (20.3) | ||
| 34 (34.0) | 16 (39.0) | 18 (30.5) | ||
| Malnutrition risk | ||||
| 9 (9.0) | 1 (2.4) | 8 (13.6) | 0.093 |
| 11 (11.0) | 3 (7.3) | 8 (13.6) | ||
| 80 (80.0) | 37 (90.2) | 43 (72.9) | ||
| Muscle depletion according to FFMI (kg/m2) | ||||
| 35 (35.0) | 12 (29.3) | 23 (39.0) | 0.216 |
| 65 (65.0) | 29 (70.7) | 36 (61.0) | ||
| MUAMA (cm2) | ||||
| 40 (40.0) | 14 (34.1) | 26 (44.1) | 0.397 |
| 60 (60.0) | 27 (65.9) | 33 (55.9) | ||
| Dietary intake | ||||
| 40 (40.0) | 13 (31.7) | 27 (45.8) | 0.114 |
| 60 (60.0) | 28 (68.3) | 32 (54.2) | ||
| Healthcare scale | ||||
| 70 (70.0) | 27 (65.9) | 43 (72.9) | 0.296 |
| 30 (30.0) | 14 (34.1) | 16 (27.1) | ||
| Functional scale | ||||
| 36 (36.0) | 16 (39.0) | 20 (33.9) | 0.376 |
| 64 (64.0) | 25 (61.0) | 39 (66.1) | ||
| Symptoms scale | ||||
| 32 (32.0) | 12 (29.3) | 20 (33.9) | 0.395 |
| 68 (68.0) | 29 (70.7) | 39 (66.1) | ||
| Cancer stage | ||||
| 33 (33.0) | 9 (22.0) | 24 (40.7) | 0.056 |
| 67 (67.0) | 32 (78.0) | 35 (59.3) | ||
| Time since diagnosis | ||||
| 68 (68.0) | 27 (65.9) | 41 (69.5) | 0.825 |
| 32 (32.0) | 14 (34.1) | 18 (30.5) | ||
| Variable | Male (n = 60) | p-Value | Female (n = 40) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of Cancer | Type of Cancer | |||||
| Gastric (n = 23) n (%) | Colorectal (n = 37) n (%) | Gastric (n = 18) n (%) | Colorectal (n = 22) n (%) | |||
| BMI score (kg/m2) | ||||||
| 11 (47.8) | 17 (45.9) | 1.000 | 6 (33.3) | 17 (77.3) | 0.004 |
| 8 (34.8) | 14 (37.8) | 8 (44.4) | 5 (22.7) | |||
| 4 (17.4) | 6 (16.2) | 4 (22.3) | 0.5 (0.0) ^ | |||
| Weight loss score (%) | ||||||
| 1 (4.3) | 2 (5.4) | 1.000 | ^ 0.5 (0.0) | 6 (27.3) | 0.016 |
| 3 (13.0) | 5 (13.5) | 2 (11.1) | 5 (22.7) | |||
| 19 (82.6) | 30 (81.1) | 16 (88.9) | 11 (50.0) | |||
| Acute disease score | ||||||
| 7 (30.4) | 13 (35.1) | 0.524 | 10 (55.6) | 16 (72.7) | 0.424 |
| 4 (17.4) | 10 (27.0) | 4 (22.4) | 2 (22.4) | |||
| 12 (52.2) | 14 (37.8) | 4 (22.4) | 4 (18.2) | |||
| Malnutrition risk | ||||||
| 1 (4.3) | 2 (5.4) | 0.633 | ^ 0.5 (0.0) | 6 (27.3) | 0.039 |
| 1 (4.3) | 5 (13.5) | 2 (11.1) | 3 (13.6) | |||
| 21 (91.4) | 30 (81.1) | 16 (88.9) | 13 (59.1) | |||
| Muscle depletion according to FFMI (kg/m2) | ||||||
| 7 (30.4) | 8 (21.6) | 0.320 | 5 (27.8) | 15 (68.2) | 0.012 |
| 16 (59.6) | 29 (78.4) | 13 (72.2) | 7 (31.8) | |||
| Muscle depletion according to MUAMA (cm2) | ||||||
| 8 (43.8) | 11 (29.7) | 0.448 | 6 (33.3) | 15 (68.2) | 0.028 |
| 15 (65.2) | 26 (70.3) | 12 (66.7) | 7 (31.8) | |||
| Dietary intake | ||||||
| 8 (34.8) | 13 (35.1) | 0.601 | 5 (27.8) | 14 (63.6) | 0.025 |
| 15 (65.2) | 24 (64.9) | 13 (72.2) | 8 (36.4) | |||
| Healthcare scale | ||||||
| 15 (65.2) | 26 (70.3) | 0.778 | 12 (66.7) | 17 (77.3) | 0.347 |
| 8 (34.8) | 11 (29.7) | 6 (33.3) | 5 (22.7) | |||
| Functional scale | ||||||
| 7 (30.4) | 8 (21.6) | 0.320 | 9 (50.0) | 12 (54.2) | 0.512 |
| 16 (69.6) | 29 (78.4) | 9 (50.0) | 10 (45.5) | |||
| Symptoms scale | ||||||
| 6 (26.1) | 9 (24.3) | 0.556 | 6 (33.3) | 11 (50.0) | 0.230 |
| 17 (73.9) | 28 (75.7) | 12 (66.7) | 11 (50.0) | |||
| Cancer stage | ||||||
| 6 (26.1) | 13 (35.1) | 0.573 | 5 (27.8) | 9 (40.9) | 0.510 |
| 17 (73.9) | 24 (64.9) | 13 (72.2) | 13 (59.1) | |||
| Time since diagnosis | ||||||
| 12 (52.2) | 23 (62.2) | 0.446 | 15 (83.3) | 18 (81.8) | 1.000 |
| 11 (47.8) | 14 (34.8) | 3 (16.7) | 4 (18.2) | |||
| Variable | Cancer Stage | Time Since Diagnosis | Male Cancer Stage | Female Cancer Stage | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I and II (n = 33) | III and IV (n = 67) | p | ≤4 Months (n = 68) | >4 Months (n = 32) | p | I and II (n = 19) | III and IV (n = 41) | p | I and II (n = 14) | III and IV (n = 26) | p | |
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |||||
| Sex | ||||||||||||
| 19 (57.6) | 41 (61.2) | 0.829 | 35 (51.5) | 25 (78.1) | 0.016 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| 14 (42.4) | 26 (38.8) | 33 (48.5) | 7 (21.9) | |||||||||
| Type of cancer | ||||||||||||
| 9 (27.3) | 32 (47.8) | 0.056 | 27 (39.7) | 14 (43.8) | 0.828 | 6 (31.6) | 17 (41.5) | 0.573 | 5 (35.7) | 13 (50.0) | 0.510 |
| 24 (72.7) | 35 (52.2) | 41 (60.3) | 18 (56.3) | 13 (68.4) | 24 (58.5) | 9 (64.3) | 13 (50.0) | |||||
| BMI score (kg/m2) | ||||||||||||
| 25 (75.8) | 26 (38.8) | 35 (51.5) | 16 (50.0) | 13 (68.4) | 15 (36.6) | 8 (57.1) | 15 (57.7) | ||||
| 7 (21.2) | 28 (41.8) | 0.001 | 26 (38.2) | 9 (28.1) | 0.245 | 4 (21.1) | 18 (43.9) | 0.092 | 6 (42.9) | 7 (26.9) | 0.339 | |
| 1 (3.0) | 13 (19.4) | 7 (10.3) | 7 (21.9) | 2 (10.5) | 8 (19.5) | ^ 0.5 (0.0) | 4 (15.4) | |||||
| Weight loss score (%) | ||||||||||||
| 9 (27.3) | ^ 0.5 (0.0) | 5 (7.4) | 4 (12.5) | 3 (15.8) | ^ 0.5 (0.0) | 3 (21.4) | 3 (11.5) | ||||
| 13 (39.4) | 2 (3.0) | <0.001 | 11 (16.2) | 4 (12.5) | 0.661 | 6 (31.6) | 2 (4.9) | <0.001 | 1 (7.1) | 6 (23.1) | 0.422 | |
| 11 (33.3) | 65 (97.0) | 52 (76.5) | 24 (75.0) | 10 (52.6) | 39 (95.1) | 10 (71.4) | 17 (65.4) | |||||
| Acute disease score | ||||||||||||
| 24 (72.7) | 22 (32.8) | 33 (48.5) | 13 (40.6) | 13 (68.4) | 7 (17.1) | 9 (64.3) | 17 (65.4) | ||||
| 4 (12.1) | 16 (23.9) | <0.001 | 12 (17.6) | 8 (25.0) | 0.669 | 1 (5.3) | 13 (31.7) | <0.001 | 1 (7.1) | 5 (19.2) | 0.492 | |
| 5 (15.2) | 29 (43.3) | 23 (33.8) | 11 (34.4) | 5 (26.3) | 21 (51.2) | 4 (28.6) | 4 (15.4) | |||||
| Malnutrition risk | ||||||||||||
| 9 (27.3) | ^ 0.5 (0.0) | 5 (7.4) | 4 (12.5) | 3 (15.8) | ^ 0.5 (0.0) | 3 (21.4) | 3 (11.5) | ||||
| 11 (33.3) | ^ 0.5 (0.0) | <0.001 | 8 (11.8) | 3 (9.4) | 0.727 | 6 (31.6) | ^ 0.5 (0.0) | <0.001 | ^ 0.5 (0.0) | 5 (19.2) | 0.210 | |
| 13 (39.4) | 67 (100.0) | 55 (80.9) | 25 (78.1) | 10 (52.6) | 41 (100.0) | 11 (78.6) | 18 (6.2) | |||||
| Muscle depletion according to | ||||||||||||
FFMI (kg/m2)
| ||||||||||||
| 20 (60.6) | 15 (22.4) | <0.001 | 25 (36.8) | 10 (31.3) | 0.657 | 8 (42.1) | 7 (17.1) | 0.060 | 7 (50.0) | 13 (50.0) | 1.000 | |
| 13 (39.4) | 52 (77.6) | 43 (63.2) | 22 (68.8) | 11 (57.9) | 34 (82.9) | 7 (50.0) | 13 (50.0) | |||||
| 24 (72.7) | 16 (23.9) | <0.001 | 30 (44.1) | 10 (31.2) | 0.220 | 4 (21.1) | 15 (36.6) | 0.254 | 10(71.4) | 17 (65.4) | 1.000 | |
| 9 (27.3) | 51 (76.1) | 38(55.9) | 22 (68.8) | 15 (78.9) | 26 (63.4) | 4 (28.6) | 9 (34.6) | |||||
| Dietary intake | ||||||||||||
| 24 (72.7) | 16 (23.9) | <0.001 | 26 (38.2) | 14 (43.8) | 0.664 | 10 (52.6) | 11 (26.8) | 0.080 | 7 (50.0) | 12 (46.2) | 1.000 |
| 9 (27.3) | 51 (76.1) | 42 (61.8) | 18 (56.3) | 9 (47.6) | 30 (73.2) | 7 (50.0) | 14 (53.8) | |||||
| Healthcare scale | ||||||||||||
| 27 (81.8) | 43 (64.2) | 0.104 | 47 (69.1) | 23 (71.9) | 0.820 | 12 (63.2) | 29 (70.7) | 0.766 | 11 (78.6) | 18 (69.2) | 0.715 |
| 6 (18.2) | 24 (35.8) | 21 (30.9) | 9 (28.1) | 7 (36.8) | 12 (29.3) | 3 (21.4) | 8 (30.8) | |||||
| Functional scale | ||||||||||||
| 17 (51.5) | 19 (28.4) | 0.028 | 24 (35.3) | 12 (37.5) | 1.000 | 8 (42.1) | 7 (17.1) | 0.055 | 10 (71.4) | 11 (42.3) | 0.105 |
| 16 (48.5) | 48 (71.6) | 44 (64.7) | 20 (62.5) | 11 (57.9) | 34 (82.9) | 4 28.6) | 15 (57.7) | |||||
| Symptoms scale | ||||||||||||
| 17 (51.5) | 15 (22.4) | 0.006 | 23 (33.8) | 9 (28.1) | 0.650 | 8 (42.1) | 7 (17.1) | 0.055 | 6 (42.9) | 11 (42.3) | 1.000 |
| 16 (48.5) | 52 (77.6) | 45 (66.2) | 23 (71.9) | 11 (57.9) | 34 (82.9) | 8 (57.1) | 15 (57.7) | |||||
| Macronutrients | Intake Mean ± SD | RDA Mean ± SD | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total energy (Kcal) | 1574.8 ± 655.8 | 1796.0 ± 251.4 * | <0.001 |
| Protein (g) | 96.8 ± 36.4 | 119.7 ± 16.8 ^ | <0.001 |
| Carbohydrates (g) | 167.0 ± 96.3 | 100.0 ± 0.0 | <0.001 |
| Fat (g) | 57.8 ± 17.1 | 55.0 ± 0.0 | 0.108 |
| Fiber (g) | 26.9 ± 7.2 | 30.0 ± 0.0 | <0.001 |
| Omega 3 and 6 (g) | 1.9 ± 2.3 | 0.25 ± 0.0 | <0.001 |
| Variable | Dietary Intake | Male | Female | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adequate (n = 40) | Inadequate (n = 60) | p | Adequate (n = 21) | Inadequate (n = 39) | p | Adequate (n = 19) | Inadequate (n = 21) | p | |
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | ||||
| Sex | |||||||||
| 21 (52.5) | 39 (65.0) | 0.149 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| 19 (47.5) | 21 (35.0) | ||||||||
| BMI score (kg/m2) | |||||||||
| 39 (97.5) | 12 (20.0) | 21 (100.0) | 7 (17.9) | 18 (94.7) | 5 (23.8) | |||
| 1 (2.5) | 34 (56.7) | <0.001 | ^ 0.5 (0.0) | 22 (56.4) | <0.001 | 1 (5.3) | 12 (57.2) | <0.001 | |
| ^ 0.5 (0.0) | 14 (23.3) | ^ 0.5 (0.0) | 10 (25.6) | ^ 0.5 (0.0) | 4 (19.0) | ||||
| Weight loss score (%) | |||||||||
| 9 (22.5) | ^ 0.5 (0.0) | 3 (14.3) | ^ 0.5 (0.0) | 6 (31.6) | ^ 0.5 (0.0) | |||
| 15 (37.5) | ^ 0.5 (0.0) | <0.001 | 8 (38.1) | ^ 0.5 (0.0) | <0.001 | 7 (36.8) | ^ 0.5 (0.0) | <0.001 | |
| 16 (40.0) | 60 (100.0) | 10 (47.6) | 39 (100.0) | 6 (31.6) | 21 (100.0) | ||||
| Acute disease score | |||||||||
| 26 (65.0) | 20 (33.3) | 13 (61.9) | 7 (17.9) | 13 (68.4) | 13 (61.9) | |||
| 8 (20.0) | 12 (20.0) | 0.002 | 5 (23.8) | 9 (23.1) | 0.001 | 3 (15.8) | 3 (14.3) | 0.897 | |
| 6 (15.0) | 28 (46.7) | 3 (14.3) | 23 (59.0) | 3 (15.8) | 5 (23.8) | ||||
| Malnutrition risk | |||||||||
| 9 (22.5) | ^ 0.5 (0.0) | 3 (14.3) | ^ 0.5 (0.0) | 6 (31.6) | ^ 0.5 (0.0) | |||
| 11 (27.5) | ^ 0.5 (0.0) | <0.001 | 6 (28.6) | ^ 0.5 (0.0) | <0.001 | 5 (26.3) | ^ 0.5 (0.0) | <0.001 | |
| 20 (50.0) | 60 (100.0) | 12 (57.1) | 39 (100.0) | 8 (42.1) | 21 (100.0) | ||||
| Muscle depletion according to | |||||||||
FFMI (kg/m2)
| |||||||||
| 30 (75.0) | 5 (8.3) | <0.001 | 13 (61.9) | 2 (5.1) | <0.001 | 17 (89.5) | 3 (14.3) | <0.001 | |
| 10(25.0) | 55 (91.7) | 8 (38.1) | 37 (94.9) | 2 (10.5) | 18 (85.7) | ||||
| 25 (62.5) | 17 (28.3) | 0.0007 | 14 (66.7) | 12 (30.8) | 0.007 | 11 (57.9) | 5 (23.8) | 0.028 | |
| 15 (37.5) | 43 (71.7) | 7 (33.3) | 27 (69.2) | 8 (42.1) | 16 (76.2) | ||||
| Type of cancer | |||||||||
| 13 (32.5) | 28 (46.7) | 0.114 | 8 (38.1) | 15 (38.5) | 1.00 | 5 (26.3) | 13 (61.9) | 0.031 |
| 27 (67.5) | 32 (53.3) | 13 (61.9) | 24 (61.5) | 14 (73.7) | 8 (38.1) | ||||
| Healthcare scale | |||||||||
| 32 (80.0) | 38 (63.3) | 0.058 | 17 (81.0) | 24 (61.5) | 0.154 | 15 (78.9) | 14 (66.7) | 0.488 |
| 8 (20.0) | 22 (36.7) | 4 (19.0) | 15 (38.5) | 4 (21.1) | 7 (33.3) | ||||
| Functional scale | |||||||||
| 23 (57.5) | 13 (21.7) | <0.001 | 10 (47.6) | 5 (12.8) | 0.005 | 13 (68.4) | 8 (38.1) | 0.067 |
| 17 (42.5) | 47 (78.3) | 11 (52.4) | 34 (87.2) | 6 (31.6) | 13 (61.9) | ||||
| Symptoms scale | |||||||||
| 26 (65.0) | 6 (10.0) | <0.001 | 13 (61.9) | 2 (5.1) | <0.001 | 13 (68.4) | 4 (19.0) | 0.003 |
| 14 (35.0) | 54 (90.0) | 8 (38.1) | 37 (94.9) | 6 (31.6) | 17 (81.0) | ||||
| Cancer stage | |||||||||
| 24 (60.0) | 9 (15.0) | <0.001 | 10 (47.6) | 9 (23.1) | 0.080 | 7 (36.8) | 7 (33.3) | 1.000 |
| 16 (40.0) | 51 (85.0) | 11 (52.4) | 30 (76.9) | 12 (63.2) | 14 (66.7) | ||||
| Time since diagnosis | |||||||||
| 26 (65.0) | 42 (70.0) | 0.664 | 10 (47.6) | 25 (64.1) | 0.276 | 16 (84.2) | 17 (81.0) | 1.000 |
| 14 (35.0) | 18 (30.0) | 11 (52.4) | 14 (35.9) | 3 (15.8) | 4 (19.0) | ||||
| Total Effect: Dietary Intake -> Malnutrition Risk | Direct Effect: Dietary Intake -> Malnutrition Risk | Relationship | Indirect Effect | 95% Confidence Interval | t-Statistics | Conclusions | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||||
| 0.4012 (0.0001) | 0.2849 (0.0091) | Dietary intake -> FFMI -> Malnutrition risk | 0.0285 | 0.0416 | 0.1556 | 0.5852 | Partial mediation |
| Dietary intake -> MUAMA -> Malnutrition risk | 0.0878 | 0.0145 | 0.2105 | 1.5791 | Partial mediation | ||
| Variables in the Equation | B | S.E. | p-Value | OR | 95% C.I. for OR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| Sex | 2.676 | 1.260 | 0.034 | 14.526 | 1.229 | 171.701 |
| Energy intake (Kcal/day) | −0.007 | 0.003 | 0.020 | 0.993 | 0.987 | 0.999 |
| MUAMA (cm2) | 2.774 | 1.143 | 0.015 | 16.024 | 1.706 | 150.507 |
| Type of cancer | 2.667 | 1.126 | 0.018 | 14.393 | 1.583 | 130.867 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Bayyari, N.; Hailat, M.; Baylin, A. Gender-Specific Malnutrition and Muscle Depletion in Gastric and Colorectal Cancer: Role of Dietary Intake in a Jordanian Cohort. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4000. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16234000
Al-Bayyari N, Hailat M, Baylin A. Gender-Specific Malnutrition and Muscle Depletion in Gastric and Colorectal Cancer: Role of Dietary Intake in a Jordanian Cohort. Nutrients. 2024; 16(23):4000. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16234000
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Bayyari, Nahla, Marah Hailat, and Ana Baylin. 2024. "Gender-Specific Malnutrition and Muscle Depletion in Gastric and Colorectal Cancer: Role of Dietary Intake in a Jordanian Cohort" Nutrients 16, no. 23: 4000. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16234000
APA StyleAl-Bayyari, N., Hailat, M., & Baylin, A. (2024). Gender-Specific Malnutrition and Muscle Depletion in Gastric and Colorectal Cancer: Role of Dietary Intake in a Jordanian Cohort. Nutrients, 16(23), 4000. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16234000






