Anticancer Activity of Plant Tocotrienols, Fucoxanthin, Fucoidan, and Polyphenols in Dietary Supplements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Compounds and Dietary Supplements
2.2. Liquid Chromatography—Mass Spectrometry Analysis
2.3. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
2.4. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.5. Cell Morphology
2.6. Wound and Healing Assay
2.7. Dual Acridine Orange/Ethidium Bromide (AO/EB) Fluorescent Staining
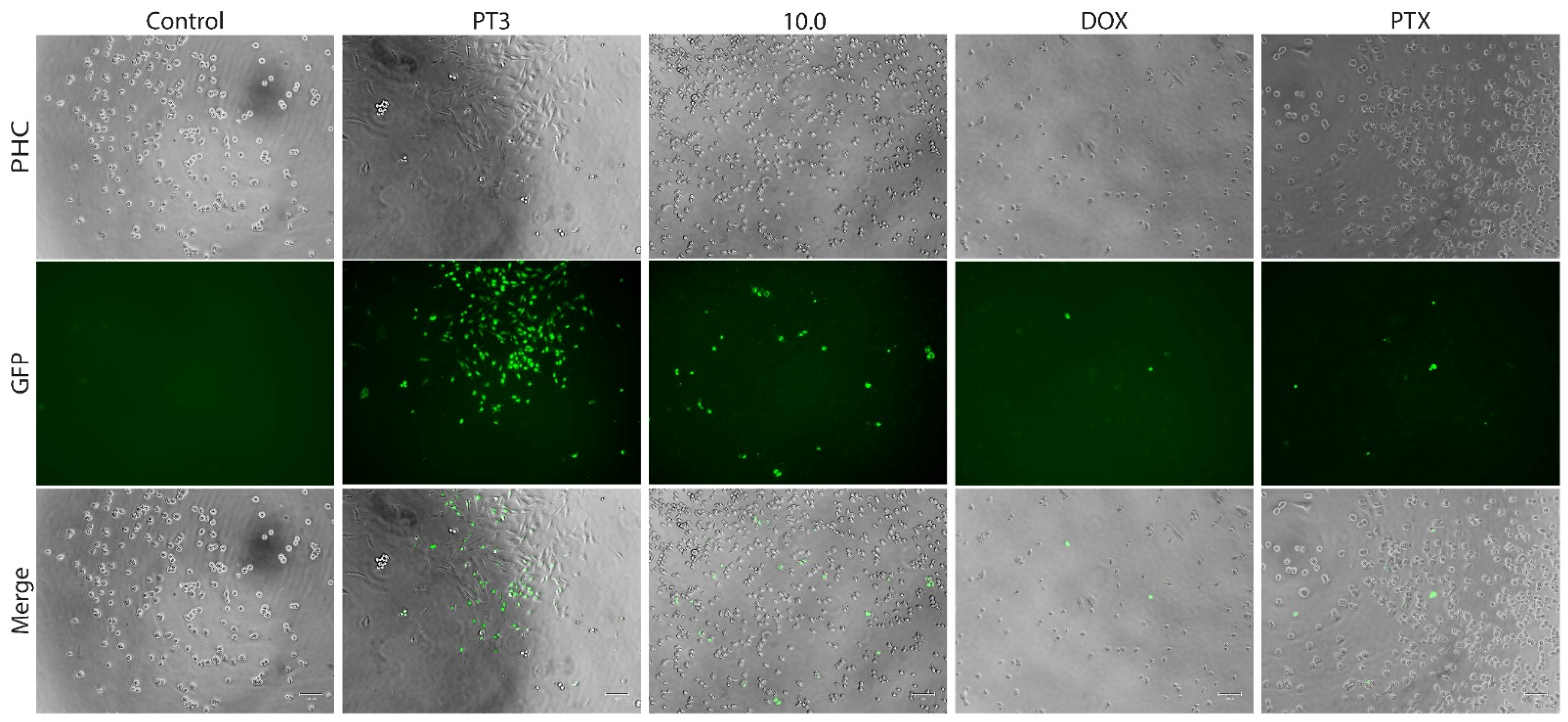
2.8. Caspase Assay
2.9. Determination of Total Antioxidant Capacity (TAC) of Natural Compounds and Dietary Supplements
2.10. Statistical Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cytotoxic Activity of Natural Compounds and Dietary Supplements on Different Human Cancer Cell Lines
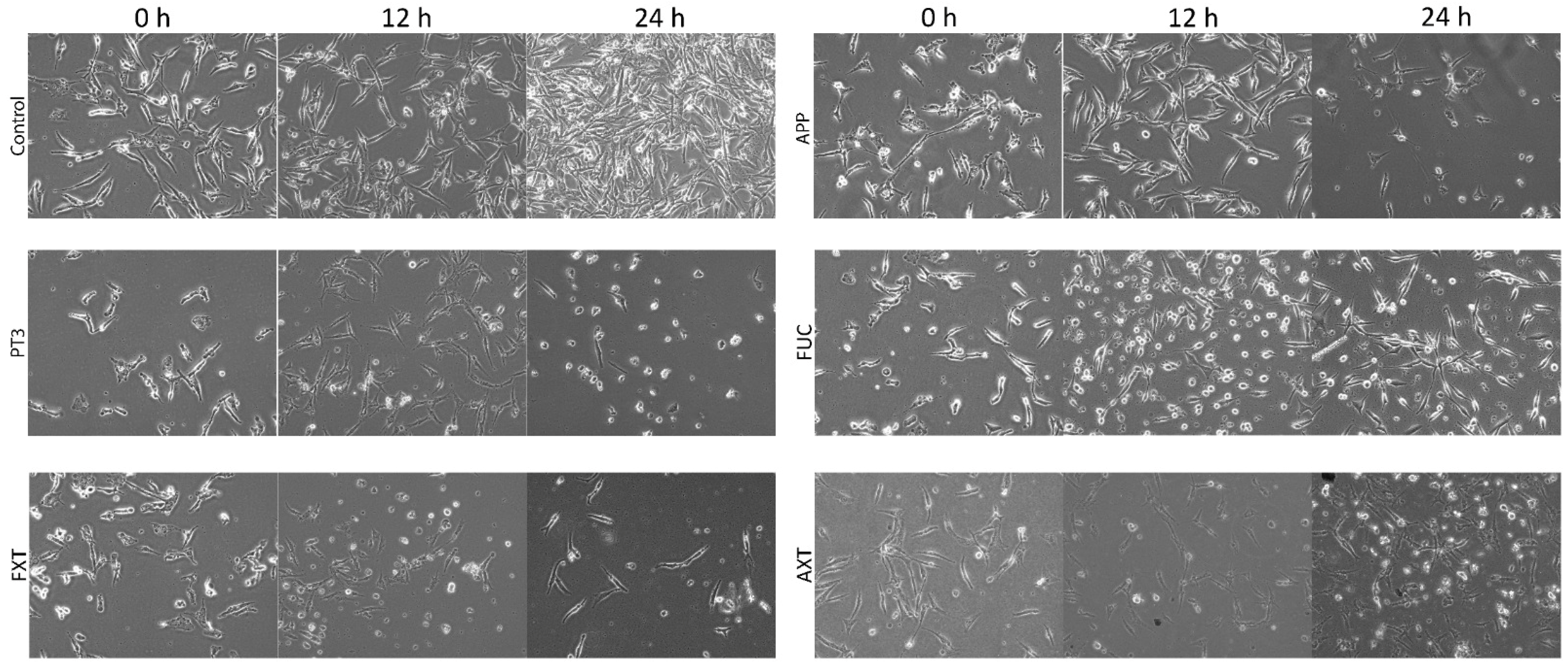
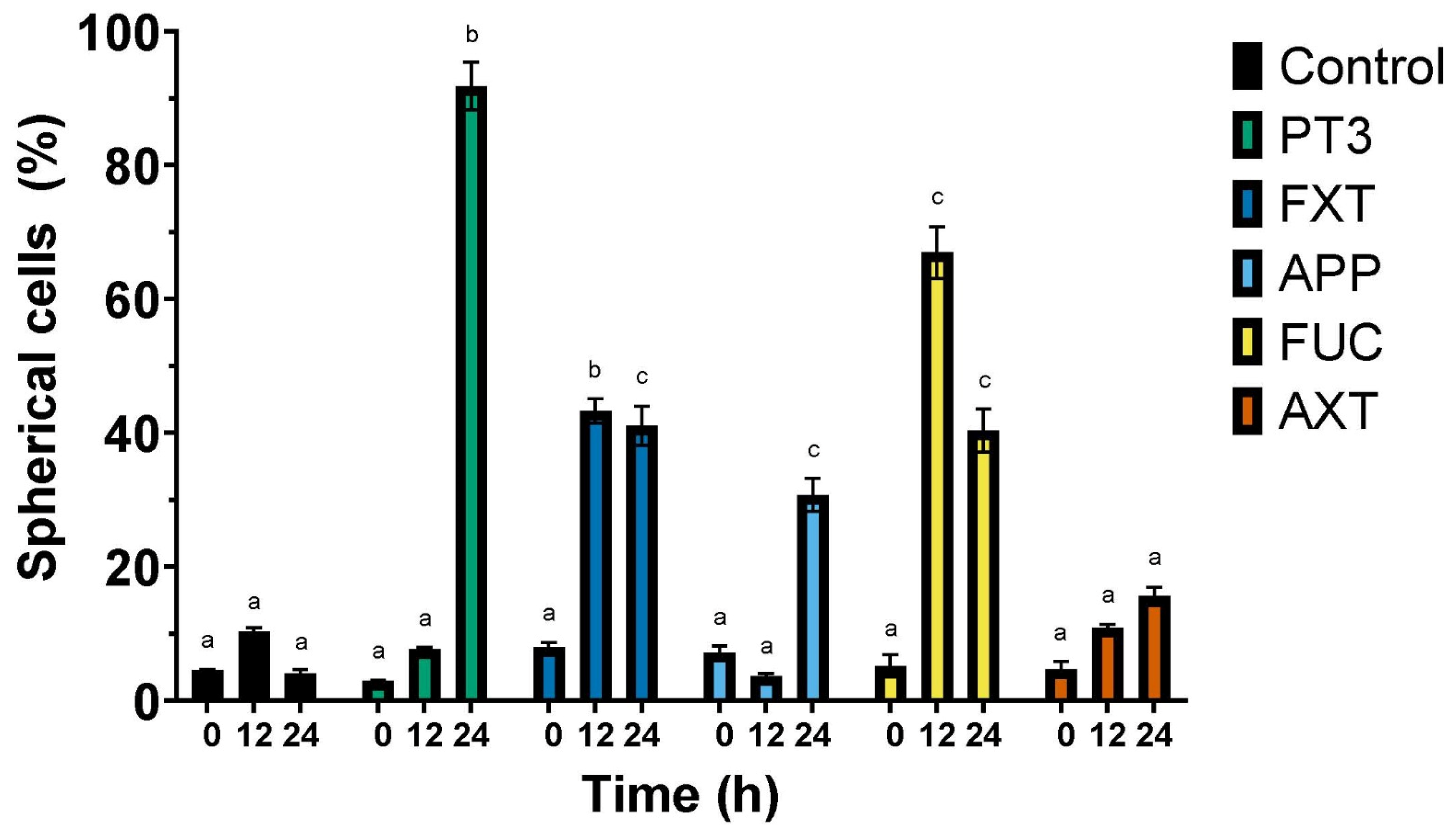
3.2. Morphological Changes in a Human Cancer Cell Line Exposed to Natural Compounds from Plants and Algae
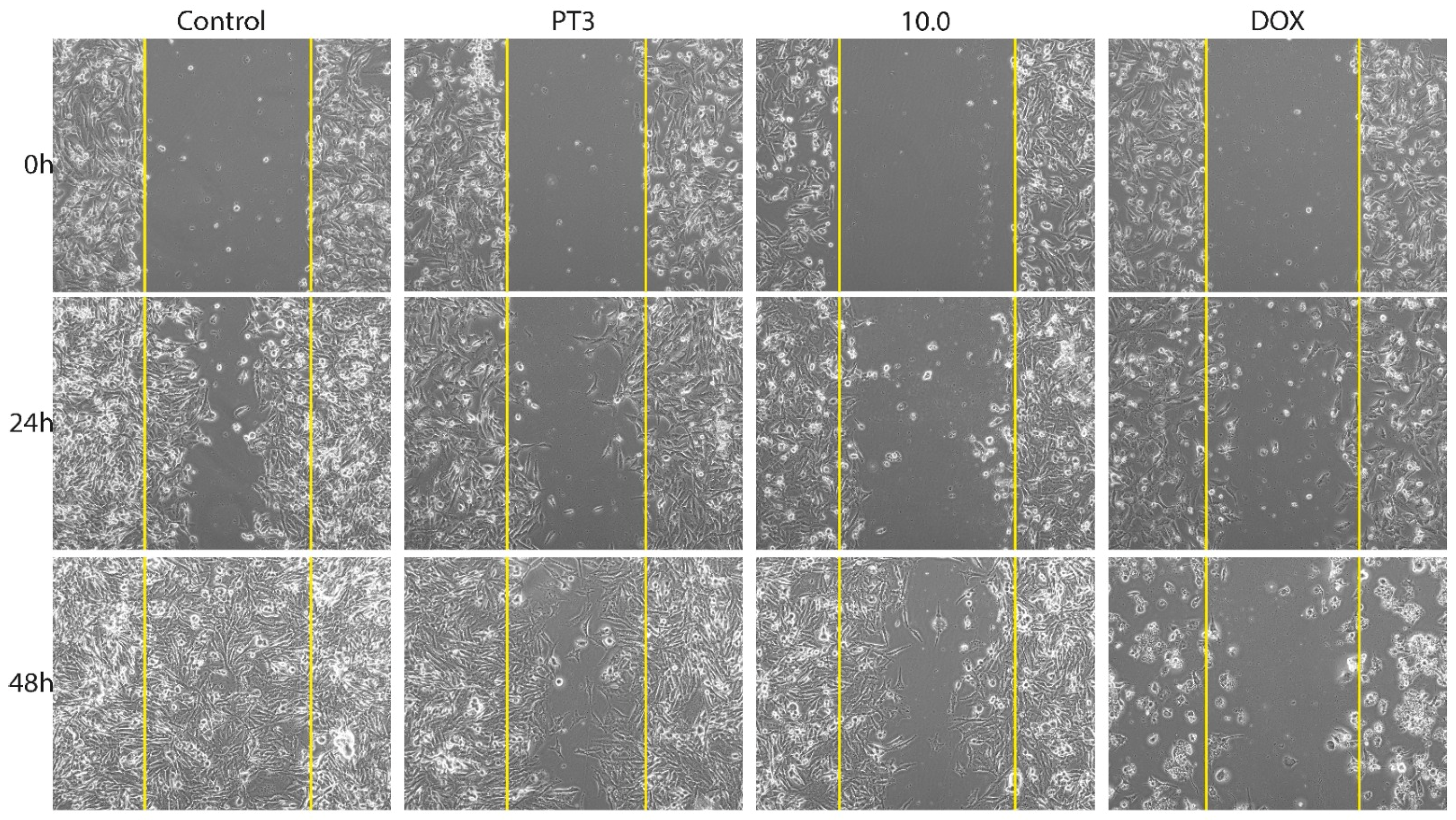
3.3. Migration of Bone Cancer Cells In Vitro
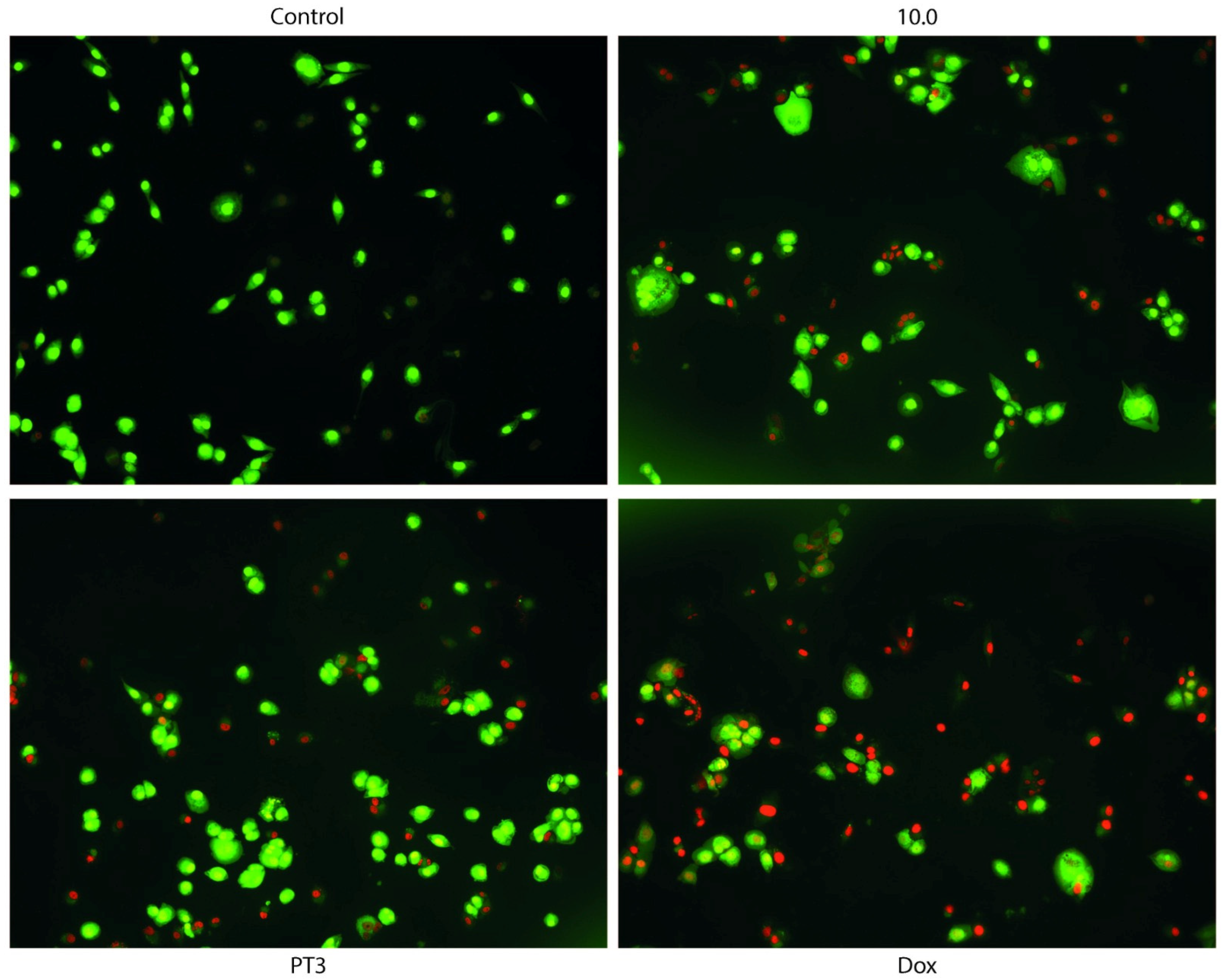
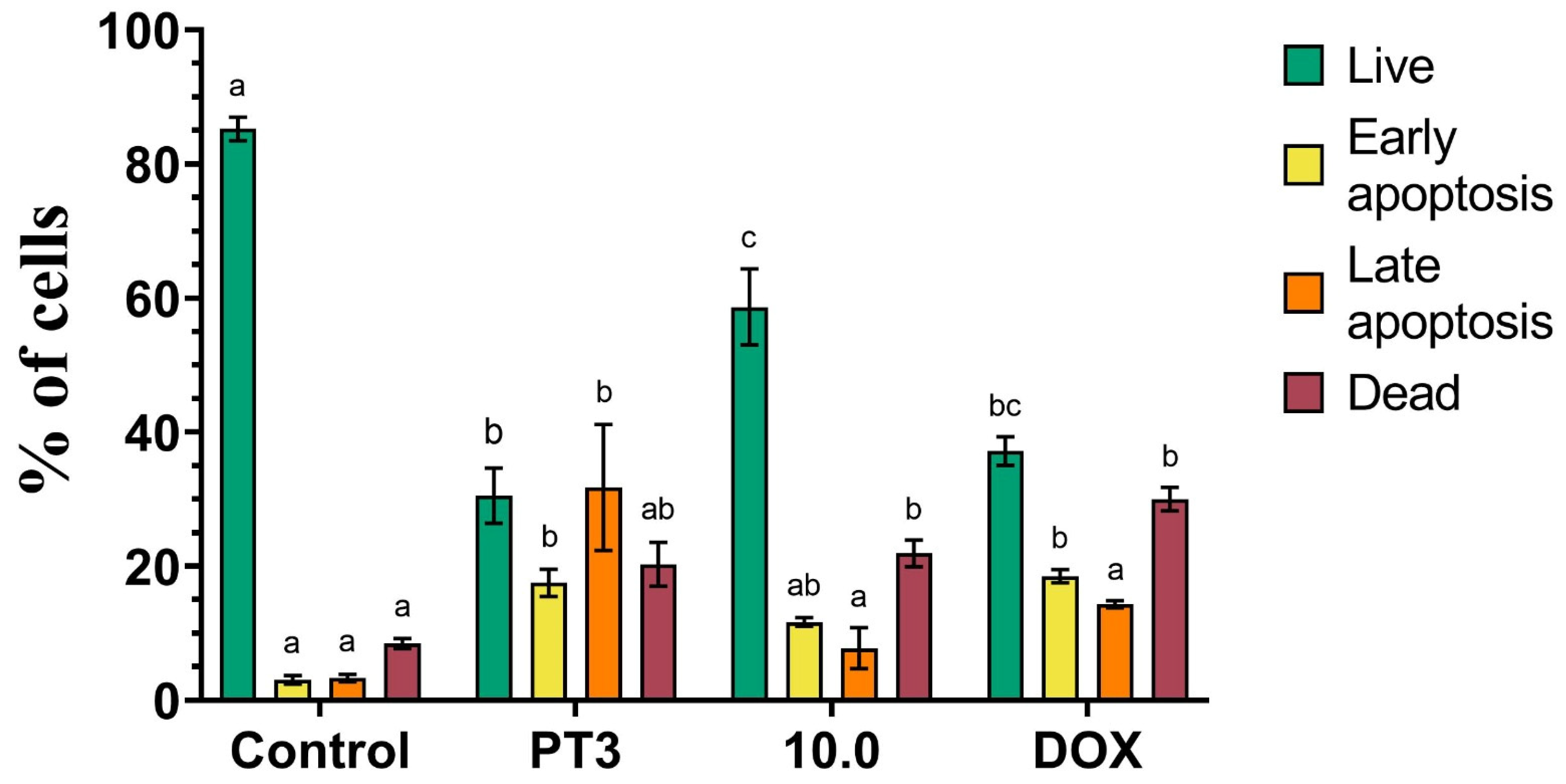
3.4. Dual Acridine Orange/Ethidium Bromide (AO/EB) Fluorescent Staining
3.5. Caspase Activity in Cancer Cells Treated with Plant Tocotrienols and Food Supplement 10.0
3.6. Total Antioxidant Capacity (TAC) of Natural Compounds and Dietary Supplements According to the FRAP Assay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keum, N.; Giovannucci, E. Global burden of colorectal cancer: Emerging trends, risk factors and prevention strategies. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 713–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biller, L.H.; Schrag, D. Diagnosis and Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Review. JAMA 2021, 325, 669–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, A.T.; Baek, J.; Alexander, J.H.; Voskuil, R.T.; Khan, S.N.; Scharschmidt, T.J. Malignant fibrous histiocytoma of bone: A survival analysis from the National Cancer Database. J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 121, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Sundaram, C.; Prasad, S.; Kannappan, R. Tocotrienols, the vitamin E of the 21st century: Its potential against cancer and other chronic diseases. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 1613–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, P.; Janmeda, P.; Docea, A.O.; Yeskaliyeva, B.; Razis, A.F.A.; Modu, B.; Calina, D.; Sharifi-Rad, J. Oxidative stress, free radicals and antioxidants: Potential crosstalk in the pathophysiology of human diseases. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1158198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurlek, C.; Yarkent, C.; Kose, A.; Tugcu, B.; Gebeloglu, I.K.; Oncel, S.S.; Elibol, M. Screening of antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of several microalgal extracts with pharmaceutical potential. Health Technol.-Ger. 2020, 10, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hassan, S.H.A.; Awasthi, M.K.; Gajendran, B.; Sharma, M.; Ji, M.K.; Salama, E. The recent progress on the bioactive compounds from algal biomass for human health applications. Food Biosci. 2023, 51, 102267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asma, S.T.; Acaroz, U.; Imre, K.; Morar, A.; Shah, S.R.A.; Hussain, S.Z.; Arslan-Acaroz, D.; Demirbas, H.; Hajrulai-Musliu, Z.; Istanbullugil, F.R.; et al. Natural Products/Bioactive Compounds as a Source of Anticancer Drugs. Cancers 2022, 14, 6203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.; Silva, J.; Pinteus, S.; Gaspar, H.; Alpoim, M.C.; Botana, L.M.; Pedrosa, R. From Marine Origin to Therapeutics: The Antitumor Potential of Marine Algae-Derived Compounds. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimento, A.; De Luca, A.; D’Amico, M.; De Amicis, F.; Pezzi, V. The Involvement of Natural Polyphenols in Molecular Mechanisms Inducing Apoptosis in Tumor Cells: A Promising Adjuvant in Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.H.; Huang, C.C.; Hsu, L.S.; Kao, S.H.; Wang, C.J. Apple polyphenol inhibits colon carcinoma metastasis via disrupting Snail binding to focal adhesion kinase. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 12, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.A.; Mendonca, P.; Elhag, R.; Soliman, K.F.A. Anticancer Effects of Fucoxanthin through Cell Cycle Arrest, Apoptosis Induction, Angiogenesis Inhibition, and Autophagy Modulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 16091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayin, V.I.; Ibrahim, M.X.; Larsson, E.; Nilsson, J.A.; Lindahl, P.; Bergo, M.O. Antioxidants Accelerate Lung Cancer Progression in Mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 221ra15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mut-Salud, N.; Alvarez, P.J.; Garrido, J.M.; Carrasco, E.; Aránega, A.; Rodríguez-Serrano, F. Antioxidant Intake and Antitumor Therapy: Toward Nutritional Recommendations for Optimal Results. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2016, 2016, 6719534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonner, M.Y.; Arbiser, J.L. The antioxidant paradox: What are antioxidants and how should they be used in a therapeutic context for cancer. Future Med. Chem. 2014, 6, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B. The antioxidant paradox: Less paradoxical now? Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 75, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Meerloo, J.; Kaspers, G.J.; Cloos, J. Cell sensitivity assays: The MTT assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 731, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebaugh, J.L. Guidelines for accurate EC50/IC50 estimation. Pharm. Stat. 2011, 10, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonkman, J.E.; Cathcart, J.A.; Xu, F.; Bartolini, M.E.; Amon, J.E.; Stevens, K.M.; Colarusso, P. An introduction to the wound healing assay using live-cell microscopy. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2014, 8, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haykal, T.; Nasr, P.; Hodroj, M.H.; Taleb, R.I.; Sarkis, R.; Moujabber, M.N.E.; Rizk, S. Annona cherimola Seed Extract Activates Extrinsic and Intrinsic Apoptotic Pathways in Leukemic Cells. Toxins 2019, 11, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geback, T.; Schulz, M.M.; Koumoutsakos, P.; Detmar, M. TScratch: A novel and simple software tool for automated analysis of monolayer wound healing assays. Biotechniques 2009, 46, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribble, D.; Goldstein, N.B.; Norris, D.A.; Shellman, Y.G. A simple technique for quantifying apoptosis in 96-well plates. BMC Biotechnol. 2005, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Liu, P.C.; Liu, R.; Wu, X. Dual AO/EB staining to detect apoptosis in osteosarcoma cells compared with flow cytometry. Med. Sci. Monit. Basic. Res. 2015, 21, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, I.F.; Strain, J.J. The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: The FRAP assay. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 239, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Berre, M.; Gerlach, J.Q.; Dziembala, I.; Kilcoyne, M. Calculating Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC(50)) Values from Glycomics Microarray Data Using GraphPad Prism. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2460, 89–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannappan, R.; Gupta, S.C.; Kim, J.H.; Aggarwal, B.B. Tocotrienols fight cancer by targeting multiple cell signaling pathways. Genes Nutr. 2012, 7, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, M.T.; Luk, S.U.; Al-Ejeh, F.; Khanna, K.K. Tocotrienol as a potential anticancer agent. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eitsuka, T.; Tatewaki, N.; Nishida, H.; Nakagawa, K.; Miyazawa, T. Synergistic Anticancer Effect of Tocotrienol Combined with Chemotherapeutic Agents or Dietary Components: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.A.; Mendonca, P.; Messeha, S.S.; Oriaku, E.T.; Soliman, K.F.A. The Anticancer Effects of Marine Carotenoid Fucoxanthin through Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase (PI3K)-AKT Signaling on Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Molecules 2024, 29, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.R.; Hosokawa, M.; Miyashita, K. Fucoxanthin: A Marine Carotenoid Exerting Anti-Cancer Effects by Affecting Multiple Mechanisms. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 5130–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Y.; Fu, C.B.; Lin, M.T.; Lu, Y.S.; Lian, S.; Xie, X.D.; Zhou, G.Y.; Li, W.L.; Zhang, Y.P.; Jia, L.; et al. Fucoxanthin prevents breast cancer metastasis by interrupting circulating tumor cells adhesion and transendothelial migration. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 960375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.X.; Hu, X.M.; Xu, S.Q.; Jiang, Z.J.; Yang, W. Effects of fucoxanthin on proliferation and apoptosis in human gastric adenocarcinoma MGC-803 cells via JAK/STAT signal pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 657, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satomi, Y. Antitumor and Cancer-preventative Function of Fucoxanthin: A Marine Carotenoid. Anticancer. Res. 2017, 37, 1557–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, K.L.; Foong, L.C.; Abd Ghafar, N.; Soelaiman, I.N.; Law, J.X.; Leong, L.M.; Chin, K.Y. Transcriptomic Analysis of the Anticancer Effects of Annatto Tocotrienol, Delta-Tocotrienol and Gamma-Tocotrienol on Chondrosarcoma Cells. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.W.; Loh, H.S.; Ting, K.N.; Bradshaw, T.D.; Zeenathul, N.A. Cytotoxicity and apoptotic activities of alpha-, gamma- and delta-tocotrienol isomers on human cancer cells. BMC Complem Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, V.; Kashyap, D.; Sak, K.; Tuli, H.S.; Jain, A.; Chaudhary, A.; Garg, V.K.; Sethi, G.; Yerer, M.B. Molecular Mechanisms of Action of Tocotrienols in Cancer: Recent Trends and Advancements. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atashrazm, F.; Lowenthal, R.M.; Woods, G.M.; Holloway, A.F.; Dickinson, J.L. Fucoidan and cancer: A multifunctional molecule with anti-tumor potential. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2327–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.H.; Chang, Y.C.; Hsu, C.C.; Lin, C.H.; Chen, I.J.; Wu, Y.T.; Lan, Y.Y. Fucoidan Enhances Cisplatin-induced Effects on SCC-25 Human Oral Cancer Cells by Inhibiting the PI3K/AKT Pathway. Anticancer. Res. 2023, 43, 4015–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D. Fucoidan induces cancer cell apoptosis by modulating the endoplasmic reticulum stress cascades. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiselevskiy, M.V.; Anisimova, N.Y.; Ustyuzhanina, N.E.; Vinnitskiy, D.Z.; Tokatly, A.I.; Reshetnikova, V.V.; Chikileva, I.O.; Shubina, I.Z.; Kirgizov, K.I.; Nifantiev, N.E. Perspectives for the Use of Fucoidans in Clinical Oncology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayani, S.S.; Saravanan, S.; Ravindran, J.; Ramasamy, M.S.; Chitra, J. In vitro anticancer activity of fucoidan extracted from Sargassum cinereum against Caco-2 cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 138, 618–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somasundaram, S.N.; Shanmugam, S.; Subramanian, B.; Jaganathan, R. Cytotoxic effect of fucoidan extracted from Sargassum cinereum on colon cancer cell line HCT-15. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 1215–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Sun, L.; Wei, X.; Lu, H.; Tan, Y.; Sun, Z.; Jiang, J. Antitumor effect and molecular mechanism of fucoidan in NSCLC. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wayakanon, K.; Rueangyotchanthana, K.; Wayakanon, P.; Suwannachart, C. The inhibition of Caco-2 proliferation by astaxanthin from Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Hosokawa, M.; Kasajima, H.; Hatanaka, K.; Kudo, K.; Shimoyama, N.; Miyashita, K. Anticancer effects of fucoxanthin and fucoxanthinol on colorectal cancer cell lines and colorectal cancer tissues. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 1463–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, M.; Kudo, M.; Maeda, H.; Kohno, H.; Tanaka, T.; Miyashita, K. Fucoxanthin induces apoptosis and enhances the antiproliferative effect of the PPARgamma ligand, troglitazone, on colon cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1675, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, M.; Pahlke, G.; Balavenkatraman, K.K.; Bohmer, F.D.; Marko, D. Apple polyphenols affect protein kinase C activity and the onset of apoptosis in human colon carcinoma cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 4999–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, J.; Liu, R.H. Apple phytochemicals and their health benefits. Nutr. J. 2004, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.N.; Heo, S.J.; Kang, S.M.; Ahn, G.; Jeon, Y.J. Fucoxanthin induces apoptosis in human leukemia HL-60 cells through a ROS-mediated Bcl-xL pathway. Toxicol. Vitr. 2010, 24, 1648–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliaccio, G.; Ferraro, R.; Wang, Z.; Cristini, V.; Dogra, P.; Caserta, S. Exploring Cell Migration Mechanisms in Cancer: From Wound Healing Assays to Cellular Automata Models. Cancers 2023, 15, 5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.C.; Park, A.Y.; Guan, J.L. In vitro scratch assay: A convenient and inexpensive method for analysis of cell migration in vitro. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.K.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Sun, W.G.; Liu, J.R.; Yang, Y.M.; Xu, W.L.; Sun, X.R.; Chen, B.Q. Inhibitory effects of gamma-tocotrienol on invasion and metastasis of human gastric adenocarcinoma SGC-7901 cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2010, 21, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idriss, M.; Hodroj, M.H.; Fakhoury, R.; Rizk, S. Beta-Tocotrienol Exhibits More Cytotoxic Effects than Gamma-Tocotrienol on Breast Cancer Cells by Promoting Apoptosis via a P53-Independent PI3-Kinase Dependent Pathway. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coombe, D.R.; Parish, C.R.; Ramshaw, I.A.; Snowden, J.M. Analysis of the inhibition of tumour metastasis by sulphated polysaccharides. Int. J. Cancer 1987, 39, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.M.; Bignon, J.; Haroun-Bouhedja, F.; Bittoun, P.; Vassy, J.; Fermandjian, S.; Wdzieczak-Bakala, J.; Boisson-Vidal, C. Inhibitory effect of fucoidan on the adhesion of adenocarcinoma cells to fibronectin. Anticancer. Res. 2005, 25, 2129–2133. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.W.; Chen, Y.C.; Yin, T.C.; Chen, P.J.; Chang, T.K.; Su, W.C.; Ma, C.J.; Li, C.C.; Tsai, H.L.; Wang, J.Y. Low-Molecular-Weight Fucoidan as Complementary Therapy of Fluoropyrimidine-Based Chemotherapy in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comitato, R.; Guantario, B.; Leoni, G.; Nesaretnam, K.; Ronci, M.B.; Canali, R.; Virgili, F. Tocotrienols induce endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in cervical cancer cells. Genes Nutr. 2016, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, R.; Selvaduray, K.R.; Nesaretnam, K.; Radhakrishnan, A.K. Tocotrienols promote apoptosis in human breast cancer cells by inducing poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage and inhibiting nuclear factor kappa-B activity. Cell Proliferat 2013, 46, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Simmons-Menchaca, M.; Gapor, A.; Sanders, B.G.; Kline, K. Induction of apoptosis in human breast cancer cells by tocopherols and tocotrienols. Nutr. Cancer 1999, 33, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turrini, E.; Maffei, F.; Fimognari, C. Ten Years of Research on Fucoidan and Cancer: Focus on Its Antiangiogenic and Antimetastatic Effects. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, J.H. Fucoidan present in brown algae induces apoptosis of human colon cancer cells. BMC Gastroenterol. 2010, 10, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Li, J.; Jing, X.; Ding, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, Q. Fucoidan Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Proliferation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma via the p38 MAPK/ERK and PI3K/Akt Signal Pathways. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 1713–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Wei, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Ning, L.; Luo, S.H.; Liu, C.L.; Song, G.; Yao, Q. Fucoidan Inhibits the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Causing lncRNA LINC00261 Overexpression. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 653902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sylvester, P.W. Synergistic anticancer effects of combined gamma-tocotrienol with statin or receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment. Genes Nutr. 2012, 7, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohen, R.; Nyska, A. Oxidation of biological systems: Oxidative stress phenomena, antioxidants, redox reactions, and methods for their quantification. Toxicol. Pathol. 2002, 30, 620–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B. Antioxidants in human health and disease. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1996, 16, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| TIB-223 | K562 | Caco2 | MCF-7 | DU 145 | Detroit 548 | Vero | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PT3 | 4.3 ± 1.51 a | 29.2 ± 6.38 a | 39.89 ± 9.04 ab | 46.8 ± 6.26 a | 78.76 ± 14.27 a | 31.20 ± 7.37 a | 162 ± 26.50 a |
| FXT | 14 ± 8.24 a | 342 ± 65.20 a | 262.6 ± 58.80 b | 138 ± 33.48 a | 448 ± 32.34 a | 195 ± 83.80 ab | 466 ± 29.20 b |
| APP | 43 ± 21.40 a | 977 ± 20.9 b | 259.9 ± 64.20 b | 985 ± 64.66 b | 910 ± 58.02 b | 425 ± 130 b | 25 ± 4.15 a |
| FUC | 2524 ± 87 b | 4189 ± 103 c | 2643 ± 126 c | 1885 ± 73 c | 1066 ± 70 b | 2630 ± 122 c | 1130 ± 129 c |
| AXT | 2973 ± 179 b | 3862 ± 187 c | 2277 ± 184 c | 1709 ± 64 c | 2265 ± 77 c | 2984 ± 102 c | 1226 ± 216 c |
| DOX | 1.16 ± 0.21 a | 3.25 ± 0.34 a | 6.5 ± 0.29 a | 0.67 ± 0.10 a | 102.60 ± 9.30 a | 1.21 ± 0.29 a | 1.68 ± 0.60 a |
| PTX | 1.31 ± 0.26 a | 125 ± 34.40 a | 0.23 ± 0.08 a | 11.3 ± 0.39 a | 1.49 ± 0.07 a | 0.67 ± 0.25 a | 5.19 ± 1.17 a |
| TIB-223 | Caco2 | MCF-7 | K562 | DU 145 | Detroit 548 | Vero | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.1 | 1160 ± 121.50 b | 340.50 ± 59.13 a | 821.2 ± 105.7 b | 295.10 ± 59.68 b | 1943 ± 175.60 b | 191.40 ± 49.82 b | 2238 ± 150.30 c |
| 4.0 | 2302 ± 89.33 c | 2373 ± 306.60 b | 2296 ± 111 c | 7300 ± 18 c | 7185 ± 176 c | 5391 ± 80 c | 8770 ± 247 c |
| 10.0 | 126 ± 25.32 a | 158.70 ± 17.79 a | 200.5 ± 44.04 a | 243.70 ± 32.90 b | 396 ± 10.05 a | 166.90 ± 21.38 b | 386.30 ± 26.71 b |
| DOX | 1.16 ± 0.21 a | 6.50 ± 0.29 a | 0.67 ± 0.10 a | 3.25 ± 0.34 a | 102.60 ± 9.30 a | 1.21 ± 0.29 a | 1.68 ± 0.60 a |
| PTX | 1.31 ± 0.26 a | 0.23 ± 0.08 a | 11.3 ± 0.39 a | 0.12 ± 0.03 a | 1.49 ± 0.07 a | 0.67 ± 0.25 a | 5.19 ± 1.17 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lara-Hernández, G.; Ramos-Silva, J.A.; Pérez-Soto, E.; Figueroa, M.; Flores-Berrios, E.P.; Sánchez-Chapul, L.; Andrade-Cabrera, J.L.; Luna-Angulo, A.; Landa-Solís, C.; Avilés-Arnaut, H. Anticancer Activity of Plant Tocotrienols, Fucoxanthin, Fucoidan, and Polyphenols in Dietary Supplements. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4274. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16244274
Lara-Hernández G, Ramos-Silva JA, Pérez-Soto E, Figueroa M, Flores-Berrios EP, Sánchez-Chapul L, Andrade-Cabrera JL, Luna-Angulo A, Landa-Solís C, Avilés-Arnaut H. Anticancer Activity of Plant Tocotrienols, Fucoxanthin, Fucoidan, and Polyphenols in Dietary Supplements. Nutrients. 2024; 16(24):4274. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16244274
Chicago/Turabian StyleLara-Hernández, Gabriel, José Alberto Ramos-Silva, Elvia Pérez-Soto, Mario Figueroa, Ericka Patricia Flores-Berrios, Laura Sánchez-Chapul, José Luis Andrade-Cabrera, Alexandra Luna-Angulo, Carlos Landa-Solís, and Hamlet Avilés-Arnaut. 2024. "Anticancer Activity of Plant Tocotrienols, Fucoxanthin, Fucoidan, and Polyphenols in Dietary Supplements" Nutrients 16, no. 24: 4274. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16244274
APA StyleLara-Hernández, G., Ramos-Silva, J. A., Pérez-Soto, E., Figueroa, M., Flores-Berrios, E. P., Sánchez-Chapul, L., Andrade-Cabrera, J. L., Luna-Angulo, A., Landa-Solís, C., & Avilés-Arnaut, H. (2024). Anticancer Activity of Plant Tocotrienols, Fucoxanthin, Fucoidan, and Polyphenols in Dietary Supplements. Nutrients, 16(24), 4274. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16244274





