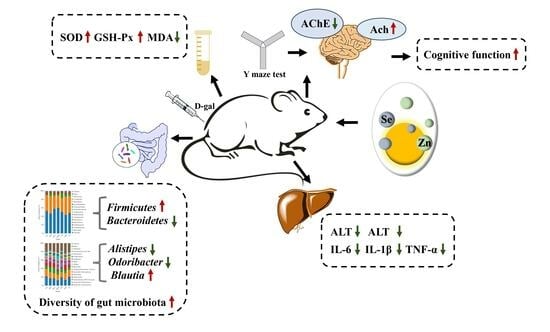
Selenium- and/or Zinc-Enriched Egg Diet Improves Oxidative Damage and Regulates Gut Microbiota in D-Gal-Induced Aging Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Pre-Treatment of Egg Powder
2.3. Detection of Basic Nutrients
2.4. ICP-MS Analysis
2.5. Animal Experimental Design
2.6. Animal’s Weight Change and Relative Organ Weight
2.7. Spontaneous Alternating Behavior Test
2.8. New Arm Behavioral Test
2.9. Determination of Se and Zn Content in Tissue
2.10. Analysis of Ach and AChE Levels in the Brain
2.11. Analysis of Serum Antioxidant Activity
2.12. Analysis of Oxidative Stress Injury in Liver Issue
2.13. Gut Microbiota Analysis
2.14. Histopathological Analysis of Brain and Liver
2.15. Pathological Scores
2.16. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Basic Nutritional Components and Mineral Composition of Eggs
3.2. SZE Regulated the Physical Condition of Mice
3.3. Distribution of Se and Zn in Tissue
3.4. SZE Alleviated D-Gal-Induced Oxidative Stress
3.5. SZE Reversed Learning Memory Impairment Caused by D-Gal
3.6. SZE Improved D-Gal-Induced Brain Dysfunction
3.7. SZE Attenuated D-Gal-Induced Hepatic Impairment and Inflammation
3.8. Effects of SZE on Intestinal Flora in Aging Mice
4. Discussion
4.1. SZE Can Resist Oxidative Stress Aging and Improve Cognitive Impairment
4.2. SZE Can Maintain Intestinal Microbial Diversity and Protect Intestinal Health
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, S.Y.; Jiang, N.; Tu, J.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Y. Antioxidant and Anti-aging Activities of Silybum Marianum Protein Hydrolysate in Mice Treated with D-galactose. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2017, 30, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Mills, K.; le Cessie, S.; Noordam, R.; van Heemst, D. Ageing, age-related diseases and oxidative stress: What to do next? Ageing Res. Rev. 2020, 57, 100982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzid, M.A.; Filaire, E.; McCall, A.; Fabre, C. Radical Oxygen Species, Exercise and Aging: An Update. Sports Med. 2015, 45, 1245–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Xu, B.J.; Huang, W.S.; Amrouche, A.T.; Maurizio, B.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Tundis, R.; Xiao, J.B.; Zou, L.; Lu, B.Y. Edible flowers as functional raw materials: A review on anti-aging properties. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 106, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreini, C.; Banci, L.; Bertini, I.; Rosato, A. Counting the zinc-proteins encoded in the human genome. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2006, 5, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, G.; Lauria, G.; Catalano, A.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Carocci, A. Biological Activity of Selenium and Its Impact on Human Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.L.; Zhang, J.Z.; Li, H.J. Selenium, aging and aging-related diseases. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 31, 1035–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorklund, G.; Shanaida, M.; Lysiuk, R.; Antonyak, H.; Klishch, I.; Shanaida, V.; Peana, M. Selenium: An Antioxidant with a Critical Role in Anti-Aging. Molecules 2022, 27, 6613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Rocourt, C.; Cheng, W.H. Selenoproteins and the aging brain. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2010, 131, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.; Farooq, M.U.; Zhang, G.; Tang, Z.C.; Zheng, T.D.; Su, Y.; Hussain, S.; Liang, Y.K.; Ye, X.Y.; Jia, X.M.; et al. Dissecting the Potential of Selenoproteins Extracted from Selenium-Enriched Rice on Physiological, Biochemical and Anti-Ageing Effects In Vivo. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 196, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.Z.; Wang, J.; Feng, J.; Cao, B. Zinc in Cognitive Impairment and Aging. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Gao, Z.; Hu, C.L.; Zhang, J.J.; Sun, X.Y.; Rong, C.B.; Jia, L. Antioxidant, antibacterial and anti-aging activities of intracellular zinc polysaccharides from Grifola frondosa SH-05. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 95, 778–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.C.; Zheng, H.; Guo, J.C.; Tan, X.Y.; Zhao, T.; Song, Y.F.; Wei, X.L.; Luo, Z. Effects of Different Dietary Zinc (Zn) Sources on Growth Performance, Zn Metabolism, and Intestinal Health of Grass Carp. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Qu, L.; Shen, M.M.; Hu, Y.P.; Guo, J.; Dou, T.C.; Wang, K.H. Comparison of dynamic change of egg selenium deposition after feeding sodium selenite or selenium-enriched yeast. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 3102–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs-Nolan, J.; Phillips, M.; Mine, Y. Advances in the value of eggs and egg components for human health. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 8421–8431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesnierowski, G.; Stangierski, J. What’s new in chicken egg research and technology for human health promotion?—A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 71, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, Q.; He, P.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, L.M.; Chen, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, M.M. Heat-induced gel properties and gastrointestinal digestive properties of egg white produced by hens fed with selenium-enriched yeast. Food Chem. 2022, 366, 130712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. GB 5009.3-2016; National Food Safety Standard-Determination of Moisture in Food. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. GB 5009.4-2016; National Food Safety Standard-Determination of Ash in Food. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. GB 5009.5-2016; National Food Safety Standard-Determination of Protein in Food. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. GB 5009.6-2016; National Food Safety Standard-Determination of Lipid in Food. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. GB/T 5537-2008; National Food Safety Standard-Determination of Phospholipids in Grain and Oil. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Kong, S.Z.; Li, J.C.; Li, S.D.; Liao, M.N.; Li, C.P.; Zheng, P.J.; Guo, M.H.; Tan, W.X.; Zheng, Z.H.; Hu, Z. Anti-Aging Effect of Chitosan Oligosaccharide on D-Galactose-Induced Subacute Aging in Mice. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Research Council (US) Institute for Laboratory Animal Research. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, Y.L.; Ma, Q.Y.; Guo, Y.; Sun, L.P. Protective effects of rambutan (Nephelium lappaceum) peel phenolics on H2O2-induced oxidative damages in HepG2 cells and D-galactose induced aging mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 108, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. GB 5009.93-2017; National Food Safety Standard-Determination of Selenium in Food. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. GB 5009.14-2017; National Food Safety Standard-Determination of Zinc in Food. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Luo, J.X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, X.Y.; Zhong, S.; Chen, G.; Wang, Y.Y.; Lin, W.; Yi, C.; Zhu, H. The effects of modified sini decoction on liver injury and regeneration in acute liver failure induced by D-galactosamine in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 161, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Qu, L.; Ma, M.; Li, Y.F.; Wang, X.G.; Yang, Z.; Wang, K.H. Efficacy evaluation of selenium-enriched yeast in laying hens: Effects on performance, egg quality, organ development, and selenium deposition. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 6267–6277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornescu, G.M.; Panaite, T.D.; Untea, A.E.; Varzaru, I.; Saracila, M.; Dumitru, M.; Vlaicu, P.A.; Gavris, T. Mitigation of heat stress effects on laying hens’ performances, egg quality, and some blood parameters by adding dietary zinc-enriched yeasts, parsley, and their combination. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1202058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.S.; Wang, H.L.; Hu, N. Long-Term Dietary Lycium ruthenicum Murr. Anthocyanins Intake Alleviated Oxidative Stress-Mediated Aging-Related Liver Injury and Abnormal Amino Acid Metabolism. Foods 2022, 11, 3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.T.; Zhong, S.Y.; Xu, J.C.; Jiao, W.J.; Liu, W.F.; Huang, L.H.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.S. PAYCS Alleviates Scopolamine-Induced Memory Deficits in Mice by Reducing Oxidative and Inflammatory Stress and Modulation of Gut Microbiota-Fecal Metabolites-Brain Neurotransmitter Axis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 2864–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, H.C.; Kuan, V.; Johnen, R.; Zwierzyna, M.; Hingorani, A.D.; Beyer, A.; Partridge, L. Biological mechanisms of aging predict age-related disease co-occurrence in patients. Aging Cell 2022, 21, e13524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Chen, F.C.; Zhou, B.H. Antioxidative, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects of ellagic acid in liver and brain of rats treated by D-galactose. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, W.; Noreen, H.; Rehman, S.; Kamal, M.A.; da Rocha, J.B.T. Association of Oxidative Stress with Neurological Disorders. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2022, 20, 1046–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Lei, J.X.; Chen, F.C.; Zhou, B.H. Ameliorative effect of urolithin A on d-gal-induced liver and kidney damage in aging mice via its antioxidative, anti-inflammatory and antiapoptotic properties. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 8027–8038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, E.K.; Chung, K.W.; Chung, S.; Lee, B.; Seo, A.Y.; Chung, J.H.; Jung, Y.S.; Im, E.; et al. Redefining Chronic Inflammation in Aging and Age-Related Diseases: Proposal of the Senoinflammation Concept. Aging Dis. 2019, 10, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Shi, H.Q.; Ying, S.H.; Feng, M.G. Distinct contributions of one Fe- and two Cu/Zn-cofactored superoxide dismutases to antioxidation, UV tolerance and virulence of Beauveria bassiana. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2015, 81, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundakovic, T.; Dukic, N.M.; Kovacevic, N. Free radical scavenging activity of Achillea alexandri-regis extracts. Fitoterapia 2005, 76, 574–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.J.; Zhao, T.; Luo, Z.; Zhong, C.C.; Zheng, H.; Tan, X.Y. Effects of dietary supplementation with manganese dioxide nanoparticles on growth, Mn metabolism and kidney health of yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco. Aquacul. Rep. 2023, 33, 101815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.H.; Zhao, Z.P.; Wang, Y.G.; Huang, K.H. Preparation of Selenium/Zinc-Enriched Probiotics and Their Effect on Blood Selenium and Zinc Concentrations, Antioxidant Capacities, and Intestinal Microflora in Canine. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2011, 141, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, F.; Mobarez, S.; Mohamed, M.; Attia, Y.; Mekawy, A.; Mahrose, K. Zinc and/or Selenium Enriched Spirulina as Antioxidants in Growing Rabbit Diets to Alleviate the Deleterious Impacts of Heat Stress during Summer Season. Animals 2021, 11, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cempel, M.; Janicka, K. Distribution of nickel, zinc, and copper in rat organs after oral administration of nickel(II) chloride. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2002, 90, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesik, V.; Lenk, M.K.; Kurekci, A.E.; Acikel, C.H.; Akgul, E.O.; Aydin, A.; Erdem, O.; Gamsizkan, M. Do zinc and selenium prevent the antioxidant, hepatic and renal system impairment caused by aspirin in rats? Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2008, 123, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.Y.; Wang, X.L.; Li, C.M.; Li, F.F.; Yan, Z.X.; Ma, N.; Sun, M. Probiotics combined with zinc and selenium preparation in the treatment of child rotavirus enteritis. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2022, 14, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Li, R.J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.Y. Perspectives on lecithin from egg yolk: Extraction, physicochemical properties, modification, and applications. Front. Nutr. 2023, 9, 1082671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.X.; Fu, X.Y.; Zhang, L.Y.; Gao, X.; Wen, M.; Du, L.; Xue, C.H.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.M. Neuroprotective Effects of n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid-Enriched Phosphatidylserine against Oxidative Damage in PC12 Cells. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 38, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.J.; Zhang, P.L.; Chen, J.; Gao, J.; Lin, S.Y.; Sun, N. Egg yolk phospholipids reverse scopolamine-induced spatial memory deficits in mice by attenuating cholinergic damage. J. Func. Foods 2020, 69, 103948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Xie, C.X.; Li, Z.R.; Zeng, H.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, Z.M. Selenium Intake and its Interaction with Iron Intake Are Associated with Cognitive Functions in Chinese Adults: A Longitudinal Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Sun, W.J.; Zhang, D.F. Association of Zinc, Iron, Copper, and Selenium Intakes with Low Cognitive Performance in Older Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). J Alzheimers Dis. 2019, 72, 1145–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, K.A.; Chu, Y.; Grider, A.; Coffield, J.A. Supplementation with L-histidine during dietary zinc repletion improves short-term memory in zinc-restricted young adult male rats. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1633–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Ma, T.; Sakandar, H.A.; Menghe, B.; Sun, Z.H. Gut microbiome and aging nexus and underlying mechanism. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2022, 106, 5349–5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.F.; Yan, H.; Li, C.Y.; Wen, F.; Jize, X.; Zhang, C.W.; Liu, S.Q.; Zhao, Y.Z.; Fu, Y.P.; Li, L.X.; et al. A Pectic Polysaccharide from Codonopsis pilosula Alleviates Inflammatory Response and Oxidative Stress of Aging Mice via Modulating Intestinal Microbiota-Related Gut-Liver Axis. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campagnoli, L.I.M.; Marchesi, N.; Vairetti, M.; Pascale, A.; Ferrigno, A.; Barbieri, A. Age-Related NAFLD: The Use of Probiotics as a Supportive Therapeutic Intervention. Cells 2022, 11, 2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajarillo, E.A.B.; Lee, E.; Kang, D.K. Trace metals and animal health: Interplay of the gut microbiota with iron, manganese, zinc, and copper. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 7, 750–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.D.; Jiang, Z.H.; Song, Y.W.; Xing, Y.T.; He, S.M.; Boomi, P. Gut microbiota contribution to selenium deficiency-induced gut-liver inflammation. Biofactors 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Liu, F.; Xu, C.; Liu, Z.J.; Ma, J.G.; Gu, L.Y.; Jiang, Z.M.; Hou, J.C. Lactobacillus plantarum 69-2 Combined with Galacto-Oligosaccharides Alleviates D-Galactose-Induced Aging by Regulating the AMPK/SIRT1 Signaling Pathway and Gut Microbiota in Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 2745–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.X.; Sun, J.Q.; Bai, H.J.; Ma, H.L.; Wang, K.; Wang, J.; Yu, X.F.; Pan, Y.R.; Yao, J.F. Influence of Flax Seeds on the Gut Microbiota of Elderly Patients with Constipation. J. Multidiscip. Health 2022, 15, 2407–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Wu, X. Modulation of the Gut Microbiota in Memory Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease via the Inhibition of the Parasympathetic Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, B.Y.; Guo, W.L.; Liu, X.M.; Cui, S.M.; Zhang, Q.X.; Zhao, J.X.; Tang, X.; Zhang, H. Potential Probiotic Properties of Blautia producta Against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Liver Injury. Probiotics Antimicrob. 2023, 15, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasaikina, M.V.; Kravtsova, M.A.; Lee, B.C.; Seravalli, J.; Peterson, D.A.; Walter, J.; Legge, R.; Benson, A.K.; Hatfield, D.L.; Gladyshev, V.N. Dietary selenium affects host selenoproteome expression by influencing the gut microbiota. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 2492–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C.; Ortega, E.F.; Meydani, S.N.; Adkins, Y.; Stephensen, C.B.; Thompson, B.; Zwickey, H. Nutrition, Immunosenescence, and Infectious Disease: An Overview of the Scientific Evidence on Micronutrients and on Modulation of the Gut Microbiota. Adv. Nutr. 2022, 13, 1S–26S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Gao, Q.; Su, J.X.; Shang, H.; Meng, X.; Jiang, S.Q.; Liu, D.H.; Huang, B. Gut Microbiome and Metabolomics Study of Selenium-Enriched Kiwifruit Regulating Hyperlipidemia in Mice Induced by a High-Fat Diet. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 20386–20401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.X.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Huang, X.Y.; Sun, W.Y.; Liang, X.J.; Zhang, E.P. The Effect of Dietary Supplementation with Zinc Amino Acids on Immunity, Antioxidant Capacity, and Gut Microbiota Composition in Calves. Animals 2023, 13, 1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Parameter Name | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Radio frequency power (W) | 1500 |
| Plasma flow rate (L/min) | 15 |
| Carrier gas flow rate (L/min) | 0.8 |
| Helium flow rate (mL/min) | 4 |
| Atomization chamber temperature (°C) | 2 |
| Nebulizer type | Concentric |
| Sampling depth (mm) | 8 |
| Sampling mode | Spectrum |
| Number of measurements per peak | 3 |
| Repetition number | 3 |
| Items | Whole Egg | Albumen | Yolk | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SZE | NE | SZE | NE | SZE | NE | |
| Nutritional components | ||||||
| Moisture (g/100 g WW) | 74.49 ± 0.08 | 73.32 ± 0.54 | 86.88 ± 0.02 | 87.22 ± 0.02 | 49.18 ± 1.28 | 48.25 ± 1.96 |
| Total sugar (mg/g DW) | 6.24 ± 0.29 | 4.88 ± 0.21 | 30.34 ± 0.93 * | 19.95 ± 0.94 | 1.94 ± 0.06 | 1.60 ± 0.93 |
| Ash (g/100 g DW) | 4.27 ± 0.03 | 4.23 ± 0.05 | 5.70 ± 0.14 | 5.69 ± 0.33 | 3.82 ± 0.10 | 3.72 ± 0.03 |
| Protein (g/100 g DW) | 54.31 ± 0.38 * | 51.31 ± 0.39 | 90.87 ± 0.25 | 90.41 ± 0.93 | 35.84 ± 0.11 | 35.81 ± 0.16 |
| Total lipid (g/100 g DW) | 35.94 ± 0.20 | 36.23 ± 0.11 | - | - | 50.89 ± 0.09 | 51.06 ± 0.01 |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/g DW) | 0.027 ± 0.0001 * | 0.031 ± 0.0001 | - | - | 0.036 ± 0.0001 * | 0.049 ± 0.001 |
| Phosphatide (mg/g DW) | 59.51 ± 0.28 * | 50.09 ± 0.46 | - | - | 89.01 ± 0.70 * | 76.68 ± 0.89 * |
| Mineral composition (mg/kg DW) | ||||||
| Se | 2.32 ± 0.09 * | 1.40 ± 0.02 | 4.27 ± 0.21 * | 2.44 ± 0.24 | 1.60 ± 0.04 * | 1.18 ± 0.07 |
| Zn | 58.61 ± 0.79 * | 51.76 ± 0.38 | 3.36 ± 0.06 * | 1.26 ± 0.17 | 80.87 ± 1.56 * | 65.84 ± 0.86 |
| Mg | 499.79 ± 14.65 | 502.64 ± 5.09 | 1404.31 ± 11.94 * | 1187.1 ± 6.74 | 308.03 ± 2.26 | 299.83 ± 5.1 |
| Fe | 76.53 ± 6.46 * | 50.09 ± 2.8 | 16.77 ± 1.54 | 14.57 ± 1.44 | 58.12 ± 3.95 | 74.89 ± 3.09 |
| Ca | 2717.09 ± 6.01 | 2660.56 ± 19.85 | 534.21 ± 8.34 | 532.44 ± 13.39 | 3536.64 ± 64.19 | 3604.34 ± 37.19 |
| Al | 4.39 × 10−3 ± 2.59 × 10−4 * | 7.80 × 10−2 ± 2.29 × 10−3 | 1.12 ± 0.23 | 1.33 ± 0.19 | 0.94 ± 0.03 | 1.41 ± 0.12 |
| Co | 7.75 × 10−3 ± 1.06 × 10−3 | 7.29 × 10−3 ± 5.73 × 10−4 | 3.63 × 10−3 ± 5.06 × 10−5 | 3.19 × 10−3 ± 1.13 × 10−3 | 1.05 × 10−2 ± 1.72 × 10−3 | 1.01 × 10−2 ± 5.37 × 10−4 |
| As | 8.00 × 10−3 ± 1.85 × 10 * | 1.27 × 10−2 ± 1.41 × 10−3 | 1.54 × 10−2 ± 1.77 × 10−5 | 1.83 × 10−2 ± 8.13 × 10−4 | 3.74 × 10−3 ± 6.01 × 10−4 | 2.55 × 10−3 ± 4.61 × 10−4 |
| Mn | 1.55 ± 0.03 * | 1.28 ± 0.02 | 1.45 × 10−1 ± 2.92 × 10−3 * | 9.11 × 10−2 ± 1.81 × 10−3 | 1.67 ± 0.02 * | 2.53 ± 0.06 |
| Cu | 2.17 ± 0.02 | 2.43 ± 0.11 | 0.97 ± 0.03 * | 1.23 ± 0.03 | 3.52 ± 0.05 * | 3.30 ± 0.01 |
| V | 6.12 × 10−4 ± 3.21 × 10−4 * | 1.01 × 10−2 ± 2.48 × 10−3 | 7.65 × 10−4 ± 07.78 × 10−5 * | 1.45 × 10−2 ± 3.34 × 10−4 | 1.45 × 10−2 ± 3.34 × 10−4 | 1.22 × 10−2 ± 1.54 × 10−3 |
| Ni | 4.52 × 10−2 ± 9.48 × 10−3 * | 2.72 × 10−1 ± 6.27 × 10−2 | 7.17 × 10−2 ± 6.46 × 10−3 | 4.41 × 10−2 ± 2.06 × 10−3 | 9.24 × 10−2 ± 3.90 × 10−3 * | 7.13 × 10−2 ± 1.14 × 10−3 |
| Mo | 0.40 ± 0.03 | 0.34 ± 0.01 | 1.43 × 10−1 ± 2.64 × 10−3 * | 6.43 × 10−2 ± 4.96 × 10−3 | 2.22 × 10−1 ± 1.27 × 10−3 | 2.49 × 10−1 ± 3.73 × 10−2 |
| Ag | 1.46 × 10−4 ± 4.42 × 10−4 | 8.20 × 10−4 ± 1.26 × 10−4 | 5.73 × 10−4 ± 2.27 × 10−5 | 3.88 × 10−4 ± 5.49 × 10−5 | 3.55 × 10−4 ± 2.89 × 10−5 * | 5.34 × 10−4 ± 6.53 × 10−6 |
| Cd | 6.71 × 10−4 ± 7.80 × 10−5 * | 2.86 × 10−3 ± 6.28 × 10−4 | 3.13 × 10−3 ± 3.62 × 10−4 | 4.19 × 10−3 ± 6.85 × 10−4 | 2.53 × 10−3 ± 6.58 × 10−4 | 3.34 × 10−3 ± 9.97 × 10−4 |
| Ba | 1.29 ± 0.07 | 1.27 ± 0.02 | 3.58 × 10−2 ± 2.82 × 10−3 * | 6.47 × 10−2 ± 8.41 × 10−4 | 1.42 ± 0.07 * | 1.91 ± 0.09 |
| Cr | 3.75 × 10−3 ± 1.59 × 10−3 * | 3.37 × 10−2 ± 2.64 × 10−3 | 4.40 × 10−2 ± 3.93 × 10−3 | 9.67 × 10−2 ± 8.79 × 10−3 | 8.16 × 10−2 ± 2.16 × 10−2 * | 1.13 × 10−1 ± 1.94 × 10−2 |
| Pb | 4.14 × 10−3 ± 6.05 × 10−4 * | 3.76 × 10−2 ± 3.31 × 10−3 | 4.44 × 10−3 ± 3.93 × 10−3 * | 2.86 × 10−2 ± 6.26 × 10−4 | 3.00 × 10−2 ± 2.02 × 10−3 | 3.43 × 10−2 ± 1.11 × 10−3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wan, Y.; Liang, Y.; Tan, Y.; Wei, M.; Hou, T. Selenium- and/or Zinc-Enriched Egg Diet Improves Oxidative Damage and Regulates Gut Microbiota in D-Gal-Induced Aging Mice. Nutrients 2024, 16, 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16040512
Liu Q, Wang Y, Wan Y, Liang Y, Tan Y, Wei M, Hou T. Selenium- and/or Zinc-Enriched Egg Diet Improves Oxidative Damage and Regulates Gut Microbiota in D-Gal-Induced Aging Mice. Nutrients. 2024; 16(4):512. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16040512
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qiaocui, Yulin Wang, Yuan Wan, Yu Liang, Yali Tan, Mengya Wei, and Tao Hou. 2024. "Selenium- and/or Zinc-Enriched Egg Diet Improves Oxidative Damage and Regulates Gut Microbiota in D-Gal-Induced Aging Mice" Nutrients 16, no. 4: 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16040512
APA StyleLiu, Q., Wang, Y., Wan, Y., Liang, Y., Tan, Y., Wei, M., & Hou, T. (2024). Selenium- and/or Zinc-Enriched Egg Diet Improves Oxidative Damage and Regulates Gut Microbiota in D-Gal-Induced Aging Mice. Nutrients, 16(4), 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16040512