White Blood Cell and C-Reactive Protein Levels Are Similar in Obese Hispanic White Women Reporting Adherence to a Healthy Plant, Unhealthy Plant, or Animal-Based Diet, unlike in Obese Non-Hispanic White Women
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample
2.2. Data Extracted
2.2.1. BMI and Waist Circumference
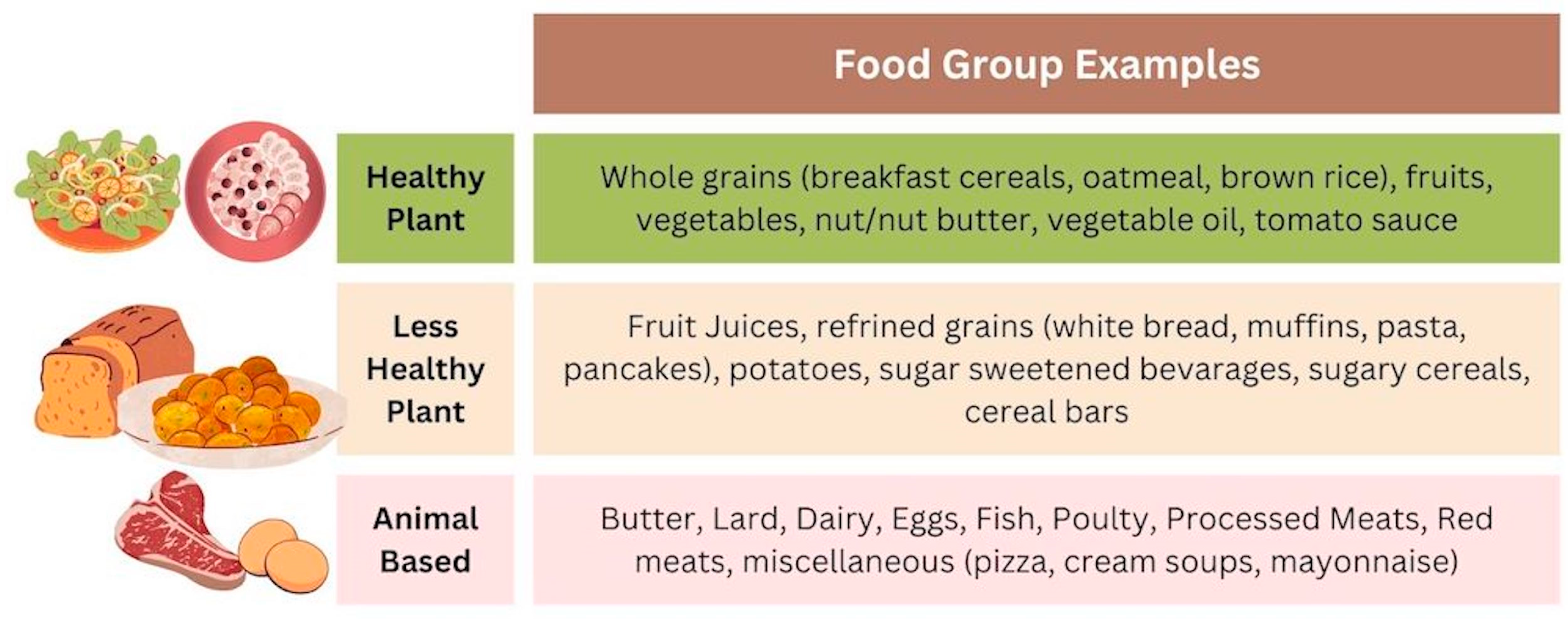
2.2.2. Dietary Pattern
2.2.3. Laboratory Values
2.2.4. Demographics
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Higher WBC Count in Obese Hispanic Women despite Younger Age and Higher Numbers of Individuals Reporting a Healthy Plant Dietary Pattern
3.2. WBC Count Is Higher in Obese Hispanic Women Reporting a Healthy and Less Healthy Plant Dietary Pattern Compared to Non-Hispanic Women Reporting the Same Dietary Pattern
3.3. WBCs and CRP Are Elevated in Obese Non-Hispanic Women Reporting an Animal-Based Dietary Pattern Compared to Those Reporting a Healthy Plant Dietary Patter, Unlike Hispanic Women, Where There Is No Difference
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Alemán, J.O.; Almandoz, J.P.; Frias, J.P.; Galindo, R.J. Obesity among Latinx People in the United States: A Review. Obesity 2023, 31, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, C.L.; Fryar, C.D.; Martin, C.B.; Freedman, D.S.; Carroll, M.D.; Gu, Q.; Hales, C.M. Trends in Obesity Prevalence by Race and Hispanic Origin-1999–2000 to 2017–2018. JAMA-J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2021, 324, 1208–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flegal, K.M.; Carroll, M.D.; Ogden, C.L.; Johnson, C.L. Prevalence and Trends in Obesity among US Adults, 1999–2000. JAMA 2002, 288, 1723–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, A.S.; Toth, A.T.; Stanford, F.C. Racial Disparities in Obesity Treatment. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2018, 7, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stierman, B.; Afful, J.; Carroll, M.D.; Chen, T.C.; Davy, O.; Fink, S.; Fryar, C.D.; Gu, Q.; Hales, C.M.; Hughes, J.P.; et al. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2017–March 2020 Prepandemic Data Files Development of Files and Prevalence Estimates for Selected Health Outcomes. Natl Health Stat Report 2021, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, U.J.; Choi, M.S. Obesity and Its Metabolic Complications: The Role of Adipokines and the Relationship between Obesity, Inflammation, Insulin Resistance, Dyslipidemia and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 6184–6223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellulu, M.S.; Patimah, I.; Khaza’ai, H.; Rahmat, A.; Abed, Y. Obesity and Inflammation: The Linking Mechanism and the Complications. Arch. Med. Sci. 2017, 13, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cawley, J.; Biener, A.; Meyerhoefer, C.; Ding, Y.; Zvenyach, T.; Gabriel Smolarz, N.B.; Ramasamy, A. Direct Medical Costs of Obesity in the United States and the Most Populous States. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2021, 27, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verde, L.; Frias-Toral, E.; Cardenas, D. Editorial: Environmental Factors Implicated in Obesity. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1171507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, D.; Nóbrega, C.; Manco, L.; Padez, C. The Contribution of Genetics and Environment to Obesity. Br. Med. Bull. 2017, 123, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, B.; Moorthy, M. Causes of Obesity: A Review. Clin. Med. 2023, 23, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Caulfield, L.E.; Garcia-Larsen, V.; Steffen, L.M.; Coresh, J.; Rebholz, C.M. Plant-Based Diets Are Associated With a Lower Risk of Incident Cardiovascular Disease, Cardiovascular Disease Mortality, and All-Cause Mortality in a General Population of Middle-Aged Adults. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e012865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMacken, M.; Shah, S. A Plant-Based Diet for the Prevention and Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinu, M.; Abbate, R.; Gensini, G.F.; Casini, A.; Sofi, F. Vegetarian, Vegan Diets and Multiple Health Outcomes: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3640–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleksandrova, K.; Koelman, L.; Rodrigues, C.E. Dietary Patterns and Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: A Systematic Review of Observational and Intervention Studies. Redox. Biol. 2021, 42, 101869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Lopez, O.; Martinez-Urbistondo, D.; Vargas-Nuñez, J.A.; Martinez, J.A. The Role of Nutrition on Meta-Inflammation: Insights and Potential Targets in Communicable and Chronic Disease Management. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2022, 11, 305–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, M.; Xu, L.F.; Hu, D.; Wu, J.; Bai, M.J. Dietary Patterns and Overweight/Obesity: A Review Article. Iran J. Public Health 2017, 46, 869. [Google Scholar]
- McTigue, K.M.; Chang, Y.F.; Eaton, C.; Garcia, L.; Johnson, K.C.; Lewis, C.E.; Liu, S.; Mackey, R.H.; Robinson, J.; Rosal, M.C.; et al. Severe Obesity, Heart Disease, and Death among White, African American, and Hispanic Postmenopausal Women. Obesity 2014, 22, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Brief Statistical Portrait of U.S. Hispanics|Pew Research Center. Available online: https://www.pewresearch.org/science/2022/06/14/a-brief-statistical-portrait-of-u-s-hispanics/ (accessed on 15 January 2024).
- Turner-McGrievy, G.; Mandes, T.; Crimarco, A. A Plant-Based Diet for Overweight and Obesity Prevention and Treatment. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiśniewska, K.; Okręglicka, K.M.; Nitsch-Osuch, A.; Oczkowski, M. Plant-Based Diets and Metabolic Syndrome Components: The Questions That Still Need to Be Answered—A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.N.; Jaceldo-Siegl, K.; Shih, W.; Collado, N.; Le, L.T.; Silguero, K.; Estevez, D.; Jordan, M.; Flores, H.; Hayes-Bautista, D.E.; et al. Plant-Based Diets Are Associated With Lower Adiposity Levels Among Hispanic/Latino Adults in the Adventist Multi-Ethnic Nutrition (AMEN) Study. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuercher, M.D.; Harvey, D.J.; Santiago-Torres, M.; Au, L.E.; Shivappa, N.; Shadyab, A.H.; Allison, M.; Snetselaar, L.; Liu, B.; Robbins, J.A.; et al. Dietary Inflammatory Index and Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Hispanic Women from the Women’s Health Initiative. Nutr. J. 2023, 22, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabung, F.K.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Giulianini, F.; Liang, L.; Chandler, P.D.; Balasubramanian, R.; Manson, J.A.E.; Feliciano, E.M.C.; Hayden, K.M.; Van Horn, L.; et al. An Empirical Dietary Inflammatory Pattern Score Is Associated with Circulating Inflammatory Biomarkers in a Multi-Ethnic Population of Postmenopausal Women in the United States. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Gastélum, M.; Lindberg, N.M.; Leo, M.C.; Bruening, M.; Whisner, C.M.; Der Ananian, C.; Hooker, S.P.; LeBlanc, E.S.; Stevens, V.J.; Shuster, E.; et al. Dietary Patterns with Healthy and Unhealthy Traits Among Overweight/Obese Hispanic Women with or at High Risk for Type 2 Diabetes. J. Racial Ethn. Health Disparities 2021, 8, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramal, E.; Champlin, A.; Bahjri, K. Impact of a Plant-Based Diet and Support on Mitigating Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Latinos Living in Medically Underserved Areas. Am. J. Health Promot. 2018, 32, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, A.C.; Heron, C.; Kim, J.I.; Martin, B.; Al-Shaar, L.; Tucker, K.L.; Gao, X. Prospective Study of Plant-Based Dietary Patterns and Diabetes in Puerto Rican Adults. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 3795–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Q.; Strizich, G.; Hanna, D.B.; Giacinto, R.E.; Castañeda, S.F.; Sotres-Alvarez, D.; Pirzada, A.; Llabre, M.M.; Schneiderman, N.; Avilés-Santa, L.M.; et al. Comparing Measures of Overall and Central Obesity in Relation to Cardiometabolic Risk Factors among US Hispanic/Latino Adults. Obesity 2015, 23, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, M.H.; Liu, J.L.; Nguyen, U.S.D.T. Trends in Diet Quality by Race/Ethnicity among Adults in the United States for 2011–2018. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satija, A.; Bhupathiraju, S.N.; Spiegelman, D.; Chiuve, S.E.; Manson, J.A.E.; Willett, W.; Rexrode, K.M.; Rimm, E.B.; Hu, F.B. Healthful and Unhealthful Plant-Based Diets and the Risk of Coronary Heart Disease in U.S. Adults. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, M.D.; Sevoyan, M.; Hofseth, L.; Shivappa, N.; Hurley, T.G.; Hébert, J.R. The Dietary Inflammatory Index Is Associated with Elevated White Blood Cell Counts in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 69, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczmarski, M.F.; Mason, M.A.; Allegro, D.; Zonderman, A.B.; Evans, M.K. Diet Quality Inversely Associated with C-Reactive Protein Levels in Urban, Low-Income African American and White Adults. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet 2013, 113, 1620–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, J.; Jacobs, A.G.; Ortiz, S.; Diaz Rios, L.K. A Systematic Review of Literature on the Representation of Racial and Ethnic Minority Groups in Clinical Nutrition Interventions. Adv. Nutr. 2022, 13, 1505–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Qiu, T.; Li, L.; Yu, R.; Chen, X.; Li, C.; Proud, C.G.; Jiang, T. Pathophysiology of Obesity and Its Associated Diseases. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, P.; Jain, S.K. Obesity, Oxidative Stress, Adipose Tissue Dysfunction, and the Associated Health Risks: Causes and Therapeutic Strategies. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2015, 13, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Lee, I.S.; Choue, R. Obesity, Inflammation and Diet. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2013, 16, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muscatell, K.A.; Brosso, S.N.; Humphreys, K.L. Socioeconomic Status and Inflammation: A Meta-Analysis. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, M.R. Sleep and Inflammation: Partners in Sickness and in Health. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 702–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuevas, A.G.; Ong, A.D.; Carvalho, K.; Ho, T.; Chan, S.W.C.; Allen, J.D.; Chen, R.; Rodgers, J.; Biba, U.; Williams, D.R. Discrimination and Systemic Inflammation: A Critical Review and Synthesis. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 89, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasishta, S.; Ganesh, K.; Umakanth, S.; Joshi, M.B. Ethnic Disparities Attributed to the Manifestation in and Response to Type 2 Diabetes: Insights from Metabolomics. Metabolomics 2022, 18, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmeer, K.K.; Tarrence, J. Racial/Ethnic Disparities in Inflammation: Evidence of Weathering in Childhood? J. Health Soc. Behav. 2018, 59, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, H.R.; Wray, L.A.; Xian, Y.; Xu, H.; Pagidipati, N.; Peterson, E.D.; Dupre, M.E. Racial Differences in Elevated C-Reactive Protein Among US Older Adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2020, 68, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stowe, R.P.; Peek, M.K.; Cutchin, M.P.; Goodwin, J.S. Plasma Cytokine Levels in a Population-Based Study: Relation to Age and Ethnicity. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2010, 65A, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazmi, A.; Victora, C.G. Socioeconomic and Racial/Ethnic Differentials of C-Reactive Protein Levels: A Systematic Review of Population-Based Studies. BMC Public Health 2007, 7, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.M.; Epel, E.S.; To, T.M.; Lee, A.; Aiello, A.E.; Haan, M.N. Cross-Border Ties, Nativity, and Inflammatory Markers in a Population-Based Prospective Study of Latino Adults. Soc. Sci. Med. 2018, 211, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.L.; Haan, M.N.; Fernandez-Rhodes, L.; Lee, A.; Aiello, A.E. Association between Immigration History and Inflammatory Marker Profiles among Older Adult Mexican Americans. Biodemography Soc. Biol. 2018, 64, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hook, J.; Quirós, S.; Dondero, M.; Altman, C.E. Healthy Eating Among Mexican Immigrants: Migration in Childhood and Time in the U.S. J. Health Soc. Behav. 2018, 59, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reininger, B.; Lee, M.; Jennings, R.; Evans, A.; Vidoni, M. Healthy Eating Patterns Associated with Acculturation, Sex and BMI among Mexican Americans. Public Health Nutr. 2017, 20, 1267–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acculturation, Familial Support, and Unhealthful Dietary Patterns on JSTOR. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/48546766 (accessed on 21 January 2024).
- Yoshida, Y.; Scribner, R.; Chen, L.; Broyles, S.; Phillippi, S.; Tseng, T.S. Role of Age and Acculturation in Diet Quality Among Mexican Americans—Findings From the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999–2012. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2019, 14, E59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, H.R.; Slavish, D.C.; Ruiz, J.; Dietch, J.R.; Ruggero, C.J.; Messman, B.A.; Kelly, K.; Kohut, M.; Taylor, D.J. Racial/Ethnic Variations in Inflammatory Markers: Exploring the Role of Sleep Duration and Sleep Efficiency. J. Behav. Med. 2022, 45, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, A.G.; Chen, R.; Slopen, N.; Thurber, K.A.; Wilson, N.; Economos, C.; Williams, D.R. Assessing the Role of Health Behaviors, Socioeconomic Status, and Cumulative Stress for Racial/Ethnic Disparities in Obesity. Obesity 2020, 28, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, R.; Kusunoki, T.; Abe, M.; Kohara, K.; Miki, T. An Association between Body Mass Index and High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein Concentrations Is Influenced by Age in Community-Dwelling Persons. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 50, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stȩpień, M.; Stȩpień, A.; Wlazeł, R.N.; Paradowski, M.; Banach, M.; Rysz, J. Obesity Indices and Inflammatory Markers in Obese Non-Diabetic Normo- and Hypertensive Patients: A Comparative Pilot Study. Lipids Health Dis. 2014, 13, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Qian, P.; Huang, H. Inflammation and Aging: Signaling Pathways and Intervention Therapies. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, R.; Popham, M.; Santanasto, A.J.; Hardy, R.; Glynn, N.W.; Kuh, D. Are BMI and Inflammatory Markers Independently Associated with Physical Fatigability in Old Age? Int. J. Obes. 2018, 43, 832–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denova-Gutiérrez, E.; Tucker, K.L.; Flores, M.; Barquera, S.; Salmerón, J. Dietary Patterns Are Associated with Predicted Cardiovascular Disease Risk in an Urban Mexican Adult Population. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riseberg, E.; Lopez-Cepero, A.; Mangano, K.M.; Tucker, K.L.; Mattei, J. Specific Dietary Protein Sources Are Associated with Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in the Boston Puerto Rican Health Study. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet 2022, 122, 298–308.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazidi, M.; Gao, H.K.; Kengne, A.P. Inflammatory Markers Are Positively Associated with Serum Trans -Fatty Acids in an Adult American Population. J. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storz, M.A. What Makes a Plant-Based Diet? A Review of Current Concepts and Proposal for a Standardized Plant-Based Dietary Intervention Checklist. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 76, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.P.; Karan, A.; Hootman, K.C.; Graves, M.; Steller, I.; Abel, B.; Giannita, A.; Tils, J.; Hayashi, L.; O’Connor, M.; et al. A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study of the Food Order Behavioral Intervention in Prediabetes. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-Prado, S.; Schmidt-Riovalle, J.; Montero-Alonso, M.A.; Fernández-Aparicio, Á.; González-Jiménez, E. Stricter Adherence to Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) and Its Association with Lower Blood Pressure, Visceral Fat, and Waist Circumference in University Students. Nutrients 2020, 12, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, A.S.; Tresserra-Rimbau, A.; Karavasiloglou, N.; Jennings, A.; Cantwell, M.; Hill, C.; Perez-Cornago, A.; Bondonno, N.P.; Murphy, N.; Rohrmann, S.; et al. Association of Healthful Plant-Based Diet Adherence With Risk of Mortality and Major Chronic Diseases Among Adults in the UK. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e234714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiloglou, M.F.; Elortegui Pascual, P.; Scuccimarra, E.A.; Plestina, R.; Mainardi, F.; Mak, T.N.; Ronga, F.; Drewnowski, A. Assessing the Quality of Simulated Food Patterns with Reduced Animal Protein Using Meal Data from NHANES 2017–2018. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarem, N.; Zuraikat, F.M.; Caceres, B.; Sears, D.D.; St-Onge, M.P.; Lai, Y.; Aggarwal, B. Variable Eating Patterns: A Potential Novel Risk Factor for Systemic Inflammation in Women. Ann. Behav. Med. 2023, 57, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, D.; Peltzer, C.; Kahar, P.; Parmar, M.S. Body Mass Index (BMI): A Screening Tool Analysis. Cureus 2022, 14, e22119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymsfield, S.B.; Scherzer, R.; Pietrobelli, A.; Lewis, C.E.; Grunfeld, C. Body Mass Index as a Phenotypic Expression of Adiposity: Quantitative Contribution of Muscularity in a Population-Based Sample. Int. J. Obes. 2009, 33, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevill, A.M.; Stewart, A.D.; Olds, T.; Holder, R. Relationship between Adiposity and Body Size Reveals Limitations of BMI. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2006, 129, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, X.; Limei, E.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Jiang, X. The Mediating Effect of Central Obesity on the Association between Dietary Quality, Dietary Inflammation Level and Low-Grade Inflammation-Related Serum Inflammatory Markers in Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Waist Circumference and Waist–Hip Ratio. WHO Expert 2011, 64, 2–5. [Google Scholar]
- Salinas-Mandujano, R.G.; Reynoso-Camacho, R.; Salgado, L.M.; Ramos-Gomez, M.; Pérez-Ramírez, I.F.; Aguilar-Galarza, A.; Moreno-Celis, U.; Anaya-Loyola, M.A. A New Approach Using BMI and FMI as Predictors of Cardio-Vascular Risk Factors among Mexican Young Adults. Eur. J. Investig. Health Psychol. Educ. 2023, 13, 2063–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macias, N.; Quezada, A.D.; Flores, M.; Valencia, M.E.; Denova-Gutiérrez, E.; Quiterio-Trenado, M.; Gallegos-Carrillo, K.; Barquera, S.; Salmerón, J. Accuracy of Body Fat Percent and Adiposity Indicators Cut off Values to Detect Metabolic Risk Factors in a Sample of Mexican Adults. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutunchi, H.; Ebrahimi-Mameghani, M.; Ostadrahimi, A.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M. What Are the Optimal Cut-off Points of Anthropometric Indices for Prediction of Overweight and Obesity? Predictive Validity of Waist Circumference, Waist-to-Hip and Waist-to-Height Ratios. Health Promot. Perspect. 2020, 10, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios, C.; Daniel, C.R.; Tirado-Gómez, M.; Gonzalez-Mercado, V.; Vallejo, L.; Lozada, J.; Ortiz, A.; Hughes, D.C.; Basen-Engquist, K. Dietary Patterns in Puerto Rican and Mexican-American Breast Cancer Survivors: A Pilot Study. J. Immigr. Minor. Health 2017, 19, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Overall | Non-Hispanic | Hispanic 1 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age—Mean (SE) N (Weighted N) | 48.69 (0.53) 2651 (31,233,652) | 50.20 (0.66) 1569 (25,820,642) | 41.49 (0.61) 1082 (5,413,010) | <0.001 2 |
| BMI—Mean (SE) N (Weighted N) | 36.23 (0.20) 2651 (31,233,652) | 36.34 (0.23) 1569 (25,820,642) | 35.68 (0.18) 1082 (5,413,010) | 0.015 2 |
| Waist Circumference (cm)—Mean (SE) N (Weighted N) | 111.42 (0.48) 2750 (30,298,973) | 112.02 (0.53) 1513 (24,945,847) | 108.58 (0.48) 1057 (5,293,126) | <0.001 2 |
| WBC Count—Mean (SE) N (Weighted N) | 8.01 (0.07) 2572 (30,279,467) | 7.93 (0.08) 1515 (24,996,737) | 8.35 (0.10) 1057 (5,282,730) | 0.002 2 |
| CRP—Mean (SE) N (Weighted N) | 0.74 (0.02) 2550 (29,942,864) | 0.73 (0.03) 1497 (24,675,108) | 0.76 (0.04) 1053 (5,267,756) | 0.561 2 |
| Reported Dietary Pattern | 0.004 3 | |||
| Healthy Plant | 223 (2,315,262) 7.41% | 117 (1,774,678) 6.87% | 106 (540,585) 9.99% | |
| Less Healthy Plant | 2224 (26,031,238) 83.34% | 1301 (21,455,217) 83.09% | 923 (4,576,020) 84.54% | |
| Animal | 204 (2,887,152) 9.24% | 151 (2,590,747) 10.03% | 53 (296,405) 5.48% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bruins, A.; Keeley, J.; Uhley, V.; Anyadike, K.; Kemp, K. White Blood Cell and C-Reactive Protein Levels Are Similar in Obese Hispanic White Women Reporting Adherence to a Healthy Plant, Unhealthy Plant, or Animal-Based Diet, unlike in Obese Non-Hispanic White Women. Nutrients 2024, 16, 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16040556
Bruins A, Keeley J, Uhley V, Anyadike K, Kemp K. White Blood Cell and C-Reactive Protein Levels Are Similar in Obese Hispanic White Women Reporting Adherence to a Healthy Plant, Unhealthy Plant, or Animal-Based Diet, unlike in Obese Non-Hispanic White Women. Nutrients. 2024; 16(4):556. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16040556
Chicago/Turabian StyleBruins, Anna, Jacob Keeley, Virginia Uhley, Kimberly Anyadike, and Kyeorda Kemp. 2024. "White Blood Cell and C-Reactive Protein Levels Are Similar in Obese Hispanic White Women Reporting Adherence to a Healthy Plant, Unhealthy Plant, or Animal-Based Diet, unlike in Obese Non-Hispanic White Women" Nutrients 16, no. 4: 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16040556
APA StyleBruins, A., Keeley, J., Uhley, V., Anyadike, K., & Kemp, K. (2024). White Blood Cell and C-Reactive Protein Levels Are Similar in Obese Hispanic White Women Reporting Adherence to a Healthy Plant, Unhealthy Plant, or Animal-Based Diet, unlike in Obese Non-Hispanic White Women. Nutrients, 16(4), 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16040556






