Mendelian Randomization Analysis Identifies Inverse Causal Relationship between External Eating and Metabolic Phenotypes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
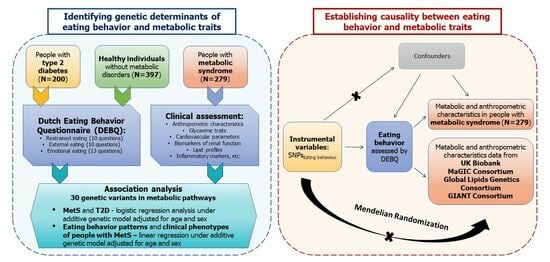
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Group
2.2. Ethics, Consent, and Permissions
2.3. Anthropometric Measurements and Biochemical Assays
2.4. Eating Behaviour
2.5. Genotyping and Quality Control
2.6. Association Analysis
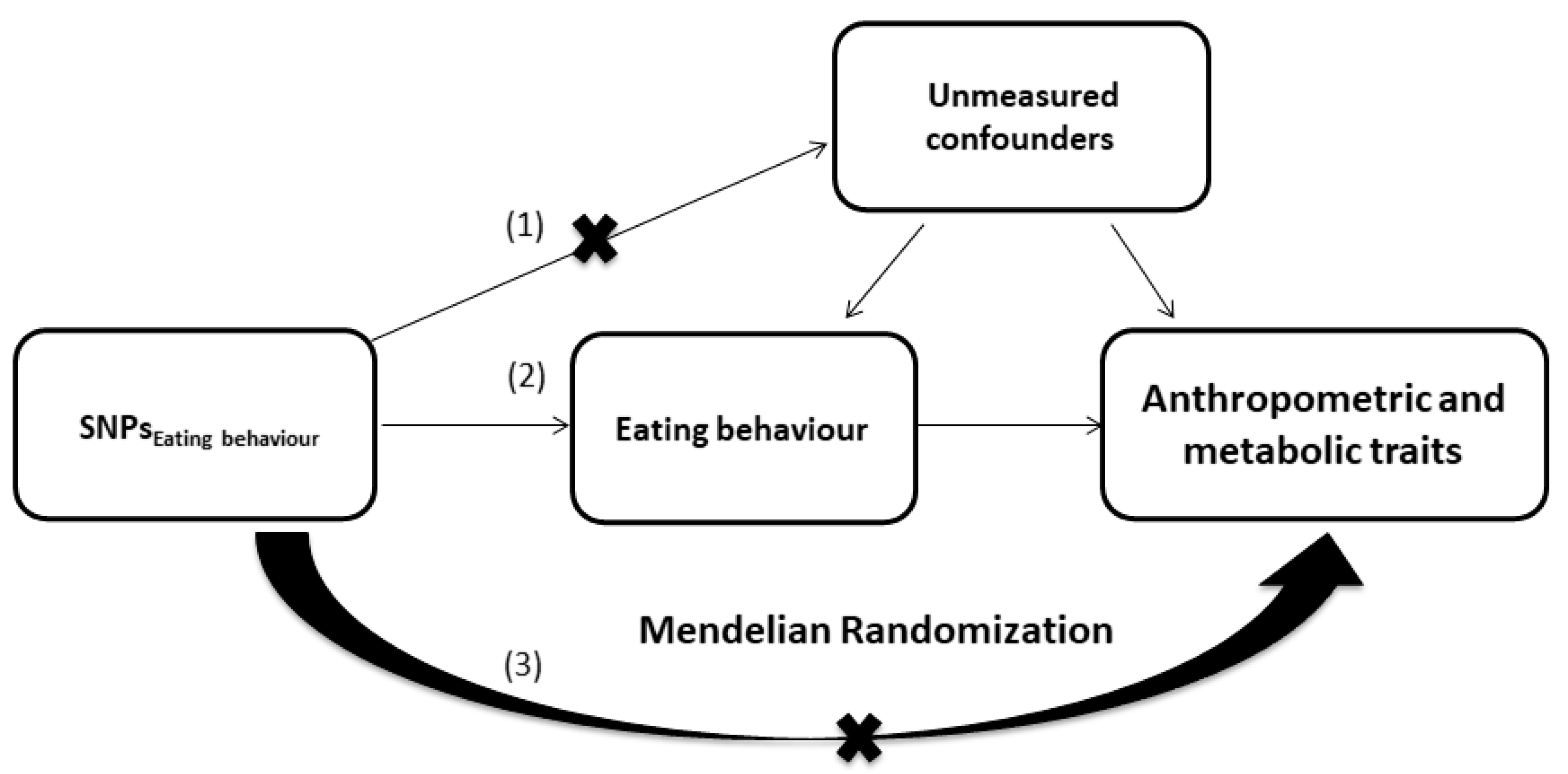
2.7. Mendelian Randomization
3. Results
3.1. Association Analysis
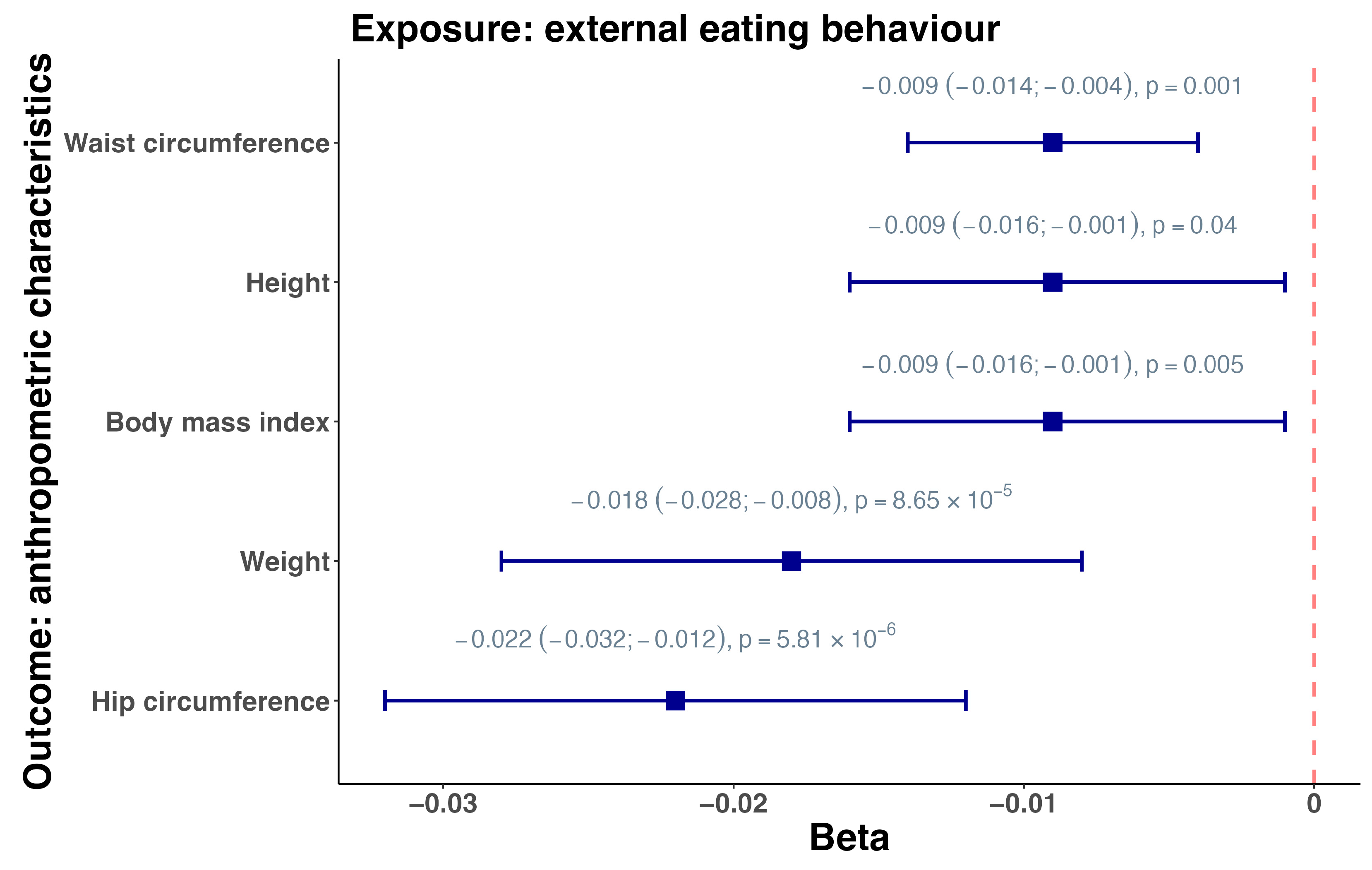
3.2. Mendelian Randomization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Franz, M.J. Weight Management: Obesity to Diabetes. Diabetes Spectr. 2017, 30, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, O.T.; Czech, M.P.; Corvera, S. What causes the insulin resistance underlying obesity? Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2012, 19, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouwen, A.; Speight, J.; Pouwer, F.; Holt, R.I.G. How psychosocial and behavioural research has shaped our understanding of diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2020, 37, 377–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, K.S. Food reinforcement architecture: A framework for impulsive and compulsive overeating and food abuse. Obesity 2023, 31, 1734–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leigh, S.J.; Morris, M.J. The role of reward circuitry and food addiction in the obesity epidemic: An update. Biol. Psychol. 2018, 131, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabut, J.M.; Crane, J.D.; Green, A.E.; Keating, D.J.; Khan, W.I.; Steinberg, G.R. Emerging Roles for Serotonin in Regulating Metabolism: New Implications for an Ancient Molecule. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 1092–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFadden, K.L.; Cornier, M.A.; Tregellas, J.R. The role of alpha-7 nicotinic receptors in food intake behaviors. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinelli, I.; Tayebati, S.K.; Roy, P.; Micioni Di Bonaventura, M.V.; Moruzzi, M.; Cifani, C.; Amenta, F.; Tomassoni, D. Obesity-Related Brain Cholinergic System Impairment in High-Fat-Diet-Fed Rats. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Chang, S.; Jing, R.; Yue, W.; Lu, L.; Chen, D.; Sun, Y.; Fan, Y.; et al. Gabra2 rs279858-linked variants are associated with disrupted structural connectome of reward circuits in heroin abusers. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallard, T.T.; Ashenhurst, J.R.; Harden, K.P.; Fromme, K. Gabra2, alcohol, and illicit drug use: An event-level model of genetic risk for polysubstance use. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2018, 127, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, D.; Tian, Y.; Feng, G.; Lu, Z. Gab2 deficiency suppresses high-fat diet-induced obesity by reducing adipose tissue inflammation and increasing brown adipose function in mice. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, E.; Geets, E.; Sorber, L.; Beckers, S.; Verrijken, A.; Massa, G.; Van Hoorenbeeck, K.; Verhulst, S.L.; Van Gaal, L.F.; Van Hul, W. Evaluation of a Role for NPY and NPY2R in the Pathogenesis of Obesity by Mutation and Copy Number Variation Analysis in Obese Children and Adolescents. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2018, 82, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loid, P.; Mustila, T.; Mäkitie, R.E.; Viljakainen, H.; Kämpe, A.; Tossavainen, P.; Lipsanen-Nyman, M.; Pekkinen, M.; Mäkitie, O. Rare Variants in Genes Linked to Appetite Control and Hypothalamic Development in Early-Onset Severe Obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Delessa, C.T.; Augustin, R.; Bakhti, M.; Colldén, G.; Drucker, D.J.; Feuchtinger, A.; Caceres, C.G.; Grandl, G.; Harger, A.; et al. The glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) regulates body weight and food intake via CNS-GIPR signaling. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 833–844.e835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, E.A.; Wald, H.S.; Suarez, A.N.; Zubcevic, J.; Liu, C.M.; Cortella, A.M.; Kamitakahara, A.K.; Polson, J.W.; Arnold, M.; Grill, H.J.; et al. Ghrelin Signaling Affects Feeding Behavior, Metabolism, and Memory through the Vagus Nerve. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, 4510–4518.e4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.Z.; Wang, Y.X.; Jiang, C.L. Inflammation: The Common Pathway of Stress-Related Diseases. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yao, H.; Liu, T.; Gou, T.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Tian, Y.; et al. Novel Role of the SIRT1 in Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 484–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavey, C.; Lazennec, G.; Lagarrigue, S.; Clapé, C.; Iankova, I.; Teyssier, J.; Annicotte, J.S.; Schmidt, J.; Mataki, C.; Yamamoto, H.; et al. CXC ligand 5 is an adipose-tissue derived factor that links obesity to insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2009, 9, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, B.E.; Lantier, L.; Engman, C.; Garciafigueroa, Y.; Singhi, A.; Trucco, M.; Mantzoros, C.; Wasserman, D.; Giannoukakis, N. Improvement in insulin sensitivity and prevention of high fat diet-induced liver pathology using a CXCR2 antagonist. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelli, V.; Brandolini, L.; d’Angelo, M.; Giorgio, C.; Alfonsetti, M.; Cocchiaro, P.; Lombardi, F.; Cimini, A.; Allegretti, M. CXCR1/2 Inhibitor Ladarixin Ameliorates the Insulin Resistance of 3T3-L1 Adipocytes by Inhibiting Inflammation and Improving Insulin Signaling. Cells 2021, 10, 2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Zhang, T.T.; Han, W.J.; Yin, L.P.; Ma, N.Z.; Shi, X.Y.; Sun, J.J. Association of CDKAL1 RS10946398 Gene Polymorphism with Susceptibility to Diabetes Mellitus Type 2: A Meta-Analysis. J. Diabetes Res. 2021, 2021, 1254968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davey Smith, G.; Hemani, G. Mendelian randomization: Genetic anchors for causal inference in epidemiological studies. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, R89–R98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, S.; Davey Smith, G.; Davies, N.M.; Dudbridge, F.; Gill, D.; Glymour, M.M.; Hartwig, F.P.; Kutalik, Z.; Holmes, M.V.; Minelli, C.; et al. Guidelines for performing Mendelian randomization investigations: Update for summer 2023. Wellcome Open Res. 2019, 4, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, Z.E.; Micali, N.; Bulik, C.M.; Davey Smith, G.; Wade, K.H. Assessing the causal role of adiposity on disordered eating in childhood, adolescence, and adulthood: A Mendelian randomization analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, T.; Antel, J.; Naaresh, R.; Laabs, B.-H.; Föcker, M.; Albers, N.; Bühlmeier, J.; Hinney, A.; Libuda, L.; Hebebrand, J. Suggestive Evidence for Causal Effect of Leptin Levels on Risk for Anorexia Nervosa: Results of a Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 733606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgson, S.; Huang, Q.Q.; Sallah, N.; Genes & Health Research Team; Griffiths, C.J.; Newman, W.G.; Trembath, R.C.; Wright, J.; Lumbers, R.T.; Kuchenbaecker, K.; et al. Integrating polygenic risk scores in the prediction of type 2 diabetes risk and subtypes in British Pakistanis and Bangladeshis: A population-based cohort study. PLoS Med. 2022, 19, e1003981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borisenkov, M.F.; Popov, S.V.; Pecherkina, A.A.; Dorogina, O.I.; Martinson, E.A.; Vetosheva, V.I.; Gubin, D.G.; Solovieva, S.V.; Turovinina, E.F.; Symaniuk, E.E. Food addiction in young adult residents of Russia: Associations with emotional and anthropometric characteristics. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2020, 28, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikbov, M.M.; Kazakbaeva, G.M.; Gilmanshin, T.R.; Zainullin, R.M.; Iakupova, E.M.; Fakhretdinova, A.A.; Tuliakova, A.M.; Rusakova, I.A.; Panda-Jonas, S.; Nuriev, I.F.; et al. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in a Russian population: The Ural Eye and Medical Study and the Ural Very Old Study. Metab. Open 2022, 14, 100183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochetova, O.V.; Avzaletdinova, D.S.; Morugova, T.V.; Mustafina, O.E. Chemokine gene polymorphisms association with increased risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Tatar ethnic group, Russia. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochetova, O.V.; Avzaletdinova, D.S.; Korytina, G.F.; Morugova, T.V.; Mustafina, O.E. The association between eating behavior and polymorphisms in GRIN2B, GRIK3, GRIA1 and GRIN1 genes in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 2035–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, W.G.; on behalf of the UK Department of Health Advisory Committee on Diabetes. Use of HbA1c in the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus in the UK. The implementation of World Health Organization guidance 2011. Diabet. Med. 2012, 29, 1350–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundy, S.M.; Cleeman, J.I.; Daniels, S.R.; Donato, K.A.; Eckel, R.H.; Franklin, B.A.; Gordon, D.J.; Krauss, R.M.; Savage, P.J.; Smith, S.C.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of the Metabolic Syndrome. Circulation 2005, 112, 2735–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.L. A comprehensive definition for metabolic syndrome. Dis. Models Mech. 2009, 2, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Physical Status: The Use and Interpretation of Anthropometry. Report of a WHO Expert Committee; World Health Organization Technical Report Series; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995; Volume 854, pp. 1–452. [Google Scholar]
- Parati, G.; Stergiou, G.; O‘Brien, E.; Asmar, R.; Beilin, L.; Bilo, G.; Clement, D.; de la Sierra, A.; de Leeuw, P.; Dolan, E.; et al. European Society of Hypertension practice guidelines for ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. J. Hypertens. 2014, 32, 1359–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, D.R.; Hosker, J.P.; Rudenski, A.S.; Naylor, B.A.; Treacher, D.F.; Turner, R.C. Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildiz, B.O.; Bolour, S.; Woods, K.; Moore, A.; Azziz, R. Visually scoring hirsutism. Hum. Reprod. Update 2010, 16, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Strien, T.; Frijters, J.E.R.; Bergers, G.P.A.; Defares, P.B. The Dutch Eating Behavior Questionnaire (DEBQ) for assessment of restrained, emotional, and external eating behavior. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 1986, 5, 295–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polivy, J.; Herman, C.P. Restrained eating and food cues: Recent findings and conclusions. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2017, 6, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savchikova, Y. Psychological Traits of Women with Body Weight Problems; Saint Petersburg State University: Saint Petersburg, Russia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Korytina, G.F.; Aznabaeva, Y.G.; Akhmadishina, L.Z.; Kochetova, O.V.; Nasibullin, T.R.; Zagidullin, N.S.; Zagidullin, S.Z.; Viktorova, T.V. The Relationship Between Chemokine and Chemokine Receptor Genes Polymorphisms and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Susceptibility in Tatar Population from Russia: A Case Control Study. Biochem. Genet. 2022, 60, 54–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avzaletdinova, D.S.; Sharipova, L.F.; Kochetova, O.V.; Morugova, T.V.; Mustafina, O.E. Association of adiponectin gene alleles with type 2 diabetes mellitus in residents of Bashkortostan. Probl. Endokrinol. 2019, 65, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krylov, M.Y.e.; Benevolenskaya, L.; Myakotkin, V.; Krylov, M.Y. Leptin A19G polymorphism and leptin receptor Gln223Arg and Lys109Arg polymorphismsin postmenopausal osteoporosis. Nauchno-Prakt. Revmatol. 2010, 48, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.A.; Jahan, P.; Hasan, Q.; Rao, P. Validation of the association of TCF7L2 and SLC30A8 gene polymorphisms with post-transplant diabetes mellitus in Asian Indian population. Intractable Rare Dis. Res. 2015, 4, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yan, G.; Zhang, J.; Gao, K.; Zhang, M.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhai, Y.; You, H.; et al. Association of LRP5, TCF7L2, and GCG variants and type 2 diabetes mellitus as well as fasting plasma glucose and lipid metabolism indexes. Hum. Immunol. 2015, 76, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz-Barrios, S.; Guzman-Guzman, I.P.; Munoz-Valle, J.F.; Salgado-Bernabe, A.B.; Salgado-Goytia, L.; Parra-Rojas, I. Association of the HindIII and S447X polymorphisms in LPL gene with hypertension and type 2 diabetes in Mexican families. Dis. Markers 2012, 33, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, M.N.; da Silva do Amaral Herrera, A.C.; Amarante, M.K.; do Val Carneiro, J.L.; Fungaro, M.H.P.; Watanabe, M.A.E. CCR5 and p53 codon 72 gene polymorphisms: Implications in breast cancer development. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2009, 23, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Chow, C.C.; Tellier, L.C.; Vattikuti, S.; Purcell, S.M.; Lee, J.J. Second-generation PLINK: Rising to the challenge of larger and richer datasets. Gigascience 2015, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathan, N.; Deng, W.Q.; Di Scipio, M.; Khan, M.; Mao, S.; Morton, R.W.; Lali, R.; Pigeyre, M.; Chong, M.R.; Paré, G. A method to estimate the contribution of rare coding variants to complex trait heritability. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobin, M.D.; Sheehan, N.A.; Scurrah, K.J.; Burton, P.R. Adjusting for treatment effects in studies of quantitative traits: Antihypertensive therapy and systolic blood pressure. Stat. Med. 2005, 24, 2911–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate—A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemani, G.; Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G. Evaluating the potential role of pleiotropy in Mendelian randomization studies. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, R195–R208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, L. Genome-Wide Association Study of the Metabolic Syndrome in UK Biobank. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2019, 17, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Spracklen, C.N.; Marenne, G.; Varshney, A.; Corbin, L.J.; Luan, J.a.; Willems, S.M.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Horikoshi, M.; et al. The trans-ancestral genomic architecture of glycemic traits. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 840–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, S.E.; Clarke, S.L.; Wu, K.-H.H.; Kanoni, S.; Zajac, G.J.M.; Ramdas, S.; Surakka, I.; Ntalla, I.; Vedantam, S.; Winkler, T.W.; et al. The power of genetic diversity in genome-wide association studies of lipids. Nature 2021, 600, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shungin, D.; Winkler, T.W.; Croteau-Chonka, D.C.; Ferreira, T.; Locke, A.E.; Mägi, R.; Strawbridge, R.J.; Pers, T.H.; Fischer, K.; Justice, A.E.; et al. New genetic loci link adipose and insulin biology to body fat distribution. Nature 2015, 518, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemani, G.; Zheng, J.; Elsworth, B.; Wade, K.H.; Haberland, V.; Baird, D.; Laurin, C.; Burgess, S.; Bowden, J.; Langdon, R.; et al. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. eLife 2018, 7, e34408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, X.; Ong, R.T.; Suo, C.; Tay, W.T.; Liu, J.; Ng, D.P.; Boehnke, M.; Chia, K.S.; Wong, T.Y.; Seielstad, M.; et al. Transferability of type 2 diabetes implicated loci in multi-ethnic cohorts from Southeast Asia. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1001363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.J.; Jin, H.S.; Kim, S.S.; Shin, D. Dietary Protein and Fat Intake Affects Diabetes Risk with CDKAL1 Genetic Variants in Korean Adults. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surendran, P.; Feofanova, E.V.; Lahrouchi, N.; Ntalla, I.; Karthikeyan, S.; Cook, J.; Chen, L.; Mifsud, B.; Yao, C.; Kraja, A.T.; et al. Discovery of rare variants associated with blood pressure regulation through meta-analysis of 1.3 million individuals. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 1314–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botticelli, L.; Micioni Di Bonaventura, E.; Del Bello, F.; Giorgioni, G.; Piergentili, A.; Quaglia, W.; Bonifazi, A.; Cifani, C.; Micioni Di Bonaventura, M.V. The neuromedin U system: Pharmacological implications for the treatment of obesity and binge eating behavior. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 195, 106875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.C.; Xu, X.; Ferrante, A.W.; Krakoff, J. Reduced plasma albumin predicts type 2 diabetes and is associated with greater adipose tissue macrophage content and activation. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2019, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lufrano, D.; Trejo, S.A.; Llovera, R.E.; Salgueiro, M.; Fernandez, G.; Martínez Damonte, V.; González Flecha, F.L.; Raingo, J.; Ermácora, M.R.; Perelló, M. Ghrelin binding to serum albumin and its biological impact. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2016, 436, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basolo, A.; Ando, T.; Chang, D.C.; Hollstein, T.; Krakoff, J.; Piaggi, P.; Votruba, S. Reduced Albumin Concentration Predicts Weight Gain and Higher Ad Libitum Energy Intake in Humans. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 642568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricca, V.; Nacmias, B.; Cellini, E.; Di Bernardo, M.; Rotella, C.M.; Sorbi, S. 5-HT2A receptor gene polymorphism and eating disorders. Neurosci. Lett. 2002, 323, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccarini, M.R.; Tasegian, A.; Franzago, M.; Patria, F.F.; Albi, E.; Codini, M.; Conte, C.; Bertelli, M.; Dalla Ragione, L.; Stuppia, L.; et al. 5-HT2AR and BDNF gene variants in eating disorders susceptibility. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2020, 183, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, K.M.; Bujac, S.R.; Mann, E.T.; Campbell, D.A.; Stubbins, M.J.; Blundell, J.E. Further evidence of association of OPRD1 & HTR1D polymorphisms with susceptibility to anorexia nervosa. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 61, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyuncu, Z.; Kadak, M.T.; Tarakçıoğlu, M.C.; Bingöl Çağlayan, R.H.; Doğangün, B.; Ercan, O. Eating behaviors and alexithymic features of obese and overweight adolescents. Pediatr. Int. 2022, 64, e15008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, J.; Lee, K.; Song, Y.-M.; Lee, M.K.; Lee, D.-H. Heritability of Eating Behavior Assessed Using the DEBQ (Dutch Eating Behavior Questionnaire) and Weight-related Traits: The Healthy Twin Study. Obesity 2010, 18, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbaibeche, H.; Saidi, H.; Bounihi, A.; Koceir, E.A. Emotional and external eating styles associated with obesity. J. Eat. Disord. 2023, 11, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Strien, T.; Konttinen, H.M.; Ouwens, M.A.; van de Laar, F.A.; Winkens, L.H.H. Mediation of emotional and external eating between dieting and food intake or BMI gain in women. Appetite 2020, 145, 104493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal, A.M.; Iatcu, C.O.; Popa, A.D.; Arhire, L.I.; Mihalache, L.; Gherasim, A.; Nita, O.; Soimaru, R.M.; Gheorghita, R.; Graur, M.; et al. Understanding the Interplay of Dietary Intake and Eating Behavior in Type 2 Diabetes. Nutrients 2024, 16, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoek, H.M.; Engels, R.C.M.E.; van Strien, T.; Otten, R. Emotional, external and restrained eating behaviour and BMI trajectories in adolescence. Appetite 2013, 67, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chechlacz, M.; Rotshtein, P.; Klamer, S.; Porubská, K.; Higgs, S.; Booth, D.; Fritsche, A.; Preissl, H.; Abele, H.; Birbaumer, N.; et al. Diabetes dietary management alters responses to food pictures in brain regions associated with motivation and emotion: A functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakin, C.; Beaulieu, K.; Hopkins, M.; Gibbons, C.; Finlayson, G.; Stubbs, R.J. Do eating behavior traits predict energy intake and body mass index? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2023, 24, e13515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulkadir, M.; Herle, M.; De Stavola, B.L.; Hübel, C.; Santos Ferreira, D.L.; Loos, R.J.F.; Bryant-Waugh, R.; Bulik, C.M.; Micali, N. Polygenic Score for Body Mass Index Is Associated with Disordered Eating in a General Population Cohort. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoek, H.M.; Van Strien, T.; Janssens, J.M.A.M.; Engels, R.C.M.E. Emotional, external, restrained eating and overweight in Dutch adolescents. Scand. J. Psychol. 2007, 48, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainik, U.; García-García, I.; Dagher, A. Uncontrolled eating: A unifying heritable trait linked with obesity, overeating, personality and the brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2019, 50, 2430–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | All | Men | Women | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control (N = 397) | T2D (N = 200) | MetS (N = 279) | Control (N = 201) | T2D (N = 57) | MetS (N = 80) | Control (N = 196) | T2D (N = 143) | MetS (N = 199) | |
| Age (years) | 49.65 ± 10.88 | 61.49 ± 9.55 | 57.01 ± 6.97 | 47.24 ± 11.06 | 60.44 ± 9.78 | 56.19 ± 7.50 | 52.12 ± 10.13 | 61.92 ± 9.46 | 57.35 ± 6.73 |
| External Eating | 3.33 ± 1.02 | 3.54 ± 0.74 | NA | 3.09 ± 1.07 | 3.35 ± 0.55 | NA | 3.48 ± 0.96 | 3.62 ± 0.79 | NA |
| Emotional Eating | 2.64 ± 1.27 | 4.46 ± 1.1 | NA | 2.18 ± 1.3 | 4.24 ± 1.07 | NA | 2.92 ± 1.16 | 4.54 ± 1.1 | NA |
| Restraint | 2.86 ± 1.13 | 2.89 ± 0.75 | NA | 2.56 ± 1.28 | 2.83 ± 0.86 | NA | 3.05 ± 0.98 | 2.91 ± 0.71 | NA |
| Height (cm) | 173.26 ± 8.21 | 161.7 ± 7.96 | 169.43 ± 7.23 | 176.32 ± 6.25 | 168.79 ± 6.76 | 175.72 ± 4.57 | 163.24 ± 5.41 | 158.87 ± 6.53 | 166.90 ± 6.53 |
| Weight (kg) | 79.38 ± 13.09 | 80.97 ± 15.46 | 89.29 ± 5.46 | 82.79 ± 12.12 | 86.82 ± 16.19 | 93.06 ± 5.95 | 68.20 ± 9.46 | 78.64 ± 14.57 | 87.77 ± 4.42 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.68 ± 4.5 | 30.92 ± 5.25 | 31.17 ± 2.45 | 27.39 ± 4.26 | 30.41 ± 5.07 | 30.11 ± 2.00 | 27.98 ± 4.73 | 31.12 ± 5.32 | 31.60 ± 2.49 |
| Cholesterol (mmol/L) | 5.09 ± 0.64 | 5.43 ± 1.14 | 5.88 ± 0.71 | 5.17 ± 0.55 | 5.57 ± 0.95 | 5.91 ± 0.72 | 5.06 ± 0.67 | 5.38 ± 1.21 | 5.86 ± 0.71 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 1.48 ± 0.6 | 1.68 ± 1.33 | 1.72 ± 0.51 | 1.48 ± 0.61 | 1.93 ± 1.45 | 1.74 ± 0.47 | 1.48 ± 0.60 | 1.58 ± 1.28 | 1.71 ± 0.53 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 1.09 ± 0.37 | 1.2 ± 0.51 | 1.01 ± 0.13 | 1.07 ± 0.34 | 1.27 ± 0.58 | 0.96 ± 0.10 | 1.09 ± 0.38 | 1.17 ± 0.48 | 1.02 ± 0.13 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 2.96 ± 1.08 | 3.05 ± 1.43 | 3.17 ± 0.19 | 3.03 ± 0.98 | 3.18 ± 1.57 | 3.23 ± 0.16 | 2.93 ± 1.11 | 3 ± 1.37 | 3.15 ± 0.20 |
| HbA1c (%) | 4.89 ± 0.6 | 7.48 ± 0.99 | 5.28 ± 1.00 | 4.87 ± 0.65 | 7.47 ± 0.94 | 5.12 ± 0.91 | 4.89 ± 0.58 | 7.48 ± 1.01 | 5.34 ± 1.03 |
| Fasting Glucose (mmol/L) | 4.88 ± 0.71 | 7.22 ± 1.95 | 5.33 ± 1.38 | 4.79 ± 0.66 | 7.2 ± 2 | 5.19 ± 1.31 | 4.90 ± 0.73 | 7.22 ± 1.93 | 5.38 ± 1.41 |
| 2 h glucose (mmol/L) | NA | 9.93 ± 2.2 | 6.58 ± 2.42 | NA | 10.17 ± 2.36 | 6.35 ± 2.48 | NA | 9.83 ± 2.13 | 6.67 ± 2.40 |
| C-peptide (ng/mL) | 2.31 ± 0.94 | 2.65 ± 5.39 | NA | 2.39 ± 0.87 | 2.18 ± 0.94 | NA | 2.28 | 2.83 ± 6.34 | NA |
| Gene | SNP | EA | NEA | EAF | N | Beta/OR | SE | P | PFDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emotional eating | |||||||||
| HTR2A | rs6313 | A | G | 0.47 | 286 | 0.36 | 0.11 | 0.001 | 0.041 |
| External eating | |||||||||
| HTR1D | rs623988 | A | G | 0.29 | 295 | 0.32 | 0.08 | 1.20 × 10−4 | 3.60 × 10−3 |
| CDKAL1 | rs9295474 | C | G | 0.64 | 294 | 0.22 | 0.08 | 0.003 | 0.047 |
| Type 2 diabetes | |||||||||
| CXCR2 | rs2230054 | T | C | 0.44 | 595 | 1.8 | 0.15 | 8.87 × 10−5 | 8.87 × 10−4 |
| HTR1F | rs56398417 | C | T | 0.84 | 597 | 2.61 | 0.24 | 5.01 × 10−5 | 7.52 × 10−4 |
| NPY2R | rs1047214 | T | C | 0.62 | 400 | 1.82 | 0.17 | 4.56 × 10−4 | 3.42 × 10−3 |
| HTR3A | rs1062613 | T | C | 0.19 | 596 | 2.13 | 0.18 | 4.03 × 10−5 | 7.52 × 10−4 |
| HTR2A | rs6313 | A | G | 0.47 | 572 | 1.58 | 0.15 | 0.002 | 0.012 |
| HTR2C | rs6318 | C | G | 0.09 | 593 | 2.07 | 0.24 | 0.002 | 0.012 |
| Metabolic syndrome | |||||||||
| CRP | rs2794521 | C | T | 0.21 | 621 | 6.64 | 0.17 | 4.83 × 10−28 | 1.45 × 10−26 |
| ADCY3 | rs17799872 | A | G | 0.09 | 641 | 1.90 | 0.19 | 0.001 | 0.004 |
| GHRL | rs696217 | T | G | 0.08 | 639 | 2.20 | 0.18 | 2.02 × 10−5 | 1.51 × 10−4 |
| CDKAL1 | rs9295474 | G | C | 0.36 | 634 | 1.70 | 0.13 | 4.26 × 10−5 | 2.56 × 10−4 |
| BDNF | rs11030107 | G | A | 0.13 | 627 | 1.91 | 0.17 | 1.23 × 10−4 | 0.001 |
| CHRM4 | rs2067482 | T | C | 0.08 | 641 | 0.45 | 0.28 | 0.005 | 0.017 |
| CHRM1 | rs2067477 | A | C | 0.04 | 637 | 3.33 | 0.26 | 3.80 × 10−6 | 3.80 × 10−5 |
| HTR3A | rs1062613 | T | C | 0.19 | 636 | 2.10 | 0.16 | 2.53 × 10−6 | 3.79 × 10−5 |
| AKT1 | rs3803300 | A | G | 0.03 | 637 | 2.48 | 0.31 | 0.003 | 0.012 |
| Height | |||||||||
| HTR2C | rs6318 | C | G | 0.09 | 242 | −3.60 | 0.89 | 7.32 × 10−5 | 0.002 |
| Body mass index | |||||||||
| ADCY3 | rs17799872 | A | G | 0.09 | 245 | 1.13 | 0.30 | 1.90 × 10−4 | 0.003 |
| HTR2C | rs6318 | C | G | 0.09 | 242 | 1.53 | 0.34 | 1.28 × 10−5 | 3.83 × 10−4 |
| Waist circumference | |||||||||
| HTR2C | rs6318 | C | G | 0.09 | 242 | 4.88 | 1.36 | 3.90 × 10−4 | 0.012 |
| Waist–hip ratio | |||||||||
| SIRT1 | rs3758391 | C | T | 0.52 | 234 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.001 | 0.040 |
| Albumin | |||||||||
| CDKAL1 | rs9295474 | G | C | 0.36 | 237 | −1.48 | 0.43 | 0.001 | 0.020 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Timasheva, Y.; Balkhiyarova, Z.; Avzaletdinova, D.; Morugova, T.; Korytina, G.F.; Nouwen, A.; Prokopenko, I.; Kochetova, O. Mendelian Randomization Analysis Identifies Inverse Causal Relationship between External Eating and Metabolic Phenotypes. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081166
Timasheva Y, Balkhiyarova Z, Avzaletdinova D, Morugova T, Korytina GF, Nouwen A, Prokopenko I, Kochetova O. Mendelian Randomization Analysis Identifies Inverse Causal Relationship between External Eating and Metabolic Phenotypes. Nutrients. 2024; 16(8):1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081166
Chicago/Turabian StyleTimasheva, Yanina, Zhanna Balkhiyarova, Diana Avzaletdinova, Tatyana Morugova, Gulnaz F. Korytina, Arie Nouwen, Inga Prokopenko, and Olga Kochetova. 2024. "Mendelian Randomization Analysis Identifies Inverse Causal Relationship between External Eating and Metabolic Phenotypes" Nutrients 16, no. 8: 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081166
APA StyleTimasheva, Y., Balkhiyarova, Z., Avzaletdinova, D., Morugova, T., Korytina, G. F., Nouwen, A., Prokopenko, I., & Kochetova, O. (2024). Mendelian Randomization Analysis Identifies Inverse Causal Relationship between External Eating and Metabolic Phenotypes. Nutrients, 16(8), 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081166