Abstract
The Mediterranean diet, renowned for its health benefits, especially in reducing cardiovascular risks and protecting against diseases like diabetes and cancer, emphasizes virgin olive oil as a key contributor to these advantages. Despite being a minor fraction, the phenolic compounds in olive oil significantly contribute to its bioactive effects. This review examines the bioactive properties of hydroxytyrosol and related molecules, including naturally occurring compounds (-)-oleocanthal and (-)–oleacein, as well as semisynthetic derivatives like hydroxytyrosyl esters and alkyl ethers. (-)-Oleocanthal and (-)–oleacein show promising anti-tumor and anti-inflammatory properties, which are particularly underexplored in the case of (-)–oleacein. Additionally, hydroxytyrosyl esters exhibit similar effectiveness to hydroxytyrosol, while certain alkyl ethers surpass their precursor’s properties. Remarkably, the emerging research field of the effects of phenolic molecules related to virgin olive oil on cell autophagy presents significant opportunities for underscoring the anti-cancer and neuroprotective properties of these molecules. Furthermore, promising clinical data from studies on hydroxytyrosol, (-)–oleacein, and (-)–oleocanthal urge further investigation and support the initiation of clinical trials with semisynthetic hydroxytyrosol derivatives. This review provides valuable insights into the potential applications of olive oil-derived phenolics in preventing and managing diseases associated with cancer, angiogenesis, and atherosclerosis.
1. Mediterranean Diet: More Than a Dietary Choice
Derived from the culinary traditions of the Mediterranean region, the Mediterranean diet has captured significant attention in both academic discourse and public health research. This is primarily due to its well-documented association with numerous health benefits. Centered around the predominant consumption of an array of healthy food products, this dietary pattern is not only renowned for its appetizing flavors but also for its potential to mitigate the risk of chronic diseases, extend life expectancy, and enhance overall well-being [1,2]. With centuries of historical heritage and a growing body of empirical evidence, the Mediterranean diet stands as an exemplary case study for investigating the intricate relationship between culture, nutrition, and health [3,4].
Since the Mediterranean diet derives from the traditional way of eating in countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea, such as Spain, Italy, Greece, Morocco, Tunisia, Libya, and others, there is not just one Mediterranean diet; rather, it varies slightly from one country to another, adapting to their unique cultures and lifestyles. However, the use of virgin olive oil (VOO) is a common feature in all these dietary variations [1,4]. Notably, UNESCO has recognized the Mediterranean diet as an intangible cultural heritage deeply connected to its place of origin, promoting responsible interactions with the environment through its agricultural and culinary practices [5].
The Mediterranean diet typically features a high intake of olive oil, olives, fruits, vegetables, unrefined cereals, legumes, and nuts (Figure 1). In addition, it includes a moderate consumption of fish and dairy products, while meat products are consumed in lower quantities [4]. One controversial aspect of the Mediterranean diet is the inclusion of red wine, which contains a higher concentration of phytochemical compounds compared to other alcoholic beverages. An ongoing debate centers around whether the potential benefits of bioactive molecules in red wine outweigh the potential drawbacks of alcohol consumption, even when consumed moderately [6]. Furthermore, considerations such as religious and social factors that may limit alcohol intake should be considered [1,7].
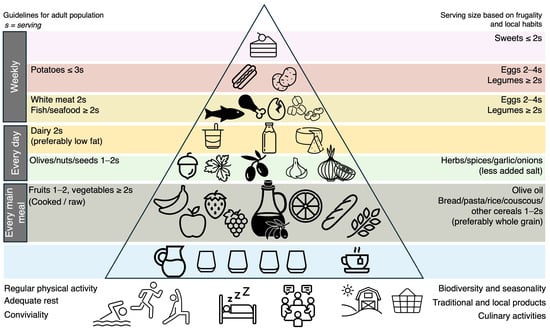
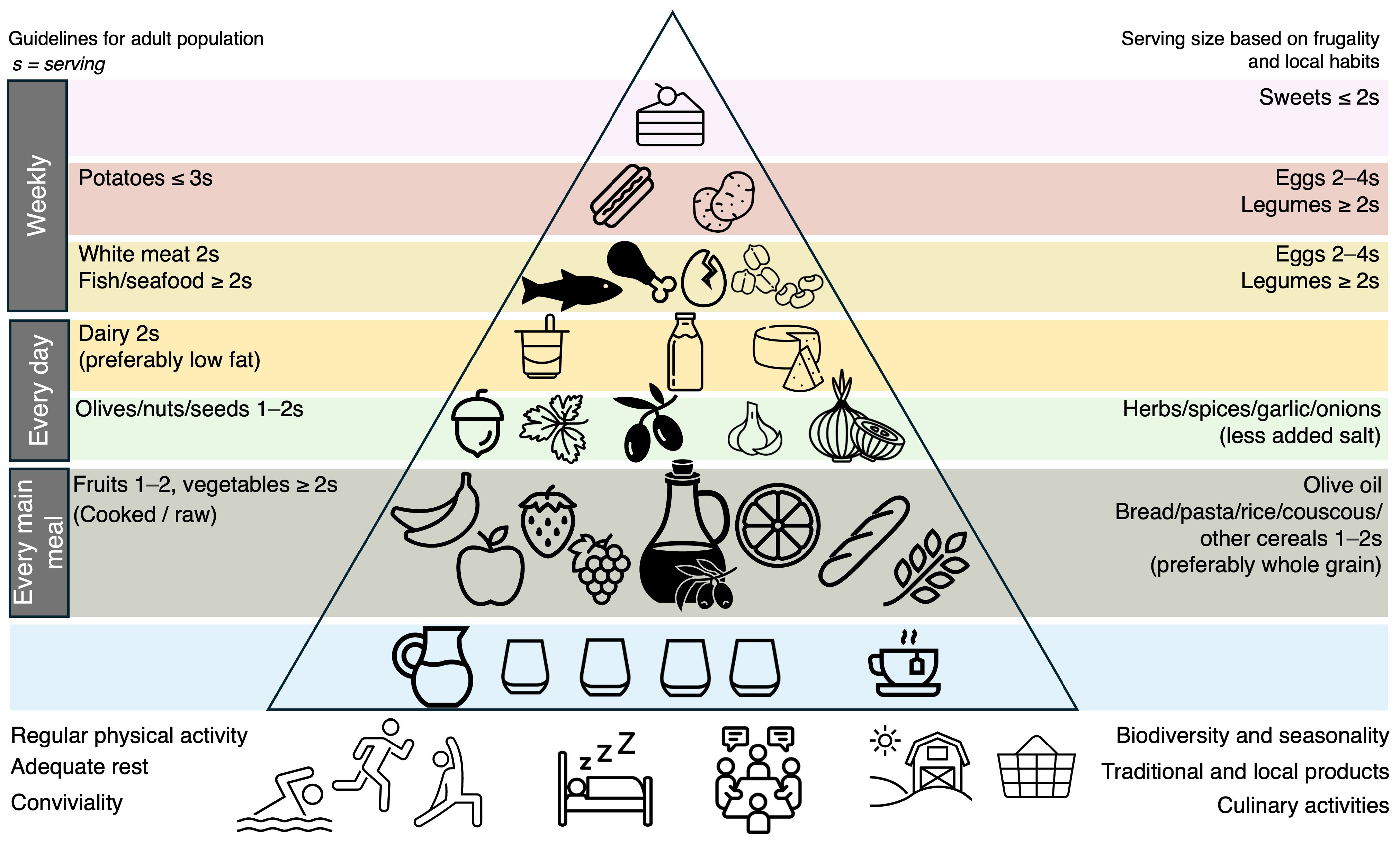
Figure 1.
The Mediterranean diet pyramid. Inspired by “Fundación Dieta Mediterránea, 2010 edition”.
A wide array of health benefits has been associated with the Mediterranean diet. The most consistent and robust body of evidence supports its positive impact on cardiovascular risk factors and cardiovascular disease [8,9,10,11,12,13]. Furthermore, a substantial body of literature also highlights its potential benefits for many other health outcomes, including diabetes [14,15,16,17], obesity [18,19], cancer [20,21,22,23,24], and cognitive decline [25,26], among others [8,13].
Despite all the reported benefits to health, measuring and implementing a complete Mediterranean diet presents challenges, resulting in limited interventional studies conducted on humans. The majority of these studies are of short-term duration and focus on the measurement of intermediate factors, such as plasma lipid concentrations, inflammation markers, blood pressure, fasting glucose, and weight loss, rather than assessing the ultimate disease outcomes like myocardial infarction, stroke, dementia, and cancer development [1]. Contrary to this, the PREDIMED study aimed to establish a strong correlation between the Mediterranean diet and a reduced incidence of cardiovascular events [9]. Similarly, the CORDIOPREV study, which has been completed but is awaiting results, seeks to assess the impact of the Mediterranean diet compared to a low-fat diet in the secondary prevention of cardiovascular diseases [27].
An advantage of the Mediterranean dietary pattern lies in the concept that “the whole is greater than the sum of its parts”. In other words, the protective effect of consuming the typical Mediterranean diet foods is more significant when they are consumed together. Notably, the consumption of VOO should be emphasized, as it serves as a common thread in all variations of the Mediterranean diet across different regions and countries. An overview of the bioactivities of VOO natural-contained and synthetic-derived phenolic compounds regarding anti-cancer, anti-angiogenic, and anti-atherogenic effects is the main focus of this review.
2. Virgin Olive Oil
Olive oil is a product derived from the mechanical extraction of the fruit Olea europaea L. (Oleaceae family) [28]. Among the various types of olive oils, VOO stands out for its method of production. It is obtained through mechanical or other physical processes, such as washing, decantation, centrifugation, or filtration, conducted under specific thermal conditions that do not cause any alterations in the oil [29]. Importantly, these high-quality oils, namely extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) and VOO, are never subjected to solvent-based extraction, chemical treatments, re-esterification processes, or any mixing with other types of oils [29,30].
The composition of olive oil is predominantly lipidic, with triacylglycerols accounting for approximately 99% of its composition. Additionally, it contains smaller proportions of free fatty acids, mono- and diacylglycerols, and various lipids, including hydrocarbons, sterols, aliphatic alcohols, tocopherols, and pigments. Triacylglycerols in VOO are rich in monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs), particularly oleic acid, with palmitic acid as the main saturated fatty acid, and some polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), such as linoleic and linolenic acid [28,29,30,31] (Table 1).

Table 1.
Virgin olive oil composition.
Traditionally, the cardioprotective effects of VOO have been attributed to its lipid profile, which has indeed been linked to improvements in cardiovascular parameters like low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels [34,35,36]. However, it is now recognized that many of these benefits, among others, are primarily mediated by minor components of this food, namely, phenolic compounds, which play a pivotal role in determining the biological properties and sensory attributes of VOO [29,31,37].
Together with molecules like carotenoids and tocopherols, phenolic compounds are the primary antioxidants found in VOO. These compounds play a crucial role in determining the oil’s sensory attributes, such as bitterness, pungency, and stability, shaping the organoleptic characteristics of aroma and flavor in each VOO [28,29]. However, what is particularly intriguing is that these antioxidants not only enhance the organoleptic properties and stability of VOO but also serve vital roles in human health, exhibiting antioxidant properties [38], among other beneficial effects.
3. Bioactive Phenolic Compounds in Virgin Olive Oil and Their Derivatives
The concentration of phenolic compounds in VOO exhibits significant variation due to agronomic factors, including the geographical origin, olive cultivar, fruit ripeness stage, and extraction process. This concentration can span from 50 to 940 mg/kg of oil [32,33], with concentrations typically falling within the range of 100 to 300 mg/kg [29], illustrating substantial differences among different varieties and conditions.
In terms of their chemical structure, phenolic compounds found in VOO encompass a diverse array of molecules from various classes (Table 2). These include simple and alcoholic phenols, such as vanillic, gallic, coumaric, and caffeic acids, as well as tyrosol and hydroxytyrosol. Additionally, VOO contains more complex compounds like secoiridoids (e.g., oleuropein and ligstroside, along with their derivatives), lignans, hydroxychromans, and flavones. Notably, among these compounds, alcoholic phenols and secoiridoids are present in substantial quantities in VOO [28,39].

Table 2.
Phenolic compounds in virgin olive oils.
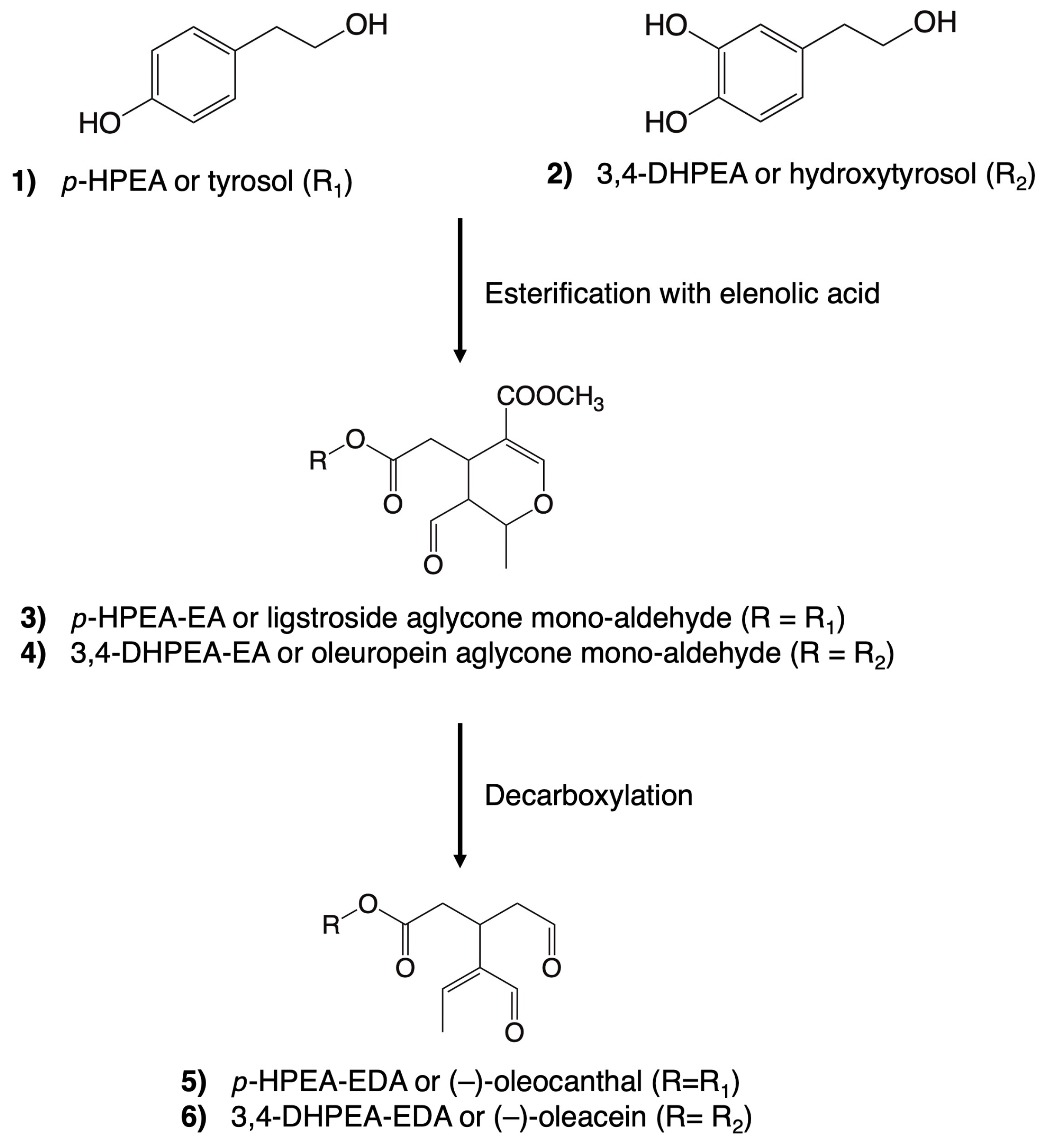
Remarkably, the alcoholic phenols, tyrosol and hydroxytyrosol, and the secoiridoids share close structural relationships (Figure 2). Tyrosol (p-hydroxyphenethyl ethanol, p-HPEA (1)) and hydroxytyrosol (3,4-dihydroxyphenylethyl ethanol, 3,4-DHPEA (2)) can exist independently in VOO. However, upon esterification with elenolic acid, they undergo derivatization into secoiridoids. These compounds constitute a prominent and intricate family within the polar fraction of VOO. The most prevalent secoiridoids in VOO include the mono-aldehydic forms of ligstroside aglycones (p-HPEA-EA (3)) and oleuropein (3,4-DHPEA-EA (4)), as well as the di-aldehydic forms of their decarboxymethylated derivatives, (-)–oleocanthal (p-HPEA-EDA (5)) and (-)–oleacein (3,4-DHPEA-EDA (6)) [40].
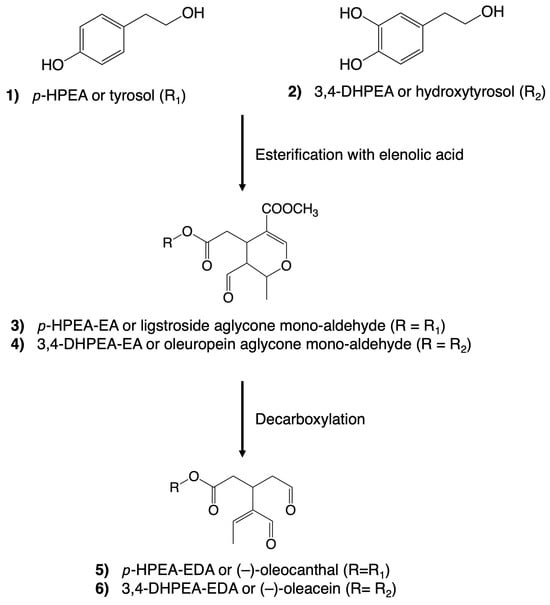
Figure 2.
Chemical structures of some of the most abundant phenolic compounds in virgin olive oil. A simplified version of the natural derivatization process is illustrated.
All the previously mentioned molecules occur naturally in VOO and exert remarkable bioactivities that will be further discussed. Interestingly, in the contemporary research landscape, a considerable effort is dedicated to exploring novel formulations of hydroxytyrosol to enhance its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) processes, as well as improving its stability and biological health features. These investigations primarily concentrate on altering the solubility of hydroxytyrosol to enhance both its bioavailability and plasma half-life [41]. A comprehensive review conducted by Bernini and colleagues examines various newly isolated hydroxytyrosol-derived compounds, their associated biological activities, and synthesis methods. Noteworthy categories of these compounds include hydroxytyrosol esters, hydroxytyrosol alkyl ethers, and others such as hydroxytyrosol analogs, thioderivatives and hydroxytyrosol-derived isochromans [42].
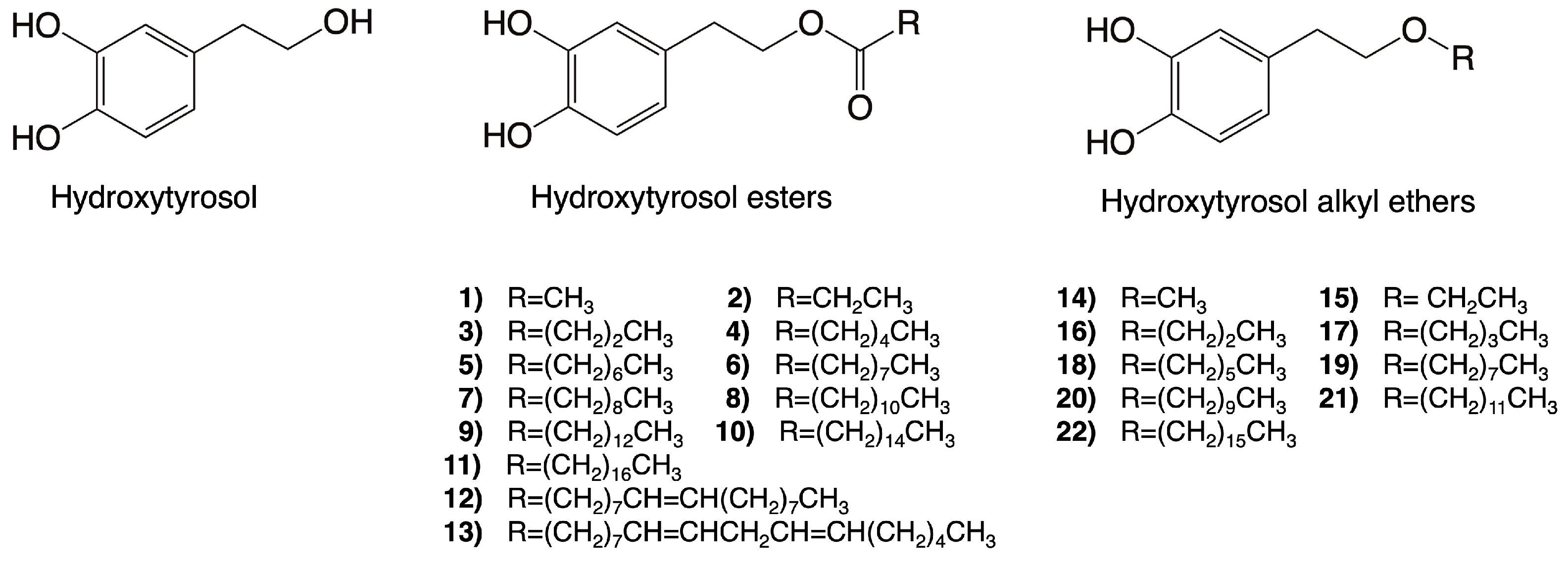
Hydroxytyrosol esters are some of the most studied synthetic derivatives of hydroxytyrosol. Interestingly, once hydroxytyrosol esters enter a cell, they can be hydrolyzed by cell lipases and esterases, thus possibly generating both the precursor hydroxytyrosol, which is largely responsible for the observed bioactivities, and a novel molecule that might be responsible for different activities [42]. Hydroxytyrosol acetate is one of the most prominent molecules within this group and can also be naturally present in VOO. Furthermore, representing a novel class of lipophilic hydroxytyrosol derivatives, hydroxytyrosyl alkyl-ethers exhibit improved chemical stability compared to hydroxytyrosol and hydroxytyrosol acetate [43]. Contrary to hydroxytyrosol esters, these compounds will likely remain invariant once inside the cell and act in either a similar or a different way compared to their precursor [42]. The molecular structures of hydroxytyrosol esters and alkyl ethers are provided in Figure 3.
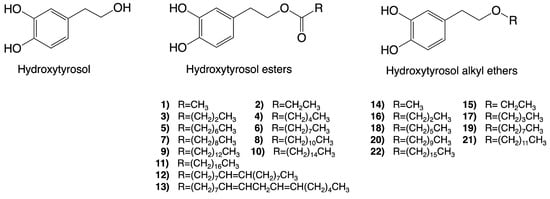
Figure 3.
Molecular structures of some of the synthetic derivatives of hydroxytyrosol. Structures of hydroxytyrosol, hydroxytyrosol esters (1–13), and hydroxytyrosl alkyl ethers (14–22) are shown.
Numerous studies have highlighted the positive impacts of phenolic compounds derived from VOO on human health. However, while tyrosol and hydroxytyrosol have been extensively studied, other structurally related molecules, such as (-)–oleocanthal and, especially, (-)–oleacein, have garnered comparatively less attention. Furthermore, while not naturally occurring in VOO, the semisynthetic derivatives of hydroxytyrosol deserve recognition due to their promising outcomes in enhancing the effects of their precursors and the growing interest in their development. This review focuses on key pre-clinical and clinical investigations into the antioxidant, anti-cancer, anti-angiogenic, and anti-atherosclerotic effects of hydroxytyrosol and some of its derivatives and related compounds.
4. Preclinical Data on the Anti-Cancer, Anti-Angiogenic, and Anti-Atherosclerotic Effects of Primary Phenolic Compounds from Virgin Olive Oils
4.1. Antioxidant Characteristics
Despite having been extensively investigated, we deemed it crucial to incorporate a concise discussion on the primary mechanisms governing the antioxidant properties of key phenolic molecules from VOO. This inclusion is considered significant, given the profound interconnection between these antioxidant attributes and various anti-cancer and anti-atherosclerotic properties, which will be further addressed. In this section, we examine the antioxidant properties exerted by key phenolic compounds found in VOOs (Table 3), mainly reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging or the promotion of antioxidant systems, which encompasses their roles in cellular protection mechanisms.

Table 3.
Molecular mechanisms in antioxidant effects of key phenolic compounds from VOO.
Among tyrosol and hydroxytyrosol, the latter exerts the most important health-related effects. Tyrosol exhibits antioxidant capacities, although they are generally weaker than hydroxytyrosol. Nonetheless, tyrosol remains an effective cellular antioxidant, likely due to its intracellular accumulation [64]. It is worth noting that tyrosol can be converted into hydroxytyrosol in the liver through the enzymatic activity of cytochrome P450 (CYP) CYP2A6 and CYP2D6, suggesting that tyrosol may serve as a precursor to hydroxytyrosol [65,66]. Regarding its biological effects, antioxidant [67,68] and anti-inflammatory properties [69] have been described for this molecule. However, in comparative studies, hydroxytyrosol typically exhibits stronger biological properties than tyrosol, as observed in various contexts, including antioxidant [70], anti-angiogenic [71], and anti-atherogenic effects [72].
The antioxidant properties of hydroxytyrosol arise from its capacity to function as a potent scavenger of free radicals [44,45,46], its chelating effect on metals—diminishing the production of ROS from derived reactions [47]—and its ability to stimulate various antioxidant systems by promoting the activity of enzymes like catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) [48,49,50,51], or by activating the transcription factor Nrf2 [52,53]. Additionally, (-)–oleocanthal and (-)–oleacein, while not as well studied as hydroxytyrosol for their antioxidant properties, have been shown to act as free radical scavengers [54,55,56].
Hydroxytyrosol derivatives also yield remarkable antioxidant effects. Hydroxytyrosol acetate is one of the most prominent molecules within this group and is naturally occurring in VOO. Remarkably, hydroxytyrosol acetate and propionate exerted similar or slightly higher antioxidant capacities than hydroxytyrosol [57,58,60]. Nitro-ester derivatives have also been found to enhance the antioxidant properties of hydroxytyrosol [59]. Interestingly, in those studies where a set of derivatives with increasing lengths of chains were compared, a decrease in activity with longer side chains in keeping with their lipophilic nature was detected. Hydroxytyrosyl alkyl-ethers demonstrated robust antioxidant effects, surpassing those of hydroxytyrosol [61,62,73].
4.2. Anti-Cancer Properties
The anti-cancer properties of primary phenolic compounds extracted from VOOs stand as a crucial area of investigation in pharmacological research. Globally, cancer remains a predominant cause of mortality worldwide, contributing to nearly ten million deaths, or almost one in six deaths, in 2020 [74]. Despite substantial advancements in understanding the nature of cancer, the persistently high incidence of this disease underscores the necessity for innovative approaches that complement traditional interventions. Over recent decades, attention has been turned towards cancer chemoprevention, a concept initially enunciated by Sporn in 1976 and encompassing the use of natural, synthetic, or biological agents to reverse, suppress, or prevent tumor progression [75]. Moreover, numerous cancer types exhibit close associations with dietary patterns linked to the Western lifestyle, such as low fruit and vegetable consumption [76]. Therefore, diet becomes an invaluable tool in the focus on cancer chemoprevention. This section aims to elucidate the anti-tumoral attributes of important bioactive constituents of VOO, shedding light on their mechanisms and implications in mitigating cancer-related risks (Table 4).

Table 4.
Anti-cancer effects of key phenolic compounds from VOO.
Hydroxytyrosol exerts significant effects on cancer progression, which are worth highlighting. Notably, ROS play a pivotal role in tumor formation, contributing to cancer initiation, promotion, and progression. The anti-tumor properties of this phenolic compound were primarily attributed to its role as an ROS scavenger and its capacity to modulate the antioxidant system. However, over the past decade, numerous studies have focused on demonstrating exclusive anti-tumor effects [41,83]. In this line, hydroxytyrosol has been shown to inhibit tumor cell proliferation by inducing cell cycle arrest through the modulation of cyclins [77,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88]. Additional mechanisms of impeding cell proliferation exerted by this compound include the inhibition of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) pathway [77,78], the induction of apoptosis by activating caspases and the mitochondrial pathway [80,83,85,86,87], and the reduction in the pro-survival protein kinase B (AKT) signaling pathway [88]. Additionally, hydroxytyrosol has demonstrated other effects, such as reducing epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) levels in colon cancer cells [79] and affecting the WNT pathway in breast cancer models [80]. Interestingly, the molecule exhibited pro-oxidant effects specifically in cancer cells [89,90,91].
Clear anti-cancer effects have been documented for (-)–oleocanthal in various human cancers, including colorectal [92], prostate [96], breast [95,96], myeloma [94], and melanoma [97] and non-melanoma skin cancer [93], both in vitro and in vivo. These effects encompass defects in cell survival, proliferation, migration, and invasion, with underlying mechanisms including the reduction in hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) [95,96] and inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), STAT3 [97], and the AKT and ERK signaling pathways [92,93,94]. The induction of apoptosis in cancer cells by (-)–oleocanthal through the intrinsic or mitochondrial pathway [92,94] and decreased proliferation caused by cell cycle arrest [95] have also been observed. Furthermore, (-)–oleacein reduced the activation of the AKT and ERK signaling pathways, with implications for cancer and angiogenesis [93].
There is limited research on the anti-cancer effects of semisynthetic derivatives of hydroxytyrosol. However, studies have indicated a decrease in tumor cell proliferation through the inhibition of the AKT and ERK signaling pathways and cell cycle arrest, as well as a reduction in cell migration [58,98,99,101].
4.3. Modulatory Effects on Angiogenesis
Angiogenesis, the process by which blood vessels originate from preexisting ones, is directly related to cancer progression [102,103,104]. In this context, the concept of angioprevention arises, denoting the prevention of cancer through the inhibition and/or stabilization of tumor angiogenesis [105]. Aligned with this notion, plant-derived compounds emerge as excellent angiopreventive candidates as their consumption entails low or non-existent toxicities, and they are readily accessible as integral components of dietary plant foods. Moreover, these compounds usually exhibit pleiotropic biological activity, extending their impact beyond tumor cells to include endothelial and immune cells. Importantly, other components of VOO, distinct from those addressed herein, have been suggested as angio-preventive phytochemicals [106]. Within this section, we comprehensively examine the existing literature concerning the modulatory mechanisms of hydroxytyrosol and its derivatives, (-)–oleocanthal, and (-)–oleacein on angiogenesis (Table 5) as modulators of angiogenesis and as angiopreventive molecules.

Table 5.
Modulation of angiogenesis-related mechanisms by key phenolic compounds from VOO.
Both cancer-related and cancer-independent effects of hydroxytyrosol on angiogenesis have been documented. Hydroxytyrosol can inhibit cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) activity [107]. In addition, data support a reduction in the AKT [88,108], nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) [88], and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) signaling pathways [108] by this molecule. Remarkably, our research group demonstrated that hydroxytyrosol exhibited anti-angiogenic effects by targeting extracellular remodeling and reducing matrix metalloproteinases’ (MMPs) production [71,109], in alignment with the findings of Scoditti and colleagues [107].
Regarding the derivatives of secoiridoids, a modulatory effect could be foreseen provided the reduction in the CD31 microvessel marker when endothelial cells were treated with (-)–oleocanthal [96]. Remarkably, other groups, including ourselves, demonstrated this anti-angiogenic effect of (-)–oleocanthal directly on endothelial cells [97,111]. Anti-angiogenic effects of (-)–oleacein were suggested by Carpi and colleagues, involving the reduced expression of VEGF, COX2 and MMP2 [55]. In this line, our group has recently outlined potent anti-angiogenic properties of (-)–oleacein in vitro and in vivo [111].
Limited but promising findings underscore the potential angiogenesis-modulating properties of hydroxytyrosol derivatives. Research by our group has evidenced more robust anti-angiogenic activity for hydroxytyrosol acetate compared to its precursor [112]. Nonetheless, no enhanced effects on angiogenesis in vitro or in vivo were observed in this study, suggesting that the modulatory effects of these derivatives on angiogenesis are independent of their antioxidant capacity [112]. Notably, our group also documented enhanced angiogenesis-inhibiting effects of ethyl hydroxytyrosyl ether compared to hydroxytyrosol [112]. These results laid the foundation for a comparative study of a set of alkyl hydroxytyrosol ethers, among which hexyl hydroxytyrosyl ether (HT-C6) emerged as the derivative that showed the best anti-angiogenic performance [110].
4.4. Anti-Atherosclerotic Properties
The investigation into the potential health benefits of dietary components has garnered significant attention in biomedical research, particularly in the context of preventing cardiovascular diseases. Atherosclerosis, characterized by the accumulation of lipid-rich plaque in arterial walls, stands as a major contributor to cardiovascular morbidity and mortality [113]. Historically considered a disease of cholesterol accumulation, it is currently recognized as an inflammation-driven syndrome [114]. In this context, the vascular endothelium actively contributes to the development of atherosclerosis through endothelial dysfunction. When exposed to various harmful stimuli, the endothelium undergoes a phenotypical shift towards such a maladaptive state, characterized by a specific gene expression profile that favors the expression of immune chemoattractant and adhesion molecules, thereby contributing to the progression of the pathology [115]. This section delves into an exploration of the molecular mechanisms governing the anti-atherosclerotic attributes inherent in primary phenolic compounds, with a focus on their hypolipidemic action and inflammation-related effects (Table 6).

Table 6.
Anti-atherosclerotic effects of key phenolic compounds from VOO.
The anti-atherosclerotic and cardioprotective effects of hydroxytyrosol can also be related, or not, to its antioxidant properties. For instance, the antioxidant action of hydroxytyrosol yields protection of LDL from oxidation [45,49,50]. In addition, this phenolic compound promotes hypocholesterolemia itself, lowering plasma levels of cholesterol, LDL, and triglycerides and increasing high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels [49,50]. Other effects rely on its anti-inflammatory capacity. As an example, hydroxytyrosol reduces the expression of proinflammatory cytokines like tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) [51,117] and chemokines like C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2) or C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10 (CXCL10) [117]. In addition, it decreases the expression of adhesion molecules by the endothelium [72,120,121,122]. Furthermore, it reduces COX-2 activity [116,118] and decreases inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) activity and nitric oxide (NO) production [44,116,117,118,119]. The mechanism behind hydroxytyrosol’s anti-inflammatory effects seems to be interfering with NF-κB signaling [51,72,116,117].
(-)–Oleocanthal has shown an inhibition of COX-2 [55,123,124], iNOS [123,125], and NF-κB [55,123] and its target genes. Furthermore, –(-)oleocanthal acts as an mTOR inhibitor [132]. Additionally, (-)–oleacein has been described to inhibit COX-2 [55,126,127] and NO production [127] and to reduce NF-κB signaling [55,56,126], resulting in decreased expression of proinflammatory cytokines and adhesion molecules in the endothelium.
Scarce preclinical studies address the anti-atherosclerotic effects of the derivatives of hydroxytyrosol. Nevertheless, the anti-inflammatory properties of hydroxytyrosol esters include COX-2 inhibition and the reduction in NO, proinflammatory cytokines’, and prostaglandins’ production [127,128,129]. Remarkably, hydroxytyrosyl alkyl-ethers demonstrated robust anti-inflammatory effects [63,130,131], surpassing those of hydroxytyrosol.
4.5. Effects on Autophagy
Markedly, a general overview of the impact of phenolic compounds derived from VOO on cell autophagy is worth acknowledging [133]. This influence contributes significantly to the overall beneficial effects of VOO polyphenols, particularly in addressing neurodegenerative conditions characterized by heightened oxidative stress and disruptions in proteostasis: the intricate process of eliminating protein accumulations and defective organelles [134].
Autophagy maintains cellular homeostasis through the removal and recycling of damaged macromolecules and organelles. In neurological contexts, phenolic compounds present in VOO, such as (-)–oleocanthal, have been documented to enhance autophagy through mTOR inhibition [132,135]. However, conflicting evidence from some studies suggests an inhibitory effect on autophagy [136,137].
Interestingly, the modulatory effect of autophagy by phenolic compounds has also been related to cancer progression. For instance, there appear to be autophagy-mediated anti-migration and invasive effects in tumor cell lines induced by hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein [138]. Nevertheless, the role of autophagy in cancer is also controversial and varies according to tumor type, stage, and therapy. Additionally, (-)–oleacein has emerged as a promising inhibitor of the histone demethylase LSD1/KDM1A. This enzyme holds a central epigenetic role in nutrient-driven metabolic adaptation and reprogramming, influencing multifactorial diseases such as obesity-associated disorders, neurological conditions, and cancer [139].
The evolving body of evidence positions the study of the effects of phenolic compounds on cell autophagy as a rapidly growing and intriguing field. Remarkably, its potential implications span diverse fields, including nutrition, and lead to the exploration of new therapeutic avenues for disorders such as cancer and neurodegenerative diseases.
5. Clinical Evidence on the Bioactivities of Key Phenolic Molecules from Virgin Olive Oil
A substantial body of clinical and correlational studies has addressed the positive impacts associated with VOO consumption in the realms of cancer and cardiovascular risk [9,13,22,23,26]. Despite the abundance of research in this field, limited attention has been directed towards the examination of individual components within VOO. This section provides a comprehensive overview of the existing clinical evidence, shedding light on the bioactivities of the principal phenolic constituents found in VOO and their relevance in the context of health promotion and disease prevention.
In the context of cancer research, a limited yet promising body of studies has emerged. One pilot study focused on assessing the impact of hydroxytyrosol on mammographic density among women at a heightened risk of developing breast cancer [140]. Notably, hydroxytyrosol demonstrated a significant reduction in breast density, particularly in women aged over 60 and those with elevated baseline breast density. Moreover, supplementation with hydroxytyrosol exhibited effects on tumor cell proliferation and influenced the WNT signaling pathway. While these findings are currently awaiting peer review, they offer a preliminary basis for future, more extensive investigations into the potential chemopreventive role of this natural compound in breast cancer. Additionally, an ongoing randomized clinical trial aims to elucidate the impact of hydroxytyrosol’s antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties on the intestinal microbiota in patients with colon cancer, although conclusive results have yet to be reported [141].
As discussed previously, (-)–oleocanthal and (-)–oleacein exhibit significant in vitro and in vivo anti-tumor properties. However, data regarding their anti-cancer activity in humans are currently lacking. A pilot clinical study sought to determine the feasibility and tolerability of an intervention with VOO high in (-)–oleocanthal and (-)–oleacein for patients at an early stage of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) [142]. Remarkably, only VOO with elevated (-)–oleocanthal and (-)–oleacein content demonstrated beneficial effects on hematological and apoptotic markers. The intervention led to an increase in apoptotic markers, caspase-cleaved keratin 18 (CCK18) and Fas, and negative regulators of the cell cycle (p21), along with a decrease in the anti-apoptotic protein survivin and the cell cycle regulator cyclin D. These promising results suggest that this specific type of VOO could serve as a potential dietary intervention to enhance CLL outcomes by inducing cancer cell apoptosis and improving patient metabolism.
In the realm of atherosclerosis and the prevention of cardiovascular diseases, an increasing number of studies have delved into hydroxytyrosol and its related molecules. This exploration may be connected to the historically examined and discussed beneficial effects of the Mediterranean diet and VOO on cardiovascular health. In this line, a randomized, crossover trial added valuable insights, revealing that oral supplementation with hydroxytyrosol and punicalagin improved early atherosclerosis markers in middle-aged, healthy adults [143]. Notably, the supplement exerted anti-atherosclerotic effects by enhancing endothelial function, reducing blood pressure, and lowering circulating oxidized LDL levels, particularly in individuals with altered parameters. Similarly, a double-blind, controlled trial investigated the impact of the daily intake of VOO rich in various phenolic compounds on platelet reactivity in healthy adult males [144]. The study found that the only olive oil lacking beneficial effects on platelet aggregation was the one without (-)–oleacein and (-)–oleocanthal. Additionally, another study demonstrated that treatment with VOO rich in (-)–oleocanthal and (-)–oleacein substantially improved the oxidative and inflammatory status in people with obesity and prediabetes [145], in line with the results obtained in preclinical studies [146].
Moreover, several ongoing trials aim to further our understanding. For instance, one study evaluates the effects of a commercially available standardized olive extract (Tensiofytol®; Tilman, Baillonville, Belgium) containing 100 mg of oleuropein and 20 mg of hydroxytyrosol and administered daily to individuals with elevated blood pressure [147]. Another study explores the impact of chronic consumption of a hydroxytyrosol-rich extract from olives (Hytolive®; Genosa I+D, Málaga, Spain) on a population at high risk of age-related pathologies like type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases [148]. Markers measured will include oxidative stress, inflammation, and glucose and lipid profiles. Lastly, an additional study compares two olive oil extracts, one containing hydroxytyrosol (Olivomed®; Intermed, Attica, Greece) and another containing a combination of oleuropein, hydroxytyrosol, and (-)–oleocanthal, examining their effects on endothelial, cardiac, and vascular functions in patients with coronary artery disease [149].
Shifting to the context of neurodegeneration and cognitive decline, few clinical studies are available. Nevertheless, a pilot study demonstrated that VOO consumption led to improvements in the blood–brain barrier function, enhanced brain function, and memory in individuals with mild cognitive impairments [150]. Importantly, findings revealed similar beneficial effects with refined olive oil (ROO), suggesting that the monounsaturated fats present in both VOO and ROO, such as oleic acid, contribute to these positive outcomes.
6. Concluding Remarks
The Mediterranean diet has gained significant recognition for its association with numerous health benefits. This dietary pattern, characterized by the consumption of healthy foods, not only offers flavorful meals but also demonstrates potential in mitigating the risk of chronic diseases, extending life expectancy, and enhancing overall well-being.
Recent research focuses on VOO, a cornerstone of the Mediterranean diet, as a key contributor to this diet’s health-promoting properties. Currently, emphasis has shifted to the minor components of VOO, particularly phenolic compounds, rather than the lipidic fraction, recognizing them as the primary contributors to its biological effects. In this line, hydroxytyrosol and structurally related molecules, such as (-)–oleocanthal and (-)–oleacein, stand out due to their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-angiogenic, and anti-cancer properties. In addition, the role of phenolic molecules in VOO on autophagy is an emerging field with significant potential for understanding their mechanisms of action and identifying new therapeutic targets.
Exploring the therapeutic potential of hydroxytyrosol derivatives, such as esters and alkyl ethers, presents a promising avenue for enhancing the bioactivities of the precursor or even finding new ones. Importantly, in the search and development of improved derivatives of this phenolic compound, the length and volume of the substituents seem crucial in determining optimal performance.
In clinical research, limited yet encouraging studies endorse the pharmacological promise of hydroxytyrosol, (-)–oleocanthal, and (-)–oleacein. Further investigations involving these compounds, either individually or in combination, as well as olive oils enriched with them, would enhance our understanding of their actual capacity for disease prevention and establish the foundation for clinical interventions. Moreover, certain hydroxytyrosol derivatives, particularly alkyl ethers, exhibit therapeutic potential that demands clinical evaluation.
In summary, the Mediterranean diet, with a central focus on VOO and its phenolic compounds, represents a holistic approach to health, offering a multitude of benefits that extend beyond cardioprotective effects and contribute to the prevention of prevalent diseases. The ongoing exploration of derivatives of these natural molecules and the expansion of our understanding of their effects on autophagy open new avenues for future research and therapeutic applications in various health issues.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.R.Q., B.M.-P. and M.Á.M.; investigation, A.D.M. and B.M.-P.; writing—original draft preparation, A.D.M. and B.M.-P.; writing—review and editing, A.D.M., A.R.Q., B.M.-P. and M.Á.M.; supervision, A.R.Q., B.M.-P. and M.Á.M.; funding acquisition, A.R.Q., B.M.-P. and M.Á.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants PID2019-105010RB-I00 and PID2023-148504OB-I00 (Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities), UMA18-FEDERJA-220 and P20Y_00257 (Andalusian Government and FEDER), and funds from group BIO 267 (Andalusian Government). Currently, our group has no grant funding our research. The “CIBER de Enfermedades Raras” and “CIBER de Enfermedades Cardiovasculares” are initiatives from the ISCIII (Spain). The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
Freepik provided essential graphic resources that contributed to the visual clarity of our figures.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Corella, D.; Coltell, O.; Macian, F.; Ordovás, J.M. Advances in Understanding the Molecular Basis of the Mediterranean Diet Effect. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 9, 227–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.; Bryan, J.; Hodgson, J.; Murphy, K. Definition of the Mediterranean Diet; A Literature Review. Nutrients 2015, 7, 9139–9153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dernini, S.; Berry, E.M.; Serra-Majem, L.; Vecchia, C.L.; Capone, R.; Medina, F.X.; Aranceta-Bartrina, J.; Belahsen, R.; Burlingame, B.; Calabrese, G.; et al. Med Diet 4.0: The Mediterranean Diet with Four Sustainable Benefits. Public Health Nutr. 2017, 20, 1322–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dernini, S.; Berry, E.M. Mediterranean Diet: From a Healthy Diet to a Sustainable Dietary Pattern. Front. Nutr. 2015, 2, 00015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guasch-Ferré, M.; Willett, W.C. The Mediterranean Diet and Health: A Comprehensive Overview. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 290, 549–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, M.; Feraco, A.; Camajani, E.; Caprio, M.; Armani, A. Health Effects of Red Wine Consumption: A Narrative Review of an Issue That Still Deserves Debate. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach-Faig, A.; Berry, E.M.; Lairon, D.; Reguant, J.; Trichopoulou, A.; Dernini, S.; Medina, F.X.; Battino, M.; Belahsen, R.; Miranda, G.; et al. Mediterranean Diet Pyramid Today. Science and Cultural Updates. Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 2274–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinu, M.; Pagliai, G.; Casini, A.; Sofi, F. Mediterranean Diet and Multiple Health Outcomes: An Umbrella Review of Meta-Analyses of Observational Studies and Randomised Trials. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estruch, R.; Ros, E.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Covas, M.-I.; Corella, D.; Arós, F.; Gómez-Gracia, E.; Ruiz-Gutiérrez, V.; Fiol, M.; Lapetra, J.; et al. Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease with a Mediterranean Diet Supplemented with Extra-Virgin Olive Oil or Nuts. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, T.T.; Rexrode, K.M.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Manson, J.E.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B. Mediterranean Diet and Incidence of and Mortality From Coronary Heart Disease and Stroke in Women. Circulation 2009, 119, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guallar-Castillón, P.; Rodríguez-Artalejo, F.; Tormo, M.J.; Sánchez, M.J.; Rodríguez, L.; Quirós, J.R.; Navarro, C.; Molina, E.; Martínez, C.; Marín, P.; et al. Major Dietary Patterns and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease in Middle-Aged Persons from a Mediterranean Country: The EPIC-Spain Cohort Study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2012, 22, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-García, E.; Rodriguez-Artalejo, F.; Li, T.Y.; Fung, T.T.; Li, S.; Willett, W.C.; Rimm, E.B.; Hu, F.B. The Mediterranean-Style Dietary Pattern and Mortality among Men and Women with Cardiovascular Disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra-Majem, L.; Román-Viñas, B.; Sanchez-Villegas, A.; Guasch-Ferré, M.; Corella, D.; La Vecchia, C. Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet: Epidemiological and Molecular Aspects. Mol. Aspects Med. 2019, 67, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koloverou, E.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Pitsavos, C.; Chrysohoou, C.; Georgousopoulou, E.N.; Grekas, A.; Christou, A.; Chatzigeorgiou, M.; Skoumas, I.; Tousoulis, D.; et al. Adherence to Mediterranean Diet and 10-Year Incidence (2002–2012) of Diabetes: Correlations with Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in the ATTICA Cohort Study. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2016, 32, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas-Salvadó, J.; Bulló, M.; Estruch, R.; Ros, E.; Covas, M.-I.; Ibarrola-Jurado, N.; Corella, D.; Arós, F.; Gómez-Gracia, E.; Ruiz-Gutiérrez, V.; et al. Prevention of Diabetes with Mediterranean Diets. Ann. Intern. Med. 2014, 160, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirabelli, M.; Chiefari, E.; Arcidiacono, B.; Corigliano, D.M.; Brunetti, F.S.; Maggisano, V.; Russo, D.; Foti, D.P.; Brunetti, A. Mediterranean Diet Nutrients to Turn the Tide against Insulin Resistance and Related Diseases. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirabelli, M.; Brunetti, A. The Rise and Fall of the Mediterranean Diet and Related Nutrients in Preventing Diabetes. Nutrients 2022, 14, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendall, C.L.; Mayr, H.L.; Opie, R.S.; Bes-Rastrollo, M.; Itsiopoulos, C.; Thomas, C.J. Central Obesity and the Mediterranean Diet: A Systematic Review of Intervention Trials. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 3070–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estruch, R.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Corella, D.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Fitó, M.; Chiva-Blanch, G.; Fiol, M.; Gómez-Gracia, E.; Arós, F.; Lapetra, J.; et al. Effect of a High-Fat Mediterranean Diet on Bodyweight and Waist Circumference: A Prespecified Secondary Outcomes Analysis of the PREDIMED Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, e6–e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckland, G.; Travier, N.; Cottet, V.; González, C.A.; Luján-Barroso, L.; Agudo, A.; Trichopoulou, A.; Lagiou, P.; Trichopoulos, D.; Peeters, P.H.; et al. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and Risk of Breast Cancer in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition Cohort Study. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 2918–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelló, A.; Amiano, P.; Fernández de Larrea, N.; Martín, V.; Alonso, M.H.; Castaño-Vinyals, G.; Pérez-Gómez, B.; Olmedo-Requena, R.; Guevara, M.; Fernandez-Tardon, G.; et al. Low Adherence to the Western and High Adherence to the Mediterranean Dietary Patterns Could Prevent Colorectal Cancer. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 1495–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morze, J.; Danielewicz, A.; Przybyłowicz, K.; Zeng, H.; Hoffmann, G.; Schwingshackl, L. An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on Adherence to Mediterranean Diet and Risk of Cancer. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 1561–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, L.; Su, L.J.; Arab, L.; Bensen, J.T.; Farnan, L.; Fontham, E.T.H.; Song, L.; Hussey, J.; Merchant, A.T.; Mohler, J.L.; et al. Dietary Patterns Based on the Mediterranean Diet and DASH Diet Are Inversely Associated with High Aggressive Prostate Cancer in PCaP. Ann. Epidemiol. 2019, 29, 16–22.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo, E.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Donat-Vargas, C.; Buil-Cosiales, P.; Estruch, R.; Ros, E.; Corella, D.; Fitó, M.; Hu, F.B.; Arós, F.; et al. Mediterranean Diet and Invasive Breast Cancer Risk Among Women at High Cardiovascular Risk in the PREDIMED Trial: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2015, 175, 1752–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Brink, A.C.; Brouwer-Brolsma, E.M.; Berendsen, A.A.M.; van de Rest, O. The Mediterranean, Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH), and Mediterranean-DASH Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay (MIND) Diets Are Associated with Less Cognitive Decline and a Lower Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease—A Review. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, 1040–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Sun, D. Adherence to Mediterranean Diet and Risk of Developing Cognitive Disorders: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Lista, J.; Perez-Martinez, P.; García-Ríos, A.; Alcalá-Díaz, J.F.; Perez-Caballero, A.I.; Gomez-Delgado, F.; Fuentes, F.; Quintana-Navarro, G.; Lopez-Segura, F.; Ortiz-Morales, A.M.; et al. CORonary Diet Intervention with Olive Oil and Cardiovascular PREVention Study (the CORDIOPREV Study): Rationale, Methods, and Baseline Characteristics: A Clinical Trial Comparing the Efficacy of a Mediterranean Diet Rich in Olive Oil versus a Low-Fat Diet on Cardiovascular Disease in Coronary Patients. Am. Heart J. 2016, 177, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripoli, E.; Giammanco, M.; Tabacchi, G.; Di Majo, D.; Giammanco, S.; La Guardia, M. The Phenolic Compounds of Olive Oil: Structure, Biological Activity and Beneficial Effects on Human Health. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2005, 18, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-López, C.; Carpena, M.; Lourenço-Lopes, C.; Gallardo-Gomez, M.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Barba, F.J.; Prieto, M.A.; Simal-Gandara, J. Bioactive Compounds and Quality of Extra Virgin Olive Oil. Foods 2020, 9, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yubero-Serrano, E.M.; Lopez-Moreno, J.; Gomez-Delgado, F.; Lopez-Miranda, J. Extra Virgin Olive Oil: More than a Healthy Fat. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 72, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boskou, D.; Blekas, G.; Tsimidou, M. 4—Olive Oil Composition. In Olive Oil, 2nd ed.; Boskou, D., Ed.; AOCS Press: Urbana, IL, USA, 2006; pp. 41–72. ISBN 978-1-893997-88-2. [Google Scholar]
- Borges, T.H.; Pereira, J.A.; Cabrera–Vique, C.; Seiquer, I. Study of the Antioxidant Potential of Arbequina Extra Virgin Olive Oils from Brazil and Spain Applying Combined Models of Simulated Digestion and Cell Culture Markers. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 37, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servili, M.; Sordini, B.; Esposto, S.; Urbani, S.; Veneziani, G.; Di Maio, I.; Selvaggini, R.; Taticchi, A. Biological Activities of Phenolic Compounds of Extra Virgin Olive Oil. Antioxidants 2013, 3, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estruch, R.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Corella, D.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Ruiz-Gutiérrez, V.; Covas, M.I.; Fiol, M.; Gómez-Gracia, E.; López-Sabater, M.C.; Vinyoles, E.; et al. Effects of a Mediterranean-Style Diet on Cardiovascular Risk Factors. Ann. Intern. Med. 2006, 145, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitó, M.; Estruch, R.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Martínez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Arós, F.; Vila, J.; Corella, D.; Díaz, O.; Sáez, G.; de la Torre, R.; et al. Effect of the Mediterranean Diet on Heart Failure Biomarkers: A Randomized Sample from the PREDIMED Trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2014, 16, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katan, M.B.; Zock, P.L.; Mensink, R.P. Dietary Oils, Serum Lipoproteins, and Coronary Heart Disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 61, 1368S–1373S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambra, R.; Natella, F.; Lucchetti, S.; Forte, V.; Pastore, G. α-Tocopherol, β-Carotene, Lutein, Squalene and Secoiridoids in Seven Monocultivar Italian Extra-Virgin Olive Oils. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 68, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrugat, J.; Covas, M.-I.; Fitó, M.; Schröder, H.; Miró-Casas, E.; Gimeno, E.; López-Sabater, M.C.; de la Torre, R.; Farré, M.; SOLOS Investigators. Effects of Differing Phenolic Content in Dietary Olive Oils on Lipids and LDL Oxidation—A Randomized Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Nutr. 2004, 43, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-López, P.; Lozano-Sánchez, J.; Borras-Linares, I.; Emanuelli, T.; Menendez, J.A.; Segura-Carretero, A. Chapter 10—Polyphenols in Olive Oil: The Importance of Phenolic Compounds in the Chemical Composition of Olive Oil. In Olives and Olive Oil in Health and Disease Prevention, 2nd ed.; Preedy, V.R., Watson, R.R., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2021; pp. 111–122. ISBN 978-0-12-819528-4. [Google Scholar]
- Celano, R.; Piccinelli, A.L.; Pugliese, A.; Carabetta, S.; di Sanzo, R.; Rastrelli, L.; Russo, M. Insights into the Analysis of Phenolic Secoiridoids in Extra Virgin Olive Oil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 6053–6063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Almazan, M.; Pulido-Moran, M.; Moreno-Fernandez, J.; Ramirez-Tortosa, C.; Rodriguez-Garcia, C.; Quiles, J.L.; Ramirez-Tortosa, M. Hydroxytyrosol: Bioavailability, Toxicity, and Clinical Applications. Food Res. Int. 2018, 105, 654–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernini, R.; Gilardini Montani, M.S.; Merendino, N.; Romani, A.; Velotti, F. Hydroxytyrosol-Derived Compounds: A Basis for the Creation of New Pharmacological Agents for Cancer Prevention and Therapy. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 9089–9107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Caro, G.; Sarriá, B.; Madrona, A.; Espartero, J.L.; Escuderos, M.E.; Bravo, L.; Mateos, R. Digestive Stability of Hydroxytyrosol, Hydroxytyrosyl Acetate and Alkyl Hydroxytyrosyl Ethers. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 63, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rietjens, S.J.; Bast, A.; de Vente, J.; Haenen, G.R.M.M. The Olive Oil Antioxidant Hydroxytyrosol Efficiently Protects against the Oxidative Stress-Induced Impairment of the NO• Response of Isolated Rat Aorta. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2007, 292, H1931–H1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rietjens, S.J.; Bast, A.; Haenen, G.R.M.M. New Insights into Controversies on the Antioxidant Potential of the Olive Oil Antioxidant Hydroxytyrosol. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 7609–7614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visioli, F.; Bellomo, G.; Galli, C. Free Radical-Scavenging Properties of Olive Oil Polyphenols. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 247, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitsati, N.; Mantzaris, M.D.; Galaris, D. Hydroxytyrosol Inhibits Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Apoptotic Signaling via Labile Iron Chelation. Redox Biol. 2016, 10, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmaksoud, H.A.A.; Motawea, M.H.; Desoky, A.A.; Elharrif, M.G.; Ibrahimi, A. Hydroxytyrosol Alleviate Intestinal Inflammation, Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis Resulted in Ulcerative Colitis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 142, 112073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fki, I.; Sahnoun, Z.; Sayadi, S. Hypocholesterolemic Effects of Phenolic Extracts and Purified Hydroxytyrosol Recovered from Olive Mill Wastewater in Rats Fed a Cholesterol-Rich Diet. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jemai, H.; Fki, I.; Bouaziz, M.; Bouallagui, Z.; El Feki, A.; Isoda, H.; Sayadi, S. Lipid-Lowering and Antioxidant Effects of Hydroxytyrosol and Its Triacetylated Derivative Recovered from Olive Tree Leaves in Cholesterol-Fed Rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 2630–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudi, A.; Hadrich, F.; Feki, I.; Ghorbel, H.; Bouallagui, Z.; Marrekchi, R.; Fourati, H.; Sayadi, S. Oleuropein and Hydroxytyrosol Rich Extracts from Olive Leaves Attenuate Liver Injury and Lipid Metabolism Disturbance in Bisphenol A-Treated Rats. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 3220–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, X.; Feng, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wertz, K.; Weber, P.; Fu, Y.; Liu, J. Stimulation of GSH Synthesis to Prevent Oxidative Stress-Induced Apoptosis by Hydroxytyrosol in Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells: Activation of Nrf2 and JNK-P62/SQSTM1 Pathways. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 994–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zrelli, H.; Matsuoka, M.; Kitazaki, S.; Araki, M.; Kusunoki, M.; Zarrouk, M.; Miyazaki, H. Hydroxytyrosol Induces Proliferation and Cytoprotection against Oxidative Injury in Vascular Endothelial Cells: Role of Nrf2 Activation and HO-1 Induction. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 4473–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuffaro, D.; Pinto, D.; Silva, A.M.; Bertolini, A.; Bertini, S.; Saba, A.; Macchia, M.; Rodrigues, F.; Digiacomo, M. Insights into the Antioxidant/Antiradical Effects and In Vitro Intestinal Permeation of Oleocanthal and Its Metabolites Tyrosol and Oleocanthalic Acid. Molecules 2023, 28, 5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpi, S.; Scoditti, E.; Massaro, M.; Polini, B.; Manera, C.; Digiacomo, M.; Esposito Salsano, J.; Poli, G.; Tuccinardi, T.; Doccini, S.; et al. The Extra-Virgin Olive Oil Polyphenols Oleocanthal and Oleacein Counteract Inflammation-Related Gene and miRNA Expression in Adipocytes by Attenuating NF-κB Activation. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-Miranda, B.; Gallardo, I.; Melliou, E.; Cabero, I.; Álvarez, Y.; Magiatis, P.; Hernández, M.; Nieto, M.L. Oleacein Attenuates the Pathogenesis of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis through Both Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grasso, S.; Siracusa, L.; Spatafora, C.; Renis, M.; Tringali, C. Hydroxytyrosol Lipophilic Analogues: Enzymatic Synthesis, Radical Scavenging Activity and DNA Oxidative Damage Protection. Bioorganic Chem. 2007, 35, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouallagui, Z.; Bouaziz, M.; Lassoued, S.; Engasser, J.M.; Ghoul, M.; Sayadi, S. Hydroxytyrosol Acyl Esters: Biosynthesis and Activities. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 163, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillo, M.; Gallardo, E.; Madrona, A.; Bravo, L.; Sarriá, B.; González-Correa, J.A.; Mateos, R.; Espartero, J.L. Synthesis and Antioxidant Activity of Nitrohydroxytyrosol and Its Acyl Derivatives. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 10297–10303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, X.; Zeng, M.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, A.; Cui, L.; Cao, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Xu, J.; Feng, Z. Comparative Study of Hydroxytyrosol Acetate and Hydroxytyrosol in Activating Phase II Enzymes. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Marín, J.; De la Cruz, J.P.; Reyes, J.J.; López-Villodres, J.A.; Guerrero, A.; López-Leiva, I.; Espartero, J.L.; Labajos, M.T.; González-Correa, J.A. Hydroxytyrosyl Alkyl Ether Derivatives Inhibit Platelet Activation after Oral Administration to Rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 58, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Caro, G.; Sarriá, B.; Madrona, A.; Espartero, J.L.; Goya, L.; Bravo, L.; Mateos, R. Alkyl Hydroxytyrosyl Ethers Show Protective Effects against Oxidative Stress in HepG2 Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 5964–5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Marín, J.; De La Cruz, J.P.; Guerrero, A.; López-Leiva, I.; López-Villodres, J.A.; Reyes, J.J.; Espartero, J.L.; Madrona, A.; Labajos, M.T.; González-Correa, J.A. Cytoprotective Effect of Hydroxytyrosyl Alkyl Ether Derivatives after Oral Administration to Rats in a Model of Glucose–Oxygen Deprivation in Brain Slices. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 7659–7664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetto, R.D.; Varì, R.; Scazzocchio, B.; Filesi, C.; Santangelo, C.; Giovannini, C.; Matarrese, P.; D’Archivio, M.; Masella, R. Tyrosol, the Major Extra Virgin Olive Oil Compound, Restored Intracellular Antioxidant Defences in Spite of Its Weak Antioxidative Effectiveness. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2007, 17, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karković Marković, A.; Torić, J.; Barbarić, M.; Jakobušić Brala, C. Hydroxytyrosol, Tyrosol and Derivatives and Their Potential Effects on Human Health. Molecules 2019, 24, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Morató, J.; Robledo, P.; Tanner, J.-A.; Boronat, A.; Pérez-Mañá, C.; Oliver Chen, C.-Y.; Tyndale, R.F.; de la Torre, R. CYP2D6 and CYP2A6 Biotransform Dietary Tyrosol into Hydroxytyrosol. Food Chem. 2017, 217, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.M.; Hur, J.; Lee, Y.; Yoon, B.-R.; Choi, S.Y. Protective Effects of Tyrosol Against Oxidative Damage in L6 Muscle Cells. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2018, 24, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarna, L.K.; Sid, V.; Wang, P.; Siow, Y.L.; House, J.D.; O, K. Tyrosol Attenuates High Fat Diet-Induced Hepatic Oxidative Stress: Potential Involvement of Cystathionine β-Synthase and Cystathionine γ-Lyase. Lipids 2016, 51, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.-Y.; Huang, I.-T.; Shih, H.-J.; Chang, Y.-Y.; Kao, M.-C.; Shih, P.-C.; Huang, C.-J. Cluster of Differentiation 14 and Toll-like Receptor 4 Are Involved in the Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Tyrosol. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 53, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Puerta, R.; Domínguez, M.E.M.; Ruíz-Gutíerrez, V.; Flavill, J.A.; Hoult, J.R.S. Effects of Virgin Olive Oil Phenolics on Scavenging of Reactive Nitrogen Species and upon Nitrergic Neurotransmission. Life Sci. 2001, 69, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortes, C.; García-Vilas, J.A.; Quesada, A.R.; Medina, M.Á. Evaluation of the Anti-Angiogenic Potential of Hydroxytyrosol and Tyrosol, Two Bio-Active Phenolic Compounds of Extra Virgin Olive Oil, in Endothelial Cell Cultures. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carluccio, M.A.; Siculella, L.; Ancora, M.A.; Massaro, M.; Scoditti, E.; Storelli, C.; Visioli, F.; Distante, A.; De Caterina, R. Olive Oil and Red Wine Antioxidant Polyphenols Inhibit Endothelial Activation: Antiatherogenic Properties of Mediterranean Diet Phytochemicals. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cert, R.; Madrona, A.; Espartero, J.L.; Pérez-Camino, M.C. Antioxidant activity of alkyl hydroxytyrosyl ethers in unsaturated lipids. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 1999–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Parking, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: An overview. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sporn, M.B. Approaches to Prevention of Epithelial Cancer during the Preneoplastic Period. Cancer Res. 1976, 36, 2699–2702. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization Cancer. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- Corona, G.; Deiana, M.; Incani, A.; Vauzour, D.; Dessì, M.A.; Spencer, J.P.E. Hydroxytyrosol Inhibits the Proliferation of Human Colon Adenocarcinoma Cells through Inhibition of ERK1/2 and Cyclin D1. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirianni, R.; Chimento, A.; De Luca, A.; Casaburi, I.; Rizza, P.; Onofrio, A.; Iacopetta, D.; Puoci, F.; Andò, S.; Maggiolini, M.; et al. Oleuropein and Hydroxytyrosol Inhibit MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation Interfering with ERK1/2 Activation. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terzuoli, E.; Giachetti, A.; Ziche, M.; Donnini, S. Hydroxytyrosol, a Product from Olive Oil, Reduces Colon Cancer Growth by Enhancing Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Degradation. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granados-Principal, S.; Quiles, J.L.; Ramirez-Tortosa, C.; Camacho-Corencia, P.; Sanchez-Rovira, P.; Vera-Ramirez, L.; Ramirez-Tortosa, M. Hydroxytyrosol Inhibits Growth and Cell Proliferation and Promotes High Expression of Sfrp4 in Rat Mammary Tumours. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, S117–S126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouallagui, Z.; Han, J.; Isoda, H.; Sayadi, S. Hydroxytyrosol Rich Extract from Olive Leaves Modulates Cell Cycle Progression in MCF-7 Human Breast Cancer Cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulotta, S.; Corradino, R.; Celano, M.; D’Agostino, M.; Maiuolo, J.; Oliverio, M.; Procopio, A.; Iannone, M.; Rotiroti, D.; Russo, D. Antiproliferative and Antioxidant Effects on Breast Cancer Cells of Oleuropein and Its Semisynthetic Peracetylated Derivatives. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 1609–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabiani, R. Anti-Cancer Properties of Olive Oil Secoiridoid Phenols: A Systematic Review of: In Vivo Studies. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 4145–4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabiani, R.; Rosignoli, P.; De Bartolomeo, A.; Fuccelli, R.; Morozzi, G. Inhibition of Cell Cycle Progression by Hydroxytyrosol Is Associated with Upregulation of Cyclin-Dependent Protein Kinase Inhibitors p21WAF1/Cip1 and p27Kip1 and with Induction of Differentiation in HL60 Cells1. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Goldsmith, C.D.; Bond, D.R.; Jankowski, H.; Weidenhofer, J.; Stathopoulos, C.E.; Roach, P.D.; Scarlett, C.J. The Olive Biophenols Oleuropein and Hydroxytyrosol Selectively Reduce Proliferation, Influence the Cell Cycle, and Induce Apoptosis in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Talorete, T.P.N.; Yamada, P.; Isoda, H. Anti-Proliferative and Apoptotic Effects of Oleuropein and Hydroxytyrosol on Human Breast Cancer MCF-7 Cells. Cytotechnology 2009, 59, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López de las Hazas, M.-C.; Piñol, C.; Macià, A.; Motilva, M.-J. Hydroxytyrosol and the Colonic Metabolites Derived from Virgin Olive Oil Intake Induce Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Colon Cancer Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 6467–6476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Ma, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, D.; Pan, S.; Wu, Y.; Pan, H.; Xu, D.; et al. Hydroxytyrosol, a Natural Molecule from Olive Oil, Suppresses the Growth of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells via Inactivating AKT and Nuclear Factor-Kappa B Pathways. Cancer Lett. 2014, 347, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabiani, R.; Sepporta, M.V.; Rosignoli, P.; De Bartolomeo, A.; Crescimanno, M.; Morozzi, G. Anti-Proliferative and pro-Apoptotic Activities of Hydroxytyrosol on Different Tumour Cells: The Role of Extracellular Production of Hydrogen Peroxide. Eur. J. Nutr. 2012, 51, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosignoli, P.; Fuccelli, R.; Sepporta, M.V.; Fabiani, R. In Vitro Chemo-Preventive Activities of Hydroxytyrosol: The Main Phenolic Compound Present in Extra-Virgin Olive Oil. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Luo, C.; Liu, J. Hydroxytyrosol Induces Apoptosis in Human Colon Cancer Cells through ROS Generation. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1909–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, P.; Oh, W.-K.; Yun, H.J.; Namgoong, G.M.; Ahn, S.-G.; Kwon, S.-M.; Choi, H.-K.; Choi, H.S. P-HPEA-EDA, a Phenolic Compound of Virgin Olive Oil, Activates AMP-Activated Protein Kinase to Inhibit Carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 2011, 32, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polini, B.; Digiacomo, M.; Carpi, S.; Bertini, S.; Gado, F.; Saccomanni, G.; Macchia, M.; Nieri, P.; Manera, C.; Fogli, S. Oleocanthal and Oleacein Contribute to the in Vitro Therapeutic Potential of Extra Virgin Oil-Derived Extracts in Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer. Toxicol. Vitr. 2018, 52, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotece, M.; Gomez, R.; Conde, J.; Lopez, V.; Gomez-Reino, J.J.; Lago, F.; Iii, A.B.S.; Gualillo, O. Oleocanthal Inhibits Proliferation and MIP-1α Expression in Human Multiple Myeloma Cells. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 2467–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akl, M.R.; Ayoub, N.M.; Mohyeldin, M.M.; Busnena, B.A.; Foudah, A.I.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Sayed, K.A.E. Olive Phenolics as C-Met Inhibitors: (-)-Oleocanthal Attenuates Cell Proliferation, Invasiveness, and Tumor Growth in Breast Cancer Models. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elnagar, A.Y.; Sylvester, P.W.; Sayed, K.A.E. (−)-Oleocanthal as a c-Met Inhibitor for the Control of Metastatic Breast and Prostate Cancers. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Wang, J.; Peng, L. (−)-Oleocanthal Exerts Anti-Melanoma Activities and Inhibits STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- León-González, A.J.; Sáez-Martínez, P.; Jiménez-Vacas, J.M.; Herrero-Aguayo, V.; Montero-Hidalgo, A.J.; Gómez-Gómez, E.; Madrona, A.; Castaño, J.P.; Espartero, J.L.; Gahete, M.D.; et al. Comparative Cytotoxic Activity of Hydroxytyrosol and Its Semisynthetic Lipophilic Derivatives in Prostate Cancer Cells. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernini, R.; Crisante, F.; Merendino, N.; Molinari, R.; Soldatelli, M.C.; Velotti, F. Synthesis of a Novel Ester of Hydroxytyrosol and α-Lipoic Acid Exhibiting an Antiproliferative Effect on Human Colon Cancer HT-29 Cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laghezza Masci, V.; Bernini, R.; Villanova, N.; Clemente, M.; Cicaloni, V.; Tinti, L.; Salvini, L.; Taddei, A.R.; Tiezzi, A.; Ovidi, E. In Vitro Anti-Proliferative and Apoptotic Effects of Hydroxytyrosyl Oleate on SH-SY5Y Human Neuroblastoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Montaño, J.M.; Madrona, A.; Burgos-Morón, E.; Orta, M.L.; Mateos, S.; Espartero, J.L.; López-Lázaro, M. Selective Cytotoxic Activity of New Lipophilic Hydroxytyrosol Alkyl Ether Derivatives. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 5046–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, P.; Jain, R.K. Angiogenesis in Cancer and Other Diseases. Nature 2000, 407, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkman, J. Tumor Angiogenesis: Therapeutic Implications. N. Engl. J. Med. 1971, 285, 1182–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eelen, G.; Treps, L.; Li, X.; Carmeliet, P. Basic and Therapeutic Aspects of Angiogenesis Updated. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 310–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albini, A.; Tosetti, F.; Li, V.W.; Noonan, D.M.; Li, W.W. Cancer Prevention by Targeting Angiogenesis. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 9, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Dabrosin, C.; Yin, X.; Fuster, M.M.; Arreola, A.; Rathmell, W.K.; Generali, D.; Nagaraju, G.P.; El-Rayes, B.; Ribatti, D.; et al. Broad Targeting of Angiogenesis for Cancer Prevention and Therapy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015, 35, S224–S243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scoditti, E.; Calabriso, N.; Massaro, M.; Pellegrino, M.; Storelli, C.; Martines, G.; Caterina, R.D.; Carluccio, M.A. Mediterranean Diet Polyphenols Reduce Inflammatory Angiogenesis through MMP-9 and COX-2 Inhibition in Human Vascular Endothelial Cells: A Potentially Protective Mechanism in Atherosclerotic Vascular Disease and Cancer. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2012, 527, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo-Fernández, M.; Cerezo, A.B.; Hornedo-Ortega, R.; Troncoso, A.M.; Garcia-Parrilla, M.C. Anti-VEGF Effect of Bioactive Indolic Compounds and Hydroxytyrosol Metabolites. Foods 2022, 11, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Vilas, J.A.; Quesada, A.R.; Medina, M.Á. Hydroxytyrosol Targets Extracellular Matrix Remodeling by Endothelial Cells and Inhibits Both Ex Vivo and in Vivo Angiogenesis. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1741–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrero, A.D.; Castilla, L.; Espartero, J.L.; Madrona, A.; Quesada, A.R.; Medina, M.Á.; Martínez-Poveda, B. A Comparative Study of the Antiangiogenic Activity of Hydroxytyrosyl Alkyl Ethers. Food Chem. 2020, 333, 127476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrero, A.D.; Ortega-Vidal, J.; Salido, S.; Castilla, L.; Vidal, I.; Quesada, A.R.; Altarejos, J.; Martínez-Poveda, B.; Medina, M.Á. Anti-Angiogenic Effects of Oleacein and Oleocanthal: New Bioactivities of Compounds from Extra Virgin Olive Oil. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Jiménez, A.; Gallardo, E.; Espartero, J.L.; Madrona, A.; Quesada, A.R.; Medina, M.Á. Comparison of the Anti-Angiogenic Potential of Hydroxytyrosol and Five Derivatives. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 4310–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, D.; Ley, K. Immunity and Inflammation in Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, P.; Cui, Z.-Y.; Huang, X.-F.; Zhang, D.-D.; Guo, R.-J.; Han, M. Inflammation and Atherosclerosis: Signaling Pathways and Therapeutic Intervention. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimbrone, M.A.; García-Cardeña, G. Endothelial Cell Dysfunction and the Pathobiology of Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 620–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiuri, M.C.; De Stefano, D.; Di Meglio, P.; Irace, C.; Savarese, M.; Sacchi, R.; Cinelli, M.P.; Carnuccio, R. Hydroxytyrosol, a Phenolic Compound from Virgin Olive Oil, Prevents Macrophage Activation. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2005, 371, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, N.; Arnold, S.; Hoeller, U.; Kilpert, C.; Wertz, K.; Schwager, J. Hydroxytyrosol Is the Major Anti-Inflammatory Compound in Aqueous Olive Extracts and Impairs Cytokine and Chemokine Production in Macrophages. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 1890–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Cao, J.; Zhong, L. Hydroxytyrosol Inhibits Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines, iNOS, and COX-2 Expression in Human Monocytic Cells. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2009, 379, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Correa, J.A.; Navas, M.D.; Muñoz-Marín, J.; Trujillo, M.; Fernández-Bolaños, J.; de la Cruz, J.P. Effects of Hydroxytyrosol and Hydroxytyrosol Acetate Administration to Rats on Platelet Function Compared to Acetylsalicylic Acid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 7872–7876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalán, Ú.; López de las Hazas, M.-C.; Rubió, L.; Fernández-Castillejo, S.; Pedret, A.; de la Torre, R.; Motilva, M.-J.; Solà, R. Protective Effect of Hydroxytyrosol and Its Predominant Plasmatic Human Metabolites against Endothelial Dysfunction in Human Aortic Endothelial Cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 2523–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Agli, M.; Fagnani, R.; Mitro, N.; Scurati, S.; Masciadri, M.; Mussoni, L.; Galli, G.V.; Bosisio, E.; Crestani, M.; De Fabiani, E.; et al. Minor Components of Olive Oil Modulate Proatherogenic Adhesion Molecules Involved in Endothelial Activation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 3259–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, C.; Napoli, D.; Cacciapuoti, G.; Porcelli, M.; Zappia, V. Olive Oil Phenolic Compounds Inhibit Homocysteine-Induced Endothelial Cell Adhesion Regardless of Their Different Antioxidant Activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 3478–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotece, M.; Conde, J.; Abella, V.; López, V.; Francisco, V.; Ruiz, C.; Campos, V.; Lago, F.; Gomez, R.; Pino, J.; et al. Oleocanthal Inhibits Catabolic and Inflammatory Mediators in LPS-Activated Human Primary Osteoarthritis (OA) Chondrocytes Through MAPKs/NF-κB Pathways. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 49, 2414–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchamp, G.K.; Keast, R.S.J.; Morel, D.; Lin, J.; Pika, J.; Han, Q.; Lee, C.-H.; Smith, A.B.; Breslin, P.A.S. Ibuprofen-like Activity in Extra-Virgin Olive Oil. Nature 2005, 437, 45–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacono, A.; Gómez, R.; Sperry, J.; Conde, J.; Bianco, G.; Meli, R.; Gómez-Reino, J.J.; Smith III, A.B.; Gualillo, O. Effect of Oleocanthal and Its Derivatives on Inflammatory Response Induced by Lipopolysaccharide in a Murine Chondrocyte Cell Line. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 1675–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirmi, S.; Maugeri, A.; Russo, C.; Musumeci, L.; Navarra, M.; Lombardo, G.E. Oleacein Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation in THP-1-Derived Macrophages by the Inhibition of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, V.; Costa, M.; Videira, R.A.; Andrade, P.B.; Paiva-Martins, F. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Olive Oil Polyphenols—The Role of Oleacein and Its Metabolites. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plastina, P.; Benincasa, C.; Perri, E.; Fazio, A.; Augimeri, G.; Poland, M.; Witkamp, R.; Meijerink, J. Identification of Hydroxytyrosyl Oleate, a Derivative of Hydroxytyrosol with Anti-Inflammatory Properties, in Olive Oil by-Products. Food Chem. 2019, 279, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Jin, Z.; Lv, X.; Zheng, Z.; Gao, H.; Deng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, W.; He, J.; et al. Hydroxytyrosol Acetate Inhibits Vascular Endothelial Cell Pyroptosis via the HDAC11 Signaling Pathway in Atherosclerosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 656272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrero, A.D.; Castilla, L.; Bernal, M.; Manrique, I.; Posligua-García, J.D.; Moya-Utrera, F.; Porras-Alcalá, C.; Espartero, J.L.; Sarabia, F.; Quesada, A.R.; et al. Inhibition of Endothelial Inflammatory Response by HT-C6, a Hydroxytyrosol Alkyl Ether Derivative. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, J.J.; De La Cruz, J.P.; Muñoz-Marin, J.; Guerrero, A.; Lopez-Villodres, J.A.; Madrona, A.; Espartero, J.L.; Gonzalez-Correa, J.A. Antiplatelet Effect of New Lipophilic Hydroxytyrosol Alkyl Ether Derivatives in Human Blood. Eur. J. Nutr. 2013, 52, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanfar, M.A.; Bardaweel, S.K.; Akl, M.R.; El Sayed, K.A. Olive Oil-Derived Oleocanthal as Potent Inhibitor of Mammalian Target of Rapamycin: Biological Evaluation and Molecular Modeling Studies. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 1776–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigacci, S. Olive Oil Phenols as Promising Multi-Targeting Agents Against Alzheimer’s Disease. In Natural Compounds as Therapeutic Agents for Amyloidogenic Diseases; Vassallo, N., Ed.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 1–20. ISBN 978-3-319-18365-7. [Google Scholar]
- Angeloni, C.; Malaguti, M.; Barbalace, M.; Hrelia, S. Bioactivity of Olive Oil Phenols in Neuroprotection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigacci, S.; Miceli, C.; Nediani, C.; Berti, A.; Cascella, R.; Pantano, D.; Nardiello, P.; Luccarini, I.; Casamenti, F.; Stefani, M. Oleuropein Aglycone Induces Autophagy via the AMPK/mTOR Signalling Pathway: A Mechanistic Insight. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 35344–35357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achour, I.; Arel-Dubeau, A.-M.; Renaud, J.; Legrand, M.; Attard, E.; Germain, M.; Martinoli, M.-G. Oleuropein Prevents Neuronal Death, Mitigates Mitochondrial Superoxide Production and Modulates Autophagy in a Dopaminergic Cellular Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliván, S.; Martínez-Beamonte, R.; Calvo, A.C.; Surra, J.C.; Manzano, R.; Arnal, C.; Osta, R.; Osada, J. Extra Virgin Olive Oil Intake Delays the Development of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Associated with Reduced Reticulum Stress and Autophagy in Muscle of SOD1G93A Mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.-Y.; Zhu, J.-S.; Xie, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, S.; Shen, W.-J.; Wu, B.; Ding, T.; Wang, S.-L. Hydroxytyrosol and Oleuropein Inhibit Migration and Invasion via Induction of Autophagy in ER-Positive Breast Cancer Cell Lines (MCF7 and T47D). Nutr. Cancer 2021, 73, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuyàs, E.; Gumuzio, J.; Lozano-Sánchez, J.; Carreras, D.; Verdura, S.; Llorach-Parés, L.; Sanchez-Martinez, M.; Selga, E.; Pérez, G.J.; Scornik, F.S.; et al. Extra Virgin Olive Oil Contains a Phenolic Inhibitor of the Histone Demethylase LSD1/KDM1A. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.C. A Pilot Study of Hydroxytyrosol, a Component of Olive Oil for Breast Cancer Prevention In Women at High Risk of Breast Cancer. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02068092 (accessed on 13 March 2024).
- Fundación Pública Andaluza para la Investigación de Málaga en Biomedicina y Salud. Effect of a Dietary Supplement with Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties on the Intestinal Microbiota in Patients with Colon Cancer. Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. TERATROPHO Study. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05472753 (accessed on 13 March 2024).
- Rojas Gil, A.P.; Kodonis, I.; Ioannidis, A.; Nomikos, T.; Dimopoulos, I.; Kosmidis, G.; Katsa, M.E.; Melliou, E.; Magiatis, P. The Effect of Dietary Intervention With High-Oleocanthal and Oleacein Olive Oil in Patients With Early-Stage Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: A Pilot Randomized Trial. Front. Oncol. 2022, 11, 810249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quirós-Fernández, R.; López-Plaza, B.; Bermejo, L.M.; Palma-Milla, S.; Gómez-Candela, C. Supplementation with Hydroxytyrosol and Punicalagin Improves Early Atherosclerosis Markers Involved in the Asymptomatic Phase of Atherosclerosis in the Adult Population: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, K.; Melliou, E.; Li, X.; Pedersen, T.L.; Wang, S.C.; Magiatis, P.; Newman, J.W.; Holt, R.R. Oleocanthal-Rich Extra Virgin Olive Oil Demonstrates Acute Anti-Platelet Effects in Healthy Men in a Randomized Trial. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 36, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-García, I.; Ortíz-Flores, R.; Badía, R.; García-Borrego, A.; García-Fernández, M.; Lara, E.; Martín-Montañez, E.; García-Serrano, S.; Valdés, S.; Gonzalo, M.; et al. Rich Oleocanthal and Oleacein Extra Virgin Olive Oil and Inflammatory and Antioxidant Status in People with Obesity and Prediabetes. The APRIL Study: A Randomised, Controlled Crossover Study. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 42, 1389–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepore, S.M.; Maggisano, V.; Bulotta, S.; Mignogna, C.; Arcidiacono, B.; Procopio, A.; Brunetti, A.; Russo, D.; Celano, M. Oleacein Prevents High Fat Diet-Induced Adiposity and Ameliorates Some Biochemical Parameters of Insulin Sensitivity in Mice. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, N. Olive Polyphenols in Cardiovascular Prevention: Efficacy and Tolerability of a Commercially Available Standardized Olive Extract (Tensiofytol®) as Compared to Placebo in Patients With Elevated Blood Pressure: A RDBPC Trial. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04874961 (accessed on 14 March 2024).
- Briz, M.R.M. Health Effects of Chronic Supplementation With a Natural Extract High in Hydroxytyrosol (Hytolive®) in Individuals at High Risk of Developing Age-Related Diseases. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06295913 (accessed on 14 March 2024).
- Ikonomidis, I. Effect of Olivomed (Olive Extract) on Endothelial, Cardiac and Vascular Function of Patients With Stable Coronary Artery Disease. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04520126 (accessed on 14 March 2024).
- Kaddoumi, A.; Denney, T.S.; Deshpande, G.; Robinson, J.L.; Beyers, R.J.; Redden, D.T.; Praticò, D.; Kyriakides, T.C.; Lu, B.; Kirby, A.N.; et al. Extra-Virgin Olive Oil Enhances the Blood-Brain Barrier Function in Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).