Vitamin Metabolism and Its Dependency on Genetic Variations Among Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review for Precision Nutrition Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Study Selection and Data Extraction
2.4. Risk of Bias Assessment
3. Results
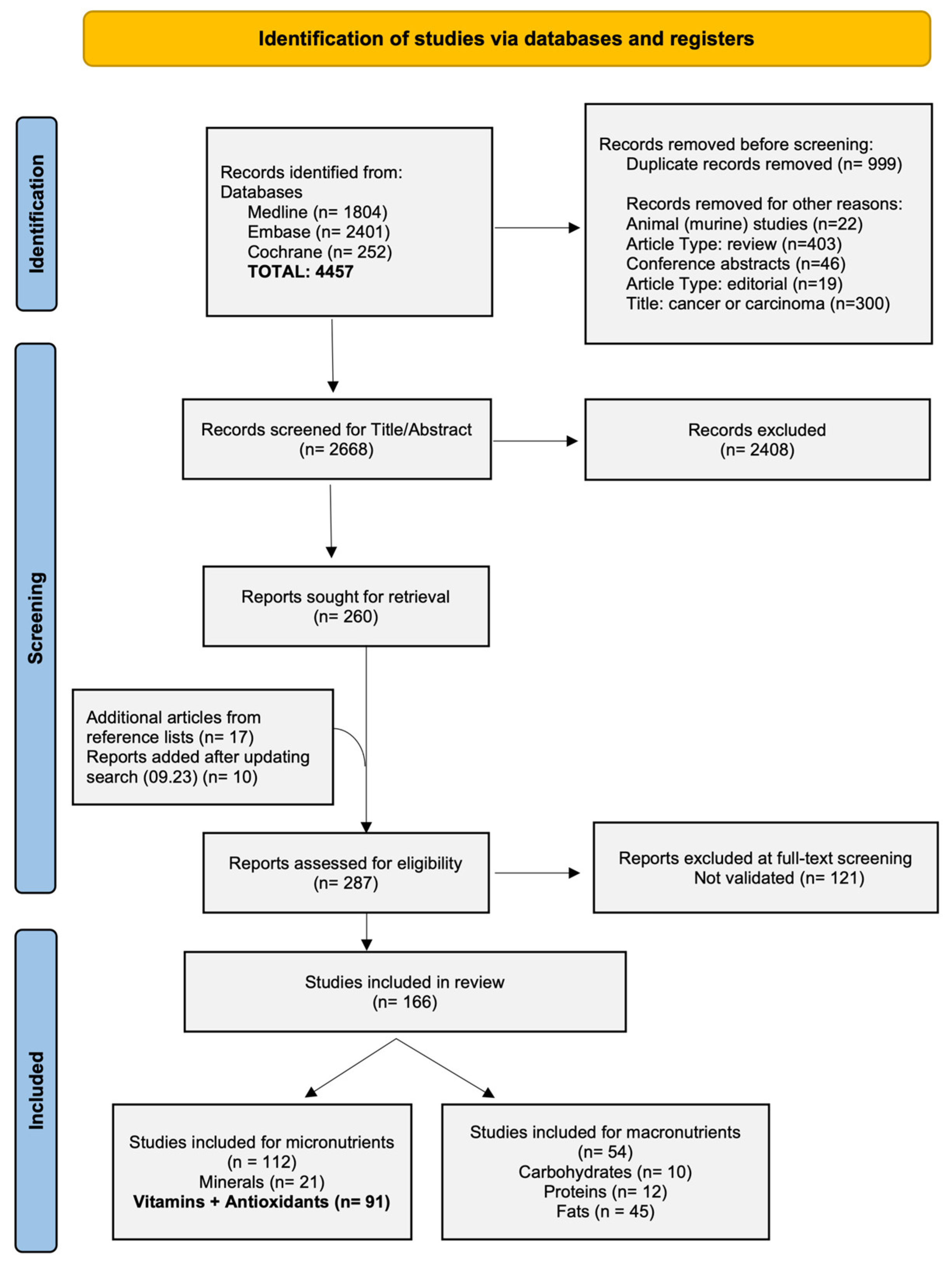
3.1. Study Selection and Characteristics
3.2. Assessment of Risk of Bias
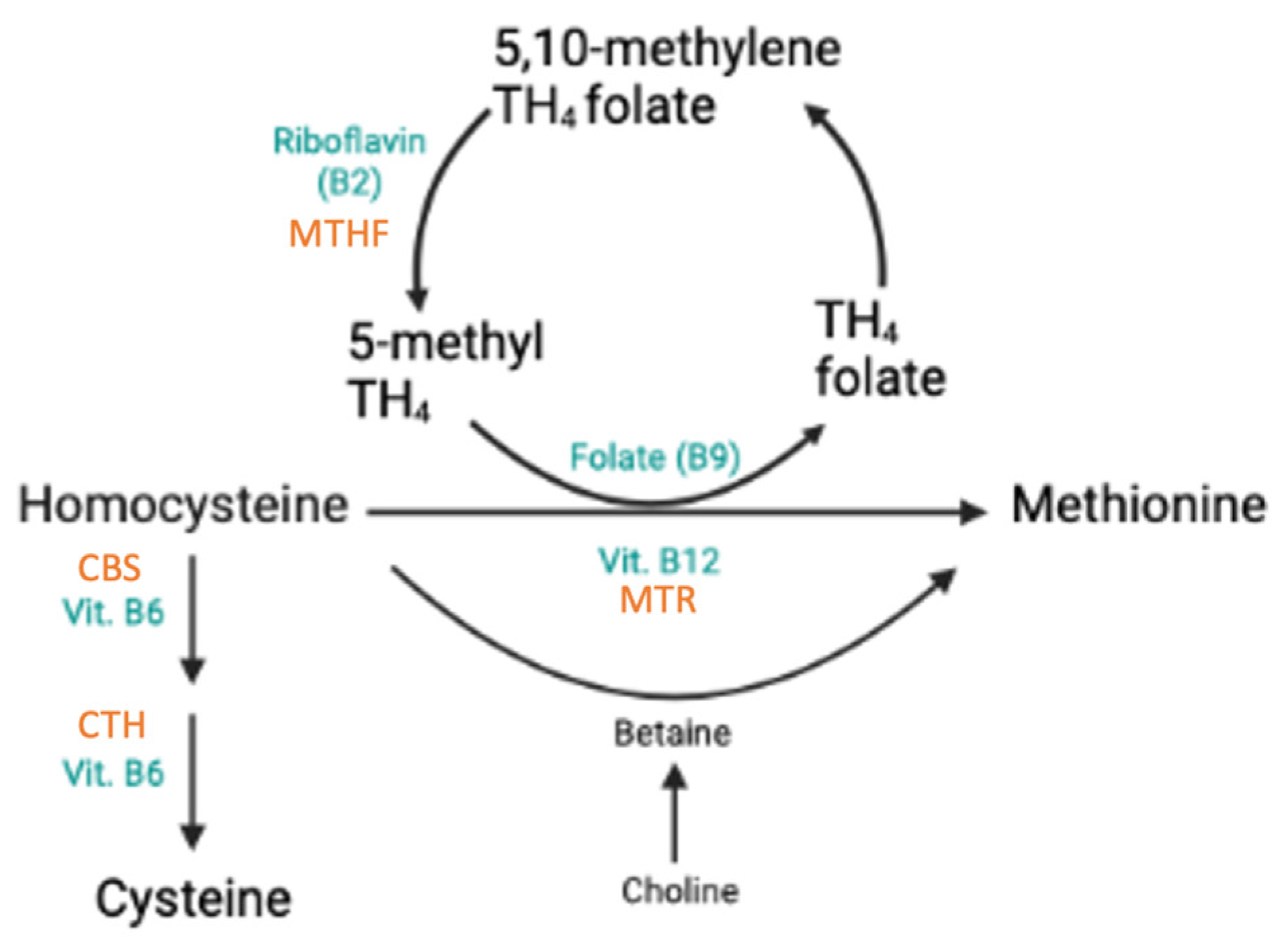
3.3. SNPs Associated with Homocysteine, Folate, and Vitamin B12
3.3.1. Effects of rs1801133 in MTHFR
3.3.2. Effects of rs1801131 in MTHFR
3.3.3. Effects of rs2274976 in MTHFR
3.3.4. Effects of rs1801394 in MTRR
3.3.5. Effects of rs1805087 (MTR), rs1051266 (RFC1), and 844ins68 (CBS)
3.3.6. Effects of rs1801198 in TCN2 and rs34530014 in TCN1
3.3.7. Effects of 19 bp Deletion in DHFR
3.4. SNPs Associated with Vitamin D
3.4.1. Polymorphisms in GC
3.4.2. Haplotypes in GC
3.4.3. Polymorphisms in CYP2R1
| SNP | Effect on 25(OH)D Compared to Wt | Sources | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rs10766197 | Negative | −4% to −10% | [46,53,54,60] |
| rs12794714 | Negative | −10% to −20% | [49,60,66,68,82] |
| rs11023374 | Negative | −10% to −20% | [62,88] |
| rs10500804 | Negative | −6% to −13% | [62,68,82] |
| rs2060793 | Positive | +4.5% to 15% | [62,71] |
| rs1562902 | Positive | +3 to 9% (per minor allele) | [53,60] |
| rs1993116 | Positive | +6 to 20% | [49,71] |
| rs731236 | Positive | +6% (per minor allele) | [53] |
| rs10741657 * | Positive | +5 to 53% | [48,49,53,54,56,60,68,70,77] |
| rs7116978 | Inconclusive | [53,90] | |
3.4.4. Polymorphisms in CYP24A1
3.4.5. Polymorphisms in VDR
3.4.6. Polymorphisms in NADSYN1/DHCR7
3.4.7. Other Polymorphisms
3.5. SNPs Associated with Antioxidants
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swiss Society of Nutrition (SSN). Swiss Food Pyramid; Federal Food Safety and Veterinary Office, Ed.; Swiss Society for Nutrition SSN: Bern, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bashiardes, S.; Godneva, A.; Elinav, E.; Segal, E. Towards Utilization of the Human Genome and Microbiome for Personalized Nutrition. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018, 51, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullins, V.A.; Bresette, W.; Johnstone, L.; Hallmark, B.; Chilton, F.H. Genomics in Personalized Nutrition: Can You “Eat for Your Genes”? Nutrients 2020, 12, 3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aruoma, O.I.; Hausman-Cohen, S.; Pizano, J.; Schmidt, M.A.; Minich, D.M.; Joffe, Y.; Brandhorst, S.; Evans, S.J.; Brady, D.M. Personalized Nutrition: Translating the Science of NutriGenomics Into Practice: Proceedings From the 2018 American College of Nutrition Meeting. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2019, 38, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirk, D.; Catal, C.; Tekinerdogan, B. Precision Nutrition: A Systematic Literature Review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 133, 104365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorland, W.A.N.; Saunders, W.B. Dorland’s Illustrated Medical Dictionary, 32nd ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. PRISMA 2020 Explanation and Elaboration: Updated Guidance and Exemplars for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourad, O.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan—A Web and Mobile App for Systematic Reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. Available online: https://www.rayyan.ai (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Bösch, E.S.; Spörri, J.; Scherr, J. Genetic Variants Affecting Iron Metabolism in Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review to Support Personalized Nutrition Strategies. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanislawska-Sachadyn, A.; Brown, K.S.; Mitchell, L.E.; Woodside, J.V.; Young, I.S.; Scott, J.M.; Murray, L.; Boreham, C.A.; McNulty, H.; Strain, J.J.; et al. An Insertion/Deletion Polymorphism of the Dihydrofolate Reductase (DHFR) Gene is Associated with Serum and Red Blood Cell Folate Concentrations in Women. Hum. Genet. 2008, 123, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solis, C.; Veenema, K.; Ivanov, A.A.; Tran, S.; Li, R.; Wang, W.; Moriarty, D.J.; Maletz, C.V.; Caudill, M.A. Folate Intake at RDA Levels is Inadequate for Mexican American Men with the Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase 677TT Genotype. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crider, K.S.; Zhu, J.-H.; Hao, L.; Yang, Q.-H.; Yang, T.P.; Gindler, J.; Maneval, D.R.; Quinlivan, E.P.; Li, Z.; Bailey, L.B.; et al. MTHFR 677C->T Genotype is Associated with Folate and Homocysteine Concentrations in a Large, Population-Based, Double-Blind Trial of Folic Acid Supplementation. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, T.; Xu, W.-J.; Xue, J.-L.; Cao, N.; Wang, X. Association Between the MTHFR C677T Polymorphism, Blood Folate and Vitamin B12 Deficiency, and Elevated Serum Total Homocysteine in Healthy Individuals in Yunnan Province, China. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2017, 80, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhou, S.; Xu, J.J.; Guo, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Gao, L.; Yuan, L. Gender-Specific Association of SLC19A1 and MTHFR Genetic Polymorphism with Oxidative Stress Biomarkers and Plasma Folate Levels in Older Adults. Exp. Gerontol. 2023, 178, 112208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.H.; Botto, L.D.; Gallagher, M.; Friedman, J.M.; Sanders, C.L.; Koontz, D.; Nikolova, S.; Erickson, J.D.; Steinberg, K. Prevalence and Effects of Gene-Gene and Gene-Nutrient Interactions on Serum Folate and Serum Total Homocysteine Concentrations in the United States: Findings from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey DNA Bank. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 88, 232–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caudill, M.A.; Dellschaft, N.; Solis, C.; Hinkis, S.; Ivanov, A.A.; Nash-Barboza, S.; Randall, K.E.; Jackson, B.; Solomita, G.N.; Vermeylen, F. Choline Intake, Plasma Riboflavin, and the Phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase G5465A Genotype Predict Plasma Homocysteine in Folate-Deplete Mexican-American Men with the Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase 677TT Genotype. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredriksen, A.; Meyer, K.; Ueland, P.M.; Vollset, S.E.; Grotmol, T.; Schneede, J. Large-Scale Population-Based Metabolic Phenotyping of Thirteen Genetic Polymorphisms Related to One-Carbon Metabolism. Hum. Mutat. 2007, 28, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuesen, B.H.; Husemoen, L.L.N.; Ovesen, L.; Jørgensen, T.; Fenger, M.; Linneberg, A. Lifestyle and Genetic Determinants of Folate and Vitamin B12 Levels in a General Adult Population. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 103, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, N.; Hamajima, N.; Wakai, K.; Suzuki, K. A Cross-Sectional Study to Find Out the Relationship of Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase (MTHFR) C677t Genotype with Plasma Levels of Folate and Total Homocysteine by Daily Folate Intake in Japanese. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2014, 60, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Al-Batayneh, K.M.; Al Zoubi, M.S.; Shehab, M.; Al-Trad, B.; Bodoor, K.; Al Khateeb, W.; Aljabali, A.A.A.; Al Hamad, M.; Eaton, G. Association Between MTHFR 677C>T Polymorphism and Vitamin B12 Deficiency: A Case-Control Study. J. Med. Biochem. 2018, 37, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zittan, E.; Preis, M.; Asmir, I.; Cassel, A.; Lindenfeld, N.; Alroy, S.; Halon, D.A.; Lewis, B.S.; Shiran, A.; Schliamser, J.E.; et al. High Frequency of Vitamin B12 Deficiency in Asymptomatic Individuals Homozygous to MTHFR C677T Mutation is Associated with Endothelial Dysfunction and Homocysteinemia. Am. J. Physiol.Heart Circ. Physiol. 2007, 293, H860–H865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupalika; Naorem, K.D.; Gupta, V.; Sachdeva, M.P.; Kumar, A.; Saraswathy, K.N. MTHFR C677T Polymorphism and Nutritional Deficiencies: A Study Among Bhil Tribe of India. Gene Rep. 2018, 13, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Tian, H.; Tian, D.; Zhang, C.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Ge, M.; Hou, Q.; Zhang, W. Genetic Polymorphisms of Key Enzymes in Folate Metabolism Affect the Efficacy of Folate Therapy in Patients with Hyperhomocysteinaemia. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 119, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, H.; Yamamoto, A.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Saito, Y.; Yamada, N.; Oikawa, S.; Mabuchi, H.; Teramoto, T.; Sasaki, J.; Nakaya, N.; et al. Polymorphisms of Apolipoprotein E and Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase in the Japanese Population. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2007, 14, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- du Plessis, J.P.; Melse-Boonstra, A.; Zandberg, L.; Nienaber-Rousseau, C. Gene Interactions Observed with the HDL-c Blood Lipid, Intakes of Protein, Sugar and Biotin in Relation to Circulating Homocysteine Concentrations in a Group of Black South Africans. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2020, 22, 100556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Garg, G.; Kumar, A.; Sundaramoorthy, E.; Sanapala, K.R.; Ghosh, S.; Karthikeyan, G.; Ramakrishnan, L.; Indian Genome Variation, C.; Sengupta, S. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Homocysteine Metabolism Pathway Genes: Association of CHDH A119C and MTHFR C677T with Hyperhomocysteinemia. Circulation. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2009, 2, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naushad, S.M.; Rama Devi, A.R.; Nivetha, S.; Lakshmitha, G.; Stanley, A.B.; Hussain, T.; Kutala, V.K. Neuro-Fuzzy Model of Homocysteine Metabolism. J. Genet. 2017, 96, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nienaber-Rousseau, C.; Ellis, S.M.; Moss, S.J.; Melse-Boonstra, A.; Towers, G.W. Gene-Environment and Gene-Gene Interactions of Specific MTHFR, MTR and CBS Gene Variants in Relation to Homocysteine in Black South Africans. Gene 2013, 530, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petr, M.; Steffl, M.; Kohlikova, E. Effect of the MTHFR 677C/T Polymorphism on Homocysteinemia in Response to Creatine Supplementation: A Case Study. Physiol. Res. 2013, 62, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukla, K.K.; Raman, R. Association of MTHFR and RFC1 Gene Polymorphism with Hyperhomocysteinemia and Its Modulation by Vitamin B12 and Folic Acid in an Indian Population. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 66, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Song, J.; Liu, K.; Fang, K.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Tang, X.; Wu, Y.; Qin, X.; et al. Associations Between Homocysteine Metabolism Related SNPs and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness: A Chinese Sib Pair Study. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2017, 43, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Sui, X.; Xu, N.; Yang, J.; Zhao, H.; Fei, X.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, Z.; Xin, Y.; Qin, B.; et al. The Relationship Between Plasma Homocysteine Levels and MTHFR Gene Variation, Age, and Sex in Northeast China. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2019, 22, 380–385. [Google Scholar]
- Waśkiewicz, A.; Piotrowski, W.; Broda, G.; Sobczyk-Kopcioł, A.; Płoski, R. Impact of MTHFR C677T Gene Polymorphism and Vitamins Intake on Homocysteine Concentration in the Polish Adult Population. Kardiol. Pol. 2011, 69, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar]
- Habib, S.S.; Al-Khlaiwi, T.; Almushawah, A.; Alsomali, A.; Habib, S.A. Homocysteine as a Predictor and Prognostic Marker of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 8598–8608. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lucock, M.; Yates, Z.; Boyd, L.; Naylor, C.; Choi, J.H.; Ng, X.; Skinner, V.; Wai, R.; Kho, J.; Tang, S.; et al. Vitamin C-Related Nutrient-Nutrient and Nutrient-Gene Interactions That Modify Folate Status. Eur. J. Nutr. 2012, 52, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanislawska-Sachadyn, A.; Woodside, J.V.; Sayers, C.M.; Yarnell, J.W.; Young, I.S.; Evans, A.E.; Mitchell, L.E.; Whitehead, A.S. The Transcobalamin (TCN2) 776C>G Polymorphism Affects Homocysteine Concentrations Among Subjects with Low Vitamin B(12) Status. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 1338–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Al-Batayneh, K.M.; Salim Al Zoubi, M.; Al-Trad, B.; Hussein, E.; Al Khateeb, W.; Aljabali, A.A.A.; Bodoor, K.; Shehab, M.; Al Hamad, M.A.; Eaton, G.J.; et al. Homologous G776G Variant of Transcobalamin-II Gene is Linked to Vitamin B12 Deficiency. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2020, 90, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrod, M.G.; Allen, L.H.; Haan, M.N.; Green, R.; Miller, J.W. Transcobalamin C776G Genotype Modifies the Association Between Vitamin B12 and Homocysteine in Older Hispanics. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCBI. Reference SNP (rs) Report: Rs34530014. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/snp/rs34530014 (accessed on 7 June 2023).
- Hu, Y.; Raffield, L.M.; Polfus, L.M.; Moscati, A.; Nadkarni, G.; Preuss, M.H.; Zhong, X.; Wei, Q.; Rich, S.S.; Li, Y.; et al. A Common TCN1 Loss-of-Function Variant is Associated with Lower Vitamin B12 Concentration in African Americans. Blood 2018, 131, 2859–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmbach, R.D.; Choumenkovitch, S.F.; Troen, A.P.; Jacques, P.F.; D’Agostino, R.; Selhub, J. A 19-Base Pair Deletion Polymorphism in Dihydrofolate Reductase is Associated with Increased Unmetabolized Folic Acid in Plasma and Decreased Red Blood Cell Folate. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 2323–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steluti, J.; Reginaldo, C.; Selhub, J.; Paul, L.; Fisberg, R.M.; Marchioni, D.M. Presence of Circulating Folic Acid in Plasma and Its Relation with Dietary Intake, Vitamin B Complex Concentrations and Genetic Variants. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 58, 3069–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinotte, M.; Diorio, C.; Bérubé, S.; Pollak, M.; Brisson, J. Genetic Polymorphisms of the Vitamin D Binding Protein and Plasma Concentrations of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D in Premenopausal Women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Sun, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, W.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Q.; Ning, Z.; Pei, Y.; et al. Association of Genetic Variants of Vit D Binding Protein (DBP/GC) and of the Enzyme Catalyzing Its 25-Hydroxylation (DCYP2R1) and Serum Vit D in Postmenopausal Women. Hormones 2014, 13, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalowka, M.; Glowka, A.K.; Karazniewicz-Lada, M.; Kosewski, G. Clinical Significance of Analysis of Vitamin D Status in Various Diseases. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; He, J.W.; Fu, W.Z.; Zhang, C.Q.; Zhang, Z.L. An Analysis of the Association Between the Vitamin D Pathway and Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D levels in a Healthy Chinese Population. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2013, 28, 1784–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, B.R.; Costa, N.C.; Silva, T.R.; Oppermann, K.; Magalhães, J.A.; Casanova, G.; Mara Spritzer, P. Prevalence of Vitamin D deficiency in Women from Southern Brazil and Association with Vitamin D-Binding Protein Levels and GC-DBP Gene Polymorphisms. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallinen, R.J.; Dethlefsen, O.; Ruotsalainen, S.; Mills, R.D.; Miettinen, T.A.; Jääskeläinen, T.E.; Lundqvist, A.; Kyllönen, E.; Kröger, H.; Karppinen, J.I.; et al. Genetic Risk Score for Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentration Helps to Guide Personalized Vitamin D Supplementation in Healthy Finnish Adults. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robien, K.; Butler, L.M.; Wang, R.; Beckman, K.B.; Walek, D.; Koh, W.P.; Yuan, J.M. Genetic and Environmental Predictors of Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentrations Among Middle-Aged and Elderly Chinese in Singapore. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 109, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Paredez, B.; Hidalgo-Bravo, A.; de la Cruz-Montoya, A.; Martínez-Aguilar, M.M.; Ramírez-Salazar, E.G.; Flores, M.; Quezada-Sánchez, A.D.; Ramírez-Palacios, P.; Cid, M.; Martínez-Hernández, A.; et al. Association Between Vitamin D Deficiency and Common Variants of Vitamin D Binding Protein Gene Among Mexican Mestizo and Indigenous Postmenopausal Women. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2020, 43, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, L.; Felix, J.F.; Breitling, L.P.; Haug, U.; Raum, E.; Burwinkel, B.; Schottker, B.; Brenner, H. Genetic Variations in the Vitamin D Binding Protein and Season-Specific Levels of Vitamin D Among Older Adults. Epidemiology 2013, 24, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pooyan, S.; Rahimi, M.H.; Mollahosseini, M.; Khorrami-Nezhad, L.; Maghbooli, Z.; Mirzaei, K. The Association Between Vitamin D Deficiency and Variants of Vitamin D Binding Protein Gene Among Healthy Iranian Adults. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2020, 90, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, J.; Rasmussen, L.B.; Ravn-Haren, G.; Andersen, E.W.; Hansen, B.; Andersen, R.; Mejborn, H.; Madsen, K.H.; Vogel, U. Common Variants in CYP2R1 and GC Genes Predict Vitamin D Concentrations in Healthy Danish Children and Adults. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, J.; Vogel, U.; Ravn-Haren, G.; Andersen, E.W.; Nexø, B.A.; Andersen, R.; Mejborn, H.; Madsen, K.H.; Rasmussen, L.B. Real-Life Use of Vitamin D3-Fortified Bread and Milk During a Winter Season: The Effects of CYP2R1 and GC Genes on 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentrations in Danish Families, the VitmaD Study. Genes Nutr. 2014, 9, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.H.; Yin, X.Y.; Wu, X.H.; Zhang, L.; Pan, S.Y.; Zheng, Z.J.; Wang, J.G. Serum 25(OH)D and Vitamin D Status in Relation to VDR, GC and CYP2R1 Variants in Chinese. Endocr. J. 2014, 61, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafi, Z.M.; Irshaid, Y.M.; El-Khateeb, M.; Ajlouni, K.M.; Hyassat, D. Association of rs7041 and rs4588 Polymorphisms of the Vitamin D Binding Protein and the rs10741657 Polymorphism of CYP2R1 with Vitamin D Status Among Jordanian Patients. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2015, 19, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssens, W.; Bouillon, R.; Claes, B.; Carremans, C.; Lehouck, A.; Buysschaert, I.; Coolen, J.; Mathieu, C.; Decramer, M.; Lambrechts, D. Vitamin D Deficiency is Highly Prevalent in COPD and Correlates with Variants in the Vitamin D-Binding Gene. Thorax 2010, 65, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffney-Stomberg, E.; Lutz, L.J.; Shcherbina, A.; Ricke, D.O.; Petrovick, M.; Cropper, T.L.; Cable, S.J.; McClung, J.P. Association Between Single Gene Polymorphisms and Bone Biomarkers and Response to Calcium and Vitamin D Supplementation in Young Adults Undergoing Military Training. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2017, 32, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelman, C.D.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Langefeld, C.D.; Hicks, P.J.; Rich, S.S.; Wagenknecht, L.E.; Bowden, D.W.; Norris, J.M. Genetic and Environmental Determinants of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D Levels in Hispanic and African Americans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 3381–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, E.L.; Rees, J.R.; Peacock, J.L.; Mott, L.A.; Amos, C.I.; Bostick, R.M.; Figueiredo, J.C.; Ahnen, D.J.; Bresalier, R.S.; Burke, C.A.; et al. Genetic Variants in CYP2R1, CYP24A1, and VDR Modify the Efficacy of Vitamin D3 Supplementation for Increasing Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Levels in a Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E2133–E2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozdzik, A.; Zhu, J.; Wong, B.Y.; Fu, L.; Cole, D.E.; Parra, E.J. Association of Vitamin D Binding Protein (VDBP) Polymorphisms and Serum 25(OH)D Concentrations in a Sample of Young Canadian Adults of Different Ancestry. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 127, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelman, C.D.; Meyers, K.J.; Iyengar, S.K.; Liu, Z.; Karki, C.K.; Igo, R.P., Jr.; Truitt, B.; Robinson, J.; Sarto, G.E.; Wallace, R.; et al. Vitamin D Intake and Season Modify the Effects of the GC and CYP2R1 Genes on 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentrations. J. Nutr. 2012, 143, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szili, B.; Szabo, B.; Horvath, P.; Bakos, B.; Kirschner, G.; Kosa, J.P.; Toldy, E.; Putz, Z.; Lakatos, P.; Tabak, A.; et al. Impact of Genetic Influence on Serum Total- and Free 25-Hydroxyvitamin-D in Humans. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 183, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshkibaf, M.H.; Mousazadeh, S.; Maleknia, M.; Takhshid, M.A. Association of Vitamin D Deficiency with Vitamin D Binding Protein (DBP) and CYP2R1 Polymorphisms in Iranian Population. Meta Gene 2021, 27, 100824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Sheng, H.; Li, H.; Gan, W.; Liu, C.; Zhu, J.; Loos, R.J.; Lin, X. Associations Between Common Variants in GC and DHCR7/NADSYN1 and Vitamin D Concentration in Chinese Hans. Hum. Genet. 2011, 131, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, F.X.; Armas, L.; Lappe, J.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, G.; Wang, H.W.; Recker, R.; Zhao, L.J. Comprehensive Association Analysis of Nine Candidate Genes with Serum 25-Hydroxy Vitamin D Levels Among Healthy Caucasian Subjects. Hum. Genet. 2010, 128, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Paredez, B.; Macías, N.; Martínez-Aguilar, M.M.; Hidalgo-Bravo, A.; Flores, M.; Quezada-Sánchez, A.D.; Denova-Gutiérrez, E.; Cid, M.; Martínez-Hernández, A.; Orozco, L.; et al. Association Between Vitamin D Deficiency and Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in the Vitamin D Receptor and GC Genes and Analysis of Their Distribution in Mexican Postmenopausal Women. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkum, N.; Alkayal, F.; Noronha, F.; Ali, M.M.; Melhem, M.; Al-Arouj, M.; Bennakhi, A.; Behbehani, K.; Alsmadi, O.; Abubaker, J. Vitamin D Insufficiency in Arabs and South Asians Positively Associates with Polymorphisms in GC and CYP2R1 Genes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batai, K.; Murphy, A.B.; Shah, E.; Ruden, M.; Newsome, J.; Agate, S.; Dixon, M.A.; Chen, H.Y.; Deane, L.A.; Hollowell, C.M.; et al. Common Vitamin D Pathway Gene Variants Reveal Contrasting Effects on Serum Vitamin D Levels in African Americans and European Americans. Hum. Genet. 2014, 133, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.J.; Zhang, F.; Richards, J.B.; Kestenbaum, B.; Van Meurs, J.B.; Berry, D.; Kiel, D.P.; Streeten, E.A.; Ohlsson, C.; Koller, D.L.; et al. Common Genetic Determinants of Vitamin D insufficiency: A Genome-Wide Association Study. Lancet 2010, 376, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Yu, K.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.; Simon, K.C.; McCullough, M.L.; Gallicchio, L.; Jacobs, E.J.; Ascherio, A.; Helzlsouer, K.; Jacobs, K.B.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study of Circulating Vitamin D Levels. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 2739–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slow, S.; Pearson, J.P.; Florkowski, C.M.; Elder, P.A.; Lewis, J.G.; Kennedy, M.A.; Murdoch, D.R. Effect of Genetic Factors on the Response to Vitamin D3 Supplementation in the VIDARIS Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrition 2020, 75, 110761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.Y.; Yongjoo Park, C.; Jo, G.; Yoen Kim, O.; Shin, M.J. Association Among Genetic Variants in the Vitamin D Pathway and Circulating 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Levels in Korean Adults: Results from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011–2012. Endocr. J. 2018, 65, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, P.W.; Böhringer, S.; Houwink, E.J.F.; Lin, W.; Numans, M.E.; Lips, P.; Middelkoop, B.J.C. Common Genetic Variant of GC Associated with Vitamin D Deficiency in a Chinese Population in the Netherlands. medRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, M.; Tran, B.; Armstrong, B.K.; Baxter, C.; Ebeling, P.R.; English, D.R.; Gebski, V.; Hill, C.; Kimlin, M.G.; Lucas, R.M.; et al. Environmental, Personal, and Genetic Determinants of Response to Vitamin D Supplementation in Older Adults. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E1332–E1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, C.L.; Lau, K.S.; Sham, P.C.; Tan, K.C.; Kung, A.W. Genetic Variant in Vitamin D Binding Protein is Associated with Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and Vitamin D Insufficiency in Southern Chinese. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 58, 749–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didriksen, A.; Grimnes, G.; Hutchinson, M.S.; Kjaergaard, M.; Svartberg, J.; Joakimsen, R.M.; Jorde, R. The Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Response to Vitamin D Supplementation is Related to Genetic Factors, BMI, and Baseline Levels. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 169, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trummer, O.; Schwetz, V.; Walter-Finell, D.; Lerchbaum, E.; Renner, W.; Gugatschka, M.; Dobnig, H.; Pieber, T.R.; Obermayer-Pietsch, B. Allelic Determinants of Vitamin D Insufficiency, Bone Mineral Density, and Bone Fractures. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, E1234–E1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, N.A.; Rager, M.L.; Havrda, D.E.; Harralson, A.F. Genetic Variation in CYP2R1 and GC Genes Associated with Vitamin D Deficiency Status. J. Pharm. Pract. 2017, 30, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, K.C.; Munger, K.L.; Kraft, P.; Hunter, D.J.; De Jager, P.L.; Ascherio, A. Genetic Predictors of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Levels and Risk of Multiple Sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2011, 258, 1676–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongthai, P.; Chailurkit, L.O.; Chanprasertyothin, S.; Nimitphong, H.; Sritara, P.; Aekplakorn, W.; Ongphiphadhanakul, B. Vitamin D Binding Protein Gene Polymorphism as a Risk Factor for Vitamin D Deficiency in Thais. Endocr. Pract. 2015, 21, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Woo, H.W.; Kim, J.; Shin, M.H.; Koh, I.; Choi, B.Y.; Kim, M.K. Independent and Interactive Associations of Season, Dietary Vitamin D, and vitaMin D-Related Genetic Variants with Serum 25(OH)D in Korean Adults Aged 40 Years or Older. Endocr. J. 2021, 68, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.G.; Tang, W.; Hootman, K.C.; Brannon, P.M.; Houston, D.K.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Harris, T.B.; Garcia, M.; Lohman, K.; Liu, Y.; et al. Genetic and Environmental Factors are Associated with Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentrations in Older African Americans. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larcombe, L.; Mookherjee, N.; Slater, J.; Slivinski, C.; Singer, M.; Whaley, C.; Denechezhe, L.; Matyas, S.; Turner-Brannen, E.; Nickerson, P.; et al. Vitamin D in a Northern Canadian First Nation Population: Dietary Intake, Serum Concentrations and Functional Gene Polymorphisms. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parlato, L.A.; Welch, R.; Ong, I.M.; Long, J.; Cai, Q.; Steinwandel, M.D.; Blot, W.J.; Zheng, W.; Warren Andersen, S. Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) of Circulating Vitamin D Outcomes Among Individuals of African Ancestry. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 117, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, M.J.; Wu, Z.; Snell, R.; Sluyter, J.; Khaw, K.-T.; Waayer, D.; Camargo, C.A.J.; Scragg, R. Genetic Control of Serum 25(OH)D Levels and Its Association with Ethnicity. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2022, 222, 106149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammar, M.; Heni, S.; Tira, M.S.; Khalij, Y.; Hamdouni, H.; Amor, D.; Ksibi, S.; Omezzine, A.; Bouslama, A. Variability in Response to Vitamin D Supplementation According to Vitamin D Metabolism Related Gene Polymorphisms in Healthy Adults. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 77, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fohner, A.E.; Wang, Z.; Yracheta, J.; O’Brien, D.M.; Hopkins, S.E.; Black, J.; Philip, J.; Wiener, H.W.; Tiwari, H.K.; Stapleton, P.L.; et al. Genetics, Diet, and Season Are Associated with Serum 25-Hydroxycholecalciferol Concentration in a Yup’ik Study Population from Southwestern Alaska. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Mao, J.; Zhang, M.; Liu, H.; Li, H.; Lei, H.; Han, L.; Gao, M. Vitamin D Deficiency in Uygurs and Kazaks is Associated with Polymorphisms in CYP2R1 and DHCR7/NADSYN1 Genes. Med. Sci. Monit. 2015, 21, 1960–1968. [Google Scholar]
- Tomei, S.; Singh, P.; Mathew, R.; Mattei, V.; Garand, M.; Alwakeel, M.; Sharif, E.; Al Khodor, S. The Role of Polymorphisms in Vitamin D-Related Genes in Response to Vitamin D Supplementation. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandemiş, E.; Tuncel, G.; Fahrioğlu, U.; Temel, Ş.; Mocan, G.; Ergören, M.Ç. Natural Selection at Work? Vitamin D Deficiency Rates and Rising Health Problems in Young Turkish Cypriot Professionals. Cent. Eur. J. Public Health 2021, 29, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncel, G.; Temel, S.G.; Ergoren, M.C. Strong Association Between VDR FokI (rs2228570) Gene Variant and Serum Vitamin D Levels in Turkish Cypriots. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 3349–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retamoso, V.R.; Barbisan, F.; Moro, G.M.; Maurer, P.; Rubio, D.V.; Dos Santos, L.F.V.; Feijoo, L.B.; Frizzo, M.N.; Manica da Cruz, I.B.; Manfredini, V.; et al. VDR, SOD-2, and CYP24A1 Gene Expression in Different Genotypes of BsmI SNP of the Vitamin D Receptor Gene in Individuals with Hypovitaminosis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.H.; AlKhafaji, R.S.; Al-Saadi, A.H. Association between Vitamin D Deficiency and Vitamin D Receptor Gene Polymorphism (FokI-rs2228570) Among Men with Anemia in Babylon Province, Iraq. Arch. Razi Inst. 2022, 77, 1693–1698. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.Y.; Li, R.Y.; Fu, L.J.; Adu-Gyamfi, E.A.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, L.T.; Zhang, T.F.; Bao, H.Q.; Xu, X.O.; et al. SNP rs12794714 of CYP2R1 is Associated with Serum Vitamin D Levels and Recurrent Spontaneous Abortion (RSA): A Case-Control Study. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2021, 304, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelman, C.D.; Meyers, K.J.; Ziegler, J.T.; Taylor, K.D.; Palmer, N.D.; Haffner, S.M.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Wagenknecht, L.E.; Rotter, J.I.; Bowden, D.W.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study of Vitamin D Concentrations in Hispanic Americans: The IRAS Family Study. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 122, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabuta, S.; Urata, M.; Kun, R.Y.W.; Masaki, M.; Shidoji, Y. Common SNP rs6564851 in the BCO1 Gene Affects the Circulating Levels of β-Carotene and the Daily Intake of Carotenoids in Healthy Japanese Women. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrucci, L.; Perry, J.R.; Matteini, A.; Perola, M.; Tanaka, T.; Silander, K.; Rice, N.; Melzer, D.; Murray, A.; Cluett, C.; et al. Common Variation in the Beta-Carotene 15,15′-Monooxygenase 1 Gene Affects Circulating Levels of Carotenoids: A Genome-Wide Association Study. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 84, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batai, K.; Trejo, M.J.; Chen, Y.; Kohler, L.N.; Lance, P.; Ellis, N.A.; Cornelis, M.C.; Chow, H.S.; Hsu, C.H.; Jacobs, E.T. Genome-Wide Association Study of Response to Selenium Supplementation and Circulating Selenium Concentrations in Adults of European Descent. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combs, G.F., Jr.; Watts, J.C.; Jackson, M.I.; Johnson, L.K.; Zeng, H.; Scheett, A.J.; Uthus, E.O.; Schomburg, L.; Hoeg, A.; Hoefig, C.S.; et al. Determinants of Selenium Status in Healthy Adults. Nutr. J. 2011, 10, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, T.I.; Outzen, M.; Olsen, A.; Vogel, U.; Ravn-Haren, G. Genetic Polymorphism in Selenoprotein P Modifies the Response to Selenium-Rich Foods on Blood Levels of Selenium and Selenoprotein P in a Randomized Dietary Intervention Study in Danes. Genes Nutr. 2018, 13, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méplan, C.; Crosley, L.K.; Nicol, F.; Beckett, G.J.; Howie, A.F.; Hill, K.E.; Horgan, G.; Mathers, J.C.; Arthur, J.R.; Hesketh, J.E. Genetic Polymorphisms in the Human Selenoprotein P Gene Determine the Response of Selenoprotein Markers to Selenium Supplementation in a Gender-Specific Manner (the SELGEN Study). FASEB J. 2007, 21, 3063–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Batlle, J.; Matejcic, M.; Chajes, V.; Moreno-Macias, H.; Amadou, A.; Slimani, N.; Cox, D.G.; Clavel-Chapelon, F.; Fagherazzi, G.; Romieu, I. Determinants of Folate and Vitamin B12 Plasma Levels in the French E3N-EPIC Cohort. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michels, A.J.; Hagen, T.M.; Frei, B. Human genetic variation influences vitamin C homeostasis by altering vitamin C transport and antioxidant enzyme function. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2013, 33, 45–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niforou, A.; Konstantinidou, V.; Naska, A. Genetic Variants Shaping Inter-individual Differences in Response to Dietary Intakes-A Narrative Review of the Case of Vitamins. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 558598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Haplotype | Effect on Hcy | |
|---|---|---|
| rs1801133 x rs1801131 | ||
| T | A * | ↑ 72–84% odds of high Hcy |
| C * | A/C | ↓ 44–69% odds of high Hcy |
| TT | CC | Never observed |
| rs1801133 x rs1801394 | ||
| TT | GG | ↓ 25.6% compared to TT + AA * |
| rs1801133 x T833/844ins68 | ||
| TT | CC | ↓ 50% compared to TT + TT * |
| TT | TC | ↓ 39% compared to TT + TT * |
| rs1801133 x rs7946 | ||
| TT | GA | ↓ 41% compared to TT + AA * |
| TT | GG | ↓ 47% compared to TT + AA * |
| rs1801133 x rs9001 | ||
| CC * | CC | ↓ 50% compared to TT + AA * |
| SNP | Effect on 25(OH)D Compared to Wt | Sources | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rs4588 | Negative | −12% to −27% | [43,46,48,49,51,53,54,56,57,60,61] |
| rs7041 | Negative | −9% to −27% | [43,47,49,56,57,60,62,63,68,77,82,83] |
| rs17467825 | Negative | −13.8% to −28.5% | [53,68] |
| rs3755967 | Negative | −17.7% to −27% | [68] |
| rs2298850 | Negative | −16.1% to −28.5% | [68] |
| rs2282679 | Negative | −13% to −34% | [46,47,51,53,68,70,71,75,78,80,81] |
| rs1155563 | Negative | −16% to −28% | [51,60,68] |
| rs222020 | Positive | +3.21% to 8.42% (per minor allele) | [60,66] |
| rs2298849 | Positive | +3.4% to + 13% (per minor allele) | [49,66] |
| rs12512631 | Inconclusive | [53,60,67] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bösch, E.S.; Spörri, J.; Scherr, J. Vitamin Metabolism and Its Dependency on Genetic Variations Among Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review for Precision Nutrition Strategies. Nutrients 2025, 17, 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17020242
Bösch ES, Spörri J, Scherr J. Vitamin Metabolism and Its Dependency on Genetic Variations Among Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review for Precision Nutrition Strategies. Nutrients. 2025; 17(2):242. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17020242
Chicago/Turabian StyleBösch, Elana Sophie, Jörg Spörri, and Johannes Scherr. 2025. "Vitamin Metabolism and Its Dependency on Genetic Variations Among Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review for Precision Nutrition Strategies" Nutrients 17, no. 2: 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17020242
APA StyleBösch, E. S., Spörri, J., & Scherr, J. (2025). Vitamin Metabolism and Its Dependency on Genetic Variations Among Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review for Precision Nutrition Strategies. Nutrients, 17(2), 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17020242








