A Guinea Pig Model of Pediatric Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis: Poor Vitamin C Status May Advance Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
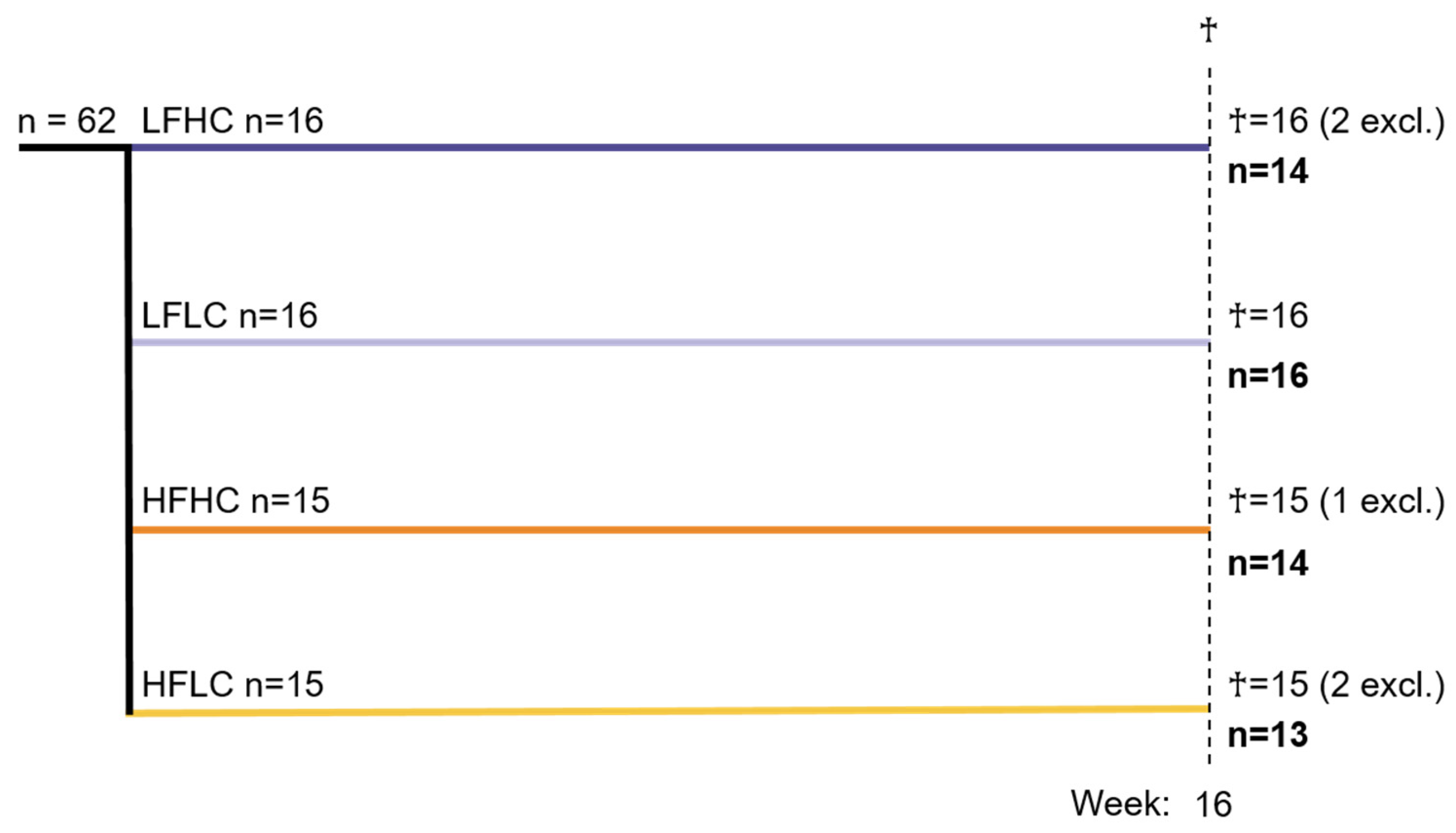
2.1. Animal Experiments
2.2. Excluded Animals
2.3. Plasma Samples
2.4. Liver Samples
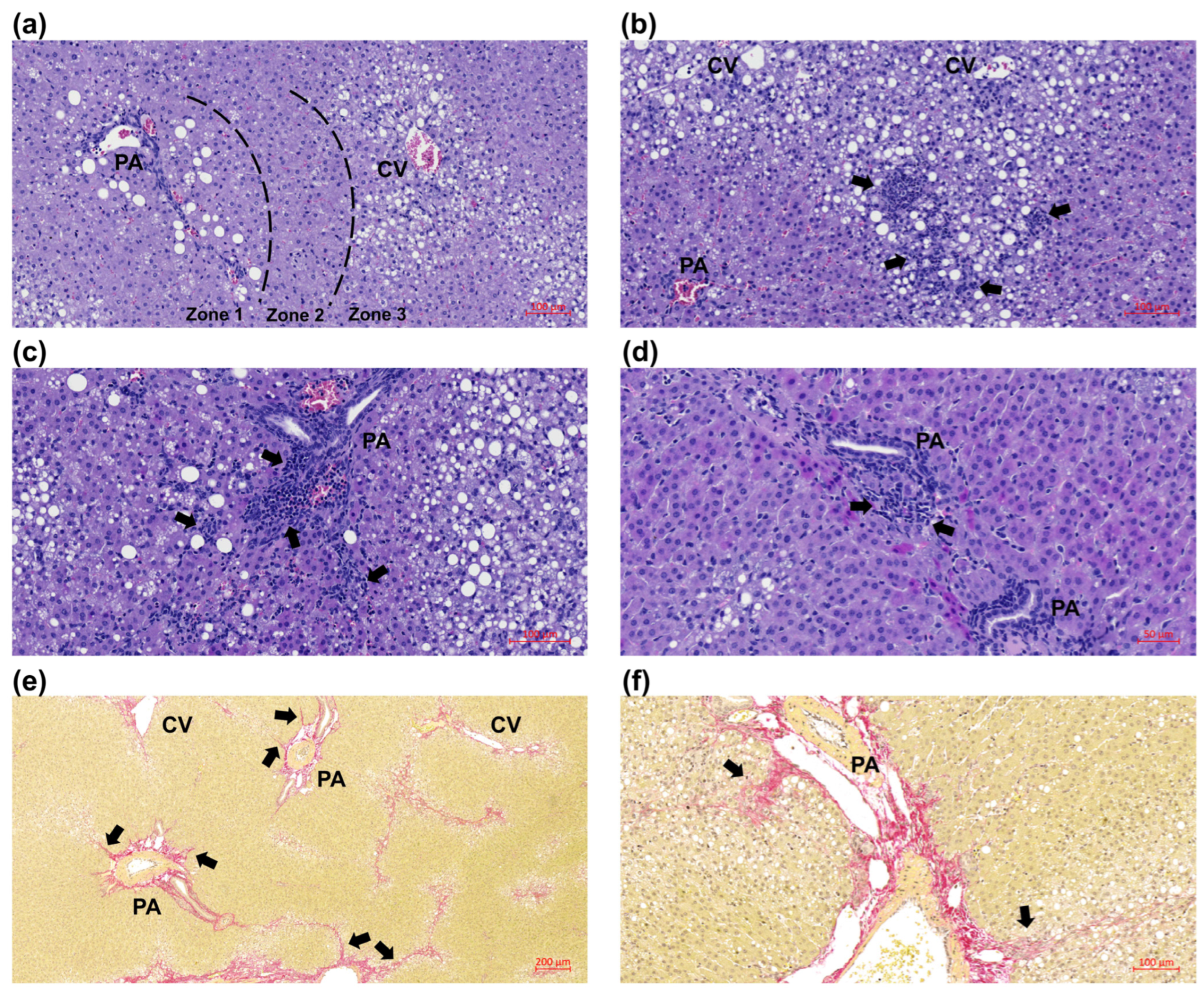
2.5. Histology
2.6. Gene Expression
| Gene | Accession No. | Forward | Reverse | Product (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNF (TNFα) [51] | NM_001173025.1 | GCCGTCTCCTACCCGGAAAA | TAGATCTGCCCGGAATCGGC | 203 |
| NLRP3 | XM_003479423.4 | AAGTGGGGACCCATAAGGAC | GTAGCCAGCCAGCTTACACC | 108 |
| CXCL8 (IL8) | NM_001173399.2 | GGCAGCCTTCCTGCTCTCT | CAGCTCCGAGACCAACTTTGT | 67 |
| IL18 | AB025722.1 | CTCCGACTGTGCAGACAATG | TACACCTCTCGCGTTGCTAT | 76 |
| CCL2 (MCP1) [48] | NM_001172926.1 | TGCCAAACTGGACCAGAGAA | CGAATGTTCAAAGGCTTTGAAGT | 75 |
| SOD1 [49] | U39844 | TGTCCATGAGTTTGGCGATA | ATTTGCTCCGGAGAGTGAGA | 193 |
| TET1 | XM_013156854.2 | CAGTCAACGGCAACCTGAAA | ACCACTGTAATTCCGCCTGA | 235 |
| TET2 | XM_003468037.3 | AACTTCTGCGACTTCCAGGA | GGGTAAGAGCTGACTGGGTT | 205 |
| TET3 | XM_013151565.2 | GTGATGCCTCTTGTCCTCCT | GAGAGGCAAGAAGAGGGGTT | 239 |
| ACTB (β-ACTIN) [49] | AF508792 | GTAAGGACCTCTATGCCAACACA | ATGCCAATCTCATCTCGTTTTCT | 346 |
| DCTN5 [50] | XM_003477819.4 | TTGACGGGATTCTGAGGTGC | CACAACACTGACTGGCGACT | 122 |
2.7. Global Methylation and Hydroxymethylation Levels
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
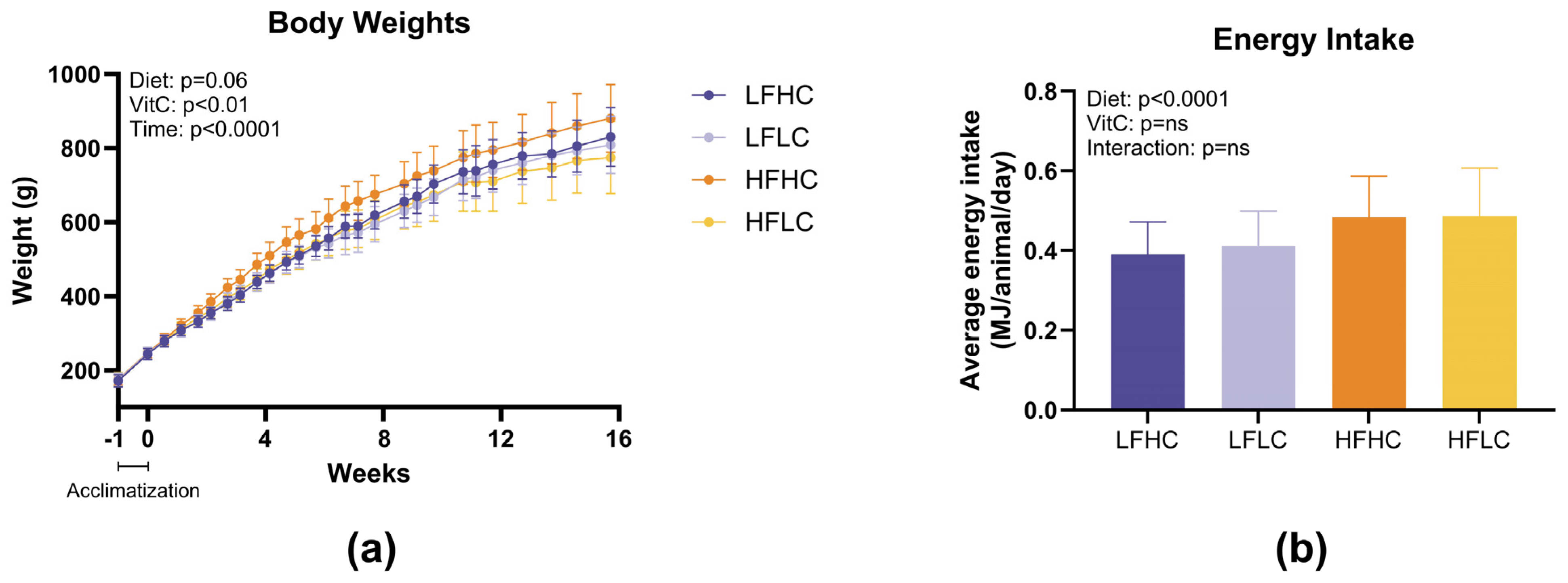
3.1. Body Weights and Energy Intake
3.2. Plasma and Liver Biochemistry
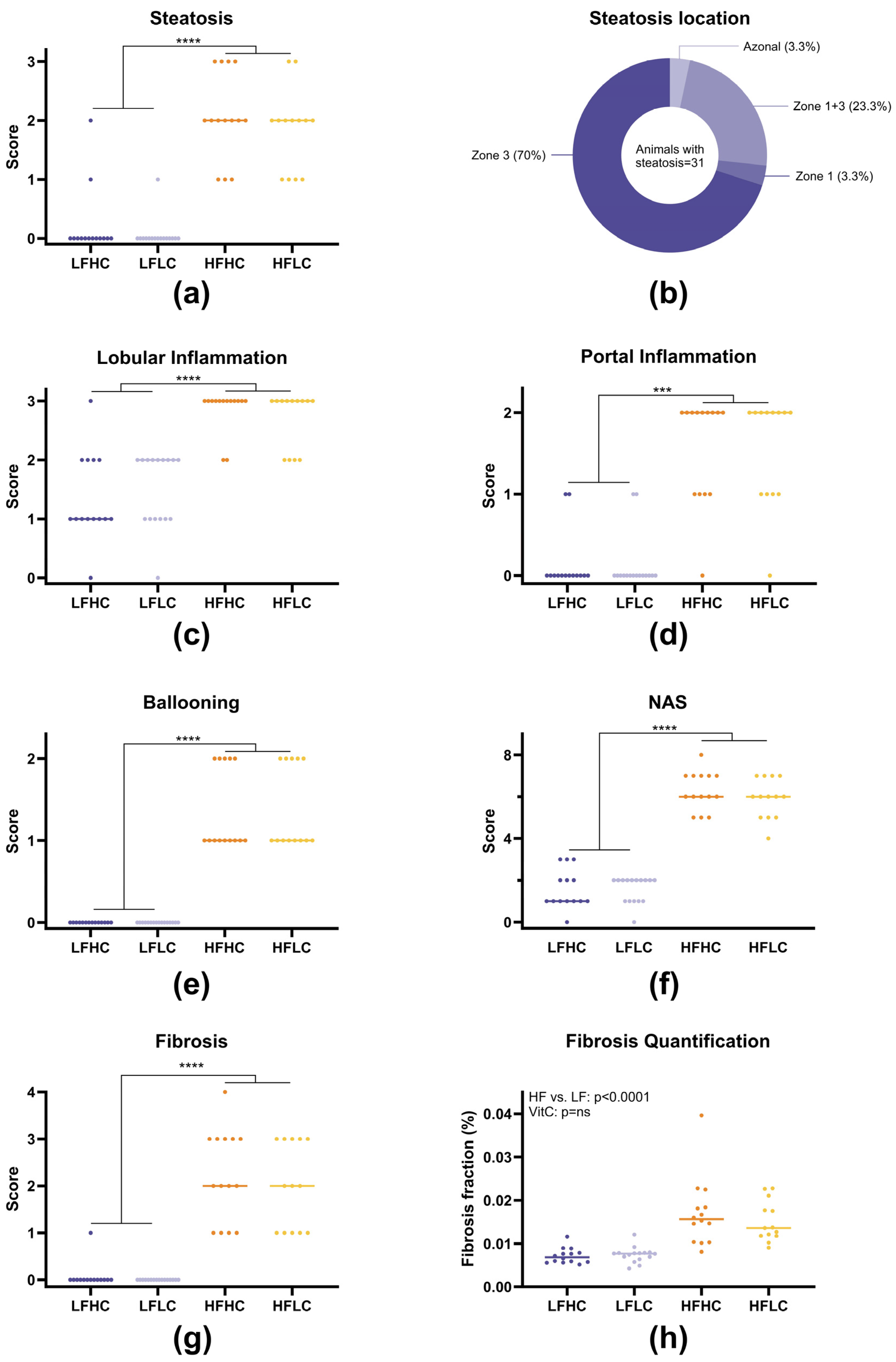
3.3. Juvenile Histopathology
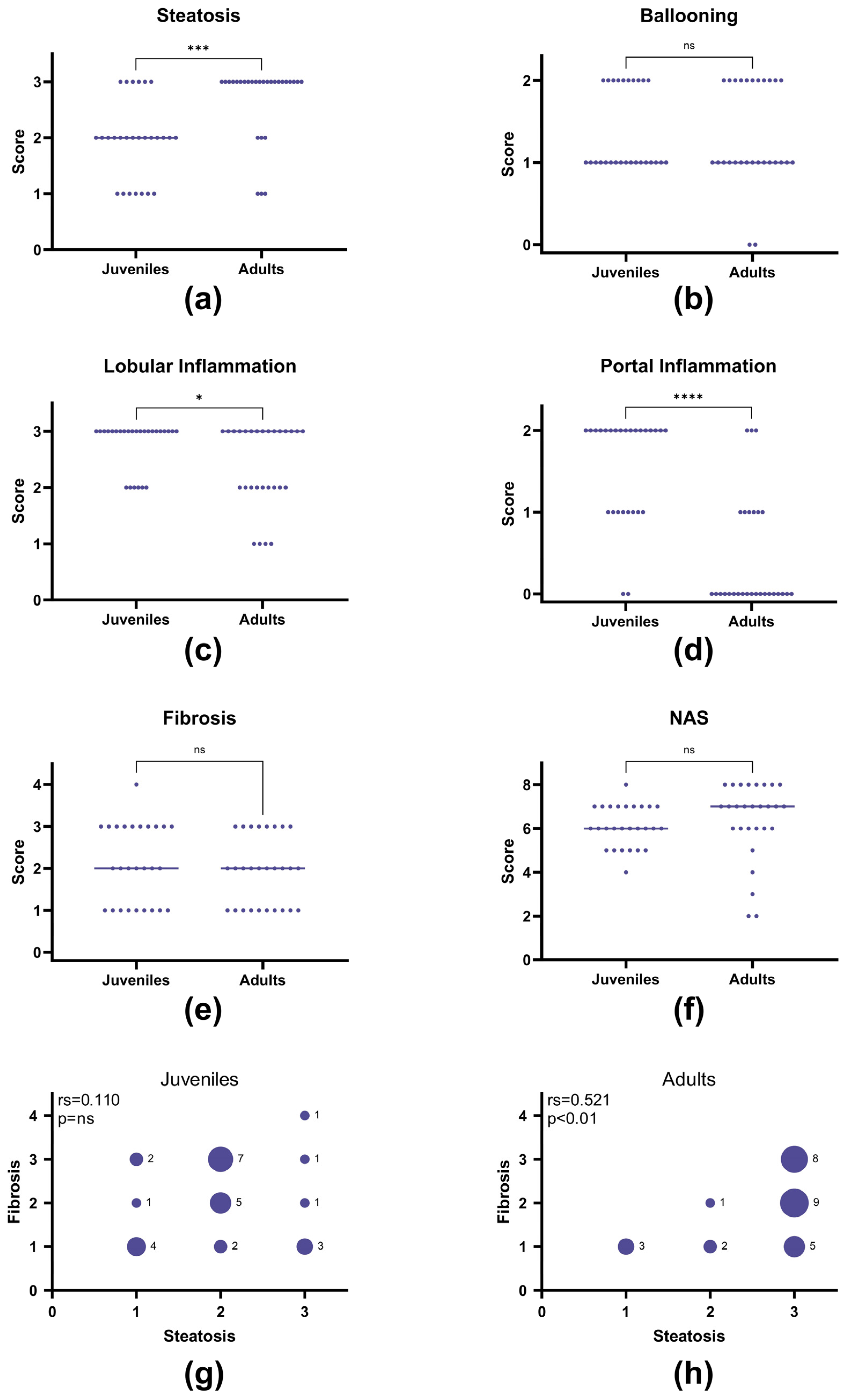
3.4. Juvenile Compared to Adult Histopathology
3.5. Gene Expression and Epigenetic Modifications
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schwimmer, J.B.; Deutsch, R.; Kahen, T.; Lavine, J.E.; Stanley, C.; Behling, C. Prevalence of Fatty Liver in Children and Adolescents. Pediatrics 2006, 118, 1388–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, E.L.; Howe, L.D.; Jones, H.E.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Lawlor, D.A.; Fraser, A. The Prevalence of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, H.; Adachi, H.; Hakoshima, M.; Iida, S.; Katsuyama, H. Metabolic-Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease—Its Pathophysiology, Association with Atherosclerosis and Cardiovascular Disease, and Treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faienza, M.F.; Farella, I.; Khalil, M.; Portincasa, P. Converging Pathways between Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) and Diabetes in Children. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldstein, A.E.; Charatcharoenwitthaya, P.; Treeprasertsuk, S.; Benson, J.T.; Enders, F.B.; Angulo, P. The Natural History of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children: A Follow-up Study for up to 20 Years. Gut 2009, 58, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holterman, A.X.L.; Guzman, G.; Fantuzzi, G.; Wang, H.; Aigner, K.; Browne, A.; Holterman, M. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Severely Obese Adolescent and Adult Patients. Obesity 2013, 21, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwimmer, J.B.; Behling, C.; Newbury, R.; Deutsch, R.; Nievergelt, C.; Schork, N.J.; Lavine, J.E. Histopathology of Pediatric Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology 2005, 42, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldner, D.; Lavine, J.E. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children: Unique Considerations and Challenges. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1967–1983.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobili, V.; Marcellini, M.; Devito, R.; Ciampalini, P.; Piemonte, F.; Comparcola, D.; Sartorelli, M.R.; Angulo, P. NAFLD in Children: A Prospective Clinical-Pathological Study and Effect of Lifestyle Advice. Hepatology 2006, 44, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter-Kent, C.; Yerian, L.M.; Brunt, E.M.; Angulo, P.; Kohli, R.; Ling, S.C.; Xanthakos, S.A.; Whitington, P.F.; Charatcharoenwitthaya, P.; Yap, J.; et al. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Children: A Multicenter Clinicopathological Study. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Inui, A.; Fujisawa, T.; Takikawa, H.; Fukusato, T. Histopathological Characteristics of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children: Comparison with Adult Cases. Hepatol. Res. 2011, 41, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, J.P.; De Vito, R.; Mosca, A.; Alisi, A.; Armstrong, M.J.; Raponi, M.; Baumann, U.; Nobili, V. Portal Inflammation Is Independently Associated with Fibrosis and Metabolic Syndrome in Pediatric Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology 2016, 63, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xanthakos, S.A.; Lavine, J.E.; Yates, K.P.; Schwimmer, J.B.; Molleston, J.P.; Rosenthal, P.; Murray, K.F.; Vos, M.B.; Jain, A.K.; Scheimann, A.O.; et al. Progression of Fatty Liver Disease in Children Receiving Standard of Care Lifestyle Advice. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 1731–1751.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinman, J.B.; Salomao, M.A.; Pajvani, U.B. Zonation in NASH—A Key Paradigm for Understanding Pathophysiology and Clinical Outcomes. Liver Int. 2021, 41, 2534–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinella, M.E.; Tacke, F.; Sanyal, A.J.; Anstee, Q.M. Report on the AASLD/EASL Joint Workshop on Clinical Trial Endpoints in NAFLD. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1424–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molleston, J.P.; Schwimmer, J.B.; Yates, K.P.; Murray, K.F.; Cummings, O.W.; Lavine, J.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Scheimann, A.O.; Unalp-Arida, A. Histological Abnormalities in Children with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Normal or Mildly Elevated Alanine Aminotransferase Levels. J. Pediatr. 2014, 164, 707–713.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, M.B.; Abrams, S.H.; Barlow, S.E.; Caprio, S.; Daniels, S.R.; Kohli, R.; Mouzaki, M.; Sathya, P.; Schwimmer, J.B.; Sundaram, S.S.; et al. NASPGHAN Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children: Recommendations from the Expert Committee on NAFLD (ECON) and the North American Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (NASPGHAN). J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 64, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, V.; Rosso, N.; Dal Ben, M.; Raseni, A.; Boschelle, M.; Degrassi, C.; Nemeckova, I.; Nachtigal, P.; Avellini, C.; Tiribelli, C.; et al. An Animal Model for the Juvenile Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.F.; Fang, Y.L.; Liang, L.; Wang, C.L.; Hong, F.; Dong, G.P. A Rabbit Model of Pediatric Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: The Role of Adiponectin. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panasevich, M.R.; Meers, G.M.; Linden, M.A.; Booth, F.W.; Perfield, J.W.; Fritsche, K.L.; Wankhade, U.D.; Chintapalli, S.V.; Shankar, K.; Ibdah, J.A.; et al. High-Fat, High-Fructose, High-Cholesterol Feeding Causes Severe NASH and Cecal Microbiota Dysbiosis in Juvenile Ossabaw Swine. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 314, E78–E92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tveden-Nyborg, P.; Birck, M.M.; Ipsen, D.H.; Thiessen, T.; de Bie Feldmann, L.; Lindblad, M.M.; Jensen, H.E.; Lykkesfeldt, J. Diet-Induced Dyslipidemia Leads to Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Oxidative Stress in Guinea Pigs. Transl. Res. 2016, 168, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skat-Rørdam, J.; Ipsen, D.H.; Seemann, S.E.; Latta, M.; Lykkesfeldt, J.; Tveden-Nyborg, P. Modelling Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Vivo—A Close Transcriptomic Similarity Supports the Guinea Pig Disease Model. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, A.C.; Rowe, S. Factors Affecting Vitamin C Status and Prevalence of Deficiency: A Global Health Perspective. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frikke-Schmidt, H.; Tveden-Nyborg, P.; Birck, M.M.; Lykkesfeldt, J. High Dietary Fat and Cholesterol Exacerbates Chronic Vitamin C Deficiency in Guinea Pigs. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 105, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.Q.; Li, H.X.; Tan, W.L.; Yang, L.; Ma, X.W.; Li, W.X.; Wang, Q.-B.; Shang, C.Z.; Chen, Y.J. Association of Serum Vitamin C With NAFLD and MAFLD Among Adults in the United States. Front. Nutr. 2022, 8, 795391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, A.C.; Block, G.; Lykkesfeldt, J. Estimation of Vitamin C Intake Requirements Based on Body Weight: Implications for Obesity. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morelli, M.B.; Gambardella, J.; Castellanos, V.; Trimarco, V.; Santulli, G. Vitamin C and Cardiovascular Disease: An Update. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, M.; Conry-Cantilena, C.; Wang, Y.; Welch, R.W.; Washko, P.W.; Dhariwal, K.R.; Park, J.B.; Lazarev, A.; Graumlich, J.F.; King, J.; et al. Vitamin C Pharmacokinetics in Healthy Volunteers: Evidence for a Recommended Dietary Allowance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 3704–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, C.S.; Corte, C. People with Marginal Vitamin C Status Are at High Risk of Developing Vitamin C Deficiency. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1999, 99, 854–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, G.A.; Beal, T.; Mbuya, M.N.N.; Luo, H.; Neufeld, L.M.; Addo, O.Y.; Adu-Afarwuah, S.; Alayón, S.; Bhutta, Z.; Brown, K.H.; et al. Micronutrient Deficiencies among Preschool-Aged Children and Women of Reproductive Age Worldwide: A Pooled Analysis of Individual-Level Data from Population-Representative Surveys. Lancet Glob. Health 2022, 10, e1590–e1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camarena, V.; Wang, G. The Epigenetic Role of Vitamin C in Health and Disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 1645–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, O.P.; Ronquillo, D.; Del Carmen Caamaño, M.; Martínez, G.; Camacho, M.; López, V.; Rosado, J.L. Zinc, Iron and Vitamins A, C and e Are Associated with Obesity, Inflammation, Lipid Profile and Insulin Resistance in Mexican School-Aged Children. Nutrients 2013, 5, 5012–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Ye, X.; Shi, X. Association Between Serum Vitamin C and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 34, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, M.B.; Colvin, R.; Belt, P.; Molleston, J.P.; Murray, K.F.; Rosenthal, P.; Schwimmer, J.B.; Tonascia, J.; Unalp, A.; Lavine, J.E.; et al. Correlation of Vitamin E, Uric Acid and Diet Composition with Histologic Features of Pediatric Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2012, 54, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebouche, C.J. Ascorbic Acid and Carnitine Biosynthesis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1991, 54, 1147S–1152S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minor, E.A.; Court, B.L.; Young, J.I.; Wang, G. Ascorbate Induces Ten-Eleven Translocation (Tet) Methylcytosine Dioxygenase-Mediated Generation of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 13669–13674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.K.; Ki, M.R.; Lee, H.R.; Hong, I.H.; Ji, A.R.; Ishigami, A.; Park, S.I.; Kim, J.M.; Chung, H.Y.; Yoo, S.E.; et al. Vitamin C Deficiency Attenuates Liver Fibrosis by Way of Up-Regulated Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-Gamma Expression in Senescence Marker Protein 30 Knockout Mice. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1766–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, H. Association of Serum Vitamin C with Liver Fibrosis in Adults with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 57, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linster, C.L.; Van Schaftingen, E. Vitamin C: Biosynthesis, Recycling and Degradation in Mammals. FEBS J. 2007, 274, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percie du Sert, N.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alam, S.; Avey, M.T.; Baker, M.; Browne, W.J.; Clark, A.; Cuthill, I.C.; Dirnagl, U.; Emerson, M.; et al. Reporting Animal Research: Explanation and Elaboration for the ARRIVE Guidelines 2.0. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasselholt, S.; Tveden-Nyborg, P.; Lykkesfeldt, J. Distribution of Vitamin C Is Tissue Specific with Early Saturation of the Brain and Adrenal Glands Following Differential Oral Dose Regimens in Guinea Pigs. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, 1539–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lykkesfeldt, J. Determination of Ascorbic Acid and Dehydroascorbic Acid in Biological Samples by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Using Subtraction Methods: Reliable Reduction with Tris [2-Carboxyethyl]Phosphine Hydrochloride. Anal. Biochem. 2000, 282, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lykkesfeldt, J. Measurement of Ascorbic Acid and Dehydroascorbic Acid in Biological Samples. In Current Protocols in Toxicology; Maines, M., Costa, L.G., Hodson, E., Reed, D.J., Sipes, I.G., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 7.6.1–7.6.15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A.; et al. Design and Validation of a Histological Scoring System for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skat-Rørdam, J.; Pedersen, K.; Skovsted, G.F.; Gregersen, I.; Vangsgaard, S.; Ipsen, D.H.; Latta, M.; Lykkesfeldt, J.; Tveden-Nyborg, P. Vitamin C Deficiency May Delay Diet-Induced NASH Regression in the Guinea Pig. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunt, E.M.; Kleiner, D.E.; Wilson, L.A.; Unalp, A.; Behling, C.E.; Lavine, J.E.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A. Portal Chronic Inflammation in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: An Histologic Marker of Advanced NAFLD Clinicopathologic Correlations from the NASH Clinical Research Network. Hepatology 2009, 49, 809–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.Y.; Cho, M.Y.; Baik, S.K.; Park, H.J.; Jeon, H.K.; Im, C.K.; Won, C.S.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, H.S.; Kwon, S.O.; et al. Histological Subclassification of Cirrhosis Using the Laennec Fibrosis Scoring System Correlates with Clinical Stage and Grade of Portal Hypertension. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ipsen, D.H.; Skat-Rørdam, J.; Tsamouri, M.M.; Latta, M.; Lykkesfeldt, J.; Tveden-Nyborg, P. Molecular Drivers of Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis Are Sustained in Mild-to-Late Fibrosis Progression in a Guinea Pig Model. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2019, 294, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tveden-Nyborg, P.; Hasselholt, S.; Miyashita, N.; Moos, T.; Poulsen, H.E.; Lykkesfeldt, J. Chronic Vitamin C Deficiency Does Not Accelerate Oxidative Stress in Ageing Brains of Guinea Pigs. Basic. Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2012, 110, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, K.; Ipsen, D.H.; Skat-Rørdam, J.; Lykkesfeldt, J.; Tveden-Nyborg, P. Dietary Long-Chain Fatty Acids Accelerate Metabolic Dysfunction in Guinea Pigs with Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarr, O.; Thompson, J.A.; Zhao, L.; Lee, T.Y.; Regnault, T.R.H. Low Birth Weight Male Guinea Pig Offspring Display Increased Visceral Adiposity in Early Adulthood. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Stransky, S.; Aguilan, J.; Koul, S.; Garforth, S.J.; Brenowitz, M.; Sidoli, S. High Throughput and Low Bias DNA Methylation and Hydroxymethylation Analysis by Direct Injection Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1180, 338880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipsen, D.H.; Skat-Rørdam, J.; Svenningsen, M.; Andersen, M.; Latta, M.; Buelund, L.E.; Lintrup, K.; Skaarup, R.; Lykkesfeldt, J.; Tveden-Nyborg, P. The Effect of Acetylsalicylic Acid and Pentoxifylline in Guinea Pigs with Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Basic. Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2021, 128, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skat-Rørdam, J.; Ipsen, D.H.; Hardam, P.D.; Latta, M.; Lykkesfeldt, J.; Tveden-Nyborg, P. Differential Effects of Dietary Components on Glucose Intolerance and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Friedman, S.L.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms and Disease Consequences of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Cell 2021, 184, 2537–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, S.; Cabrera, D.; Arrese, M.; Feldstein, A.E. Triggering and Resolution of Inflammation in NASH. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Z.; Zhai, Y.; Liang, S.; Mori, Y.; Han, R.; Sutterwala, F.S.; Qiao, L. TRPM2 Links Oxidative Stress to NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braunersreuther, V.; Viviani, G.L.; Mach, F.; Montecucco, F. Role of Cytokines and Chemokines in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchida, T.; Friedman, S.L. Mechanisms of Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Branicky, R.; Noë, A.; Hekimi, S. Superoxide Dismutases: Dual Roles in Controlling ROS Damage and Regulating ROS Signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 1915–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Tian, R.; She, Z.; Cai, J.; Li, H. Role of Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 152, 116–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videla, L.A.; Rodrigo, R.; Orellana, M.; Fernandez, V.; Tapia, G.; Quiñones, L.; Varela, N.; Contreras, J.; Lazarte, R.; Csendes, A.; et al. Oxidative Stress-Related Parameters in the Liver of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients. Clin. Sci. 2004, 106, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, A.C.; Lykkesfeldt, J. Factors Affecting the Vitamin C Dose-Concentration Relationship: Implications for Global Vitamin C Dietary Recommendations. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Song, S.; Li, L.; Yuan, Z.; Li, Y. Association between the Composite Dietary Antioxidant Index and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease in Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study from NHANES 2017–2020. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaschke, K.; Ebata, K.T.; Karimi, M.M.; Zepeda-Martínez, J.A.; Goyal, P.; Mahapatra, S.; Tam, A.; Laird, D.J.; Hirst, M.; Rao, A.; et al. Vitamin C Induces Tet-Dependent DNA Demethylation and a Blastocyst-like State in ES Cells. Nature 2013, 500, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Z.; Chen, J.; Ding, C.; Wong, K.; Chen, X.; Pu, L.; Huang, Q.; Chen, X.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, Y.; et al. Association of Hepatic Global DNA Methylation and Serum One-Carbon Metabolites with Histological Severity in Patients with NAFLD. Obesity 2020, 28, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, H.; Zhou, B.; Yang, J.; Lu, Y.; Mao, F.; Song, Y. Whole-Genome DNA Methylation and Gene Expression Profiling in the Livers of Mice with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Life Sci. 2023, 329, 121951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyall, M.J.; Thomson, J.P.; Cartier, J.; Ottaviano, R.; Kendall, T.J.; Meehan, R.R.; Drake, A.J. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Is Associated with Dynamic Changes in DNA Hydroxymethylation. Epigenetics 2020, 15, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirola, C.J.; Scian, R.; Gianotti, T.F.; Dopazo, H.; Rohr, C.; Martino, J.S.; Castaño, G.O.; Sookoian, S. Epigenetic Modifications in the Biology of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The Role of DNA Hydroxymethylation and TET Proteins. Medicine 2015, 94, e1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riazi, K.; Azhari, H.; Charette, J.H.; Underwood, F.E.; King, J.A.; Afshar, E.E.; Swain, M.G.; Congly, S.E.; Kaplan, G.G.; Shaheen, A.A. The Prevalence and Incidence of NAFLD Worldwide: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamada, Y.; Kiso, S.; Yoshida, Y.; Chatani, N.; Kizu, T.; Hamano, M.; Tsubakio, M.; Takemura, T.; Ezaki, H.; Hayashi, N.; et al. Estrogen Deficiency Worsens Steatohepatitis in Mice Fed High-Fat and High-Cholesterol Diet. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 301, G1031–G1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Experimental Groups | 2-Way ANOVA | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LFHC | LFLC | HFHC | HFLC | HFvs. LF | VitC | Int. | |
| Plasma | |||||||
| ALT (U/L) 1 | 68 (56–87) | 62 (51–74) | 105 (69–118) | 86 (59–94) | ** | ns | ns |
| AST (U/L) 1 | 220 (86–472) | 227 (89–382) | 279 (157–390) | 193(147–372) | ns | ns | ns |
| GGT (U/L) 1 | 73 (64–80) | 57 (49–72) | 89 (73–105) | 93 (77–113) | **** | ns | * |
| TG (mM) 2 | 0.70 (0.60–0.81) | 0.79 (0.62–1.03) | 0.56 (0.53–0.69) | 0.74 (0.65–1.00) | ns | ** | ns |
| TC (mM) 3 | <0.65 | <0.65 | 0.81 (0.56–0.94) | 0.95 (0.74–1.08) | - | ns | - |
| Total VitC (µM) 1 | 33.89 (26.91–38.77) | 2.69 (2.27–2.88) | 28.70 (21.59–38.39) | 2.71 (2.49–2.88) | ns | **** | ns |
| Liver | |||||||
| TG (µmol/g) 1 | 16.3 (15.7–21.1) | 19.9 (14.9–23.9) | 36.8 (32.6–43.0) | 38.7 (34.7–41.5) | **** | ns | ns |
| TC (µmol/g) 4 | 17.7 ± 2.8 | 17.6 ± 4.4 | 39.7 ± 6.1 | 38.9 ± 6.6 | **** | ns | ns |
| TotalVitC (nmol/g) 5 | 1136 (886–1396) | 68.0 (49.6–154) | 889 (738–1036) | 61.2 (33.3–107) | ** | **** | ns |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pedersen, K.; Poojari, A.; Colberg, S.F.; Mechernsee, S.M.; Iversen, J.F.; Barrès, R.; Lykkesfeldt, J.; Tveden-Nyborg, P. A Guinea Pig Model of Pediatric Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis: Poor Vitamin C Status May Advance Disease. Nutrients 2025, 17, 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17020291
Pedersen K, Poojari A, Colberg SF, Mechernsee SM, Iversen JF, Barrès R, Lykkesfeldt J, Tveden-Nyborg P. A Guinea Pig Model of Pediatric Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis: Poor Vitamin C Status May Advance Disease. Nutrients. 2025; 17(2):291. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17020291
Chicago/Turabian StylePedersen, Kamilla, Ankita Poojari, Simone Frederikke Colberg, Stine Marguerite Mechernsee, Jo Frøkjær Iversen, Romain Barrès, Jens Lykkesfeldt, and Pernille Tveden-Nyborg. 2025. "A Guinea Pig Model of Pediatric Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis: Poor Vitamin C Status May Advance Disease" Nutrients 17, no. 2: 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17020291
APA StylePedersen, K., Poojari, A., Colberg, S. F., Mechernsee, S. M., Iversen, J. F., Barrès, R., Lykkesfeldt, J., & Tveden-Nyborg, P. (2025). A Guinea Pig Model of Pediatric Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis: Poor Vitamin C Status May Advance Disease. Nutrients, 17(2), 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17020291








