The Interplay Between Gut Microbiota, Adipose Tissue, and Migraine: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results in the Literature
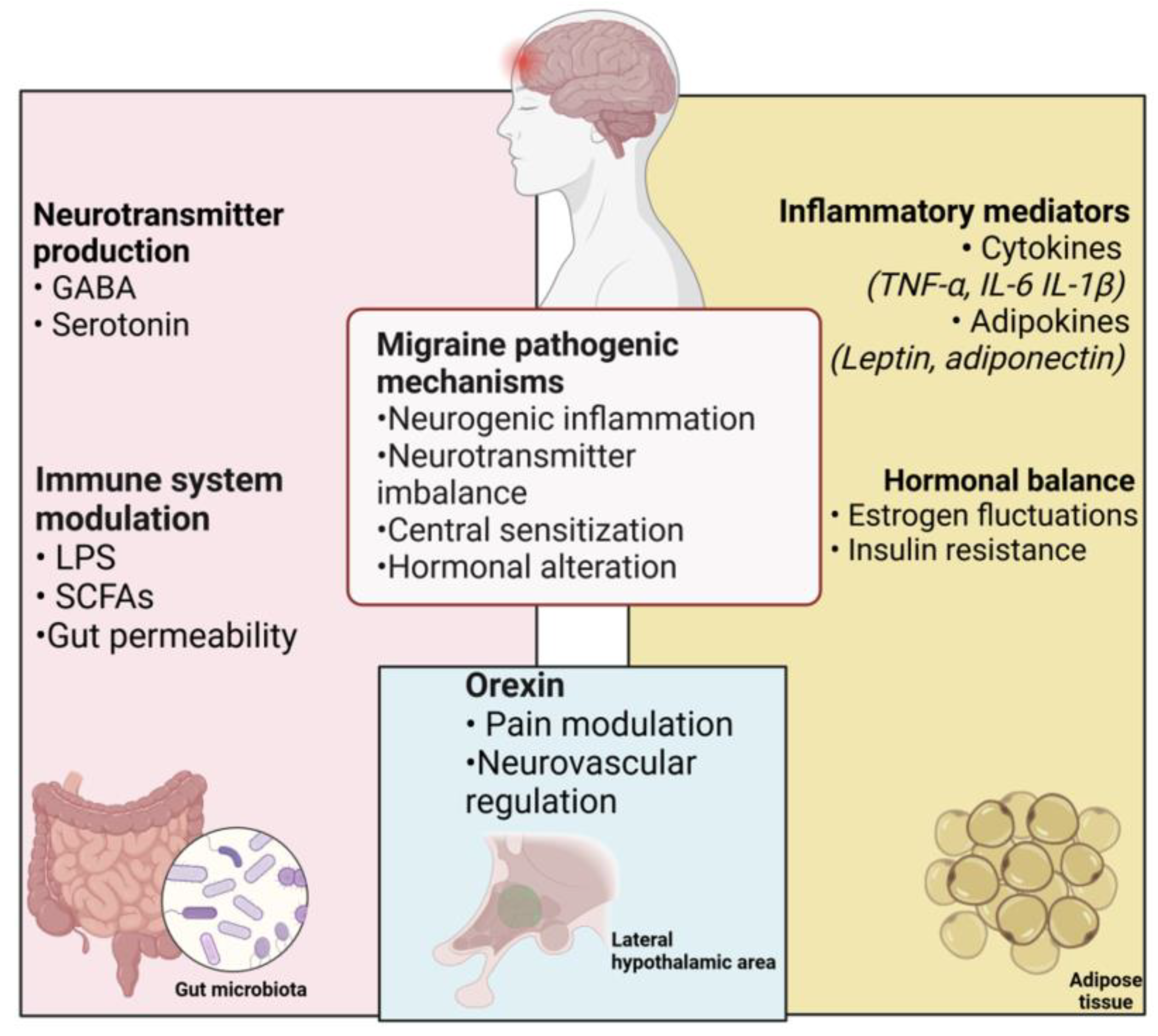
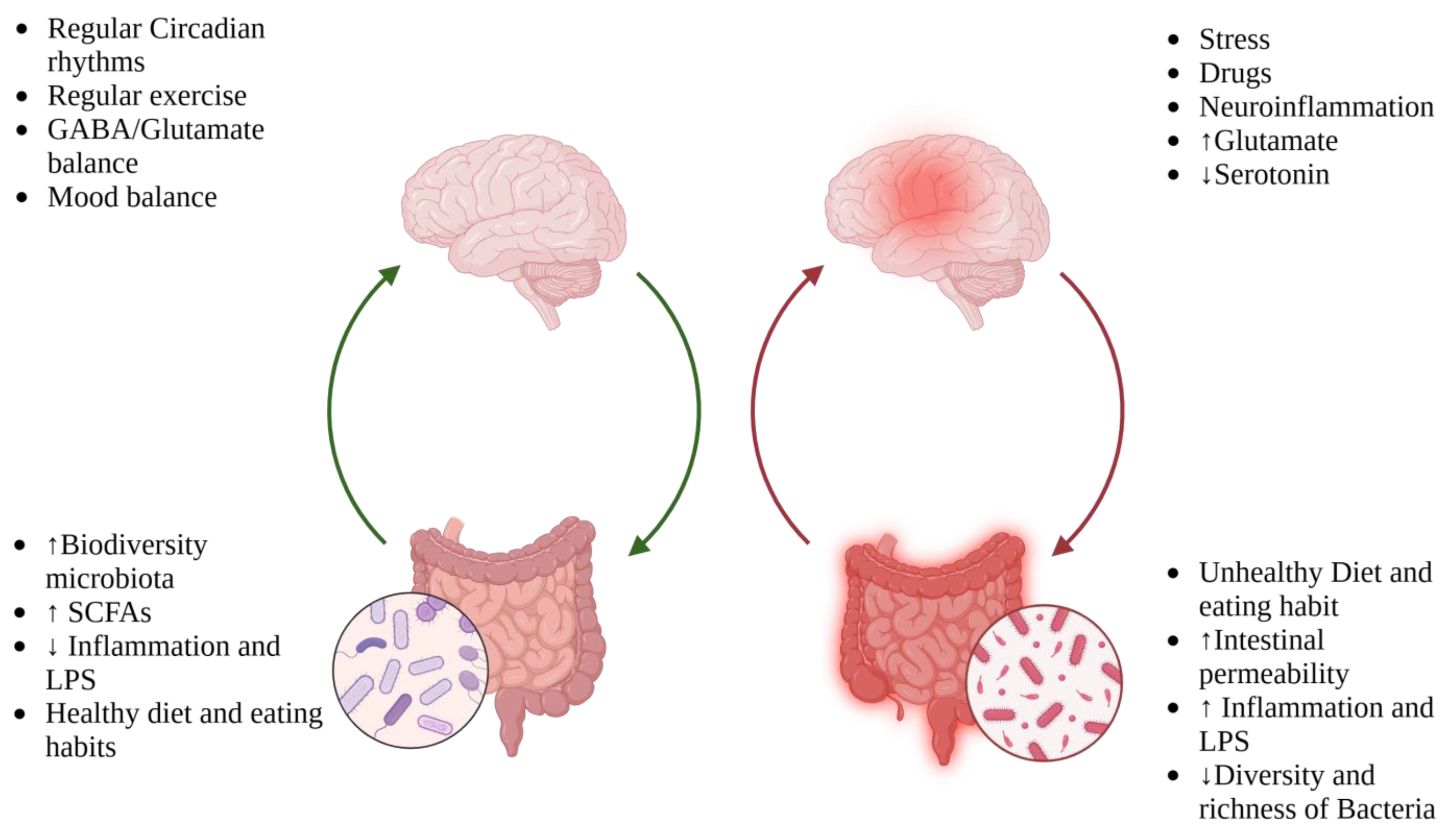
3.1. Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis and Role of Inflammation in Migraine
3.2. Migraine and Gastrointestinal Disorders: Is There a Link?
3.3. Obesity–Migraine Linkage
4. Discussion
Neurotransmitters and Postbiotics: The Silent Messengers of the Microbiota
5. Diet: What We Know and Future Directions
5.1. Diet Triggers
5.2. Elimination Diet
5.3. Dash and Mediterranean Diet
5.4. Low Glycemic Index Diet
5.5. Functional Food and Administrations of Supplements: Prebiotics, Probiotics and Postbiotics
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grangeon, L.; Lange, K.S.; Waliszewska-Prosół, M.; Onan, D.; Marschollek, K.; Wiels, W.; Mikulenka, P.; Farham, F.; Gollion, C.; Ducros, A.; et al. Genetics of migraine: Where are we now? J. Headache Pain 2023, 24, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, P.E.; Mack, K.J. Episodic and chronic migraine in children. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2020, 62, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, N.R.; Whitehouse, W.P.; Howells, R. What is new in migraine management in children and young people? Arch. Dis. Child. 2022, 107, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Arafeh, I.; Howells, R. Management of migraine in children and adolescents. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2024, 199, 487–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patniyot, I.; Qubty, W. Short-term Treatment of Migraine in Children and Adolescents. JAMA Pediatr. 2020, 174, 789–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seng, E.K.; Martin, P.R.; Houle, T.T. Lifestyle factors and migraine. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazerani, P. Diet and migraine: What is proven? Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2023, 36, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santangelo, A.; Corsello, A.; Spolidoro, G.C.I.; Trovato, C.M.; Agostoni, C.; Orsini, A.; Milani, G.P.; Peroni, D.G. The Influence of Ketogenic Diet on Gut Microbiota: Potential Benefits, Risks and Indications. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskatel, L.S.; Zhang, N. Migraine and Diet: Updates in Understanding. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2022, 22, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correnti, E.; Cascio, S.L.; Cernigliaro, F.; Rossi, R.; D’agnano, D.; Grasso, G.; Pellegrino, A.; Lauria, B.; Santangelo, A.; Santangelo, G.; et al. Idiopathic Non-Dental Facial Pain Syndromes in Italian Children: A Clinical Case Series. Life 2023, 13, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, A.; Lin, Z. Structural and Functional Characterization of the Gut Microbiota in Elderly Women with Migraine. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 9, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen-Liaw, A.; Aggarwala, V.; Mogno, I.; Haifer, C.; Li, Z.; Eggers, J.; Helmus, D.; Hart, A.; Wehkamp, J.; Lamousé-Smith, E.S.N.; et al. Gut microbiota bacterial strain richness is species specific and limits therapeutic engraftment. Nature 2025, 637, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biagioli, V.; Volpedo, G.; Riva, A.; Mainardi, P.; Striano, P. From Birth to Weaning: A Window of Opportunity for Microbiota. Nutrients 2024, 16, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Integrative HMP (iHMP) Research Network Consortium. The Integrative Human Microbiome Project. Nature 2019, 569, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, L. Role and Mechanism of Gut Microbiota in Human Disease. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 625913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Q.; Cai, M.; Xiao, B.; Zhan, Q.; Zeng, C. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis and Epilepsy. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 42, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankiensztajn, L.M.; Elliott, E.; Koren, O. The microbiota and the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenocortical (HPA) axis, implications for anxiety and stress disorders. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2020, 62, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagioli, V.; Sortino, V.; Falsaperla, R. Role of Human Milk Microbiota in Infant Neurodevelopment: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Children 2024, 11, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuralli, D.; Akgor, M.C.; Dagidir, H.G.; Onat, P.; Yalinay, M.; Sezerman, U.; Bolay, H. Microbiota alterations are related to migraine food triggers and inflammatory markers in chronic migraine patients with medication overuse headache. J. Headache Pain 2024, 25, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, D.J.; Preston, T. Formation of short chain fatty acids by the gut microbiota and their impact on human metabolism. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Guo, W.; Xiao, D.; Guan, M.; Liao, T.; Peng, S.; Feng, A.; Wang, Z.; Yin, H.; Li, M.; et al. Microbiota-gut-brain axis drives overeating disorders. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 2011–2027.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Shen, N.; Liu, Y. Associations between the Gut Microbiome and Migraines in Children Aged 7-18 Years: An Analysis of the American Gut Project Cohort. Pain Manag. Nurs. 2023, 24, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, D.G.; Vieira, A.T.; Soares, A.C.; Pinho, V.; Nicoli, J.R.; Vieira, L.Q.; Teixeira, M.M.; At, V. The essential role of the intestinal microbiota in facilitating acute inflammatory responses. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 4137–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.W.; Cho, Y.-S.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, E.-S.; Cho, H.; Shin, H.E.; Suh, G.I.; Choi, M.-G. Concomitant functional gastrointestinal symptoms influence psychological status in Korean migraine patients. Gut Liver 2013, 7, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Rhew, K. Association between Gastrointestinal Diseases and Migraine. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurora, S.K.; Kori, S.H.; Barrodale, P.; McDonald, S.A.; Haseley, D. Gastric stasis in migraine: More than just a paroxysmal abnormality during a migraine attack. Headache 2006, 46, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cámara-Lemarroy, C.R.; Rodriguez-Gutierrez, R.; Monreal-Robles, R.; Marfil-Rivera, A. Gastrointestinal disorders associated with migraine: A comprehensive review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 8149–8160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, R. Neurogenic inflammation and its role in migraine. Semin. Immunopathol. 2018, 40, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bortoli, N.; Tolone, S.; Frazzoni, M.; Martinucci, I.; Sgherri, G.; Albano, E.; Ceccarelli, L.; Stasi, C.; Bellini, M.; Savarino, V.; et al. Gastroesophageal reflux disease, functional dyspepsia and irritable bowel syndrome: Common overlapping gastrointestinal disorders. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2018, 31, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.F.; Hay, D.L. CGRP physiology, pharmacology, and therapeutic targets: Migraine and beyond. Physiol. Rev. 2023, 103, 1565–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ailani, J.; Kaiser, E.A.; Mathew, P.G.; McAllister, P.; Russo, A.F.; Vélez, C.; Ramajo, A.P.; Abdrabboh, A.; Xu, C.; Rasmussen, S.; et al. Role of Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide on the Gastrointestinal Symptoms of Migraine-Clinical Considerations: A Narrative Review. Neurology 2022, 99, 841–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Wang, W.; Xiong, Y.; Tao, C.; Ma, L.; Ma, J.; You, C. A causal effects of gut microbiota in the development of migraine. J. Headache Pain 2023, 24, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindiyeh, N.; Aurora, S.K. What the Gut Can Teach Us About Migraine. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2015, 19, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, N.S.; Marciani, L.; Blackshaw, E.; Wright, J.; Parker, M.; Yano, T.; Yamazaki, S.; Chan, P.Q.; Wilde, K.; Gowland, P.A.; et al. Effect of a novel 5-HT3 receptor agonist MKC-733 on upper gastrointestinal motility in humans. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 18, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare, M.; Sorić, M.; Bovet, P.; Miranda, J.J.; Bhutta, Z.; Stevens, G.A.; Laxmaiah, A.; Kengne, A.-P.; Bentham, J. The epidemiological burden of obesity in childhood: A worldwide epidemic requiring urgent action. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentice, A.M. The Triple Burden of Malnutrition in the Era of Globalization. Nestle Nutr. Inst. Workshop Ser. 2023, 97, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahromi, S.R.; Martami, F.; Morad Soltani, K.; Togha, M. Migraine and obesity: What is the real direction of their association? Expert. Rev. Neurother. 2023, 23, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershey, A.D.; Powers, S.W.; Nelson, T.D.; Kabbouche, M.A.; Winner, P.; Yonker, M.; Linder, S.L.; Bicknese, A.; Sowel, M.K.; McClintock, W.; et al. Obesity in the pediatric headache population: A multicenter study. Headache 2009, 49, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinik, S.T.; Alehan, F.; Erol, I.; Kanra, A.R. Obesity and paediatric migraine. Cephalalgia 2010, 30, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, S.M.; Clarke, G.; Borre, Y.E.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Serotonin, tryptophan metabolism and the brain-gut-microbiome axis. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 277, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaput, J.-P. Sleep patterns, diet quality and energy balance. Physiol. Behav. 2014, 134, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agus, A.; Planchais, J.; Sokol, H. Gut Microbiota Regulation of Tryptophan Metabolism in Health and Disease. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, J.M.; Yu, K.; Donaldson, G.P.; Shastri, G.G.; Ann, P.; Ma, L.; Nagler, C.R.; Ismagilov, R.F.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Hsiao, E.Y. Indigenous bacteria from the gut microbiota regulate host serotonin biosynthesis. Cell 2015, 161, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Galen, K.A.; Ter Horst, K.W.; Serlie, M.J. Serotonin, food intake, and obesity. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22, e13210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamel, E. Serotonin and migraine: Biology and clinical implications. Cephalalgia 2007, 27, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leser, T.; Baker, A. Bifidobacterium adolescentis—A beneficial microbe. Benef. Microbes 2023, 14, 525–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Qi, Y.; Qu, S.; Chen, X.; Li, A.; Hendi, M.; Xu, C.; Wang, L.; Hou, T.; Si, J.; et al. B. adolescentis ameliorates chronic colitis by regulating Treg/Th2 response and gut microbiota remodeling. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1826746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, D.; Naffah-Mazacoratti, M.; Zukerman, E.; Soares, C.S.; Alonso, E.; Faulhaber, M.; Cavalheiro, E.; Peres, M. Cerebrospinal fluid GABA levels in chronic migraine with and without depression. Brain Res. 2006, 1090, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, L.G.; Scherer, P.E. Metabolic Messengers: Adiponectin. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterlin, B.L.; Sacco, S.; Bernecker, C.; Scher, A.I. Adipokines and Migraine: A Systematic Review. Headache 2016, 56, 622–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obradovic, M.; Sudar-Milovanovic, E.; Soskic, S.; Essack, M.; Arya, S.; Stewart, A.J.; Gojobori, T.; Isenovic, E.R. Leptin and Obesity: Role and Clinical Implication. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 585887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, M.; Noori-Zadeh, A.; Seidkhani-Nahal, A.; Kaffashian, M.; Bakhtiyari, S.; Panahi, S. Leptin, adiponectin, and resistin blood adipokine levels in migraineurs: Systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Cephalalgia 2019, 39, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez, C.; Vieites-Prado, A.; Pérez-Mato, M.; Sobrino, T.; Rodríguez-Osorio, X.; López, A.; Campos, F.; Martínez, F.; Castillo, J.; Leira, R. Role of adipocytokines in the pathophysiology of migraine: A cross-sectional study. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 904–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubino, E.; Vacca, A.; Govone, F.; Gai, A.; Boschi, S.; Zucca, M.; De Martino, P.; Gentile, S.; Pinessi, L.; Rainero, I. Investigating the role of adipokines in chronic migraine. Cephalalgia 2017, 37, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strother, L.C.; Srikiatkhachorn, A.; Supronsinchai, W. Targeted Orexin and Hypothalamic Neuropeptides for Migraine. Neurother. J. Am. Soc. Exp. Neurother. 2018, 15, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomi, K.; Logomarsino, J.V. Bacterial Lipopolysaccharide, Lipopolysaccharide-Binding Protein, and Other Inflammatory Markers in Obesity and After Bariatric Surgery. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2016, 14, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papetti, L.; Del Chierico, F.; Frattale, I.; Toto, F.; Scanu, M.; Mortera, S.L.; Rapisarda, F.; Di Michele, M.; Monte, G.; Ursitti, F.; et al. Pediatric migraine is characterized by traits of ecological and metabolic dysbiosis and inflammation. J. Headache Pain 2024, 25, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, S. Effect of exclusion of frequently consumed dietary triggers in a cohort of children with chronic primary headache. Nutr. Health 2017, 23, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering-Hanit, R.; Gadoth, N. Caffeine-induced headache in children and adolescents. Cephalalgia 2003, 23, 332–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliano, L.M.; Griffiths, R.R. A critical review of caffeine withdrawal: Empirical validation of symptoms and signs, incidence, severity, and associated features. Psychopharmacology 2004, 176, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watemberg, N.; Matar, M.; Har-Gil, M.; Mahajnah, M. The influence of excessive chewing gum use on headache frequency and severity among adolescents. Pediatr. Neurol. 2014, 50, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arzani, M.; Jahromi, S.R.; Ghorbani, Z.; Vahabizad, F.; Martelletti, P.; Ghaemi, A.; Sacco, S.; Togha, M.; School of Advanced Studies of the European Headache Federation (EHF-SAS). Gut-brain Axis and migraine headache: A comprehensive review. J. Headache Pain 2020, 21, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazerani, P. Migraine and Diet. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindiyeh, N.A.; Zhang, N.; Farrar, M.; Banerjee, P.; Lombard, L.; Aurora, S.K. The Role of Diet and Nutrition in Migraine Triggers and Treatment: A Systematic Literature Review. Headache 2020, 60, 1300–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotchetkoff, E.C.D.A.; Oliveira, L.C.L.D.; Sarni, R.O.S. Elimination diet in food allergy: Friend or foe? J. Pediatr. 2024, 100 (Suppl. S1), S65–S73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickman, B.E.; Enkhmaa, B.; Ridberg, R.; Romero, E.; Cadeiras, M.; Meyers, F.; Steinberg, F. Dietary Management of Heart Failure: DASH Diet and Precision Nutrition Perspectives. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-González, M.A.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Estruch, R.; Corella, D.; Fitó, M.; Ros, E. Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet: Insights From the PREDIMED Study. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 58, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondhi, V.; Agarwala, A.; Pandey, R.M.; Chakrabarty, B.; Jauhari, P.; Lodha, R.; Toteja, G.S.; Sharma, S.; Paul, V.K.; Kossoff, E.; et al. Efficacy of Ketogenic Diet, Modified Atkins Diet, and Low Glycemic Index Therapy Diet Among Children With Drug-Resistant Epilepsy: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Pediatr. 2020, 174, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tereshko, Y.; Bello, S.D.; Di Lorenzo, C.; Pez, S.; Pittino, A.; Sartor, R.; Filippi, F.; Lettieri, C.; Belgrado, E.; Garbo, R.; et al. 2:1 ketogenic diet and low-glycemic-index diet for the treatment of chronic and episodic migraine: A single-center real-life retrospective study. J. Headache Pain 2023, 24, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younas, A.; Naqvi, S.A.; Khan, M.R.; Shabbir, M.A.; Jatoi, M.A.; Anwar, F.; Inam-Ur-Raheem, M.; Saari, N.; Aadil, R.M. Functional food and nutra-pharmaceutical perspectives of date (Phoenix dactylifera L.) fruit. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.R.; Hutkins, R.; Sanders, M.E.; Prescott, S.L.; Reimer, R.A.; Salminen, S.J.; Scott, K.; Stanton, C.; Swanson, K.S.; Cani, P.D.; et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holscher, H.D. Dietary fiber and prebiotics and the gastrointestinal microbiota. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okburan, G.; Kızıler, S. Human milk oligosaccharides as prebiotics. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2023, 64, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghavami, A.; Khorvash, F.; Heidari, Z.; Khalesi, S.; Askari, G. Effect of synbiotic supplementation on migraine characteristics and inflammatory biomarkers in women with migraine: Results of a randomized controlled trial. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 169, 105668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anhê, F.F.; Marette, A. A microbial protein that alleviates metabolic syndrome. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martami, F.; Togha, M.; Seifishahpar, M.; Ghorbani, Z.; Ansari, H.; Karimi, T.; Jahromi, S.R. The effects of a multispecies probiotic supplement on inflammatory markers and episodic and chronic migraine characteristics: A randomized double-blind controlled trial. Cephalalgia 2019, 39, 841–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, F.; Salemi, G.; Capizzi, M.; Lo Cascio, S.; Marino, A.; Santangelo, G.; Santangelo, A.; Mineri, M.; Brighina, F.; Raieli, V.; et al. Orofacial Migraine and Other Idiopathic Non-Dental Facial Pain Syndromes: A Clinical Survey of a Social Orofacial Patient Group. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 6946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biagioli, V.; Mela, F.; Ferraro, P.; Villano, G.; Orsini, A.; Diana, M.C.; Striano, P.; Santangelo, A. The Interplay Between Gut Microbiota, Adipose Tissue, and Migraine: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2025, 17, 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17020337
Biagioli V, Mela F, Ferraro P, Villano G, Orsini A, Diana MC, Striano P, Santangelo A. The Interplay Between Gut Microbiota, Adipose Tissue, and Migraine: A Narrative Review. Nutrients. 2025; 17(2):337. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17020337
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiagioli, Valentina, Federica Mela, Paola Ferraro, Gianmichele Villano, Alessandro Orsini, Maria Cristina Diana, Pasquale Striano, and Andrea Santangelo. 2025. "The Interplay Between Gut Microbiota, Adipose Tissue, and Migraine: A Narrative Review" Nutrients 17, no. 2: 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17020337
APA StyleBiagioli, V., Mela, F., Ferraro, P., Villano, G., Orsini, A., Diana, M. C., Striano, P., & Santangelo, A. (2025). The Interplay Between Gut Microbiota, Adipose Tissue, and Migraine: A Narrative Review. Nutrients, 17(2), 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17020337






