The Gut Microbiome and Its Impact on Mood and Decision-Making: A Mechanistic and Therapeutic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
Scope and Rationale
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Effects on Decision-Making and Cognition
3.2. Influence on Cognitive Function
3.3. Impact on Risk Assessment
3.4. Connection to Impulsive Behavior
3.5. Role in Addiction and Substance Abuse
3.6. Factors Shaping Microbiome Composition
3.7. Methods to Study Microbiome–Mood Links
3.8. Therapeutic Approaches
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peters, D.L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Ning, Z.; Mayne, J.; Figeys, D. Metaproteomic and metabolomic approaches for characterizing the gut microbiome. Proteomics 2019, 19, e1800363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manor, O.; Levy, R.; Borenstein, E. Mapping the inner workings of the microbiome: Genomic- and metagenomic-based study of metabolism and metabolic interactions in the human microbiome. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 742–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raethong, N.; Nakphaichit, M.; Suratannon, N.; Sathitkowitchai, W.; Weerapakorn, W.; Keawsompong, S.; Vongsangnak, W. Analysis of human gut microbiome: Taxonomy and metabolic functions in Thai adults. Genes 2021, 12, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cheng, K.; Ning, Z.; Mayne, J.; Chi, H.; Farnsworth, C.L.; Lee, K.; Figeys, D. Exploring the microbiome-wide lysine acetylation, succinylation, and propionylation in human gut microbiota. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 6594–6598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Kim, Y.; Choi, H.; Kim, W.; Park, S.; Lee, D.; Kim, D.K.; Kim, H.J.; Choi, H.; Hyun, D.-W.; et al. Transfer of a healthy microbiota reduces amyloid and tau pathology in an Alzheimer’s disease animal model. Gut 2020, 69, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yankovsky, D.S.; Shirobokov, V.P.; Dyment, G.S. Innovation technologies for human microbiome improvement. Sci. Innov. 2018, 14, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenblum, S.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Borenstein, E. Metagenomic systems biology of the human gut microbiome reveals topological shifts associated with obesity and inflammatory bowel disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.Y.; Fan, J.G. Gut microbiome and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2023, 22, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, H.; Jain, S.; Bissi, L.; Marotta, F. Gut microbiome derived metabolites to regulate energy homeostasis: How microbiome talks to host. Metabolomics 2016, 6, e150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiser, H.J.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Chatman, K.; Sirasani, G.; Balskus, E.P.; Turnbaugh, P.J. Predicting and manipulating cardiac drug inactivation by the human gut bacterium Eggerthella lenta. Science 2013, 341, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, W.A.; Sahu, S.C. The human microbiome: History and future. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 23, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, P.; Bian, X.; Chi, L.; Gao, B.; Ru, H.; Knobloch, T.J.; Weghorst, C.M.; Lu, K. Characterization of the functional changes in mouse gut microbiome associated with increased Akkermansia muciniphila population modulated by dietary black raspberries. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 10927–10937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldini, F.; Hertel, J.; Sandt, E.; Thinnes, C.C.; Neuberger-Castillo, L.; Pavelka, L.; Betsou, F.; Krüger, R.; Thiele, I.; on behalf of the NCER-PD Consortium. Parkinson’s disease-associated alterations of the gut microbiome can invoke disease-relevant metabolic changes. BioRxiv 2019, 691030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Abo, R.P.; Schlieper, K.A.; Graffam, M.E.; Levine, S.; Wishnok, J.S.; Swenberg, J.A.; Tannenbaum, S.R.; Fox, J.G. Arsenic exposure perturbs the gut microbiome and its metabolic profile in mice: An integrated metagenomics and metabolomics analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmanski, T.; Rappaport, N.; Earls, J.C.; Magis, A.T.; Manor, O.; Lovejoy, J.; Omenn, G.S.; Hood, L.; Gibbons, S.M.; Price, N.D. Blood metabolome predicts gut microbiome α-diversity in humans. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1217–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, B.; Zhang, M.; Rantalainen, M.; Wang, S.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.; Pang, X.; Zhang, M.; et al. Symbiotic gut microbes modulate human metabolic phenotypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2117–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. What is the Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition? A Changing Ecosystem across Age, Environment, Diet, and Diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanborn, V.; Azcarate-Peril, M.A.; Updegraff, J.; Manderino, L.M.; Gunstad, J. A randomized clinical trial examining the impact of LGG probiotic supplementation on psychological status in middle-aged and older adults. Contemp. Clin. Trials Commun. 2018, 12, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.C.; Wei, C.C.; Huang, C.C.; Chen, W.L.; Huang, H.Y. The Beneficial Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum PS128 on High-Intensity, Exercise-Induced Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Performance in Triathletes. Nutrients 2019, 11, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, F.; Yu, X.; Ling, Z.; Li, H.; Chen, W.; Pang, M.; Yu, J.; He, Y.; et al. Neuroprotective effects of Clostridium butyricum against vascular dementia in mice via metabolic butyrate. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 412946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.S.; Jacobs, J.P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and the gut microbiome: Are bacteria responsible for fatty liver? Exp. Biol. Med. 2019, 244, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpton, S.R.; Yong, G.J.M.; Terrault, N.A.; Lynch, S.V. Gut microbial metabolism and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol. Commun. 2018, 3, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boccuto, L.; Tack, J.; Ianiro, G.; Abenavoli, L.; Scarpellini, E. Human genes involved in the interaction between host and gut microbiome: Regulation and pathogenic mechanisms. Genes 2023, 14, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleton, J. The Gut-Brain Axis: Influence of Microbiota on Mood and Mental Health. Integr. Med. (Encinitas) 2018, 17, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davis, C.D. The gut microbiome and its role in obesity. Nutr. Today 2016, 51, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaolapo, O.J.; Onaolapo, A.Y.; Olowe, A.O. The neurobehavioral implications of the brain and microbiota interaction. Front. Biosci. Landmark 2020, 25, 363–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.J.; Qiao, N.H.; Diao, Q.Y.; Jing, Z.; Vukanti, R.; Dai, P.L.; Ge, Y. Thiacloprid exposure perturbs the gut microbiota and reduces the survival status in honeybees. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 121818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Gu, L.; Guo, Y.; Feng, H.; Chen, S.; Jurat, J.; Zhang, D. Gut microbiota mediates the preventive effects of dietary capsaicin against depression-like behavior induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 627608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cline, E.N.; Bicca, M.A.; Viola, K.L.; Klein, W.L. The amyloid-β oligomer hypothesis: Beginning of the third decade. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 64 (Suppl. S1), S567–S610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Sun, A.; Lin, Y.; Jin, Y.; Li, X. Fecal microbiota transplantation from chronic unpredictable mild stress mice donors affects anxiety-like and depression-like behavior in recipient mice via the gut microbiota-inflammation-brain axis. Stress 2019, 22, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkent, J.; Ioannou, M.; Laman, J.D.; Haarman, B.C.; Sommer, I.E. Role of the gut microbiome in three major psychiatric disorders. Psychol. Med. 2022, 52, 1222–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, M.L.; Inserra, A.; Lewis, M.D.; Mastronardi, C.A.; Leong, L.E.X.; Choo, J.; Kentish, S.; Xie, P.; Morrison, M.; Wesselingh, S.L.; et al. Inflammasome signaling affects anxiety- and depressive-like behavior and gut microbiome composition. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Guo, P.; Zhang, J. Nutrients mediate intestinal bacteria-mucosal immune crosstalk. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keku, T.O.; Dulal, S.; Deveaux, A.; Jovov, B.; Han, X. The gastrointestinal microbiota and colorectal cancer. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2015, 308, G351–G363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarte, J.C.; Li, Y.; Hu, S.; Björk, J.R.; Gacesa, R.; Vich Vila, A.; Douwes, R.M.; Collij, V.; Kurilshikov, A.; Post, A.; et al. Gut microbiome dysbiosis is associated with increased mortality after solid organ transplantation. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabn7566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.F.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, J.H.; Wang, Q.N.; Li, S.J.; Wang, H.O.; Zhou, F.; Li, J.-M. Short-chain fatty acids ameliorate depressive-like behaviors of high fructose-fed mice by rescuing hippocampal neurogenesis decline and blood–brain barrier damage. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sze, M.A.; Baxter, N.T.; Ruffin, M.T.; Rogers, M.A.; Schloss, P.D. Normalization of the microbiota in patients after treatment for colonic lesions. Microbiome 2017, 5, 150663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimova, B.; Novotny, M.; Valis, M. The impact of nutrition and intestinal microbiome on elderly depression—A systematic review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Klipfell, E.; Bennett, B.J.; Koeth, R.; Levison, B.S.; DuGar, B.; Feldstein, A.E.; Britt, E.B.; Fu, X.; Chung, Y.-M.; et al. Gut flora metabolism of phosphatidylcholine promotes cardiovascular disease. Nature 2011, 472, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarandi, S.S.; Peterson, D.A.; Treisman, G.J.; Moran, T.H.; Pasricha, P.J. Modulatory effects of gut microbiota on the central nervous system: How gut could play a role in neuropsychiatric health and diseases. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 22, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandpal, M.; Indari, O.; Baral, B.; Jakhmola, S.; Tiwari, D.; Bhandari, V.; Pandey, R.K.; Bala, K.; Sonawane, A.; Jha, H.C. Dysbiosis of gut microbiota from the perspective of the gut–brain axis: Role in the provocation of neurological disorders. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, E.E.; Hsu, T.M.; Kanoski, S.E. Gut to brain dysbiosis: Mechanisms linking Western diet consumption, the microbiome, and cognitive impairment. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, T.R.; Mazmanian, S.K. Control of brain development, function, and behavior by the microbiome. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartochowski, Z.; Conway, J.; Wallach, Y.; Chakkamparambil, B.; Alakkassery, S.; Grossberg, G.T. Dietary interventions to prevent or delay Alzheimer’s disease: What the evidence shows. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2020, 9, 210–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalesi, S.; Bellissimo, N.; Vandelanotte, C.; Williams, S.; Stanley, D.; Irwin, C. A review of probiotic supplementation in healthy adults: Helpful or hype? Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 73, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugita, H.; Tahir, A.; Kinjo, A. Microbiome-targeted therapy in the treatment of cognitive impairment and postoperative cognitive dysfunction: A systematic review. Nutr. Neurosci. 2023, 26, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, S.M.S.; Mohajeri, M.H. The role of gut bacterial metabolites in brain development, aging and disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, L.E.; Cooke, G.E.; Johnson, L.M.; Quinn, E. Individual differences in the gut microbiome and cognitive performance. Brain Cogn. 2018, 126, 102–109. [Google Scholar]
- Romo-Araiza, A.; Ibarra, A. Prebiotics and probiotics as potential therapy for cognitive impairment. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 134, 109410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Cowan, C.S.M.; Sandhu, K.V.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S. The microbiota-gut-brain axis. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1877–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Arribas, M.V.; Bartolomé, B.; Peñalvo, J.L.; Pérez-Matute, P.; Motilva, M.J. Relationship between wine consumption, diet and microbiome modulation in Alzheimer’s disease. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.H.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Long, C.Y.; Peng, Q.; Yue, R.S. The gut microbiota-astrocyte axis: Implications for type 2 diabetic cognitive dysfunction. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023, 29, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medawar, E.; Hühn, S.; Villringer, A.; Witte, A.V. The effects of plant-based diets on the body and the brain: A systematic review. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahmasbi, F.; Mirghafourvand, M.; Shamekh, A.; Mahmoodpoor, A.; Sanaie, S. Effects of probiotic supplementation on cognitive function in elderly: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Aging Ment. Health 2022, 26, 1778–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, R.; Neth, B.J.; Wang, S. Gut mycobiome and its interaction with diet, gut bacteria and Alzheimer’s disease markers in subjects with mild cognitive impairment: A pilot study. eBioMedicine 2020, 59, 102950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkenstein, M.; Simon, M.C.; Mantri, A.; Weber, B.; Koban, L.; Plassmann, H. Impact of the gut microbiome composition on social decision-making. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Nexus 2024, 3, pgae166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, Y. Regulation of neurotransmitters by the gut microbiota and effects on cognition in neurological disorders. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.R.; Kennedy, P.J.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G.; Clarke, G.; Hyland, N.P. Breaking down the barriers: The gut microbiome, intestinal permeability and stress-related psychiatric disorders. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrattan, A.M.; McGuinness, B.; McKinley, M.C.; Kee, F.; Passmore, P.; Woodside, J.V.; McEvoy, C.T. Diet and inflammation in cognitive ageing and Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2019, 8, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2021, 134, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postler, T.S.; Ghosh, S. Understanding the Holobiont: How Microbial Metabolites Affect Human Health and Shape the Immune System. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 110–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpino, G.D.C.Á.; Pereira-Sol, G.A.; Dias, M.D.M.E.; Aguiar, A.S.D.; Peluzio, M.D.C.G. Beneficial effects of butyrate on brain functions: A view of epigenetic. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 3961–3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.A.; Baker, G.B.; Dursun, S.M. The relationship between the gut microbiome-immune system-brain axis and major depressive disorder. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 721126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hao, Y.; Fan, F.; Zhang, B. The role of microbiome in insomnia, circadian disturbance and depression. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrio, C.; Arias-Sánchez, S.; Martín-Monzón, I. The gut microbiota-brain axis, psychobiotics and its influence on brain and behaviour: A systematic review. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2022, 137, 105640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, T.; Choi, Y.; Koo, J. Mental disorders linked to crosstalk between the gut microbiome and the brain. Exp. Neurobiol. 2020, 29, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makris, A.P.; Karianaki, M.; Tsamis, K.I.; Paschou, S.A. The role of the gut-brain axis in depression: Endocrine, neural, and immune pathways. Hormones 2021, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlo, G.; Bachtel, G.; Sugden, S.G. Gut microbiota, nutrition, and mental health. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1337889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Wouw, M.; Schellekens, H.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Microbiota-gut-brain axis: Modulator of host metabolism and appetite. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 727–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Hong, M.; Kim, S.; Shin, W.Y.; Kim, J.H. Inverse association between dietary fiber intake and depression in premenopausal women: A nationwide population-based survey. Menopause 2021, 28, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mac Giollabhui, N.; Ng, T.H.; Ellman, L.M.; Alloy, L.B. The longitudinal associations of inflammatory biomarkers and depression revisited: Systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 3302–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias-Vázquez, L.; Riba, A.; Arija, V.; Canals, J. Composition of Gut Microbiota in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrien, M.; Alvarez, A.-S.; de Vos, W.M. The Gut Microbiota in the First Decade of Life. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 997–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackie, A.; Mulet-Cabero, A.I.; Torcello-Gómez, A. Simulating human digestion: Developing our knowledge to create healthier and more sustainable foods. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 9397–9431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Wang, G. Probiotics for mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Foods 2021, 10, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Xie, L.; Zhuang, Z.; Zhao, N.; Huang, B.; Tang, Y.; Yu, S.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, Q. Gut microbiota: A new strategy to study the mechanism of electroacupuncture and moxibustion in treating ulcerative colitis. Evid. Based Complement Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 9730176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.R.; Banerjee, S. Gut microbiota in neurodegenerative disorders. J. Neuroimmunol. 2019, 328, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Sun, B.; Yu, D.; Zhu, C. Gut microbiota: An important player in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 834485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Li, G.; Huang, P.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, B. The gut microbiota and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 58, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorboni, S.G.; Moghaddam, H.S.; Jafarzadeh-Esfehani, R.; Soleimanpour, S. A comprehensive review on the role of the gut microbiome in human neurological disorders. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2022, 35, e00338-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobby, G.P.; Karaduta, O.; Dusio, G.F.; Singh, M.; Zybailov, B.L.; Arthur, J.M. Chronic kidney disease and the gut microbiome. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2019, 316, F1211–F1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grochowska, M.; Laskus, T.; Radkowski, M. Gut Microbiota in Neurological Disorders. Arch. Med. Sci. 2019, 15, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strandwitz, P. Neurotransmitter modulation by the gut microbiota. Brain Res. 2018, 1693, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, J.A.; Forsythe, P.; Chew, M.V.; Escaravage, E.; Savignac, H.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Ingestion of Lactobacillus strain regulates emotional behavior and central GABA receptor expression in a mouse via the vagus nerve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16050–16055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naufel, M.F.; de Martin Truzzi, G.; Ferreira, C.M.; Coelho, F.M.S. The brain-gut-microbiota axis in the treatment of neurologic and psychiatric disorders. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2023, 81, 670–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dezfouli, M.A.; Rashidi, S.K.; Yazdanfar, N.; Khalili, H.; Goudarzi, M.; Saadi, A.; Kiani Deh Kiani, A. The emerging roles of neuroactive components produced by gut microbiota. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2025, 52, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varesi, A.; Pierella, E.; Romeo, M.; Piccini, G.B.; Alfano, C.; Bjørklund, G.; Oppong, A.; Ricevuti, G.; Esposito, C.; Chirumbolo, S.; et al. The potential role of gut microbiota in Alzheimer’s disease: From diagnosis to treatment. Nutrients 2022, 14, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, A.; Prabhavalkar, K.S.; Bhatt, L.K. Gastrointestinal hormones in regulation of memory. Peptides 2018, 102, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistollato, F.; Sumalla Cano, S.; Elio, I.; Masias Vergara, M.; Giampieri, F.; Battino, M. Role of gut microbiota and nutrients in amyloid formation and pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease. Nutr. Rev. 2016, 74, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicks, L.M. Gut bacteria and neurotransmitters. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vannier, N.; Agler, M.; Hacquard, S. Microbiota-mediated disease resistance in plants. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeligowski, T.; Yun, A.L.; Lennox, B.R.; Burnet, P.W.J. The gut microbiome and schizophrenia: The current state of the field and clinical applications. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.E.; Teixeira, A.L. Inflammation in psychiatric disorders: What comes first? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2018, 1437, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, B.D.; Daskalakis, Z.J.; Carvalho, A.F.; Strawbridge, R.; Young, A.H.; Mulsant, B.H.; Husain, M.I. Inflammation as a treatment target in mood disorders. BJPsych Open 2020, 6, e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenblat, J.D.; Kakar, R.; Berk, M.; Kessing, L.V.; Vinberg, M.; Baune, B.T.; McIntyre, R.S. Anti-inflammatory agents in the treatment of bipolar depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Bipolar Disord. 2016, 18, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haroon, E.; Miller, A.H.; Sanacora, G. Inflammation, glutamate, and glia: A trio of trouble in mood disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 42, 193–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liang, X.; Jiang, M.; Wei, L.; Shi, X.; Fang, F.; Cang, J. Systemic inflammation as a mediator in the link between obesity and depression: Evidence from a nationwide cohort study. BMC Psychiatry 2025, 25, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodes, G.E.; Pfau, M.L.; Leboeuf, M.; Golden, S.A.; Christoffel, D.J.; Bregman, D.; Rebusi, N.; Heshmati, M.; Aleyasin, H.; Warren, B.L.; et al. Individual differences in the peripheral immune system promote resilience versus susceptibility to social stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 16040–16045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, M.I.; Strawbridge, R.; Stokes, P.R.; Young, A.H. Anti-inflammatory treatments for mood disorders: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Psychopharmacol. 2017, 31, 1137–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Yu, Y.; Bai, F.; Wang, L.; Yang, D.; Zhang, C.; Qin, C.; Yang, M.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Effect of fecal microbiota transplantation on neurological restoration in a spinal cord injury mouse model: Involvement of brain-gut axis. Microbiome 2021, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Zhu, M.; Yan, X.; Cheng, Y.; Shao, L.; Liu, X.; Jiang, R.; Wu, S. Structural and functional dysbiosis of fecal microbiota in Chinese patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 634069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Generoso, J.S.; Giridharan, V.V.; Lee, J.; Macedo, D.; Barichello, T. The role of the microbiota-gut-brain axis in neuropsychiatric disorders. Braz. J. Psychiatry 2020, 43, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, D.; Upadhayay, S.; Dhureja, M.; Arthur, R.; Kumar, P. Crosstalk between gut–brain axis: Unveiling the mysteries of gut ROS in progression of Parkinson’s disease. Inflammopharmacology 2024, 32, 2921–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmes, L.; Collins, J.M.; O’Riordan, K.J.; O’Mahony, S.M.; Cryan, J.F.; Clarke, G. Of bowels, brain and behavior: A role for the gut microbiota in psychiatric comorbidities in irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2021, 33, e14095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moser, G.; Fournier, C.; Peter, J. Intestinal microbiome-gut-brain axis and irritable bowel syndrome. Wien. Med. Wochenschr. 2017, 168, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Kasper, L.H. The role of microbiome in central nervous system disorders. Brain Behav. Immun. 2014, 38, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, J.A.; McVey Neufeld, K. Gut–brain axis: How the microbiome influences anxiety and depression. Trends Neurosci. 2013, 36, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, E.A.; Knight, R.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Cryan, J.F.; Tillisch, K. Gut microbes and the brain: Paradigm shift in neuroscience. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 15490–15496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Fu, Y.; Cao, W.T.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Jiang, Z.; Jia, X.; Liu, C.-Y.; Lin, H.-R.; Zhong, H.; et al. Gut microbiome, cognitive function and brain structure: A multi-omics integration analysis. Transl. Neurodegener. 2022, 11, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairamian, D.; Sha, S.; Rolhion, N.; Sokol, H.; Dorothée, G.; Lemere, C.A.; Krantic, S. Microbiota in neuroinflammation and synaptic dysfunction: A focus on Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2022, 17, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasser, C.I.; Mercieca, E.C.; Kong, G.; Hannan, A.J.; McKeown, S.J.; Glikmann-Johnston, Y.; Stout, J.C. Gut dysbiosis in Huntington’s disease: Associations among gut microbiota, cognitive performance and clinical outcomes. Brain Commun. 2020, 2, fcaa110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Kosciolek, T.; Maldonado, Y.; Daly, R.E.; Martin, A.S.; McDonald, D.; Knight, R. Differences in gut microbiome composition between persons with chronic schizophrenia and healthy comparison subjects. Schizophr. Res. 2018, 204, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.P.; Easson, C.; Lyle, S.M.; Kapoor, R.; Donnelly, C.P.; Davidson, E.J.; Ross, T.M. Gut microbiome diversity is associated with sleep physiology in humans. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miri, S.; Yeo, J.; Abubaker, S.; Hammami, R. Neuromicrobiology, an emerging neurometabolic facet of the gut microbiome? Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1098412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glinert, A.; Turjeman, S.; Elliott, E.; Koren, O. Microbes, metabolites and (synaptic) malleability, oh my! The effect of the microbiome on synaptic plasticity. Biol. Rev. 2022, 97, 582–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, L.; Whyte, A.; Duysburgh, C.; Marzorati, M.; Van den Abbeele, P.; Le Cozannet, R.; Fança-Berthon, P.; Fromentin, E.; Williams, C. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial investigating the acute and chronic benefits of American Ginseng (Cereboost®) on mood and cognition in healthy young adults, including in vitro investigation of gut microbiota changes as a possible mechanism of action. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Han, Y.; Du, J.; Liu, R.; Jin, K.; Yi, W. Microbiota-gut-brain axis and the central nervous system. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 53829–53838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, E.Y.; McBride, S.W.; Hsien, S.; Sharon, G.; Hyde, E.R.; McCue, T.; Codelli, J.A.; Chow, J.; Reisman, S.E.; Petrosino, J.F.; et al. Microbiota modulate behavioral and physiological abnormalities associated with neurodevelopmental disorders. Cell 2013, 155, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijtz, R.D.; Wang, S.; Anuar, F.; Qian, Y.; Björkholm, B.; Samuelsson, A.; Hibberd, M.L.; Forssberg, H.; Pettersson, S. Normal gut microbiota modulates brain development and behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3047–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, T.; Bäckhed, F. The gut microbiota and metabolic disease: Current understanding and future perspectives. J. Intern. Med. 2016, 280, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, K.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Gut microbiota: A perspective for psychiatrists. Neuropsychobiology 2020, 79, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce-Keller, A.J.; Salbaum, J.M.; Berthoud, H.R. Harnessing Gut Microbes for Mental Health: Getting from Here to There. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 83, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, K.; Thuret, S. Gut Microbiota: A Modulator of Brain Plasticity and Cognitive Function in Ageing. Healthcare 2015, 3, 898–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, C.T.; Sharma, V.; Elmén, L.; Peterson, S.N. Immune homeostasis, dysbiosis and therapeutic modulation of the gut microbiota. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 179, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmajerová, M.; Ježková, J.; Kreisinger, J.; Semerád, J.; Titov, I.; Procházková, P.; Cajthaml, T.; Jiřička, V.; Vevera, J.; Roubalová, R. Gut microbiome in impulsively violent female convicts. Neuropsychobiology 2025, 84, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dam, S.A.; Mostert, J.C.; Szopinska-Tokov, J.W.; Bloemendaal, M.; Amato, M.; Arias-Vasquez, A. The Role of the Gut-Brain Axis in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Gastroenterology Clinics 2019, 48, 407–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fineberg, N.A.; Chamberlain, S.R.; Goudriaan, A.E.; Stein, D.J.; Vanderschuren, L.J.; Gillan, C.M.; Shekar, S.; Gorwood, P.A.P.M.; Voon, V.; Morein-Zamir, S.; et al. New Developments in Human Neurocognition: Clinical, Genetic, and Brain Imaging Correlates of Impulsivity and Compulsivity. CNS Spectr. 2014, 19, 69–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Mahony, S.M. The Microbiome-Gut-Brain Axis: From Bowel to Behavior. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 23, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günüç, S.; Şendemir, A. Cognitive, Emotional, Behavioral and Physiological Evaluation of the Relationship Between Brain and Gut Microbiota. Psikiyatr. Güncel Yaklaşımlar 2022, 14, 446–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Cabrerizo, R.; Carbia, C.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Schellekens, H.; Cryan, J.F. Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis as a Regulator of Reward Processes. J. Neurochem. 2021, 157, 1495–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Guan, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Yan, Y.; He, M. Gut microbiota deficiency aggravates arsenic-induced toxicity by affecting bioaccumulation and biotransformation in C57BL/6J mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2024, 186, 114564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulder, D.; Aarts, E.; Arias Vasquez, A.; Bloemendaal, M. A Systematic Review Exploring the Association Between the Human Gut Microbiota and Brain Connectivity in Health and Disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 5037–5061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homer, B.; Judd, J.; Mohammadi Dehcheshmeh, M.; Ebrahimie, E.; Trott, D.J. Gut Microbiota and Behavioural Issues in Production, Performance, and Companion Animals: A Systematic Review. Animals 2023, 13, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, V.L.; Richards, J.B.; Meyer, P.J.; Cabrera-Rubio, R.; Tripi, J.A.; King, C.P.; Polesskaya, O.; Baud, A.; Chitre, A.S.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.; et al. Sex-Dependent Associations Between Addiction-Related Behaviors and the Microbiome in Outbred Rats. eBioMedicine 2020, 55, 102769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.D.; Chen, J.; Hoffmann, C.; Bittinger, K.; Chen, Y.Y.; Keilbaugh, S.A.; Bewtra, M.; Knights, D.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R.; et al. Linking Long-Term Dietary Patterns with Gut Microbial Enterotypes. Science 2011, 334, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.; Cheng, J.; Wei, Q.; Pan, R.; Song, S.; He, Y.; Tang, C.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Su, H. Effect of Temperature Stress on Gut-Brain Axis in Mice: Regulation of Intestinal Microbiome and Central NLRP3 Inflammasomes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 144568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, D.; Shorten, G.D.; O’Mahony, S.M. Postoperative Pain and the Gut Microbiome. Neurobiol. Pain 2021, 10, 100070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.M.; Al-Nakkash, L.; Herbst-Kralovetz, M.M. Estrogen–Gut Microbiome Axis: Physiological and Clinical Implications. Maturitas 2017, 103, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matenchuk, B.A.; Mandhane, P.J.; Kozyrskyj, A.L. Sleep, Circadian Rhythm, and Gut Microbiota. Sleep Med. Rev. 2020, 53, 101340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, R.M.; Forsyth, C.B.; Green, S.J.; Mutlu, E.; Engen, P.; Vitaterna, M.H.; Turek, F.W.; Keshavarzian, A. Circadian Disorganization Alters Intestinal Microbiota. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, C.; Guo, S.; Hu, S.; Chen, J.; Ye, M.; Liu, Z.; Su, H. The Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis and Its Modulation in the Therapy of Depression: Comparison of Efficacy of Conventional Drugs and Traditional Chinese Medicine Approaches. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 183, 106372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widhiati, S.; Purnomosari, D.; Wibawa, T.; Soebono, H. The Role of Gut Microbiome in Inflammatory Skin Disorders: A Systematic Review. Dermatol. Rep. 2021, 14, 9188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhernakova, A.; Kurilshikov, A.; Bonder, M.J.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; Schirmer, M.; Vatanen, T.; Mujagic, Z.; Vila, A.V.; Falony, G.; Vieira-Silva, S.; et al. Population-Based Metagenomics Analysis Reveals Markers for Gut Microbiome Composition and Diversity. Science 2016, 352, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkar, S.G.; Kalsbeek, A.; Cheeseman, J.F. Potential Role for the Gut Microbiota in Modulating Host Circadian Rhythms and Metabolic Health. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qamar, A.; Waheed, J.; Hamza, A.; Mohyuddin, S.G.; Lu, Z.; Namula, Z.; Chen, J.J. The Role of Intestinal Microbiota in Chicken Health, Intestinal Physiology and Immunity. JAPS J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2021, 31, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Tang, R.; Li, B.; Ma, X.; Schnabl, B.; Tilg, H. Gut Microbiome, Liver Immunology, and Liver Diseases. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henao-Mejia, J.; Elinav, E.; Thaiss, C.A.; Licona-Limon, P.; Flavell, R.A. Role of the Intestinal Microbiome in Liver Disease. J. Autoimmun. 2013, 46, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forouzan, S.; McGrew, K.; Kosten, T.A. Drugs and Bugs: Negative Affect, Psychostimulant Use and Withdrawal, and the Microbiome. Am. J. Addict. 2021, 30, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, J.T.; Zhou, Y.; Weinstock, G.M.; Bubier, J.A. The Gut Microbiome and Substance Use Disorder. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 725500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, B.D.; Kirkland, A.E.; Green, R.; Engevik, M.; Alekseyenko, A.V.; Leggio, L.; Tomko, R.L.; Squeglia, L.M. The Adolescent and Young Adult Microbiome and Its Association with Substance Use: A Scoping Review. Alcohol Alcoholism 2024, 59, agad055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molavi, N.; Rasouli-Azad, M.; Mirzaei, H.; Matini, A.H.; Banafshe, H.R.; Valiollahzadeh, M.; Ghaderi, A. The Effects of Probiotic Supplementation on Opioid-Related Disorder in Patients under Methadone Maintenance Treatment Programs. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2022, 2022, 1206914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Chen, T.; Cai, J.; Liu, B.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, X. The Microbiome–Gut–Brain Axis, a Potential Therapeutic Target for Substance-Related Disorders. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 738401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Lotfipour, S. The Role of the Gut Microbiome in Opioid Use. Behav. Pharmacol. 2020, 31, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Liang, Q.; Balakrishnan, B.; Belobrajdic, D.P.; Feng, Q.J.; Zhang, W. Role of Dietary Nutrients in the Modulation of Gut Microbiota: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egerton, S.; Culloty, S.; Whooley, J.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P.; O’Sullivan, L. The Gut Microbiota of Marine Fish. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, A.; Inoue, R.; Inatomi, O.; Bamba, S.; Naito, Y.; Andoh, A. Gut Microbiota in the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cukrowska, B. Microbial and Nutritional Programming—The Importance of the Microbiome and Early Exposure to Potential Food Allergens in the Development of Allergies. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.Y.; Groer, M.; Dutra, S.V.O.; Sarkar, A.; McSkimming, D.I. Gut Microbiota and Immune System Interactions. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angoa-Pérez, M.; Zagorac, B.; Winters, A.D.; Greenberg, J.M.; Ahmad, M.; Theis, K.R.; Kuhn, D.M. Differential Effects of Synthetic Psychoactive Cathinones and Amphetamine Stimulants on the Gut Microbiome in Mice. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barengolts, E.; Green, S.J.; Eisenberg, Y.; Akbar, A.; Reddivari, B.; Layden, B.T.; Dugas, L.; Chlipala, G. Gut Microbiota Varies by Opioid Use, Circulating Leptin and Oxytocin in African American Men with Diabetes and High Burden of Chronic Disease. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Sullivan, A.; Monk, C. Maternal and Environmental Influences on Perinatal and Infant Development. Future Child. 2020, 30, 11–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull-Otterson, L.; Feng, W.; Kirpich, I.; Wang, Y.; Qin, X.; Liu, Y.; Gobejishvili, L.; Joshi-Barve, S.; Ayvaz, T.; Petrosino, J.; et al. Metagenomic Analyses of Alcohol Induced Pathogenic Alterations in the Intestinal Microbiome and the Effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Treatment. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malan-Muller, S.; Valles-Colomer, M.; Raes, J.; Lowry, C.A.; Seedat, S.; Hemmings, S.M. The Gut Microbiome and Mental Health: Implications for Anxiety- and Trauma-Related Disorders. Omics 2018, 22, 90–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couch, C.E.; Epps, C.W. Host, Microbiome, and Complex Space: Applying Population and Landscape Genetic Approaches to Gut Microbiome Research in Wild Populations. J. Hered. 2022, 113, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothschild, D.; Weissbrod, O.; Barkan, E.; Kurilshikov, A.; Korem, T.; Zeevi, D.; Costea, P.I.; Godneva, A.; Kalka, I.N.; Bar, N.; et al. Environment Dominates over Host Genetics in Shaping Human Gut Microbiota. Nature 2018, 555, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassour, M.; Vatanen, T.; Siljander, H.; Hämäläinen, A.M.; Härkönen, T.; Ryhänen, S.J.; Franzosa, E.A.; Vlamakis, H.; Huttenhower, C.; Gevers, D.; et al. Natural History of the Infant Gut Microbiome and Impact of Antibiotic Treatment on Bacterial Strain Diversity and Stability. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 343ra81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, L.; Pruteanu, M.; Kuhn, M.; Zeller, G.; Telzerow, A.; Anderson, E.E.; Brochado, A.R.; Fernandez, K.C.; Dose, H.; Mori, H.; et al. Extensive Impact of Non-Antibiotic Drugs on Human Gut Bacteria. Nature 2018, 555, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymann, K.; Shaffer, Z.; Moran, N.A. Antibiotic Exposure Perturbs the Gut Microbiota and Elevates Mortality in Honeybees. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2001861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takami, M.; Aoi, W.; Matsumoto, K.; Kato, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Kuwahata, M. High-Intensity Exercise Impairs Intestinal Barrier Function by Generating Oxidative Stress. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2023, 74, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegierska, A.E.; Charitos, I.A.; Topi, S.; Potenza, M.A.; Montagnani, M.; Santacroce, L. The Connection Between Physical Exercise and Gut Microbiota: Implications for Competitive Sports Athletes. Sports Med. 2022, 52, 2355–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmytriv, T.R.; Storey, K.B.; Lushchak, V.I. Intestinal Barrier Permeability: The Influence of Gut Microbiota, Nutrition, and Exercise. Front. Physiol. 2024, 15, 1380713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, J.P.; Bernard, J.R.; Hsu, H.C.; Hsu, C.L.; Liao, S.F.; Cheng, I.S. Short-Term Oral Quercetin Supplementation Improves Post-Exercise Insulin Sensitivity, Antioxidant Capacity and Enhances Subsequent Cycling Time to Exhaustion in Healthy Adults: A Pilot Study. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 875319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauter, A.; Epping, L.; Semmler, T.; Antao, E.M.; Kannapin, D.; Stoeckle, S.D.; Gehlen, H.; Lübke-Becker, A.; Günther, S.; Wieler, L.H.; et al. The Gut Microbiome of Horses: Current Research on Equine Enteral Microbiota and Future Perspectives. Anim. Microbiome 2019, 1, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, S.G.; Ferrari, F.; Ciebiera, M.; Zgliczyńska, M.; Rapisarda, A.M.C.; Vecchio, G.M.; Pino, A.; Angelico, G.; Knafel, A.; Riemma, G.; et al. The Role of Genital Tract Microbiome in Fertility: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloor, G.B.; Macklaim, J.M.; Pawlowsky-Glahn, V.; Egozcue, J.J. Microbiome Datasets Are Compositional: And This Is Not Optional. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libiger, O.; Schork, N.J. Partial Least Squares Regression Can Aid in Detecting Differential Abundance of Multiple Features in Sets of Metagenomic Samples. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Pedersen, O. Gut Microbiota in Human Metabolic Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Yang, Z.; Lu, N. Imbalance of Gastrointestinal Microbiota in the Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori-Associated Diseases. Helicobacter 2016, 21, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.L. Defining Gardnerella spp. Diversity, Phenotypes, and Ecological Roles in the Vaginal Microbiome. Ph.D. Thesis, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Santiago-Rodriguez, T.M.; Le François, B.; Macklaim, J.M.; Doukhanine, E.; Hollister, E.B. The Skin Microbiome: Current Techniques, Challenges, and Future Directions. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yang, Y. Gut Microbiome and Its Meta-Omics Perspectives: Profound Implications for Cardiovascular Diseases. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1936379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzosa, E.A.; Hsu, T.; Sirota-Madi, A.; Shafquat, A.; Abu-Ali, G.; Morgan, X.C.; Huttenhower, C. Sequencing and Beyond: Integrating Molecular ‘Omics’ for Microbial Community Profiling. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Armour, C.R.; Hu, C.; Mei, M.; Tian, C.; Sharpton, T.J.; Jiang, Y. Microbiome Multi-Omics Network Analysis: Statistical Considerations, Limitations, and Opportunities. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Indias, I.; Lahti, L.; Nedyalkova, M.; Elbere, I.; Roshchupkin, G.; Adilovic, M.; Aydemir, O.; Bakir-Gungor, B.; Pau, E.C.-D.S.; D’eLia, D.; et al. Statistical and Machine Learning Techniques in Human Microbiome Studies: Contemporary Challenges and Solutions. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 635781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nasiry, S.; Ambrosino, E.; Schlaepfer, M.; Morré, S.A.; Wieten, L.; Voncken, J.W.; Spinelli, M.; Mueller, M.; Kramer, B.W. The Interplay Between Reproductive Tract Microbiota and Immunological System in Human Reproduction. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzenpichler, R.; Krukenberg, V.; Spietz, R.L.; Jay, Z.J. Next-Generation Physiology Approaches to Study Microbiome Function at Single Cell Level. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.M.; Le, S.M.; Wilson, A.E.; Warner, D.A. The Microbiome as a Maternal Effect: A Systematic Review on Vertical Transmission of Microbiota. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2023, 63, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Fang, X.; Zhong, Q.; Liao, Z.; Wang, L. Colonization Potential to Reconstitute a Microbe Community in Pseudo Germ-Free Mice After Fecal Microbe Transplant from Equol Producer. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Kim, J.; Kim, D. Orally Administered Antibiotics Vancomycin and Ampicillin Cause Cognitive Impairment with Gut Dysbiosis in Mice with Transient Global Forebrain Ischemia. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 564271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tengeler, A.; Emmerzaal, T.; Geenen, B.; Verweij, V.; Bodegom, M.; Morava, E.; Kozicz, T. Early-Adolescent Antibiotic Exposure Results in Mitochondrial and Behavioral Deficits in Adult Male Mice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Eun, C.; Jo, S.; Lee, A.; Park, C.; Han, D. The Impact of Gut Microbiota Manipulation with Antibiotics on Colon Tumorigenesis in a Murine Model. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagga, D.; Reichert, J.; Koschutnig, K.; Aigner, C.; Holzer, P.; Koskinen, K.; Schöpf, V. Probiotics Drive Gut Microbiome Triggering Emotional Brain Signatures. Gut Microbes 2018, 9, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, S.W.; Barnett, M.L.; MacFadden, D.R.; Lipsitch, M.; Grad, Y.H. Trends in Outpatient Antibiotic Use and Prescribing Practice Among US Older Adults, 2011–2015: Observational Study. BMJ 2018, 362, k3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammarota, G.; Ianiro, G.; Gasbarrini, A. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation for the Treatment of Clostridium difficile Infection: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 48, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuck, C.J.; Caminero, A.; Jiménez Vargas, N.N.; Soltys, C.L.; Jaramillo Polanco, J.O.; Lopez Lopez, C.D.; Vanner, S.J. The Impact of Dietary Fermentable Carbohydrates on a Postinflammatory Model of Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 31, e13675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheppach, W.; Luehrs, H.; Menzel, T. Beneficial Health Effects of Low-Digestible Carbohydrate Consumption. Br. J. Nutr. 2001, 85 (Suppl. S1), S23–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mefferd, C.C.; Bhute, S.S.; Phan, J.R.; Villarama, J.V.; Do, D.M.; Alarcia, S.; Hedlund, B.P. A High-Fat/High-Protein, Atkins-Type Diet Exacerbates Clostridioides (Clostridium) difficile Infection in Mice, Whereas a High-Carbohydrate Diet Protects. mSystems 2020, 5, e00765-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Gupta, D.; Mehrotra, R.; Mago, P. Psychobiotics: The Next-Generation Probiotics for the Brain. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 449–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Walton, D.; O’Connor, C.; Wammes, M.; Burton, J.; Osuch, E. Drugs, Guts, Brains, but Not Rock and Roll: The Need to Consider the Role of Gut Microbiota in Contemporary Mental Health and Wellness of Emerging Adults. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehin, S.; Caron, P.; Cespuglio, R. Psychobiotics as Modulators of Gut-Brain Influences. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2022, 45, 36373–36380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanavel, S. Psychobiotics: The Latest Psychotropics. Indian J. Psychol. Med. 2015, 37, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anker-Ladefoged, C.; Langkamp, T.; Mueller-Alcazar, A. The Potential Impact of Selected Bacterial Strains on the Stress Response. Healthcare 2021, 9, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabbir, M.; Mehak, F.; Khan, Z.; Ahmed, W.; Abrar-ul-Haq, S.; Khan, M.; Aadil, R. Delving the Role of Nutritional Psychiatry to Mitigate the COVID-19 Pandemic Induced Stress, Anxiety and Depression. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 120, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccariello, E.; Nguyen, T. Microbes and Geriatric Mental Health: Past, Present, and Future. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2021, 34, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacka, F. Nutritional Psychiatry: Where to Next? EBioMedicine 2017, 17, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peirce, J.; Alviña, K. The Role of Inflammation and the Gut Microbiome in Depression and Anxiety. J. Neurosci. Res. 2019, 97, 1223–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameringen, M.; Turna, J.; Patterson, B.; Pipe, A.; Mao, R.; Anglin, R.; Surette, M. The Gut Microbiome in Psychiatry: A Primer for Clinicians. Depress. Anxiety 2019, 36, 1004–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, G.; Keating, D.; Young, R.; Wong, M.-L.; Licinio, J.; Wesselingh, S. From Gut Dysbiosis to Altered Brain Function and Mental Illness: Mechanisms and Pathways. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knippel, R.; Sears, C. The Microbiome Colorectal Cancer Puzzle: Initiator, Propagator, and Avenue for Treatment and Research. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2021, 19, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, V. The Microbiome and Mental Health: Hope or Hype? J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2019, 44, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ademe, M. Benefits of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation: A Comprehensive Review. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2020, 14, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biazzo, M.; Deidda, G. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation as New Therapeutic Avenue for Human Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdier, C.; Denis, S.; Gasc, C.; Boucinha, L.; Uriot, O.; Delmas, D.; Dore, J.; Le Camus, C.; Schwintner, C.; Blanquet-Diot, S. An Oral FMT Capsule as Efficient as an Enema for Microbiota Reconstruction Following Disruption by Antibiotics, as Assessed in an In Vitro Human Gut Model. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, L.; Galley, J.; Hade, E.; Schoppe-Sullivan, S.; Dush, C.; Bailey, M. Gut Microbiome Composition Is Associated with Temperament During Early Childhood. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 45, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flannery, J.; Stagaman, K.; Burns, A.; Hickey, R.; Roos, L.; Giuliano, R.; Sharpton, T. Gut Feelings Begin in Childhood: The Gut Metagenome Correlates with Early Environment, Caregiving, and Behavior. mBio 2020, 11, e02780-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, P.; Xi, C.; Wu, L.; Gao, X.; Hu, S. Gut Microbial Clues to Bipolar Disorder: State-of-the-Art Review of Current Findings and Future Directions. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020, 10, e146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, N.; Bakacs, E.; Combellick, J.; Grigoryan, Z.; Domínguez-Bello, M. The Infant Microbiome Development: Mom Matters. Trends Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraaij, R.; Schuurmans, I.; Radjabzadeh, D.; Tiemeier, H.; Dinan, T.; Uitterlinden, A.; Cecil, C. The Gut Microbiome and Child Mental Health: A Population-Based Study. Brain Behav. Immun. 2023, 108, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adar, S.; Huffnagle, G.; Curtis, J. The Respiratory Microbiome: An Underappreciated Player in the Human Response to Inhaled Pollutants? Ann. Epidemiol. 2016, 26, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Sharma, P.; Pal, N.; Kumawat, M.; Shubham, S.; Sarma, D.; Nagpal, R. Impact of Environmental Pollutants on Gut Microbiome and Mental Health via the Gut–Brain Axis. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, G.; Letchumanan, V.; Tan, L.; Law, J. Gut Microbiome in Obsessive Compulsive Disorder: Potential of Probiotics as an Adjuvant Therapy. Prog. Microbes Mol. Biol. 2022, 5, a0000272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquivel, M. Probiotics for Mental Health: A Review of Recent Clinical Trials. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2021, 16, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramon-Krauel, M.; Amat-Bou, M.; Serrano, M.; Martinez-Monseny, A.; Lerin, C. Targeting the Gut Microbiome in Prader-Willi Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousa, W.; Chehadeh, F.; Husband, S. Recent Advances in Understanding the Structure and Function of the Human Microbiome. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 825338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, M.; Druss, B.; Horvitz-Lennon, M.; Norquist, G.; Ptakowski, K.; Brinkley, A.; Dixon, L. Mental Health Policy in the Era of COVID-19. Psychiatr. Serv. 2020, 71, 1158–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, K.; Blashki, G.; Wiseman, J.; Burke, S.; Reifels, L. Climate Change and Mental Health: Risks, Impacts and Priority Actions. Int. J. Ment. Health Syst. 2018, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, B.; Santoro, N.; Kaplan, R.; Qi, Q. Spotlight on the Gut Microbiome in Menopause: Current Insights. Int. J. Women’s Health 2022, 14, 1059–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagbosu, C.; Nadler, E.; Levy, S.; Hourigan, S. The Role of the Gut Microbiome in Pediatric Obesity and Bariatric Surgery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, L.; Berg, G.; Cernava, T.; Champomier-Vergès, M.; Charles, T.; Cocolin, L.; Sessitsch, A. Microbiome Ethics, Guiding Principles for Microbiome Research, Use and Knowledge Management. Environ. Microbiome 2022, 17, 50. [Google Scholar]
- Nazaroff, W.W. Embracing Microbes in Exposure Science. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2018, 29, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainz, T.; Pignataro, V.; Bonifazi, D.; Ravera, S.; Mellado, M.; Pérez-Martínez, A.; Calvo, C. Human Microbiome in Children, at the Crossroad of Social Determinants of Health and Personalized Medicine. Children 2021, 8, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagerty, S.; Hutchison, K.; Lowry, C.; Bryan, A. An Empirically Derived Method for Measuring Human Gut Microbiome Alpha Diversity: Demonstrated Utility in Predicting Health-Related Outcomes Among a Human Clinical Sample. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, P.J.; Murphy, A.B.; Cryan, J.F.; Ross, P.R.; Dinan, T.G.; Stanton, C. Microbiome in Brain Function and Mental Health. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 57, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieder, R.; Wisniewski, P.J.; Alderman, B.L.; Campbell, S.C. Microbes and Mental Health: A Review. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 66, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padilla, A.B.; Sahai, S.; Pizarro, R.R.; Añonuevo, J.J.J.; Enamno, K. Human microbiome and mental health. In Human Microbiome Drug Targets; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025; pp. 55–68. [Google Scholar]
- Buffington, S.A.; Di Prisco, G.V.; Auchtung, T.A.; Ajami, N.J.; Petrosino, J.F.; Costa-Mattioli, M. Microbial Reconstitution Reverses Maternal Diet-Induced Social and Synaptic Deficits in Offspring. Cell 2016, 165, 1762–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
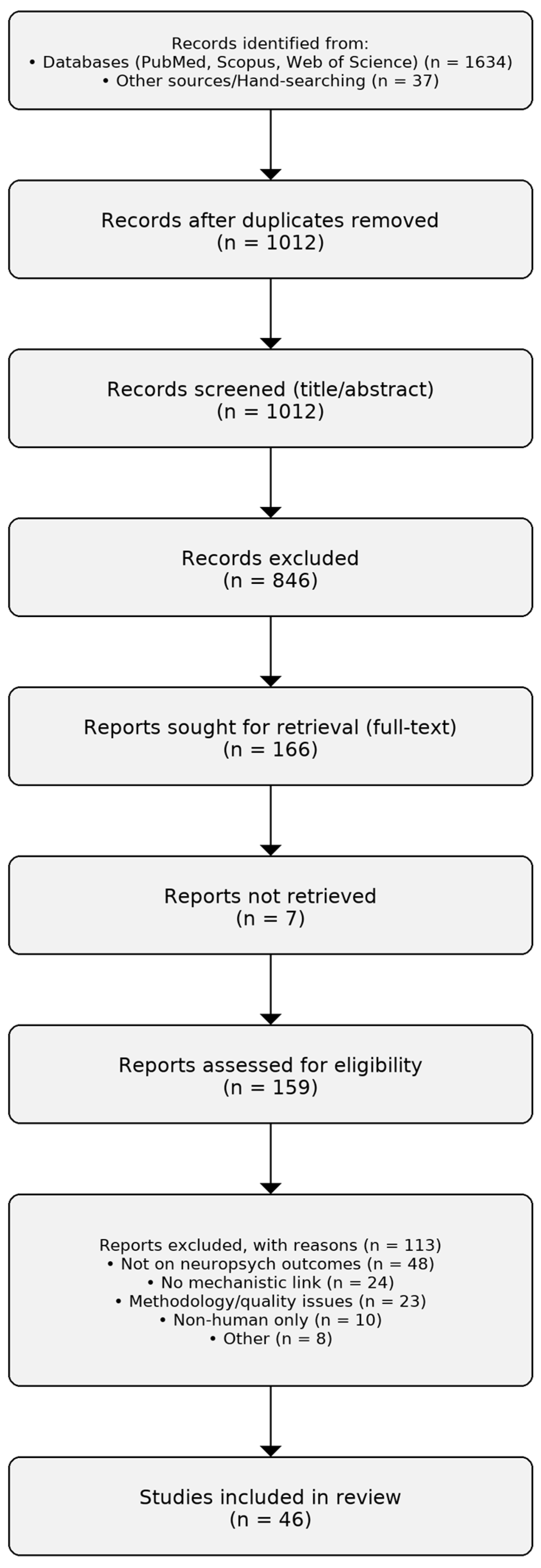
| Category | Exemplar (Strain/Substrate) | Primary Mechanisms | Human Outcome Domains | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probiotic | Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (ATCC 53103) | Barrier reinforcement (tight junctions); HPA-axis attenuation; immunomodulation; GABAergic signaling (preclinical) | Stress/anxiety indicators; mood; gastrointestinal symptoms | [17,18,19,20,21] |
| Probiotic | Lactobacillus plantarum PS128 | Neurotransmitter modulation (dopamine/serotonin, preclinical); anti-inflammatory actions; SCFA shifts | Mood/stress; exercise performance and recovery | [17,18,19,20,21] |
| Probiotic | Bifidobacterium longum 1714 | Vagal signaling; cortisol modulation; attentional/cognitive effects (human experimental evidence) | Perceived stress; attention/memory; mood | [17,18,19,20,21] |
| Probiotic | Saccharomyces boulardii | Barrier/trophic effects; pathogen exclusion; anti-inflammatory pathways | GI symptom improvement; adjunct benefits potentially impacting mood via gut symptom relief | [17,18,19,20,21] |
| Prebiotic | Inulin-type fructans | Bifidogenic effects; fermentation to SCFAs (butyrate); immune modulation | Mood/stress-related measures; GI function; metabolic/inflammatory markers | [52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,61,62] |
| Prebiotic | Galacto-oligosaccharides (GOS) | Bifidogenic; SCFA production; HPA-axis/cortisol modulation (human experimental evidence) | Anxiety- and stress-related measures; attentional bias | [52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,61,62] |
| Prebiotic | Resistant starch (types 2–3) | Marked butyrate production; improved barrier integrity; bile-acid signaling | Stress resilience proxies; metabolic and inflammatory markers; GI function | [52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,61,62] |
| Prebiotic | Arabinoxylans | Fermentation to SCFAs; immunomodulation; bile-acid interactions | Immune/metabolic markers; select mood/stress proxies | [52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,61,62] |
| Prebiotic | β-Glucans | Innate immune modulation (e.g., Dectin-1); SCFA-related effects via co-fermentation | Stress/fatigue; immune function; inflammatory markers | [52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,61,62] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diotaiuti, P.; Misiti, F.; Marotta, G.; Falese, L.; Calabrò, G.E.; Mancone, S. The Gut Microbiome and Its Impact on Mood and Decision-Making: A Mechanistic and Therapeutic Review. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3350. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17213350
Diotaiuti P, Misiti F, Marotta G, Falese L, Calabrò GE, Mancone S. The Gut Microbiome and Its Impact on Mood and Decision-Making: A Mechanistic and Therapeutic Review. Nutrients. 2025; 17(21):3350. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17213350
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiotaiuti, Pierluigi, Francesco Misiti, Giulio Marotta, Lavinia Falese, Giovanna Elisa Calabrò, and Stefania Mancone. 2025. "The Gut Microbiome and Its Impact on Mood and Decision-Making: A Mechanistic and Therapeutic Review" Nutrients 17, no. 21: 3350. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17213350
APA StyleDiotaiuti, P., Misiti, F., Marotta, G., Falese, L., Calabrò, G. E., & Mancone, S. (2025). The Gut Microbiome and Its Impact on Mood and Decision-Making: A Mechanistic and Therapeutic Review. Nutrients, 17(21), 3350. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17213350








