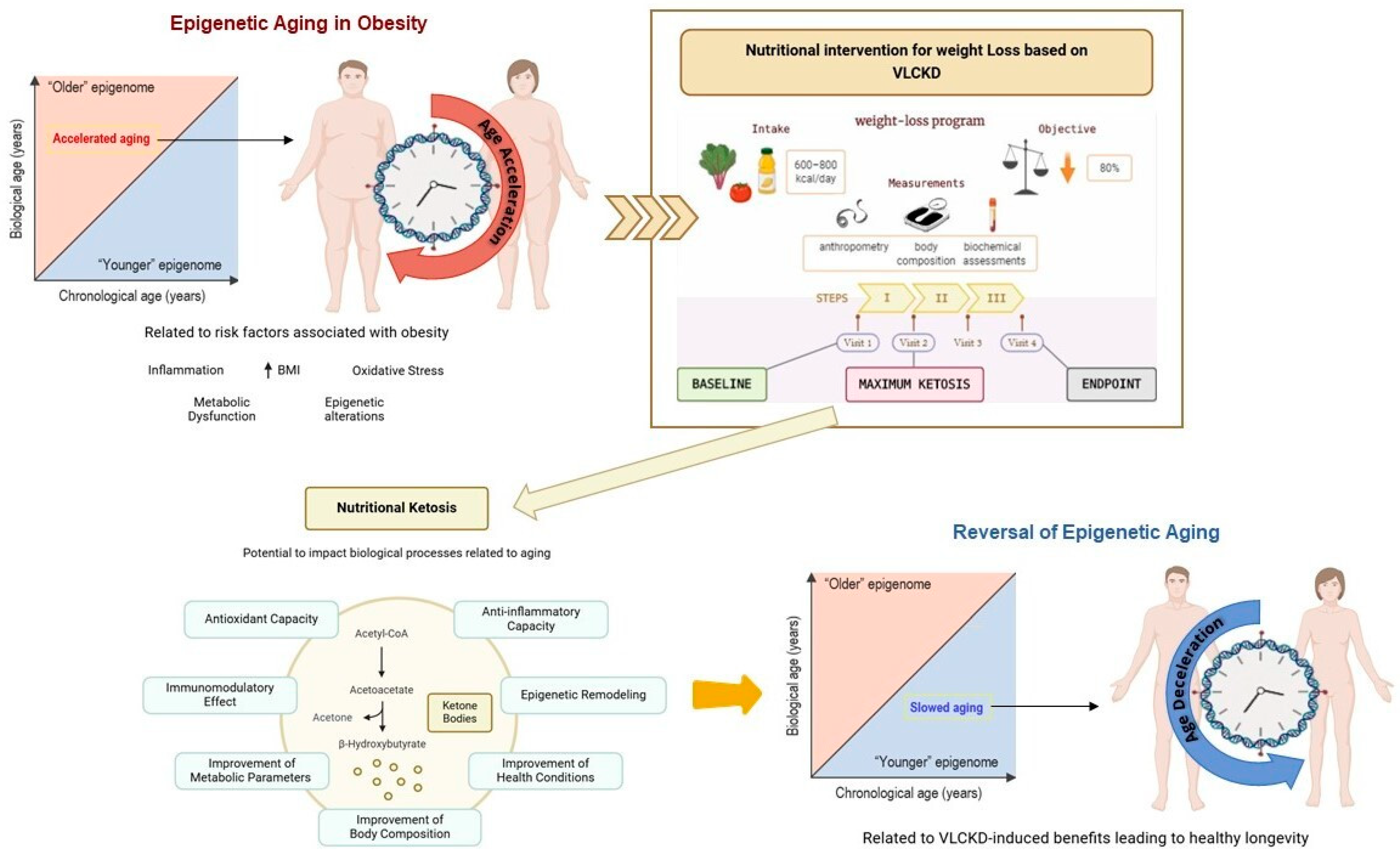
Epigenetic Aging Acceleration in Obesity Is Slowed Down by Nutritional Ketosis Following Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet (VLCKD): A New Perspective to Reverse Biological Age
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Populations
2.2. Blood DNA Methylation Dataset and Epigenetic Age
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Epigenetic Aging Is Accelerated by Obesity and Correlates with BMI
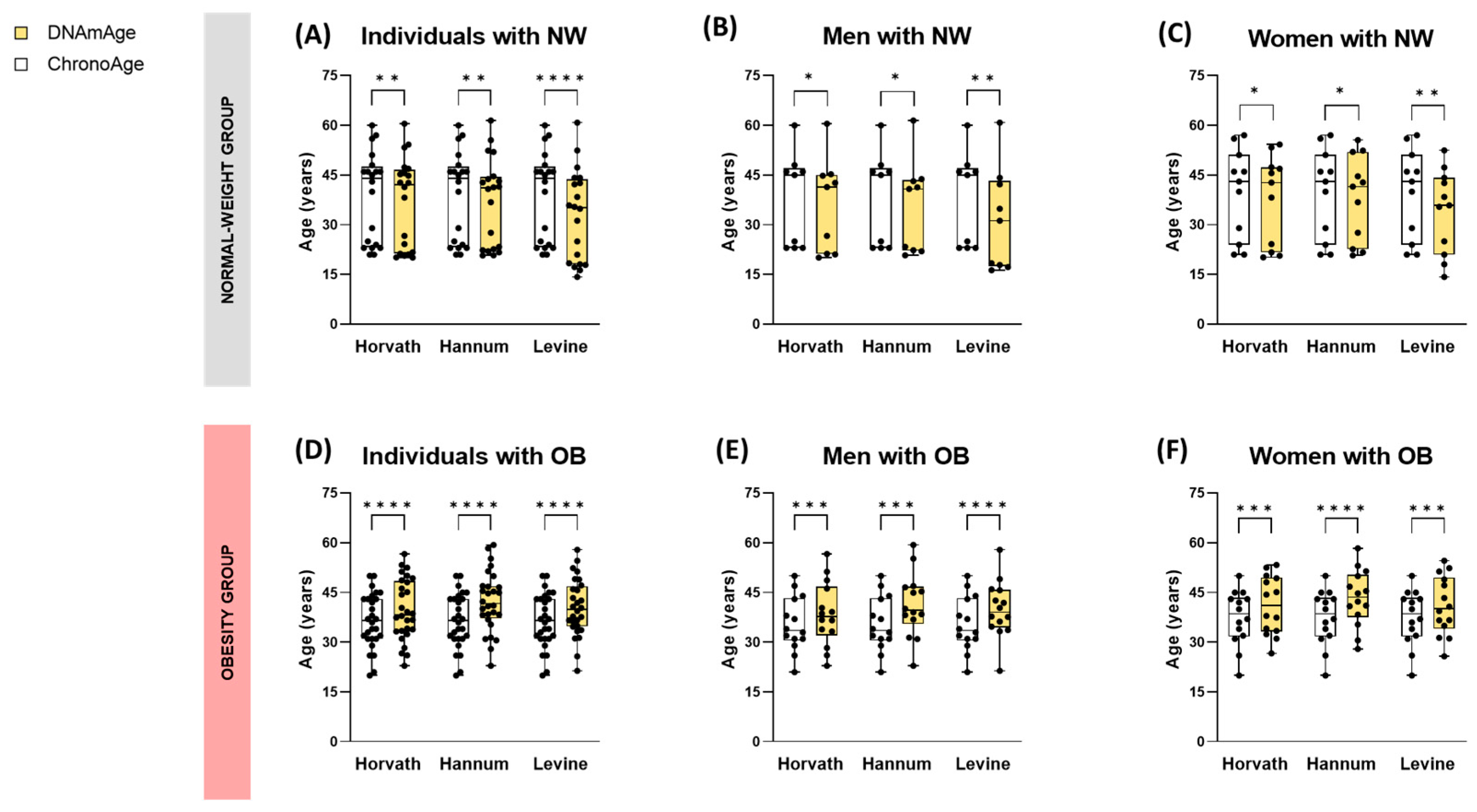
3.1.1. Individuals with Obesity Exhibit Higher Biological Age (DNAmAge) Compared to Healthy Normal-Weight Subjects
3.1.2. Epigenetic Age Acceleration (AgeAccel) in Obesity Is Associated with BMI
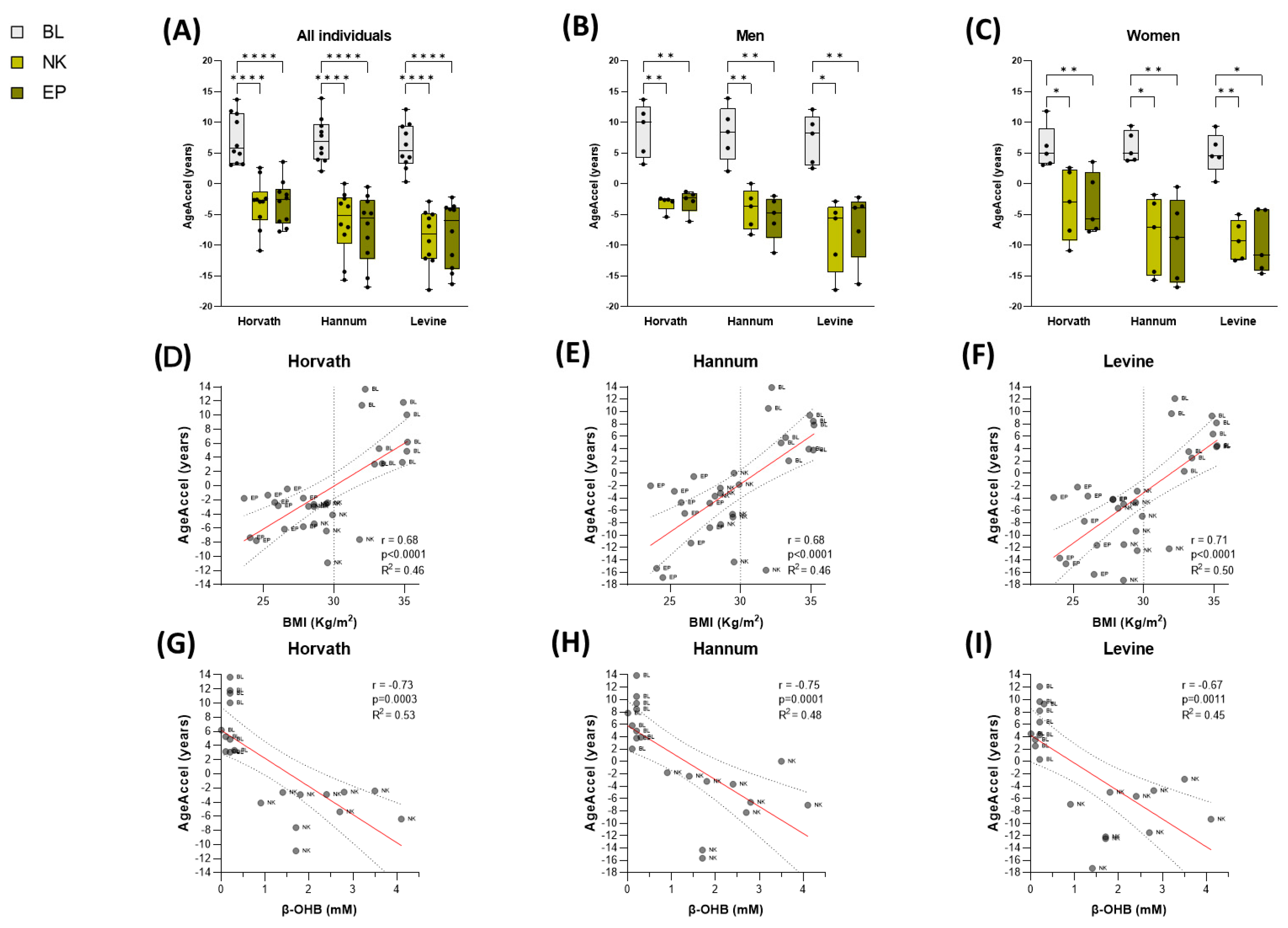
3.2. VLCKD Slows Down Obesity-Associated Epigenetic Aging Through Nutritional Ketosis
3.2.1. DNAmAge Is Reduced in Patients with Obesity Following a Nutritional Body Weight Loss Therapy
3.2.2. DNAmAge Deceleration Is Associated with Nutritional Ketosis and Improvement in Metabolic Health in Patients with Obesity During Diet
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide Trends in Underweight and Obesity from 1990 to 2022: A Pooled Analysis of 3663 Population-Representative Studies with 222 Million Children, Adolescents, and Adults. Lancet 2024, 403, 1027–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blüher, M. Obesity: Global Epidemiology and Pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, H.T.A.; Addo, K.M.; Findlay, H. Public Health Challenges and Responses to the Growing Ageing Populations. Public Health Chall. 2024, 3, e213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Otín, C.; Blasco, M.A.; Partridge, L.; Serrano, M.; Kroemer, G. The Hallmarks of Aging. Cell 2013, 153, 1194–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Otín, C.; Blasco, M.A.; Partridge, L.; Serrano, M.; Kroemer, G. Hallmarks of Aging: An Expanding Universe. Cell 2023, 186, 243–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannini, D.R.; Joyce, B.T.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, T.; Liu, L.; Yoon, G.; Huan, T.; Ma, J.; Jacobs, D.R.; Wilkins, J.T.; et al. Epigenetic Age Acceleration and Metabolic Syndrome in the Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults Study. Clin. Epigenet. 2019, 11, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.L.; Sinha, S. Obesity and Aging: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Approaches. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 67, 101268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, B.T.; Morais, J.A.; Santosa, S. Obesity and Ageing: Two Sides of the Same Coin. Obes. Rev. 2020, 21, e12991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jylhävä, J.; Pedersen, N.L.; Hägg, S. Biological Age Predictors. eBioMedicine 2017, 21, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, M.F.; Esteller, M. Epigenetics and Aging: The Targets and the Marks. Trends Genet. 2007, 23, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Leung, D.; Thrush, K.; Zhao, W.; Ratliff, S.; Tanaka, T.; Schmitz, L.L.; Smith, J.A.; Ferrucci, L.; Levine, M.E. Underlying Features of Epigenetic Aging Clocks In Vivo and In Vitro. Aging Cell 2020, 19, e13229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Vallerga, C.L.; Walker, R.M.; Lin, T.; Henders, A.K.; Montgomery, G.W.; He, J.; Fan, D.; Fowdar, J.; Kennedy, M.; et al. Improved Precision of Epigenetic Clock Estimates across Tissues and Its Implication for Biological Ageing. Genome Med. 2019, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, S. DNA Methylation Age of Human Tissues and Cell Types. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannum, G.; Guinney, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, L.; Hughes, G.; Sadda, S.; Klotzle, B.; Bibikova, M.; Fan, J.-B.; Gao, Y.; et al. Genome-Wide Methylation Profiles Reveal Quantitative Views of Human Aging Rates. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, M.E.; Lu, A.T.; Quach, A.; Chen, B.H.; Assimes, T.L.; Bandinelli, S.; Hou, L.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Stewart, J.D.; Li, Y.; et al. An Epigenetic Biomarker of Aging for Lifespan and Healthspan. Aging 2018, 10, 573–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gems, D.; Virk, R.S.; de Magalhães, J.P. Epigenetic Clocks and Programmatic Aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 101, 102546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekola-Ayele, F. Invited Commentary: Epigenetic Clocks and Obesity-Towards the Next Frontier Using Integrative Approaches and Early-Life Models. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 190, 994–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jura, M.; Kozak, L.P. Obesity and Related Consequences to Ageing. Age 2016, 38, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Toro-Martín, J.; Guénard, F.; Tchernof, A.; Hould, F.-S.; Lebel, S.; Julien, F.; Marceau, S.; Vohl, M.-C. Body Mass Index Is Associated with Epigenetic Age Acceleration in the Visceral Adipose Tissue of Subjects with Severe Obesity. Clin. Epigenet. 2019, 11, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, S.; Erhart, W.; Brosch, M.; Ammerpohl, O.; von Schönfels, W.; Ahrens, M.; Heits, N.; Bell, J.T.; Tsai, P.-C.; Spector, T.D.; et al. Obesity Accelerates Epigenetic Aging of Human Liver. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 15538–15543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevalainen, T.; Kananen, L.; Marttila, S.; Jylhävä, J.; Mononen, N.; Kähönen, M.; Raitakari, O.T.; Hervonen, A.; Jylhä, M.; Lehtimäki, T.; et al. Obesity Accelerates Epigenetic Aging in Middle-Aged but Not in Elderly Individuals. Clin. Epigenet. 2017, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etzel, L.; Hastings, W.J.; Hall, M.A.; Heim, C.M.; Meaney, M.J.; Noll, J.G.; O’Donnell, K.J.; Pokhvisneva, I.; Rose, E.J.; Schreier, H.M.C.; et al. Obesity and Accelerated Epigenetic Aging in a High-Risk Cohort of Children. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundgren, S.; Kuitunen, S.; Pietiläinen, K.H.; Hurme, M.; Kähönen, M.; Männistö, S.; Perola, M.; Lehtimäki, T.; Raitakari, O.; Kaprio, J.; et al. BMI Is Positively Associated with Accelerated Epigenetic Aging in Twin Pairs Discordant for Body Mass Index. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 292, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quach, A.; Levine, M.E.; Tanaka, T.; Lu, A.T.; Chen, B.H.; Ferrucci, L.; Ritz, B.; Bandinelli, S.; Neuhouser, M.L.; Beasley, J.M.; et al. Epigenetic Clock Analysis of Diet, Exercise, Education, and Lifestyle Factors. Aging 2017, 9, 419–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, E.; Qualls, C.; Villareal, D.T. Effect of Diet, Exercise, or Both on Biological Age and Healthy Aging in Older Adults with Obesity: Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2022, 26, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.-H. Effect of Modifiable Lifestyle Factors on Biological Aging. JAR Life 2024, 13, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Huan, T.; Joehanes, R.; McKeown, N.M.; Horvath, S.; Levy, D.; Ma, J. Higher Diet Quality Relates to Decelerated Epigenetic Aging. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 115, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruci, A.; Tuccinardi, D.; Tozzi, R.; Balena, A.; Santucci, S.; Frontani, R.; Mariani, S.; Basciani, S.; Spera, G.; Gnessi, L.; et al. Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet: A Safe and Effective Tool for Weight Loss in Patients with Obesity and Mild Kidney Failure. Nutrients 2020, 12, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verde, L.; Barrea, L.; Galasso, M.; Lucà, S.; Camajani, E.; Pisani, A.; Colao, A.; Caprio, M.; Muscogiuri, G. Efficacy and Safety of Phase 1 of Very Low Energy Ketogenic Therapy (VLEKT) in Subjects with Obesity and Mild Renal Impairment. Nutrients 2025, 17, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tragni, E.; Vigna, L.; Ruscica, M.; Macchi, C.; Casula, M.; Santelia, A.; Catapano, A.L.; Magni, P. Reduction of Cardio-Metabolic Risk and Body Weight through a Multiphasic Very-Low Calorie Ketogenic Diet Program in Women with Overweight/Obesity: A Study in a Real-World Setting. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellana, M.; Conte, E.; Cignarelli, A.; Perrini, S.; Giustina, A.; Giovanella, L.; Giorgino, F.; Trimboli, P. Efficacy and Safety of Very Low Calorie Ketogenic Diet (VLCKD) in Patients with Overweight and Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2019, 21, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa, L.L.; Moretti, A.; de Sousa, P.A.M.; Dinis, L.; de Souza, M.F.; Tostes, I.; Nuñez-Garcia, M.; Sajoux, I. Effectiveness and Safety of a Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet on Weight Regain Following Bariatric Surgery. Obes. Surg. 2021, 31, 5383–5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriconi, E.; Camajani, E.; Fabbri, A.; Lenzi, A.; Caprio, M. Very-Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet as a Safe and Valuable Tool for Long-Term Glycemic Management in Patients with Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Nutrients 2021, 13, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muscogiuri, G.; El Ghoch, M.; Colao, A.; Hassapidou, M.; Yumuk, V.; Busetto, L.; Obesity Management Task Force (OMTF) of the European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). European Guidelines for Obesity Management in Adults with a Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes. Facts 2021, 14, 222–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanueva, F.F.; Castellana, M.; Bellido, D.; Trimboli, P.; Castro, A.I.; Sajoux, I.; Rodriguez-Carnero, G.; Gomez-Arbelaez, D.; Crujeiras, A.B.; Martinez-Olmos, M.A. Ketogenic Diets as Treatment of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2020, 21, 381–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crujeiras, A.B.; Izquierdo, A.G.; Primo, D.; Milagro, F.I.; Sajoux, I.; Jácome, A.; Fernandez-Quintela, A.; Portillo, M.P.; Martínez, J.A.; Martinez-Olmos, M.A.; et al. Epigenetic Landscape in Blood Leukocytes Following Ketosis andbody weight loss Induced by a Very Low Calorie Ketogenic Diet (VLCKD) in Patients with Obesity. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 3959–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, P.M.; Sajoux, I.; Izquierdo, A.G.; Gomez-Arbelaez, D.; Zulet, M.A.; Abete, I.; Castro, A.I.; Baltar, J.; Portillo, M.P.; Tinahones, F.J.; et al. Immunomodulatory Effect of a Very-Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet Compared with Bariatric Surgery and a Low-Calorie Diet in Patients with Excessive Body Weight. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 1566–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, S.; Arribas, C.; Esteller, M. Validation of a DNA Methylation Microarray for 850,000 CpG Sites of the Human Genome Enriched in Enhancer Sequences. Epigenomics 2016, 8, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, J.; Heyn, H.; Moran, S.; Serra-Musach, J.; Pujana, M.A.; Bibikova, M.; Esteller, M. Validation of a DNA Methylation Microarray for 450,000 CpG Sites in the Human Genome. Epigenetics 2011, 6, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crujeiras, A.B.; Diaz-Lagares, A.; Sandoval, J.; Milagro, F.I.; Navas-Carretero, S.; Carreira, M.C.; Gomez, A.; Hervas, D.; Monteiro, M.P.; Casanueva, F.F.; et al. DNA Methylation Map in Circulating Leukocytes Mirrors Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Methylation Pattern: A Genome-Wide Analysis from Non-Obese and Obese Patients. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, S.; Gurven, M.; Levine, M.E.; Trumble, B.C.; Kaplan, H.; Allayee, H.; Ritz, B.R.; Chen, B.; Lu, A.T.; Rickabaugh, T.M.; et al. An Epigenetic Clock Analysis of Race/Ethnicity, Sex, and Coronary Heart Disease. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoletti, C.F.; Pinhel, M.A.S.; Diaz-Lagares, A.; Casanueva, F.F.; Jácome, A.; Pinhanelli, V.C.; de Oliveira, B.A.P.; Crujeiras, A.B.; Nonino, C.B. DNA Methylation Screening after Roux-En Y Gastric Bypass Reveals the Epigenetic Signature Stems from Genes Related to the Surgery per Se. BMC Med. Genom. 2019, 12, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraszczyk, E.; Luijten, M.; Spijkerman, A.M.W.; Snieder, H.; Wackers, P.F.K.; Bloks, V.W.; Nicoletti, C.F.; Nonino, C.B.; Crujeiras, A.B.; Buurman, W.A.; et al. The Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Clinical Profile, DNA Methylation, and Ageing in Severely Obese Patients. Clin. Epigenet. 2020, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fransquet, P.D.; Wrigglesworth, J.; Woods, R.L.; Ernst, M.E.; Ryan, J. The Epigenetic Clock as a Predictor of Disease and Mortality Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Epigenet. 2019, 11, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margiotti, K.; Monaco, F.; Fabiani, M.; Mesoraca, A.; Giorlandino, C. Epigenetic Clocks: In Aging-Related and Complex Diseases. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2023, 163, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.-C.; Lillycrop, K.A.; Beilin, L.J.; Godfrey, K.M.; Anderson, D.; Mori, T.A.; Rauschert, S.; Craig, J.M.; Oddy, W.H.; Ayonrinde, O.T.; et al. Epigenetic Age Acceleration in Adolescence Associates with BMI, Inflammation, and Risk Score for Middle Age Cardiovascular Disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 3012–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, C.A.; Barker-Kamps, M.; Goering, M.; Patki, A.; Tiwari, H.K.; Mrug, S. Epigenetic Age Acceleration Correlates with BMI in Young Adults. Aging 2023, 15, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvestrini, V.; Sell, C.; Lorenzini, A. Obesity May Accelerate the Aging Process. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasca, D. Several Areas of Overlap between Obesity and Aging Indicate Obesity as a Biomarker of Accelerated Aging of Human B Cell Function and Antibody Responses. Immun. Ageing 2022, 19, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimazu, T.; Hirschey, M.D.; Newman, J.; He, W.; Shirakawa, K.; Le Moan, N.; Grueter, C.A.; Lim, H.; Saunders, L.R.; Stevens, R.D.; et al. Suppression of Oxidative Stress by β-Hydroxybutyrate, an Endogenous Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor. Science 2013, 339, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanashi, T.; Iwata, M.; Kamiya, N.; Tsunetomi, K.; Kajitani, N.; Wada, N.; Iitsuka, T.; Yamauchi, T.; Miura, A.; Pu, S.; et al. Beta-Hydroxybutyrate, an Endogenic NLRP3 Inflammasome Inhibitor, Attenuates Stress-Induced Behavioral and Inflammatory Responses. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paoli, A.; Bianco, A.; Moro, T.; Mota, J.F.; Coelho-Ravagnani, C.F. The Effects of Ketogenic Diet on Insulin Sensitivity and body weight loss, Which Came First: The Chicken or the Egg? Nutrients 2023, 15, 3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.; Kim, S.R.; Lee, J.E.; Lee, S.; Son, H.J.; Choe, W.; Yoon, K.-S.; Kim, S.S.; Yeo, E.-J.; Kang, I. Molecular Mechanisms of Neuroprotection by Ketone Bodies and Ketogenic Diet in Cerebral Ischemia and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puchalska, P.; Crawford, P.A. Multi-Dimensional Roles of Ketone Bodies in Fuel Metabolism, Signaling, and Therapeutics. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 262–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.P.; Shryack, G.; Alessi, I.; Wieschhaus, N.; Meers, G.M.; Johnson, S.A.; Wheeler, A.A.; Ibdah, J.A.; Parks, E.J.; Rector, R.S. Relationship between Serum β-Hydroxybutyrate and Hepatic Fatty Acid Oxidation in Individuals with Obesity and NAFLD. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 326, E493–E502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, C.G.; Chakraborty, S.; Singh, G.; Yeoh, B.S.; Schreckenberger, Z.J.; Singh, A.; Mell, B.; Bearss, N.R.; Yang, T.; Cheng, X.; et al. Ketone Body β-Hydroxybutyrate Is an Autophagy-Dependent Vasodilator. JCI Insight 2021, 6, 149037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.N.; Wallace, M.A.; Tomilov, A.A.; Zhou, Z.; Marcotte, G.R.; Tran, D.; Perez, G.; Gutierrez-Casado, E.; Koike, S.; Knotts, T.A.; et al. A Ketogenic Diet Extends Longevity and Healthspan in Adult Mice. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 539–546.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astrup, A.; Hjorth, M.F. Ageing: Improvement in Age-Related Cognitive Functions and Life Expectancy by Ketogenic Diets. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 695–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuruta, H.; Yamahara, K.; Yasuda-Yamahara, M.; Kume, S. Emerging Pathophysiological Roles of Ketone Bodies. Physiology 2024, 39, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasser, B.; Wolters, M.; Weyh, C.; Krüger, K.; Ticinesi, A. The Effects of Lifestyle and Diet on Gut Microbiota Composition, Inflammation and Muscle Performance in Our Aging Society. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badal, V.D.; Vaccariello, E.D.; Murray, E.R.; Yu, K.E.; Knight, R.; Jeste, D.V.; Nguyen, T.T. The Gut Microbiome, Aging, and Longevity: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambrano, A.K.; Cadena-Ullauri, S.; Guevara-Ramírez, P.; Frias-Toral, E.; Ruiz-Pozo, V.A.; Paz-Cruz, E.; Tamayo-Trujillo, R.; Chapela, S.; Montalván, M.; Sarno, G.; et al. The Impact of a Very-Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet in the Gut Microbiota Composition in Obesity. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celano, G.; Calabrese, F.M.; Riezzo, G.; D’Attoma, B.; Ignazzi, A.; Di Chito, M.; Sila, A.; De Nucci, S.; Rinaldi, R.; Linsalata, M.; et al. A Multi-Omics Approach to Disclose Metabolic Pathways Impacting Intestinal Permeability in Obese Patients Undergoing Very Low Calorie Ketogenic Diet. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Repiso, C.; Hernández-García, C.; García-Almeida, J.M.; Bellido, D.; Martín-Núñez, G.M.; Sánchez-Alcoholado, L.; Alcaide-Torres, J.; Sajoux, I.; Tinahones, F.J.; Moreno-Indias, I. Effect of Synbiotic Supplementation in a Very-Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet on Weight Loss Achievement and Gut Microbiota: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1900167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondanelli, M.; Gasparri, C.; Peroni, G.; Faliva, M.A.; Naso, M.; Perna, S.; Bazire, P.; Sajuox, I.; Maugeri, R.; Rigon, C. The Potential Roles of Very Low Calorie, Very Low Calorie Ketogenic Diets and Very Low Carbohydrate Diets on the Gut Microbiota Composition. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 662591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Glu | Ins | AST | ALT | GGT | TC | HDL | LDL | TG | Lep | Res | Adi | WC | %BWL | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AgeAccel Horvath | r | 0.555 | 0.663 | 0.017 | 0.273 | 0.551 | 0.530 | 0.182 | 0.215 | 0.504 | 0.456 | −0.295 | −0.193 | 0.393 | 0.585 |
| p | 0.0015 | <0.0001 | 0.9303 | 0.1451 | 0.0016 | 0.0031 | 0.3442 | 0.2625 | 0.0045 | 0.0114 | 0.1132 | 0.306 | 0.0319 | 0.0007 | |
| sig. | ** | **** | ns | ns | ** | ** | ns | ns | ** | * | ns | ns | * | *** | |
| AgeAccel Hannum | r | 0.513 | 0.630 | −0.029 | 0.314 | 0.510 | 0.478 | 0.085 | 0.156 | 0.492 | 0.444 | −0.270 | −0.170 | 0.572 | 0.664 |
| p | 0.0038 | 0.0002 | 0.8785 | 0.0907 | 0.004 | 0.0087 | 0.6618 | 0.4199 | 0.0058 | 0.0139 | 0.1486 | 0.3686 | 0.001 | <0.0001 | |
| sig. | ** | *** | ns | ns | ** | ** | ns | ns | ** | * | ns | ns | *** | **** | |
| AgeAccel Levine | r | 0.614 | 0.777 | −0.097 | 0.206 | 0.486 | 0.401 | 0.076 | 0.082 | 0.380 | 0.516 | −0.138 | −0.268 | 0.449 | 0.621 |
| p | 0.0003 | <0.0001 | 0.6109 | 0.2742 | 0.0065 | 0.031 | 0.6954 | 0.6713 | 0.0384 | 0.0035 | 0.4666 | 0.1528 | 0.0127 | 0.0003 | |
| sig. | *** | **** | ns | ns | ** | * | ns | ns | * | ** | ns | ns | * | *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Izquierdo, A.G.; Lorenzo, P.M.; Costa-Fraga, N.; Primo-Martin, D.; Rodriguez-Carnero, G.; Nicoletti, C.F.; Martínez, J.A.; Casanueva, F.F.; de Luis, D.; Diaz-Lagares, A.; et al. Epigenetic Aging Acceleration in Obesity Is Slowed Down by Nutritional Ketosis Following Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet (VLCKD): A New Perspective to Reverse Biological Age. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17061060
Izquierdo AG, Lorenzo PM, Costa-Fraga N, Primo-Martin D, Rodriguez-Carnero G, Nicoletti CF, Martínez JA, Casanueva FF, de Luis D, Diaz-Lagares A, et al. Epigenetic Aging Acceleration in Obesity Is Slowed Down by Nutritional Ketosis Following Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet (VLCKD): A New Perspective to Reverse Biological Age. Nutrients. 2025; 17(6):1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17061060
Chicago/Turabian StyleIzquierdo, Andrea G., Paula M. Lorenzo, Nicolás Costa-Fraga, David Primo-Martin, Gemma Rodriguez-Carnero, Carolina F. Nicoletti, J. Alfredo Martínez, Felipe F. Casanueva, Daniel de Luis, Angel Diaz-Lagares, and et al. 2025. "Epigenetic Aging Acceleration in Obesity Is Slowed Down by Nutritional Ketosis Following Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet (VLCKD): A New Perspective to Reverse Biological Age" Nutrients 17, no. 6: 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17061060
APA StyleIzquierdo, A. G., Lorenzo, P. M., Costa-Fraga, N., Primo-Martin, D., Rodriguez-Carnero, G., Nicoletti, C. F., Martínez, J. A., Casanueva, F. F., de Luis, D., Diaz-Lagares, A., & Crujeiras, A. B. (2025). Epigenetic Aging Acceleration in Obesity Is Slowed Down by Nutritional Ketosis Following Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet (VLCKD): A New Perspective to Reverse Biological Age. Nutrients, 17(6), 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17061060








