Child and Adolescent Health Programs in Obesity and Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Risk of Bias and Quality Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
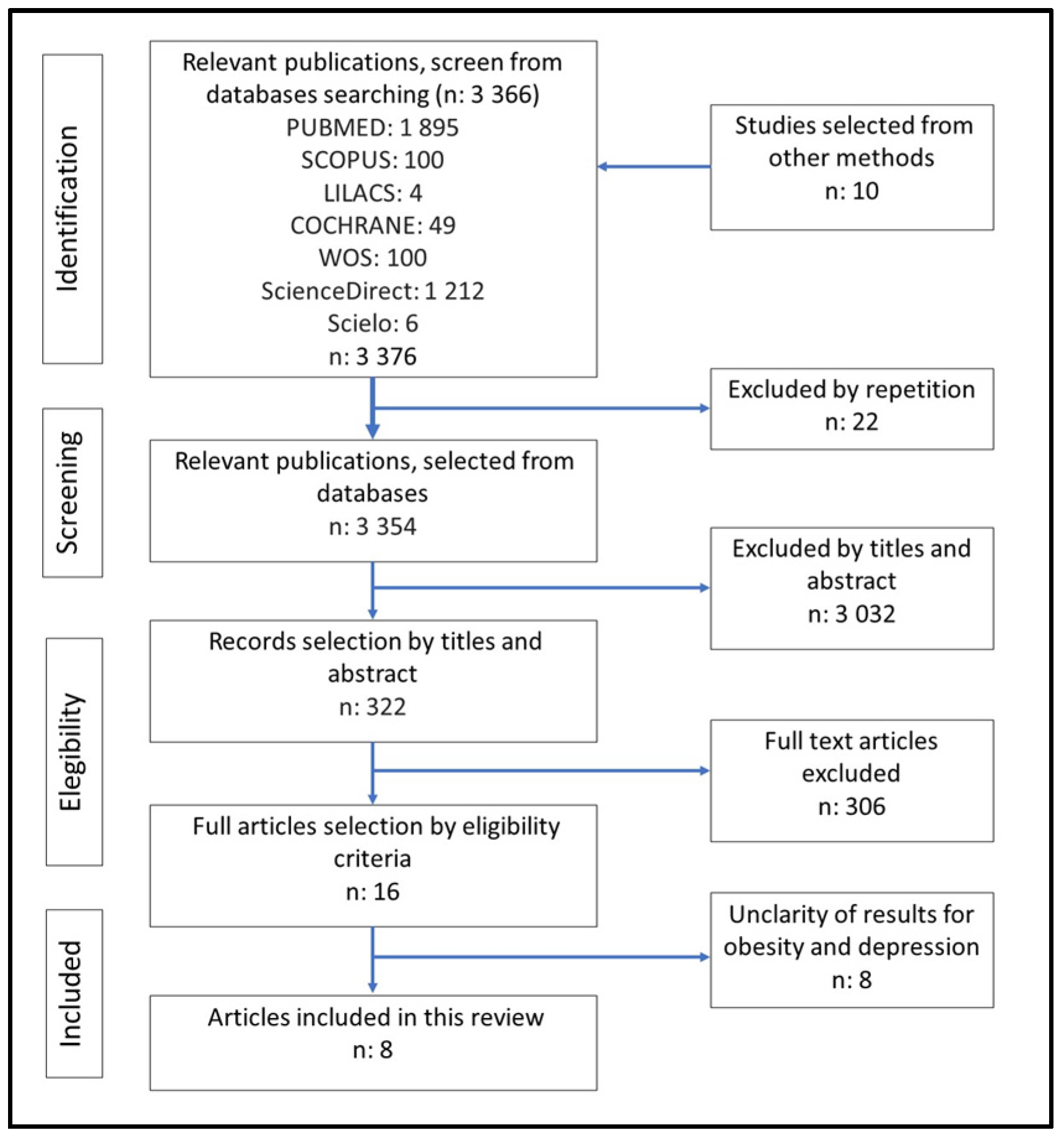
3. Results
3.1. Selection of Studies
3.2. Overall Characteristics of the Studies
| Authors | Type of Study | Country | Age Range (Years) | Total Sample (N) | Type of Intervention |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barnes and Kristeller, 2016 [52] | RCT | USA | 15–17 | 40 | Behavioral Therapy |
| Goldfield et al., 2015 [53] | RCT | Canadá | 14–18 | 304 | Diet/Exercise |
| López et al., 2021 [58] | RCT | USA | 14–18 | 76 | Diet/Exercise Behavioral Therapy |
| Luca et al., 2014 [57] | NRCT | Canadá | 14–17 | 116 | Diet Behavioral Therapy |
| Sen et al., 2018 [59] | RCT | Turquía | 9–12 | 108 | Diet/Exercise Behavioral Therapy |
| Strugnell et al., 2024 [54] | RCT | Australia | 13–16 | 2400 | Diet/Exercise |
| Vidmar et al., 2022 [56] | RCT | USA | 14–18 | 117 | Diet Behavioral Therapy |
| Williams et al., 2019 [55] | RCT | USA | 8–11 | 175 | Diet/Exercise |
| Author/Year | Intervention Program | Extension (Months) | Partial Duration (Weeks) | Direct Intervention (Hours) | Variables Evaluated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barnes and Kristeller, 2016 [52] | Program MB-EAT-A | 6 | 12 | 9 | BMI Diet Exercise Binge eating Feeding Depression Risk behaviors |
| Goldfield et al., 2015 [53] | Resistance, aerobic and combines traditional program | 6 | 22 | 7–16.5 | Mood Body image Physical self-perceptions Overall self-esteem |
| López et al., 2021 [58] | Management program with APP | 6 | 24 | 12–24 | BMI Executive function Childhood depression |
| Luca et al., 2014 [57] | Program STOMP | 12 | 48 | no informed | BMI quality of life Childhood depression Readiness to change HOMA-IR Diet Waist circumference Physical activity |
| Sen et al., 2018 [59] | Comparative program of family behavioral intervention vs. Kaledo game | 3 | no information | 6 | Psychiatric symptoms Physical activity Diet Anthropometry (weight, height, BMI, Z-BMI) |
| Strugnell et al., 2024 [54] | Program Healthy Together Victoria | 24 | 12 | no informed | BMI Waist circumference School Health Quality of diet Quality of life Depressive symptoms |
| Vidmar et al., 2022 [56] | mHealth intervention program with APP | 6 | 24 | 16–18 | BMI Food addiction Executive function Behavior Emotion Cognition Depression Stress |
| Williams et al., 2019 [55] | Exercise program | 8 | 32 | 92 | Quality of Life Anger Self-esteem Body composition Fat percentage Cardiovascular fitness. |
3.3. Findings of the Systematic Review
- (i)
- Effect of obesity programs
- (ii)
- Effect of programs for depressive symptoms
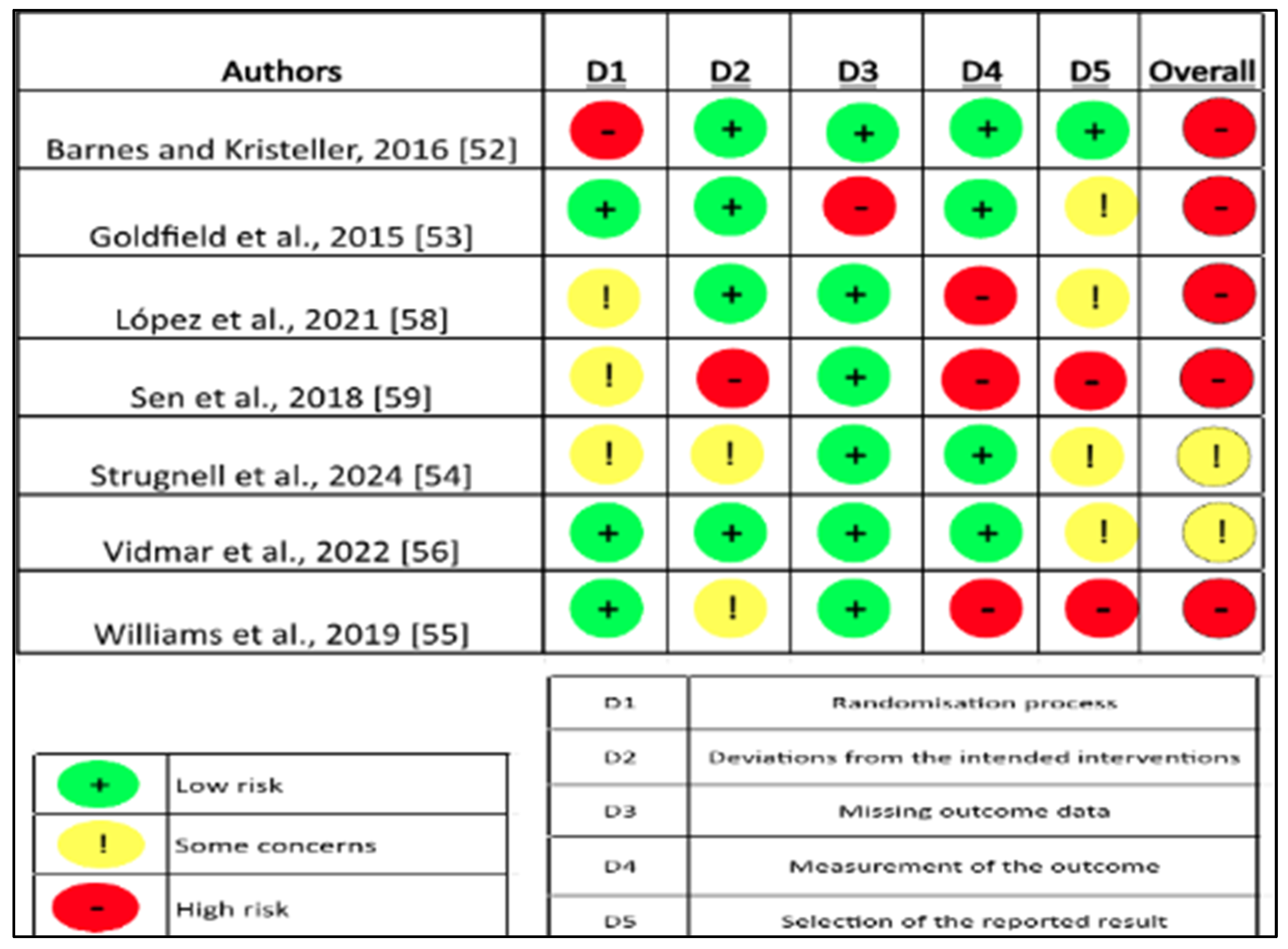
3.4. Risk of Bias in Individual Studies
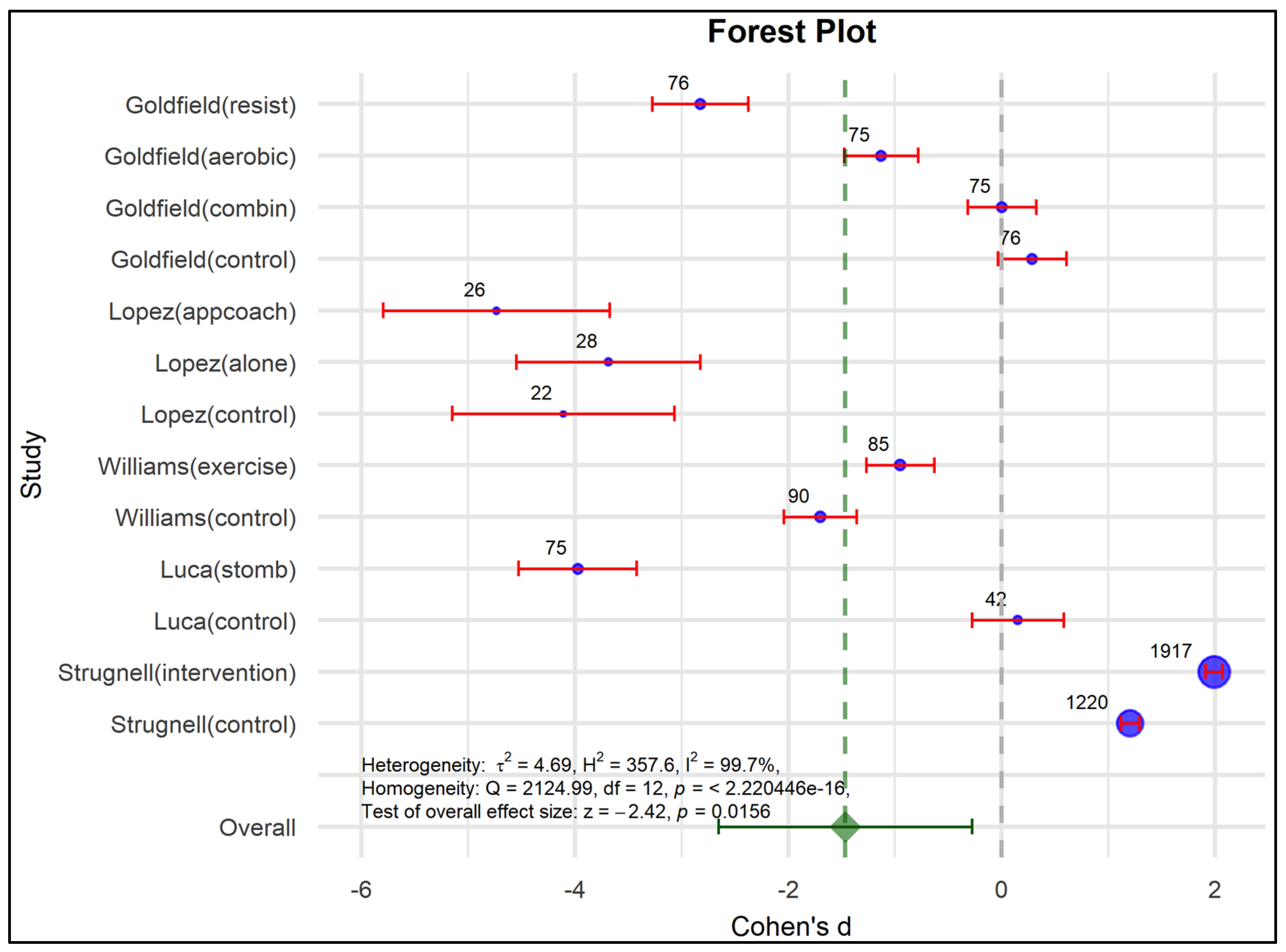
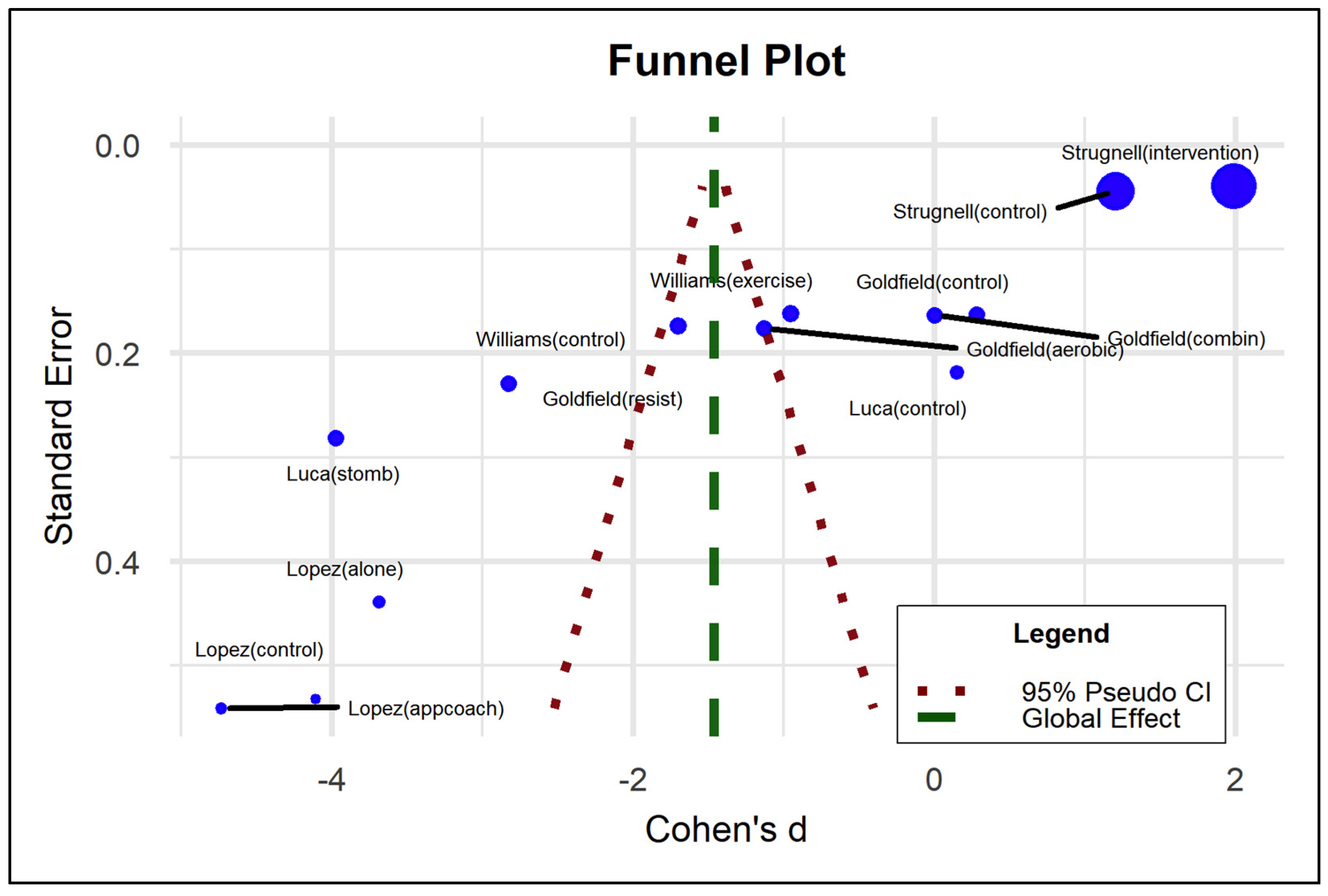
3.5. Meta-Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Database Search Strategy
| Database | Boolean Descriptors and Operators |
| PUBMED | (“Program”) OR (“health programs”) AND (“Pediatric obesity”) AND (“Obesity and depression”) AND (“Depression”) (“Child*”) OR (“Childhood”) AND (school-aged children) |
| BVS (Lilacs) | (“Program”) OR (health programs) AND (Pediatric obesity) AND (“Depression”) (“Child*”) OR (“Childhood”) AND (school-aged children) |
| COCHRANE | (program):ti,ab,kw AND (prevention):ti,ab,kw AND (obesity):ti,ab,kw AND (depression):ti,ab,kw AND (childhood):ti,ab,kw” |
| SCOPUS | (“Program”) OR (“health programs”) AND (“Pediatric obesity”) AND (“Obesity and depression”) AND (“Depression”) (“Child*”) OR (“Childhood”) AND (school-aged children) |
| WOS | (“Program”) OR (“health programs”) AND (“Pediatric obesity”) AND (“Obesity and depression”) AND (“Depression”) (“Child*”) OR (“Childhood”) AND (school-aged children) |
| ScienceDirect | (“Program”) OR (“health programs”) AND (“Pediatric obesity”) AND (“Obesity and depression”) AND (“Depression”) (“Child*”) OR (“Childhood”) AND (school-aged children) |
| Scielo | (“Program”) OR (“health programs”) AND (“Pediatric obesity”) AND (“Obesity and depression”) AND (“Depression”) (“Child*”) OR (“Childhood”) |
Appendix B. Abbreviations
| Acronym | Definition |
| BASC-2 | Behavior assessment System for children-second edition. |
| BRUMS | Brunel Mood Scale |
| CDI | Children’s Depression Inventory |
| CES-DC | Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale for Children |
| COCHRANE | High quality health data source |
| ECA | Randomized Controlled Trials. |
| HOMA-IR | Homeostatic model assessment-Insulin Resistent |
| IMC | Body Mass Index |
| LILACS | Latin American and Caribbean literature on health sciences |
| m2 | Square meter. |
| MB-EAT-A | Mindful Eating |
| mHealth | Mobile Health |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses. |
| PROSPERO | International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews. |
| PUBMED | Medical Publications. |
| ROB-2 | Risk of Bias-2 |
| ROBINS 1 | Risk Of Bias In Non-randomized Studies of Interventions. |
| RS | Risk of Bias. |
| SCOPUS | Elsevier Database |
| SMFQ | Short Mood and Feelings Questionnaire |
| STOMP | Solutions, Treatments in Obesity Management Prevention |
| WOS | World of Science |
| z-IMC | Average-Body Mass Index |
References
- Alonso, R.; Olivos, C. La relación entre la obesidad y estados depresivos. Rev. Med. Clin. Condes 2020, 31, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okunogbe, A.; Nugent, R.; Spencer, G.; Powis, J.; Ralston, J.; Wilding, J. Economic impacts of overweight and obesity: Current and future estimates for 161 countries. BMJ Glob. Health 2022, 7, e009773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- JUNAEB, Junta Nacional de Auxilio Escolar y Becas de Chile. Mapa Nutricional. 2023. Available online: https://www.junaeb.cl/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/Mapa-Nutricional-2023-Resultados.pdf (accessed on 8 December 2024).
- Thapar, A.; Collishaw, S.; Pine, D.S.; Thapar, A.K. Depression in adolescence. Lancet 2012, 379, 1056–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2019 Mental Disorders Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of 12 mental disorders in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Psychiatry 2022, 9, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gundersen, C.; Mahatmya, D.; Garasky, S.; Lohman, B. Linking psychosocial stressors and childhood obesity. Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, e54–e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, W.; Lane, M.; Hockey, M.; Aslam, H.; Berk, M.; Walder, K.; Borsini, A.; Firth, J.; Pariante, C.M.; Berding, K.; et al. Diet and depression: Exploring the biological mechanisms of action. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 134–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Cortez, E.A.; Goicochea—Ríos, E.S.; Linares-Reyes, E. Definición de obesidad: Más allá del índice de masa corporal. Rev. Med. Vallejiana 2020, 9, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.D.; Fu, E.; Kobayashi, M.A. Prevention and Management of Childhood Obesity and Its Psychological and Health Comorbidities. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2020, 16, 351–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, C.; Labbé, T.; Busquets, J.; Venegas, P.; Neira, C.; Valenzuela, Á. Obesidad: ¿Factor de riesgo o enfermedad? Rev. Med. Chile 2019, 147, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, M.; Yu, G.Z.; Mian, A.; Cramer, A.; Meysami, S.; Merrill, D.A.; Samara, A.; Eisenstein, S.A.; Hershey, T.; Babulal, G.M.; et al. Neuroinflammation: A Modifiable Pathway Linking Obesity, Alzheimer’s Disease, and Depression. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2023, 31, 853–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajravelu, M.E.; Tas, E.; Arslanian, S. Pediatric Obesity: Complications and Current Day Management. Life 2023, 13, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sun, Q.; Zhai, L.; Bai, Y.; Wei, W.; Jia, L. The Prevalence of Depression and Anxiety Symptoms among Overweight/Obese and Non-Overweight/Non-Obese Children/Adolescents in China: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, W.W.; Zong, Q.Q.; Zhang, J.W.; An, F.R.; Jackson, T.; Ungvari, G.S.; Xiang, Y.; Su, Y.Y.; D’Arcy, C.; Xiang, Y.T. Obesity increases the risk of depression in children and adolescents: Results from a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 267, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Rojas, A.A.; García-Galicia, A.; Vázquez-Cruz, E.; Montiel-Jarquín, J.; Aréchiga-Santamaría, A. Self-image, self-esteem and depression in children and adolescents with and without obesity. Gac. Med. Mex. 2022, 158, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokela, M.; Laakasuo, M. Obesity as a causal risk factor for depression: Systematic review and meta-analysis of Mendelian Randomization studies and implications for population mental health. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2023, 163, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, N.B.; Baur, L.A.; Felix, J.F.; Hill, A.J.; Marcus, C.; Reinehr, T.; Summerbell, C.; Wabitsch, M. Child and adolescent obesity. Nature reviews. Dis. Primers 2023, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomiyama, A.J. Stress and Obesity. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2019, 70, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, C.; Danielsson, P.; Hagman, E. Pediatric obesity—Long-term consequences and effect of weight loss. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 292, 870–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jebeile, H.; Kelly, A.S.; O’Malley, G.; Baur, L.A. Obesity in children and adolescents: Epidemiology, causes, assessment, and management. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, E.A.; Evans, C.V.; Burda, B.U.; Walsh, E.S.; Eder, M.; Lozano, P. Screening for Obesity and Interventions for Weight Management in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Evidence Review for the U.S. Prev. Serv. Task Force 2017, 317, 2427–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro, J.A.C.; de Lima, T.R.; Santos, D.A.S. Body composition estimation in children and adolescents by bioelectrical impedance analysis: A systematic review. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2018, 22, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigolet, M.E.; Dong-Hoon, K.; Canizales-Quinteros, S.; Gutiérrez-Aguilar, R. Obesity, adipose tissue, and bariatric surgery. Boletín Médico Hosp. Infant. Méx. 2020, 77, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón, C.; Forns, M.; Varea, V. Implicación de la ansiedad y la depresión en los trastornos de alimentación de jóvenes con obesidad. Nutr. Hosp. 2010, 25, 641–647. Available online: http://scielo.isciii.es/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0212-16112010000400017&lng=es (accessed on 7 August 2024).
- Wu, T.; Liu, R.; Zhang, L.; Rifky, M.; Sui, W.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yin, J.; Zhang, M. Dietary intervention in depression—A review. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 12475–12486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattane, N.; Räikkönen, K.; Anniverno, R.; Mencacci, C.; Riva, M.A.; Pariante, C.M.; Cattaneo, A. Depression, obesity and their comorbidity during pregnancy: Effects on the offspring’s mental and physical health. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 26, 462–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutaria, S.; Devakumar, D.; Yasuda, S.S.; Das, S.; Saxena, S. Is obesity associated with depression in children? Systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Dis. Child. 2019, 104, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.C.; Lin, C.Y.; Saffari, M.; Tsai, M.C.; Chang, Y.H.; Strong, C.; Chen, J.K.; Hsieh, Y.P.; Yang, Y.N.; Latner, J.D. Weight stigma is associated with body mass index among college students in Taiwan: The mediated role of internalized weight stigma. BMC Psychol. 2023, 11, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanellopoulou, A.; Antonogeorgos, G.; Douros, K.; Panagiotakos, D.B. The Association between Obesity and Depression among Children and the Role of Family: A Systematic Review. Children 2022, 9, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, L.P.; Davis, R.; Poulton, R.; McCauley, E.; Moffitt, T.E.; Caspi, A.; Connell, F. A longitudinal evaluation of adolescent depression and adult obesity. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2003, 157, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleid, A.M.; Sabi, N.M.; Alharbi, G.S.; Alharthi, A.A.; Alshuqayfi, S.M.; Alnefiae, N.S.; Ismail, G.M.; Allhybi, A.K.; Alrasheeday, A.M.; Alshammari, B.; et al. The Impact of Parental Involvement in the Prevention and Management of Obesity in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Children 2024, 11, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antwi, F.; Fazylova, N.; Garcon, M.; López, L.; Rubiano, R.; Slyer, J.T. Effectiveness of web-based programs on the reduction of childhood obesity in school-aged children: A systematic review. JBI Database Syst. Rev. Implement. Rep. 2013, 11, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihalopoulos, N.; Spigarelli, M. Comanagement of Pediatric Depression and Obesity: A Clear Need for Evidence. Clin. Ther. 2015, 37, 1933–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsalos, O.; Keeler, J.; Schmidt, U.; Penninx, B.; Young, A.; Himmerich, H. Diet, obesity, and depression: A systematic review. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaban, M.; AbouKhatwa, S.; Hareez, S.; Mosaad, M.; Elrggal, M. Risk Factors, Clinical Consequences, Prevention, and Treatment of Childhood Obesity. Children 2022, 9, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy-Cumillaf, A.; Fuentes-Merino, P.; Díaz-González, A.; Jiménez-Díaz, J.; Martínez-Vizcaíno, V.; Álvarez-Bueno, C. The effects of physical activity and diet interventions on body mass index in Latin American children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomayko, E.J.; Tovar, A.; Fitzgerald, N.; Howe, C.L.; Hingle, M.D.; Murphy, M.P.; Muzaffar, H.; Going, S.B.; Hubbs-Tait, L. Parent Involvement in Diet or Physical Activity Interventions to Treat or Prevent Childhood Obesity: An Umbrella Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Brennan, S.E.; Chou, R.; et al. A declaração PRISMA 2020: Diretriz atualizada para relatar revisões sistemáticas [The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews Declaración PRISMA 2020: Una guía actualizada para la publicación de revisiones sistemáticas]. Rev. Panam. Salud Publica 2022, 74, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, M.B.; Frandsen, T.F. The impact of patient, intervention, comparison, outcome (PICO) as a search strategy tool on literature search quality: A systematic review. J. Med. Libr. Assoc. 2018, 106, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Methley, A.M.; Campbell, S.; Chew-Graham, C.; McNally, R.; Cheraghi-Sohi, S. PICO, PICOS, and SPIDER: A comparison study of specificity and sensitivity in three search tools for qualitative systematic reviews. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2014, 14, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.; Savović, J.; Page, M.; Sterneon, J.; behalf of the RoB2 Development Group 2.0. Revised Cochrane risk of bias tool for randomized trials (RoB 2.0). BMJ 2016, 366, l4898. Available online: https://www.unisa.edu.au/contentassets/72bf75606a2b4abcaf7f17404af374ad/rob2-0_indiv_main_guidance.pdf (accessed on 15 August 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.; Higgins, J.; Elbers, R.; Reeveson, B. Risk Of Bias In Non-randomized Studies of Interventions (ROBINS-I): Detailed guidance. BMJ 2016, 355, 4919. Available online: https://www.bristol.ac.uk/media-library/sites/social-community-medicine/images/centres/cresyda/ROBINS-I_detailed_guidance.pdf (accessed on 5 December 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Elch, V.A. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.3; The Cochrane Collaboration: London, UK, 2022; Available online: https://training.cochrane.org/handbook/current (accessed on 17 February 2025).
- Ek, A.; Brissman, M.; Nordin, K.; Eli, K.; Nowicka, P. A long-term follow-up of treatment for young children with obesity: A randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Obes. 2023, 47, 1152–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, K.; Ortega, A. Programa de intervención psicológica para el manejo de la obesidad infantil. Rev. Hum. Med. 2022, 22, 615–635. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/366369959_Program_of_psychological_intervention_for_the_handling_of_the_infantile_obesity (accessed on 8 December 2024).
- Cadenas-Sánchez, C.; Migueles, J.; Verdejo-Román, J.; Erickson, K.I.; Esteban-Cornejo, I.; Catena, A.; Ortega, F. Physical activity, sedentary time, and fitness in relation to brain shapes in children with overweight/obesity: Links to intelligence. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2023, 33, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, C.D.; Aylward, B.S.; Steele, R.G. Predictors of Attendance in a Practical Clinical Trial of Two Pediatric Weight Management Interventions. Obesity 2012, 20, 2250–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gailite, J.; Apela, D.; Dzīvīte-Krišāne, I.; Gardovska, D. Short-Term Predictors for Weight Correction Success of the First Paediatric Weight Correction Programme in Children’s Clinical University Hospital in Riga. Medicina 2019, 55, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynne, C.; Comiskey, C.; Hollywood, E.; Quirke, M.B.; O’sullivan, K.; McGilloway, S. The relationship between body mass index and health-related quality of life in urban disadvantaged children. Qual. Life Res. 2014, 23, 1895–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, D.; Melnyk, B. Psychosocial Correlates of Healthy Beliefs, Choices, and Behaviors in Overweight and Obese School-Age Children: A Primary Care Healthy Choices Intervention Pilot Study. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2011, 26, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archuleta, M.; VanLeeuwen, D.; Turner, C. Fit Families Program improves self-perception in children. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2016, 48, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, V.A.; Kristeller, J.L. Impact of mindfulness-based eating awareness on diet and exercise habits in adolescents. Int. J. Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 3, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldfield, G.S.; Kenny, G.P.; Alberga, A.S.; Prud’homme, D.; Hadjiyannakis, S.; Gougeon, R.; Phillips, P.; Tulloch, H.; Malcolm, J.; Doucette, S.; et al. Effects of aerobic training, resistance training, or both on psychological health in adolescents with obesity: The HEARTY randomized controlled trial. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 2015, 83, 1123–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strugnell, C.; Orellana, L.; Crooks, N.; Malakellis, M.; Morrissey, B.; Rennie, C.; Hayward, J.; Bliss, J.; Swinburn, B.; Gaskin, C.J.; et al. Healthy Together Victoria and childhood obesity study: Effects of a large scale, community-based cluster randomised trial of a systems thinking approach for the prevention of childhood obesity among secondary school students 2014–2016. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.F.; Bustamante, E.E.; Waller, J.L.; Davis, C.L. Exercise effects on quality of life, mood, and self-worth in overweight children: The SMART randomized controlled trial. Transl. Behav. Med. 2019, 9, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidmar, A.P.; Yamashita, N.; Fox, D.S.; Hegedus, E.; Wee, C.P.; Salvy, S.J. Can a Behavioral Weight-Loss Intervention Change Adolescents’ Food Addiction Severity? Child. Obes. 2022, 18, 147–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luca, P.; Dettmer, E.; Khoury, M.; Grewal, P.; Manlhiot, C.; McCrindle, B.W.; Birken, C.S.; Hamilton, J.K. Adolescents with severe obesity: Outcomes of participation in an intensive obesity management programme. Pediatr. Obes. 2015, 10, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, K.E.; Salvy, S.J.; Fink, C.; Werner, J.; Wee, C.P.; Hegedus, E.; González, J.; Fox, D.S.; Vidmar, A.P. Executive Functioning, Depressive Symptoms, and Intervention Engagement in a Sample of Adolescents Enrolled in a Weight Management Program. Child. Obes. 2021, 17, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, M.; Uzuner, A.; Akman, M.; Bahadir, A.T.; Borekci, N.O.; Viggiano, E. Examination of a board game approach to children’s involvement in family-based weight management vs. traditional family-based behavioral counseling in primary care. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2018, 177, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrer, M.; Cuijpers, P.; Furukawa, T.; Ebert, D. Doing Meta-Analysis With R: A Hands-On Guide; CRC Press/Chapman & Hall: New York, USA, 2022; ISBN 9780367610074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiei, F.; Salari-Moghaddam, A.; Larijani, B.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet and risk of depression: A systematic review and updated meta-analysis of observational studies. Nutr. Rev. 2019, 77, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Z.; Shao, T. Effect of exercise intervention on depression in children and adolescents: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson-Smith, D.; Halldorsson, T.I.; Bot, M.; Brouwer, I.A.; Visser, M.; Thorsdottir, I.; Birgisdottir, B.E.; Gudnason, V.; Eiriksdottir, G.; Launer, L.J.; et al. Childhood overweight and obesity and the risk of depression across the lifespan. BMC Pediatr. 2020, 20, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthoud, H.R.; Münzberg, H.; Morrison, C.D. Blaming the Brain for Obesity: Integration of Hedonic and Homeostatic Mechanisms. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1728–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, R.A.; Padhani, Z.A.; Das, J.K.; Shaikh, A.Y.; Hoodbhoy, Z.; Jeelani, S.M. Effects of lifestyle modification interventions to prevent and manage child and adolescent obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Qi, Z.; Wang, R.; Cui, Y.; An, S.; Wu, G.; Feng, Q.; Lin, R.; Dai, R.; Li, A.; et al. A corticoamygdalar pathway controls reward devaluation and depression using dynamic inhibition code. Neuron 2023, 111, 3837–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agustí, A.; García-Pardo, M.P.; López-Almela, I.; Campillo, I.; Maes, M.; Romaní-Pérez, M.; Sanz, Y. Interplay Between the Gut-Brain Axis, Obesity and Cognitive Function. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.K.; Jahan, K.; Alam, N.; Rois, R.; Ferdaus, A.; Israt, S.; Karim, M.R. Perceived stress, eating behavior, and overweight and obesity among urban adolescents. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2021, 40, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ronan, L.; Alexander-Bloch, A.; Fletcher, P.C. Childhood Obesity, Cortical Structure, and Executive Function in Healthy Children. Cereb. Cortex 2020, 30, 2519–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, J.Á.; de Cossío, T.G.; Pedraza, L.S.; Aburto, T.C.; Sánchez, T.G.; Martorell, R. Childhood and adolescent overweight and obesity in Latin America: A systematic review. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, P.L.; Valério, I.D.; de Zanatti, C.L.M.; Gonçalves, H. Revisão sistemática: Sintomas de depressão e ansiedade parental e excesso de peso da prole. Rev. Saúde Pública 2020, 54, 49. Available online: https://www.revistas.usp.br/rsp/article/view/171201 (accessed on 17 February 2025). [CrossRef]
- Alberti, A.; Araujo, D.R.; Vieira, W.F.; Moehlecke, B.; Lampert, R.M.F.; Traebert, E.; Silva, B.B.d.; Oliveira, B.H.d.; Leão, G.M.; Souza, G.d. Factors Associated with the Development of Depression and the Influence of Obesity on Depressive Disorders: A Narrative Review. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applewhite, B.; Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Young, A.H.; Schmidt, U.; Himmerich, H.; Keeler, J.L. The effect of a low-calorie diet on depressive symptoms in individuals with overweight or obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis of interventional studies. Psychol. Med. 2024, 54, 1671–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Toche, J.; Gómez-García, A.; Gómez-Alonso, C.; Álvarez-Paredes, M.A.; Álvarez-Aguilar, C. Asociación Entre Obesidad Y Depresión Infantil En Población Escolar De Una Unidad De Medicina Familiar En MORELIA, Michoacán; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 24, pp. 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesek, M.; Fornal, A.D.; Zarzycka, D. Promoting Health in Pediatric Obesity: A Decade’s Research of Physical Activity’s Influence on Cardiometabolic Parameters. Med. Sci. Monitor. 2023, 29, e940742-1–e940742-26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowey, M.; Redden, D.; Lim, C.; Janicke, D.; Dutton, G. Executive function phenotypes in pediatric obesity. Pediatr. Obes. 2020, 15, e12655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.C.; Kato, T.A.; Lee, J.H.; Yu, S.H. Exploring the Bidirectional Relationship Between Depression and Obesity. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2025, 54, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campisi, S.C.; Zasowski, C.; Shah, S.; Bradley-Ridout, G.; Madigan, S.; Szatmari, P.; Korczak, D.J. Do Healthy Dietary Interventions Improve Pediatric Depressive Symptoms? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 2495–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feretzakis, G.; Harokopou, A.; Fafoula, O.; Balaska, A.; Koulountzou, A.; Katoikou, E.; Anastasiou, A.; Zagkavieros, G.; Dalainas, I.; Gkritzelas, G. The Impact of Psychological Health on Childhood Obesity: A Cross-Developmental Stage Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mac Giollabhui, N.; Swistun, D.; Murray, S.; Moriarity, D.P.; Kautz, M.M.; Ellman, L.M.; Olino, T.M.; Coe, C.L.; Abramson, L.Y.; Alloy, L.B. Executive dysfunction in depression in adolescence: The role of inflammation and higher body mass. Psychol. Med. 2020, 50, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Cui, R.; Xie, W.; Liu, Q.; Yang, W. Shared biological mechanisms of depression and obesity: Focus on adipokines and lipokines. Aging 2023, 15, 5917–5950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uban, K.A.; Horton, M.K.; Jacobus, J.; Heyser, C.; Thompson, W.K.; Tapert, S.F.; Madden, P.A.F.; Sowell, E.R. Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development Stud. Biospecimens and the ABCD study: Rationale, methods of collection, measurement and early data. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2018, 32, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
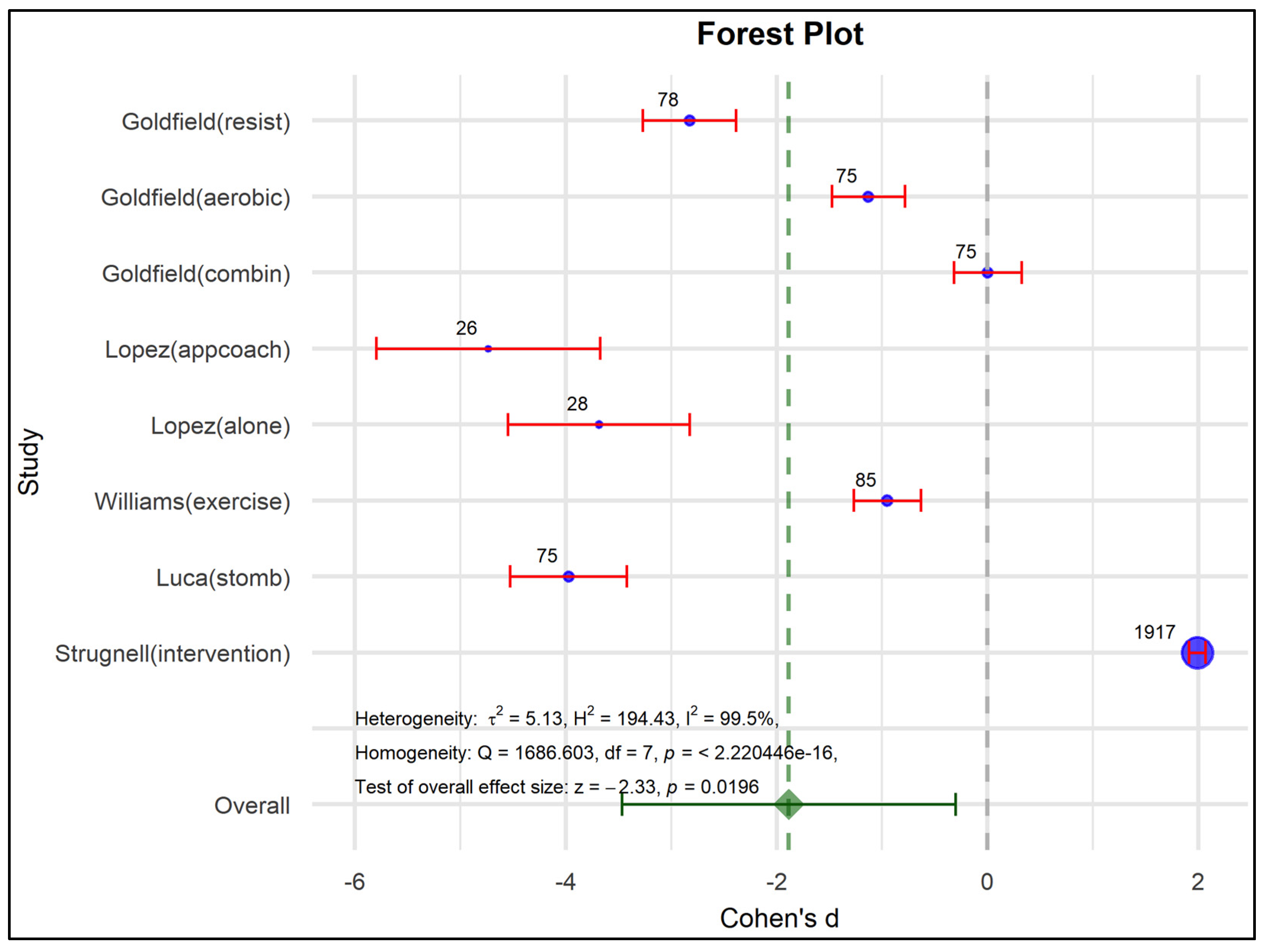
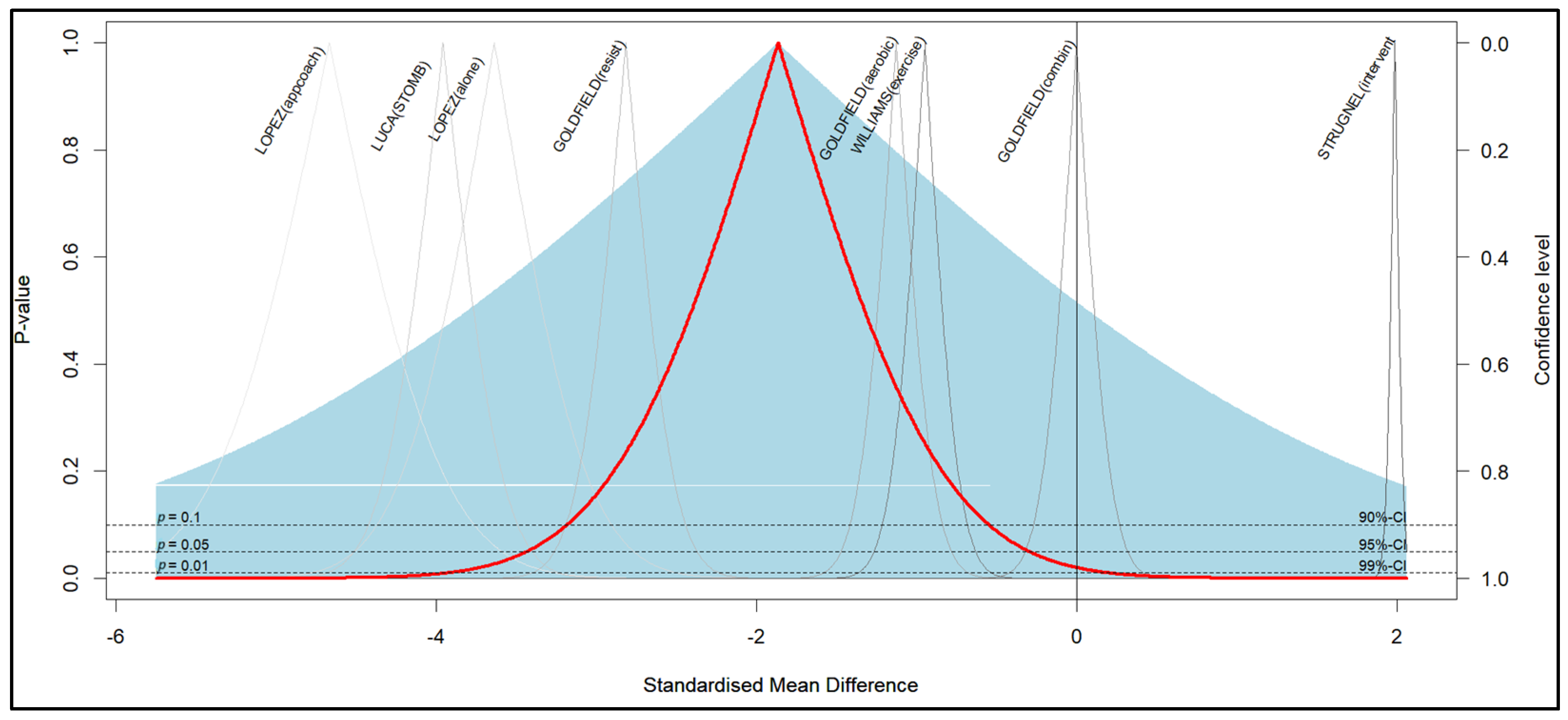
| Author/Year | Program (Interventions) | N | Obesity | Depression | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measuring Instrument | Initial | Post Intervention | Measuring Instrument | Initial | Post Intervention | |||
| Goldfield et al., 2015 [53] | (a) Aerobic training | 75 | Z-BMI | 34.6 | no informed | * BRUMS | 2.5 (0.3) | 2.1 (0.4) |
| (b) Resistance training | 78 | 35.1 | no informed | 2.7 (0.3) | 1.7 (0.4) | |||
| (c) Combined training (Aerobic + Resistance) | 75 | 34.6 | no informed | 2.6 (0.3) | 2.6 (0.4) | |||
| (d) Control without exercise | 78 | 34.1 | no informed | 2.8 (0.3) | 2.7 (0.4) | |||
| López et al., 2021 [58] | (a) App Coach | 26 | Z-BMI | no informed | no informed | * CES-DC | 8.38 | 5.22 |
| (b) App Alone | 28 | no informed | no informed | 8.21 | 5.26 | |||
| (c) Control | 22 | no informed | no informed | 7.91 | 5.41 | |||
| Strugnell et al., 2024 [54] | (a) Intervention | 1917 | Z-IMC | 34.4 | 33.5 | * SMFQ | 4.5 | 5.4 |
| Waist circumference | 75.7 | 75.2 | ||||||
| Abdominal obesity | 16.5 | 17.8 | ||||||
| (b) Comparison | 1220 | Z-BMI | 29.6 | 32.5 | 5.1 | 5.7 | ||
| Waist circumference | 74.4 | 75.2 | ||||||
| Abdominal obesity | 13 | 16 | ||||||
| Luca et al., 2014 [57] | (a) STOMP Intervention | 75 | BMI | 44.8 | 0.08 ± 0.3 | * CDI | 11.9 ± 4.2 | (11.9 ± 4.2)–(3.6 ± 1.4) |
| (b) Comparison | 42 | 34.5 | 0.7 ± 0.2 | 6.0 ± 9.0 | (6.0 ± 9.0)–(0.09 ± 1.0) | |||
| Barnes and Kristeller, 2016 [41] | (a) MB-EAT-A | 18 | BMI | 32.9 ± 8.8 | 33.0 ± 9.4 | * BASC | no informed | (ρ = −0.008, p = 1.0) |
| (b) Health education control | 22 | 32.0 ± 9.4 | 32.0 ± 9.4 | no informed | no informed | |||
| Williams et al., 2019 [55] | (a) Aerobic exercise | 85 | Body fat | 38.3 ± 6.9 | 38.3 ± 6.9 | * CDI | (7.6 ± 6.6) | (6.3 ± 5.2) |
| (b) Sedentary attention control | 90 | 36.7 ± 7.3 | 36.7 ± 7.3 | (8.1 ± 7.5) | (6.8 ± 5.9) | |||
| Vidmar, et al., 2022 CES-DC [56] | (a) control | 39 | %BMIp95c | 125.43 [101.56, 197.93] | no informed | * CES-DC | 8 | no informed |
| (b) APP | 39 | 129.53 [104.61, 193.47] | no informed | 7 | no informed | |||
| (c) APP coach | 39 | 129.53 [104.61, 193.47] | no informed | 8.5 | no informed | |||
| Sen et al., 2018 [59] | (a) Behavioral | 12 | BMI | 25.36 ± 2.37 | 24.43 ± 2.33 | * CDI | no informed | 6.30 ± 5.66 |
| (b) Game | 12 | 26.81 ± 3.10 | 26.24 ± 2.67 | no informed | 8.92 ± 4.50 | |||
| Author/Year | Type of Study | Conclusions | Assessment Instrument | Risk of Bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barnes Kristeller, 2016 [52] | RCT | The MB-EAT-A program can improve the dietary habits of school-aged adolescents. Feeding programs are a means to address obesity in high-risk youth. | ROB-2 | High risk |
| Goldfield et al., 2015 [53] | RCT | Resistance training, alone or in combination with aerobic training, can provide psychological benefits in overweight or obese adolescents. | ROB-2 | High risk |
| López et al., 2021 [58] | RCT | Family participation in intervention programs is related to greater program attendance. | ROB-2 | High risk |
| Luca et al., 2014 [57] | NRCT | The STOMP program did not show a significant reduction in BMI, but there were improvements in cardiometabolic, psychological, and behavioral outcomes. | ROBINS-I | Moderate risk |
| Strugnell et al., 2024 [54] | RCT | The program produces improvement in waist circumference and in the consumption of sugary drinks per day. For girls, there were no statistically significant differences. | ROB-2 | Moderate risk |
| Vidmar et al., 2022 [56] | RCT | No significant changes in nutrition parameters were observed in the intervention promama, but they were positive for depression and stress. | ROB-2 | Moderate risk |
| Williams et al., 2019 [55] | RCT | Sedentary programs that include games and activities of interaction with adults and peers, as well as a behavioral structure, may be more beneficial for mood than those focused solely on physical exercise. | ROB-2 | High risk |
| Sen et al., 2018 [59] | RCT | Family-based behavioral group intervention and play-based intervention (Kaledo) were equally beneficial in lowering childhood BMI. So they can be used in the treatment of childhood obesity. | ROB-2 | High risk |
| Effect Size | Std. Error | Z | Sig. (2-Tailed) | 95% Confidence Interval | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| Overall effect | −1.465 | 0.6057 | −2.418 | 0.016 | −2.652 | −0.277 |
| Parameter | Coefficient | Std. Error | t | Sig. (2-Tailed) | 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| (Intercept) | 1.405 | 0.5458 | 2.574 | 0.026 | 0.203 | 2.606 |
| SEb | −11.891 | 19.550 | −6.082 | <0.001 | −16.194 | −7.588 |
| Effect Size | Std. Error | Z | Sig. (2-Tailed) | 95% Confidence Interval | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| Overall effect | −1.885 | 0.8077 | −2.333 | 0.020 | −3.468 | −0.302 |
| Parameter | Coefficient | Std. Error | t | Sig. (2-Tailed) | 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| (Intercept) | 1.292 | 0.7634 | 1.692 | 0.142 | −0.576 | 3.159 |
| SEb | −12.589 | 26.536 | −4.744 | 0.003 | −19.082 | −6.096 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sarmiento-Riveros, A.; Aguilar-Cordero, M.J.; Barahona-Barahona, J.A.; Galindo, G.E.; Carvallo, C.; Crespo, F.A.; Burgos, H. Child and Adolescent Health Programs in Obesity and Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17061088
Sarmiento-Riveros A, Aguilar-Cordero MJ, Barahona-Barahona JA, Galindo GE, Carvallo C, Crespo FA, Burgos H. Child and Adolescent Health Programs in Obesity and Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2025; 17(6):1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17061088
Chicago/Turabian StyleSarmiento-Riveros, Ana, María José Aguilar-Cordero, Juan A. Barahona-Barahona, Gabriel E. Galindo, Claudia Carvallo, Fernando A. Crespo, and Héctor Burgos. 2025. "Child and Adolescent Health Programs in Obesity and Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Nutrients 17, no. 6: 1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17061088
APA StyleSarmiento-Riveros, A., Aguilar-Cordero, M. J., Barahona-Barahona, J. A., Galindo, G. E., Carvallo, C., Crespo, F. A., & Burgos, H. (2025). Child and Adolescent Health Programs in Obesity and Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 17(6), 1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17061088






