The Interplay Between Nutrition and Microbiota and the Role of Probiotics and Symbiotics in Pediatric Infectious Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
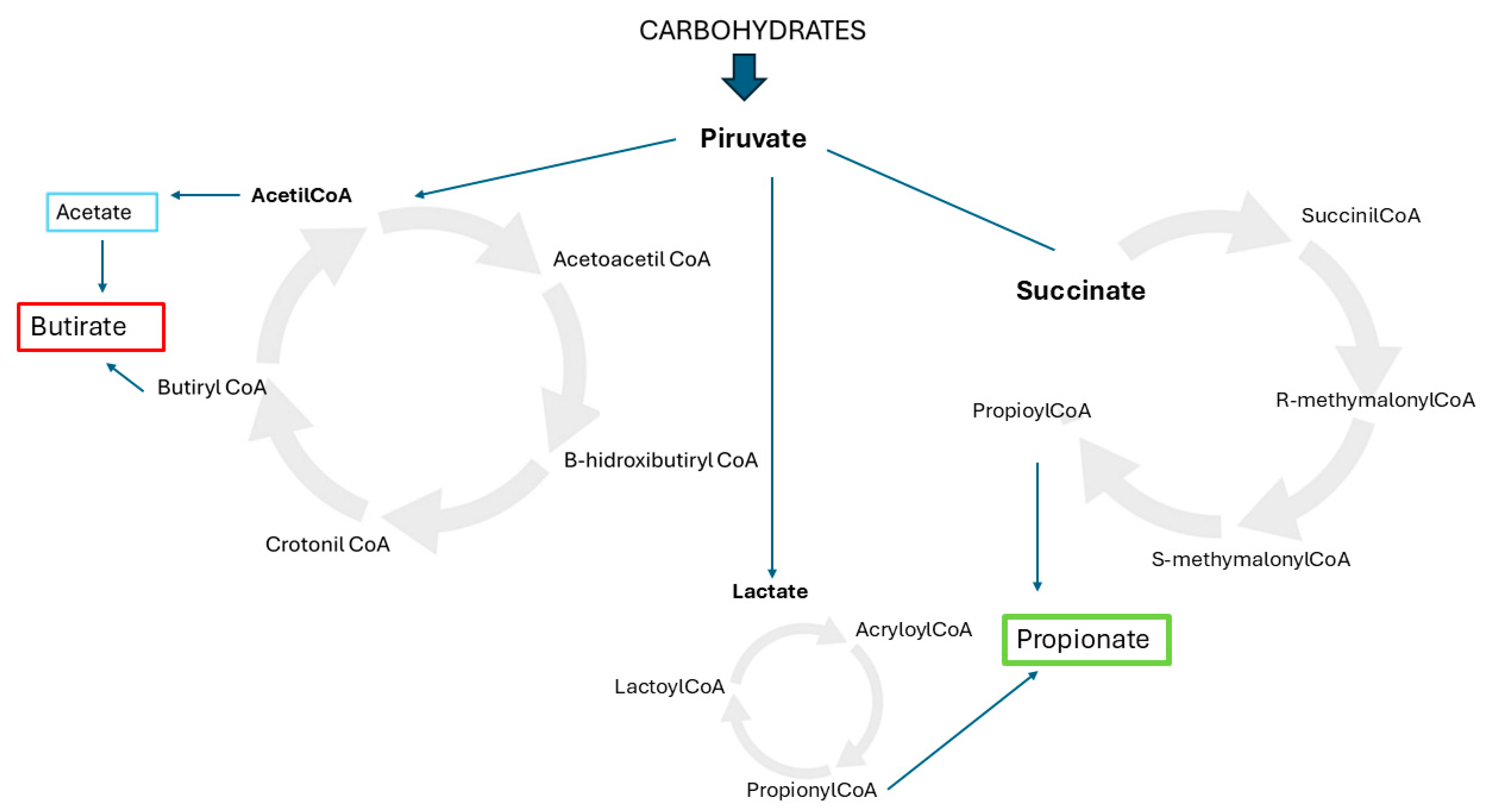
2. The Role of Nutrition in Shaping Microbiota
3. Nutrition, the Immune System, and Infectious Diseases
Malnutrition, Gut Microbiota, and Infectious Diseases in Children
4. The Role of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Symbiotics in Pediatric Infectious Diseases
4.1. Definition and Mechanism of Action of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Symbiotics
4.2. Treatment with Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Symbiotics in Pediatric Infectious Diseases
4.2.1. Acute Viral Gastroenteritis (AGE)
4.2.2. Upper Respiratory Tract Viral Infections (URTIs)
4.2.3. Sepsis
4.2.4. Healthcare-Associated Infections, Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea, and Infections Caused by Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria
5. Future Directions and Challenges
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EN | Enteral Nutrition |
| RCTs | Randomized Controlled Trials |
| ICU | Intensive Care Unit |
| SCFAs | Short-Chain Fatty Acids |
| PUFAs | Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids |
| GABA | Gamma Amino Butyric Acid |
| DOPA | Dihydroxyphenilalanine |
| CFUs | Colony-Forming Units |
| FOSs | Fructooligosaccharides |
| GOSs | Galactooligosaccharides |
| IL | Interleukin |
| TNF | Tumor Necrosis Factor |
| AGE | Acute Viral Gastroenteritis |
| RTIs | Respiratory Tract Infections |
| MV | Mechanical Ventilation |
| VAP | Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia |
| AAD | Antibiotics-Associated Diarrhea |
| MDRO | Multidrug-Resistant Microorganisms |
References
- Botrán, M.; López-Herce, J.; Mencía, S.; Urbano, J.; Solana, M.J.; García, A. Enteral nutrition in the critically ill child: Comparison of standard and protein-enriched diets. J. Pediatr. 2011, 159, 27–32.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamberlan, P.; Delgado, A.F.; Leone, C.; Feferbaum, R.; Okay, T.S. Nutrition therapy in a pediatric intensive care unit: Indications, monitoring, and complications. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2011, 35, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, N.M.; Skillman, H.E.; Irving, S.Y.; Coss-Bu, J.A.; Vermilyea, S.; Farrington, E.A.; McKeever, L.; Hall, A.M.; Goday, P.S.; Braunschweig, C. Guidelines for the Provision and Assessment of Nutrition Support Therapy in the Pediatric Critically Ill Patient: Society of Critical Care Medicine and American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2017, 41, 706–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rheenen, P.F.; Aloi, M.; Assa, A.; Bronsky, J.; Escher, J.C.; Fagerberg, U.L.; Gasparetto, M.; Gerasimidis, K.; Griffiths, A.; Henderson, P.; et al. The Medical Management of Paediatric Crohn’s Disease: An ECCO-ESPGHAN Guideline Update. J. Crohns Colitis 2020, 15, 171–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solana, M.J.; Slocker, M.; Martínez de Compañon, Z.; Olmedilla, M.; Miñambres, M.; Reyes, S.; Fernández, R.; Rodríguez, E.; Redondo, S.; Díaz, L.; et al. Prevalence, Risk Factors and Impact of Nutrition Interruptions in Critically Ill Children. Nutrients 2023, 15, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, N.M.; McAleer, D.; Hamilton, S.; Naples, E.; Leavitt, K.; Mitchell, P.; Duggan, C. Challenges to optimal enteral nutrition in a multidisciplinary pediatric intensive care unit. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2010, 34, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiertsema, S.P.; van Bergenhenegouwen, J.; Garssen, J.; Knippels, L.M.J. The interplay between the gut microbiome and the immune system in the context of infectious diseases throughout life and the role of nutrition in optimizing treatment strategies. Nutrients 2021, 13, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyland, D.K.; Stephens, K.E.; Day, A.G.; McClave, S.A. The success of enteral nutrition and ICU-acquired infections: A multicenter observational study. Clin Nutr. 2011, 30, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudsk, K.A.; Croce, M.A.; Fabian, T.C.; Minard, G.; Tolley, E.A.; Poret, H.A.; Kuhl, M.R.; Brown, R.O. Enteral versus parenteral feeding. Effects on septic morbidity after blunt and penetrating abdominal trauma. Ann. Surg. 1992, 215, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberda, C.; Gramlich, L.; Jones, N.; Jeejeebhoy, K.; Day, A.G.; Dhaliwal, R.; Heyland, D.K. The relationship between nutritional intake and clinical outcomes in critically ill patients: Results of an international multicenter observational study. Intensive Care Med. 2009, 35, 1728–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClave, S.A.; Heyland, D.K. The physiological response and associated clinical benefits from provision of early enteral nutrition. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2009, 24, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solana, M.J.; Manrique, G.; Slocker, M.; Fernández, R.; Gil, R.; Yun, C.; García, M.; Redondo, S.; Balaguer, M.; Rodríguez, E.; et al. Early vs late enteral nutrition in pediatric intensive care unit: Barriers, benefits, and complications. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2023, 38, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cianci, R.; Franza, L.; Schinzari, G.; Rossi, E.; Ianiro, G.; Tortora, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; Gambassi, G.; Cammarota, G. The Interplay between Immunity and Microbiota at Intestinal Immunological Niche: The Case of Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, V.; Capurso, G.; Ianiro, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; Arcidiacono, P.G.; Alvaro, D. Intestinal permeability changes with bacterial translocation as key events modulating systemic host immune response to SARS-CoV-2: A working hypothesis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2020, 52, 1383–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdes, A.M.; Walter, J.; Segal, E.; Spector, T.D. Role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health. BMJ 2018, 361, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ianiro, G. Levothyroxine absorption in health and disease, and new therapeutic perspectives. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 18, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kau, A.L.; Ahern, P.P.; Griffin, N.W.; Goodman, A.L.; Gordon, J.I. Human nutrition, the gut microbiome and the immune system. Nature. 2011, 474, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rooks, M.G.; Garrett, W.S. Gut microbiota, metabolites and host immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainz, T.; Delgado, J.; Mendez-Echevarría, A.; Santiago, B.; Lopez-Varela, E.; Aguilera-Alonso, D.; Saavedra-Lozano, J.; Rodríguez-Fernández, R.; Holguín, Á.; Navarro, M.L. The clinical relevance of the microbiome when managing paediatric infectious diseases-Narrative review. Acta Paediatr. 2021, 110, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesa, M.D.; Loureiro, B.; Iglesia, I.; Fernandez Gonzalez, S.; Llurba Olivé, E.; García Algar, O.; Solana, M.J.; Cabero Perez, M.J.; Sainz, T.; Martinez, L.; et al. The Evolving Microbiome from Pregnancy to Early Infancy: A Comprehensive Review. Nutrients. 2020, 12, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, L.; Klein, N. The Microbiome-The Explanation for (Almost) Everything? Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2019, 38, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaulke, C.A.; Sharpton, T.J. The influence of ethnicity and geography on human gut microbiome composition. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1495–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drago, L.; Panelli, S.; Bandi, C.; Zuccotti, G.; Perini, M.; D’Auria, E. Clinical Medicine What Pediatricians Should Know before Studying Gut Microbiota. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1206. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- David, L.A.; Maurice, C.F.; Carmody, R.N.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Button, J.E.; Wolfe, B.E.; Ling, A.V.; Devlin, A.S.; Varma, Y.; Fischbach, M.A. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature 2014, 505, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinninella, E.; Tohumcu, E.; Raoul, P.; Fiorani, M.; Cintoni, M.; Mele, M.C.; Cammarota, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; Ianiro, G. The role of diet in shaping human gut microbiota. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2023, 62–63, 101828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Stombaugh, J.I.; Gordon, J.I.; Jansson, J.K.; Knight, R. Diversity, stability and resilience of the human gut microbiota. Nature 2012, 489, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scott, K.P.; Gratz, S.W.; Sheridan, P.O.; Flint, H.J.; Duncan, S.H. The influence of diet on the gut microbiota. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 69, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, N.; Tan, H.Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, C.; Feng, Y. Function of Akkermansia muciniphila in Obesity: Interactions with Lipid Metabolism, Immune Response and Gut Systems. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 219. [Google Scholar]
- Malesza, I.J.; Malesza, M.; Walkowiak, J.; Mussin, N.; Walkowiak, D.; Aringazina, R.; Bartkowiak-Wieczorek, J.; Mądry, E. High-Fat, Western-Style Diet, Systemic Inflammation, and Gut Microbiota: A Narrative Review. Cells 2021, 10, 3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajstova, A.; Galanova, N.; Coufal, S.; Malkova, J.; Kostovcik, M.; Cermakova, M.; Pelantova, H.; Kuzma, M.; Sediva, B.; Hudcovic, T.; et al. Diet Rich in Simple Sugars Promotes Pro-Inflammatory Response via Gut Microbiota Alteration and TLR4 Signaling. Cells 2020, 9, 2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.L.; Alvarado, D.A.; Swanson, K.S.; Holscher, H.D. The Prebiotic Potential of Inulin-Type Fructans: A Systematic Review. Adv. Nutr. 2022, 13, 492–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Waliullah, S.; Godfrey, V.; Khan, M.A.W.; Ramachandran, R.A.; Cantarel, B.L.; Behrendt, C.; Peng, L.; Hooper, L.V.; Zaki, H. Dietary simple sugars alter microbial ecology in the gut and promote colitis in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, 6218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullón, P.; Gullón, B.; Tavaria, F.; Vasconcelos, M.; Gomes, A.M. In vitro fermentation of lupin seeds (Lupinus albus) and broad beans (Vicia faba): Dynamic modulation of the intestinal microbiota and metabolomic output. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 3316–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graf, D.; Monk, J.M.; Lepp, D.; Wu, W.; McGillis, L.; Roberton, K.; Brummer, Y.; Tosh, S.M.; Power, K.A. Cooked Red Lentils Dose-Dependently Modulate the Colonic Microenvironment in Healthy C57Bl/6 Male Mice. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martineau-Côté, D.; Achouri, A.; Karboune, S.; L’Hocine, L. Faba Bean: An Untapped Source of Quality Plant Proteins and Bioactives. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrea, L.; Annunziata, G.; Muscogiuri, G.; Laudisio, D.; Di Somma, C.; Maisto, M.; Tenore, G.C.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Trimethylamine N-oxide, Mediterranean diet, and nutrition in healthy, normal-weight adults: Also a matter of sex? Nutrition 2019, 62, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dostal Webster, A.; Staley, C.; Hamilton, M.J.; Huang, M.; Fryxell, K.; Erickson, R.; Kabage, A.J.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Khoruts, A. Influence of short-term changes in dietary sulfur on the relative abundances of intestinal sulfate-reducing bacteria. Gut Microbes 2019, 10, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, K.; O’Donovan, A.N.; Caplice, N.M.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C. Exploring the Gut Microbiota and Cardiovascular Disease. Metabolites 2021, 11, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gérard, P. Diet-gut microbiota interactions on cardiovascular disease. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 1528–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hara, A.M.; Shanahan, F. The gut flora as a forgotten organ. EMBO Rep. 2006, 7, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Zhong, M.; Pan, T.; Qu, H.; Chen, E. Gut Microbiota and Enteral Nutrition Tolerance in Non-Abdominal Infection Septic ICU Patients: An Observational Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLellan, A.; Connors, J.; Grant, S.; Cahill, L.; Langille, M.G.I.; Van Limbergen, J. The Impact of Exclusive Enteral Nutrition (EEN) on the Gut Microbiome in Crohn’s Disease: A Review. Nutrients 2017, 9, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcone, E.L.; Han, Y.; Kreuzburg, S.; Heller, T.; Church, J.A.; Grou, C.; Calderon, V.; Subramanian, P.; Deming, C.; Conlan, S.; et al. Exclusive enteral nutrition induced sustained changes in the microbiota and improved inflammatory bowel disease in a pediatric patient with chronic granulomatous disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 1011–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sila, S.; Jelić, M.; Trivić, I.; Tambić Andrašević, A.; Kolaček, S.; Hojsak, I. Healthy Siblings of Children With Crohn’s Disease Exhibit More Rapid Changes in Microbiota Composition as a Response to Exclusive Enteral Nutrition. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2021, 45, 1352–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sila, S.; Jelić, M.; Trivić, I.; Tambić Andrašević, A.; Kolaček, S.; Hojsak, I. Gut Microbiota Composition Changes following Discontinuation of Exclusive Enteral Nutrition in Children with Crohn’s Disease. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tourkochristou, E.; Triantos, C.; Mouzaki, A. The Influence of Nutritional Factors on Immunological Outcomes. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 665968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iddir, M.; Brito, A.; Dingeo, G.; Fernandez Del Campo, S.S.; Samouda, H.; La Frano, M.R.; Bohn, T. Strengthening the Immune System and Reducing Inflammation and Oxidative Stress through Diet and Nutrition: Considerations during the COVID-19 Crisis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham-Rundles, S.; McNeeley, D.F.; Moon, A. Mechanisms of nutrient modulation of the immune response. J. Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005, 115, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarin, H.V.; Gudelj, I.; Honkanen, J.; Ihalainen, J.K.; Vuorela, A.; Lee, J.H.; Jin, Z.; Terwilliger, J.D.; Isola, V.; Ahtiainen, J.P.; et al. Molecular Pathways Mediating Immunosuppression in Response to Prolonged Intensive Physical Training, Low-Energy Availability, and Intensive Weight Loss. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, T.C.; Olson, C.A.; Hsiao, E.Y. Interactions between the microbiota, immune and nervous systems in health and disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colbey, C.; Cox, A.J.; Pyne, D.B.; Zhang, P.; Cripps, A.W.; West, N.P. Upper Respiratory Symptoms, Gut Health and Mucosal Immunity in Athletes. Sports Med. 2018, 48 (Suppl. S1), 65–77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sommer, F.; Bäckhed, F. The gut microbiota--masters of host development and physiology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raiten, D.J.; Sakr Ashour, F.A.; Ross, A.C.; Meydani, S.N.; Dawson, H.D.; Stephensen, C.B.; Brabin, B.J.; Suchdev, P.S.; van Ommen, B.; INSPIRE Consultative Group. Inflammation and Nutritional Science for Programs/Policies and Interpretation of Research Evidence (INSPIRE). J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 1039S–1108S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hortová-Kohoutková, M.; Lázničková, P.; Frič, J. How immune-cell fate and function are determined by metabolic pathway choice: The bioenergetics underlying the immune response. Bioessays 2021, 43, 2000067. [Google Scholar]
- Hatch-McChesney, A.; Smith, T.J. Nutrition, Immune Function, and Infectious Disease in Military Personnel: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillin, O.M.; Vindry, C.; Ohlmann, T.; Chavatte, L. Selenium, Selenoproteins and Viral Infection. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillin, O.M.; Vindry, C.; Ohlmann, T.; Chavatte, L. Interplay between Selenium, Selenoproteins and HIV-1 Replication in Human CD4 T-Lymphocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasmi, A.; Tippairote, T.; Mujawdiya, P.K.; Peana, M.; Menzel, A.; Dadar, M.; Gasmi Benahmed, A.; Bjørklund, G. Micronutrients as immunomodulatory tools for COVID-19 management. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 220, 108545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrosa, L.F.C.; Barros, A.N.A.B.; Leite-Lais, L. Nutritional risk of vitamin D, vitamin C, zinc, and selenium deficiency on risk and clinical outcomes of COVID-19: A narrative review. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2022, 47, 9–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, J.D.; Nama, N.; O’Hearn, K.; Sampson, M.; Amrein, K.; Iliriani, K.; McIntyre, L.; Fergusson, D.; Menon, K. Vitamin D deficiency in critically ill children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 287. [Google Scholar]
- Madden, K.; Feldman, H.A.; Smith, E.M.; Gordon, C.M.; Keisling, S.M.; Sullivan, R.M.; Hollis, B.W.; Agan, A.A.; Randolph, A.G. Vitamin D deficiency in critically ill children. Pediatrics 2012, 130, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankar, J.; Lotha, W.; Ismail, J.; Anubhuti, C.; Meena, R.S.; Sankar, M.J. Vitamin D deficiency and length of pediatric intensive care unit stay: A prospective observational study. Ann. Intensive Care 2016, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holford, P.; Carr, A.C.; Jovic, T.H.; Ali, S.R.; Whitaker, I.S.; Marik, P.E.; Smith, A.D. Vitamin C—An adjunctive therapy for respiratory infection, sepsis and COVID-19. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somagutta, M.K.R.; Pormento, M.K.L.; Khan, M.A.; Hamdan, A.; Hange, N.; Kc, M.; Pagad, S.; Jain, M.S.; Lingarajah, S.; Sharma, V.; et al. The efficacy of vitamin C, thiamine, and corticosteroid therapy in adult sepsis patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acute Crit. Care 2021, 36, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.R.; Zhu, H. Vitamin C for sepsis intervention: From redox biochemistry to clinical medicine. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2021, 476, 4449–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokri-mashhadi, N.; Aliyari, A.; Hajhashemy, Z.; Saadat, S.; Rouhani, M.H. Is it time to reconsider the administration of thiamine alone or in combination with vitamin C in critically ill patients? A meta-analysis of clinical trial studies. J. Intensive Care 2022, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milani, G.P.; Macchi, M.; Guz-Mark, A. Vitamin c in the treatment of COVID-19. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gombart, A.F.; Pierre, A.; Maggini, S. A Review of Micronutrients and the Immune System-Working in Harmony to Reduce the Risk of Infection. Nutrients 2020, 12, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koekkoek, W.A.C.; Hettinga, K.; De Vries, J.H.M.; van Zanten, A.R.H. Micronutrient deficiencies in critical illness. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 3780–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, N.M.; Duggan, C.P. Nutritional Deficiencies During Critical Illness. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 56, 1143–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alker, W.; Haase, H. Zinc and sepsis. Nutrients 2018, 10, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehab, R.F.; Cross, T.W.L.; Forman, M.R. The Gut Microbiota: A Promising Target in the Relation between Complementary Feeding and Child Undernutrition. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 969–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoghi, S.; Sadeghpour Heravi, F.; Nikniaz, Z.; Shirmohamadi, M.; Moaddab, S.Y.; Ebrahimzadeh Leylabadlo, H. Gut microbiota and childhood malnutrition: Understanding the link and exploring therapeutic interventions. Eng. Life Sci. 2023, 24, 2300070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solana, M.J.; Manrique, G.; Fernández, R.; Slocker, M.; García, M.; Redondo, S.; Yun, C.; Gil, R.; Balaguer, M.; Rodríguez, E. Nutritional status and nutrition support in critically ill children in Spain: Results of a multicentric study. Nutrition 2021, 84, 110993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, R.E.; Victora, C.G.; Walker, S.P.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Christian, P.; de Onis, M.; Ezzati, M.; Grantham-McGregor, S.; Katz, J.; Martorell, R.; et al. Maternal and child undernutrition and overweight in low-income and middle-income countries. Lancet 2013, 382, 427–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iddrisu, I.; Monteagudo-Mera, A.; Poveda, C.; Pyle, S.; Shahzad, M.; Andrews, S.; Walton, G.E. Malnutrition and Gut Microbiota in Children. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanmiguel, C.; Gupta, A.; Mayer, E.A. Gut Microbiome and Obesity: A Plausible Explanation for Obesity. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2015, 4, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosek, M.N.; Ahmed, T.; Bhutta, Z.A. Causal Pathways from Enteropathogens to Environmental Enteropathy: Findings from the MAL-ED Birth Cohort Study. EBioMedicine 2017, 18, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, T.S.; Gupta, S.S.; Bhattacharya, T.; Yadav, D.; Barik, A.; Chowdhury, A.; Das, B.; Mande, S.S.; Nair, G.B. Gut microbiomes of Indian children of varying nutritional status. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreiro Guridi, C.; Romeo Serena, A.; Gallego Cabrera, S.; Fernández, I.A.; Hernández, C.R.; Vivanco, B.M.; Melguizo, M.C.; Suárez-Almarza, J.; Nieto-Magro, C. Clinical evaluation of the synbiotic Prodefen Plus® in the prevention of the antibiotic-associated diarrhoea in subjects requiring antibiotic treatment. Benef. Microbes 2020, 11, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.R.; Hutkins, R.; Sanders, M.E.; Prescott, S.L.; Reimer, R.A.; Salminen, S.J.; Scott, K.; Stanton, C.; Swanson, K.S.; Cani, P.D.; et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hojsak, I.; Kolaček, S.; Mihatsch, W.; Mosca, A.; Shamir, R.; Szajewska, H.; Vandenplas, Y.; Working Group on Probiotics and Prebiotics of the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition. Synbiotics in the Management of Pediatric Gastrointestinal Disorders. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2023, 76, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdoǧan, Ö.; Tanyeri, B.; Torun, E.; Gönüllü, E.; Arslan, H.; Erenberk, U.; Oktem, F. The comparition of the efficacy of two different probiotics in rotavirus gastroenteritis in children. J. Trop. Med. 2012, 2012, 787240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maftei, N.M.; Raileanu, C.R.; Balta, A.A.; Ambrose, L.; Boev, M.; Marin, D.B.; Lisa, E.L. The Potential Impact of Probiotics on Human Health: An Update on Their Health-Promoting Properties. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhu, K.N.C.; Sowmyanarayanan, T.V.; Paul, A.; Babji, S.; Ajjampur, S.S.; Priyadarshini, S.; Sarkar, R.; Balasubramanian, K.A.; Wanke, C.A.; Ward, H.D.; et al. Immune Response and Intestinal Permeability in Children With Acute Gastroenteritis Treated With Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. Clin. Infec Dis. 2014, 58, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, E.M.S.; da Silva, L.C.N.; Carmo, M.S. Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics in childhood diarrhea. Brazilian, J. Med. Biol. Res. 2024, 57, e13205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanauchi, O.; Andoh, A.; AbuBakar, S.; Yamamoto, N. Probiotics and Paraprobiotics in Viral Infection: Clinical Application and Effects on the Innate and Acquired Immune Systems. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Săsăran, M.O.; Mărginean, C.O.; Adumitrăchioaiei, H.; Meliț, L.E. Pathogen-Specific Benefits of Probiotic and Synbiotic Use in Childhood Acute Gastroenteritis: An Updated Review of the Literature. Nutrients 2023, 15, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altomare, A.; Giovanetti, M.; Baldaro, F.; Ciccozzi, M.; Cicala, M.; Guarino, M.P.L. The Prevention of Viral Infections: The Role of Intestinal Microbiota and Nutritional Factors. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Vecchio, A.; Dias, J.A.; Berkley, J.A.; Boey, C.; Cohen, M.B.; Cruchet, S.; Liguoro, I.; Salazar Lindo, E.; Sandhu, B.; Sherman, P.; et al. Comparison of recommendations in clinical practice guidelines for acute gastroenteritis in children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2016, 63, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szajewska, H.; Kołodziej, M. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Saccharomyces boulardii in the prevention of antibiotic-associated diarrhoea. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 42, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- do Carmo, M.S.; Santos Citapary dos Araújo, M.C.; Girón, J.A.; Fernandes, E.S.; Monteiro-Neto, V. Probiotics, mechanisms of action, and clinical perspectives for diarrhea management in children. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 5074–5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedman, S.B.; Williamson-Urquhart, S.; Farion, K.J.; Gouin, S.; Willan, A.R.; Poonai, N.; Hurley, K.; Sherman, P.M.; Finkelstein, Y.; Lee, B.E.; et al. Multicenter Trial of a Combination Probiotic for Children with Gastroenteritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2015–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedman, S.B.; Xie, J.; Nettel-Aguirre, A.; Pang, X.L.; Chui, L.; Williamson-Urquhart, S.; Schnadower, D.; Schuh, S.; Sherman, P.M.; Lee, B.E.; et al. A randomized trial evaluating virus-specific effects of a combination probiotic in children with acute gastroenteritis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collinson, S.; Deans, A.; Padua-Zamora, A.; Gregorio, G.V.; Li, C.; Dans, L.F.; Allen, S.J. Probiotics for treating acute infectious diarrhoea. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 12, CD003048. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Lu, P.; Li, M.X.; Cai, X.L.; Xiong, W.Y.; Hou, H.J.; Ha, X.Q. A meta-analysis of the effects of probiotics and synbiotics in children with acute diarrhea. Medicine 2019, 98, e16618. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vassilopoulou, L.; Spyromitrou-Xioufi, P.; Ladomenou, F. Effectiveness of probiotics and synbiotics in reducing duration of acute infectious diarrhea in pediatric patients in developed countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2021, 180, 2907–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahbazi, R.; Yasavoli-sharahi, H.; Alsadi, N.; Ismail, N.; Matar, C. Probiotics in Treatment of Viral Respiratory Infections and Neuroinflammatory Disorders. Molecules. 2020, 25, 4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Pan, B.; Xu, S.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Bao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, C.; et al. A meta-analysis reveals the effectiveness of probiotics and prebiotics against respiratory viral infection. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, BSR20203638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penela Sánchez, D.; Rocafort, M.; Henares, D.; Jordan, I.; Brotons, P.; Cabrerizo, M.; Launes, C.; Muñoz-Almagro, C. Impact of the bacterial nasopharyngeal microbiota on the severity of genus enterovirus lower respiratory tract infection in children: A case—Control study. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2023, 58, 1728–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.K.Y.; Tao, J.; Chan, J.; Li, H.B.; Pang, H. Preventing respiratory tract infections by synbiotic interventions: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 11, 979–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Dong, B.R.; Hao, Q. Probiotics for preventing acute upper respiratory tract infections. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022, 8, CD006895. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Williams, L.M.; Stoodley, I.L.; Berthon, B.S.; Wood, L.G. The Effects of Prebiotics, Synbiotics, and Short-Chain Fatty Acids on Respiratory Tract Infections and Immune Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Adv. Nutr. 2022, 13, 167–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khailova, L.; Frank, D.N.; Dominguez, J.A.; Wischmeyer, P.E. Probiotic Administration Reduces Mortality and Improves Intestinal Epithelial Homeostasis in Experimental Sepsis. Anesthesiology 2013, 119, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamani, A.; Mashhadi, F.; Khademi, G.; Nematy, M.; Emadzadeh, M.; Sezavar, M.; Roudi, F. Investigating the effect of synbiotic supplementation on inflammatory indices in critically ill septic children: A protocol study for randomized control trial. Trials. 2024, 25, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darbandi, A.; Banar, M.; Koupaei, M.; Afifirad, R.; Asadollahi, P.; Bafandeh, E.; Rasooli, I.; Emamie, A.; Navidifar, T.; Owlia, P. Clinical efficacy of probiotics in prevention of infectious diseases among hospitalized patients in ICU and non-ICU wards in clinical randomized trials: A systematic review. Health Sci. Rep. 2023, 6, e1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angurana, S.K.; Bansal, A.; Singhi, S.; Aggarwal, R.; Jayashree, M.; Salaria, M.; Mangat, N.K. Evaluation of effect of probiotics on cytokine levels in critically Ill children with severe sepsis: A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 46, 1656–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanaie, S.; Ebrahimi-Mameghani, M.; Hamishehkar, H.; Mojtahedzadeh, M.; Mahmoodpoor, A. Effect of a multispecies Probiotic on inflammatory markers in critically ill patients: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2014, 19, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chi, C.; Buys, N.; Li, C.; Sun, J.; Yin, C. Effects of prebiotics on sepsis, necrotizing enterocolitis, mortality, feeding intolerance, time to full enteral feeding, length of hospital stay, and stool frequency in preterm infants: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 73, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haak, B.W.; Prescott, H.C.; Wiersinga, W.J. Therapeutic potential of the gut microbiota in the prevention and treatment of sepsis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haak, B.W.; Wiersinga, W.J. The role of the gut microbiota in sepsis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.C.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, H.L.; Yuan, Y.; Lu, J.H.; Zhong, L. Probiotic in the prevention of ventilator-associated pneumonia in critically ill patients: Evidence from meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis of randomized clinical trials. BMC Pulm. Med. 2022, 22, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Li, L.Q.; Chen, C.Y.; Zhang, G.S.; Cui, W.; Tian, B.P. Do probiotics help prevent ventilator-associated pneumonia in critically ill patients? A systematic review with meta-analysis. ERJ Open Res. 2021, 7, 00302-2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, M.; Salewski, R.P.; Christman, M.C.; Girard, S.A.; Tompkins, T.A. Effectiveness of Lactobacillus helveticus and Lactobacillus rhamnosus for the management of antibiotic-associated diarrhoea in healthy adults: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trallero, O.G.; Serrano, L.H.; Inglés, M.B.; Roche Vallés, D.; Rodríguez, A.M. Effect of the administration of a probiotic with a combination of lactobacillus and bifidobacterium strains on antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Rev. Esp. Quimioter. 2019, 32, 268–272. [Google Scholar]
- Soldi, S.; Vasileiadis, S.; Lohner, S.; Uggeri, F.; Puglisi, E.; Molinari, P.; Donner, E.; Sieland, C.; Decsi, T.; Sailer, M.; et al. Prebiotic supplementation over a cold season and during antibiotic treatment specifically modulates the gut microbiota composition of 3–6 year-old children. Benef. Microbes 2019, 10, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.M.; Arshad, M. The Role of Probiotics, Prebiotics and Synbiotics in Combating Multidrug-Resistant Organisms. Clin. Ther. 2020, 42, 1637–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type of Probiotic Strain or Combination | Dosage |
|---|---|
| Bifidobacterium lactis | 14.5 × 106 CFU/100 mL milk for 7 days |
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) | 109/day–1010 CFU/2× for 5 days |
| Lactobacillus paracasei ST 11 | 5 × 109 CFU/2× for 5 days |
| Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 | 108 CFU |
| Lactobacillus acidophilus | 108−9 CFU/2× for 5 days |
| Saccharomyces boulardii | 250–500 mg/day or 4 × 109−10 viable cells for 5 days |
| Escherichia coli Nissle | 108 CFU/day–1010−11 CFU/for 5 days |
| B. longum, B. lactis, L. acidophilus, L. rhamnosus, L. plantarum, and P. pentosaceus | 108 CFU each strain |
| L rhamnosus 19070-2 and L. reuteri C+DSM 12246 | 1.7 × 1010 + 0.5 × 1010 CFU |
| LGG, S. boulardii, B. claudii, L. delbrueckii var bulgaricus, Streptococcus thermophilus, L. acidophilus, B. bifidum, and Enterococcus faecium SF68 | 107−9 CFU each strain |
| L. casei, L. rhamnosus, L. acidophilus, L. bulgaricus S. termophilus, B. breve, and B. infantis | 109 CFU/2× for 5 days |
| Type of Probiotic Strain or Combination | Dosage |
|---|---|
| Bifidobacterium lactis | 1–1.9 × 109 CFU for 3 weeks to 12 months |
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) | 109 CFU for 1–2 months |
| Lactobacillus paracasei, L. plantarum, and B. lactis | 1010 CFU for each strain for 3 months |
| L. rhamnosus, S. termophilus, and S. salivarius | 107 CFU for each strain for 12 months |
| L. acidophilus and B. lactis | 5 × 109–1 × 10 10 CFU for 2–8 weeks |
| L. bulgaricus, Streptococcus thermophilus, and B. lactis | 108 CFU for each strain for 16 weeks |
| B. longum and S. termophilus | 107 CFU for each strain for 3 months |
| L. rhamnosus, L. plantarum, and B. lactis | 1010 CFU for each strain for 2 months |
| LGG, B. infantis, B. breve, L. bulgaricus, Streptococcus thermophilus, L. acidophilus, and B. bifidum | 109 CFU total dose for 3 months |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Slöcker-Barrio, M.; López-Herce Cid, J.; Solana-García, M.J. The Interplay Between Nutrition and Microbiota and the Role of Probiotics and Symbiotics in Pediatric Infectious Diseases. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071222
Slöcker-Barrio M, López-Herce Cid J, Solana-García MJ. The Interplay Between Nutrition and Microbiota and the Role of Probiotics and Symbiotics in Pediatric Infectious Diseases. Nutrients. 2025; 17(7):1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071222
Chicago/Turabian StyleSlöcker-Barrio, María, Jesús López-Herce Cid, and María José Solana-García. 2025. "The Interplay Between Nutrition and Microbiota and the Role of Probiotics and Symbiotics in Pediatric Infectious Diseases" Nutrients 17, no. 7: 1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071222
APA StyleSlöcker-Barrio, M., López-Herce Cid, J., & Solana-García, M. J. (2025). The Interplay Between Nutrition and Microbiota and the Role of Probiotics and Symbiotics in Pediatric Infectious Diseases. Nutrients, 17(7), 1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071222






