The Influence of an AI-Driven Personalized Nutrition Program on the Human Gut Microbiome and Its Health Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
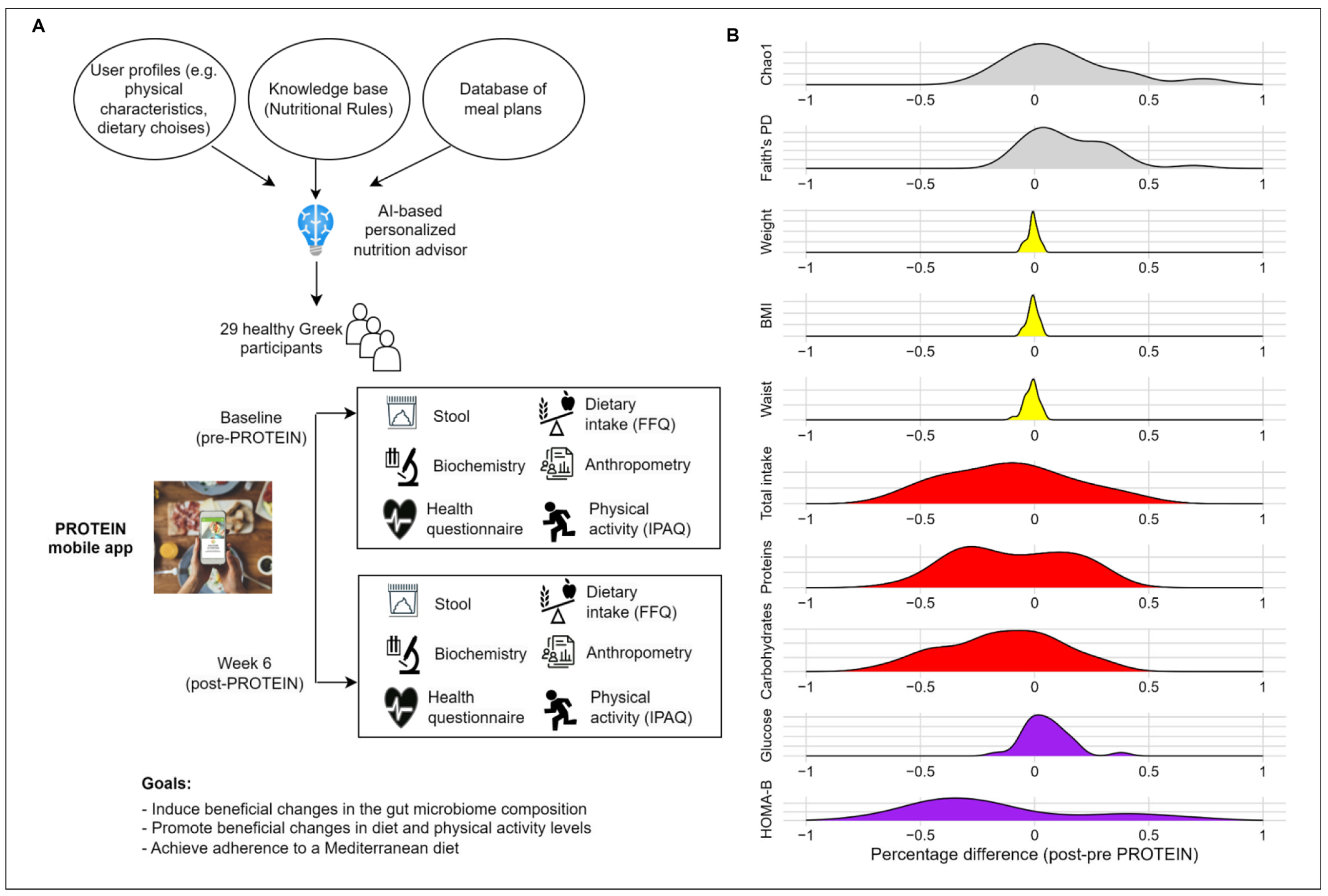
2.1. Study Population and Design
2.2. Intervention Using PROTEIN Mobile Application
2.3. Data Assessments
2.3.1. Dietary Intake
2.3.2. Anthropometry and Body Composition Analysis
2.3.3. Physical Activity
2.3.4. Biochemical Blood Indices
2.4. Fecal Sample Collection, DNA Extraction, and 16S rRNA Amplicon Sequencing
2.5. Outcomes
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Population Sample Description
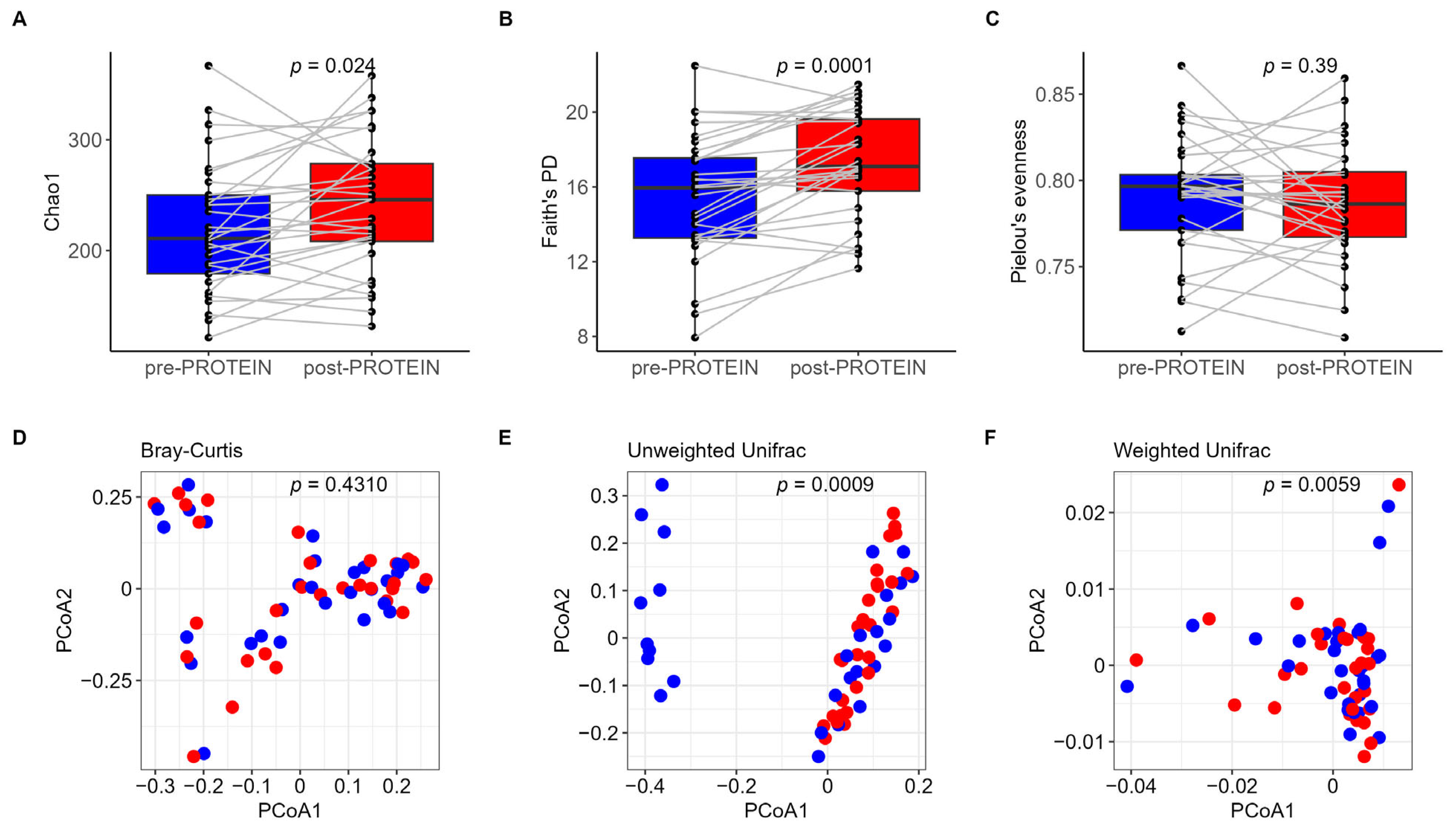
3.2. Impact of Six-Week PROTEIN Intervention on Gut Microbiome
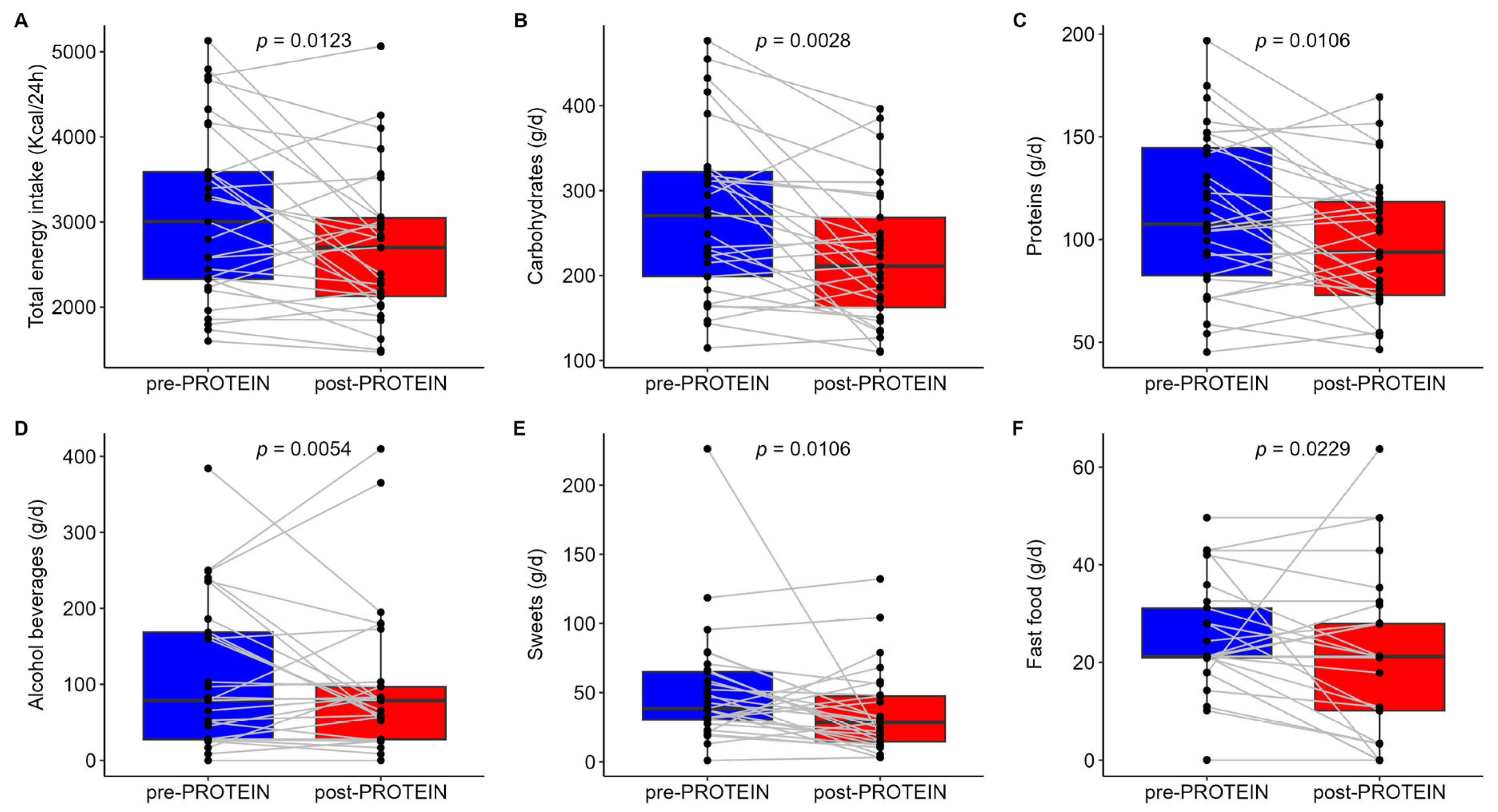
3.3. Secondary Outcomes
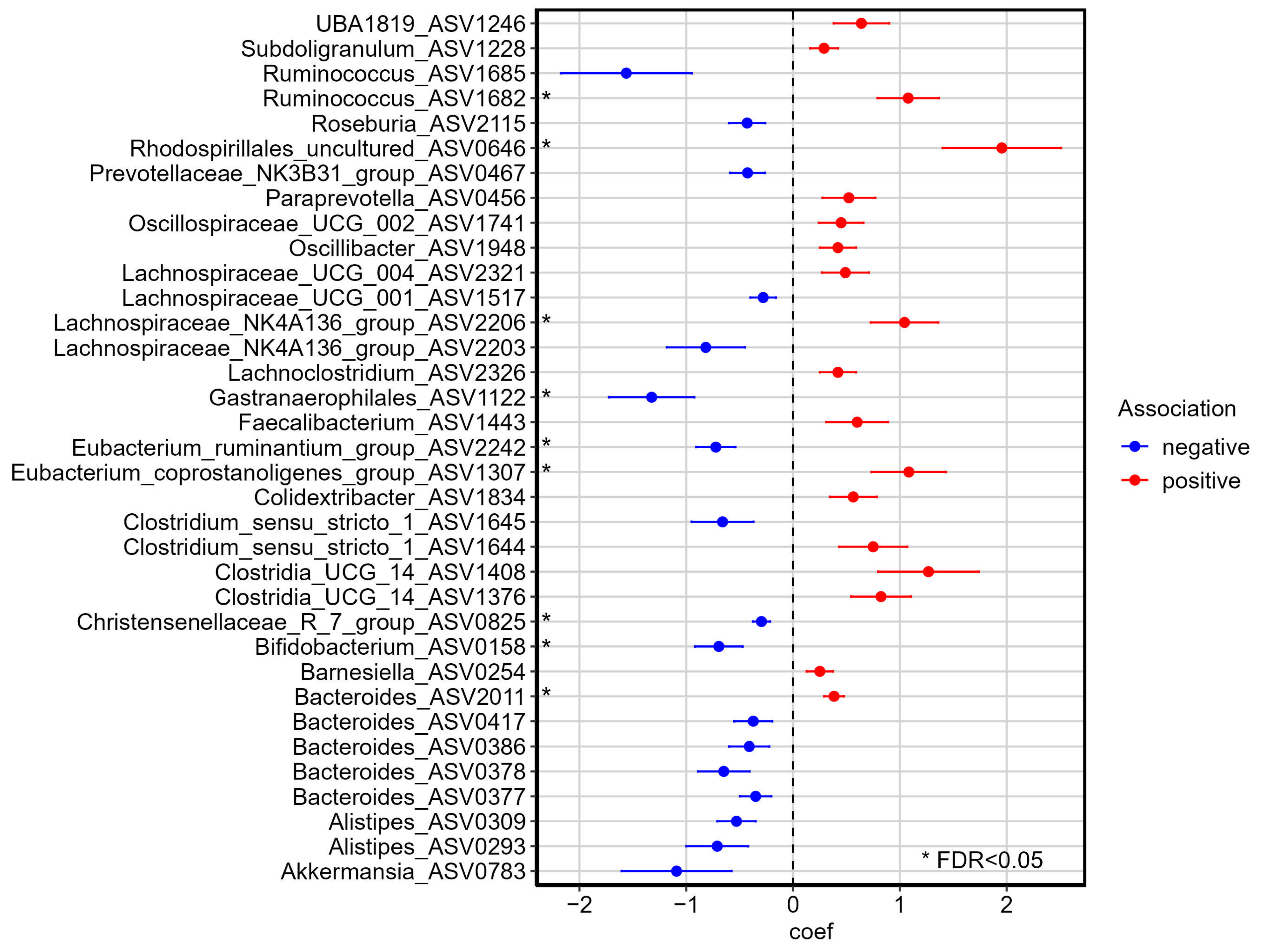
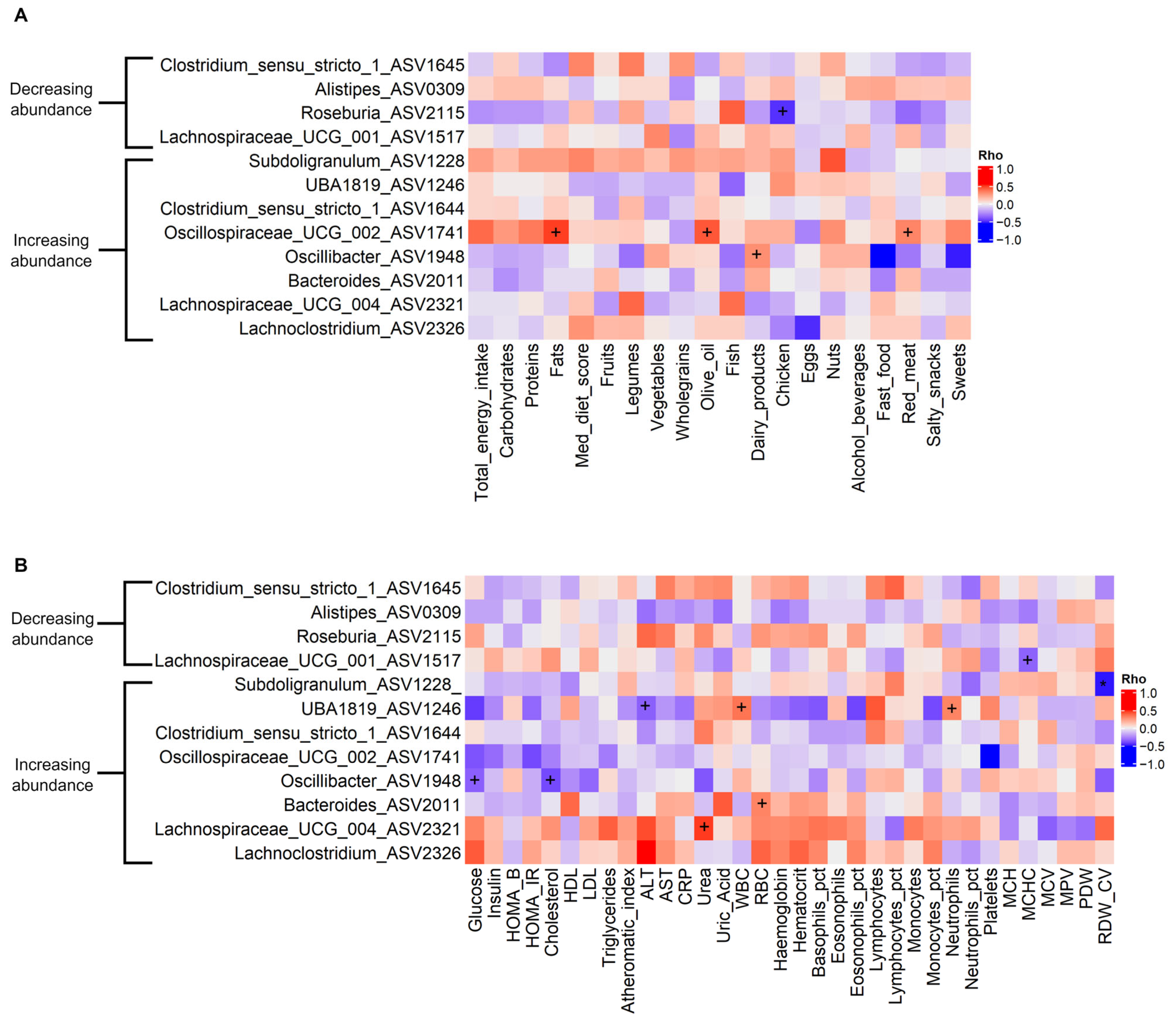
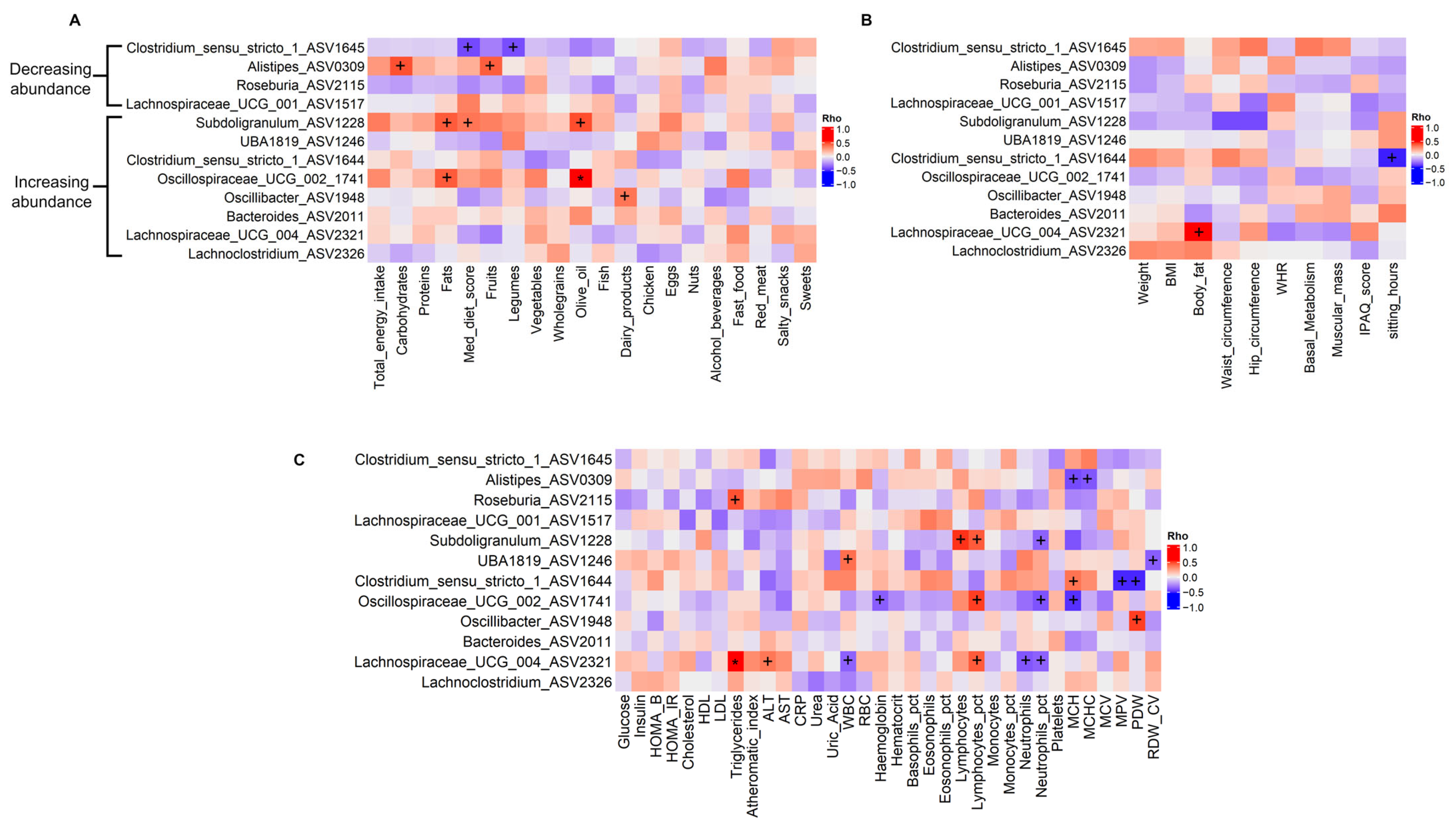
3.4. Associations Between Gut Microbiota and Dietary, Anthropometric, and Biochemistry Variables
4. Discussion
4.1. PROTEIN Intervention and Overall Gut Microbiome Community Structure
4.2. PROTEIN Intervention and Impact on Abundance of Genera of Interest
4.3. PROTEIN Intervention and Waist Circumference
4.4. Strengths, Limitations, and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | artificial intelligence |
| PROTEIN | PeRsOnalized nutrition for hEalthy livINg |
| FFQ | food frequency questionnaire |
| IPAQ | International Physical Activity Questionnaire |
| BMI | body mass index |
| HOMA | homeostasis model assessment |
| MDS | Mediterranean diet score |
| ASV | amplicon sequence variant |
| PICRUST2 | Phylogenetic Investigation of Communities by Reconstruction of Unobserved States |
| PCoA | principal coordinates analysis |
| FDR | false discovery rate |
| PA | physical activity |
| DA | differentially abundant |
References
- GBD 2019 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global burden of 87 risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1223–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, C.D.; Trepanowski, J.F.; Del Gobbo, L.C.; Hauser, M.E.; Rigdon, J.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Desai, M.; King, A.C. Effect of Low-Fat vs Low-Carbohydrate Diet on 12-Month Weight Loss in Overweight Adults and the Association with Genotype Pattern or Insulin Secretion: The DIETFITS Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2018, 319, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Berry, S.E.; Valdes, A.M.; Drew, D.A.; Asnicar, F.; Mazidi, M.; Wolf, J.; Capdevila, J.; Hadjigeorgiou, G.; Davies, R.; Al Khatib, H.; et al. Human postprandial responses to food and potential for precision nutrition. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 964–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, S.; Campos-Medina, L.; Leal-Mercado, L. Personalized nutrition: The end of the one-diet-fits-all era. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1370595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordovas, J.M.; Ferguson, L.R.; Tai, E.S.; Mathers, J.C. Personalised nutrition and health. BMJ 2018, 361, bmj.k2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, A.E. (Ed.) Challenges and Opportunities for Precision and Personalized Nutrition: Proceedings of a Workshop-in Brief; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bermingham, K.M.; Linenberg, I.; Polidori, L.; Asnicar, F.; Arrè, A.; Wolf, J.; Badri, F.; Bernard, H.; Capdevila, J.; Bulsiewicz, W.J.; et al. Effects of a personalized nutrition program on cardiometabolic health: A randomized controlled trial. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 1888–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordovas, J.M.; Berciano, S. Personalized nutrition and healthy aging. Nutr. Rev. 2020, 78, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, P.C.; Mishra, A.K.; Sharma, R.; Bhunia, B.; Mishra, B.; Tiwari, A.; Nayak, P.K.; Sharma, M.; Bhuyan, T.; Kaushal, S.; et al. Recent advances in artificial intelligence towards the sustainable future of agri-food industry. Food Chem. 2024, 447, 138945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namkhah, Z.; Fatemi, S.F.; Mansoori, A.; Nosratabadi, S.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M.; Sobhani, S.R. Advancing sustainability in the food and nutrition system: A review of artificial intelligence applications. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1295241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa-Holwerda, A.; Park, O.-H.; Albracht-Schulte, K.; Niraula, S.; Thompson, L.; Oldewage-Theron, W. The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Nutrition Research: A Scoping Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papastratis, I.; Konstantinidis, D.; Daras, P.; Dimitropoulos, K. AI nutrition recommendation using a deep generative model and ChatGPT. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassem, H.; Beevi, A.A.; Basheer, S.; Lutfi, G.; Ismail, L.C.; Papandreou, D. Investigation and Assessment of AI’s Role in Nutrition—An Updated Narrative Review of the Evidence. Nutrients 2025, 17, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodore Armand, T.P.; Nfor, K.A.; Kim, J.I.; Kim, H.C. Applications of Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning in Nutrition: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrario, P.G.; Gedrich, K. Machine learning and personalized nutrition: A promising liaison? Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 78, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaçar, H.K.; Kaçar, Ö.F.; Avery, A. Diet Quality and Caloric Accuracy in AI-Generated Diet Plans: A Comparative Study Across Chatbots. Nutrients 2025, 17, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naja, F.; Taktouk, M.; Matbouli, D.; Khaleel, S.; Maher, A.; Uzun, B.; Alameddine, M.; Nasreddine, L. Artificial intelligence chatbots for the nutrition management of diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 78, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchan, M.L.; Goel, K.; Schneider, C.K.; Steullet, V.; Bratton, S.; Basch, E. National Implementation of an Artificial Intelligence–Based Virtual Dietitian for Patients With Cancer. JCO Clin. Cancer Inform. 2024, 8, e2400085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veluvali, A.; Zahedani, A.D.; Hosseinian, A.; Aghaeepour, N.; McLaughlin, T.; Woodward, M.; DiTullio, A.; Hashemi, N.; Snyder, M.P. Impact of digital health interventions on glycemic control and weight management. npj Digit. Med. 2025, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeltino, A.; Riente, A.; Bianchetti, G.; Serantoni, C.; De Spirito, M.; Capezzone, S.; Esposito, R.; Maulucci, G. Digital applications for diet monitoring, planning, and precision nutrition for citizens and professionals: A state of the art. Nutr. Rev. 2024, 83, e574–e601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, E.; Kokkinopoulou, A.; Wilson-Barnes, S.; Hart, K.; Gymnopoulos, L.P.; Tsatsou, D.; Solachidis, V.; Dimitropoulos, K.; Rouskas, K.; Argiriou, A.; et al. Personal Goals, User Engagement, and Meal Adherence within a Personalised AI-Based Mobile Application for Nutrition and Physical Activity. Life 2024, 14, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidis, K.; Tsatsou, D.; Konstantinidis, D.; Gymnopoulos, L.; Daras, P.; Wilson-Barnes, S.; Hart, K.; Cornelissen, V.; Decorte, E.; Lalama, E.; et al. PROTEIN AI Advisor: A Knowledge-Based Recommendation Framework Using Expert-Validated Meals for Healthy Diets. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsolakidis, D.; Gymnopoulos, L.P.; Dimitropoulos, K. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Technologies for Personalized Nutrition: A Review. Informatics 2024, 11, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson-Barnes, S.L.; Pagkalos, I.; Patra, E.; Kokkinopoulou, A.; Hassapidou, M.; Lalama, E.; Csanalosi, M.; Kabisch, S.; Pfeiffer, A.F.H.; DeCorte, E.; et al. The development of an EU-wide nutrition and physical activity expert knowledge base to support a personalised mobile application across various EU population groups. Nutr. Bull. 2024, 49, 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zmora, N.; Elinav, E. Harnessing SmartPhones to Personalize Nutrition in a Time of Global Pandemic. Nutrients 2021, 13, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singar, S.; Nagpal, R.; Arjmandi, B.H.; Akhavan, N.S. Personalized Nutrition: Tailoring Dietary Recommendations through Genetic Insights. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celis-Morales, C.; Lara, J.; Mathers, J.C. Personalising nutritional guidance for more effective behaviour change. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2014, 74, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celis-Morales, C.A.; Livingstone, K.M.; Marsaux, C.F.M.; Macready, A.L.; Fallaize, R.; O’Donovan, C.B.; Woolhead, C.; Forster, H.; Walsh, M.C.; Navas-Carretero, S.; et al. Effect of personalized nutrition on health-related behaviour change: Evidence from the Food4Me European randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keijer, J.; Escoté, X.; Galmés, S.; Palou-March, A.; Serra, F.; Aldubayan, M.A.; Pigsborg, K.; Magkos, F.; Baker, E.J.; Calder, P.C.; et al. Omics biomarkers and an approach for their practical implementation to delineate health status for personalized nutrition strategies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 8279–8307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godny, L.; Reshef, L.; Fischler, T.S.; Elial-Fatal, S.; Pfeffer-Gik, T.; Raykhel, B.; Rabinowitz, K.; Levi-Barda, A.; Perets, T.; Barkan, R.; et al. Increasing adherence to the Mediterranean diet and lifestyle is associated with reduced fecal calprotectin and intra-individual changes in microbial composition of healthy subjects. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2120749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodziejczyk, A.A.; Zheng, D.; Elinav, E. Diet–microbiota interactions and personalized nutrition. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Sailani, M.R.; Contrepois, K.; Zhou, Y.; Ahadi, S.; Leopold, S.R.; Zhang, M.J.; Rao, V.; Avina, M.; Mishra, T.; et al. Longitudinal multi-omics of host-microbe dynamics in prediabetes. Nature 2019, 569, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cani, P.D. Human gut microbiome: Hopes, threats and promises. Gut 2018, 67, 1716–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asnicar, F.; Berry, S.E.; Valdes, A.M.; Nguyen, L.H.; Piccinno, G.; Drew, D.A.; Leeming, E.; Gibson, R.; Le Roy, C.; Al Khatib, H.; et al. Microbiome connections with host metabolism and habitual diet from 1098 deeply phenotyped individuals. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, F.C.; Patangia, D.; Grimaud, G.; Lavelle, A.; Dempsey, E.M.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C. The interplay between diet and the gut microbiome: Implications for health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 671–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.D.; Chen, J.; Hoffmann, C.; Bittinger, K.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Keilbaugh, S.A.; Bewtra, M.; Knights, D.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R.; et al. Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science 2011, 334, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, L.A.; Maurice, C.F.; Carmody, R.N.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Button, J.E.; Wolfe, B.E.; Ling, A.V.; Devlin, A.S.; Varma, Y.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature 2014, 505, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenburg, J.L.; Bäckhed, F. Diet–microbiota interactions as moderators of human metabolism. Nature 2016, 535, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.J.; Vangay, P.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Hillmann, B.M.; Ward, T.L.; Shields-Cutler, R.R.; Kim, A.D.; Shmagel, A.K.; Syed, A.N.; Walter, J.; et al. Daily Sampling Reveals Personalized Diet-Microbiome Associations in Humans. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 25, 789–802.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni Lochlainn, M.; Bowyer, R.C.E.; Moll, J.M.; García, M.P.; Wadge, S.; Baleanu, A.-F.; Nessa, A.; Sheedy, A.; Akdag, G.; Hart, D.; et al. Effect of gut microbiome modulation on muscle function and cognition: The PROMOTe randomised controlled trial. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.; Sina, C.; Ferrario, P.G.; Daniel, H.; Working Group “Personalized Nutrition” of the German Nutrition Society. Gut Microbiome Analysis for Personalized Nutrition: The State of Science. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2023, 67, e2200476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeevi, D.; Korem, T.; Zmora, N.; Israeli, D.; Rothschild, D.; Weinberger, A.; Ben-Yacov, O.; Lador, D.; Avnit-Sagi, T.; Lotan-Pompan, M.; et al. Personalized Nutrition by Prediction of Glycemic Responses. Cell 2015, 163, 1079–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunali, V.; Arslan, N.Ç.; Ermiş, B.H.; Hakim, G.D.; Gündoğdu, A.; Hora, M.; Nalbantoğlu, Ö.U. A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial of Microbiome-Based Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Personalized Diet vs Low-Fermentable Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides, and Polyols Diet: A Novel Approach for the Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 119, 1901–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakan, T.; Gundogdu, A.; Alagözlü, H.; Ekmen, N.; Ozgul, S.; Tunali, V.; Hora, M.; Beyazgul, D.; Nalbantoglu, O.U. Artificial intelligence-based personalized diet: A pilot clinical study for irritable bowel syndrome. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2138672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasiloglou, M.F.; Christodoulidis, S.; Reber, E.; Stathopoulou, T.; Lu, Y.; Stanga, Z.; Mougiakakou, S. Perspectives and Preferences of Adult Smartphone Users Regarding Nutrition and Diet Apps: Web-Based Survey Study. JMIR mHealth uHealth 2021, 9, e27885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.D.; Russo, P.; Rufián-Henares, J.Á.; Hinojosa-Nogueira, D.; Pérez-Burillo, S.; de la Cueva, S.P.; Rohn, S.; Fatouros, A.; Douros, K.; González-Vigil, V.; et al. The Stance4Health Project: Evaluating a Smart Personalised Nutrition Service for Gut Microbiota Modulation in Normal- and Overweight Adults and Children with Obesity, Gluten-Related Disorders or Allergy/Intolerance to Cow’s Milk. Foods 2022, 11, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinojosa-Nogueira, D.; Ortiz-Viso, B.; Navajas-Porras, B.; Pérez-Burillo, S.; González-Vigil, V.; de la Cueva, S.P.; Rufián-Henares, J.Á. Stance4Health Nutritional APP: A Path to Personalized Smart Nutrition. Nutrients 2023, 15, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, S.B.; Oikonomidis, Y.; Diniz, J.A.; Baptista, F.; Carnide, F.; Bensenousi, A.; Botana, J.M.; Tsatsou, D.; Stefanidis, K.; Gymnopoulos, L.; et al. Users’ Perspective on the AI-Based Smartphone PROTEIN App for Personalized Nutrition and Healthy Living: A Modified Technology Acceptance Model (mTAM) Approach. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 898031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidis, K.; Tsatso, D.; Konstantinidis, D.; Gymnopoulos, L.; Wilson-Barnes, S.; Hart, K.; Cornelissen, V.; Decort, E.; Lalama, E.; Pfeiffer, A.; et al. PROTEIN NAP Database. 2022. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/7308053 (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- Bountziouka, V.; Bathrellou, E.; Giotopoulou, A.; Katsagoni, C.N.; Bonou, M.; Vallianou, N.; Barbetseas, J.; Avgerinos, P.; Panagiotakos, D. Development, repeatability and validity regarding energy and macronutrient intake of a semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire: Methodological considerations. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2012, 22, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasiadou, E.; Kyrkou, C.; Fotiou, M.; Tsakoumaki, F.; Dimitropoulou, A.; Polychroniadou, E.; Menexes, G.; Athanasiadis, A.P.; Biliaderis, C.G.; Michaelidou, A.-M. Development and Validation of a Mediterranean Oriented Culture-Specific Semi-Quantitative Food Frequency Questionnaire. Nutrients 2016, 8, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotakos, D.B.; Pitsavos, C.; Stefanadis, C. Dietary patterns: A Mediterranean diet score and its relation to clinical and biological markers of cardiovascular disease risk. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2006, 16, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papathanasiou, G.; Georgoudis, G.; Papandreou, M.; Spyropoulos, P.; Georgakopoulos, D.; Kalfakakou, V.; Evangelou, A. Reliability measures of the short International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) in Greek young adults. Hell. J. Cardiol. 2009, 50, 283–294. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Yan, Y.; Yan, S.; Yang, Y. Does physical activity associate with gut microbiome and survival outcomes of Chinese metastatic colorectal cancer patients? A secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, R.; Fukui, T.; Hayashi, T.; Osamura, A.; Ohara, M.; Hara, N.; Higuchi, A.; Yamamoto, T.; Hirano, T. Teneligliptin, a Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor, Improves Early-Phase Insulin Secretion in Drug-Naive Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Drugs R D 2015, 15, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, T.K.; Kil Oh, B.; Lee, M.Y.; Sung, K.-C. Association between physical activity and insulin resistance using the homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance independent of waist circumference. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quispe, R.; Elshazly, M.B.; Zhao, D.; Toth, P.P.; Puri, R.; Virani, S.S.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Martin, S.S.; Jones, S.R.; Michos, E.D. Total cholesterol/HDL-cholesterol ratio discordance with LDL-cholesterol and non-HDL-cholesterol and incidence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in primary prevention: The ARIC study. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2020, 27, 1597–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klindworth, A.; Pruesse, E.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Quast, C.; Horn, M.; Glöckner, F.O. Evaluation of general 16S ribosomal RNA gene PCR primers for classical and next-generation sequencing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar]
- Callahan, B.J.; Mcmurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-24277-4. Available online: https://ggplot2.tidyverse.org (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- Cassol, I.; Ibañez, M.; Bustamante, J.P. Key features and guidelines for the application of microbial alpha diversity metrics. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallick, H.; Rahnavard, A.; McIver, L.J.; Ma, S.; Zhang, Y.; Nguyen, L.H.; Tickle, T.L.; Weingart, G.; Ren, B.; Schwager, E.H.; et al. Multivariable association discovery in population-scale meta-omics studies. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1009442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G.I. PICRUSt2 for prediction of metagenome functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caspi, R.; Billington, R.; Ferrer, L.; Foerster, H.; Fulcher, C.A.; Keseler, I.M.; Kothari, A.; Krummenacker, M.; Latendresse, M.; Mueller, L.A.; et al. The MetaCyc database of metabolic pathways and enzymes and the BioCyc collection of pathway/genome databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D471–D480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolde, R. Pheatmap: Pretty Heatmaps. 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=pheatmap (accessed on 16 June 2023).
- ELSTAT. Risk of Poverty (SILC). 2012. Available online: https://www.statistics.gr/el/statistics/-/publication/SFA10/2012 (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for energy. Efsa J. 2013, 11, 3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Human Microbiome Project Consortium. Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature 2012, 486, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoch, C.L.; Ciufo, S.; Domrachev, M.; Hotton, C.L.; Kannan, S.; Khovanskaya, R.; Leipe, D.; Mcveigh, R.; O’neill, K.; Robbertse, B.; et al. NCBI Taxonomy: A comprehensive update on curation, resources and tools. Database 2020, 2020, baaa062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Stražar, M.; Mohamed, A.M.; Pacheco, J.A.; Walker, R.L.; Lebar, T.; Zhao, S.; Lockart, J.; Dame, A.; Thurimella, K.; et al. Gut microbiome and metabolome profiling in Framingham heart study reveals cholesterol-metabolizing bacteria. Cell 2024, 187, 1834–1852.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchetti, G.; De Maio, F.; Abeltino, A.; Serantoni, C.; Riente, A.; Santarelli, G.; Sanguinetti, M.; Delogu, G.; Martinoli, R.; Barbaresi, S.; et al. Unraveling the Gut Microbiome–Diet Connection: Exploring the Impact of Digital Precision and Personalized Nutrition on Microbiota Composition and Host Physiology. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacomino, G.; Henares, J.Á.R.; Lauria, F. Editorial: Personalized nutrition and gut microbiota: Current and future directions. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1375157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeltino, A.; Hatem, D.; Serantoni, C.; Riente, A.; De Giulio, M.M.; De Spirito, M.; De Maio, F.; Maulucci, G. Unraveling the Gut Microbiota: Implications for Precision Nutrition and Personalized Medicine. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagoumintzis, G.; Patrinos, G.P. Triangulating nutrigenomics, metabolomics and microbiomics toward personalized nutrition and healthy living. Hum. Genom. 2023, 17, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Zhang, D.; Sun, W.R.; Tang, H.L.; Tian, B.; Hu, L.H.; Hu, W.Y.; Gao, Y.Y.; Li, M.Y.; Xiao, M.T.; et al. Causal associations between the gut microbiota and multiple myeloma: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1400116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Zhu, Z.; Yishajiang, Y.; Alarjani, K.M.; Hong, L.; Luo, L. Role of gut microbiota and inflammatory factors in acute respiratory distress syndrome: A Mendelian randomization analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1294692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, G.; Dinakaran, V.; Rajendhran, J.; Swaminathan, K. Blood Microbiota and Circulating Microbial Metabolites in Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 31, 835–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwek, E.; Yan, C.; Ding, H.; Hao, W.; He, Z.; Liu, J.; Ma, K.Y.; Zhu, H.; Chen, Z.-Y. Effects of hawthorn seed oil on plasma cholesterol and gut microbiota. Nutr. Metab. 2022, 19, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fan, J. Impact of gut microbiota on metabolic syndrome and its comprising traits: A two-sample mendelian randomization study. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2024, 16, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-Y.; He, L.-H.; Xu, L.-J.; Li, S.-B. Short-chain fatty acids: Bridges between diet, gut microbiota, and health. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 39, 1728–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, A.; De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Bäckhed, F. From Dietary Fiber to Host Physiology: Short-Chain Fatty Acids as Key Bacterial Metabolites. Cell 2016, 165, 1332–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyés, T.; Silaghi, C.N.; Crăciun, A.M. Diet-Related Changes of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Blood and Feces in Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. Biology 2022, 11, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimble, R.; Gouinguenet, P.; Ashor, A.; Stewart, C.; Deighton, K.; Matu, J.; Griffiths, A.; Malcomson, F.C.; Joel, A.; Houghton, D.; et al. Effects of a mediterranean diet on the gut microbiota and microbial metabolites: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials and observational studies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 63, 8698–8719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seethaler, B.; Nguyen, N.K.; Basrai, M.; Kiechle, M.; Walter, J.; Delzenne, N.M.; Bischoff, S.C. Short-chain fatty acids are key mediators of the favorable effects of the Mediterranean diet on intestinal barrier integrity: Data from the randomized controlled LIBRE trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 116, 928–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, R.; Rios-Covian, D.; Huillet, E.; Auger, S.; Khazaal, S.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G.; Sokol, H.; Chatel, J.-M.; Langella, P. Faecalibacterium: A bacterial genus with promising human health applications. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2023, 47, fuad039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hul, M.; Le Roy, T.; Prifti, E.; Dao, M.C.; Paquot, A.; Zucker, J.-D.; Delzenne, N.M.; Muccioli, G.G.; Clément, K.; Cani, P.D. From correlation to causality: The case of Subdoligranulum. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1849998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, C.; Silvestre, M.P.; Middleton, D.; Korpela, K.; Jalo, E.; Broderick, D.; de Vos, W.M.; Fogelholm, M.; Taylor, M.W.; Raben, A.; et al. Gut microbiota predicts body fat change following a low-energy diet: A PREVIEW intervention study. Genome Med. 2022, 14, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, J.L.; Ley, R.E. The human gut bacteria Christensenellaceae are widespread, heritable, and associated with health. BMC Biol. 2019, 17, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavella, T.; Rampelli, S.; Guidarelli, G.; Bazzocchi, A.; Gasperini, C.; Pujos-Guillot, E.; Comte, B.; Barone, M.; Biagi, E.; Candela, M.; et al. Elevated gut microbiome abundance of Christensenellaceae, Porphyromonadaceae and Rikenellaceae is associated with reduced visceral adipose tissue and healthier metabolic profile in Italian elderly. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1880221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Sierra, A.; de la O, V.; Higuera-Gómez, A.; Chero-Sandoval, L.; de Cuevillas, B.; Martínez-Urbistondo, M.; Moreno-Torres, V.; Pintos-Pascual, I.; Castejón, R.; Martínez, J.A. Mediterranean Diet and Olive Oil Redox Interactions on Lactate Dehydrogenase Mediated by Gut Oscillibacter in Patients with Long-COVID-19 Syndrome. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerma-Aguilera, A.M.; Pérez-Burillo, S.; Navajas-Porras, B.; León, E.D.; Ruíz-Pérez, S.; Pastoriza, S.; Jiménez-Hernández, N.; Cämmerer, B.-M.; Rufián-Henares, J.Á.; Gosalbes, M.J.; et al. Effects of different foods and cooking methods on the gut microbiota: An in vitro approach. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1334623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzeni, A.; Bastiaanssen, T.; Cryan, J.; Tinahones, F.; Vioque, J.; Corella, D.; Fitó, M.; Vidal, J.; Moreno-Indias, I.; Gómez-Pérez, A.; et al. Taxonomic and Functional Fecal Microbiota Signatures Associated With Insulin Resistance in Non-Diabetic Subjects with Overweight/Obesity Within the Frame of the PREDIMED-Plus Study. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 804455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karvela, M.; Golden, C.T.; Bell, N.; Martin-Li, S.; Bedzo-Nutakor, J.; Bosnic, N.; DeBeaudrap, P.; de Mateo-Lopez, S.; Alajrami, A.; Qin, Y.; et al. Assessment of the impact of a personalised nutrition intervention in impaired glucose regulation over 26 weeks: A randomised controlled trial. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salonen, A.; Lahti, L.; Salojärvi, J.; Holtrop, G.; Korpela, K.; Duncan, S.H.; Date, P.; Farquharson, F.; Johnstone, A.M.; Lobley, G.E.; et al. Impact of diet and individual variation on intestinal microbiota composition and fermentation products in obese men. ISME J. 2014, 8, 2218–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chávez-Carbajal, A.; Nirmalkar, K.; Pérez-Lizaur, A.; Hernández-Quiroz, F.; Ramírez-Del-Alto, S.; García-Mena, J.; Hernández-Guerrero, C. Gut Microbiota and Predicted Metabolic Pathways in a Sample of Mexican Women Affected by Obesity and Obesity Plus Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippis, F.; Pellegrini, N.; Vannini, L.; Jeffery, I.B.; La Storia, A.; Laghi, L.; Serrazanetti, D.I.; Di Cagno, R.; Ferrocino, I.; Lazzi, C.; et al. High-level adherence to a Mediterranean diet beneficially impacts the gut microbiota and associated metabolome. Gut Microbiota 2016, 65, 1812–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojinovic, D.; Radjabzadeh, D.; Kurilshikov, A.; Amin, N.; Wijmenga, C.; Franke, L.; Ikram, M.A.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; Zhernakova, A.; Fu, J.; et al. Relationship between gut microbiota and circulating metabolites in population-based cohorts. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Bonder, M.J.; Cenit, M.C.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; Maatman, A.; Dekens, J.A.M.; Brandsma, E.; Marczynska, J.; Imhann, F.; Weersma, R.K.; et al. The Gut Microbiome Contributes to a Substantial Proportion of the Variation in Blood Lipids. Circ. Res. 2015, 117, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorogood, A.; Mottillo, S.; Shimony, A.; Filion, K.B.; Joseph, L.; Genest, J.; Pilote, L.; Poirier, P.; Schiffrin, E.L.; Eisenberg, M.J. Isolated aerobic exercise and weight loss: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Med. 2011, 124, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, J.; Ni, J.; Xue, K.; Wang, F.; Zheng, J.; Cheng, J.; Wu, P.; Runyon, M.K.; Guo, H.; Du, J. Personalized Nutrition Intervention Improves Health Status in Overweight/Obese Chinese Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 919882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R.; Neeland, I.J.; Yamashita, S.; Shai, I.; Seidell, J.; Magni, P.; Santos, R.D.; Arsenault, B.; Cuevas, A.; Hu, F.B.; et al. Waist circumference as a vital sign in clinical practice: A Consensus Statement from the IAS and ICCR Working Group on Visceral Obesity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decorte, E.; Barnes, S.W.; Hart, K.; Stefanidis, K.; Gymnopoulos, L.; Rouskas, K.; Argiriou, A.; Leoni, R.; Russell, D.; Lalama, E.; et al. A pilot trial guiding development and investigating feasibility and usability as well as preliminary effectiveness of the PROTEIN application: Personalized nutrition for healthy living. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2023, 30, zwad125.220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.-S.; Oh, K.; Kim, H.C. Dietary assessment methods in epidemiologic studies. Epidemiol. Health 2014, 36, e2014009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhnle, G.G. Nutritional biomarkers for objective dietary assessment. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linseisen, J.; Renner, B.; Gedrich, K.; Wirsam, J.; Holzapfel, C.; Lorkowski, S.; Watzl, B.; Daniel, H.; Leitzmann, M.; Working Group “Personalized Nutrition” of the German Nutrition Society. Data in Personalized Nutrition: Bridging Biomedical, Psycho-behavioral, and Food Environment Approaches for Population-wide Impact. Adv. Nutr. 2025, 14, 100377. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, K.P.; Gibney, E.R.; O’Sullivan, A.M. Moving towards more sustainable diets: Is there potential for a personalised approach in practice? J. Hum. Nutr. Diet 2023, 36, 2256–2267. [Google Scholar]
- Agostoni, C.; Boccia, S.; Banni, S.; Mannucci, P.; Astrup, A. Sustainable and personalized nutrition: From earth health to public health. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 86, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, D.; Heller, M.C.; Roberto, C.A. Position of the Society for Nutrition Education and Behavior: The Importance of Including Environmental Sustainability in Dietary Guidance. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2019, 51, 3–15.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rouskas, K.; Guela, M.; Pantoura, M.; Pagkalos, I.; Hassapidou, M.; Lalama, E.; Pfeiffer, A.F.H.; Decorte, E.; Cornelissen, V.; Wilson-Barnes, S.; et al. The Influence of an AI-Driven Personalized Nutrition Program on the Human Gut Microbiome and Its Health Implications. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071260
Rouskas K, Guela M, Pantoura M, Pagkalos I, Hassapidou M, Lalama E, Pfeiffer AFH, Decorte E, Cornelissen V, Wilson-Barnes S, et al. The Influence of an AI-Driven Personalized Nutrition Program on the Human Gut Microbiome and Its Health Implications. Nutrients. 2025; 17(7):1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071260
Chicago/Turabian StyleRouskas, Konstantinos, Mary Guela, Marianna Pantoura, Ioannis Pagkalos, Maria Hassapidou, Elena Lalama, Andreas F. H. Pfeiffer, Elise Decorte, Veronique Cornelissen, Saskia Wilson-Barnes, and et al. 2025. "The Influence of an AI-Driven Personalized Nutrition Program on the Human Gut Microbiome and Its Health Implications" Nutrients 17, no. 7: 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071260
APA StyleRouskas, K., Guela, M., Pantoura, M., Pagkalos, I., Hassapidou, M., Lalama, E., Pfeiffer, A. F. H., Decorte, E., Cornelissen, V., Wilson-Barnes, S., Hart, K., Mantovani, E., Dias, S. B., Hadjileontiadis, L., Gymnopoulos, L. P., Dimitropoulos, K., & Argiriou, A. (2025). The Influence of an AI-Driven Personalized Nutrition Program on the Human Gut Microbiome and Its Health Implications. Nutrients, 17(7), 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071260









