Anti-Stress Effects of Lemon Balm-Containing Foods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Pilot Study
2.1.1. Participants
2.1.2. Treatments
2.1.3. Procedure
2.2. Study 1. Effects of Lemon Balm in Drinks on Stress and Performance
2.2.1. Participants
2.2.2. Treatments
2.2.3. Procedure
2.2.4. Cognitive and Mood Measures
2.2.4.1. Multi-Tasking Framework
2.2.4.2. Mental Arithmetic
2.2.4.3. Stroop
2.2.4.4. Memory Search
2.2.4.5. Psychomotor Tracking
2.2.5. Mood Scales and Other Pencil- and -Paper Measures
2.2.5.1. State-Trait Anxiety Inventory
2.2.5.2. Bond-Lader Visual Analogue Scales
2.2.5.3. Depression Anxiety and Stress Scale (DASS)
2.2.5.4. Symptom Checklist
2.2.6. Cortisol Measurement
2.2.7. Memory Measures
Word Recall/Recognition
2.3. Study 2: Effects of Lemon Balm Yoghurt on Stress and Performance
2.3.1. Participants
2.3.2. Treatments
2.3.3. Procedure
2.4. Statistical Treatment
3. Results
3.1. Pilot Study

3.2. Study 1
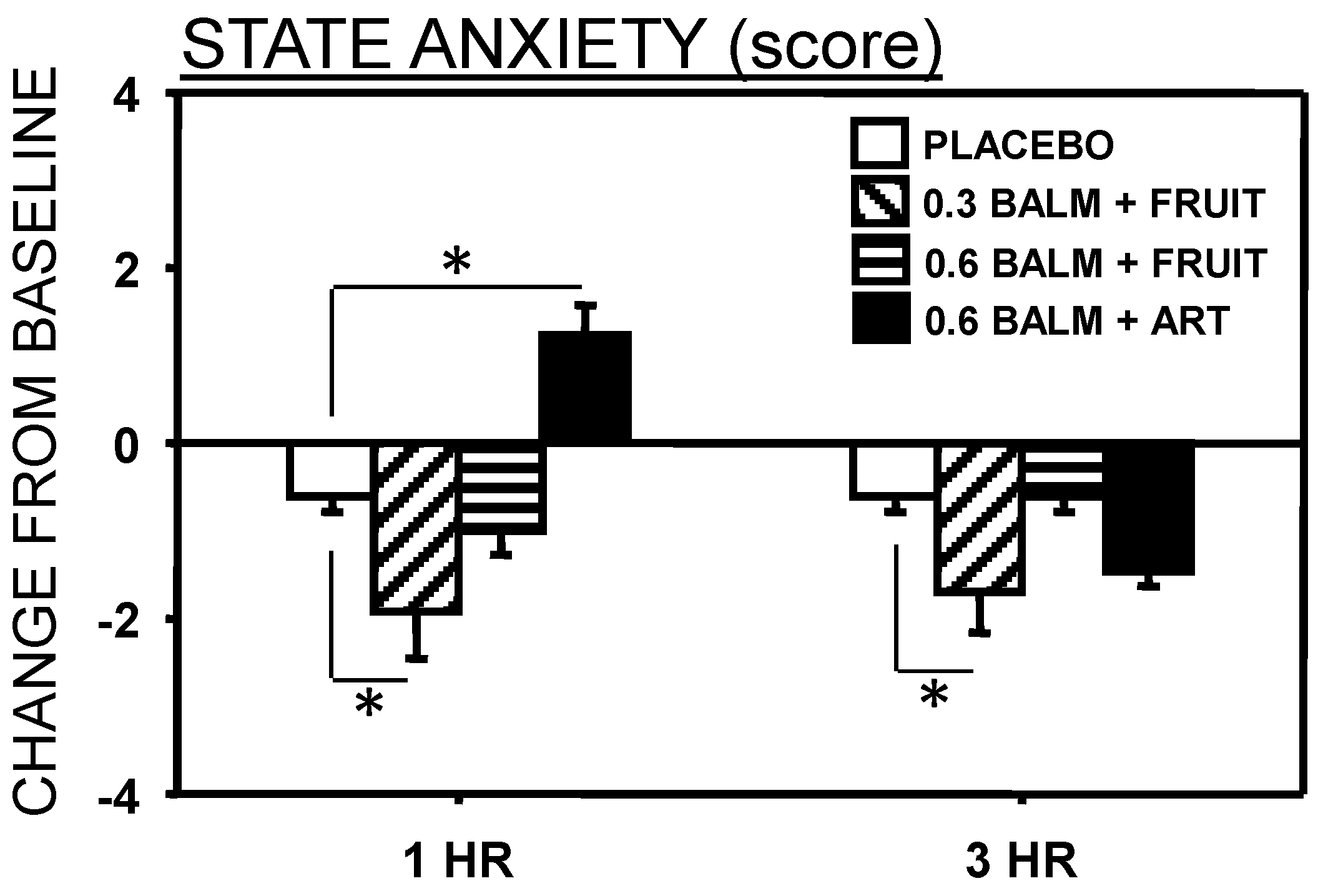


3.3. Study 2

4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflict of Interests
References
- Kennedy, D.O.; Scholey, A.B. The Psychopharmacology of European herbs with cognition-enhancing properties. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2006, 12, 4613–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wake, G.; Court, J.; Pickering, A.; Lewis, R.; Wilkins, R.; Perry, E. CNS acetylcholine receptor activity in European medicinal plants traditionally used to improve failing memory. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2000, 69, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, D.O.; Scholey, A.B.; Tildesley, N.T.J.; Perry, E.K.; Wesnes, K.A. Modulation of mood and cognitive performance following acute administration of Melissa officinalis (lemon balm). Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2002, 72, 953–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, D.; Wake, G.; Savelev, S.; Tildesley, N.; Perry, E.; Wesnes, K.; Scholey, A. Modulation of mood and cognitive performance following acute administration of single doses of Melissa officinalis (lemon balm) with human CNS nicotinic and muscarinic receptor-binding properties. Neuropsychopharmacology 2003, 28, 1871–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, D.O.; Little, W.; Scholey, A.B. Attenuation of laboratory-induced stress in humans after acute administration of Melissa officinalis (lemon Balm). Psychosom. Med. 2004, 66, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, R.; Muhammad, A.; Durst, T.; Trudeau, V.; Arnason, J. Bioassay-guided fractionation of lemon balm (Melissa officinalis L.) using an in vitro measure of GABA transaminase activity. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballard, C.G.; O’Brien, J.T.; Reichelt, K.; Perry, E.K. Aromatherapy as a safe and effective treatment for the management of agitation in severe dementia: The results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with Melissa. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2002, 63, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholey, A. Fuel for thought. Psychologist 2001, 14, 196–201. [Google Scholar]
- Scholey, A.; Sünram-Lea, S.; Greer, J.; Elliott, J.; Kennedy, D. Glucose administration prior to a divided attention task improves tracking performance but not word recognition: Evidence against differential memory enhancement? Psychopharmacology 2009, 202, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingwersen, J.; Defeyter, M.; Kennedy, D.; Wesnes, K.; Scholey, A. A low glycaemic index breakfast cereal preferentially prevents children’s cognitive performance from declining throughout the morning. Appetite 2007, 49, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, D.O.; Little, W.; Haskell, C.F.; Scholey, A.B. Anxiolytic effects of a combination of Melissa officinalis and Valeriana officinalis during laboratory induced stress. Phytother. Res. 2006, 20, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.O.; Pace, S.; Haskell, C.; Okello, E.J.; Milne, A.; Scholey, A.B. Effects of cholinesterase inhibiting sage (Salvia officinalis) on mood, anxiety and performance on a psychological stressor battery. Neuropsychopharmacology 2006, 31, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholey, A.; Haskell, C.; Robertson, B.; Kennedy, D.; Milne, A.; Wetherell, M. Chewing gum alleviates negative mood and reduces cortisol during acute laboratory psychological stress. Physiol. Behav. 2009, 97, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wetherell, M.; Crown, A.; Lightman, S.; Miles, J.; Kaye, J.; Vedhara, K. The four-dimensional stress test: Psychological, sympathetic-adrenal-medullary, parasympathetic and hypothala mic-pituitary-adrenal responses following inhalation of 35% CO2. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2006, 31, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wetherell, M.; Sidgreaves, M. Secretory immunoglobulin-A reactivity following increases in workload intensity using the Defined Intensity Stressor Simulation (DISS). Stress Health 2005, 21, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, S.; Downey, L.A.; Stough, C.; Wetherell, M.; Zangara, A.; Scholey, A. An Acute, Double-blind, placebo-controlled cross-over study of 320 mg and 640 mg doses of Bacopa monnieri (CDRI 08) on multitasking stress reactivity and mood. Phytother. Res. 2013, 28, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholey, A.B.; Kennedy, D.O. Cognitive and physiological effects of an “energy drink”: An evaluation of the whole drink and of glucose, caffeine and herbal flavouring fractions. Psychopharmacology 2004, 176, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bond, A.; Lader, M. The use of analogue scales in rating subjective feelings. Br. J. Med. Psychol. 1974, 47, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNair, D.M.; Lorr, M.; Droppleman, L. POMS: Profile of Mood States; Multi-Health Systems Inc.: North Tonawanda, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Spielberger, C.D.; Gorsuch, R.L.; Lushene, R.E. State-Trait. Anxiety Inventory; Consulting Psychologists Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Stroop, J.R. Studies of interference in serial verbal reactions. J. Exp. Psychol. 1935, 18, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, S. High-speed scanning in human memory. Science 1966, 153, 652–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovibond, P.F.; Lovibond, S.H. The structure of negative emotional states: Comparison of the depression anxiety stress scales (DASS) with the beck depression and anxiety inventories. Behav. Res. Ther. 1995, 33, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antony, M.M.; Bieling, P.J.; Cox, B.J.; Enns, M.W.; Swinson, R.P. Psychometric properties of the 42-item and 21-item versions of the depression anxiety stress scales in clinical groups and a community sample. Psychol. Assess. 1998, 10, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.; Neave, N.; Moss, M.; Scholey, A.; Wesnes, K.; Girdler, N. Sedation: Cognitive properties of sedation agents: comparison of the effects of nitrous oxide and midazolam on memory and mood. Br. Dent. J. 1999, 187, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lindseth, G.N.; Coolahan, S.E.; Petros, T.V.; Lindseth, P.D. Neurobehavioral effects of aspartame consumption. Res. Nurs. Health 2014, 37, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scholey, A.; Kennedy, D.; Wesnes, K. The psychopharmacology of herbal extracts: Issues and challenges. Psychopharmacology 2005, 179, 705–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scholey, A.; Gibbs, A.; Neale, C.; Perry, N.; Ossoukhova, A.; Bilog, V.; Kras, M.; Scholz, C.; Sass, M.; Buchwald-Werner, S. Anti-Stress Effects of Lemon Balm-Containing Foods. Nutrients 2014, 6, 4805-4821. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6114805
Scholey A, Gibbs A, Neale C, Perry N, Ossoukhova A, Bilog V, Kras M, Scholz C, Sass M, Buchwald-Werner S. Anti-Stress Effects of Lemon Balm-Containing Foods. Nutrients. 2014; 6(11):4805-4821. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6114805
Chicago/Turabian StyleScholey, Andrew, Amy Gibbs, Chris Neale, Naomi Perry, Anastasia Ossoukhova, Vanessa Bilog, Marni Kras, Claudia Scholz, Mathias Sass, and Sybille Buchwald-Werner. 2014. "Anti-Stress Effects of Lemon Balm-Containing Foods" Nutrients 6, no. 11: 4805-4821. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6114805
APA StyleScholey, A., Gibbs, A., Neale, C., Perry, N., Ossoukhova, A., Bilog, V., Kras, M., Scholz, C., Sass, M., & Buchwald-Werner, S. (2014). Anti-Stress Effects of Lemon Balm-Containing Foods. Nutrients, 6(11), 4805-4821. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6114805




