The Crystal Structure of Bacillus cereus HblL1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
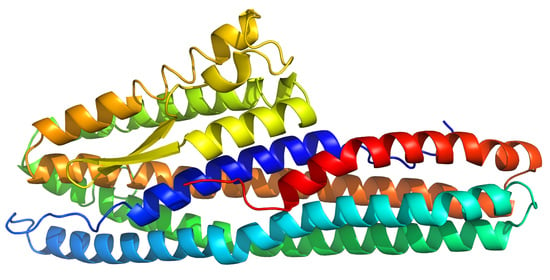
2.1. Structure Description
2.2. Comparison with Related Structures
2.3. Modelling HblL1-HblB Interactions
2.4. The Alpha Helical Pore Forming Toxins
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Protein Purification
4.2. Crystallisation and Structure Determination
4.3. Molecular Docking
4.3.1. Docking
4.3.2. Interface Analysis
4.3.3. Molecular Dynamics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Beecher, D.J.; Schoeni, J.L.; Wong, A.C. Enterotoxic activity of hemolysin BL from Bacillus cereus. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 4423–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senesi, S.; Ghelardi, E. Production, secretion and biological activity of Bacillus cereus enterotoxins. Toxins 2010, 2, 1690–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahner, V.; Cabral, D.A.; Regua-Mangia, A.H.; Rabinovitch, L.; Moreau, G.; McIntosh, D. Distribution of genes encoding putative virulence factors and fragment length polymorphisms in the vrrA gene among Brazilian isolates of Bacillus cereus and Bacillus thuringiensis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8107–8114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastalla, I.; Fattah, R.; Coppage, N.; Nandy, P.; Crown, D.; Pomerantsev, A.P.; Leppla, S.H. The Bacillus cereus Hbl and Nhe tripartite enterotoxin components assemble sequentially on the surface of target cells and are not interchangeable. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeni, J.L.; Wong, A.C. Heterogeneity observed in the components of hemolysin BL, an enterotoxin produced by Bacillus cereus. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1999, 53, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohm, M.E.; Huptas, C.; Krey, V.M.; Scherer, S. Massive horizontal gene transfer, strictly vertical inheritance and ancient duplications differentially shape the evolution of Bacillus cereus enterotoxin operons hbl, cytK and nhe. BMC Evol. Biol. 2015, 15, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beecher, D.J.; Wong, A.C. Improved purification and characterization of hemolysin BL, a hemolytic dermonecrotic vascular permeability factor from Bacillus cereus. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zuo, Z.; Sastalla, I.; Liu, C.; Jang, J.Y.; Sekine, Y.; Li, Y.; Pirooznia, M.; Leppla, S.H.; Finkel, T.; et al. Sequential CRISPR-Based Screens Identify LITAF and CDIP1 as the Bacillus cereus Hemolysin BL Toxin Host Receptors. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 402–410.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, A.; Feng, S.; Hayward, J.A.; Ngo, C.; Fox, D.; Atmosukarto, I.I.; Price, J.D.; Schauer, K.; Martlbauer, E.; Robertson, A.A.B.; et al. A multicomponent toxin from Bacillus cereus incites inflammation and shapes host outcome via the NLRP3 inflammasome. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 4, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beecher, D.J.; Macmillan, J.D. Characterization of the components of hemolysin BL from Bacillus cereus. Infect. Immun. 1991, 59, 1778–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beecher, D.J.; Wong, A.C. Tripartite hemolysin BL from Bacillus cereus. Hemolytic analysis of component interactions and a model for its characteristic paradoxical zone phenomenon. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jessberger, N.; Dietrich, R.; Schwemmer, S.; Tausch, F.; Schwenk, V.; Didier, A.; Martlbauer, E. Binding to The Target Cell Surface Is The Crucial Step in Pore Formation of Hemolysin BL from Bacillus cereus. Toxins 2019, 11, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madegowda, M.; Eswaramoorthy, S.; Burley, S.K.; Swaminathan, S. X-ray crystal structure of the B component of Hemolysin BL from Bacillus cereus. Proteins 2008, 71, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dementiev, A.; Board, J.; Sitaram, A.; Hey, T.; Kelker, M.S.; Xu, X.; Hu, Y.; Vidal-Quist, C.; Chikwana, V.; Griffin, S.; et al. The pesticidal Cry6Aa toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis is structurally similar to HlyE-family alpha pore-forming toxins. BMC Biol. 2016, 14, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crickmore, N.; Berry, C.; Panneerselvam, S.; Mishra, R.; Connor, T.R.; Bonning, B.C. A structure-based nomenclature for Bacillus thuringiensis and other bacteria-derived pesticidal proteins. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benke, S.; Roderer, D.; Wunderlich, B.; Nettels, D.; Glockshuber, R.; Schuler, B. The assembly dynamics of the cytolytic pore toxin ClyA. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, M.; Grauschopf, U.; Maier, T.; Glockshuber, R.; Ban, N. The structure of a cytolytic alpha-helical toxin pore reveals its assembly mechanism. Nature 2009, 459, 726–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, A.J.; Stillman, T.J.; Atkins, A.; Jamieson, S.J.; Bullough, P.A.J.; Green, J.; Artymiuk, P.J.E. coli hemolysin E (HlyE, ClyA, SheA): X-ray crystal structure of the toxin and observation of membrane pores by electron microscopy. Cell 2000, 100, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauning, B.; Bertosin, E.; Praetorius, F.; Ihling, C.; Schatt, A.; Adler, A.; Richter, K.; Sinz, A.; Dietz, H.; Groll, M. Structure and mechanism of the two-component alpha-helical pore-forming toxin YaxAB. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tausch, F.; Dietrich, R.; Schauer, K.; Janowski, R.; Niessing, D.; Martlbauer, E.; Jessberger, N. Evidence for Complex Formation of the Bacillus cereus Haemolysin BL Components in Solution. Toxins 2017, 9, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessberger, N.; Dietrich, R.; Schauer, K.; Schwemmer, S.; Martlbauer, E.; Benz, R. Characteristics of the Protein Complexes and Pores Formed by Bacillus cereus Hemolysin BL. Toxins 2020, 12, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilkenbrinker, U.; Dietrich, R.; Didier, A.; Zhu, K.; Lindback, T.; Granum, P.E.; Martlbauer, E. Complex formation between NheB and NheC is necessary to induce cytotoxic activity by the three-component Bacillus cereus Nhe enterotoxin. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindback, T.; Fagerlund, A.; Rodland, M.S.; Granum, P.E. Characterization of the Bacillus cereus Nhe enterotoxin. Microbiology 2004, 150, 3959–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didier, A.; Dietrich, R.; Gruber, S.; Bock, S.; Moravek, M.; Nakamura, T.; Lindback, T.; Granum, P.E.; Martlbauer, E. Monoclonal antibodies neutralize Bacillus cereus Nhe enterotoxin by inhibiting ordered binding of its three exoprotein components. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worthy, H.L.; Auhim, H.S.; Jamieson, W.D.; Pope, J.R.; Wall, A.; Batchelor, R.; Johnson, R.L.; Watkins, D.W.; Rizkallah, P.; Castell, O.K.; et al. Positive functional synergy of structurally integrated artificial protein dimers assembled by Click chemistry. Comms. Chem. 2019, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kozakov, D.; Schueler-Furman, O.; Vajda, S. Discrimination of near-native structures in protein-protein docking by testing the stability of local minima. Proteins 2008, 72, 993–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krissinel, E.; Henrick, K. Inference of macromolecular assemblies from crystalline state. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 372, 774–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radom, F.; Pluckthun, A.; Paci, E. Assessment of ab initio models of protein complexes by molecular dynamics. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1006182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobanov, M.Y.; Bogatyreva, N.S.; Galzitskaya, O.V. Radius of gyration as an indicator of protein structure compactness. Mol. Biol. 2008, 42, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyborn, N.R.; Clark, A.; Roberts, R.E.; Jamieson, S.J.; Tzokov, S.; Bullough, P.A.; Stillman, T.J.; Artymiuk, P.J.; Galen, J.E.; Zhao, L.; et al. Properties of haemolysin E (HlyE) from a pathogenic Escherichia coli avian isolate and studies of HlyE export. Microbiology 2004, 150, 1495–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Bai, P.; Bai, P.; Ye, W.; Zhang, F.; Ruan, L.; Yu, Z.; Sun, M. A novel negative regulatory factor for nematicidal Cry protein gene expression in Bacillus thuringiensis. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 18, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar]
- Bibby, J.; Keegan, R.M.; Mayans, O.; Winn, M.D.; Rigden, D.J. AMPLE: A cluster-and-truncate approach to solve the crystal structures of small proteins using rapidly computed ab initio models. Acta Cryst. D 2012, 68, 1622–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alford, R.F.; Leaver-Fay, A.; Jeliazkov, J.R.; O’Meara, M.J.; DiMaio, F.P.; Park, H.; Shapovalov, M.V.; Renfrew, P.D.; Mulligan, V.K.; Kappel, K.; et al. The Rosetta All-Atom Energy Function for Macromolecular Modeling and Design. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2017, 13, 3031–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.; Baker, D. Macromolecular modeling with Rosetta. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2008, 77, 363–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, S.; Vernon, R.; Thompson, J.; Tyka, M.; Sadreyev, R.; Pei, J.; Kim, D.; Kellogg, E.; DiMaio, F.; Lange, O.; et al. Structure prediction for CASP8 with all-atom refinement using Rosetta. Proteins 2009, 77, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; DiMaio, F.; Wang, R.Y.-R.; Kim, D.; Miles, C.; Brunette, T.; Thompson, J.; Baker, D. High-resolution comparative modeling with RosettaCM. Structure 2013, 21, 1735–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emsley, P.; Cowtan, K. Coot: Model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Cryst. D 2004, 60, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murshudov, G.N.; Vagin, A.A.; Dodson, E.J. Refinement of Macromolecular Structures by the Maximum-Likelihood Method. Acta Cryst. D 1997, 53, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.S.; Ban, Y.E.; Richter, F.; Andre, I.; Vernon, R.; Schief, W.R.; Baker, D. RosettaRemodel: A generalized framework for flexible backbone protein design. PLoS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozakov, D.; Hall, D.R.; Xia, B.; Porter, K.A.; Padhorny, D.; Yueh, C.; Beglov, D.; Vajda, S. The ClusPro web server for protein-protein docking. Nat. Protoc. 2017, 12, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhury, S.; Berrondo, M.; Weitzner, B.D.; Muthu, P.; Bergman, H.; Gray, J.J. Benchmarking and analysis of protein docking performance in Rosetta v3.2. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Schueler-Furman, O.; Baker, D. Improved side-chain modeling for protein-protein docking. Protein Sci. 2005, 14, 1328–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1–2, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindorff-Larsen, K.; Piana, S.; Palmo, K.; Maragakis, P.; Klepeis, J.L.; Dror, R.O.; Shaw, D.E. Improved side-chain torsion potentials for the Amber ff99SB protein force field. Proteins 2010, 78, 1950–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| PDB Entry | HblL1 |
|---|---|
| Data Collection | |
| Accession Code | 7NMQ |
| Wavelength | 0.91587 |
| Crystallisation Condition | 0.1 M cacodylate Bis Tris propionate, 25% w/v PEG 1500, pH 4.0 |
| Crystal Data | |
| a, b, c (Å) | 36.66, 72.96, 133.05 |
| α, β, γ | 90.0, 90.0, 90.0 |
| Space group | P 21 21 21 |
| Resolution (Å) | 1.36–63.97 |
| Outer shell | 1.36–1.38 |
| R-merge (%) | 6.3 (135.7) |
| R-pim | 3.9 (95.2) |
| R-meas (%) | 7.0 (153.4) |
| CC1/2 | 0.999 (0.397) |
| I/σ(I) | 12.5 (1.0) |
| Completeness (%) | 99.3 (99.0) |
| Multiplicity | 5.5 (4.6) |
| Total Measurements | 423,755 (16,876) |
| Unique Reflections | 77,106 (3698) |
| Wilson B-factor(Å2) | 12.7 |
| Refinement Statistics | |
| Non-H Atoms | 3498 |
| R-work reflections | 73,264 |
| R-free reflections | 3764 |
| R-work/R-free | 16.2/19.9 |
| Rms Deviations | |
| Bond lengths (Å) | 0.013 |
| Bond Angles (°) | 1.686 |
| 1 Coordinate error | 0.048 |
| Mean B value (Å2) | 17.4 |
| Ramachandran Statistics | |
| Favoured/allowed/Outliers | 290/7/0 |
| % | 97.4/2.6/0.0 |
| RosettaDock | PDBePISA | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Total Energy (REU) | Interface Score (REU) | Interface Area (Å2) | ΔiG (kcal mol−1) | H Bonds | Salt Bridges |
| r1 | −1235.6 | −30.3 | 1042.3 | −2.3 | 6 | 4 |
| r2 | −1235.5 | −32.8 | 1000.9 | −3.9 | 7 | 2 |
| r3 | −1234.9 | −30.0 | 968.1 | −3.2 | 4 | 2 |
| r4 | −1234.8 | −32.1 | 1016.2 | −3.0 | 7 | 3 |
| r5 | −1234.7 | −30.9 | 1025.9 | −3.8 | 6 | 4 |
| r6 | −1234.6 | −31.0 | 1034.9 | −3.7 | 6 | 4 |
| r7 | −1234.3 | −30.6 | 1021.6 | −3.0 | 6 | 5 |
| r8 | −1234.3 | −29.3 | 1004.6 | −5.8 | 4 | 3 |
| r9 | −1234.0 | −30.4 | 966.0 | −1.1 | 8 | 2 |
| r10 | −1233.8 | −30.2 | 991.3 | −3.9 | 7 | 4 |
| HblL1 | HblB | Type of Interaction |
|---|---|---|
| Ile259 | Asp12 | Hydrogen bond |
| Ala276 | Thr278 | Hydrogen bond |
| Gly281 | Arg150 | Hydrogen bond |
| Lys381 | Glu186 | Hydrogen bond, salt bridge |
| Lys392 | Asp268 | Hydrogen bond, salt bridge |
| Lys404 | Gln286 | Hydrogen bond |
| Lys404 | Asp12 | Hydrogen bond |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Worthy, H.L.; Williamson, L.J.; Auhim, H.S.; Leppla, S.H.; Sastalla, I.; Jones, D.D.; Rizkallah, P.J.; Berry, C. The Crystal Structure of Bacillus cereus HblL1. Toxins 2021, 13, 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13040253
Worthy HL, Williamson LJ, Auhim HS, Leppla SH, Sastalla I, Jones DD, Rizkallah PJ, Berry C. The Crystal Structure of Bacillus cereus HblL1. Toxins. 2021; 13(4):253. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13040253
Chicago/Turabian StyleWorthy, Harley L., Lainey J. Williamson, Husam Sabah Auhim, Stephen H. Leppla, Inka Sastalla, D. Dafydd Jones, Pierre J. Rizkallah, and Colin Berry. 2021. "The Crystal Structure of Bacillus cereus HblL1" Toxins 13, no. 4: 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13040253
APA StyleWorthy, H. L., Williamson, L. J., Auhim, H. S., Leppla, S. H., Sastalla, I., Jones, D. D., Rizkallah, P. J., & Berry, C. (2021). The Crystal Structure of Bacillus cereus HblL1. Toxins, 13(4), 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13040253