Botulinum Toxin for Essential Tremor and Hands Tremor in the Neurological Diseases: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
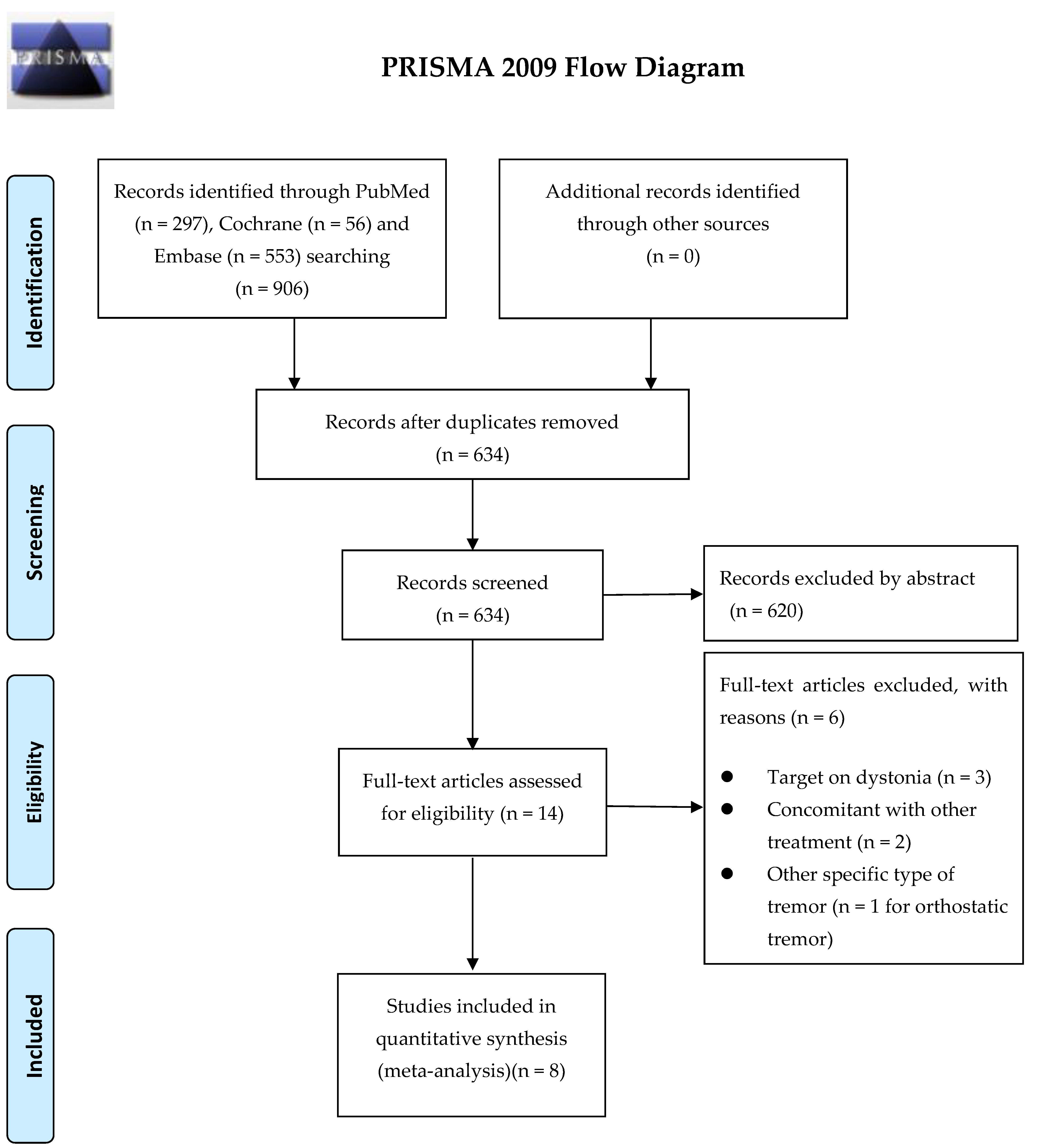
1. Introduction
2. Results
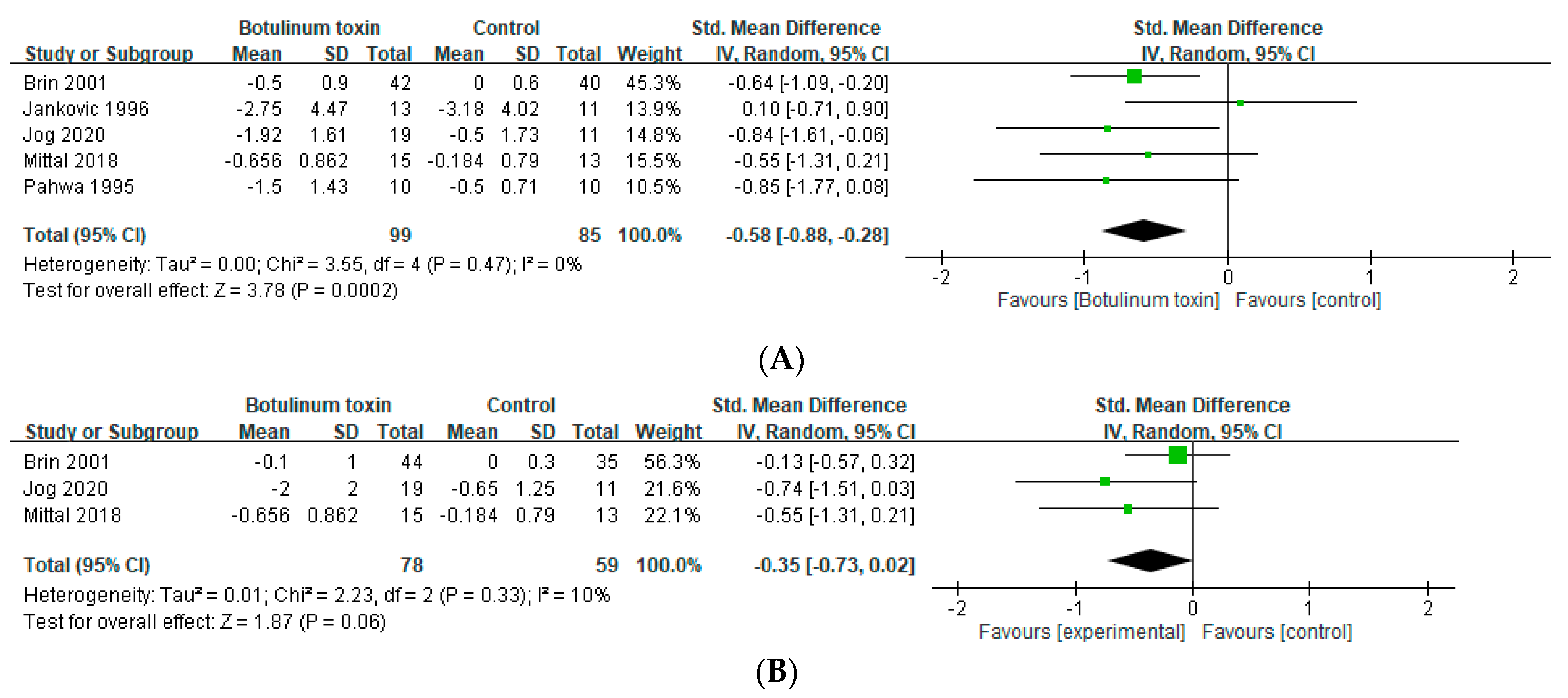
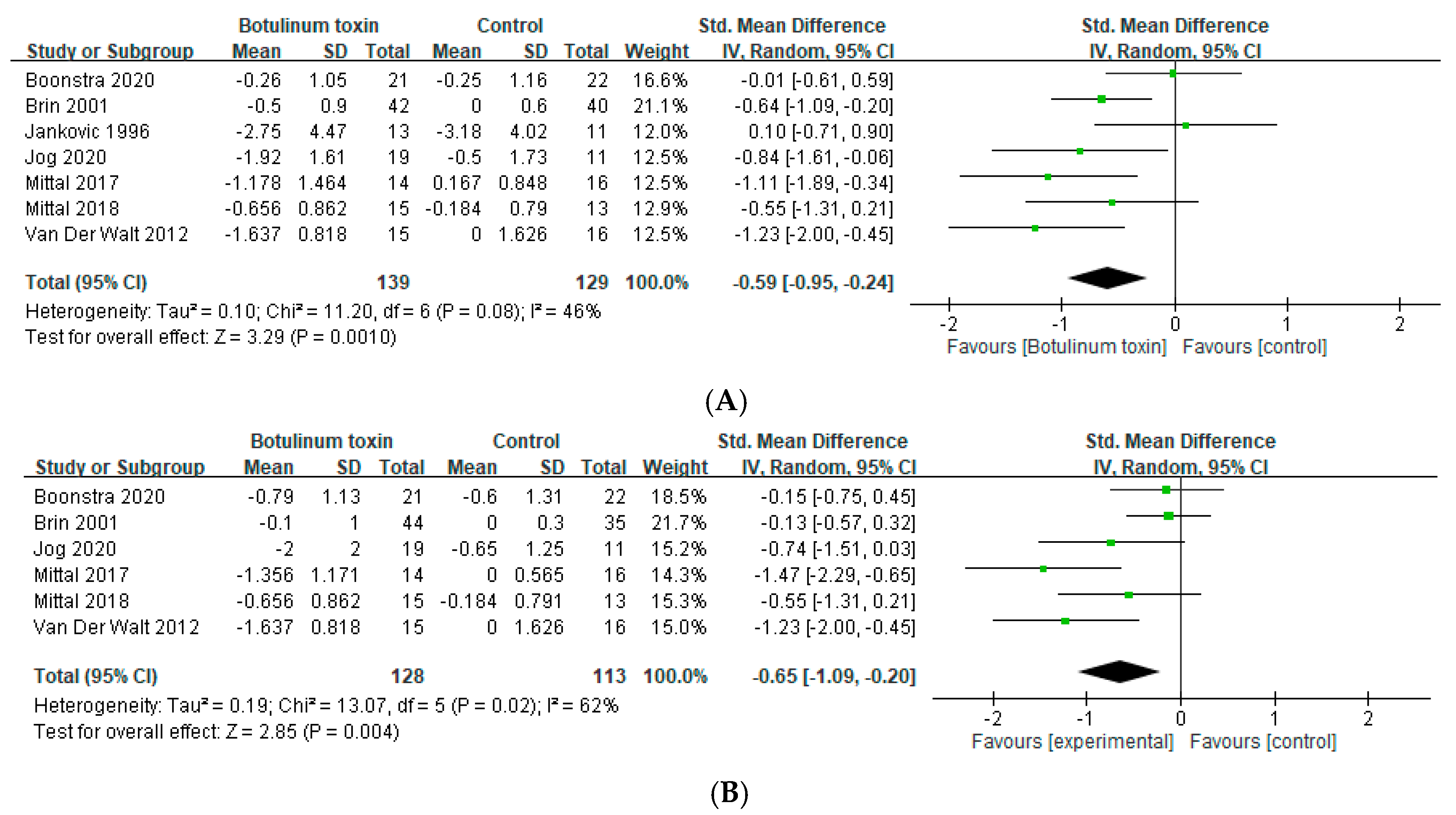
2.1. Effects in Essential Tremor
2.2. Effects in Hands Tremor
2.3. Muscle Weakness
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Inclusion Criteria
5.2. Search Strategy and Study Selection
5.3. Data Extraction
5.4. Appraisal of Methodological Quality
5.5. Outcomes
5.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhatia, K.P.; Bain, P.; Bajaj, N.; Elble, R.J.; Hallett, M.; Louis, E.D.; Raethjen, J.; Stamelou, M.; Testa, C.M.; Deuschl, G.; et al. Consensus Statement on the classification of tremors. from the task force on tremor of the International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankovic, J.; Stanley, F. Physiologic and Pathologic Tremors. Diagnosis, mechanism, and management. Ann. Intern. Med. 1980, 93, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, E.D.; Rios, E. Embarrassment in essential tremor: Prevalence, clinical correlates and therapeutic implications. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2009, 15, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Louis, E.D. Tremor. Contin. Lifelong Learn. Neurol. 2019, 25, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappia, M.; Albanese, A.; Bruno, E.; Colosimo, C.; Filippini, G.; Martinelli, P.; Nicoletti, A.; Quattrocchi, G. Treatment of essential tremor: A systematic review of evidence and recommendations from the Italian Movement Disorders Association. J. Neurol. 2013, 260, 714–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Navarro, H.; García-Martín, E.; Agundez, J.; Jiménez-Jiménez, F.J. Current and Future Neuropharmacological Options for the Treatment of Essential Tremor. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2020, 18, 518–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koller, W.C.; Vetere-Overfield, B. Acute and chronic effects of propranolol and primidone in essential tremor. Neurology 1989, 39, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Suilleabhain, P.; Dewey, R.B. Randomized trial comparing primidone initiation schedules for treating essential tremor. Mov. Disord. 2002, 17, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artusi, C.A.; Farooqi, A.; Romagnolo, A.; Marsili, L.; Balestrino, R.; Sokol, L.L.; Wang, L.L.; Zibetti, M.; Duker, A.P.; Mandybur, G.T.; et al. Deep brain stimulation in uncommon tremor disorders: Indications, targets, and programming. J. Neurol. 2018, 265, 2473–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Flora, E.; Perera, C.L.; Cameron, A.L.; Maddern, G. Deep brain stimulation for essential tremor: A systematic review. Mov. Disord. 2010, 25, 1550–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuboi, T.; Au, K.L.K.; Deeb, W.; Almeida, L.; Foote, K.D.; Okun, M.S.; Ramirez-Zamora, A. Motor outcomes and adverse effects of deep brain stimulation for dystonic tremor: A systematic review. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2020, 76, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.K.; Cauraugh, J.H.; Ho, K.W.; Broderick, M.; Ramirez-Zamora, A.; Almeida, L.; Shukla, A.W.; Wilson, C.A.; de Bie, R.M.; Weaver, F.M.; et al. STN vs. GPi deep brain stimulation for tremor suppression in Parkinson disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2019, 58, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopell, B.H.; Rezai, A.R.; Chang, J.W.; Vitek, J.L. Anatomy and physiology of the basal ganglia: Implications for deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2006, 21 (Suppl. 14), S238–S246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallapiazza, R.F.; Lee, D.J.; De Vloo, P.; Fomenko, A.; Hamani, C.; Hodaie, M.; Kalia, S.K.; Fasano, A.; Lozano, A. Outcomes from stereotactic surgery for essential tremor. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, H.H.; Galvez-Jimenez, N.; Machado, A.G.; Deogaonkar, M.; Cooper, S. Deep brain stimulation for movement disorders: Patient selection and technical options. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2012, 79 (Suppl. 2), S19–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Neimat, J.S. The treatment of movement disorders by deep brain stimulation. Neurotherapeutics 2008, 5, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, W.J.; Lipsman, N.; Ondo, W.G.; Ghanouni, P.; Kim, Y.G.; Lee, W.; Schwartz, M.; Hynynen, K.; Lozano, A.; Shah, B.B.; et al. A Randomized Trial of Focused Ultrasound Thalamotomy for Essential Tremor. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Health Quality Ontario. Magnetic Resonance-Guided Focused Ultrasound Neurosurgery for Essential Tremor: A Health Technology Assessment. Ont. Health Technol. Assess. Ser. 2018, 18, 1–141. [Google Scholar]
- Jankovic, J. Botulinum toxin: State of the art. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Castaneda, J.; Jankovic, J. Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of Botulinum Toxin Injections in Dystonia. Toxins 2013, 5, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Castaneda, J.; Jankovic, J. Long-term efficacy, safety, and side effect profile of botulinum toxin in dystonia: A 20-year follow-up. Toxicon 2014, 90, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanker, V. Essential tremor: Diagnosis and management. BMJ 2019, 366, l4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonstra, F.M.; Evans, A.; Noffs, G.; Perera, T.; Jokubaitis, V.; Stankovich, J.; Vogel, A.P.; Moffat, B.A.; Butzkueven, H.; Kolbe, S.C.; et al. OnabotulinumtoxinA treatment for MS-tremor modifies fMRI tremor response in central sensory-motor integration areas. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2020, 40, 101984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brin, M.; Lyons, K.; Doucette, J.; Adler, C.; Caviness, J.; Comella, C.; Dubinsky, R.; Friedman, J.; Manyam, B.; Matsumoto, J.; et al. A randomized, double masked, controlled trial of botulinum toxin type A in essential hand tremor. Neurology 2001, 56, 1523–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankovic, J.; Schwartz, K.; Clemence, W.; Aswad, A.; Mordaunt, J. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate botulinum toxin type A in essential hand tremor. Mov. Disord. 1996, 11, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jog, M.; Lee, J.; Scheschonka, A.; Chen, R.; Ismail, F.; Boulias, C.; Hobson, D.; King, D.; Althaus, M.; Simon, O.; et al. Tolerability and Efficacy of Customized IncobotulinumtoxinA Injections for Essential Tremor: A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Toxins 2020, 12, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, S.O.; Machado, D.; Richardson, D.; Dubey, D.; Jabbari, B. Botulinum Toxin in Parkinson Disease Tremor: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study with a Customized Injection Approach. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2017, 92, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, S.O.; Machado, D.; Richardson, D.; Dubey, D.; Jabbari, B. Botulinum toxin in essential hand tremor—A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study with customized injection approach. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2018, 56, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahwa, R.; Busenbark, K.; Swanson-Hyland, E.F.; Dubinsky, R.M.; Hubble, J.P.; Gray, C.; Koller, W.C. Botulinum toxin treatment of essential head tremor. Neurology 1995, 45, 822–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Walt, A.; Sung, S.; Spelman, T.; Marriott, M.; Kolbe, S.; Mitchell, P.; Evans, A.; Butzkueven, H. A double-blind, randomized, controlled study of botulinum toxin type A in MS-related tremor. Neurology 2012, 79, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anandan, C.; Jankovic, J. Botulinum Toxin in Movement Disorders: An Update. Toxins 2021, 13, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oates, J.A.; Wood, A.J.; Jankovic, J.; Brin, M.F. Therapeutic Uses of Botulinum Toxin. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 324, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, S.O.; Lenka, A.; Jankovic, J. Botulinum toxin for the treatment of tremor. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2019, 63, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eleopra, R.; Rinaldo, S.; Montecucco, C.; Rossetto, O.; Devigili, G. Clinical duration of action of different botulinum toxin types in humans. Toxicon 2020, 179, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirazzini, M.; Rossetto, O.; Eleopra, R.; Montecucco, C. Botulinum Neurotoxins: Biology, Pharmacology, and Toxicology. Pharmacol. Rev. 2017, 69, 200–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caleo, M.; Restani, L. Direct central nervous system effects of botulinum neurotoxin. Toxicon 2018, 147, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, C.H.; Bansberg, S.F.; Hentz, J.G.; Ramig, L.O.; Buder, E.H.; Witt, K.; Edwards, B.W.; Krein-Jones, K.; Caviness, J.N. Botulinum Toxin Type A for Treating Voice Tremor. Arch. Neurol. 2004, 61, 1416–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertram, K.; Sirisena, D.; Cowey, M.; Hill, A.; Williams, D.R. Safety and efficacy of botulinum toxin in primary orthostatic tremor. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 20, 1503–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, J.T.; Cordivari, C.; Catania, S. Treatment of Upper Limb Tremor with Botulinum Toxin: An Individualized Approach. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2019, 6, 652–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannidis, J.P. The Mass Production of Redundant, Misleading, and Conflicted Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses. Milbank Q. 2016, 94, 485–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Author (Year) | Inclusion Criteria | No. of Patients (Male, %) | Age, Mean ± SD (y) | Treatment Target | Intervention | Outcome Measurement | Side Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boonstra et al. (2020) [23] | RRMS, SPMS, or PPMS with unilateral hand tremor | 43 (11, 25.6%) | E 45.9 ± 13.5 C 47.0 ± 7.55 | Upper limbs | BT 100 U | Bain composite tremor score (0–10) at 6 and 12 weeks | Significant decrease in muscle strength |
| Brin et al. (2001) [24] | ET with bilateral postural hand tremor | 133 (90, 68%) | 68.5 ± 11.2 | Upper limbs | Low dose: BT 50 U; high dose: BT 100 U | Subjective assessment by investigator compared with baseline (−4 to 4) at 6 and 12 weeks | Weakness, pain in injection site, stiffness, cramping, hematoma, and paresthesia |
| Jankovic et al. (1996) [25] | ET with moderate to severe tremor | 25 (16, 64%) | E 56.2 ± 13.0 C 67.4 ± 12.4 | Upper limbs | BT 50 U | Functional severity of tremor (0–4) | Mild and moderate finger weakness |
| Jog et al. (2020) [26] | ET with moderate to severe tremor | 30 (15, 50.0%) | E 68.1 ± 10.6 C 68.2 ± 10.2 | Upper limbs | Mean dose: BT 116.3 U | Fahn–Tolosa–Marin Part B motor performance score | Localized muscular weakness, dry mouth, and dysphonia |
| Mittal et al. (2017) [27] | PD with moderate to severe tremor | 30 (23, 77%) | E 68.50 (range: 57–87) C 62 (range: 51–81) | Upper limbs | BT 85–110 U with follow-ups at 4 and 8 weeks | UPDRS Section 16 at 4 and 8 weeks | Weakness in some patients |
| Mittal et al. (2018) [28] | ET with moderate to severe tremor | 28 (13, 46.2%) | E 70 (range: 43–81) C 62.5 (range: 25–82) | Upper limbs | BT 80–120 U | NIHCGC (0–4) at 4 and 8 weeks | Mild hand weakness (from a few days to 4 weeks) |
| Pahwa et al. (1996) [29] | ET with horizontal head tremor | 10 (1, 10%) | 65.9 (range: 50–82) | Head | BT 100 U | Subjective assessment involving baseline comparison (−3 to 3) at 4 and 8 weeks | Neck weakness, swallowing difficulty, headache, and dizziness |
| Van Der Walt et al. (2012) [30] | RRMS or SPMS with disabling hand tremor | 23 (6, 26%) | 49.6 ± 11.0 | Upper limbs | BT 35–100 U | Bain composite tremor score (0–10) at 6 and 12 weeks | Weakness (resolved in 2 weeks) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, Y.-H.; Hong, C.-T.; Huang, T.-W. Botulinum Toxin for Essential Tremor and Hands Tremor in the Neurological Diseases: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Toxins 2022, 14, 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14030203
Liao Y-H, Hong C-T, Huang T-W. Botulinum Toxin for Essential Tremor and Hands Tremor in the Neurological Diseases: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Toxins. 2022; 14(3):203. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14030203
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Yen-Hui, Chien-Tai Hong, and Tsai-Wei Huang. 2022. "Botulinum Toxin for Essential Tremor and Hands Tremor in the Neurological Diseases: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials" Toxins 14, no. 3: 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14030203
APA StyleLiao, Y.-H., Hong, C.-T., & Huang, T.-W. (2022). Botulinum Toxin for Essential Tremor and Hands Tremor in the Neurological Diseases: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Toxins, 14(3), 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14030203





