Melittin Tryptophan Substitution with a Fluorescent Amino Acid Reveals the Structural Basis of Selective Antitumor Effect and Subcellular Localization in Tumor Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
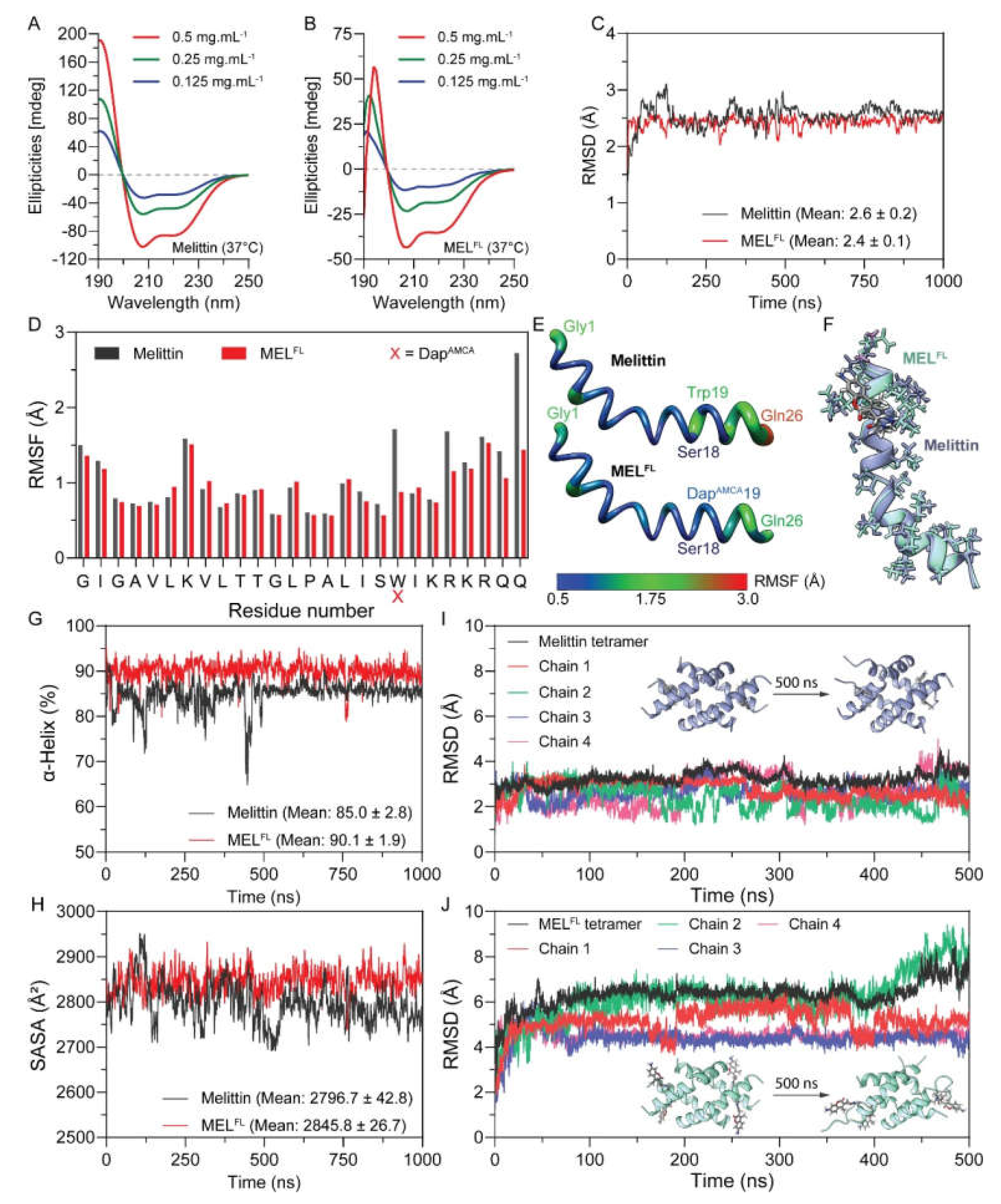
2.1. The Structural Effect of DapAMCA Substitution on Melittin
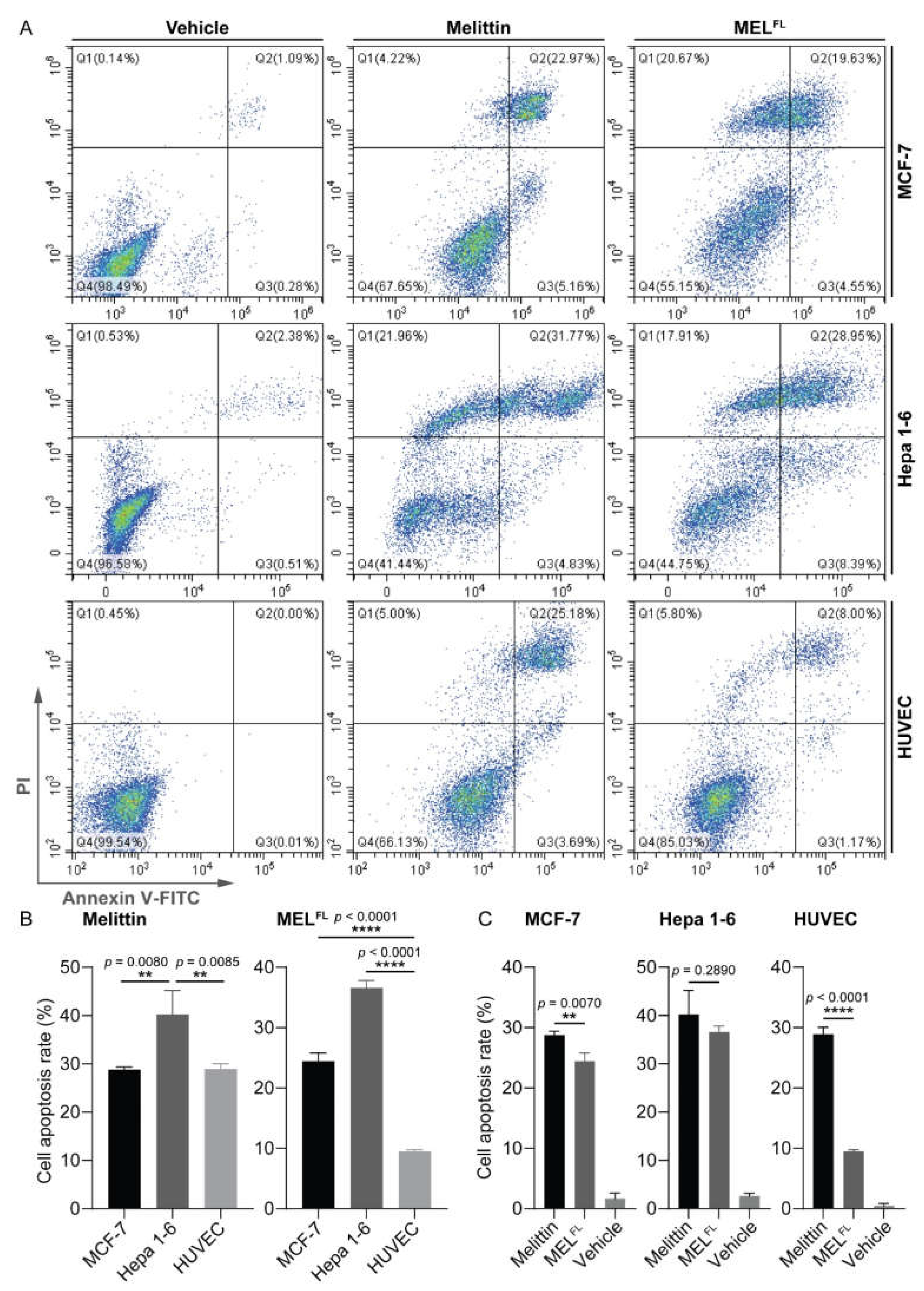
2.2. The Effects of DapAMCA Introduction on Melittin Hemolytic/Cytolytic and Cytotoxic Activity
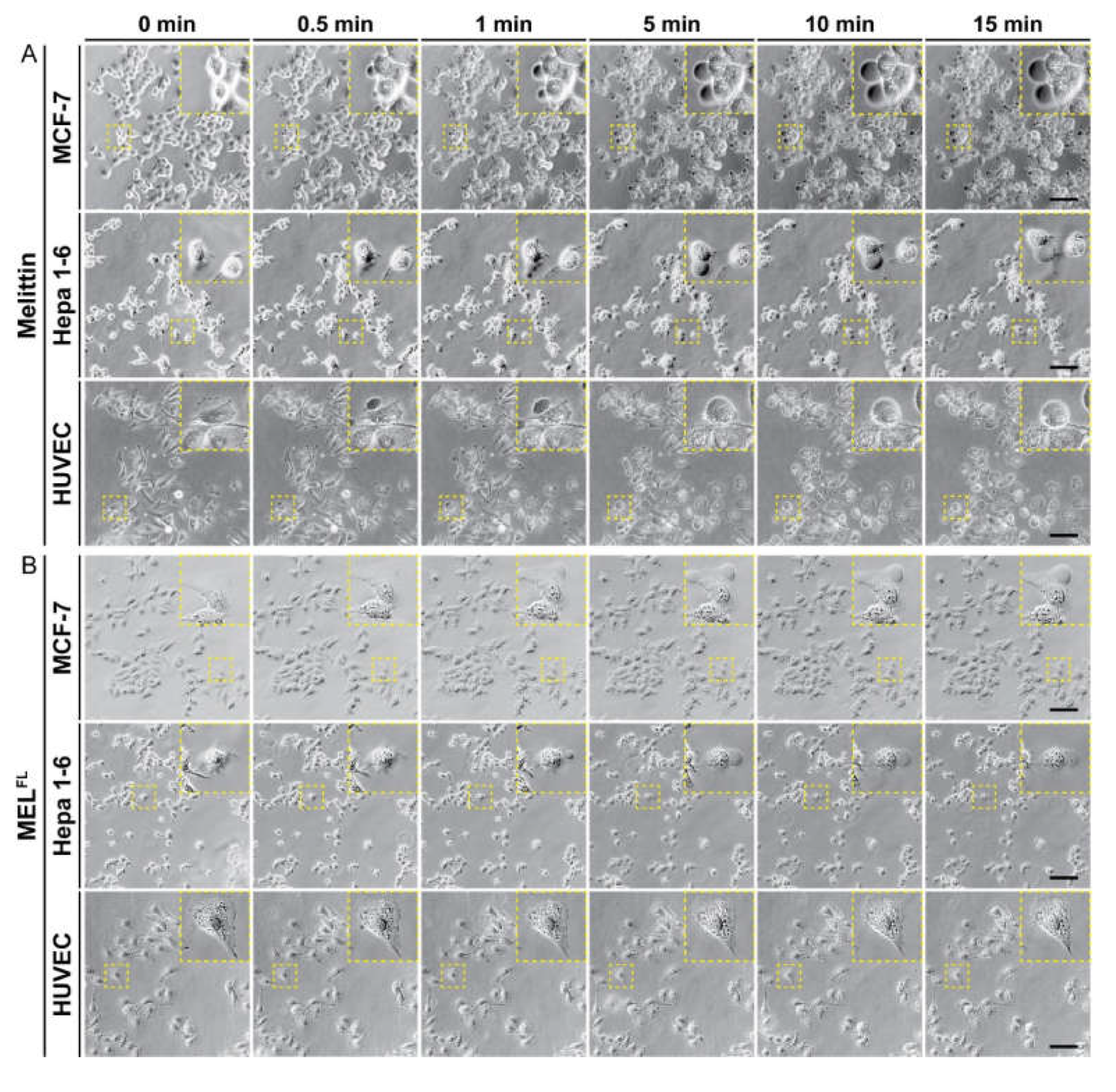
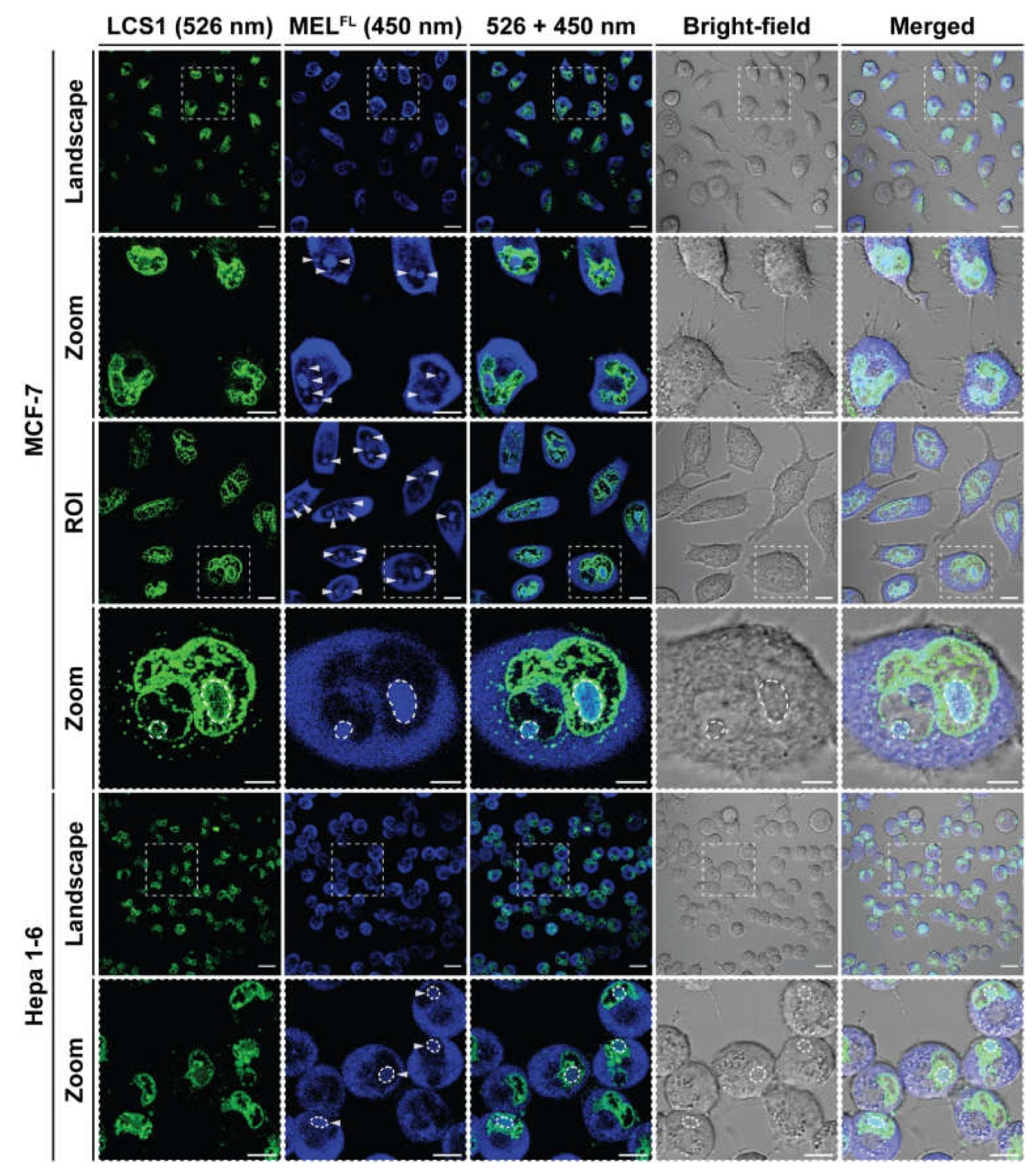
2.3. In Situ Visualization and Morphological Evaluation of MELFL in Cancerous Cell
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Regents
4.2. Polypeptide Synthesis
4.3. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
4.4. Secondary Structure Research
4.5. Hemolysis Assay
4.6. Cytotoxicity Investigation
4.7. Optical Microscopy
4.8. Flow Cytometry
4.9. Confocal Fluorescence Microscopy
4.10. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Memariani, H.; Memariani, M.; Shahidi-Dadras, M.; Nasiri, S.; Akhavan, M.M.; Moravvej, H. Melittin: From honeybees to superbugs. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 3265–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajski, G.; Garaj-Vrhovac, V. Melittin: A lytic peptide with anticancer properties. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 36, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.; Bae, H. Anti-Inflammatory Applications of Melittin, a Major Component of Bee Venom: Detailed Mechanism of Action and Adverse Effects. Molecules 2016, 21, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memariani, H.; Memariani, M.; Moravvej, H.; Shahidi-Dadras, M. Melittin: A venom-derived peptide with promising anti-viral properties. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, P.; Namaei, M.H.; Ghazvini, K.; Hosseini, M. In vitro and in vivo toxicity and antibacterial efficacy of melittin against clinical extensively drug-resistant bacteria. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2021, 22, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucca, M.B.; Cerni, F.A.; Oliveira, I.S.; Jenkins, T.P.; Argemi, L.; Sorensen, C.V.; Ahmadi, S.; Barbosa, J.E.; Laustsen, A.H. Bee Updated: Current Knowledge on Bee Venom and Bee Envenoming Therapy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pucca, M.B.; Ahmadi, S.; Cerni, F.A.; Ledsgaard, L.; Sorensen, C.V.; McGeoghan, F.T.S.; Stewart, T.; Schoof, E.; Lomonte, B.; Auf dem Keller, U.; et al. Unity Makes Strength: Exploring Intraspecies and Interspecies Toxin Synergism between Phospholipases A2 and Cytotoxins. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khemaissa, S.; Sagan, S.; Walrant, A. Tryptophan, an Amino-Acid Endowed with Unique Properties and Its Many Roles in Membrane Proteins. Crystals 2021, 11, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Rukmini, R.; Chattopadhyay, A. Modulation of Tryptophan Environment in Membrane-Bound Melittin by Negatively Charged Phospholipids: Implications in Membrane Organization and Function. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 14291–14305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondelle, S.E.; Simpkins, L.R.; Pérez-Payá, E.; Houghten, R.A. Influence of tryptophan residues on melittin’s hemolytic activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1993, 1202, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postupalenko, V.Y.; Zamotaiev, O.M.; Shvadchak, V.V.; Strizhak, A.V.; Pivovarenko, V.G.; Klymchenko, A.S.; Mely, Y. Dual-Fluorescence l-Amino Acid Reports Insertion and Orientation of Melittin Peptide in Cell Membranes. Bioconjug. Chem. 2013, 24, 1998–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ridgway, Z.; Picciano, A.L.; Gosavi, P.M.; Moroz, Y.S.; Angevine, C.E.; Chavis, A.E.; Reiner, J.E.; Korendovych, I.V.; Caputo, G.A. Functional characterization of a melittin analog containing a non-natural tryptophan analog. Biopolymers 2015, 104, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perekalin, D.S.; Novikov, V.V.; Pavlov, A.A.; Ivanov, I.A.; Anisimova, N.Y.; Kopylov, A.N.; Volkov, D.S.; Seregina, I.F.; Bolshov, M.A.; Kudinov, A.R. Selective ruthenium labeling of the tryptophan residue in the bee venom Peptide melittin. Chemistry 2015, 21, 4923–4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, R.; Balaram, P. A model for the interaction of trifluoroethanol with peptides and proteins. Int. J. Pept. Protein. Res. 1996, 48, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladokhin, A.S.; Fernandez-Vidal, M.; White, S.H. CD spectroscopy of peptides and proteins bound to large unilamellar vesicles. J. Membr. Biol. 2010, 236, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asthana, N.; Yadav, S.P.; Ghosh, J.K. Dissection of antibacterial and toxic activity of melittin: A leucine zipper motif plays a crucial role in determining its hemolytic activity but not antibacterial activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 55042–55050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banerjee, R.; Basu, G. Direct evidence for alteration of unfolding profile of a helical peptide by far-ultraviolet circular dichroism aromatic side-chain contribution. FEBS Lett. 2002, 523, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rogers, D.M.; Jasim, S.B.; Dyer, N.T.; Auvray, F.; Réfrégiers, M.; Hirst, J.D. Electronic Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy of Proteins. Chemistry 2019, 5, 2751–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumenkova, T.V.; Levtsova, O.V.; Nikolaev, I.N.; Shaitan, K.V. Comparative molecular dynamics study of the structural properties of melittin in water and trifluoroethanol/water. Biophysics 2010, 55, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccatano, D.; Colombo, G.; Fioroni, M.; Mark Alan, E. Mechanism by which 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol/water mixtures stabilize secondary-structure formation in peptides: A molecular dynamics study. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 12179–12184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berneche, S.; Nina, M.; Roux, B. Molecular dynamics simulation of melittin in a dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine bilayer membrane. Biophys. J. 1998, 75, 1603–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Othon, C.M.; Kwon, O.H.; Lin, M.M.; Zewail, A.H. Solvation in protein (un)folding of melittin tetramer-monomer transition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12593–12598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liao, C.; Esai Selvan, M.; Zhao, J.; Slimovitch, J.L.; Schneebeli, S.T.; Shelley, M.; Shelley, J.C.; Li, J. Melittin Aggregation in Aqueous Solutions: Insight from Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 10390–10398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leveritt, J.M., 3rd; Pino-Angeles, A.; Lazaridis, T. The structure of a melittin-stabilized pore. Biophys. J. 2015, 108, 2424–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Subbalakshmi, C.; Nagaraj, R.; Sitaram, N. Biological activities of C-terminal 15-residue synthetic fragment of melittin: Design of an analog with improved antibacterial activity. FEBS Lett. 1999, 448, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pierce, A.; Nester, T.; Education Committee of the Academy of Clinical Laboratory Physicists and Scientists. Pathology consultation on drug-induced hemolytic anemia. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2011, 136, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blondelle, S.E.; Houghten, R.A. Probing the relationships between the structure and hemolytic activity of melittin with a complete set of leucine substitution analogs. Pept Res. 1991, 4, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Raghuraman, H.; Chattopadhyay, A. Melittin: A membrane-active peptide with diverse functions. Biosci. Rep. 2007, 27, 189–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Nomura, F.; Yokoyama, Y.; Tanaka-Takiguchi, Y.; Homma, M.; Takiguchi, K. Multiple membrane interactions and versatile vesicle deformations elicited by melittin. Toxins 2013, 5, 637–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.T.; Sun, T.L.; Hung, W.C.; Huang, H.W. Process of inducing pores in membranes by melittin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 14243–14248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soliman, C.; Eastwood, S.; Truong, V.K.; Ramsland, P.A.; Elbourne, A. The membrane effects of melittin on gastric and colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van den Bogaart, G.; Guzman, J.V.; Mika, J.T.; Poolman, B. On the mechanism of pore formation by melittin. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 33854–33857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Helmerhorst, E.J.; Reijnders, I.M.; van ‘t Hof, W.; Veerman, E.C.; Nieuw Amerongen, A.V. A critical comparison of the hemolytic and fungicidal activities of cationic antimicrobial peptides. FEBS Lett. 1999, 449, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, P.Y.; Milton, M.N. The determination and interpretation of the therapeutic index in drug development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zink, D.; Fischer, A.H.; Nickerson, J.A. Nuclear structure in cancer cells. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wu, T.; Zhang, B.; Liu, S.; Song, W.; Qiao, J.; Ruan, H. Types of nuclear localization signals and mechanisms of protein import into the nucleus. Cell Commun. Signal. 2021, 19, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.X.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y.L.; Lin, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.B.; Jin, X.P.; Gao, H.W.; Du, F.S.; Gong, F.; et al. Truncated peptides from melittin and its analog with high lytic activity at endosomal pH enhance branched polyethylenimine-mediated gene transfection. J. Gene Med. 2012, 14, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craggs, G.; Kellie, S. A functional nuclear localization sequence in the C-terminal domain of SHP-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 23719–23725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, M.C.; Min, K.A.; Cheong, H.; Moon, C.; Huang, Y.; He, H.; Yang, V.C. Preparation and Characterization of Gelonin-Melittin Fusion Biotoxin for Synergistically Enhanced Anti-Tumor Activity. Pharm Res. 2016, 33, 2218–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorman, L.C.; Markley, L.D. Solid phase synthesis and antibacterial activity of N-terminal sequences of melittin. J. Med. Chem. 1971, 14, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenfield, N.; Fasman, G.D. Computed circular dichroism spectra for the evaluation of protein conformation. Biochemistry 1969, 8, 4108–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, S.; Abe-Dohmae, S.; Yokoyama, S.; Cavigiolio, G. Impact of self-association on function of apolipoprotein A-I. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 35610–35623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, J.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, C.; Dai, X.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Tan, W.; Luo, M.; et al. Oroxylin A inhibits hemolysis via hindering the self-assembly of alpha-hemolysin heptameric transmembrane pore. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2013, 9, e1002869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E.; Hess, B.; Groenhof, G.; Mark, A.E.; Berendsen, H. GROMACS: Fast, flexible, and free. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; MacKerell, A.D., Jr. CHARMM36 all-atom additive protein force field: Validation based on comparison to NMR data. J. Comput. Chem. 2013, 34, 2135–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zoete, V.; Cuendet, M.A.; Grosdidier, A.; Michielin, O.J. SwissParam: A fast force field generation tool for small organic molecules. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 2359–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, B.; Bekker, H.; Berendsen, H.J.; Fraaije, J.G. LINCS: A linear constraint solver for molecular simulations. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 1997, 18, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essmann, U.; Perera, L.; Berkowitz, L.M.; Darden, T.; Lee, H.; Pedersen, G.L. A smooth particle mesh Ewald method. J. Chem Phys. 1995, 103, 8577–8593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Peptide | Concentration (mg·mL−1) | α-Helix (%) * | α-Helix (%) † | Mean (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 92.0 | 60.4 | 76.2 | |
| Melittin | 0.25 | 99.3 | 65.9 | 82.6 |
| 0.125 | 112.7 | 76.3 | 94.5 | |
| 0.5 | 47.4 | 30.0 | 38.7 | |
| MELFL | 0.25 | 49.3 | 31.5 | 40.4 |
| 0.125 | 49.4 | 31.6 | 40.5 |
| Cell line | Peptide | IC50 (μg·mL−1) | SI |
|---|---|---|---|
| MCF-7 | Melittin | 10.22 ± 0.03 | 0.30 |
| MELFL | 28.01 ± 1.30 | 1.44 | |
| Hepa 1-6 | Melittin | 6.39 ± 0.15 | 0.47 |
| MELFL | 22.92 ± 0.37 | 1.76 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Shang, Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, W.; Mo, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, D.; Li, S.; et al. Melittin Tryptophan Substitution with a Fluorescent Amino Acid Reveals the Structural Basis of Selective Antitumor Effect and Subcellular Localization in Tumor Cells. Toxins 2022, 14, 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14070428
Lv Y, Chen X, Chen Z, Shang Z, Li Y, Xu W, Mo Y, Wang X, Xu D, Li S, et al. Melittin Tryptophan Substitution with a Fluorescent Amino Acid Reveals the Structural Basis of Selective Antitumor Effect and Subcellular Localization in Tumor Cells. Toxins. 2022; 14(7):428. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14070428
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Yonghui, Xu Chen, Zhidong Chen, Zhanjun Shang, Yongxiao Li, Wanting Xu, Yuan Mo, Xinpei Wang, Daiyun Xu, Shengbin Li, and et al. 2022. "Melittin Tryptophan Substitution with a Fluorescent Amino Acid Reveals the Structural Basis of Selective Antitumor Effect and Subcellular Localization in Tumor Cells" Toxins 14, no. 7: 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14070428
APA StyleLv, Y., Chen, X., Chen, Z., Shang, Z., Li, Y., Xu, W., Mo, Y., Wang, X., Xu, D., Li, S., Wang, Z., Wu, M., & Wang, J. (2022). Melittin Tryptophan Substitution with a Fluorescent Amino Acid Reveals the Structural Basis of Selective Antitumor Effect and Subcellular Localization in Tumor Cells. Toxins, 14(7), 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14070428






