Mechanism Underlying Bacillus subtilis BS-Z15 Metabolite-Induced Prevention of Grain Contamination by Aspergillus flavus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
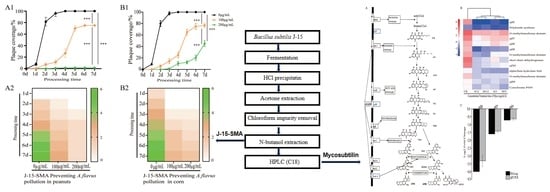
2.1. Effect of B. subtilis BS-Z15-SMA on the Prevention of A. flavus Contamination in Oil Crops
2.1.1. Effects of B. subtilis BS-Z15-SMA on the Growth of A. flavus on the Corn Surface
2.1.2. Effects of B. subtilis BS-Z15-SMA on the Growth of A. flavus on the Peanut Surface
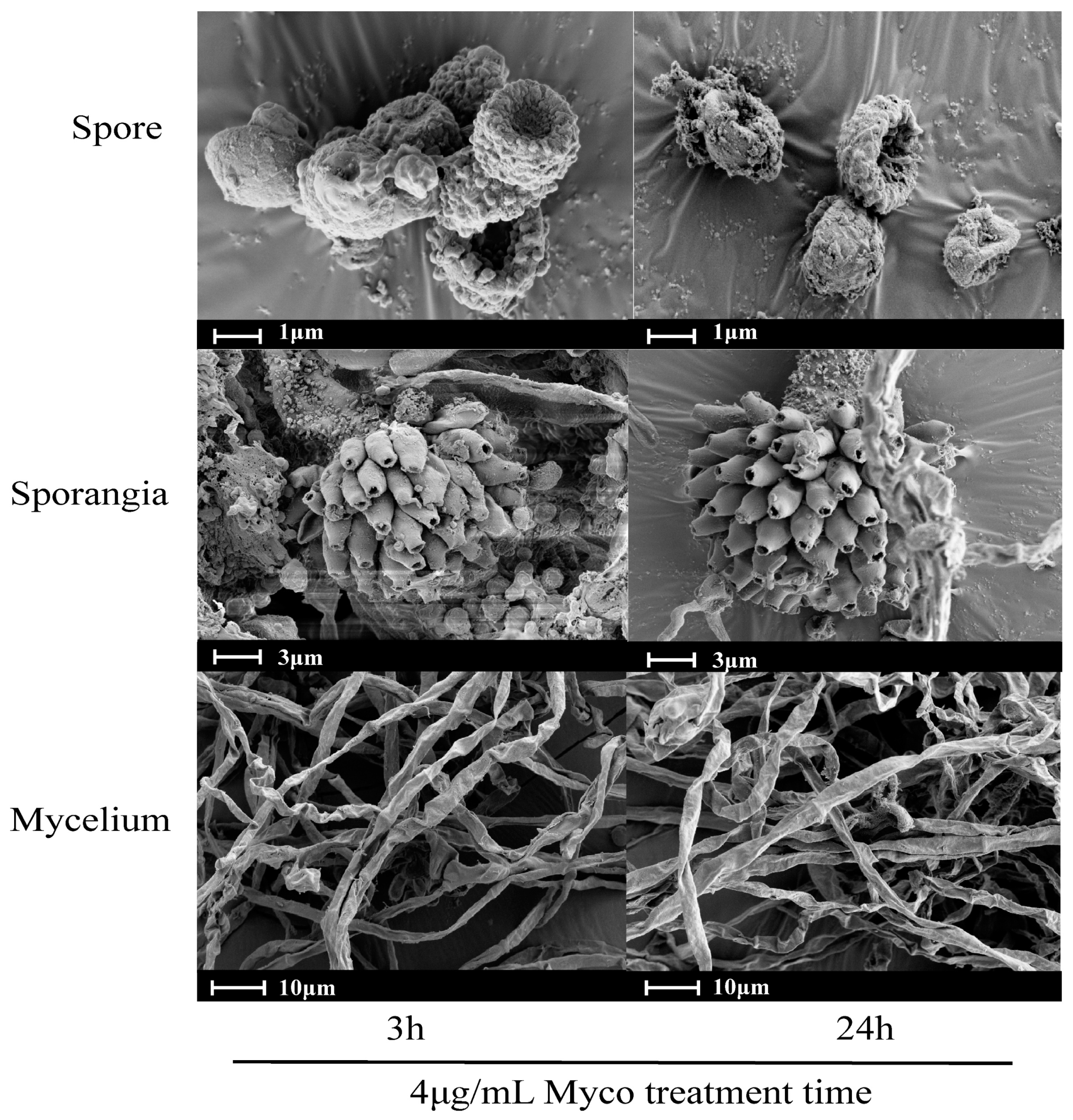
2.2. Effects of Myco on the Morphology of A. flavus Spores and Mycelia
2.3. Transcriptome-Based Analysis of the Mechanism Underlying Myco-Induced Growth Retardation of A. flavus
2.3.1. Quality Control and Correlation Analysis of Transcriptome Data
2.3.2. Statistics of Differentially Expressed Genes
2.3.3. GO Classification and KEGG Enrichment Analysis of Differential Gene Expression after Myco Treatment of A. flavus
2.3.4. Myco Downregulates the Expression of Transporter Genes on the Membrane of A. flavus
2.3.5. Myco Downregulates the Expression of Cell Wall-Related Genes in A. flavus
2.3.6. Myco Downregulates the Expression of Transcription Translation-Related Genes in A. flavus
2.3.7. Myco Downregulates Genes Related to Aflatoxin Synthesis
3. Discussion
3.1. BS-Z15-SMA Can Prevent A. flavus Contamination in Oil Crops
3.2. Myco Has Toxic Effects on A. flavus Cells
3.3. Myco Affects the Material Metabolism and Energy Metabolism of A. flavus
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Experimental Materials
5.2. Preparation of A. flavus Spore Suspension
5.3. Treatment of Corn and Peanut Samples by BS-Z15-SMA
5.4. Effects of Myco on the Morphology of A. flavus Spores and Mycelia
5.5. Treatment of Transcriptome Spore Samples
5.6. RNA Extraction, Library Construction, and Sequencing Analysis
5.7. Quantitative and Differential Expression Analysis of Gene Expression Levels
5.8. Bioinformatics Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes
5.9. Transcriptome RT-qPCR Validation
5.10. Determination of Aflatoxin G2 Content in Peanuts
5.11. Statistical Analysis
5.12. Data Submission
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suqun, S. Food Toxicology, 2nd ed.; Wuhan University of Technology Press: Wuhan, China, 2017; pp. 202–203. [Google Scholar]
- Bean, G.A.; Schillinger, J.A.; Klarman, W.L. Occurrence of aflatoxins and aflatoxin-producing strains of Aspergillus spp. in soybeans. Appl. Microbiol. 1972, 24, 437–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnár, K.; Rácz, C.; Dövényi-Nagy, T.; Bakó, K.; Pusztahelyi, T.; Kovács, S.; Adácsi, C.; Pócsi, I.; Dobos, A. The Effect of Environmental Factors on Mould Counts and AFB1 Toxin Production by Aspergillus flavus in Maize. Toxins 2023, 15, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, N.J.; Bowers, E.; Hurburgh, C.; Wu, F. Potential economic losses to the US corn industry from aflatoxin contamination. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2016, 33, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umesha, S.; Manukumar, H.M.G.; Chandrasekhar, B.; Shivakumara, P.; Shiva Kumar, J.; Raghava, S.; Avinash, P.; Shirin, M.; Bharathi, T.R.; Rajini, S.B.; et al. Aflatoxins and food pathogens: Impact of biologically active aflatoxins and their control strategies. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 1698–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, F.-G.; Zhang, C.-X. Mechanism of aflatoxin production and contamination prevention and control strategies. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 39, 13–26+64. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Li, W.; Yang, M.; Lu, L.; Li, Z.; Guo, Q. Progress in the inhibition mechanism of aflatoxin by microorganisms. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 39, 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Luan, H.; Zheng, W.; Hou, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, S. Isolation and identification of a strain of Bacillus subtilis, its biological properties and its effect on water purification. Microbiol. Bull. 2021, 48, 449–461. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.W.; Yao, J.; Pan, R.; Yu, Z. Study on the antimicrobial properties of Bacillus subtilis JA and isolation and purification of antimicrobial peptides. J. Microbiol. 2004, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huajun, Z.H.; Hu, Z.H.; Zuohua, R.E.; Erming, L.I. Extracellular antibacterial substances of Bacillus subtilis JN005 and its effect on leaf blast control in rice. China Rice Sci. 2020, 34, 470–478. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Bi, X.; Xie, X.; Xing, Y.; Li, M. Study on the inhibitory effect of Icariin A on strawberry spoilage bacteriax. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2020, 32, 1889–1895. [Google Scholar]
- Moyne, A.L.; Shelby, R.; Cleveland, T.E.; Tuzun, S.A.D.I.K. Bacillomycin D: An iturin with antifungal fungal activity against Aspergillus flavus. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 90, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L. Study on the Inhibitory Effect of the Volatile Substances Produced by Bacillus sp. on Aspergilus flavus. Master’s Thesis, Central South University of Forestry Technology, Changsha, China, 2018. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=5DzVwdTmeh-PCLRcpAYrr3FGUCrHCkKnK-j8KkDlo1uicVmb0RwLqQ6UtuHICpGXGJO7h1JXmwC88-eglbG68hGg4ronwd2R8YT6hV-iKFmoIN5dLZ2wtddKC9vOdkFAsgXZH4qd8RsBnFBAJVcxZg==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 30 June 2022).
- Shifa, H.; Tasneem, S.; Gopalakrishnan, C.; Velazhahan, R. Biological control of pre-harvest aflatoxin contamination in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) with Bacillus subtilis G1. Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Prot. 2016, 49, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Zhang, Q.; Yin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Liu, K.; Wang, Y.; Han, S.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, H. Isolation and characterization of a mycosubtilin homologue antagonizing Verticillium dahliae produced by Bacillus subtilis strain Z15. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C. A Preliminary Investigation on the Mechanism of Inhibition of Growth and Toxicity Production of Aspergillus flavus by Carvacrol and Its Application. Master’s Thesis, Shandong Normal University, Jinan, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Luo, X. Molecular biology of aflatoxin biosynthesis. J. Hyg. Res. 2003, 32, 628–631. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, P. Isolation and identification of Aspergillus flavus and toxicity test. China Vet. Anim. Husb. Dig. 2018, 34, 72–73+111. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Q.; Shan, S.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Yu, F. Biocontrol of Aspergillus flavus on peanut kernels by use of a strain of marine Bacillus megaterium. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 139, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Fang, Q.A.; Liao, Z.; Xu, C.; Liang, Z.; Liu, T.; Zhong, Q.; Wang, L.; Fang, X.; Wang, J. Detoxification of Aflatoxin B1 by a Potential Probiotic Bacillus amyloliquefaciens WF2020. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 891091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D. Inhibition of Growth and Toxicity Production of Aspergillus flavus in Maize by Three Plant Essential Oils. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Plabutong, N.; Ekronarongchai, S.; Niwetbowornchai, N.; Edwards, S.W.; Virakul, S.; Chiewchengchol, D.; Thammahong, A. The Inhibitory Effect of Validamycin A on Aspergillus flavus. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 3972415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Hu, D.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Cai, L.; Li, X.; Liao, W.; Liu, X.; Pan, W. Progress of antifungal drugs acting on the cell wall. J. Mycol. 2022, 41, 871–877. [Google Scholar]
- Siahmoshteh, F.; Hamidi-Esfahani, Z.; Spadaro, D.; Shams-Ghahfarokhi, M.; Razzaghi-Abyaneh, M. Unraveling the mode of antifungal action of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens as potential biocontrol agents against aflatoxigenic Aspergillus parasiticus. Food Control. 2018, 89, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birgit, P.; Jörg, D. The emerging importance of microbial volatile organic compounds. Plant Cell Environ. 2014, 37, 811–812. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, L.; Li, D.; Zhao, J.; Yang, G.; Wang, Y.; Yang, K.; Tumukunde, E.; Wang, S.; Yuan, J. The membrane mucin Msb2 regulates aflatoxin biosynthesis and pathogenicity in fungus Aspergillus flavus. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 14, 628–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M. A Preliminary Study on the Inhibitory Effect of Cuminaldehyde on the Growth of Aspergillus flavus and Its Mechanism. Master’s Thesis, Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, Xi’an, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ping, W. Carbon Metabolism Blocking Genes snf1 and Reg1 Regulate Growth and Development and Aflatoxin Synthesis in Aspergillus flavus. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Xie, Y. Antifungal efficacy of paeonol on Aspergillus flavus and its mode of action on cell walls and cell membranes. LWT 2021, 149, 111985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Weijun, C.; Chunxiang, M.; Yichao, L.; Li, Y.; Yuehui, Z. Effect of Chaihu saponin a on the expression of multidrug resistance protein P-glycoprotein in rats with refractory epilepsy. Chin. J. Exp. Formul. 2013, 19, 229–232. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, L.; ZhiLing, C. The role of microtubule skeleton in polar growth of filamentous fungi. Biotechnol. Bull. 2010, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Zhu, H.; Tian, M. Research progress on fungal cell wall inhibitors derived from microorganisms. Foreign Med. Antibiot. Div. 2005, 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Teng, L.; Duan, X.; Li, H.; Hu, L.; Luo, C. Screening, Identification and Characterization of an Antagonistic Antibacterial Strain of Aspergillus flavus. J. Nucl. Agric. 2019, 33, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X. Screening, Antibacterial Mechanism, Fermentation Process Conditions, and Application of High Efficiency Aspergillus flavus Antagonists. Master’s Thesis, Agricultural University of Hebei, Baoding, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Saier, M.H., Jr.; Paulsen, I.T. Phylogeny of multidrug transporters. Semin. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2001, 12, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, M.R.; Chen, J.S.; Marquez, J.L.; Sun, E.I.; Saier, M.H. Multidrug resistance: Phylogenetic characterization of superfamilies of secondary carriers that include drug exporters. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 637, 47–64. [Google Scholar]
- Lorca, G.L.; Barabote, R.D.; Zlotopolski, V.; Tran, C.; Winnen, B.; Hvorup, R.N.; Stonestrom, A.J.; Nguyen, E.; Huang, L.-W.; Kim, D.S.; et al. Transport capabilities of eleven gram-positive bacteria: Comparative genomic analyses. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1768, 1342–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.E.; Podell, S.; Sauer, J.D.; Swanson, M.S.; Saier, M.H. The phagosomal nutrient transporter (Pht) family. Microbiology 2008, 154, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locher, K.P. Review. Structure and mechanism of ATP-binding cassette transporters. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perlin, M.H.; Andrews, J.; San Toh, S. Essential letters in the fungal alphabet: ABC and MFS transporters and their roles in survival and pathogenicity. Adv. Genet. 2014, 85, 201–253. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ceccoli, R.D.; Bianchi, D.A.; Rial, D.V. Flavoprotein monooxygenases for oxidative biocatalysis: Recombinant expression in microbial hosts and applications. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chenprakhon, P.; Wongnate, T.; Chaiyen, P. Monooxygenation of aromatic compounds by flavin-dependent monooxygenases. Protein Sci. A Publ. Protein Soc. 2019, 28, 8–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, X.; Gu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yue, T.; Yuan, Y. Inhibitory Effects of Eurotium cristatum on Growth and Aflatoxin B1 Biosynthesis in Aspergillus flavus. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Shishodia, S.K.; Shankar, J. Docking analysis of hexanoic acid and quercetin with seven domains of polyketide synthase A provided insight into quercetin-mediated aflatoxin biosynthesis inhibition in Aspergillus flavus. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Jin, J.; Zheng, M.; Yang, Q.; Xing, F. Ethanol Biosynthesis Inhibits in Aspergillus Aflatoxin B1 flavus by Up-Regulating Oxidative Stress-Related Genes. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.; Steffan, B.N.; Fischer, G.J.; Venkatesh, N.; Raffa, N.L.; Wettstein, M.A.; Bok, J.W.; Greco, C.; Zhao, C.; Berthier, E.; et al. Fungal oxylipins direct programmed developmental switches in filamentous fungi. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, T.; Hu, X.; Zeng, G. Differential Expression of Genes Related to Growth and Aflatoxin Synthesis in Aspergillus flavus When Inhibited by Bacillus velezensis Strain B2. Foods 2022, 11, 3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aili, A. Toxic Effect and Mechanism of BS-Z15 Broad-Spectrum Secondary Metabolites on Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Master’s Thesis, Xinjiang Normal University, Ürümqi, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.Y.; Li, J.Q.; Wu, S.F.; Zhu, Y.P.; Chen, Y.W.; He, F.C. Integrated nr Database in Protein Annotation System and Its Localization. Comput. Eng. 2006, 5, 71–73+76. [Google Scholar]
- Apweiler, R.; Bairoch, A.; Wu, C.H.; Barker, W.C.; Boeckmann, B.; Ferro, S.; Gasteiger, E.; Huang, H.; Lopez, R.; Magrane, M.; et al. UniProt: The Universal Protein knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, D115–D119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatusov, R.L. The COG database: A tool for genome-scale analysis of protein functions and evolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S.; Kawashima, S.; Nakaya, A. The KEGG databases at GenomeNet. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene Ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.D.; Bateman, A.; Clements, J.; Coggill, P.; Eberhardt, R.Y.; Eddy, S.R.; Heger, A.; Hetherington, K.; Holm, L.; Mistry, J.; et al. Pfam: The protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 42, D222–D230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Sample Name | Detection Result (ppb) |
|---|---|
| AFG2 | |
| CK | 3.4 |
| 100 μg/mL | 0 |
| 200 μg/mL | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Yang, J.; Li, H.; Ning, H.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, H. Mechanism Underlying Bacillus subtilis BS-Z15 Metabolite-Induced Prevention of Grain Contamination by Aspergillus flavus. Toxins 2023, 15, 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15120667
Zhao J, Yang J, Li H, Ning H, Chen J, Chen Z, Zhao H, Zhao H. Mechanism Underlying Bacillus subtilis BS-Z15 Metabolite-Induced Prevention of Grain Contamination by Aspergillus flavus. Toxins. 2023; 15(12):667. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15120667
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Jingjing, Jun Yang, Haoran Li, Huanchen Ning, Jiayi Chen, Zhihui Chen, Heping Zhao, and Huixin Zhao. 2023. "Mechanism Underlying Bacillus subtilis BS-Z15 Metabolite-Induced Prevention of Grain Contamination by Aspergillus flavus" Toxins 15, no. 12: 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15120667
APA StyleZhao, J., Yang, J., Li, H., Ning, H., Chen, J., Chen, Z., Zhao, H., & Zhao, H. (2023). Mechanism Underlying Bacillus subtilis BS-Z15 Metabolite-Induced Prevention of Grain Contamination by Aspergillus flavus. Toxins, 15(12), 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15120667