Advances in the Early Warning of Shellfish Toxification by Dinophysis acuminata
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cells in the Water vs. Toxins in Shellfish
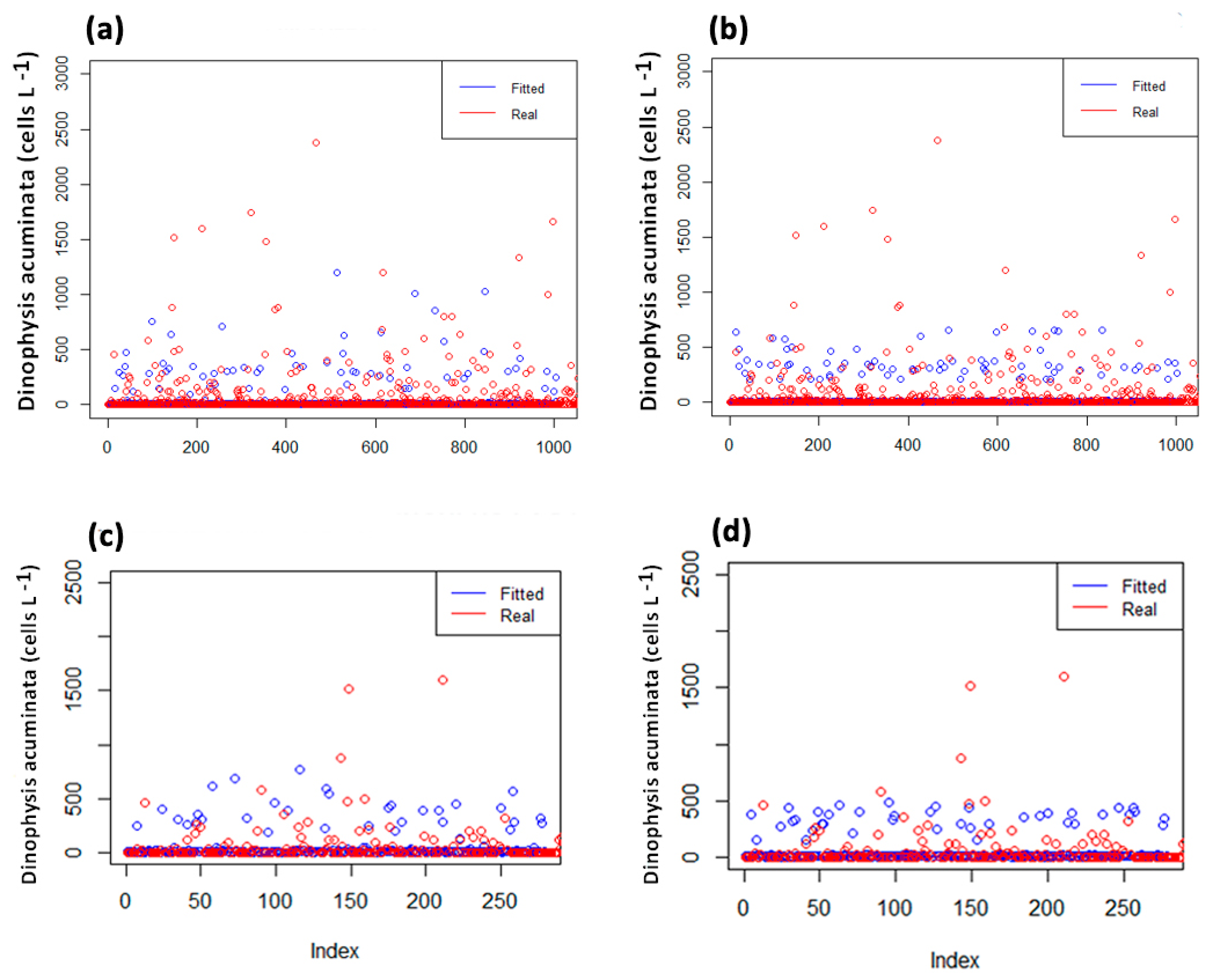
2.2. Model Fitting
- (a)
- M. galloprovincialis_1-week lag
- (b)
- M. galloprovincialis_2-week lag
- (c)
- D. trucullus_1-week lag
- (d)
- D. trucullus_2-week lag
2.3. Model Validation
- Mytilus galloprovincialis—1-week lag model
- Mytilus galloprovincialis—2-week lag model
- Donax trunculus—1-week lag model
- Donax trunculus—2-weeks lag model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
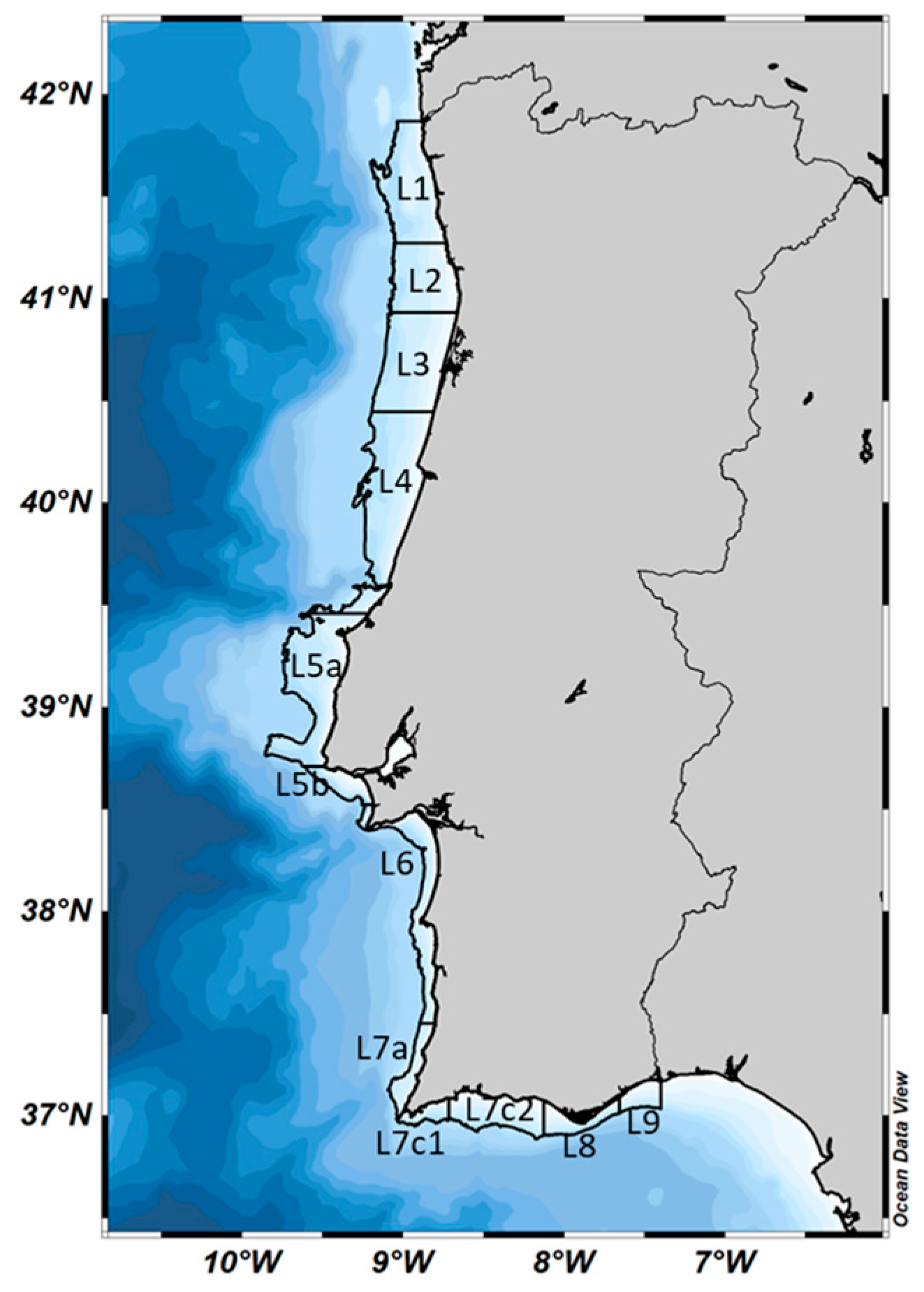
4.1. Study Area
4.2. Sampling Strategy
4.3. Cell Estimation
4.4. Biotoxins Analysis
4.5. Model Selection
4.5.1. Dataset Analysis
4.5.2. Tested Models
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kudela, R.M.; Berdalet, E.; Bernard, S.; Burford, M.; Fernand, L.; Lu, S.; Roy, S.; Tester, P.; Usup, G.; Magnien, R.; et al. Harmful Algal Blooms. A Scientific Summary for Policy Makers; IOC/UNESCO: Paris, France, 2015; Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2024).
- Hallegraeff, G.M.; Anderson, D.M.; Belin, C.; Bottein, M.-Y.D.; Bresnan, E.; Chinain, M.; Enevoldsen, H.; Iwataki, M.; Karlson, B.; McKenzie, C.H.; et al. Perceived global increase in algal blooms is attributable to intensified monitoring and emerging bloom impacts. Commun. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reguera, B.; Riobó, P.; Rodríguez, F.; Díaz, P.A.; Pizarro, G.; Paz, B.; Franco, J.M.; Blanco, J. Dinophysis Toxins: Causative Organisms, Distribution and Fate in Shellfish. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 394–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalera, L.; Pazos, Y.; Doval, M.D.; Reguera, B. A comparison of integrated and discrete depth sampling for monitoring toxic species of Dinophysis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moita, M.T.; Pazos, Y.; Rocha, C.; Nolasco, R.; Oliveira, P.B. Toward predicting Dinophysis blooms off NW Iberia: A decade of events. Harmful Algae 2016, 53, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcaillou, C.; Mondeguer, F.; Gentien, P. Contribution to toxicity assessment of Dinophysis acuminata (Dinophyceae). J. Appl. Phycol. 2005, 17, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolny, J.L.; Egerton, T.A.; Handy, S.M.; Stutts, W.L.; Smith, J.L.; Bachvaroff, T.R.; Henrichs, D.W.; Cambell, L.; Deeds, J.R. Characterization of Dinophysis spp. (Dinophyceae, Dinophysiales) from the mid-Atlantic region of the United States. J. Phycol. 2020, 56, 404–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation (EC) No 853/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2004 Laying down Specific Hygiene Rules for on the Hygiene of Foodstuffs. 2004. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/en/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A32004R0853 (accessed on 31 January 2024).
- Blanco, J. Accumulation of Dinophysis Toxins in Bivalve Molluscs. Toxins 2018, 10, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reizopoulou, S.; Strogyloudi, E.; Giannakourou, A.; Pagou, K.; Hatzianestis, I.; Pyrgaki, C.; Granéli, E. Okadaic acid accumulation in macrofilter feeders subjected to natural blooms of Dinophysis acuminata. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, P. Shellfish contamination with marine biotoxins in Portugal and spring tides: A dangerous health coincidence. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 41143–41156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rourke, W.A.; Justason, A.; Martin, J.L.; Murphy, C.J. Shellfish Toxin Uptake and Depuration in Multiple Atlantic Canadian Molluscan Species: Application to Selection of Sentinel Species in Monitoring Programs. Toxins 2021, 13, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trainer, V.L.; Hardy, F.J. Integrative Monitoring of Marine and Freshwater Harmful Algae in Washington State for Public Health Protection. Toxins 2015, 7, 1206–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moita, M.T. Estrutura, Variabilidade e Dinâmica do Fitoplâncton na Costa de Portugal Continental. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade de Lisboa, Lisbon, Portugal, 2001. Available online: https://digital.csic.es/handle/10261/131531 (accessed on 19 December 2023). (In Portuguese).
- Mafra, L.; Nolli, P.; Mota, L.; Domit, C.; Soeth, M.; Luz, L.; Sobrinho, B.; Leal, J.; Di Domenico, M. Multi-species okadaic acid contamination and human poisoning during a massive bloom of Dinophysis acuminata complex in southern Brazil. Harmful Algae 2019, 89, 101662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Report of the ICES—IOC Working Group on Harmful Algal Bloom Dynamics (WGHABD). In Proceedings of the ICES, Helsinki, Finland, 25–28 April 2017; p. 47. Available online: https://oceanexpert.org/document/26545 (accessed on 20 September 2023). [CrossRef]
- ICES. Joint ICES/IOC Working Group on Harmful Algal Bloom Dynamics (WGHABD; Outputs from 2020 Meeting). ICES Sci. Rep. 2021, 3, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Pinto, L.; Rodrigues, S.; de Pablo, H.; Santos, M.; Moita, T.; Mateus, M. A HAB warning system for shellfish harvesting in Portugal. Harmful Algae 2016, 53, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vale, P.; Sampayo, M.A.M. Dinophysistoxin-2: A rare diarrhetic toxin associated with Dinophysis acuta. Toxicon 2000, 38, 1599–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vale, P.; Botelho, M.J.; Rodrigues, S.M.; Gomes, S.S.; Sampayo, M.A.D.M. Two decades of marine biotoxin monitoring in bivalves from Portugal (1986–2006): A review of exposure assessment. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monitoring of Toxin-Producing Phytoplankton in Bivalve Mollusc Harvesting Areas. Guide to Good Practice: Technical Application. EU Working Group on Toxin-Producing Phytoplankton Monitoring in Bivalve Mollusc Harvesting Areas. 2019. Available online: https://www.aesan.gob.es/CRLMB/Phyto_Monitoring_Guide_DEC_2021.pdf (accessed on 13 December 2023).
- Direção-Geral de Recursos Naturais, Segurança e Serviços Marítimos (DGRM). Plano Estratégico para a Aquicultura 2021–2030; DGRM: Lisbon, Portugal, 2021; Available online: https://www.dgrm.pt/documents/20143/45612/PT_PEA_2021_2030.pdf/37c9c077-f248-ff56-3de9-0ffe12c89f89 (accessed on 17 October 2023).
- Instituto Nacional de Estatística (INE); Direção-Geral de Recursos Naturais, Segurança e Serviços Marítimos (DGRM). Estatística da Pesca; INE: Lisbon, Portugal, 2021; p. 99. ISBN 978-989-25-0602-9. Available online: https://www.ine.pt/xportal/xmain?xpid=INE&xpgid=ine_publicacoes&PUBLICACOESpub_boui=36828280&PUBLICACOESmodo=2 (accessed on 17 October 2023).
- Ramos, A.M. Reproductive Strategy Evaluation of Mussel Mytilus Galloprovincialis Produced in Longlines in Two Areas of Algarve Coast; Escola Superior de Turismo e Tecnologia do Mar—Peniche Instituto Politécnico de Leiria: Peniche, Portugal, 2017; p. 48. Available online: https://iconline.ipleiria.pt/ (accessed on 13 December 2023).
- Vale, P.; Antónia, M.; Sampayo, M. Esters of okadaic acid and dinophysistoxin-2 in Portuguese bivalves related to human poisonings. Toxicon 1999, 37, 1109–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, P.; Sampayo, M.A.M. First confirmation of human diarrhoeic poisonings by okadaic acid esters after ingestion of razor clams (Solen marginatus) and green crabs (Carcinus maenas) in Aveiro lagoon, Portugal and detection of okadaic acid esters in phytoplankton. Toxicon 2002, 40, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vale, P.; Maia, A.J.; Correia, A.; Rodrigues, S.M.; Botelho, M.J.; Casanova, G.; Silva, A.; Vilarinho, M.G.; Silva, A.D. An outbreak of Diarrhetic Shellfish Poisoning after ingestion of wild mussels at the northern coast in summer 2002. Electron J. Environ. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 2, 449–452. [Google Scholar]
- Braga, A.C.; Rodrigues, S.M.; Lourenço, H.M.; Costa, P.R.; Pedro, S. Bivalve Shellfish Safety in Portugal: Variability of Faecal Levels, Metal Contaminants and Marine Biotoxins during the Last Decade (2011–2020). Toxins 2023, 15, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Wang, S.; Ma, D.; Liu, B.; Lin, H.; Li, S. Meteorological Factors Affecting Pan Evaporation in the Haihe River Basin, China. Water 2019, 11, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO; IOC; IAEA. Joint FAO-IOC-IAEA Technical Guidance for the Implementation of Early Warning Systems for Harmful Algal Blooms; Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Paper No. 690; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Altares, M.; Casanova, A.; Fernández-Tejedor, M.; Diogène, J.; de la Iglesia, P. Bloom of Dinophysis spp. dominated by D. sacculus and its related diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) outbreak in Alfacs Bay (Catalonia, NW Mediterranean Sea): Identification of DSP toxins in phytoplankton, shellfish and passive samplers. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2016, 6, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, M.; Relvas, P.; Barbosa, A. Variability patterns and phenology of harmful phytoplankton blooms off southern Portugal: Looking for region-specific environmental drivers and predictors. Harmful Algae 2022, 116, 102254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coupé, C. Modeling Linguistic Variables with Regression Models: Addressing Non-Gaussian Distributions, Non-independent Observations, and Non-linear Predictors with Random Effects and Generalized Additive Models for Location, Scale, and Shape. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, T.K.; Jacobson, P.C. Landscape factors influencing lake phosphorus concentrations across Minnesota. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2013, 29, 754808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virgili, A.; Racine, M.; Authier, M.; Monestiez, P.; Ridoux, V. Comparison of habitat models for scarcely detected species. Ecol. Model. 2017, 346, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, R.; Mamán, L.; Jaén, D.; Fuentes, L.F.; Ocaña, M.A.; Gordillo, M.M. Dinophysis Species and Diarrhetic Shellfish Toxins: 20 Years of Monitoring Program in Andalusia, South of Spain. Toxins 2019, 11, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, R.; Azevedo, M.; Mamede, R.; Sousa, B.; Freitas, R.; Rocha, F.; Quintino, V.; Rodrigues, A. Sedimentary and geochemical characterization and provenance of the Portuguese continental shelf soft-bottom sediments. J. Mar. Syst. 2012, 91, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrita, M.T.; Silva, A.; Oliveira, P.B.; Angélico, M.M.; Nogueira, M. Assessing eutrophication in the Portuguese continental Exclusive Economic Zone within the European Marine Strategy Framework Directive. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 58, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPMA. Bivalves—Ponto de Situação. Available online: https://www.ipma.pt/pt/bivalves/ (accessed on 30 January 2024).
- GEOHAB. Global Ecology and Oceanography of Harmful Algal Blooms, GEOHAB Core Research Project: HABs in Upwelling Systems; Pitcher, G., Moita, T., Trainer, V., Kudela, R., Figueiras, F., Probyn, T., Eds.; IOC and SCOR: Paris, France; Baltimore, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez-Salgado, X.; Labarta, U.; Fernández-Reiriz, M.; Figueiras, F.; Rosón, G.; Piedracoba, S.; Filgueira, R.; Cabanas, J. Renewal time and the impact of harmful algal blooms on the extensive mussel raft culture of the Iberian coastal upwelling system (SW Europe). Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decastro, M.; Gómez-Gesteira, M.; Lorenzo, M.; Alvarez, I.; Crespo, A. Influence of atmospheric modes on coastal upwelling along the western coast of the Iberian Peninsula, 1985 to 2005. Clim. Res. 2008, 36, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, P.A.; Ruiz-Villarreal, M.; Pazos, Y.; Moita, T.; Reguera, B. Climate variability and Dinophysis acuta blooms in an upwelling system. Harmful Algae 2016, 53, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kida, S.; Price, J.F.; Yang, J. The Upper-Oceanic Response to Overflows: A Mechanism for the Azores Current. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2008, 38, 880–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, P.; Ruiz-Villarreal, M.; Peliz, A. Variability of river plumes off Northwest Iberia in response to wind events. J. Mar. Syst. 2008, 72, 238–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moita, M.; Sobrinho-Gonçalves, L.; Oliveira, P.; Palma, S.; Falcão, M. A bloom of Dinophysis acuta in a thin layer off North-West Portugal. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2006, 28, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 15204:2006; Water Quality—Guidance Standard on the Enumeration of Phytoplankton Using Inverted Microscopy (Utermöhl Technique). European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2006. Available online: https://standards.iteh.ai/catalog/standards/cen/d9020a71-2bd3-478f-867f-46ea3a0c0620/en-15204-2006 (accessed on 11 October 2011).
- EU-Harmonised Standard Operating Procedure for Determination of Lipophilic Marine Biotoxins in Molluscs by LC-MS/MS. Version 4, July 2011. European Reference Laboratory for Marine Biotoxins. Available online: https://www.aesan.gob.es/en/CRLMB/docs/docs/metodos_analiticos_de_desarrollo/EU-Harmonised-SOP-LIPO-LCMSMS_Version4.pdf (accessed on 11 October 2011).
- EU-Harmonised Standard Operating Procedure for Determination of Lipophilic Marine Biotoxins in Molluscs by LC-MS/MS. 5th Edition, January 2015. European Reference Laboratory for Marine Biotoxins, 2015. Available online: https://www.aesan.gob.es/en/CRLMB/docs/docs/metodos_analiticos_de_desarrollo/EU-Harmonised-SOP-LIPO-LCMSMS_Version5.pdf (accessed on 23 February 2015).
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2007; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- Wood, S.N. Mgcv: GAMs and Generalized Ridge Regression for R. 2001, Volume 1/2. Available online: https://journal.r-project.org/articles/RN-2001-015/RN-2001-015.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2022).
- Wood, S.N. Low-Rank Scale-Invariant Tensor Product Smooths for Generalized Additive Mixed Models. Biometrics 2006, 62, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
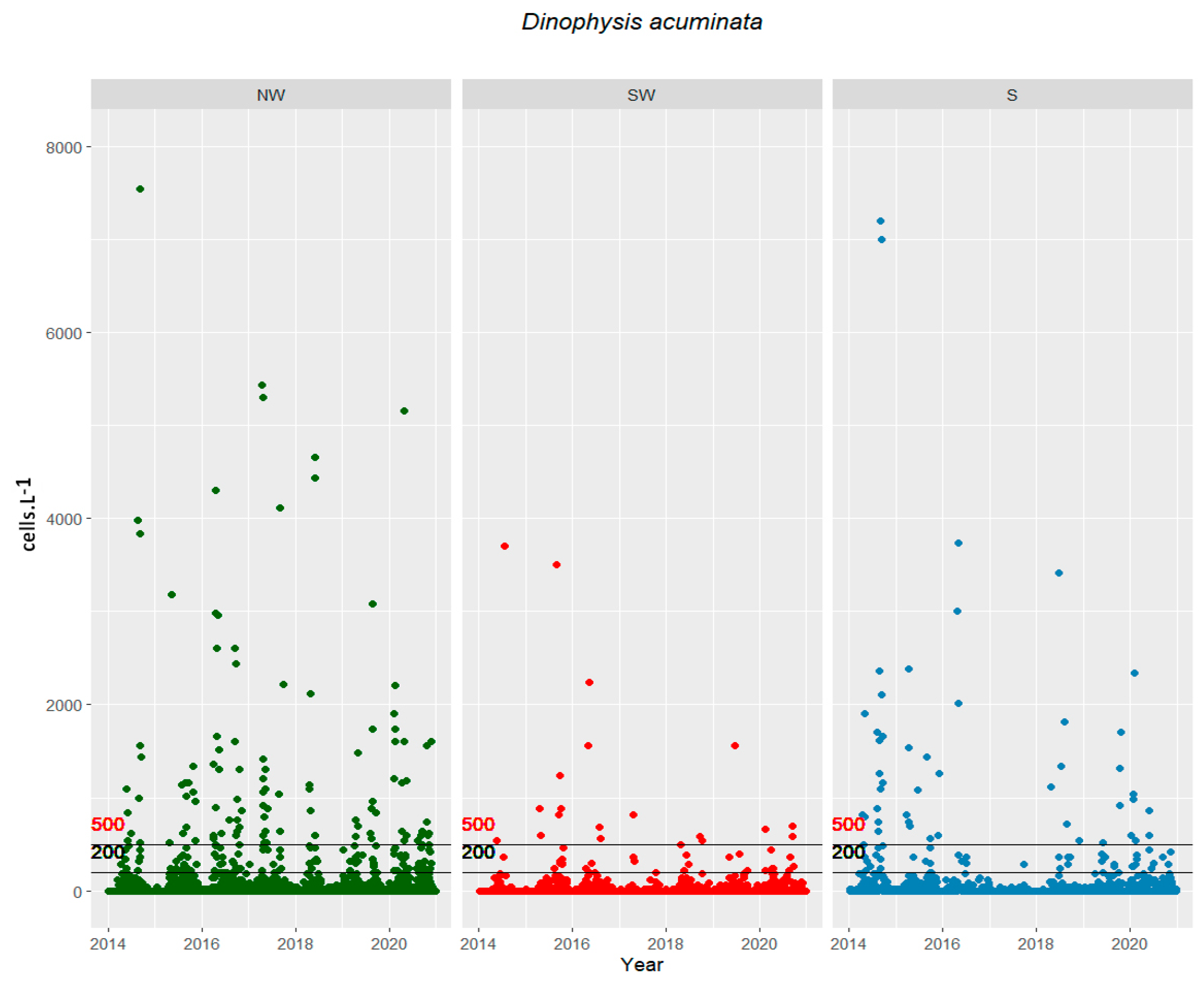
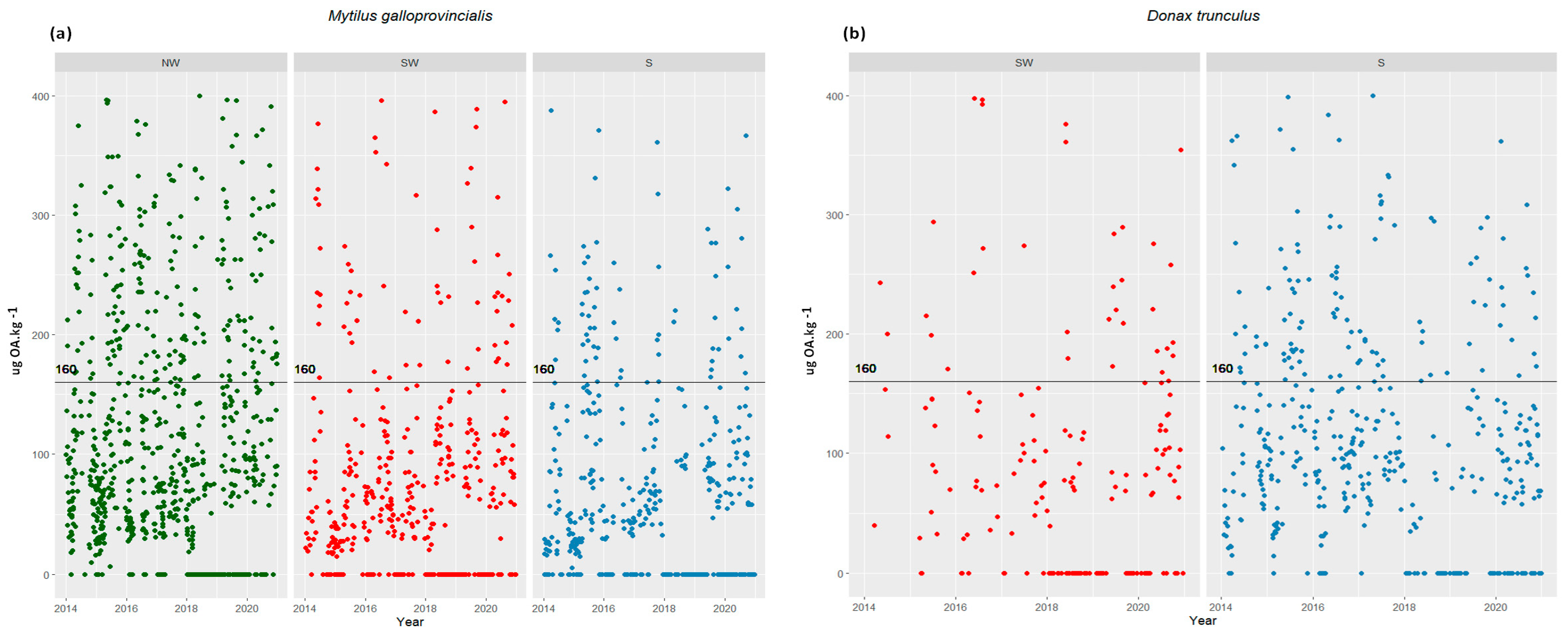

| Region | Year | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (cells L−1) | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
| NW | 7544 | 3180 | 4300 | 8140 | 4660 | 1740 | 12,960 |
| SW | 3700 | 3500 | 2240 | 820 | 580 | 1560 | 700 |
| S | 7200 | 2380 | 3740 | 280 | 3420 | 1700 | 11,660 |
| (μg OA equiv/kg) | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
| NW | >850 (12 × RL) | >850 (13 × RL) | >850 (23 × RL) | >625 (37 × RL) | >550 (50 × RL) | >550 (8 × RL) | >550 (9 × RL) |
| SW | >850 (10 × RL) | >850 (17 × RL) | >850 (23 × RL) | >625 (13 × RL) | 587 | 649 | >550 (5 × RL) |
| S | 1402 | >850 (14 × RL) | >850 (10 × RL) | >625 (4 × RL) | >550 (8 × RL) | 830 | >550 (10 × RL) |
| Number of times RL was surpassed in Mytillus | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
| NW | 72 | 68 | 41 | 40 | 20 | 58 | 52 |
| SW | 16 | 17 | 13 | 17 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| S | 20 | 23 | 16 | 13 | 19 | 18 | 23 |
| Number of times RL was surpassed in Donax | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
| NW | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| SW | 25 | 22 | 20 | 25 | 20 | 19 | 17 |
| S | 43 | 36 | 25 | 23 | 14 | 11 | 16 |
| Spearman Correlation | Shellfish | |
|---|---|---|
| Mytilus | Donax | |
| D_acuminata | 0.23 | 0.26 |
| Lag1_acuminata | 0.27 | 0.36 |
| Lag2_acuminata | 0.26 | 0.34 |
| Model Fitting | Model Accuracy (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Lag | Distribution | Deviance Explained | AIC | RMSE | n | Performance Score (%) | |
| Mytillus galloprovincialis | Lag1 | Tweedie | 68.7 | 3351 | 1.43 | 1011 | 86.46 | 79.4 |
| Poisson | 75.4 | 36471 | 2.74 | 59.55 | 8.1 | |||
| Z-Inflated | 83.7 | 17121 | 0.74 | 51.14 | 79.4 | |||
| Negative Binomial | 23.6 | 3754 | 147 | 20.00 | 79.4 | |||
| Lag2 | Tweedie | 68.1 | 3391 | 1.43 | 1009 | 86.47 | 78.7 | |
| Poisson | 75.5 | 38004 | 2.68 | 59.54 | 78.7 | |||
| Z-Inflated | 92.7 | 16606 | 0.66 | 53.04 | 78.7 | |||
| Negative binomial | 24.1 | 3805 | 137.49 | 20.00 | 78.7 | |||
| Donax trunculus | Lag1 | Tweedie | 69.00 | 1385 | 1.33 | 279 | 85.98 | 54.3 |
| Poisson | 81.9 | 10814 | 3.24 | 59.14 | 54.3 | |||
| Z-Inflated | 100.00 | 5724 | 1.04 | 48.63 | 54.3 | |||
| Negative Binomial | 28.3 | 1590 | 20.00 | 54.3 | ||||
| Lag2 | Tweedie | 64.4 | 1455 | 1.34 | 278 | 87.86 | 60.0 | |
| Poisson | 76.1 | 13943 | 2.60 | 59.4 | 8.8 | |||
| Z-Inflated | 100.0 | 7411 | 1.00 | 47.68 | 8.8 | |||
| Negative Binomial | 27.6 | 1651 | 85.26 | 20.00 | 60.0 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duarte Silva, A.; Rodrigues, S.M.; Godinho, L. Advances in the Early Warning of Shellfish Toxification by Dinophysis acuminata. Toxins 2024, 16, 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16050204
Duarte Silva A, Rodrigues SM, Godinho L. Advances in the Early Warning of Shellfish Toxification by Dinophysis acuminata. Toxins. 2024; 16(5):204. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16050204
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuarte Silva, Alexandra, Susana Margarida Rodrigues, and Lia Godinho. 2024. "Advances in the Early Warning of Shellfish Toxification by Dinophysis acuminata" Toxins 16, no. 5: 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16050204
APA StyleDuarte Silva, A., Rodrigues, S. M., & Godinho, L. (2024). Advances in the Early Warning of Shellfish Toxification by Dinophysis acuminata. Toxins, 16(5), 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16050204






