Investigation on the Tool Wear Suppression Mechanism in Non-Resonant Vibration-Assisted Micro Milling
Abstract
1. Introduction
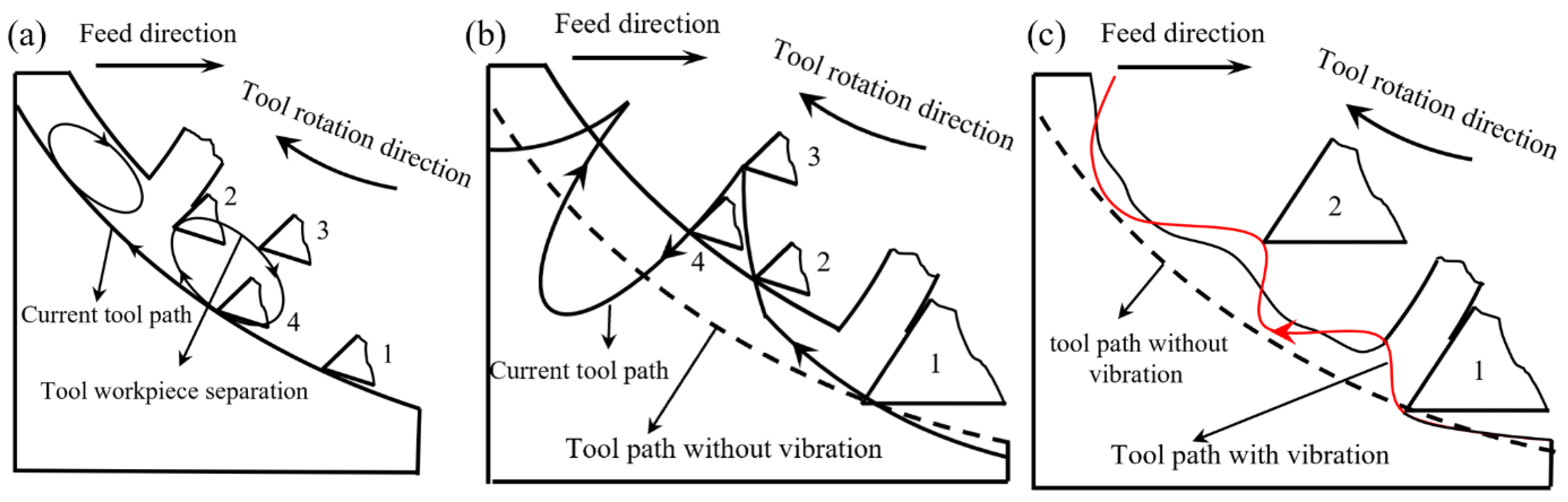
2. Analysis of Tool-Workpiece Separation
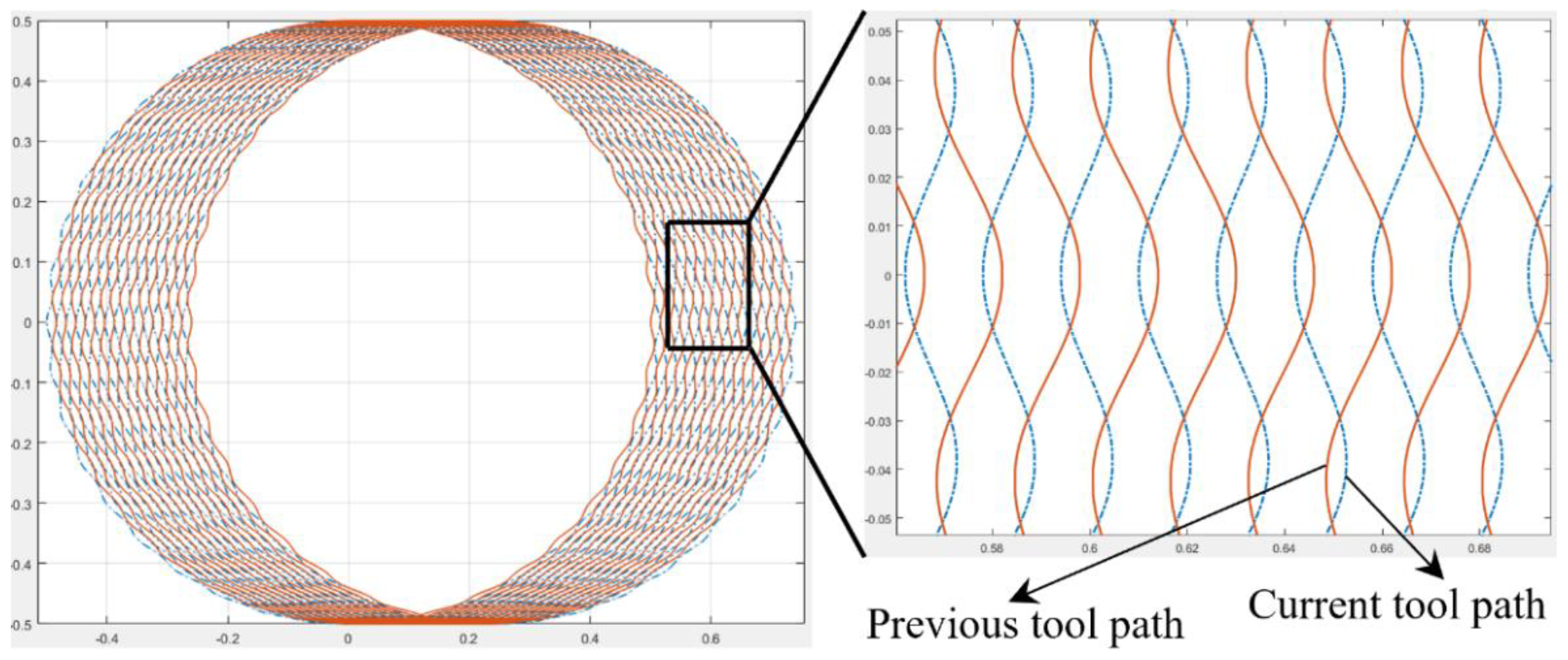
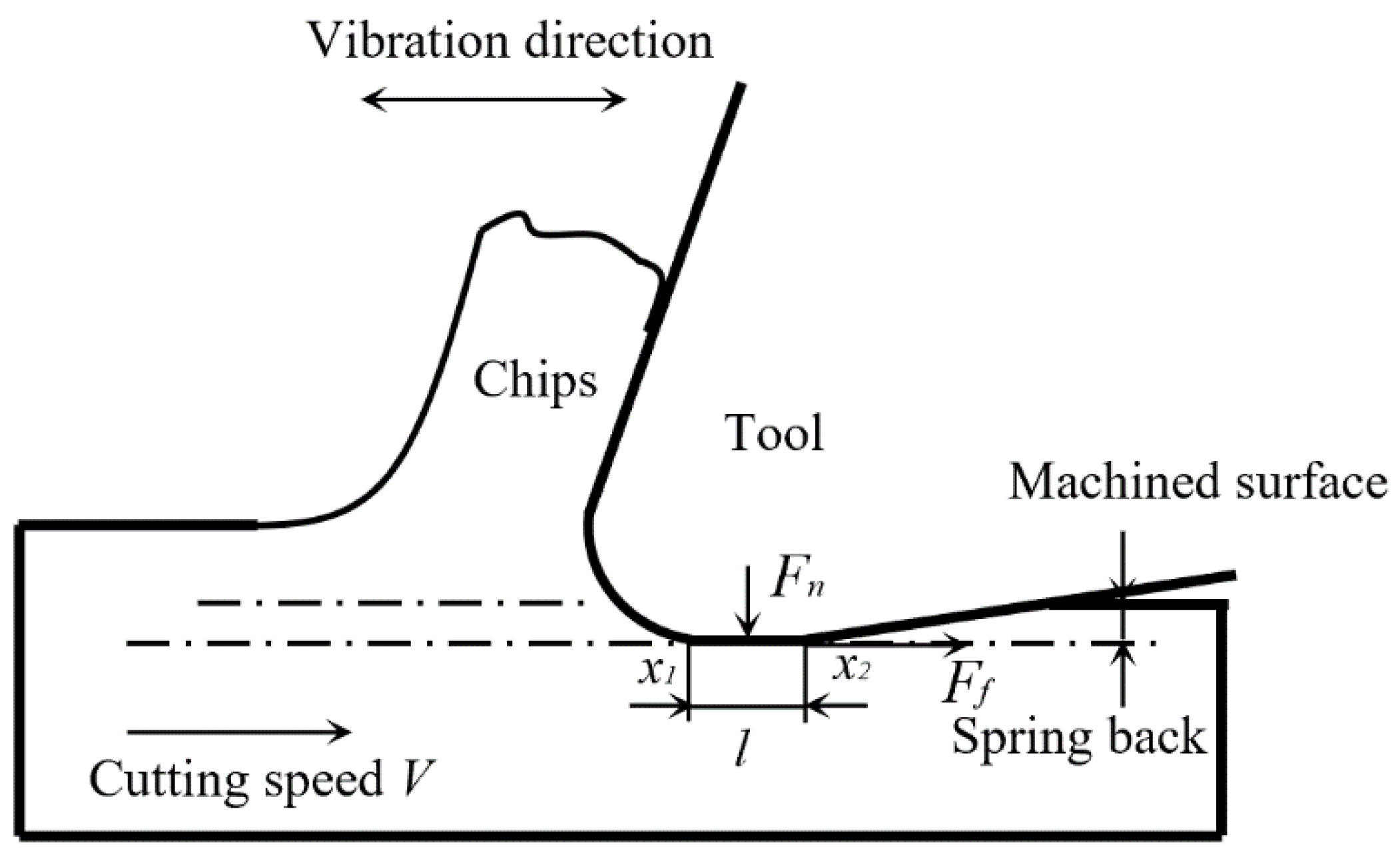
2.1. Tool Tip Trajectory
2.2. Tool-Workpiece Separation Conditions
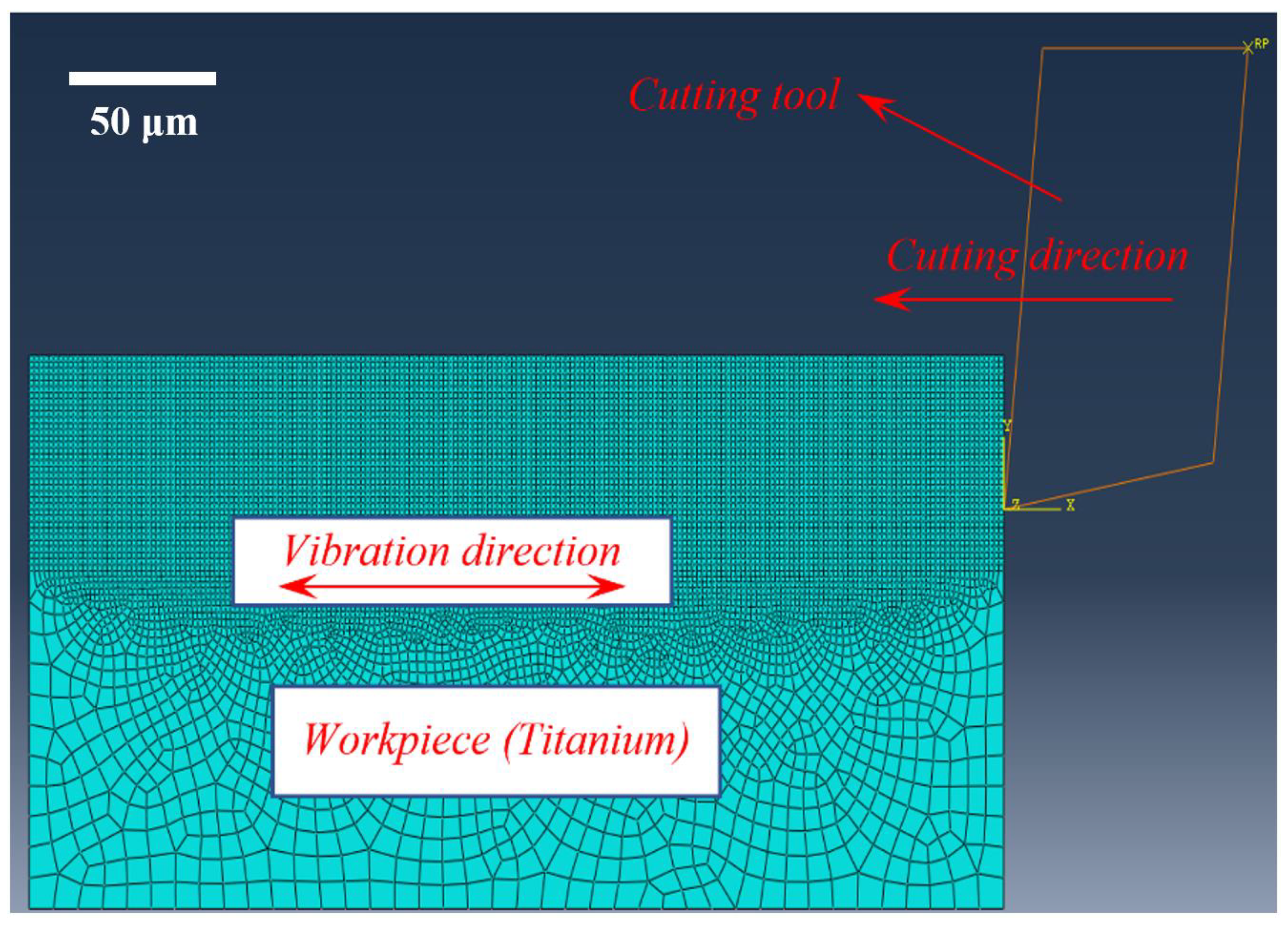
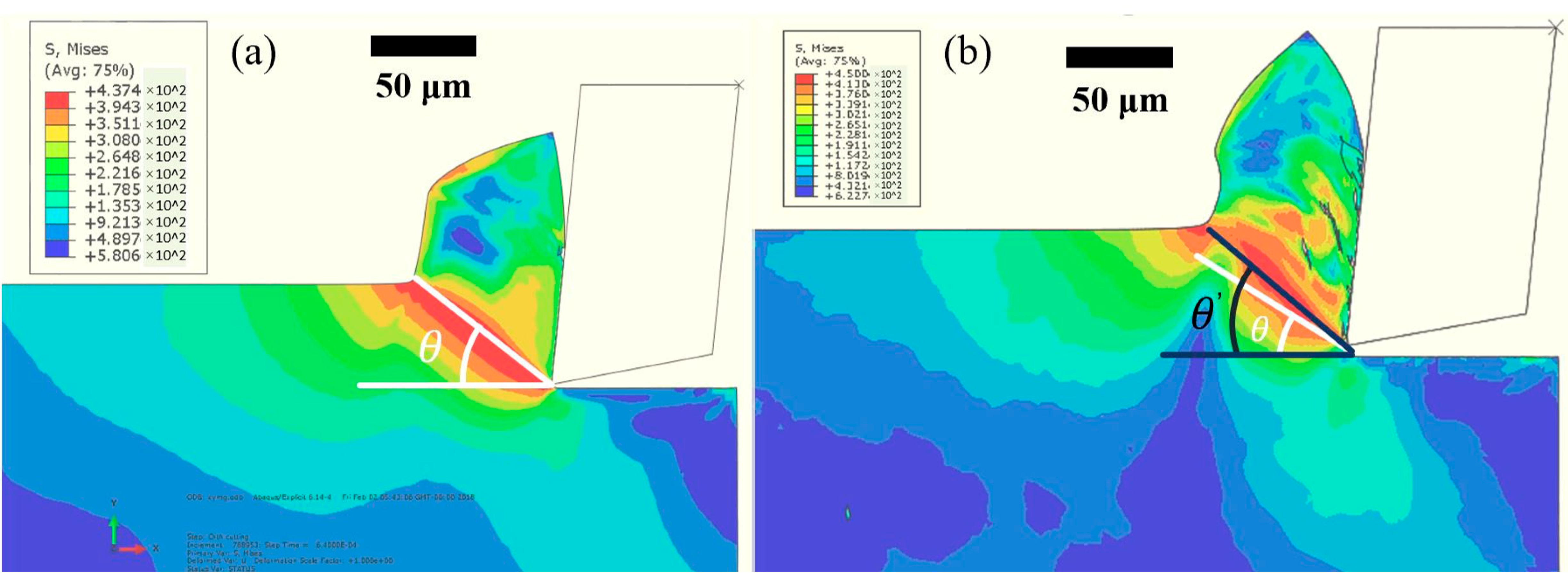
3. Finite Element Simulations
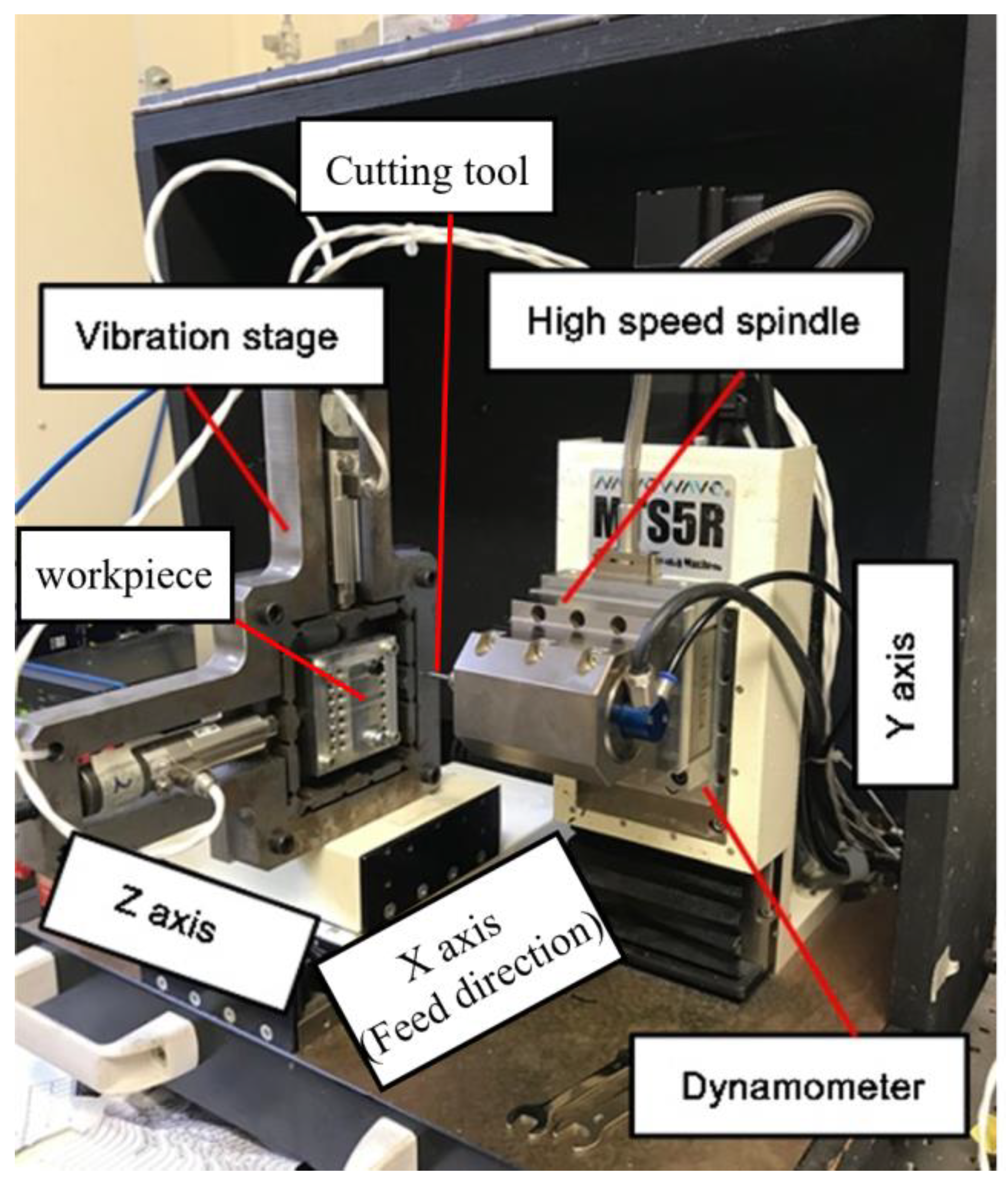
4. Experimental Setup
5. Results and Discussion
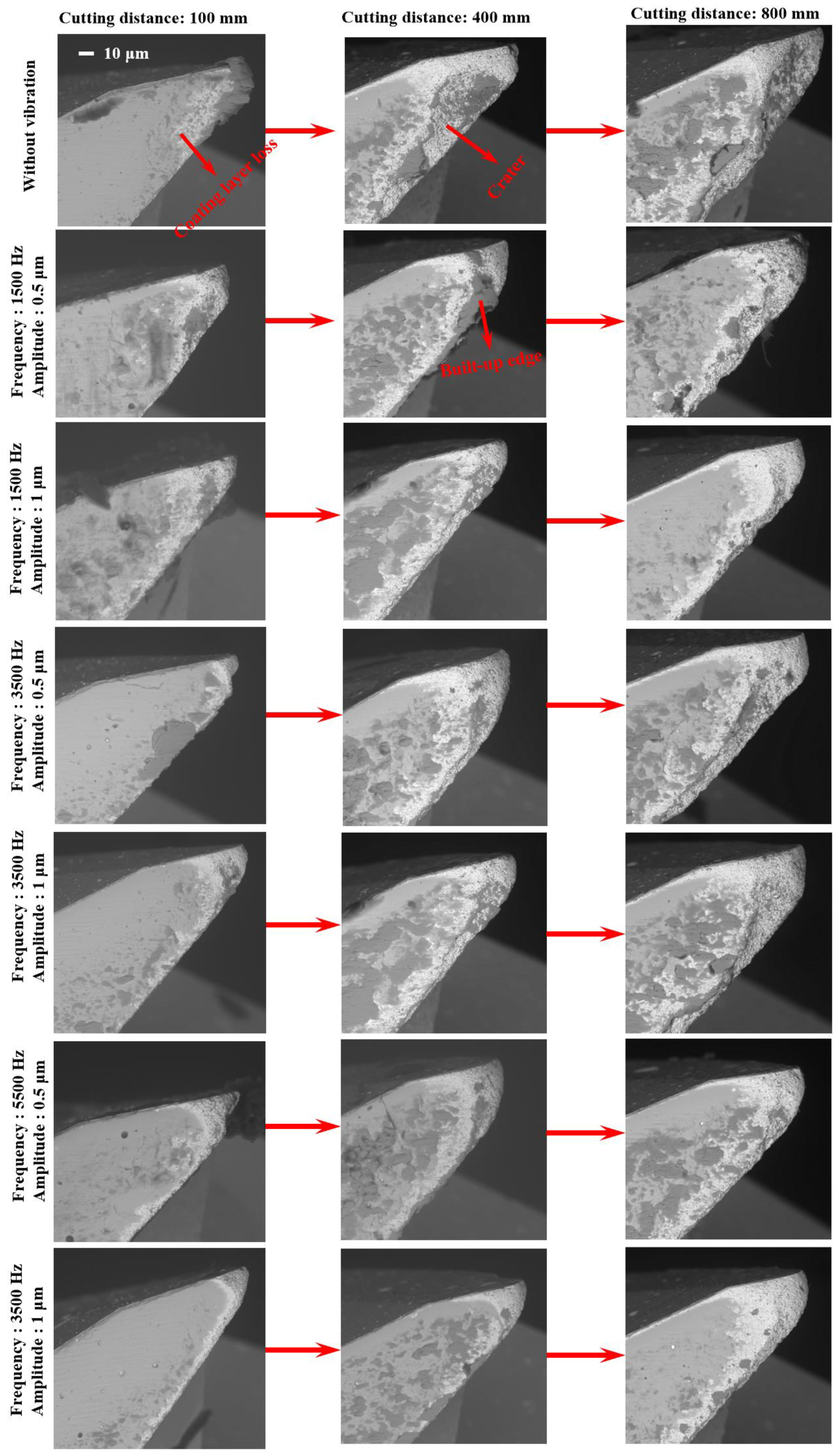
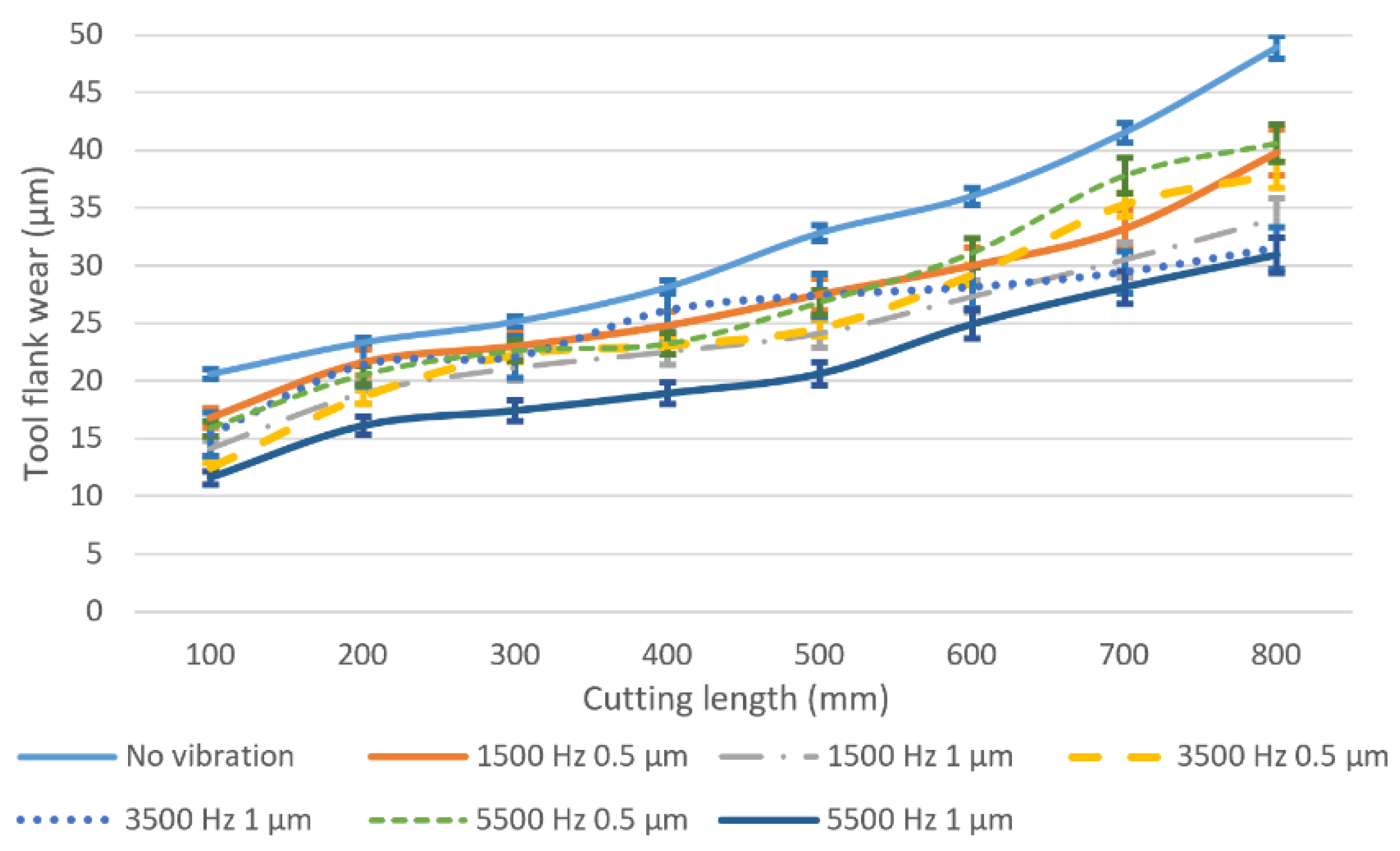
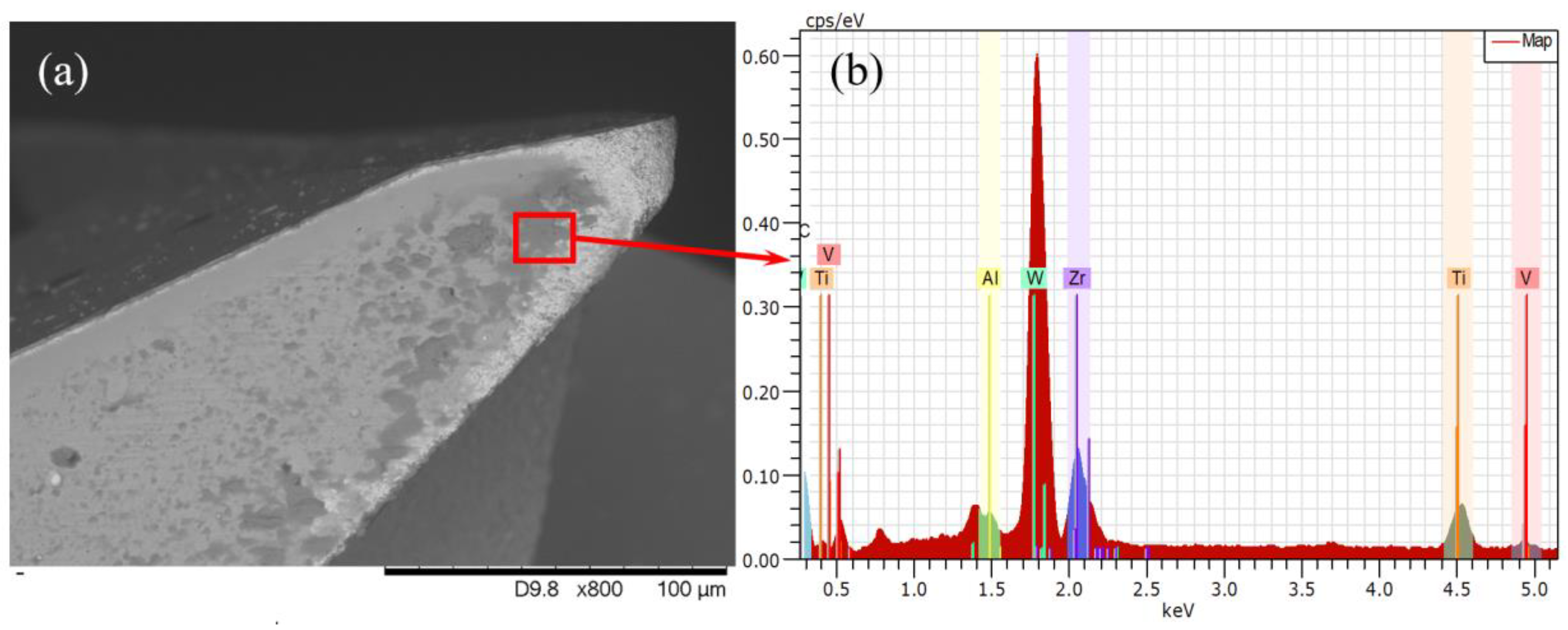
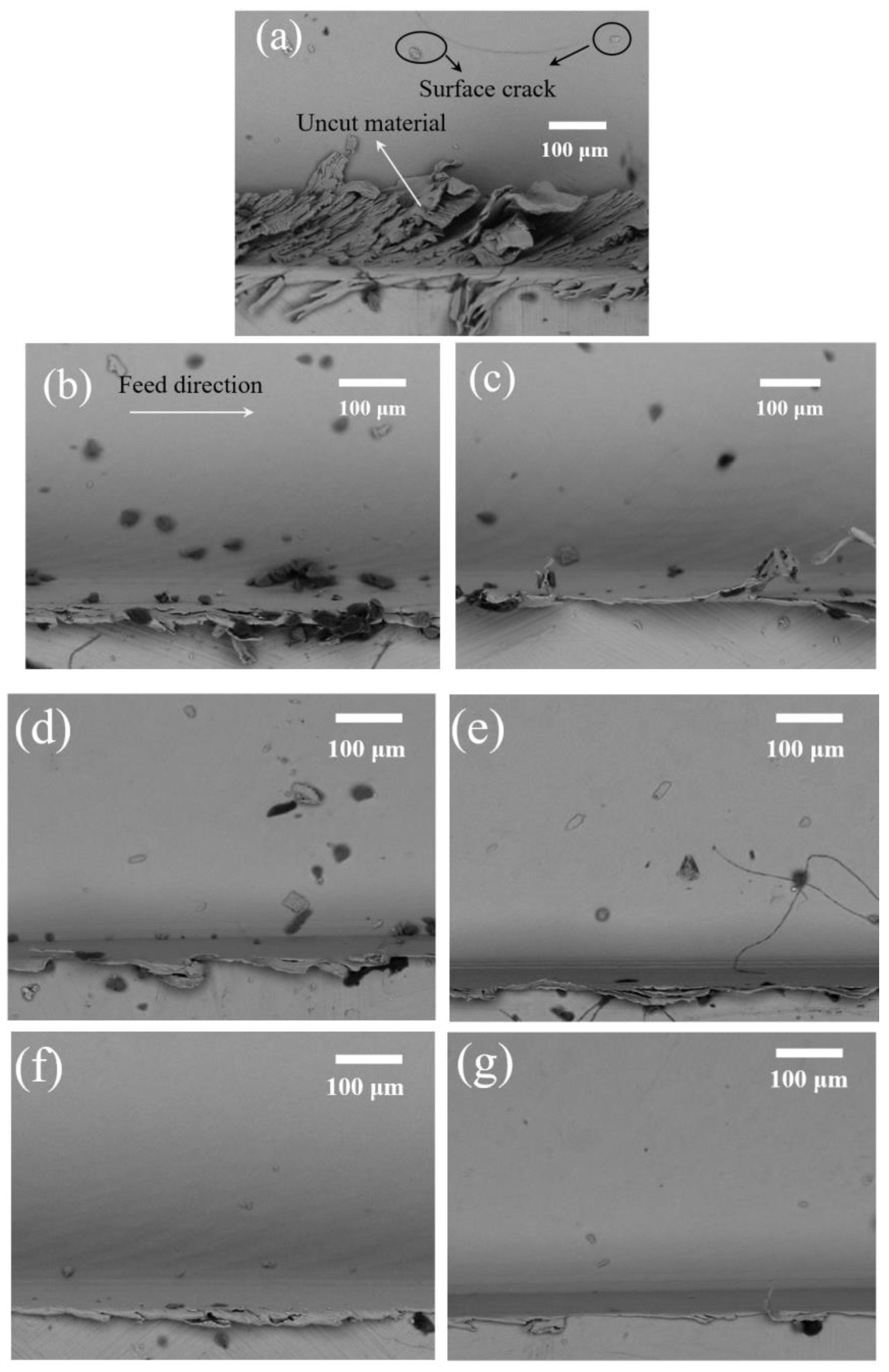
5.1. Tool Wear Results and Wear Mechanism
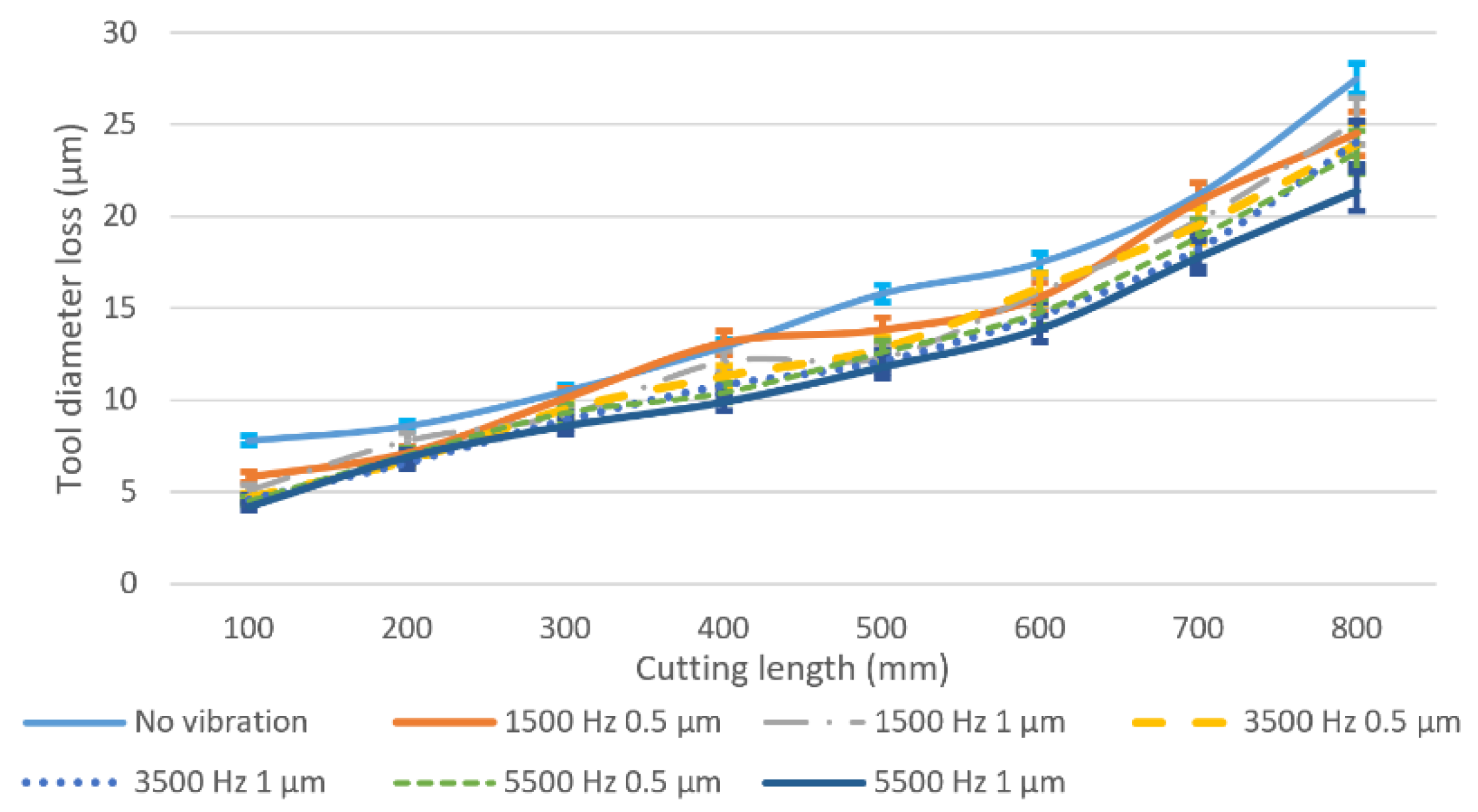
5.2. Relationship between Tool Wear and Cutting Performance
6. Conclusions
- Tool wear can be reduced effectively as vibration is added and the minimized tool wear can be obtained as the tool-workpiece separation condition is satisfied due to the suppression of size and ploughing effect.
- A coating layer loss initiates the wear mechanism for the coated tool, and adhesive and mechanical wear are the main wear mechanisms for the substrate wear of the cutting tools. These wear mechanisms can be suppressed effectively in vibration-assisted micro milling when tool-workpiece separation occurs, because the periodic separation between the cutting tool and workpiece enhances the cooling effect of the tool and reduces the cutting force as well as the generation of built-up edge.
- The relationship between tool wear and cutting performance is studied. Compared with conventional micro milling, the cutting performance in vibration-assisted micro milling can be improved. The machining results also indicate that better surface finish, smaller burr, and lesser surface crack can be obtained by increasing the vibration frequency and satisfying the tool-workpiece separation condition due to the low tool wear and the unique cutting mechanism.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, K.; Huo, D. Micro-Cutting: Fundamentals and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, D.; Choong, Z.J.; Shi, Y.; Hedley, J.; Zhao, Y. Diamond micro-milling of lithium niobate for sensing applications. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2016, 26, 095005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, X.; Huo, D.; Shyha, I.; Chen, W.; Wong, E. An experimental study on tool wear behaviour in micro milling of nano Mg/Ti metal matrix composites. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 96, 2127–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, D.; Lin, C.; Dalgarno, K. An experimental investigation on micro machining of fine-grained graphite. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 72, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, D.; Lin, C.; Choong, Z.J.; Pancholi, K.; Degenaar, P. Surface and subsurface characterisation in micro-milling of monocrystalline silicon. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 81, 1319–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadgari, A.; Huo, D.; Swailes, D. Investigation on tool wear and tool life prediction in micro-milling of Ti-6Al-4V. Nami Jishu Yu Jingmi Gongcheng/Nanotechnol. Precis. Eng. 2018, 1, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; He, N.; Li, L.; Li, X.L. An experimental investigation of effects of cooling/lubrication conditions on tool wear in high-speed end milling of Ti-6Al-4V. Wear 2006, 261, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordin, A.; Bruschi, S.; Ghiotti, A.; Bariani, P.F. Analysis of tool wear in cryogenic machining of additive manufactured Ti6Al4V alloy. Wear 2015, 328, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Hu, J.; Chou, Y.K.; Thompson, R.G. Delamination wear of nano-diamond coated cutting tools in composite machining. Wear 2009, 267, 991–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Chen, W.; Huo, D. Experimental investigation on burr formation in vibration-assisted micro-milling of Ti-6Al-4V. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2019, 233, 4112–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Chen, W.; Pozzi, M.; Teng, X.; Huo, D. Modulation of surface wettability by vibration assisted milling. Precis. Eng. 2018, 55, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zheng, L.; Huo, D. Surface texture formation by non-resonant vibration assisted micro milling. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2018, 28, 025006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehl, D.E.; Dow, T.A. Review of vibration-assisted machining. Precis. Eng. 2008, 32, 153–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, H.; Guo, Z.; Huang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Song, J. Experimental research of Al6061 on ultrasonic vibration assisted micro-milling. Procedia CIRP 2013, 6, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.H.; Zhang, J.H.; Li, H.; Wang, J.J.; Wang, X.C. Ultrasonic vibration-assisted milling of aluminum alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 63, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chern, G.L.; Chang, Y.C. Using two-dimensional vibration cutting for micro-milling. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2006, 46, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Chen, W.; Huo, D.; Lyu, X. Design, Analysis, and Control of a Two-Dimensional Vibration Device for Vibration-Assisted Micromilling. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Ibrahim, R.; Cheng, K.; Chen, S.J. Experimental study on machinability improvement of hardened tool steel using two dimensional vibration-assisted micro-end-milling. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2010, 50, 1115–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, C.; Rahman, M. Effect of machining parameters in ultrasonic vibration cutting. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2008, 48, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.M.; Wang, S.L. Effect of tool wear in ultrasonic vibration-assisted micro-milling. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2014, 228, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, K.; Kumar, A.S.; Rahman, M. A study of the diamond tool wear suppression mechanism in vibration-assisted machining of steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2014, 214, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janghorbanian, J.; Razfar, M.R.; Zarchi, M.M.A. Effect of cutting speed on tool life in ultrasonic-assisted milling process. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2013, 227, 1157–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, L.; Schaal, N.; Wegener, K. In-process Measurement of the Coefficient of Friction on Titanium. Procedia CIRP 2017, 58, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.K.; kumar, M.; Bajpai, V.; Singh, N.K.; Singh, R.K. FE modeling of burr size in high-speed micro-milling of Ti6Al4V. Precis. Eng. 2017, 49, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawaid, A.; Sharif, S.; Koksal, S. Evaluation of wear mechanisms of coated carbide tools when face milling titanium alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2000, 99, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.H.; Sasaki, S.; Umeda, K. The friction and wear characteristics of low-pressure plasma-sprayed ZrO2-BaCrO4 composite coatings at elevated temperatures. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2002, 154, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Rahim, M.Z.; Ding, S.; Sun, S. Performance and wear analysis of polycrystalline diamond (PCD) tools manufactured with different methods in turning titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 85, 825–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yi, S.; Sun, S.; Ding, S. Wear mechanisms and performance of abrasively ground polycrystalline diamond tools of different diamond grains in machining titanium alloy. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 29, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramcharoen, A.; Mativenga, P.T. Size effect and tool geometry in micromilling of tool steel. Precis. Eng. 2009, 33, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zheng, L.; Teng, X.; Yang, K.; Huo, D. Cutting Mechanism Investigation in Vibration-Assisted Machining. Nanomanuf. Metrol. 2018, 1, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| No | Vibration Amplitude (µm) | Vibration Frequency (Hz) | Spindle Speed (rpm) | Feed Rate (µm/tooth) | Axial Depth of Cut (µm) | Tool-Workpiece Separation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 30,000 | 1.5 | 50 | NO |
| 2 | 0.5 | 1500 | 30,000 | 1.5 | 50 | NO |
| 3 | 1 | 1500 | 30,000 | 1.5 | 50 | YES |
| 4 | 0.5 | 3500 | 30,000 | 1.5 | 50 | NO |
| 5 | 1 | 3500 | 30,000 | 1.5 | 50 | YES |
| 6 | 0.5 | 5500 | 30,000 | 1.5 | 50 | NO |
| 7 | 1 | 5500 | 30,000 | 1.5 | 50 | YES |
| Properties | Values |
|---|---|
| Density (ton/mm3) | 4.5 × 10−9 |
| Young’s Modulus (MPa) | 96,832.3 |
| Poisson’s Ratio | 0.32 |
| A (MPa) | 1098 |
| B (MPa) | 1092 |
| n | 0.93 |
| m | 1.1 |
| C | 0.014 |
| d1 | −0.09 |
| d2 | 0.25 |
| d3 | −0.5 |
| d4 | 0.014 |
| d5 | 3.87 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, L.; Chen, W.; Huo, D. Investigation on the Tool Wear Suppression Mechanism in Non-Resonant Vibration-Assisted Micro Milling. Micromachines 2020, 11, 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11040380
Zheng L, Chen W, Huo D. Investigation on the Tool Wear Suppression Mechanism in Non-Resonant Vibration-Assisted Micro Milling. Micromachines. 2020; 11(4):380. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11040380
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Lu, Wanqun Chen, and Dehong Huo. 2020. "Investigation on the Tool Wear Suppression Mechanism in Non-Resonant Vibration-Assisted Micro Milling" Micromachines 11, no. 4: 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11040380
APA StyleZheng, L., Chen, W., & Huo, D. (2020). Investigation on the Tool Wear Suppression Mechanism in Non-Resonant Vibration-Assisted Micro Milling. Micromachines, 11(4), 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11040380






