Doped or Quantum-Dot Layers as In Situ Etch-Stop Indicators for III/V Semiconductor Reactive Ion Etching (RIE) Using Reflectance Anisotropy Spectroscopy (RAS)
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. General Remarks
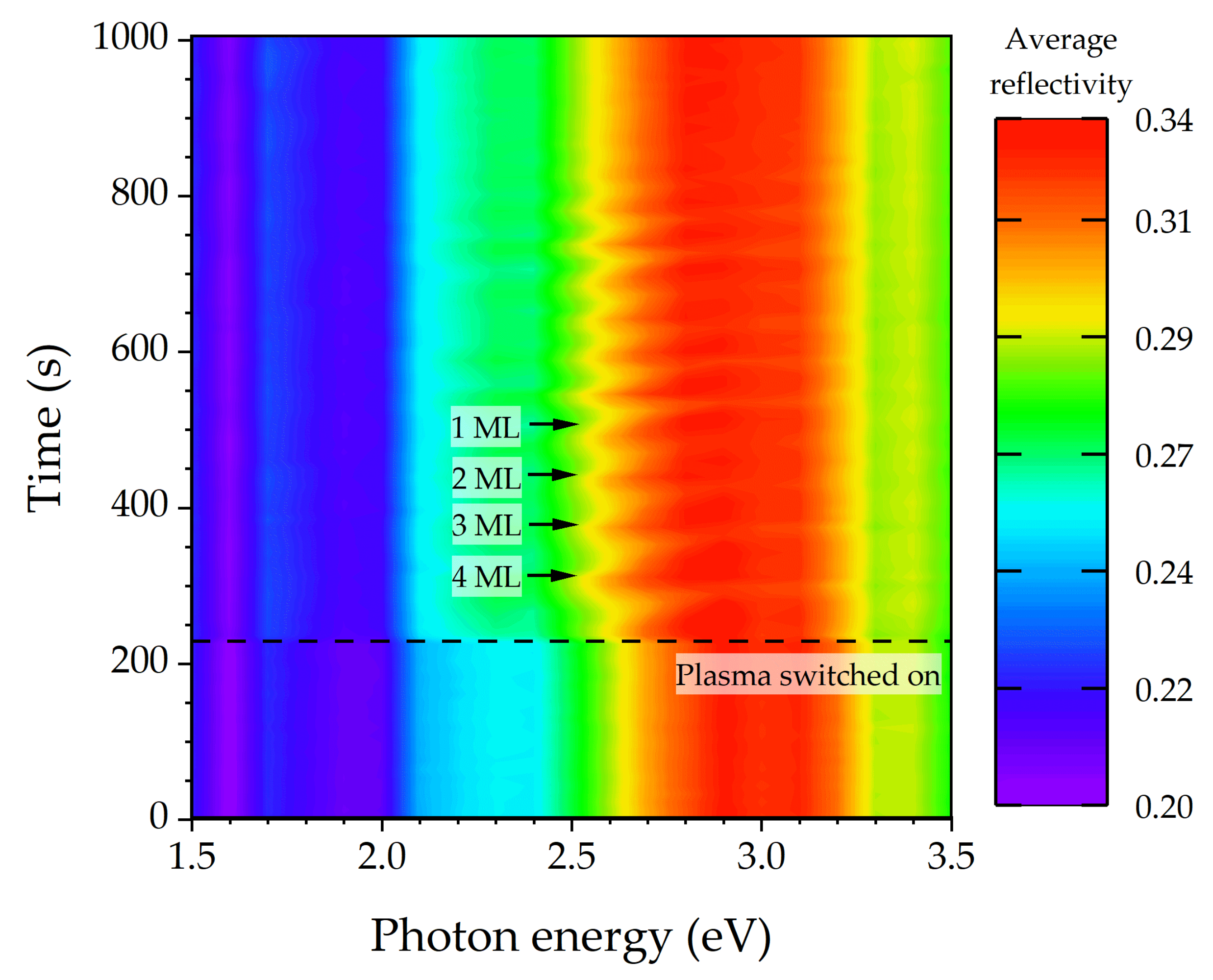
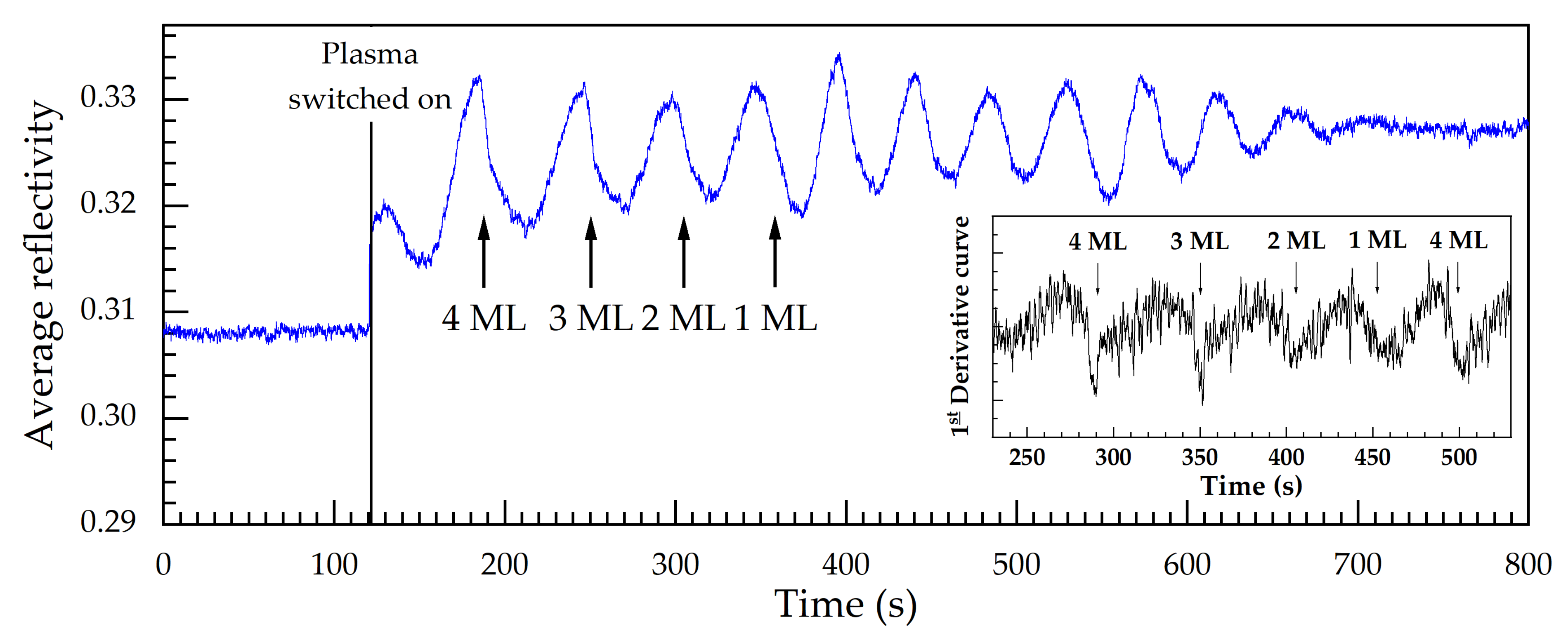
1.2. RAS Color Plot, Spectra, and Transients
1.3. Statistical Data Analysis
2. Materials and Preparation of Setup
3. Results and Discussion
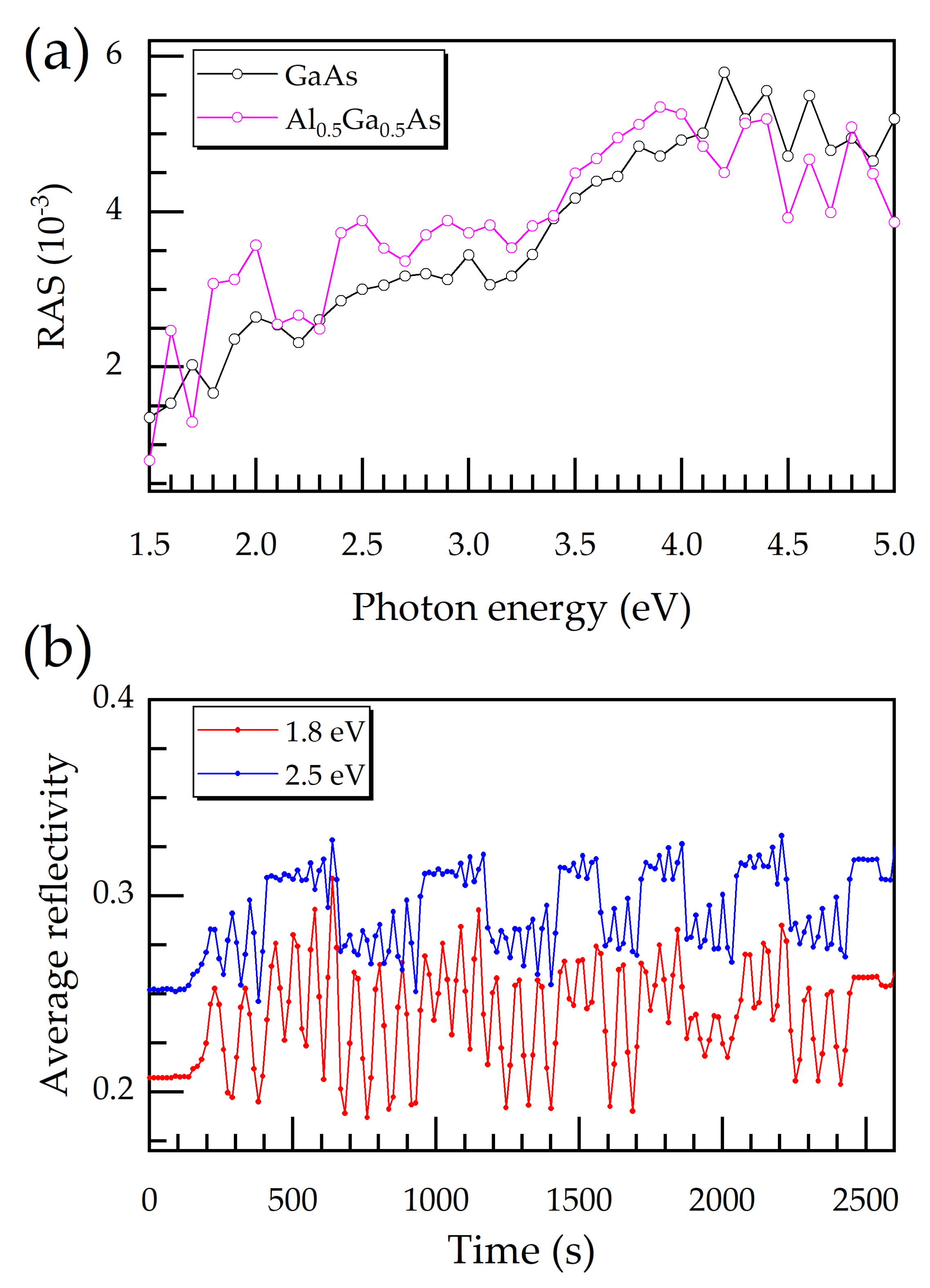
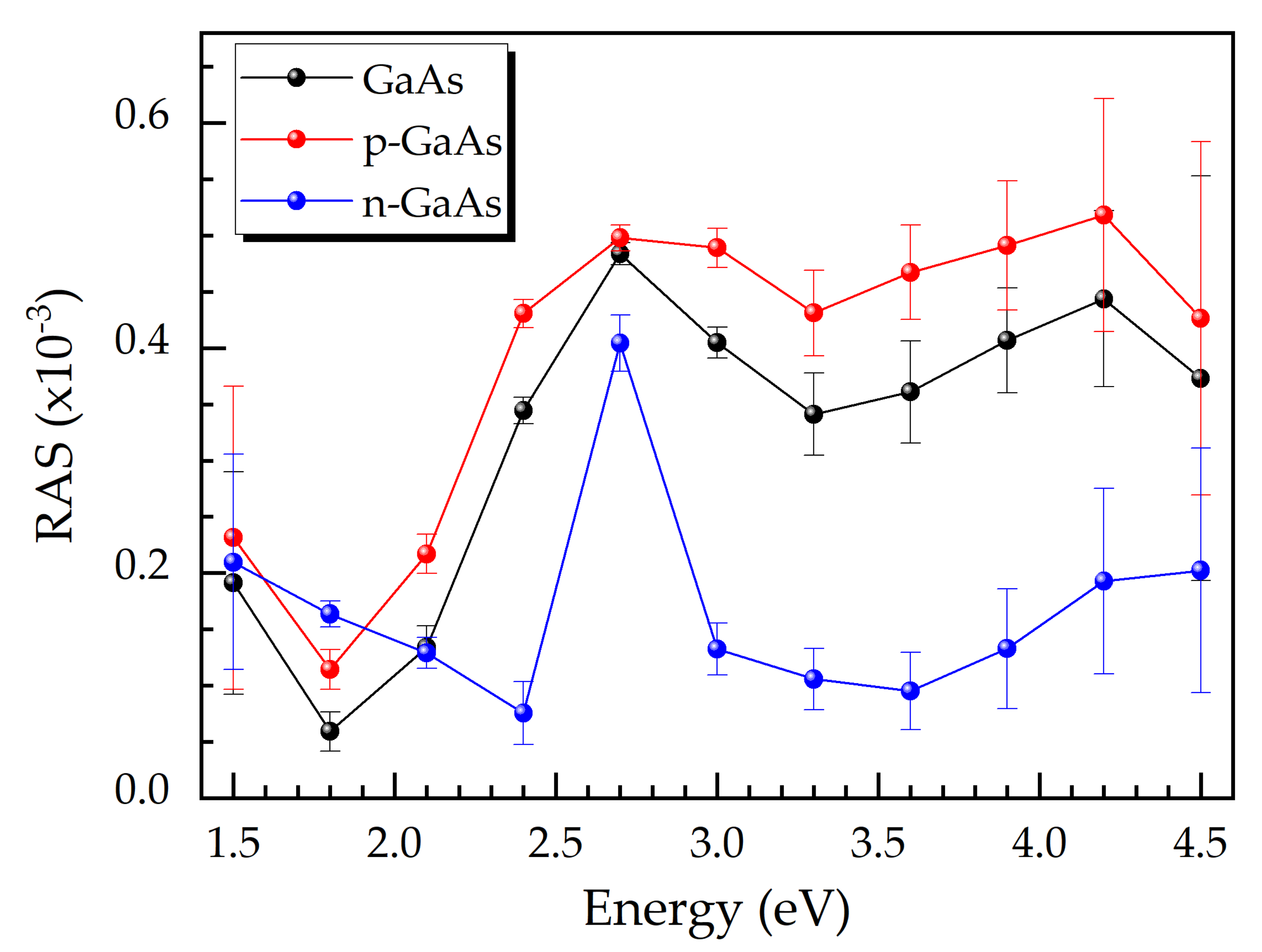
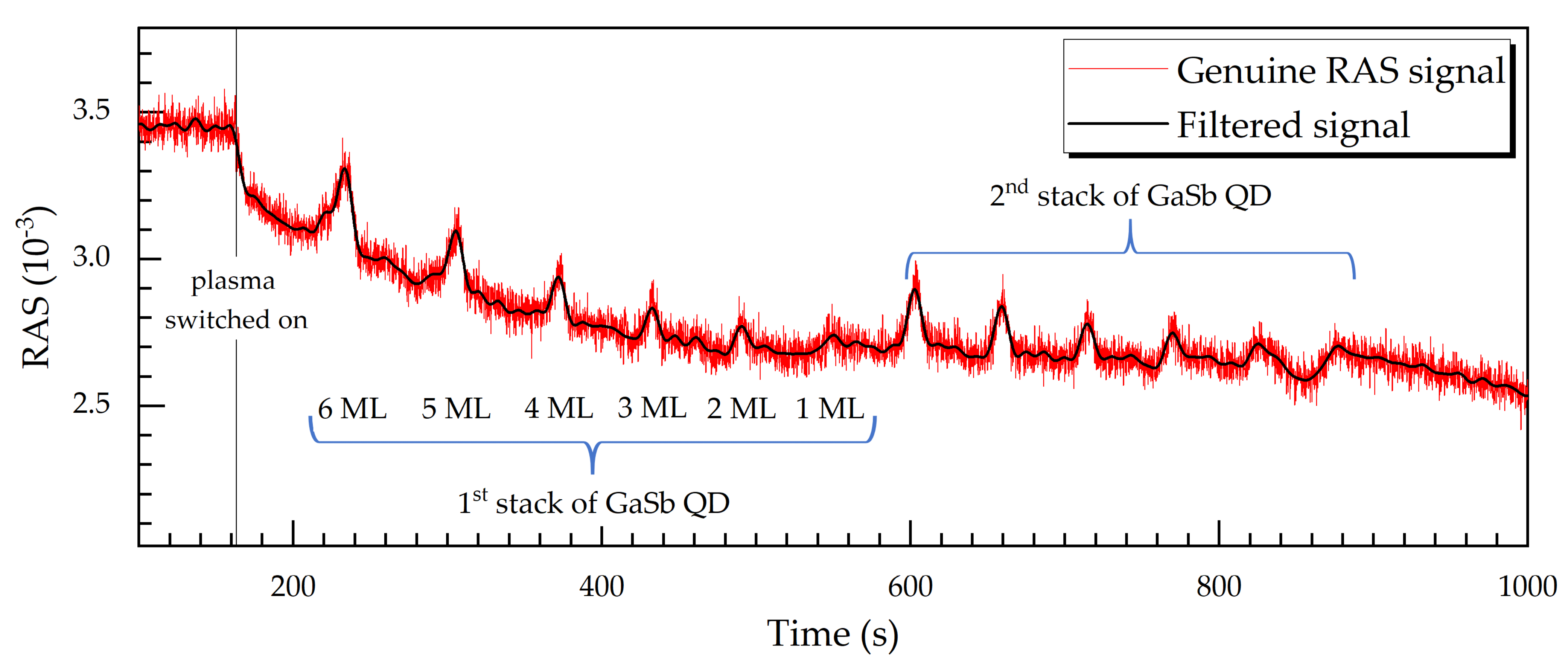
3.1. RAS Signal Fingerprints of Doped GaAs Layers and GaSb QD upon Epitaxial Growth
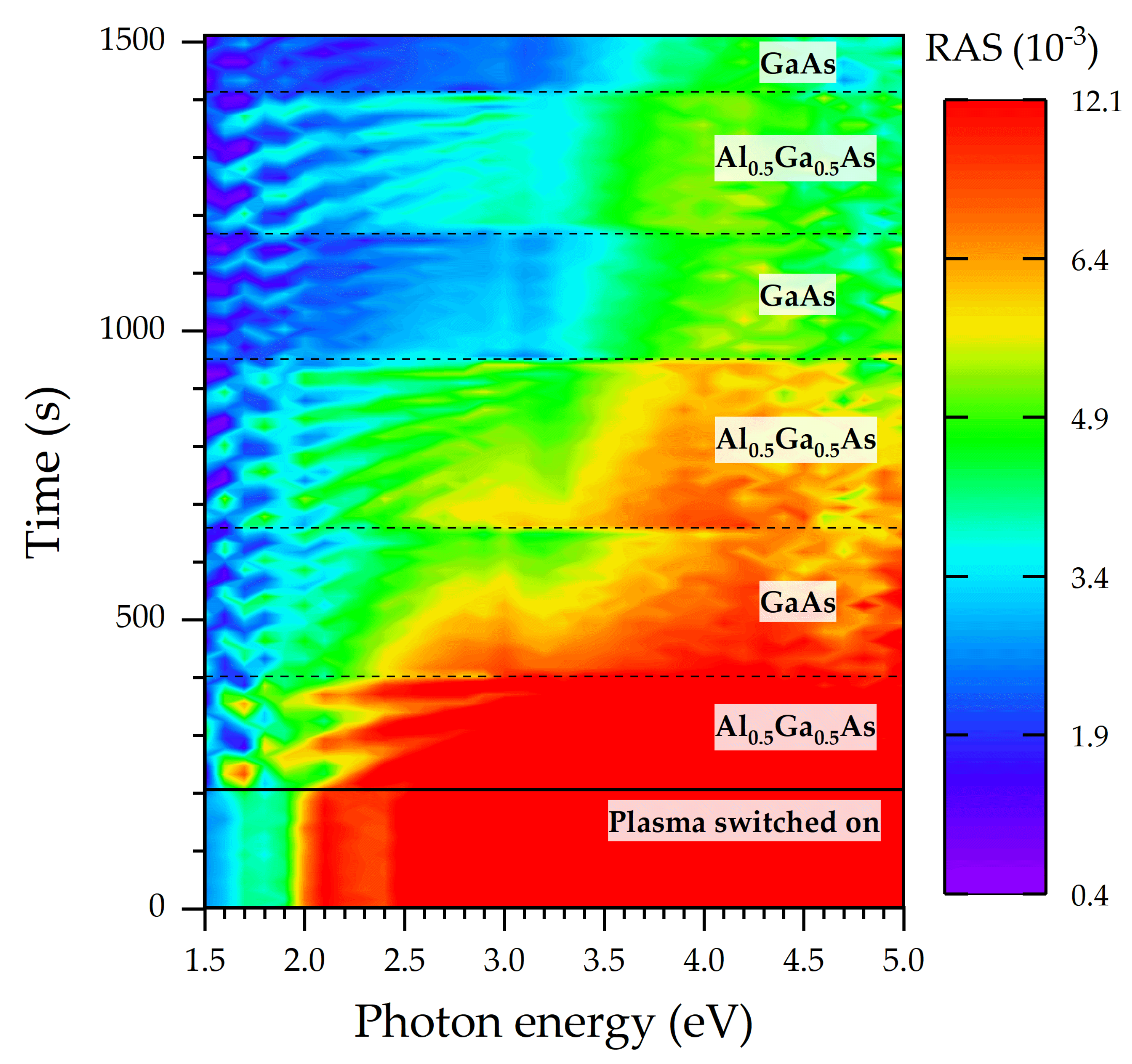
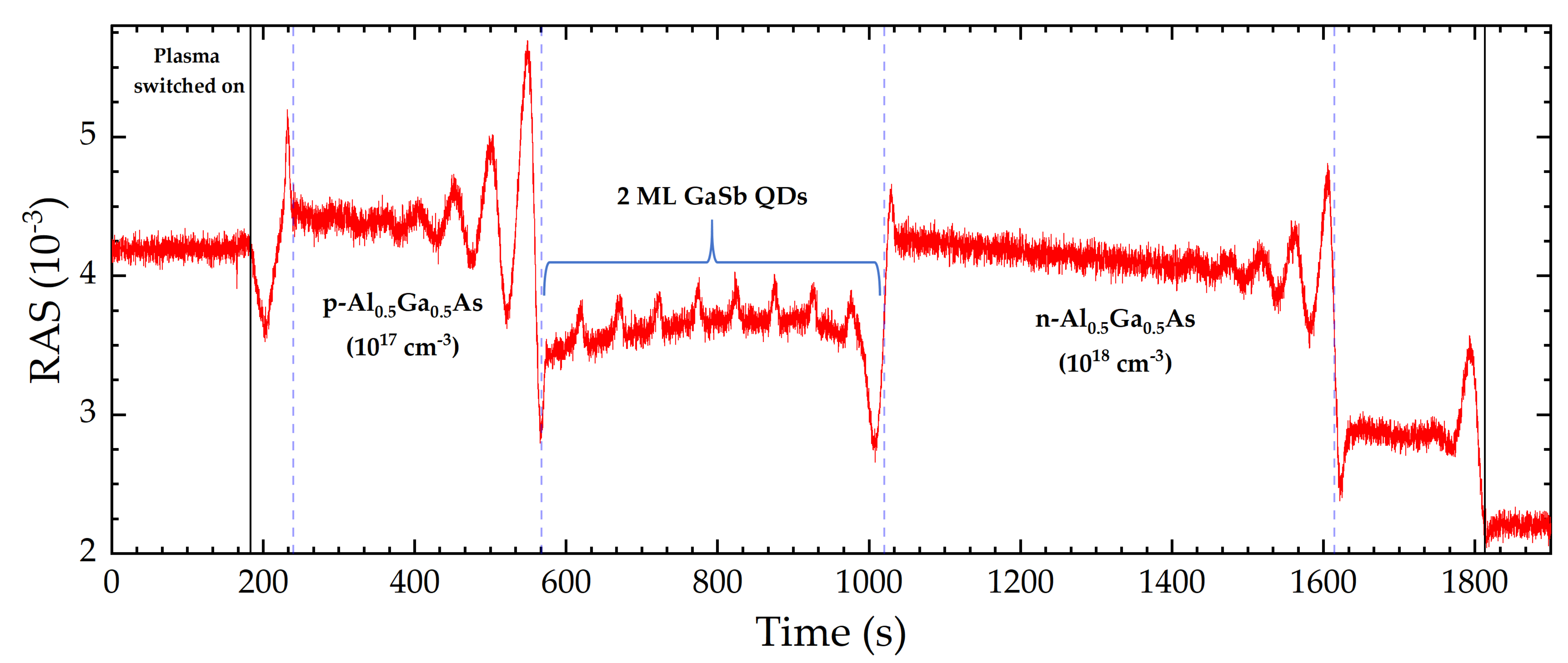
3.2. In Situ RAS Monitoring during RIE of a III/V Semiconductor Laser
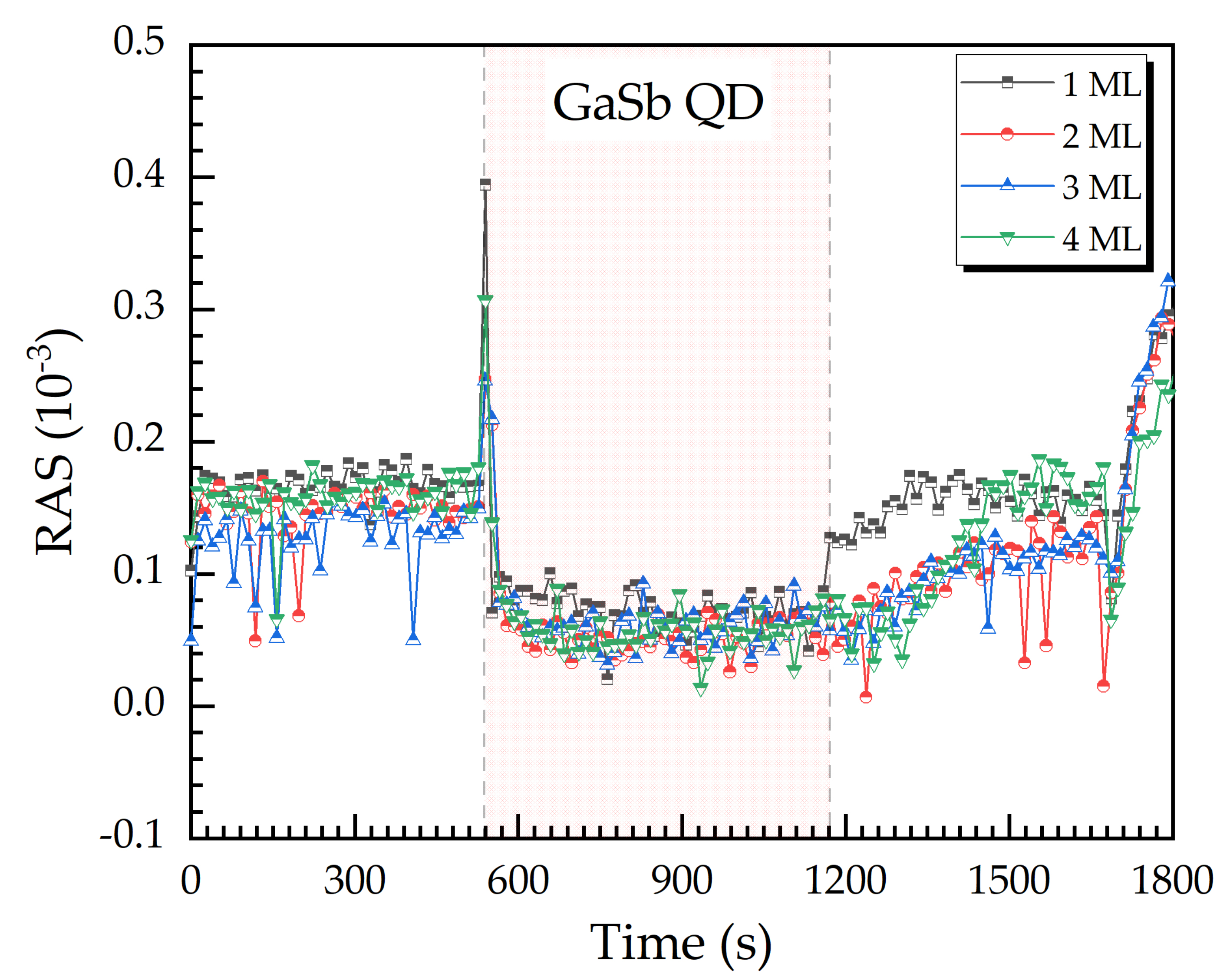
3.3. GaSb QD Layer as an Etch-Stop Indicator
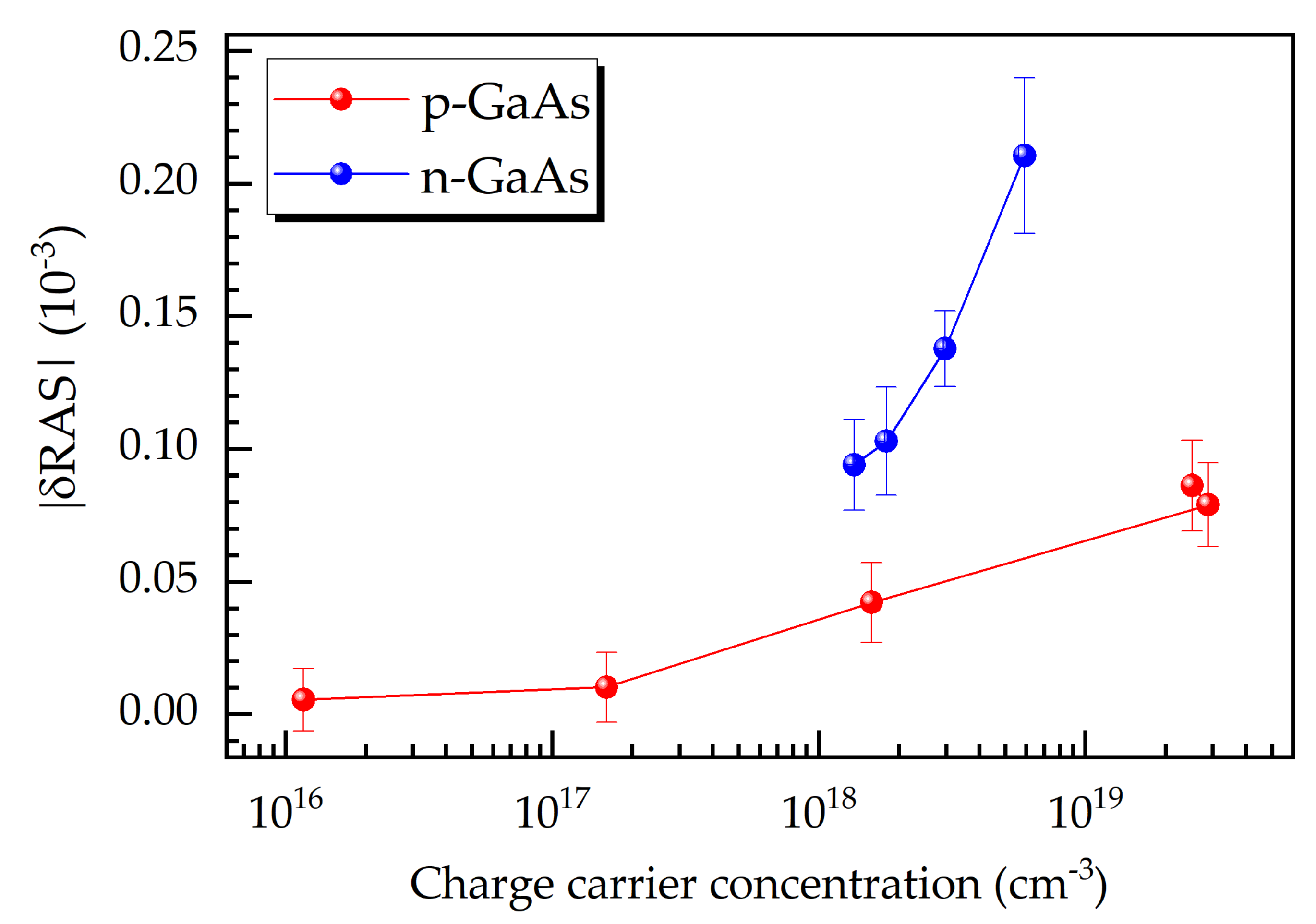
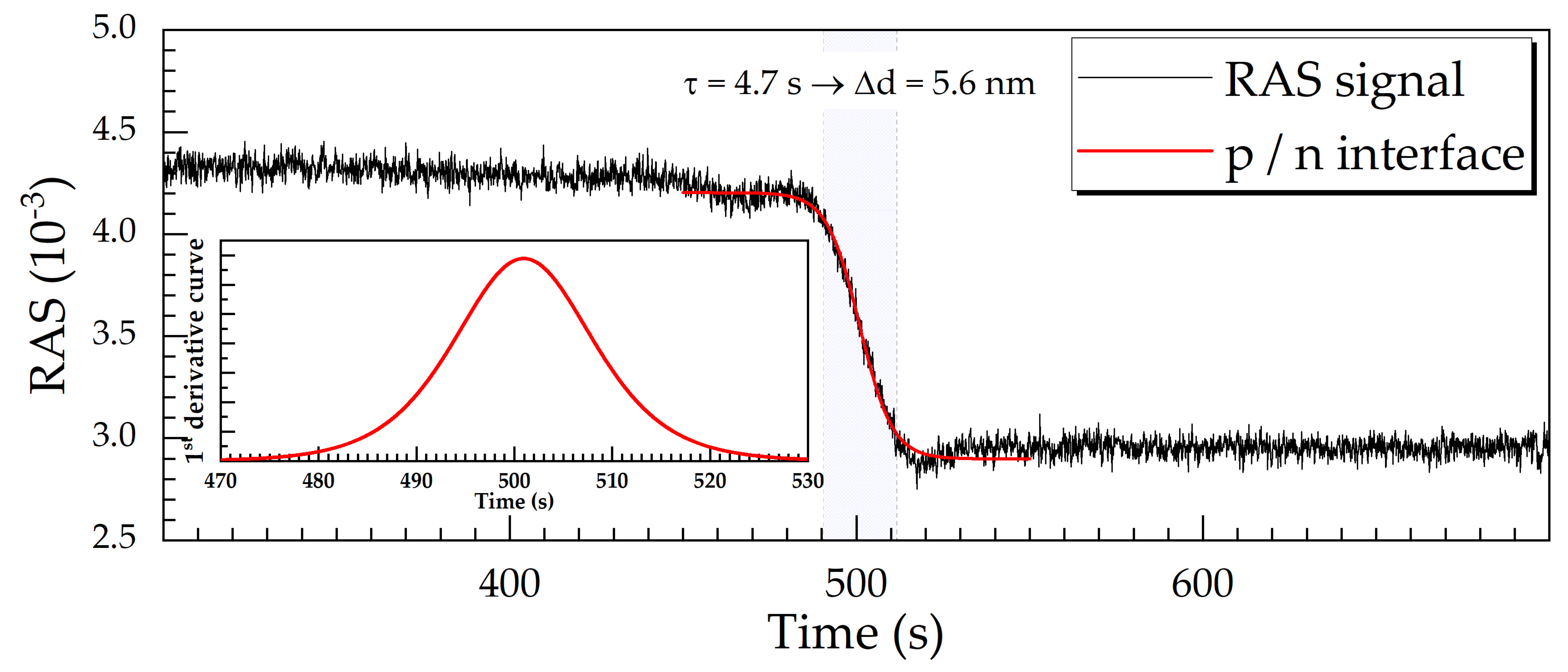
3.4. Resolution Limit of III/V Doped Layers as Etch-Stop Barrier Indicators upon RAS-RIE
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Donnelly, V.M.; Kornblit, A. Plasma Etching: Yesterday, Today, and Tomorrow. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A Vac. Surf. Film. 2013, 31, 050825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karouta, F. A Practical Approach to Reactive Ion Etching. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2014, 47, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, H.; Yoneda, M.; Fujiwara, N. Developments of Plasma Etching Technology for Fabricating Semiconductor Devices. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 47, 1435–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouckhardt, H.; Strassner, J.; Loeber, T.H.; Doering, C. 1 ML Wetting Layer upon Ga(As)Sb Quantum Dot (QD) Formation on GaAs Substrate Monitored with Reflectance Anisotropy Spectroscopy (RAS). Adv. Optoelectron. 2018, 2018, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinschmidt, A.K.; Barzen, L.; Strassner, J.; Doering, C.; Fouckhardt, H.; Bock, W.; Wahl, M.; Kopnarski, M. Precise in Situ Etch Depth Control of Multilayered III-V Semiconductor Samples with Reflectance Anisotropy Spectroscopy (RAS) Equipment. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1783–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weightman, P.; Martin, D.S.; Cole, R.J.; Farrell, T. Reflection Anisotropy Spectroscopy. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2015, 68, 1251–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doering, C.; Strassner, J.; Fouckhardt, H. In-Situ Etch-Depth Control Better than 5 nm with Reflectance Anisotropy Spectroscopy (RAS) Equipment during Reactive Ion Etching (RIE): A Technical RAS Application. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzen, L.; Kleinschmidt, A.K.; Strassner, J.; Doering, C.; Fouckhardt, H.; Bock, W.; Wahl, M.; Kopnarski, M. Influence of Plasma Composition on Reflectance Anisotropy Spectra for in Situ III-V Semiconductor Dry-Etch Monitoring. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 357, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzen, L.; Richter, J.; Fouckhardt, H.; Wahl, M.; Kopnarski, M. Monitoring of (Reactive) Ion Etching (RIE) with Reflectance Anisotropy Spectroscopy (RAS) Equipment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 328, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyne, C.; Gensch, M.; Peters, S.; Pohl, U.W.; Zettler, J.T.; Richter, W. In Situ Monitoring of ZnS/GaP and ZnSe/GaAs Metalorganic Vapor Phase Epitaxy Using Reflectance Anisotropy Spectroscopy and Spectroscopic Ellipsometry. Thin Solid Films 2000, 364, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Gallegos, J.; Guevara-Macías, L.E.; Ariza-Flores, A.D.; Castro-García, R.; Lastras-Martínez, L.F.; Balderas-Navarro, R.E.; López-Estopier, R.E.; Lastras-Martínez, A. On the Origin of Reflectance-Anisotropy Oscillations during GaAs (001) Homoepitaxy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 439, 963–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkovits, V.L.; Paget, D. Reflectance Anisotropy Spectroscopy: A New Method for Semiconductor Surface Chemistry Investigation. Thin Solid Films 1993, 233, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zettler, J.T.; Haberland, K.; Zorn, M.; Pristovsek, M.; Richter, W.; Kurpas, P.; Weyers, M. Real-Time Monitoring of MOVPE Device Growth by Reflectance Anisotropy Spectroscopy and Related Optical Techniques. J. Cryst. Growth 1998, 195, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sombrio, G.; Oliveira, E.; Strassner, J.; Doering, C.; Fouckhardt, H. In-situ III/V semiconductor dry-etch depth-control with ±0.8 nm best accuracy using reflectance anisotropy spectroscopy (RAS) equipment and a Vernier-scale like measurement. Thin Solid Films. (under review).
- Yu, J.L.; Cheng, S.Y.; Lai, Y.F.; Zheng, Q.; Chen, Y.H.; Tang, C.G. Tuning of In-Plane Optical Anisotropy by Inserting Ultra-Thin InAs Layer at Interfaces in (001)-Grown GaAs/AlGaAs Quantum Wells. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 015302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zettler, J.T. Characterization of Epitaxial Semiconductor Growth by Reflectance Anisotropy Spectroscopy and Ellipsometry. Prog. Cryst. Growth Charact. Mater. 1997, 35, 27–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Cigarrillo, O.; Lastras-Martínez, L.F.; Cerda-Méndez, E.A.; Flores-Rangel, G.; Bravo-Velazquez, C.A.; Balderas-Navarro, R.E.; Lastras-Martínez, A.; Ulloa-Castillo, N.A.; Biermann, K.; Santos, P. V Optical Anisotropies of Asymmetric Double GaAs (001) Quantum Wells. Phys. Rev. B 2021, 103, 035309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorn, M.; Weyers, M. Application of Reflectance Anisotropy Spectroscopy to Laser Diode Growth in MOVPE. J. Cryst. Growth 2005, 276, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeber, T.H.; Richter, J.; Strassner, J.; Heisel, C.; Kimmle, C.; Fouckhardt, H. Efficient Ga(As)Sb Quantum Dot Emission in AlGaAs by GaAs Intermediate Layer. In Proceedings of the Quantum Dots and Nanostructures: Synthesis, Characterization, and Modeling X, Proceedings SPIE Photonics West San Francisco, CA, USA, 29 March 2013; Eyink, K.G., Huffaker, D.L., Szmulowicz, F., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2013; Volume 8634, pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, J. Optimized Control of Epitaxial Growth of Antimonide Quantum Dots and Quantum Dot Surroundings with Reflectance Anisotropy Spectroscopy. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität Kaiserslautern (Physics Department), Kaiserslautern, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Acosta-Ortiz, S.E.; Lastras-Martínez, A. Electro-Optic Effects in the Optical Anisotropies of (001) GaAs. Phys. Rev. B 1989, 40, 1426–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laytec, A.G. EpiRAS TT, Berlin, Germany. Available online: https://www.laytec.de/epiras/ (accessed on 10 November 2020).
- Zorn, M.; Weyers, M. Comprehensive Study of (Al)GaAs Si-Doping Using Reflectance Anisotropy Spectroscopy in Metal-Organic Vapour-Phase Epitaxy. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 878–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pristovsek, M.; Tsukamoto, S.; Koguchi, N.; Han, B.; Haberland, K.; Zettler, J.-T.; Richter, W.; Zorn, M.; Weyers, M. In-Situ Determination of the Carrier Concentration of (001) GaAs by Reflectance Anisotropy Spectroscopy. Phys. Status Solidi Appl. Res. 2001, 188, 1423–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krahmer, C.; Philippens, M.; Schubert, M.; Streubel, K. MOVPE Growth Investigations of Doping and Ordering in AlGaAs and GaInP with Reflectance Anisotropy Spectroscopy. J. Cryst. Growth 2007, 298, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sombrio, G.; Oliveira, E.; Strassner, J.; Richter, J.; Doering, C.; Fouckhardt, H. Doped or Quantum-Dot Layers as In Situ Etch-Stop Indicators for III/V Semiconductor Reactive Ion Etching (RIE) Using Reflectance Anisotropy Spectroscopy (RAS). Micromachines 2021, 12, 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12050502
Sombrio G, Oliveira E, Strassner J, Richter J, Doering C, Fouckhardt H. Doped or Quantum-Dot Layers as In Situ Etch-Stop Indicators for III/V Semiconductor Reactive Ion Etching (RIE) Using Reflectance Anisotropy Spectroscopy (RAS). Micromachines. 2021; 12(5):502. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12050502
Chicago/Turabian StyleSombrio, Guilherme, Emerson Oliveira, Johannes Strassner, Johannes Richter, Christoph Doering, and Henning Fouckhardt. 2021. "Doped or Quantum-Dot Layers as In Situ Etch-Stop Indicators for III/V Semiconductor Reactive Ion Etching (RIE) Using Reflectance Anisotropy Spectroscopy (RAS)" Micromachines 12, no. 5: 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12050502
APA StyleSombrio, G., Oliveira, E., Strassner, J., Richter, J., Doering, C., & Fouckhardt, H. (2021). Doped or Quantum-Dot Layers as In Situ Etch-Stop Indicators for III/V Semiconductor Reactive Ion Etching (RIE) Using Reflectance Anisotropy Spectroscopy (RAS). Micromachines, 12(5), 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12050502






