Light-Emitting Textiles: Device Architectures, Working Principles, and Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Light Emitting Technologies: Working Principles and Textile Integration
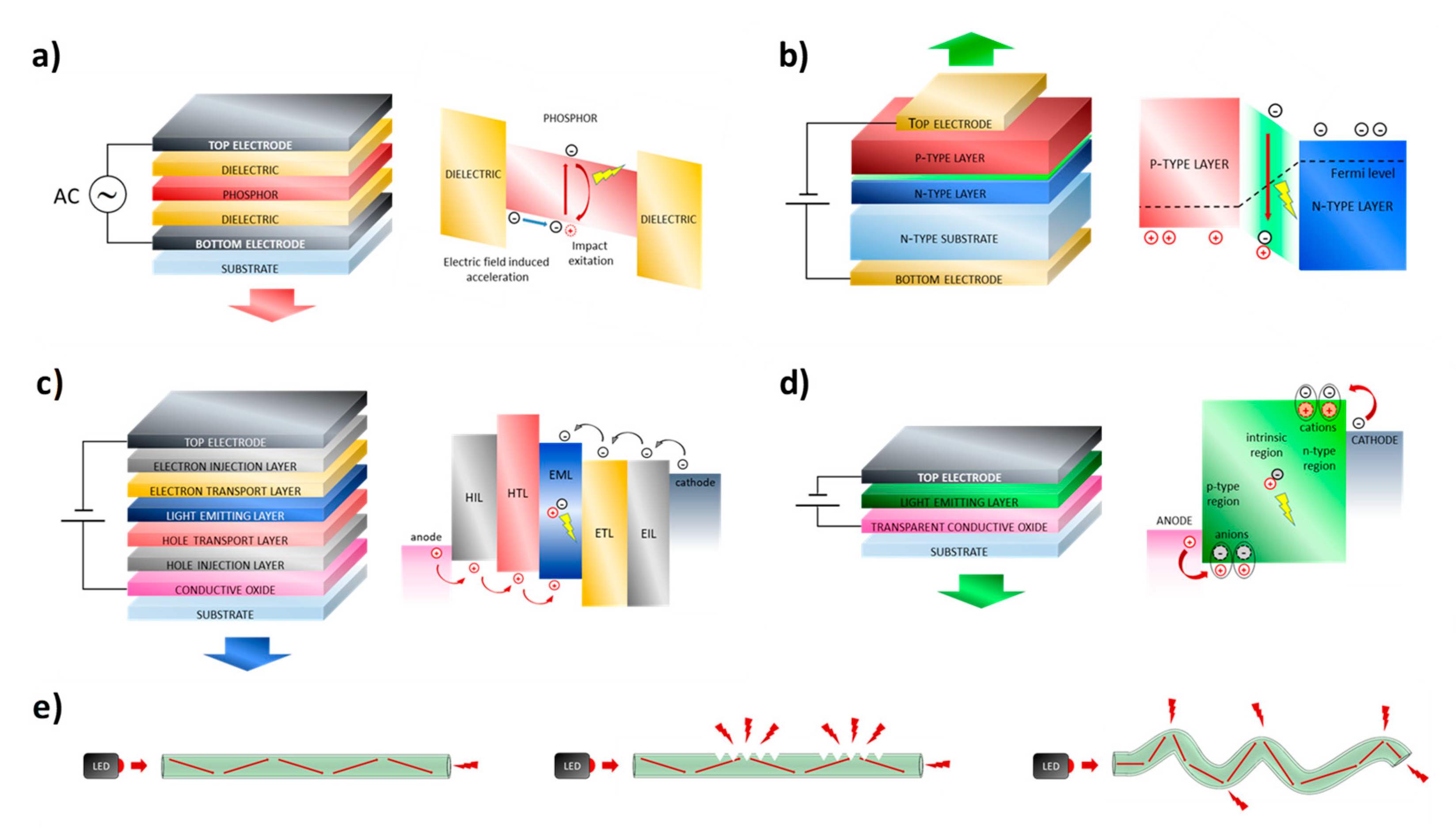
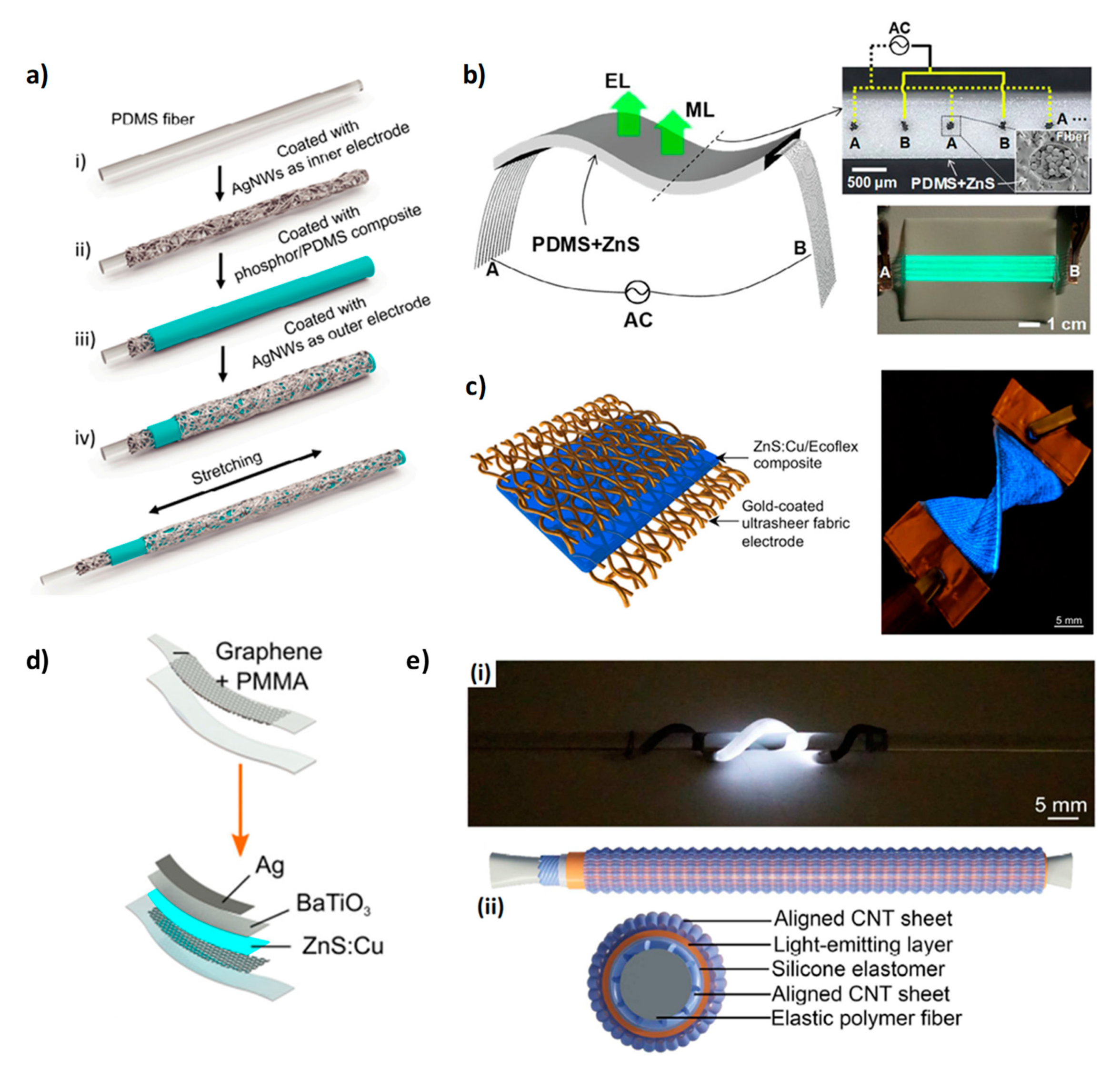
2.1. ACEL Devices
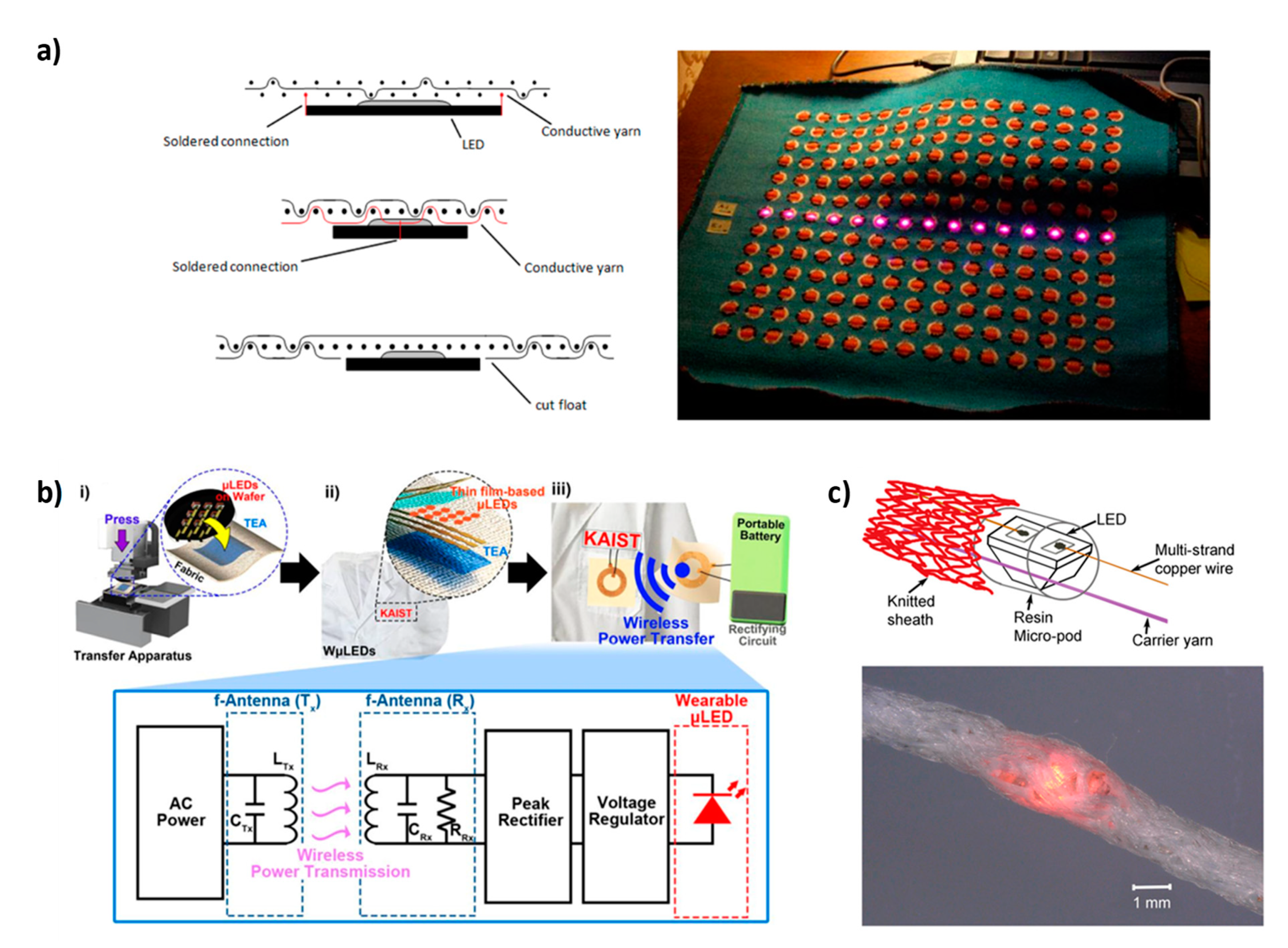
2.2. LED Devices
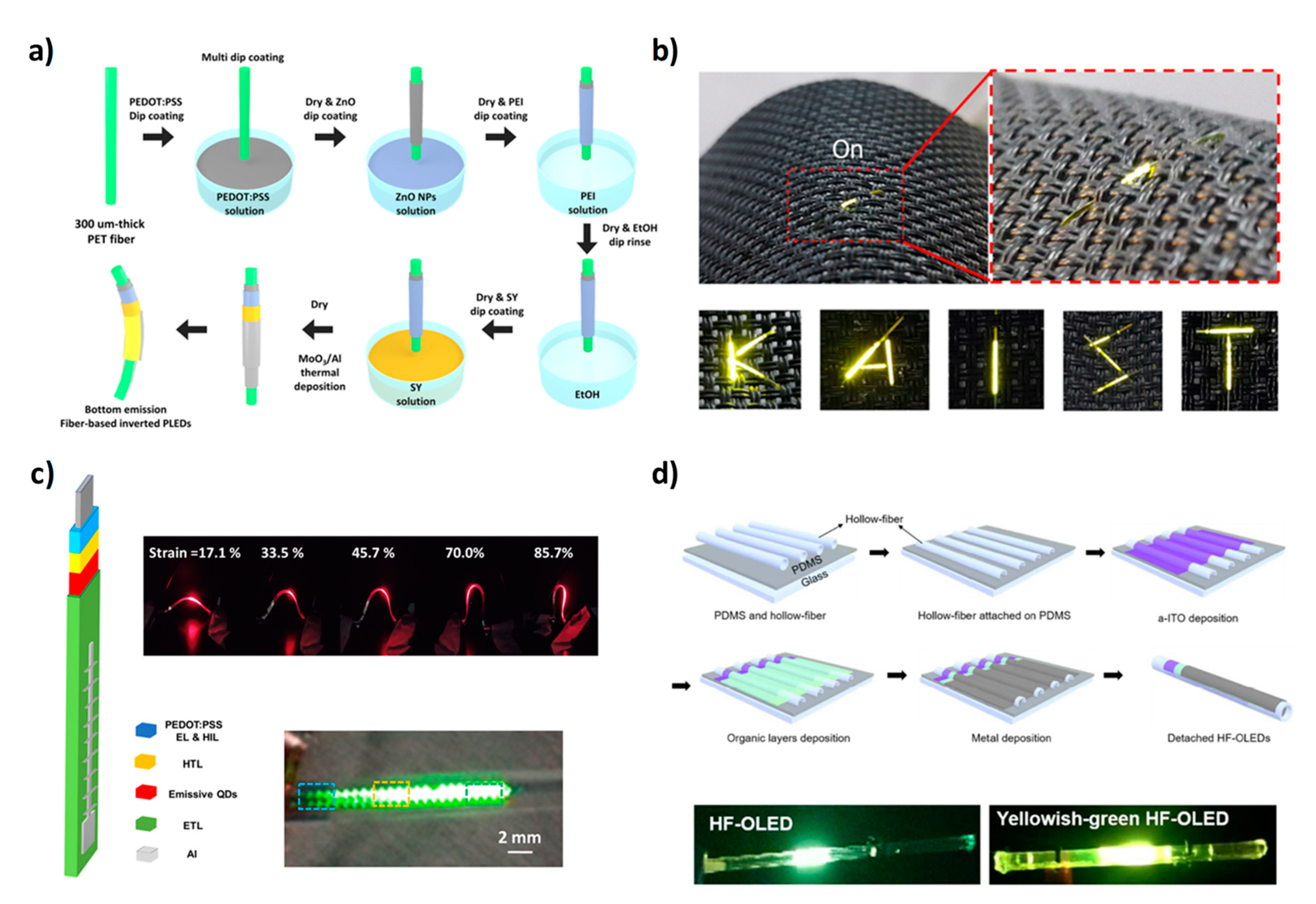
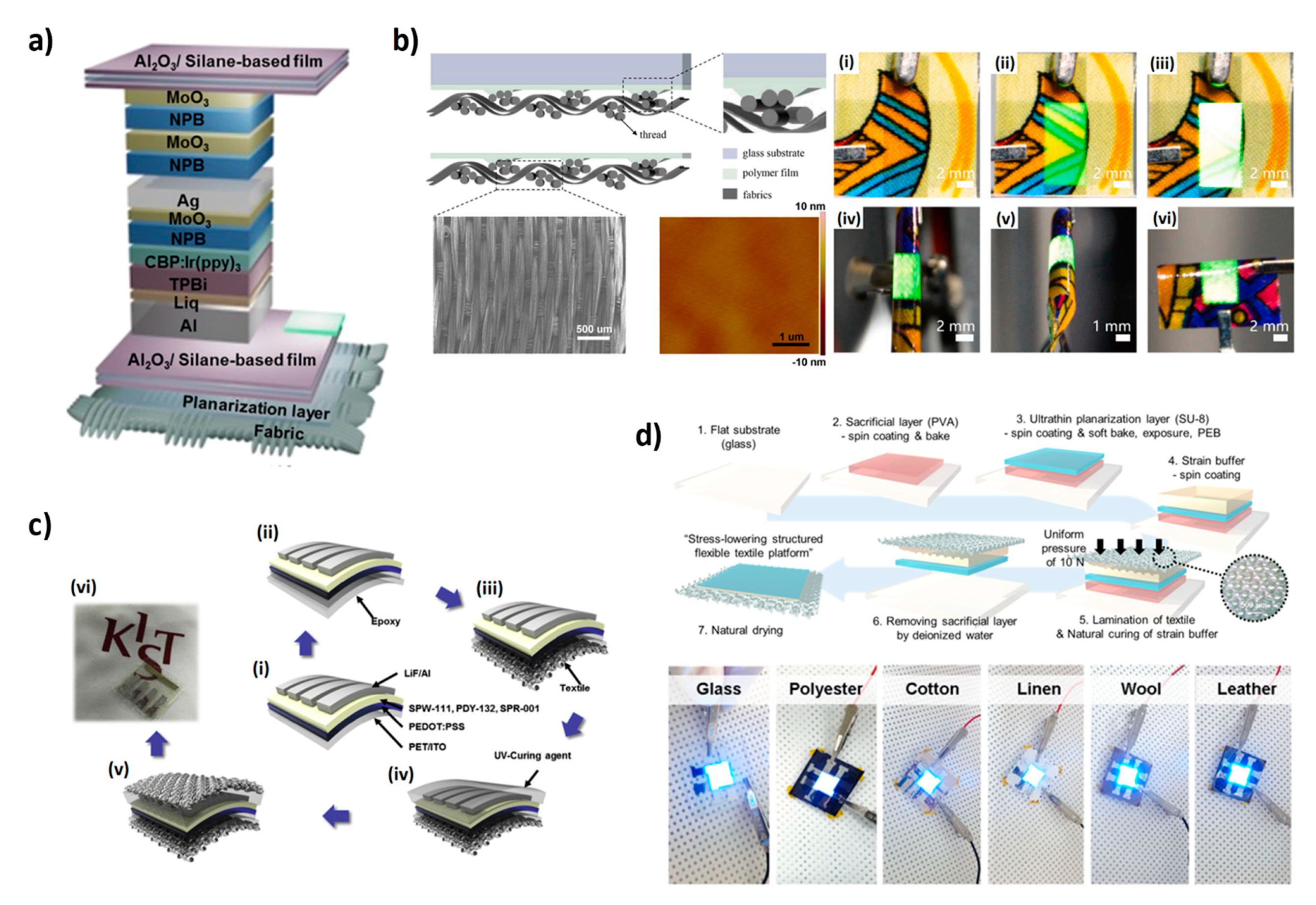
2.3. OLED Devices
2.4. LEC Devices
2.5. POFs
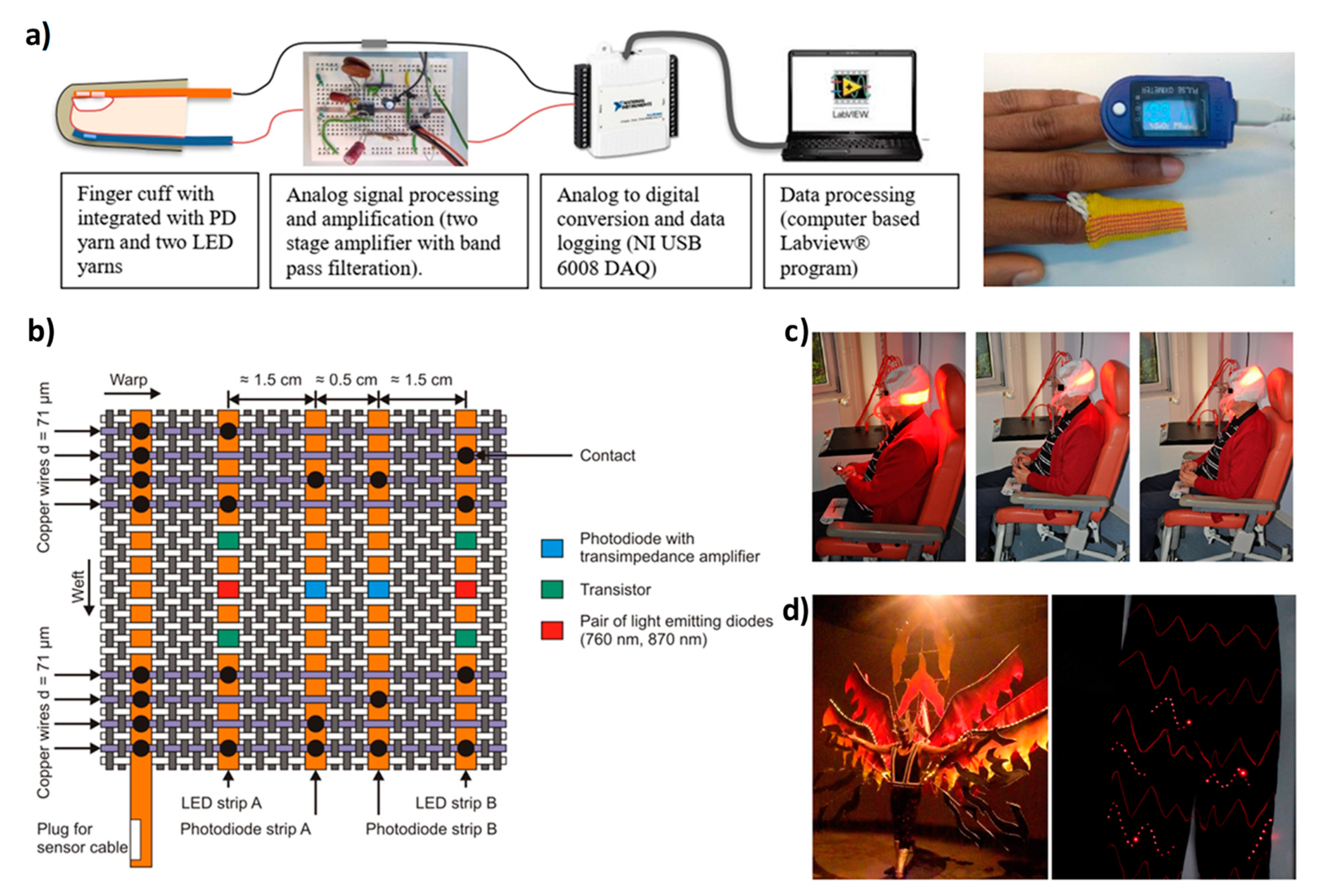
3. Health and Environmental Concerns
4. Applications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stoppa, M.; Chiolerio, A. Wearable electronics and smart textiles: A critical review. Sensors 2014, 14, 11957–11992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Pu, X.; Jiang, C.; Liu, T.; Huang, X.; Chen, L.; Du, C.; Sun, J.; Hu, W.; Wang, Z.L. Large-Area All-Textile Pressure Sensors for Monitoring Human Motion and Physiological Signals. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalay, A.; Sanchez, V.; Atalay, O.; Vogt, D.M.; Haufe, F.; Wood, R.J.; Walsh, C.J. Batch Fabrication of Customizable Silicone-Textile Composite Capacitive Strain Sensors for Human Motion Tracking. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2017, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coppedè, N.; Tarabella, G.; Villani, M.; Calestani, D.; Iannotta, S.; Zappettini, A. Human stress monitoring through an organic cotton-fiber biosensor. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 5620–5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhai, Q.; Dong, D.; An, T.; Gong, S.; Shi, Q.; Cheng, W. Highly Stretchable and Strain-Insensitive Fiber-Based Wearable Electrochemical Biosensor to Monitor Glucose in the Sweat. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 10–6569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Lee, P.S. Progress on wearable triboelectric nanogenerators in shapes of fiber, yarn, and textile. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2019, 20, 837–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, W.; Bai, S.; Yuan, M.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Jing, T. Lead zirconate titanate nanowire textile nanogenerator for wearable energy-harvesting and self-powered devices. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 6231–6235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Yang, Z.; Chen, P.; Deng, J.; Li, H.; Peng, H. Wearable Solar Cells by Stacking Textile Electrodes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 6110–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, Y.; Park, J.; Choi, D. Stitchable organic photovoltaic cells with textile electrodes. Nano Energy 2014, 9, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Xiang, X.; Tong, X.; Zou, J.; Li, Q. Wearable Double-Twisted Fibrous Perovskite Solar Cell. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 3831–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, A.M.; Zamarayeva, A.M.; Rousseau, J.; Chu, H.; Derin, I.; Steingart, D.A. Highly Stretchable Alkaline Batteries Based on an Embedded Conductive Fabric. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 5071–5076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Liu, M.; Li, L.; Han, S.; Li, X.; Jiang, C.; Du, C.; Luo, J.; Hu, W.; Wang, Z.L. Wearable Textile-Based In-Plane Microsupercapacitors. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1601254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Niu, L.; Wang, D.; Yan, C.; She, Y.; Zheng, Z. Waterproof, Ultrahigh Areal-Capacitance, Wearable Supercapacitor Fabrics. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-S.; Choi, K.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Lee, S.-Y. Wearable Supercapacitors Printed on Garments. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Pasta, M.; La Mantia, F.; Cui, L.; Jeong, S.; Deshazer, H.D.; Choi, J.W.; Han, S.M.; Cui, Y. Stretchable, porous, and conductive energy textiles. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Destriau, G. Recherches sur les scintillations des sulfures de zinc aux rayons α. J. Chim. Phys. 1936, 33, 587–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verboven, I.; Deferme, W. Direct printing of light-emitting devices on textile substrates. Narrow Smart Text. 2017, 259–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xiao, L.; Gu, H.; Sun, H. Advances in Alternating Current Electroluminescent Devices. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2019, 7, 1801154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, W.; Pan, J.; Ye, C. Alternating Current Electroluminescent Devices with Inorganic Phosphors for Deformable Displays. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2020, 1, 100213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayathilaka, W.A.D.M.; Chinnappan, A.; Tey, J.N.; Wei, J.; Ramakrishna, S. Alternative current electroluminescence and flexible light emitting devices. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 5553–5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, T.; Monaragala, R. Development and analysis of novel electroluminescent yarns and fabrics for localized automotive interior illumination. Text. Res. J. 2012, 82, 1164–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellingham, A.A.; Fontecchio, A.A. Direct Integration of Individually Controlled Emissive Pixels into Knit Fabric for Fabric-Based Dynamic Display. IEEE Photonics J. 2017, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellingham, A.; Bromhead, N.; Fontecchio, A. Rapid prototyping of slot die devices for roll to roll production of EL fibers. Materials 2017, 10, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, A.; Fontecchio, A. Effect of fabric integration on the physical and optical performance of electroluminescent fibers for lighted textile applications. Fibers 2018, 6, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, G.; Yi, M.; Hu, H.; Ding, K.; Wang, L.; Zeng, H.; Tang, J.; Liao, L.; Nan, C.; He, Y.; et al. Coaxial-Structured Weavable and Wearable Electroluminescent Fibers. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2017, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Xiu, F.; Zhou, Z.; Ban, C.; Ye, T.; Ding, Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, W. Transient fiber-shaped flexible electronics comprising dissolvable polymer composites toward multicolor lighting. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 1472–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Xu, X.; Miao, J.; Gidron, O.; Meng, H. A stretchable alternating current electroluminescent fiber. Materials 2018, 11, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Shi, X.; Lou, H.; Cheng, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Peng, H. A one-dimensional soft and color-programmable light-emitting device. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 1328–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cui, L.; Shi, X.; Tian, X.; Wang, D.; Gu, C.; Chen, E.; Cheng, X.; Xu, Y.; Hu, Y.; et al. Textile Display for Electronic and Brain-Interfaced Communications. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres Alonso, E.; Rodrigues, D.P.; Khetani, M.; Shin, D.W.; De Sanctis, A.; Joulie, H.; de Schrijver, I.; Baldycheva, A.; Alves, H.; Neves, A.I.S.; et al. Graphene electronic fibres with touch-sensing and light-emitting functionalities for smart textiles. NPJ Flex. Electron. 2018, 2, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Song, B.; Cho, C.H.; Lim, S.K.; Jeong, S.M. Textile-fiber-embedded multiluminescent devices: A new approach to soft display systems. Mater. Today 2020, 32, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Mechael, S.S.; Lerma, C.; Carmichael, R.S.; Carmichael, T.B. Stretchable Ultrasheer Fabrics as Semitransparent Electrodes for Wearable Light-Emitting e-Textiles with Changeable Display Patterns. Matter 2020, 2, 882–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vos, M.; Torah, R.; Tudor, J. Dispenser printed electroluminescent lamps on textiles for smart fabric applications. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 045016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, B.; Li, D.; Ala, O.; Manandhar, P.; Fan, Q.; Kasilingam, D.; Calvert, P.D. Textile-based flexible electroluminescent devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Li, D.; Manandharm, P.; Fan, Q.; Kasilingam, D.; Calvert, P. CNT/conducting polymer composite conductors impart high flexibility to textile electroluminescent devices. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloma, M.; Janczak, D.; Wroblewski, G.; Mlozniak, A.; Jakubowska, M. Electroluminescent structures printed on paper and textile elastic substrates. Circuit World 2014, 40, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janczak, D.; Zych, M.; Raczyński, T.; Dybowska-Sarapuk, Ł.; Pepłowski, A.; Krzemiński, J.; Sosna-Glłȩbska, A.; Znajdek, K.; Sibiński, M.; Jakubowska, M. Stretchable and washable electroluminescent display screen-printed on textile. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Shi, X.; Lou, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Cheng, X.; Peng, H. A stretchable and sensitive light-emitting fabric. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 4139–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Mechael, S.S.; Chen, Y.; Carmichael, T.B. Solution Deposition of Conformal Gold Coatings on Knitted Fabric for E-Textiles and Electroluminescent Clothing. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Zhu, H.; Feng, S.; Cao, S.; Kong, D. Stretchable High-Permittivity Nanocomposites for Epidermal Alternating-Current Electroluminescent Displays. ACS Mater. Lett. 2019, 1, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holonyak, N.; Bevacqua, S.F. Coherent (visible) light emission from Ga(As1-xPx) junctions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1962, 1, 82–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnieri, M. An Historical Survey on Light Technologies. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 25881–25897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, N.G.; Wu, C.H.; Cheng, T.C. Light-emitting diodes-Their potential in biomedical applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 2161–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buechley, L. A construction kit for electronic textiles. In Proceedings of the 10th IEEE International Symposium on Wearable Computers, Montreux, Switzerland, 11–14 October 2006; pp. 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linz, T.; Vieroth, R.; Dils, C.; Koch, M.; Braun, T.; Becker, K.F.; Kallmayer, C.; Hong, S.M. Embroidered interconnections and encapsulation for electronics in textiles for wearable electronics applications. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2008, 60, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locher, I.; Tröster, G. Fundamental building blocks for circuits on textiles. IEEE Trans. Adv. Packag. 2007, 30, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Krshiwoblozki, M.; Linz, T.; Neudeck, A.; Kallmayer, C. Electronics in Textiles—Adhesive Bonding Technology for Reliably Embedding Electronic Modules into Textile Circuits. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2012, 85, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradiso, R.; Loriga, G.; Taccini, N. A wearable health care system based on knitted integrated sensors. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2005, 9, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buechley, L.; Eisenberg, M. Fabric PCBs, electronic sequins, and socket buttons: Techniques for e-textile craft. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2009, 13, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, H.; Yoo, H.J. Electrical characterization of screen-printed circuits on the fabric. IEEE Trans. Adv. Packag. 2010, 33, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherenack, K.; Zysset, C.; Kinkeldei, T.; Münzenrieder, N.; Tröster, G. Woven electronic fibers with sensing and display functions for smart textiles. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 5178–5182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komolafe, A.; Torah, R.; Wei, Y.; Nunes-Matos, H.; Li, M.; Hardy, D.; Dias, T.; Tudor, M.; Beeby, S. Integrating Flexible Filament Circuits for E-Textile Applications. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1900176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linz, T.; Kallmayer, C.; Aschenbrenner, R.; Reichl, H. New Interconnection Technologies for the Integration of Electronics on Textile Substrates. In Proceedings of the Ambience 05, International Scientific Conference, Intelligent Ambience and Well-Being, Tampere, Finland, 19–20 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Linz, T.; von Krshiwoblozki, M.; Walter, H.; Foerster, P. Contacting electronics to fabric circuits with nonconductive adhesive bonding. J. Text. Inst. 2012, 103, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkova, I.; Parkovs, I.; Vilumsone, A. Light-emitting textile display with floats for electronics covering. Int. J. Cloth. Sci. Technol. 2015, 27, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkova, I.; Viļumsone, A. Functional and aesthetic design of woven electro-textile fabrics. J. Text. Appar. Technol. Manag. 2013, 8, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.E.; Lee, D.; Lee, T.I.; Shin, J.H.; Choi, G.M.; Kim, C.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Kang, S.M.; et al. Wireless powered wearable micro light-emitting diodes. Nano Energy 2019, 55, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nashed, M.N.; Hardy, D.A.; Hughes-Riley, T.; Dias, T. A novel method for embedding semiconductor dies within textile yarn to create electronic textiles. Fibers 2019, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rein, M.; Favrod, V.D.; Hou, C.; Khudiyev, T.; Stolyarov, A.; Cox, J.; Chung, C.C.; Chhav, C.; Ellis, M.; Joannopoulos, J.; et al. Diode fibres for fabric-based optical communications. Nature 2018, 560, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, D.A.; Anastasopoulos, I.; Nashed, M.N.; Oliveira, C.; Hughes-Riley, T.; Komolafe, A.; Tudor, J.; Torah, R.; Beeby, S.; Dias, T. Automated insertion of package dies onto wire and into a textile yarn sheath. Microsyst. Technol. 2019, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Satharasinghe, A.; Hughes-Riley, T.; Dias, T. Photodiodes embedded within electronic textiles. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, C.W.; Vanslyke, S.A. Organic electroluminescent diodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1987, 51, 913–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burroughes, J.H.; Bradley, D.D.C.; Brown, A.R.; Marks, R.N.; Mackay, K.; Friend, R.H.; Burns, P.L.; Holmes, A.B. Light-emitting diodes based on conjugated polymers. Nature 1990, 347, 539–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minaev, B.; Baryshnikov, G.; Agren, H. Principles of phosphorescent organic light emitting devices. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 1719–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volz, D. Review of organic light-emitting diodes with thermally activated delayed fluorescence emitters for energy-efficient sustainable light sources and displays. J. Photonics Energy 2016, 6, 020901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldo, M.A.; O’Brien, D.F.; You, Y.; Shoustikov, A.; Sibley, S.; Thompson, M.E.; Forrest, S.R. Highly efficient phosphorescent emission from organic electroluminescent devices. Nature 1998, 395, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.-H.; Jeong, S.-H.; Lee, Y.; Seo, H.-K.; Kwon, S.-J.; Park, M.-H.; Lee, T.-W. Flexible transparent electrodes for organic light-emitting diodes. J. Inf. Disp. 2015, 16, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, B.; An, K.H.; Zhao, Y.; Pipe, K.P.; Shtein, M. Fiber shaped organic light emitting device. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 3897–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, S.; Kim, W.; Kim, H.; Choi, S.; Park, B. High Luminance Fiber-Based Polymer Light-Emitting Devices by a Dip-Coating Method. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2015, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.; Kim, H.; Choi, S.; Jeong, E.G.; Kim, D.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.S.; Seo, Y.C.; Choi, K.C. Weavable and Highly Efficient Organic Light-Emitting Fibers for Wearable Electronics: A Scalable, Low-Temperature Process. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, K.; Lee, H.; Kim, H.M.; Lee, G.J.; Shin, S.; Kumar, N.; Song, Y.M.; Kang, J. High-performance, color-tunable fiber shaped organic light-emitting diodes. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 16184–16192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, K.; Lee, H.; Kang, J. Flexible, Wearable Organic Light-Emitting Fibers Based on PEDOT: PSS/Ag-Fiber Embedded Hybrid Electrodes for Large-Area Textile Lighting. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 2000168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Chun, Y.T. Fibertronic Quantum-Dot Light-Emitting Diode for E-Textile. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 11060–11069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.J.; Kim, J.W.; Cho, H.E.; Son, Y.H.; Lee, M.H.; Lee, J.; Choi, K.C.; Lee, S.M. Fibertronic Organic Light-Emitting Diodes toward Fully Addressable, Environmentally Robust, Wearable Displays. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.H.; Kwon, S.; Shin, J.B.; Kim, H.; Son, Y.H.; Lee, H.S.; Noh, B.; Nam, M.; Choi, K.C. Bright-Multicolor, Highly Efficient, and Addressable Phosphorescent Organic Light-Emitting Fibers: Toward Wearable Textile Information Displays. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2009336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janietz, S.; Gruber, B.; Schattauer, S.; Schulze, K. Integration of OLEDs in Textiles. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2012, 80, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Kwon, S.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, J.Y.; Han, Y.; Kim, E.; Choi, K.C.; Park, S.; Park, B.C. Soft fabric-based flexible organic light-emitting diodes. Org. Electron. 2013, 14, 3007–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Kwon, S.; Han, Y.C.; Kim, E.; Kim, H.C.; Choi, K.C.; Kang, S.H.; Park, B.-C. 28.1: OLEDs on Textile Substrates with Planarization and Encapsulation using Multilayers for Wearable Displays. In SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers; SID: Campbell, CA, USA, 2014; Volume 45, pp. 364–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Kwon, S.; Han, Y.C.; Kim, E.; Choi, K.C.; Kang, S.H.; Park, B.C. Reliable Actual Fabric-Based Organic Light-Emitting Diodes: Toward a Wearable Display. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2016, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kwon, S.; Choi, S.; Choi, K.C. Solution-processed bottom-emitting polymer light- emitting diodes on a textile substrate towards a wearable display. J. Inf. Disp. 2015, 16, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, S.; Kwon, S.; Kim, H.; Kim, W.; Kwon, J.H.; Sub, M.; Lee, H.S.; Choi, K.C. Highly Flexible and Efficient Fabric- Based Organic Light-Emitting Devices for Clothing-Shaped Wearable Displays. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Jo, W.; Jeon, Y.; Kwon, S.; Kwon, J.H.; Son, Y.H.; Kim, J.; Park, J.H.; Kim, H.; Lee, H.S.; et al. Multi-directionally wrinkle-able textile OLEDs for clothing-type displays. NPJ Flex. Electron. 2020, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Chen, Z.Y.; Jiang, N.R.; Liu, Y.F.; Bi, Y.G.; Zhang, X.L.; Han, W.; Feng, J.; Sun, H.B. Highly transparent and flexible fabric-based organic light emitting devices for unnoticeable wearable displays. Org. Electron. 2020, 76, 105494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Lee, K.S.; Shim, J.; Liu, Y.; Lee, C.; Cho, H.; Kim, M.J.; Park, S.-J.; Yun, Y.J.; Kim, H.Y.; et al. Environment friendly, transparent nano fi ber textiles consolidated with high ef fi ciency PLEDs for wearable electronics. Org. Electron. 2016, 36, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; An, M.; Bi, Y.; Yin, D.; Feng, J.; Sun, H. Flexible Efficient Top-Emitting Organic Light-Emitting Devices on a Silk Substrate. IEEE Photonics J. 2017, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, N.; Liu, Y.; Bi, Y.; Zhang, X. Highly Flexible Fabric-Based Organic Light-Emitting Devices for Conformal Wearable Displays. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 1900942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, E.G.; Jeon, Y.; Cho, S.H.; Choi, K.C. Textile-based washable polymer solar cells for optoelectronic modules: Toward self-powered smart clothing. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 1878–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Song, C.K. AMOLED panel driven by OTFTs on polyethylene fabric substrate. Org. Electron. 2016, 30, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Song, C.K. Textile display with AMOLED using a stacked-pixel structure on a polyethylene terephthalate fabric substrate. Materials 2019, 12, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verboven, I.; Stryckers, J.; Mecnika, V.; Vandevenne, G.; Jose, M.; Deferme, W. Printing smart designs of light emitting devices with maintained textile properties. Materials 2018, 11, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pei, Q.; Yu, G.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.; Heeger, A.J. Polymer Light-Emitting Electrochemical Cells. Science 1995, 269, 1086–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, S.B.; Tordera, D.; Pertegás, A.; Roldán-Carmona, C.; Ortí, E.; Bolink, H.J. Light-emitting electrochemical cells: Recent progress and future prospects. Mater. Today 2014, 17, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lightner, C.R.; Dong, L. Light-Emitting Coaxial Nanofibers. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, K.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Guan, G.; Li, H.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, B.; et al. A colour-tunable, weavable fibre-shaped polymer light-emitting electrochemical cell. Nat. Photonics 2015, 9, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, K.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Luo, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, G.; et al. Flexible electroluminescent fiber fabricated from coaxially wound carbon nanotube sheets. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 5621–5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanz, T.; Sandström, A.; Tang, S.; Chabrecek, P.; Sonderegger, U.; Edman, L. A light-emission textile device: Conformal spray-sintering of a woven fabric electrode. Flex. Print. Electron. 2016, 1, 025004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, S.; Li, Y.; Pearce, J.; Charlton, M.D.B.; Tudor, J.; Harrowven, D.; Beeby, S. Visible and Ultraviolet Light Emitting Electrochemical Cells Realised on Woven Textiles. Proceedings 2021, 68, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basarir, F.; Irani, F.S.; Kosemen, A.; Camic, B.T.; Oytun, F.; Tunaboylu, B.; Shin, H.J.; Nam, K.Y.; Choi, H. Recent progresses on solution-processed silver nanowire based transparent conducting electrodes for organic solar cells. Mater. Today Chem. 2017, 3, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, J.; Kim, H.; Youn, S.-M.; Jeong, C.; Han, E.-M.; Yun, C.; Kang, M.H. Silver-nanowire-based lamination electrode for a fully vacuum-free and solution-processed organic photovoltaic cell. Org. Electron. 2021, 89, 106046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, K.; Sekine, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Takeda, Y.; Shimizu, M.; Yamashita, N.; Kumaki, D.; Itoh, M.; Nagaoka, M.; Toda, T.; et al. Organic integrated circuits using room-temperature sintered silver nanoparticles as printed electrodes. Org. Electron. 2012, 13, 3296–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballato, J.; Dragic, P. Glass: The Carrier of Light—A Brief History of Optical Fiber. Int. J. Appl. Glas. Sci. 2016, 7, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Xiang, Z.; OuYang, X.; Zhang, J.; Lau, N.; Zhou, J.; Chan, C.C. Wearable fiber optic technology based on smart textile: A review. Materials 2019, 12, 3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhowmik, K.; Peng, G. Handbook of Optical Fibers; Springer: Singapore, 2019; ISBN 978-981-10-1477-2. [Google Scholar]
- Selm, B.; Gärel, E.A.; Rothmaier, M.; Rossi, R.M.; Scherer, L.J. Polymeric optical fiber fabrics for illumination and sensorial applications in textiles. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2010, 21, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlin, A.; Mäkinen, M.; Vuorivirta, A. Development of polymeric optical fibre fabrics as illumination elements and textile displays. Autex Res. J. 2003, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Im, M.H.; Park, E.J.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, M.S. Modification of plastic optical fiber for side-illumination. In Human-Computer Interaction. Interaction Platforms and Techniques; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 4551, pp. 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Tao, X.; Ying, D.; Hui, C.; Wang, G. Light-emitting fabrics integrated with structured polymer optical fibers treated with an infrared CO2 laser. Text. Res. J. 2013, 83, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Ziqian, B. Techy Fashion: Photonic fashion design process. In Proceedings of the International Fashion Conference, Ghent, Belgium, 20–21 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Koncar, V. Optical Fiber Fabric Displays. Opt. Photonics News 2005, 16, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, B.; Yang, B. Effect of weave structure on the side-emitting properties of polymer optical fiber jacquard fabrics. Text. Res. J. 2013, 83, 1170–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.-R.; Schoenung, J.M. Human health and ecological toxicity potentials due to heavy metal content in waste electronic devices with flat panel displays. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.R.; Kang, D.; Ogunseitan, O.A.; Schoenung, J.M. Potential environmental impacts of light-emitting diodes (LEDs): Metallic resources, toxicity, and hazardous waste classification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, J.M.; Jung, H.J.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, D.S.; Lim, S.R. Environmental Effects of the Technology Transition from Liquid-Crystal Display (LCD) to Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED) Display from an E-Waste Management Perspective. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2018, 12, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J. Photonic Patterns: Fashion Cutting with Illuminating Polymeric Optical Fibre (POF) Textiles. In Proceedings of the SecondInternational Conference for Creative Pattern Cutting, Huddersfield, UK, 24–25 February 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.E.; Kim, Y.H.; Oh, J.H.; Kim, K.D. Interactive smart fashion using user-oriented visible light communication: The case of modular strapped cuffs and zipper slider types. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2017, 2017, 5203053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hardy, D.A.; Moneta, A.; Sakalyte, V.; Connolly, L.; Shahidi, A.; Hughes-Riley, T. Engineering a costume for performance using illuminated LED-yarns. Fibers 2018, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Vos, M.; Torah, R.; Glanc-Gostkiewicz, M.; Tudor, J. A Complex Multilayer Screen-Printed Electroluminescent Watch Display on Fabric. J. Disp. Technol. 2016, 12, 1757–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivanov, A.; Wurzer, M. Integration of screen-printed electroluminescent matrix displays in smart textile items—Implementation and evaluation. In Proceedings of the EMPC 2017—21st European Microelectronics Packaging Conference & Exhibition, Warsaw, Poland, 10–13 September 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edirisinghe, R.; Blismas, N. A prototype of smart clothing for construction work health and safety. In Proceedings of the CIB W099 International Health and Safety Conference: Benefitting Workers and Society through Inherently Safe Construction, Jordanstown, Northern Ireland, 10–11 September 2015; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zysset, C.; Nasseri, N.; Büthe, L.; Münzenrieder, N.; Kinkeldei, T.; Petti, L.; Kleiser, S.; Salvatore, G.A.; Wolf, M.; Tröster, G. Textile integrated sensors and actuators for near-infrared spectroscopy. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Satharasinghe, A.; Hughes-Riley, T.; Dias, T. Photodiode and LED embedded textiles for wearable healthcare applications. In Proceedings of the 19th World Textile Conference: Textiles at the Crossroads, Ghent, Belgium, 11–15 June 2019; pp. 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Melle, S.M.; Liu, K.; Measures, R.M. Practical fiber-optic Bragg grating strain gauge system. Appl. Opt. 1993, 32, 3601–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Webb, D.J.; Peng, G.-D. Enhancing the sensitivity of poly(methyl methacrylate) based optical fiber Bragg grating temperature sensors. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 4046–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishnan, M.; Rajan, G.; Semenova, Y.; Farrell, G. Overview of Fiber Optic Sensor Technologies for Strain/Temperature Sensing Applications in Composite Materials. Sensors 2016, 16, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Chen, J.; Xu, F. Sensitive and Wearable Optical Microfiber Sensor for Human Health Monitoring. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1800296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Sun, S.; Lv, R.; Zhao, Y. Design and experiment of an optical fiber micro bend sensor for respiration monitoring. Sensors Actuators A Phys. 2016, 251, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciocchetti, M.; Massaroni, C.; Saccomandi, P.; Caponero, M.A.; Polimadei, A.; Formica, D.; Schena, E. Smart Textile Based on Fiber Bragg Grating Sensors for Respiratory Monitoring: Design and Preliminary Trials. Biosensors 2015, 5, 602–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koyama, Y.; Nishiyama, M.; Watanabe, K. Smart Textile Using Hetero-Core Optical Fiber for Heartbeat and Respiration Monitoring. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 6175–6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, B.; Mohseni, H.; Grewal, G.S.; Talal, T.K.; Menzies, R.A.; Armstrong, D.G. An Optical-Fiber-Based Smart Textile (Smart Socks) to Manage Biomechanical Risk Factors Associated with Diabetic Foot Amputation. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2017, 11, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rothmaier, M.; Selm, B.; Spichtig, S.; Haensse, D.; Wolf, M. Photonic textiles for pulse oximetry. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 12973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quandt, B.M.; Scherer, L.J.; Boesel, L.F.; Wolf, M.; Bona, G.L.; Rossi, R.M. Body-Monitoring and Health Supervision by Means of Optical Fiber-Based Sensing Systems in Medical Textiles. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 330–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, S.H.; Kwok, S.J.J. Light in diagnosis, therapy and surgery. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraresi, C.; Parizotto, N.A.; Pires de Sousa, M.V.; Kaippert, B.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Koiso, T.; Bagnato, V.S.; Hamblin, M.R. Light-emitting diode therapy in exercise-trained mice increases muscle performance, cytochrome c oxidase activity, ATP and cell proliferation. J. Biophotonics 2015, 8, 740–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, J.; Chui, C.; Tao, X. Luminous fabric devices for wearable low-level light therapy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2013, 4, 2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cochrane, C.; Mordon, S.R.; Lesage, J.C.; Koncar, V. New design of textile light diffusers for photodynamic therapy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 1170–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordon, S.; Cochrane, C.; Tylcz, J.B.; Betrouni, N.; Mortier, L.; Koncar, V. Light emitting fabric technologies for photodynamic therapy. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2015, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mordon, S.; Thécua, E.; Ziane, L.; Lecomte, F.; Deleporte, P.; Baert, G.; Vignion-Dewalle, A. Light emitting fabrics for photodynamic therapy: Technology, experimental and clinical applications. Transl. Biophotonics 2020, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonski, M.; Bossuyt, F.; Vanfleteren, J.; Vervust, T.; De Smet, H. Conformable, Low Level Light Therapy platform. In Biophotonics: Photonic Solutions for Better Health Care IV; SPIE: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; Volume 9129, p. 912921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Year | Deposition Techniques | Device Structure | Performances | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | Automatic dispensing and curing process | Silver-coated yarn/DuPont dielectric paste/DuPont phosphor ink/silver-coated yarn | 1.3 cd/m2 at 370 V and 2 kHz | [21] |
| 2017 | Slot-die coating | Silver-coated yarn/DuPont dielectric paste/DuPont phosphor ink/silver-coated yarn | 50 cd/m2 | [22] |
| 2017 | Slot-die coating | Silver-coated yarn/DuPont dielectric paste/DuPont phosphor ink/DuPont conductive paste | n.a. | [23] |
| 2017 | Dip coating | PET fiber/AgNWs/silicone/phosphor/AgNWs/silicone | 202 cd/m2 at 195 V and 2 kHz | [25] |
| 2018 | Slot-die coating | Silver-coated yarn/DuPont dielectric paste/DuPont phosphor ink/DuPont conductive paste | 50 cd/m2 at 100 V and 20 kHz | [24] |
| 2018 | Dip coating | PDMS fiber/AgNWs/phosphor:PDMS/AgNWs | 100 cd/m2 at 400 V and 1 kHz | [27] |
| 2018 | 3D printing and automatic wrapping | Elastic polymer fiber/Aligned CNT sheet/Silicone elastomer/Light-emitting layer/Aligned CNT sheet | 15 cd/m2 at 6.4 V/μm and 1.5 kHz | [28] |
| 2018 | Extrusion | Two inner hydrogel electrodes + ZnS:silicone elastomer | 250 cd/m2 at 8 V/μm and 1.5 Hz | [29] |
| 2018 | Spin coating | Graphene/ZnS:Cu/BaTiO3/Ag | n.a. | [30] |
| 2019 | Dip coating | PVA fiber/AgNWs/ZnS:Cu+PVP/AgNWs | 100 cd/m2 at 300 V and 0.4 kHz | [26] |
| Year | Deposition Techniques | Device Structure | Performances | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | Inkjet printing | PEDOT:PSS/Phosphor:epoxy resin/aluminium | 44 cd/m2 at 400 V and 0.4 kHz | [34] |
| 2012 | Inkjet printing + nozzle extrusion | CNT and/or PEDOT:PSS/dielectric layer/phosphor layer/aluminium | 70 cd/m2 at 200 V and 3.5 kHz | [35] |
| 2014 | Screen printing | Silver/dielectric layer/luminophore/CNT-GNP electrode | n.a. | [36] |
| 2016 | Dispenser printing | FabInks bottom electrode/FabInks dielectric/FabInks phoshor/ FabInks transparent tonductor | 300 cd/m2 at 370 V and 1 kHz | [33] |
| 2017 | Chemical deposition + casting | Polypirrole/ ZnS:Silicone elastomer/hydrogel film | 350 cd/m2 at 5 V/μm and 2 kHz | [38] |
| 2018 | Solution-based metallization + spin coating | Gold-coated textile/BaTiO3+PDMS/ZnS:Cu+PDMS/PEDOT:PSS | n.a. | [39] |
| 2019 | Embedding of fibers into phosphor:PDMS composite | Ag-coated fibers/ZnS phosphor+PDMS | 35 cd/m2 at 1.8 V/μm and 2 kHz | [31] |
| 2019 | Screen printing | Graphene-based electrode/BaTiO3/ZnS:Cu/BaTiO3/CNT or ATO transparent electrode | 300 cd/m2 at 160 V and 2 kHz | [37] |
| 2020 | Solution-based metallization + spin coating + lamination | Gold-coated textile/ZnS:Cu+Ecoflex/gold-coated textile | n.a. | [32] |
| Year | Deposition Techniques | Device Structure | Performances | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007 | Thermal evaporation | Al/Ni/CuPc/NPD/Alq3/LiF/Al | ηEQE 0.07 ÷ 0.15% at 0 ÷ 10 V | [68] |
| 2015 | Dip coating + thermal evaporation | PEDOT:PSS/Super Yellow/LiF/Al | 1458.8 cd/m2at 10 V 3 cd/A at 6 V | [69] |
| 2018 | Dip coating + thermal evaporation | PEDOT:PSS/ZnO NPs/PEI/Super Yellow/MoO3/Al | 11,780 cd/m2 at 10 V 11.1 cd/A at 5 V | [70] |
| 2018 | Thermal evaporation | ITO/2-TNATA/NPB/Alq3/LiF/Al | 6300 cd/m2at 13 V 11 cd/A at 12 V | [71] |
| 2020 | Spin coating + thermal evaporation | Hybrid fiber TCEs/PEDOT:PSS/PVK:TPD:PBD:Ir(mppy)3/TPBi/LiF/Al | 4200 cd/m2 at 12 V, 39.6 cd/A and 11.3% of EQE at 7 V | [72] |
| 2020 | Dip coating + thermal evaporation | PEDOT:PSS PH1000/PEDOT:PSS AI4083/TFB/QDs/AlZnO/Al | 340 cd/m2 at 13 V for CdS/ZnS (blue QLED) 2044 cd/m2 (red QLED) and 2240 cd/m2 (green QLED) at 10 V for CdSe/ZnS | [73] |
| 2020 | Thermal evaporation | ITO/HAT-CN/TAPC/TCTA:Ir(ppy)2acac/B3PYMPM/Liq/Al | 2900 cd/m2 at 5 V, 46 cd/A at 2.4 V | [74] |
| 2021 | Dip coating + thermal evaporation | PEDOT:PSS/ZnO NPs/PEI/PVK:26DCzppy:Ir(ppy)3 (30:30:1 weight ratio)/TCTA/MoO3/Al—green | 11,482 cd/m2 at 6.5 V 60.7 cd/A at 4.5 V for the green OLED | [75] |
| PEDOT:PSS/ZnO NPs/PEI/PVK:TPBi:Hex-Ir(phq)2acac (25:25:1 weight ratio)/TCTA/MoO3/Al—red | 4462 cd/m2 at 7 V 16.3 cd/A at 4.5 V for the red OLED | |||
| PEDOT:PSS/ZnO NPs/PEI/PVK:26DCzppy:Ir(Fppy)3 (30:30:1 weight ratio)/TCTA/MoO3/Al—blue | 1199 cd/m2at 6 V 16.9 cd/A at 4 V for the blue OLED |
| Year | Deposition Techniques | Device Structure | Performances | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | Thermal evaporation | Ag/WO3/NPB/Alq3/Liq/Al/Ag/NPB | 7000 cd/m2 and 8 cd/A at 6 V | [77] |
| 2014 | Thermal evaporation | Al/Liq/Alq3/NPB/WO3/Ag | 2000 cd/m2at 7.5 V 3 cd/A at 6.5 V | [78] |
| 2015 | Spin coating + thermal evaporation | PEDOT:PSS/Super Yellow(PDY-132)/LiF/Al | 5000 cd/m2 at 6 V. 9.72 cd/A at 5.5 V7.17 lm/W at 4 V. | [80] |
| 2015 | thermal evaporation | Ag/HAT-CN/NPB/TAPC/CBP: Ir(ppy)3/TPBi/LiF/Al | 64,459 cd/m2 at 12 V | [88] |
| 2016 | Spin coating + thermal evaporation | ITO/PEDOT:PSS/emission polymer(SPW-111, PDY-132, and SPR-001)/LiF/Al | 2781cd/m2 at 13 V 0.29 cd/A at 13 V for the white OLED; 2430cd/m2 at 10 V 0.10 cd/A at 10 V for the red OLED; 6305 cd/m2at 11 V 0.38 cd/A at 11 V for the yellow OLED | [84] |
| 2016 | Thermal evaporation | Al/Liq/Alq3/NPB/WO3/Ag | 1500 cd/m2 and 5 cd/A at 8.5 V | [79] |
| 2017 | Thermal evaporation | Ag/MoO3/NPB/mCP: Ir(ppy)3(6% wt)/TPBi/Ca/Ag | 45,545 cd/m2 at 10.5 V 37.7 cd/A at 7.5 V | [85] |
| 2017 | Thermal evaporation | Al/Liq/TPBi/CBP: Ir(ppy)3(8% wt)/NPB/MoO3/Ag | 93,000 cd/m2at 14 V 49 cd/A at 12 V | [81] |
| 2018 | Spin coating + thermal evaporation | Ag/PEDOT:PSS/Super Yellow/Ca/Ag | n.a. | [90] |
| 2019 | Thermal evaporation | Al/Liq/Bebq2:Ir(piq)3/NPB/MoO3/Ag | 1660 cd/m2 and 19 cd/Aat 8.71 mA/cm2 | [87] |
| 2019 | Thermal evaporation | Ag/HAT-CN/NPB/TAPC/CBP: Ir(ppy)3/TPBi/LiF/Al/Ag | 23,673 cd/m2at 7 V (bare OLED)16,636 cd/m2 at 7 V (encapsulated OLED) | [89] |
| 2020 | Thermal evaporation | Ag/MoO3/NPB/CBP: Ir(bt)2(acac)/TPBi/Ca/Ag | 15,000 cd/m2at 8 V 78 cd/A at 6 V. | [86] |
| 2020 | Thermal evaporation | Au/MoO3/NPB/mCP: Ir(ppy)3(6% wt)/TPBi/Ca/Ag | 17,900 cd/m2 at 10 V 12.4 cd/A at 4 V (anode side); 15,300 cd/m2 at 10 12.8 cd/A at 4V (cathode side); total current efficiency of the transparent OLED 25.2 cd/A at 4 V | [83] |
| 2020 | Thermal evaporation + spin coating | NPB/Ag/MoO3/NPB/Alq3/Liq/Al ZnS/Ag/ZnO/PEI/ Super Yellow(PDY-132)/MoO3/Ag/NPB | About 7000 cd/m2 at 5.5 V (OLED); 10,000 cd/m2 at 5.5 V (PLED) | [82] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cinquino, M.; Prontera, C.T.; Pugliese, M.; Giannuzzi, R.; Taurino, D.; Gigli, G.; Maiorano, V. Light-Emitting Textiles: Device Architectures, Working Principles, and Applications. Micromachines 2021, 12, 652. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12060652
Cinquino M, Prontera CT, Pugliese M, Giannuzzi R, Taurino D, Gigli G, Maiorano V. Light-Emitting Textiles: Device Architectures, Working Principles, and Applications. Micromachines. 2021; 12(6):652. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12060652
Chicago/Turabian StyleCinquino, Marco, Carmela Tania Prontera, Marco Pugliese, Roberto Giannuzzi, Daniela Taurino, Giuseppe Gigli, and Vincenzo Maiorano. 2021. "Light-Emitting Textiles: Device Architectures, Working Principles, and Applications" Micromachines 12, no. 6: 652. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12060652
APA StyleCinquino, M., Prontera, C. T., Pugliese, M., Giannuzzi, R., Taurino, D., Gigli, G., & Maiorano, V. (2021). Light-Emitting Textiles: Device Architectures, Working Principles, and Applications. Micromachines, 12(6), 652. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12060652









