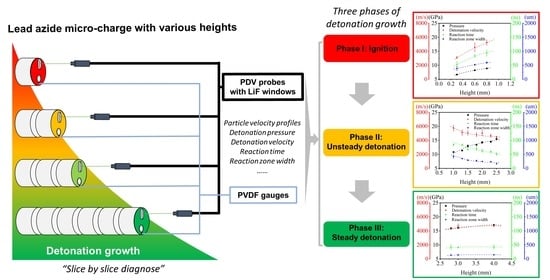
Observations on Detonation Growth of Lead Azide at Microscale
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Electric Probe Test
2.2. PVDF Gauges Test
2.3. Particle-Velocity Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Steady Detonation Velocity of LA Microcharge
3.2. Output Pressure of LA Microcharge
3.3. Particle Velocity Profile of LA Microcharge
3.4. Detonation Propagation of LA Micro Charge
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, W.; Salvati, L.; Akhtar, M.; Dlott, D.D. Shock initiation and hot spots in plastic- bonded 1,3,5-triamino-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene (TATB). Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 116, 124102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Z.; Sun, C.; Liu, Q.; Guo, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Meng, K.; Li, J.; Du, L.; et al. Design of terahertz-wave Doppler interferometric velocimetry for detonation physics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 116, 161102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Handley, C.A.; Lambourn, B.D.; Whitworth, N.J.; James, H.R.; Belfield, W.J. Understanding the shock and detonation response of high explosives at the continuum and meso scales. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2018, 5, 11303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Guo, X.; Long, Y.; Huang, G.; Ren, X.; Xu, C.; An, C. Inkjet Printing of GAP/NC/DNTF Based Microscale Booster with High Strength for PyroMEMS. Micromachines 2020, 11, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, H.; Nan, Y.; Weiming, W.; Liang, Z. Simulation Study on Influencing Factors of Flyer Driven by Micro-sized PbN6. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on IIH-MSP in Conjunction with the 12th International Conference on FITAT, Jilin, China, 18 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Olles, J.D.; Wixom, R.R.; Knepper, R.; Tappan, A.S. Observations of shock-induced chemistry with subnanosecond resolution. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 114, 214102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassett, W.P.; Johnson, B.P.; Dlott, D.D. Dynamic absorption in optical pyrometry of hot spots in plastic-bonded triaminotrinitrobenzene. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 114, 194101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassett, W.P.; Johnson, B.P.; Neelakantan, N.K.; Suslick, K.S.; Dlott, D.D. Shock initiation of explosives: High temperature hot spots explained. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 111, 61902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Li, B.; Li, M.; Wu, X. A Miniature Device for Shock Initiation of Hexanitrostilbene by High-Speed Flyer. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2016, 41, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, P.C. Initiation and Detonation in Lead Azide and Silver Azide at Sub-Millimeter Geometries. Master’s Thesis, Texas Tech University, Lubbock, TX, USA, December 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Quaresma, J.; Deimling, L.; Campos, J.; Mendes, R. Active and Passive Optical Fiber Metrology for Detonation Velocity Measurements. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2020, 45, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, B. The Detonation Electric Effect. J. Appl. Phys. 1967, 38, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachman, J.; Künzel, M.; Němec, O.; Majzlík, J. A comparison of methods for detonation pressure measurement. Shock Waves 2017, 28, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Miao, Y.; Suslick, K.S.; Dlott, D.D. Mechanochemistry of Metal–Organic Frameworks under Pressure and Shock. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 2806–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obara, T.; Bourne, N.K.; Mebar, Y. The construction and calibration of an inexpensive PVDF stress gauge for fast pressure measurements. Meas. Sci. Technol. 1995, 6, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Yi, W. Application of a PVDF-Based Stress Gauge in Determining Dynamic Stress-Strain Curves of Concrete under Impact Testing. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20, 65004. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Z.; Xie, R.; Zhang, F.; Chen, G. Application of PVDF Gauges in Solid Interface. ICEM Proc. 2018, 2, 460. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, H.; Li, Q.M. Correlation between the accuracy of a SHPB test and the stress uniformity based on numerical experiments. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2003, 28, 537–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.G. On the use of SHPB techniques to determine the dynamic behavior of materials in the range of small strains. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1996, 33, 3363–3375. [Google Scholar]
- Bassett, W.P.; Dlott, D.D. Multichannel emission spectrometer for high dynamic range optical pyrometry of shock-driven materials. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2016, 87, 225103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Miao, Y.; Shaw, W.L.; Suslick, K.S.; Dlott, D.D. Shock Wave Energy Absorption in Metal–Organic Framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 2220–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhowmick, M.; Basset, W.P.; Matveev, S.; Salvati, L.; Dlott, D.D. Optical windows as materials for high-speed shock wave detectors. Aip Adv. 2018, 8, 125123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouyer, V.; Sheffield, S.A.; Dattelbaum, D.M.; Gustavsen, R.; Stahl, D.B.; Doucet, M.; Decaris, L.; Elert, M.; Furnish, M.D.; Anderson, W.W.; et al. Experimental measurements of the chemical reaction zone of detonating liquid explosives. AIP Conf. Proc. 2009, 1195, 177–180. [Google Scholar]
- Dolan, D.H. Extreme measurements with Photonic Doppler Velocimetry (PDV). Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2020, 91, 51501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, H.; Huang, W.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, X. Measuring detonation wave profiles in plastic-bonded explosives using PDV. Aip Adv. 2019, 9, 15306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forbes, J.W. Shock Wave Compression of Condensed Matter; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kanel, G.I.; Fortov, V.E.; Razorenov, S.V. Shock-Wave Phenomena and the Properties of Condensed Matter; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, H.; Huang, W.; Qin, J.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, X. Reaction zone structure of JB-9014 explosive measured by PDV. Explos. Shock Waves 2018, 38, 485–489. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, G.F. Foundations of Wave Mechanics; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2019; pp. 262–263. [Google Scholar]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shen, R.; Ye, Y. Observations on Detonation Growth of Lead Azide at Microscale. Micromachines 2022, 13, 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13030451
Mu Y, Zhang W, Shen R, Ye Y. Observations on Detonation Growth of Lead Azide at Microscale. Micromachines. 2022; 13(3):451. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13030451
Chicago/Turabian StyleMu, Yunfei, Wei Zhang, Ruiqi Shen, and Yinghua Ye. 2022. "Observations on Detonation Growth of Lead Azide at Microscale" Micromachines 13, no. 3: 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13030451
APA StyleMu, Y., Zhang, W., Shen, R., & Ye, Y. (2022). Observations on Detonation Growth of Lead Azide at Microscale. Micromachines, 13(3), 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13030451