Partitioning of Small Hydrophobic Molecules into Polydimethylsiloxane in Microfluidic Analytical Devices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Device Fabrication
2.3. Device Operations and Experimental Setup
2.4. PDMS Surface Modifications
2.4.1. Pluronic® F127
2.4.2. 3-Aminipropyltriethoxysilane (APTES)
2.4.3. Paraffin
2.5. PDMS Bulk Modifications
2.5.1. Gradient-Induced Migration of Embedded Poloxamers
2.5.2. Thermal Aging
2.5.3. Solvent Extraction of Uncrosslinked Oligomers
2.5.4. Sol–Gel
2.6. Contact Angle Measurements
2.7. Fluorescence Spectroscopy
2.8. Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Molecule Partitioning as a Function of Solute/Solvent Pairings
3.2. Molecule Partitioning as a Function of Residence Time
3.3. Molecule Partitioning as a Function of Concentration
3.4. PDMS Modifications
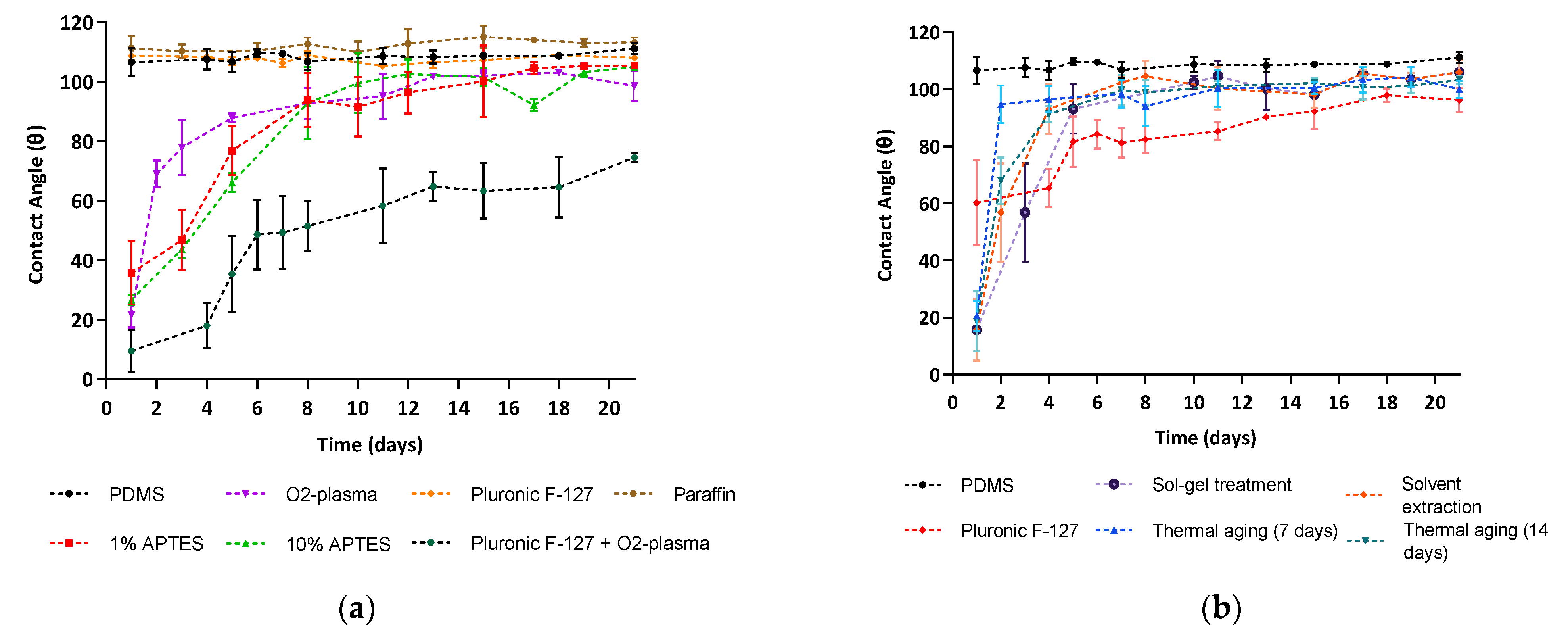
3.4.1. Contact Angle Measurements
3.4.2. Molecule Partitioning
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berthier, E.; Young, E.W.K.; Beebe, D. Engineers are from PDMS-land, Biologists are from Polystyrenia. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 1224–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCreedy, T. Fabrication techniques and materials commonly used for the production of microreactors and micro total analytical systems. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2000, 19, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wlodarczyk, K.L.; Hand, D.; Maroto-Valer, M. Maskless, rapid manufacturing of glass microfluidic devices using a picosecond pulsed laser. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitesides, G.M. The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature 2006, 442, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, M.C.; Guldiken, R. Effects of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) microchannels on surface acoustic wave-based microfluidic devices. Microelectron. Eng. 2014, 113, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, D.C.; McDonald, J.C.; Schueller, O.J.A.; Whitesides, G.M. Rapid Prototyping of Microfluidic Systems in Poly(dimethylsiloxane). Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 4974–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, J.C.; Whitesides, G.M. Poly(dimethylsiloxane) as a Material for Fabricating Microfluidic Devices. Accounts Chem. Res. 2002, 35, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bélanger, M.-C.; Marois, Y. Hemocompatibility, biocompatibility, inflammatory and in vivo studies of primary reference materials low-density polyethylene and polydimethylsiloxane: A review. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 58, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, M.A.; Eddington, D.T. Storing and releasing rhodamine as a model hydrophobic compound in polydimethylsiloxane microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toepke, M.W.; Beebe, D.J. PDMS absorption of small molecules and consequences in microfluidic applications. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 1484–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoridis, G.; Lontou, M.A.; Michopoulos, F.; Sucha, M.; Gondova, T. Study of multiple solid-phase microextraction combined off-line with high performance liquid chromatography: Application in the analysis of pharmaceuticals in urine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 516, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regehr, K.J.; Domenech, M.; Koepsel, J.T.; Carver, K.C.; Ellison-Zelski, S.J.; Murphy, W.L.; Schuler, L.A.; Alarid, E.T.; Beebe, D.J. Biological implications of polydimethylsiloxane-based microfluidic cell culture. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 2132–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.D.; Douville, N.J.; Takayama, S.; Elsayed, M. Quantitative Analysis of Molecular Absorption into PDMS Microfluidic Channels. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 40, 1862–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, J.; Özkan, A.; Oh, C.; Mahajan, G.; Prantil-Baun, R.; Ingber, D.E. Simulating drug concentrations in PDMS microfluidic organ chips. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 3509–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Meer, B.; de Vries, H.; Firth, K.; van Weerd, J.; Tertoolen, L.; Karperien, H.; Jonkheijm, P.; Denning, C.; Ijzerman, A.; Mummery, C. Small molecule absorption by PDMS in the context of drug response bioassays. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 482, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quake, S.R.; Scherer, A. From Micro- to Nanofabrication with Soft Materials. Science 2000, 290, 1536–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mukhopadhyay, R. When PDMS isn’t the best. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 3248–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, K.K.-C.; Lucy, C.A. Suppression of Electroosmotic Flow and Prevention of Wall Adsorption in Capillary Zone Electrophoresis Using Zwitterionic Surfactants. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 3435–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futrega, K.; Yu, J.; Jones, J.W.; Kane, M.A.; Lott, W.B.; Atkinson, K.; Doran, M.R. Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) modulates CD38 expression, absorbs retinoic acid and may perturb retinoid signalling. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 1473–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Łopacińska, J.M.; Emnéus, J.; Dufva, M. Poly(Dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) Affects Gene Expression in PC12 Cells Differentiating into Neuronal-Like Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carter, S.-S.D.; Atif, A.-R.; Kadekar, S.; Lanekoff, I.; Engqvist, H.; Varghese, O.P.; Tenje, M.; Mestres, G. PDMS leaching and its implications for on-chip studies focusing on bone regeneration applications. Organs-on-a-Chip 2020, 2, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beekman, P.; Enciso-Martinez, A.; Pujari, S.P.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M.; Zuilhof, H.; Le Gac, S.; Otto, C. Organosilicon uptake by biological membranes. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kima, J.; Chaudhury, M.K.; Owen, M.J. Hydrophobic Recovery of Polydimethylsiloxane Elastomer Exposed to Partial Electrical Discharge. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 226, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.N.; Park, .A.C.; Whitesides, G.M. Solvent Compatibility of Poly(dimethylsiloxane)-Based Microfluidic Devices. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 6544–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddington, D.T.; Puccinelli, J.P.; Beebe, D.J. Thermal aging and reduced hydrophobic recovery of polydimethylsiloxane. Sensors Actuators B: Chem. 2006, 114, 170–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, B.-H.; Van Lerberghe, L.; Motsegood, K.; Beebe, D. Three-dimensional micro-channel fabrication in polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) elastomer. J. Microelectromechanical Syst. 2000, 9, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beal, J.H.L.; Bubendorfer, A.; Kemmitt, T.; Hoek, I.; Arnold, W.M. A rapid, inexpensive surface treatment for enhanced functionality of polydimethylsiloxane microfluidic channels. Biomicrofluidics 2012, 6, 036503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slaughter, G.; Stevens, B. A cost-effective two-step method for enhancing the hydrophilicity of PDMS surfaces. BioChip J. 2014, 8, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adly, N.Y.; Hassani, H.; Tran, A.Q.; Balski, M.; Yakushenko, A.; Offenhäusser, A.; Mayer, D.; Wolfrum, B. Observation of chemically protected polydimethylsiloxane: Towards crack-free PDMS. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 6297–6303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossen, S.; Hossain, M.K.; Basher, M.K.; Mia, M.N.H.; Rahman, M.T.; Uddin, M.J. Smart nanocarrier-based drug delivery systems for cancer therapy and toxicity studies: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2019, 15, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, G.T.; Hlaus, T.; Bass, K.J.; Seelhammer, A.T.G.; Culbertson, C.T. Sol−Gel Modified Poly(dimethylsiloxane) Microfluidic Devices with High Electroosmotic Mobilities and Hydrophilic Channel Wall Characteristics. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 1414–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Hjort, K. Surface modification of PDMS by gradient-induced migration of embedded Pluronic. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 1500–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.-C.; Liu, W.; Tu, Q.; Ma, C.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Ouyang, J.; Pang, L.; Wang, J. High throughput and multiplex localization of proteins and cells for in situ micropatterning using pneumatic microfluidics. Analyst 2014, 140, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuah, Y.J.; Kuddannaya, S.; Lee, M.H.A.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, Y. The effects of poly(dimethylsiloxane) surface silanization on the mesenchymal stem cell fate. Biomater. Sci. 2014, 3, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, M.; Greco, G.; Cecchini, M. Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) irreversible bonding to untreated plastics and metals for microfluidics applications. APL Mater. 2019, 7, 081108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, K.; Zhao, Y.; Su, J.; Ryan, D.; Wu, H. Convenient Method for Modifying Poly(dimethylsiloxane) To Be Airtight and Resistive against Absorption of Small Molecules. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 5965–5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Sjoberg, R.; Leyrat, A.A.; Houseman, B.T.; Shokat, K.; Quake, S.R. Biocompatibility and Reduced Drug Absorption of Sol−Gel-Treated Poly(dimethyl siloxane) for Microfluidic Cell Culture Applications. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 8954–8960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dima, C.; Assadpour, E.; Dima, S.; Jafari, S.M. Bioavailability and bioaccessibility of food bioactive compounds; overview and assessment by in vitro methods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2862–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, S.D.; Greenspan, P. Application of Nile red, a fluorescent hydrophobic probe, for the detection of neutral lipid deposits in tissue sections: Comparison with oil red O. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1985, 33, 833–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, H.D.; Poejo, J.; Pinheiro, A.C.; Donsì, F.; Serra, A.T.; Duarte, C.; Ferrari, G.; Cerqueira, M.; Vicente, A. Evaluating the behaviour of curcumin nanoemulsions and multilayer nanoemulsions during dynamic in vitro digestion. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 48, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maheshwari, N.; Kottantharayil, A.; Kumar, M.; Mukherji, S. Long term hydrophilic coating on poly(dimethylsiloxane) substrates for microfluidic applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Peterson, E.; Papautsky, I. Long-term stability of plasma oxidized PDMS surfaces. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Francisco, CA, USA, 1–5 September 2004; pp. 5013–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, K.; Koomson, E.; Zou, H.; Yi, C.; Li, C.-W.; Xu, T.; Yang, M. Recent advances in microfluidic technology for manipulation and analysis of biological cells (2007–2017). Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1044, 29–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Shi, B.; Wang, L. Investigation on Three-Dimensional Solubility Parameters for Explanation and Prediction of Swelling Degree of Polydimethylsiloxane Pervaporation Membranes. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 2015, 54, 1248–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhanmu, O.; Zhao, P.; Yang, Y.; Yang, X.; Gong, H.; Li, X. Maintenance of Fluorescence During Paraffin Embedding of Fluorescent Protein-Labeled Specimens. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodrigues, P.M.; Xavier, M.; Calero, V.; Pastrana, L.; Gonçalves, C. Partitioning of Small Hydrophobic Molecules into Polydimethylsiloxane in Microfluidic Analytical Devices. Micromachines 2022, 13, 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13050713
Rodrigues PM, Xavier M, Calero V, Pastrana L, Gonçalves C. Partitioning of Small Hydrophobic Molecules into Polydimethylsiloxane in Microfluidic Analytical Devices. Micromachines. 2022; 13(5):713. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13050713
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodrigues, Patrícia M., Miguel Xavier, Victor Calero, Lorenzo Pastrana, and Catarina Gonçalves. 2022. "Partitioning of Small Hydrophobic Molecules into Polydimethylsiloxane in Microfluidic Analytical Devices" Micromachines 13, no. 5: 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13050713
APA StyleRodrigues, P. M., Xavier, M., Calero, V., Pastrana, L., & Gonçalves, C. (2022). Partitioning of Small Hydrophobic Molecules into Polydimethylsiloxane in Microfluidic Analytical Devices. Micromachines, 13(5), 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13050713







