Wireless Micro Soft Actuator without Payloads Using 3D Helical Coils
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Concept
3. Materials and Methods
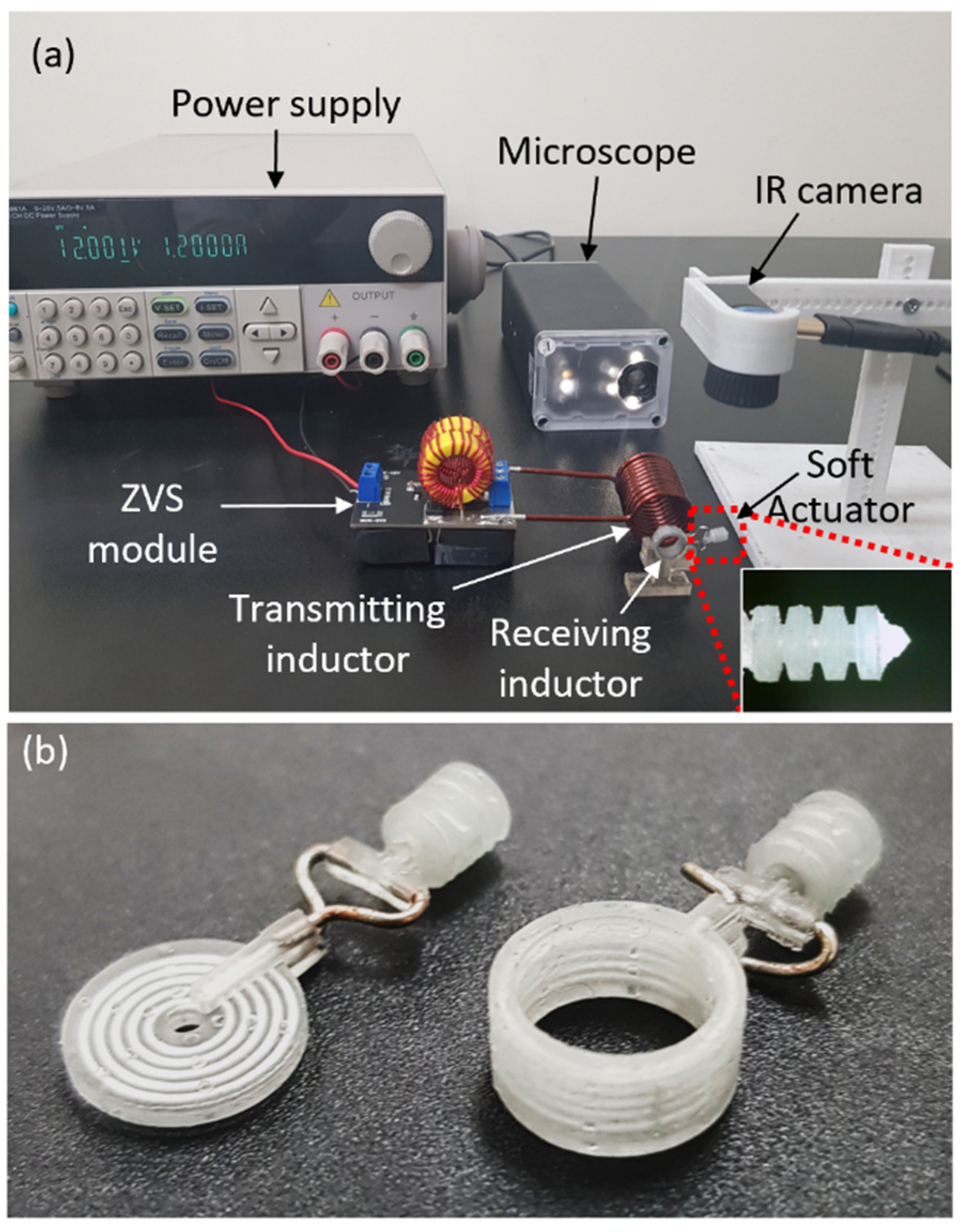
3.1. Fabrication
3.2. Experimental Setup
4. Results and Discussion
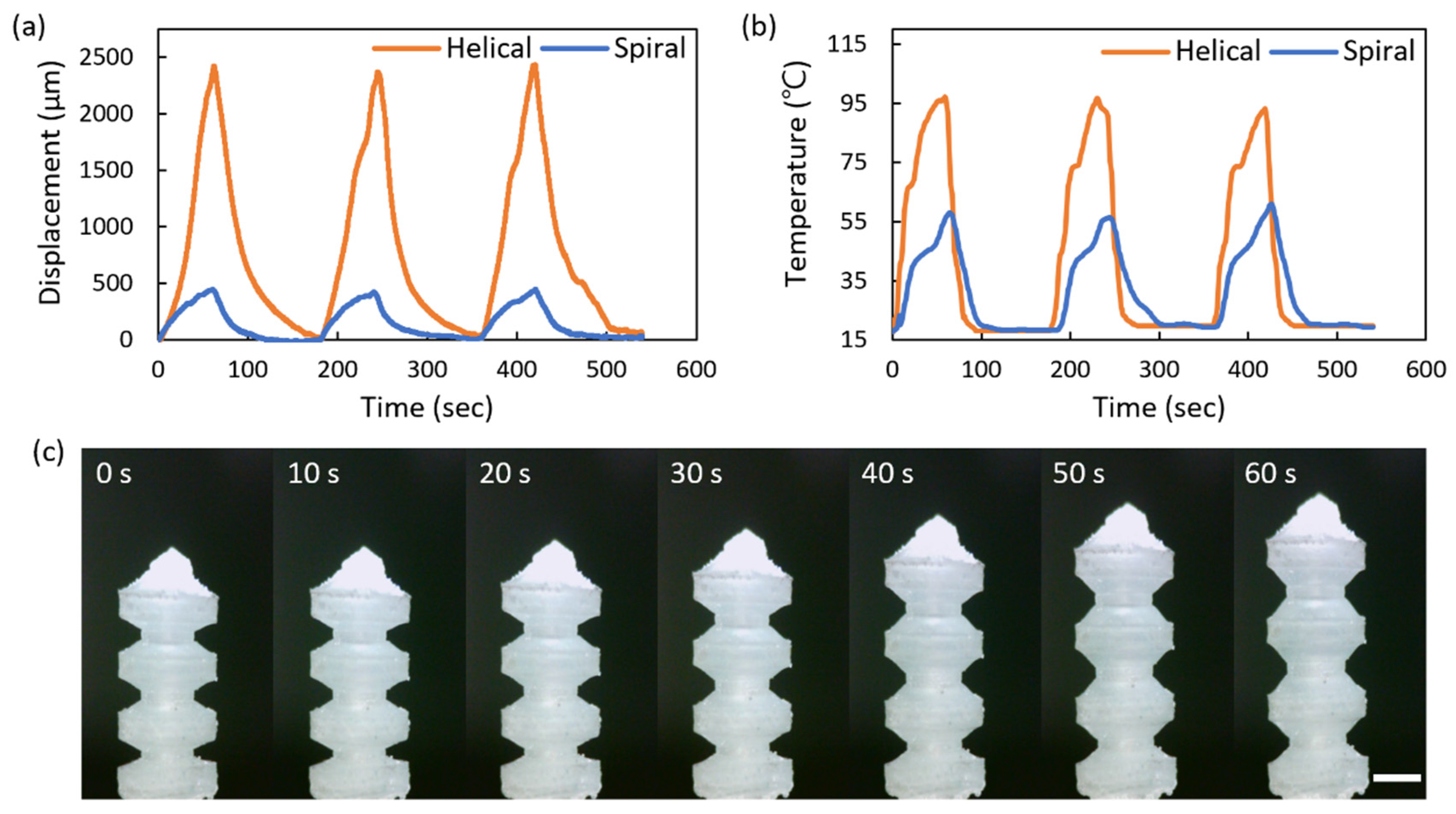
4.1. Characterization of Heater and Receiving Inductor
4.2. Characterization of Wireless Bellows-Shaped Actuator
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rus, D.; Tolley, M.T. Design, fabrication and control of soft robots. Nature 2015, 521, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.; Kim, M.; Kim, Y.J.; Hong, N.; Ryu, S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S. Soft robot review. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2017, 15, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasco, D.L.; Sheelam, A.; Ho, N.H.; Mamaril, A.M.; King, M.; Bell, J.G. Editors’ choice—review—3D printing: An innovative trend in analytical sensing. ECS Sens. Plus 2022, 1, 010602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gossweiler, G.R.; Brown, C.L.; Hewage, G.B.; Sapiro-Gheiler, E.; Trautman, W.J.; Welshofer, G.W.; Craig, S.L. Mechanochemically active soft robots. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 22431–22435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Ye, Y.; Jia, J.; Wu, C.; Xie, Q. Design of cylindrical soft vacuum actuator for soft robots. Smart Mater. Struct. 2021, 30, 045020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ren, T.; Hu, Y.; Liu, H.; Lin, S.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J. A Dual-mode actuator for soft robotic hand. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 1144–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renda, F.; Giorelli, M.; Calisti, M.; Cianchetti, M.; Laschi, C. Dynamic model of a multibending soft robot arm driven by cables. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2014, 30, 1109–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, R.; Alici, G.; Li, W. A soft mechatronic microstage mechanism based on electroactive polymer actuators. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2015, 21, 1467–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancak, C.; Yamac, F.; Itik, M.; Alici, G. Force control of electro-active polymer actuators using model-free intelligent control. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2021, 32, 2054–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, Y.; Matsumoto, M. A design of fully soft robot actuated by gas–liquid phase change. Adv. Robot. 2019, 33, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Hu, X.; Wang, Z.; Mu, J.; Li, N.; Zhou, X.; Fang, S.; Haines, C.S.; Park, J.W.; Qin, S. Unipolar stroke, electroosmotic pump carbon nanotube yarn muscles. Science 2021, 371, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Geng, S.; Walker, I.; Branson, D.T.; Liu, J.; Dai, J.S.; Kang, R. Geometric constraint-based modeling and analysis of a novel continuum robot with Shape Memory Alloy initiated variable stiffness. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2020, 39, 1620–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.; Jung, W.; Ko, K.; Lee, Y.; Lee, C.; Hwang, Y. Thermopneumatic soft micro bellows actuator for standalone operation. Micromachines 2021, 12, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Yang, G.; Deng, Y.; Zheng, T.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, X. A Pneumatic generator based on gas-liquid reversible transition for soft robots. Actuators 2021, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosshard, R.; Mühlethaler, J.; Kolar, J.W.; Stevanović, I. Optimized Magnetic Design for Inductive Power Transfer Coils. In Proceedings of the 2013 Twenty-Eighth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Long Beach, CA, USA, 17–21 March 2013; p. 1812. [Google Scholar]
- Cannon, B.L.; Hoburg, J.F.; Stancil, D.D.; Goldstein, S.C. Magnetic resonant coupling as a potential means for wireless power transfer to multiple small receivers. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2009, 24, 1819–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, K.; See, K.; Koh, W.; Zhang, J. Design of 2.45 GHz Microwave Wireless Power Transfer System for Battery Charging Applications. In Proceedings of the 2017 Progress in Electromagnetics Research Symposium—Fall (PIERS-FALL), Singapore, 19–22 November 2017; p. 2417. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Ludois, D.C. A survey of wireless power transfer and a critical comparison of inductive and capacitive coupling for small gap applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 6017–6029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, S.; Nagatomo, T.; Hiraki, T.; Ishizuka, H.; Kawahara, Y.; Miki, N. Micro elastic pouch motors: Elastically deformable and miniaturized soft actuators using liquid-to-gas phase change. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 5373–5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyvat, M.; Vogt, D.M.; Wood, R.J. Ultrastrong and high-stroke wireless soft actuators through liquid–gas phase change. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirvakili, S.M.; Sim, D.; Hunter, I.W.; Langer, R. Actuation of untethered pneumatic artificial muscles and soft robots using magnetically induced liquid-to-gas phase transitions. Sci. Robot. 2020, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Akyildiz, I.F. Magnetic induction communications for wireless underground sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2010, 58, 2426–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khoshmanesh, K.; Tang, S.-Y.; Zhu, J.Y.; Schaefer, S.; Mitchell, A.; Kalantar-zadeh, K.; Dickey, M.D. Liquid metal enabled microfluidics. Lab. Chip 2017, 17, 974–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Jiang, W.; Niu, D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, B.; Liu, H.; Shi, Y.; Chen, B.; Yin, L.; et al. Untethered soft actuators by liquid–vapor phase transition: Remote and programmable actuation. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2019, 1, 1900109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
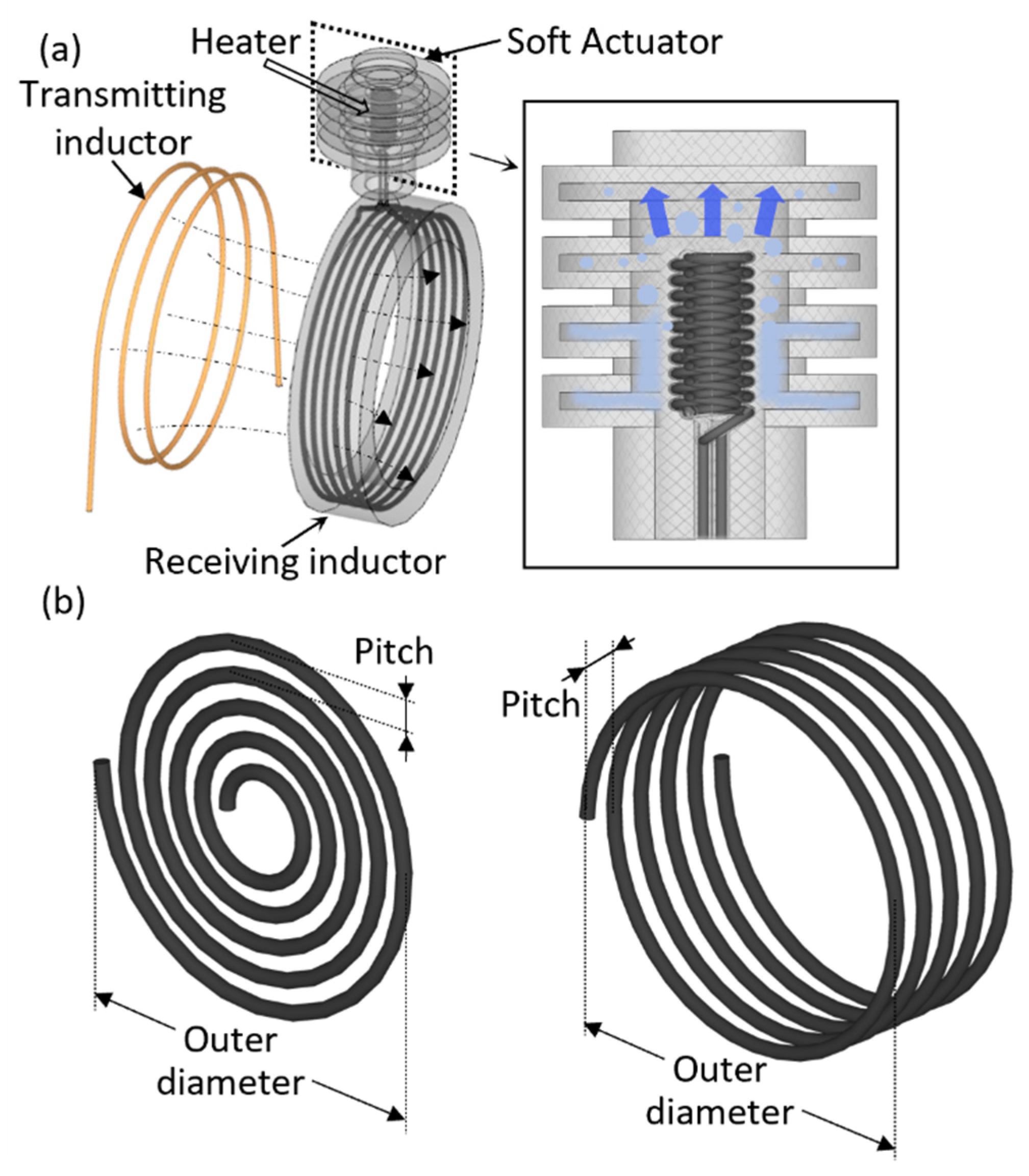
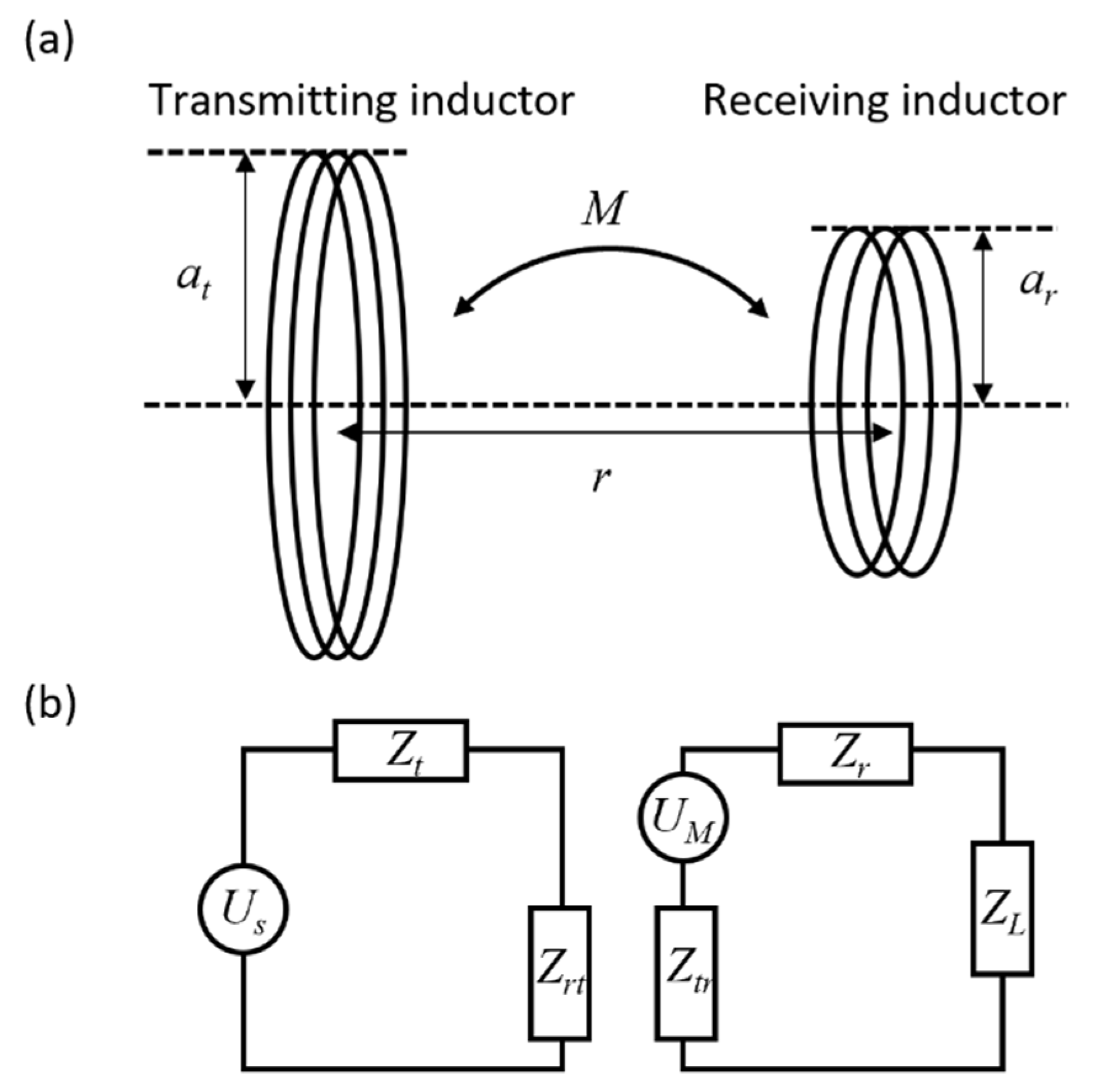
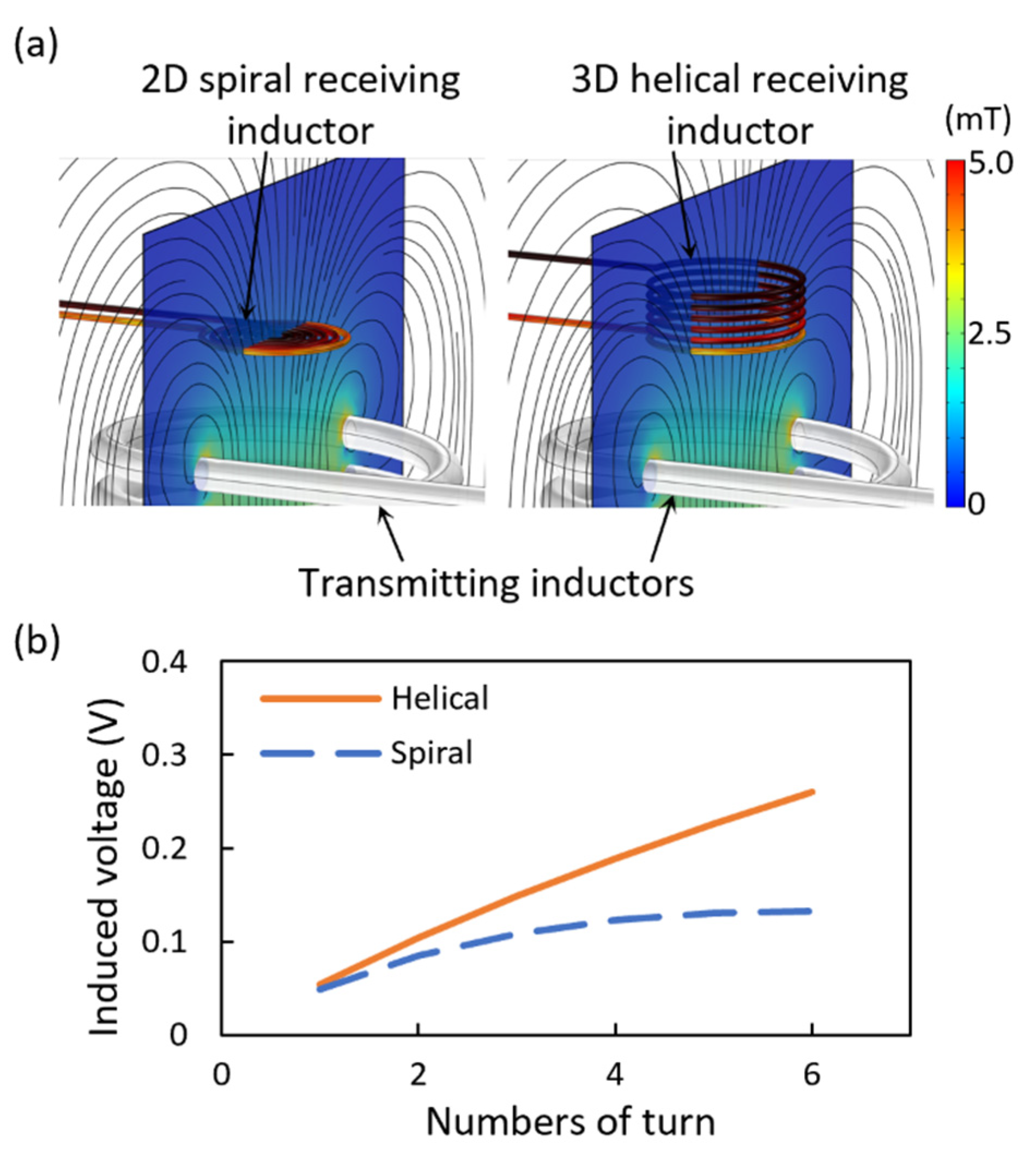
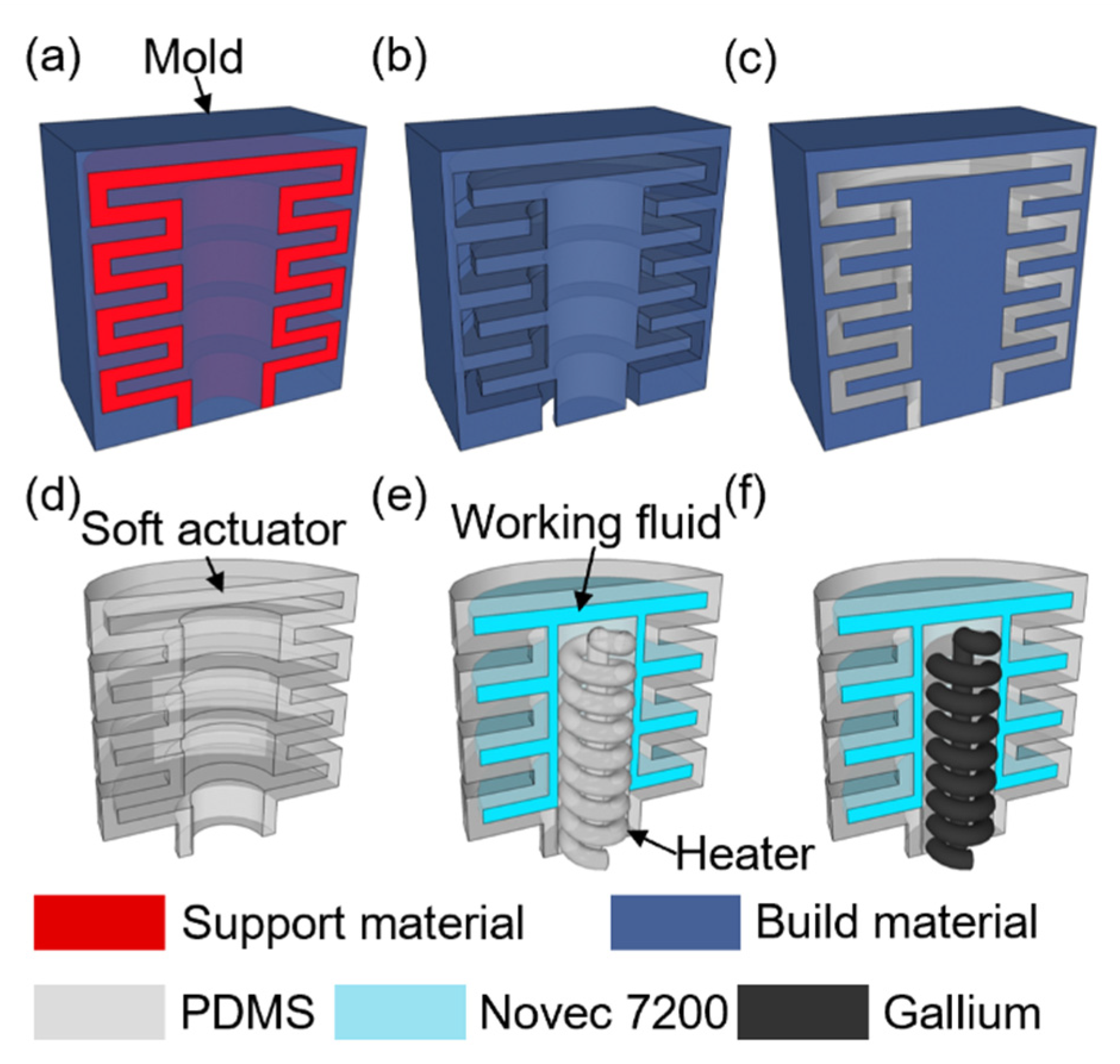


| Coil Thickness [mm] | Outer Diameter [mm] | Pitch [mm] | Turns | Resistance [mΩ] | Inductance [μH] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transmitting inductor | 2 | 20 | 1 | 10 | 3.8 | 1.32 |
| 2D spiral receiving inductor | 0.4 | 9 | 1 | 5 | 244 | 0.46 |
| 3D helical receiving inductor | 0.4 | 9 | 1 | 5 | 321 | 0.58 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.; Jung, W.; Ko, K.; Hwang, Y. Wireless Micro Soft Actuator without Payloads Using 3D Helical Coils. Micromachines 2022, 13, 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13050799
Lee S, Jung W, Ko K, Hwang Y. Wireless Micro Soft Actuator without Payloads Using 3D Helical Coils. Micromachines. 2022; 13(5):799. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13050799
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Seonghyeon, Woojun Jung, Kyungho Ko, and Yongha Hwang. 2022. "Wireless Micro Soft Actuator without Payloads Using 3D Helical Coils" Micromachines 13, no. 5: 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13050799
APA StyleLee, S., Jung, W., Ko, K., & Hwang, Y. (2022). Wireless Micro Soft Actuator without Payloads Using 3D Helical Coils. Micromachines, 13(5), 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13050799






