Accurate Micromanipulation of Optically Induced Dielectrophoresis Based on a Data-Driven Kinematic Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
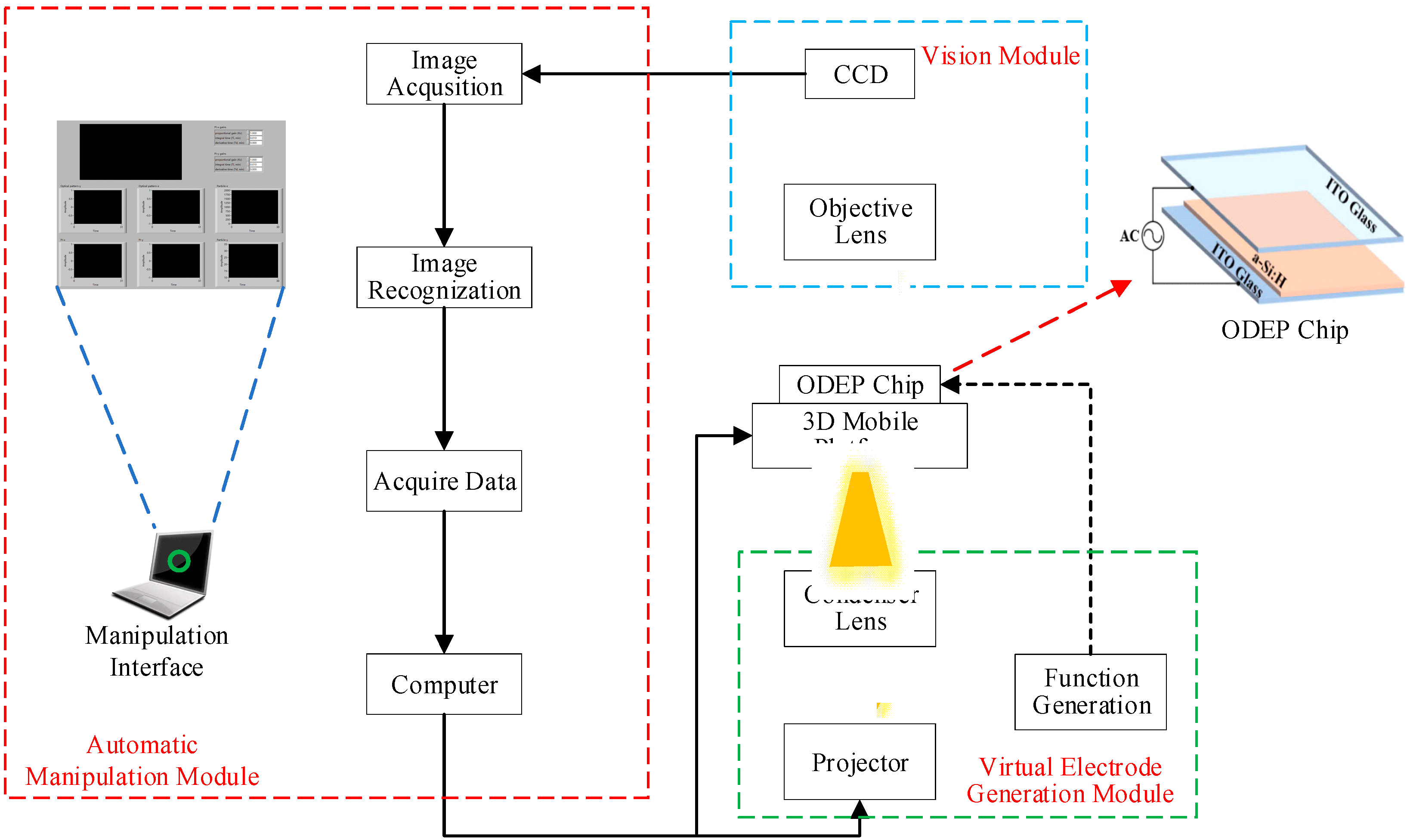
2. Materials and System
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Fabrication of ODEP Chip
2.4. Working Principle of ODEP System
3. Data-Driven Modeling
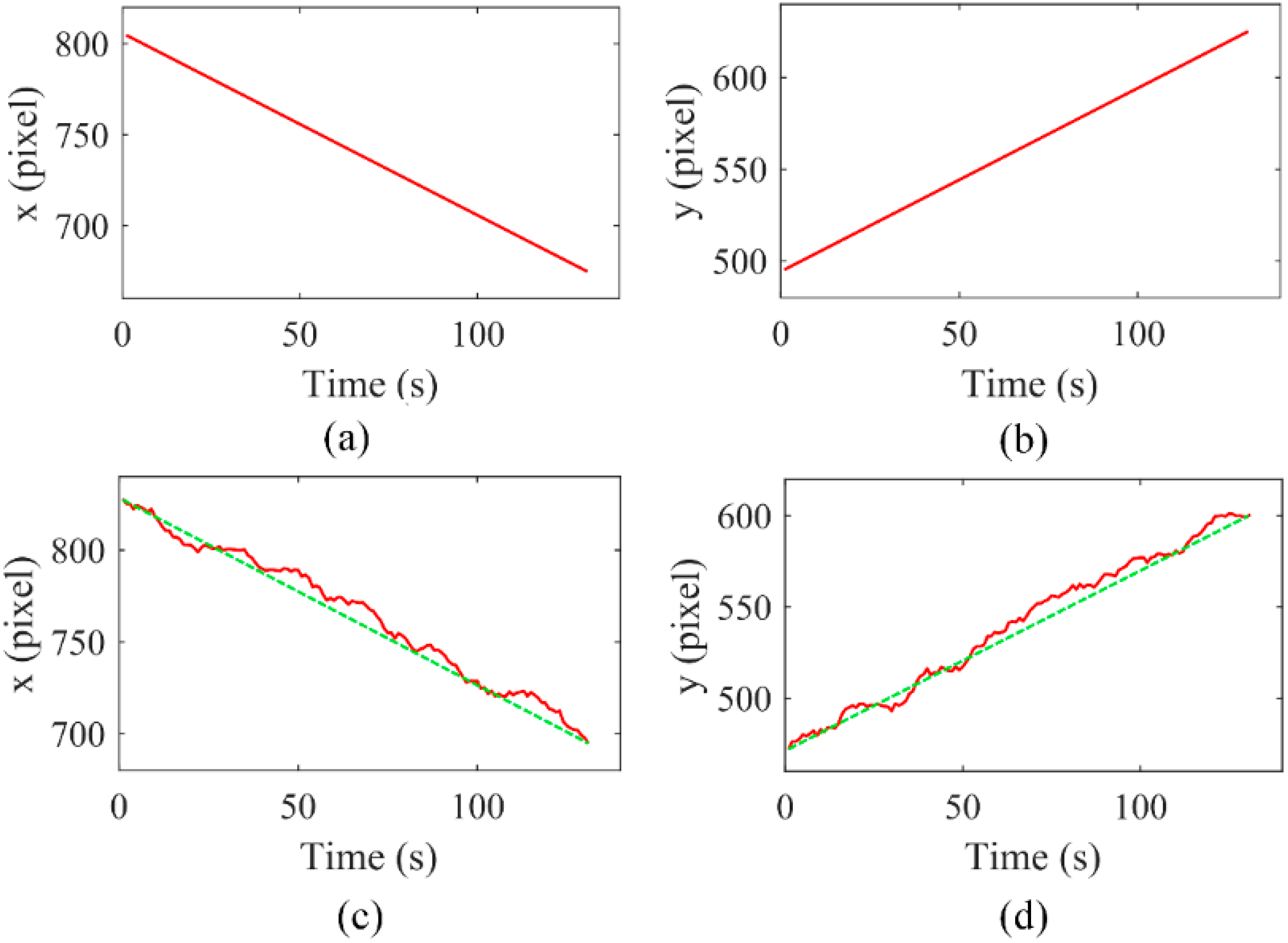
3.1. Data Acquisition
3.2. Modeling
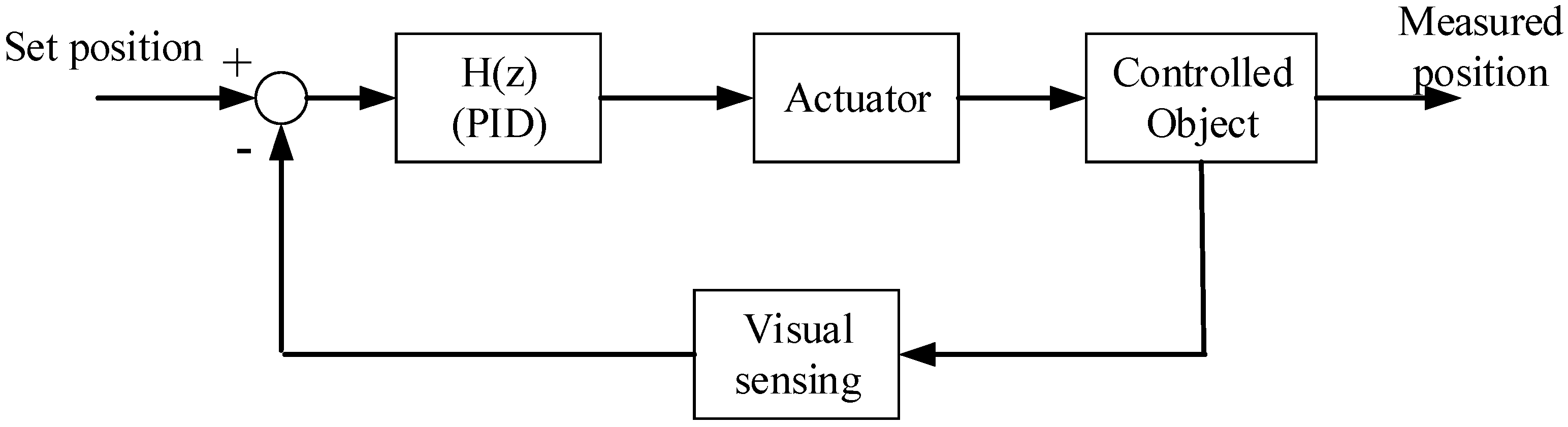
3.3. Controller Design
4. Results and Discussion
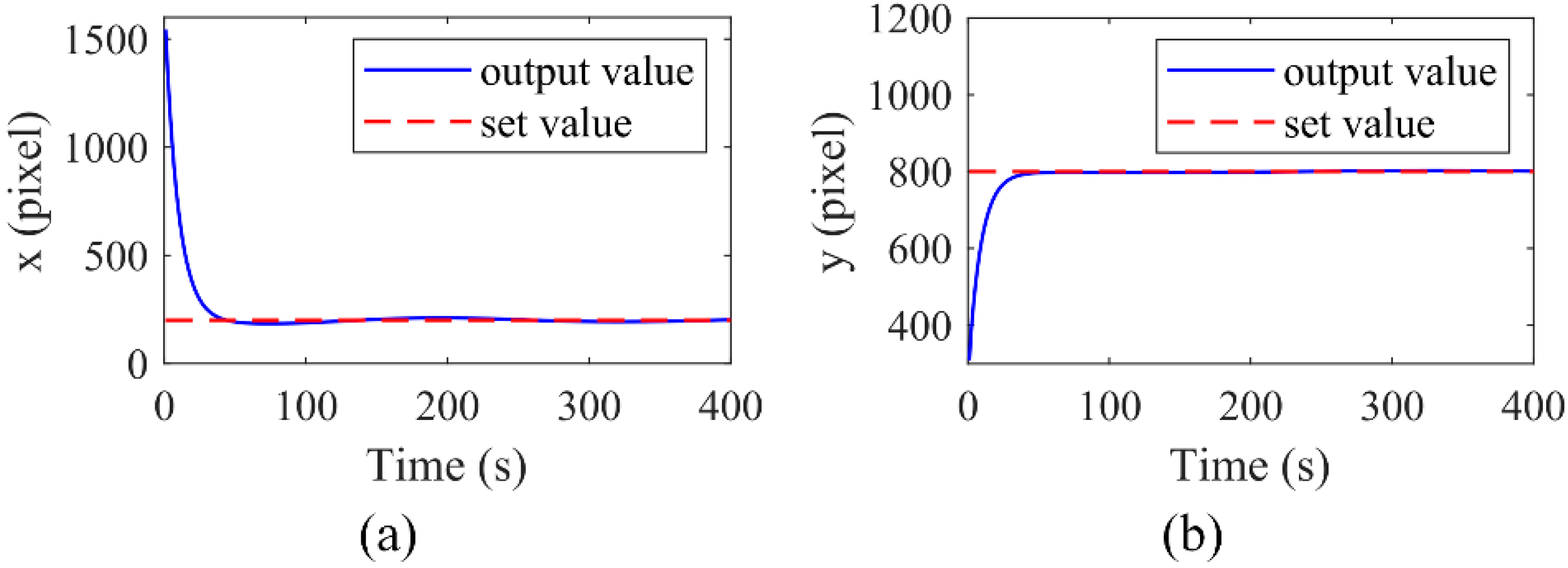
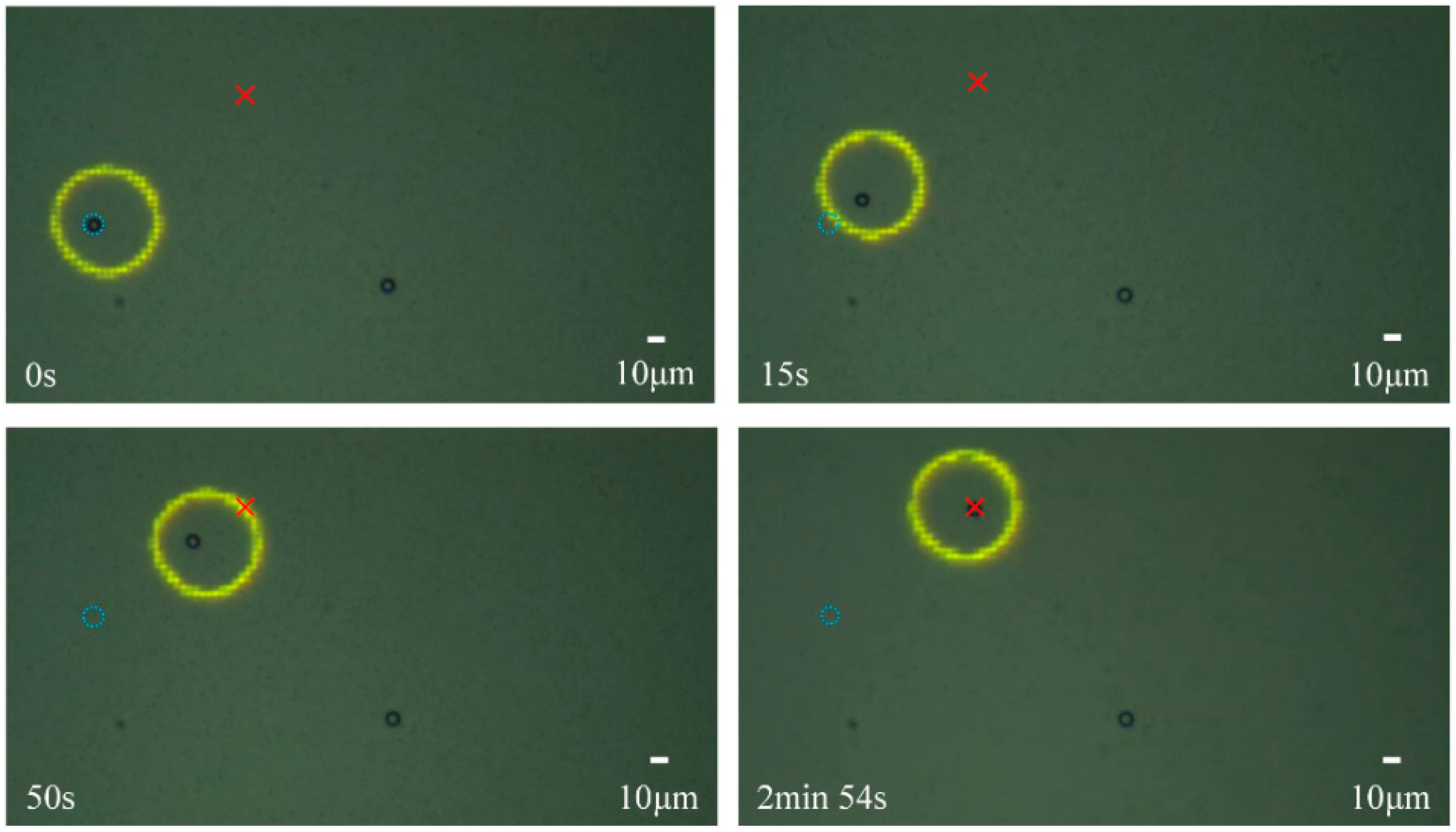
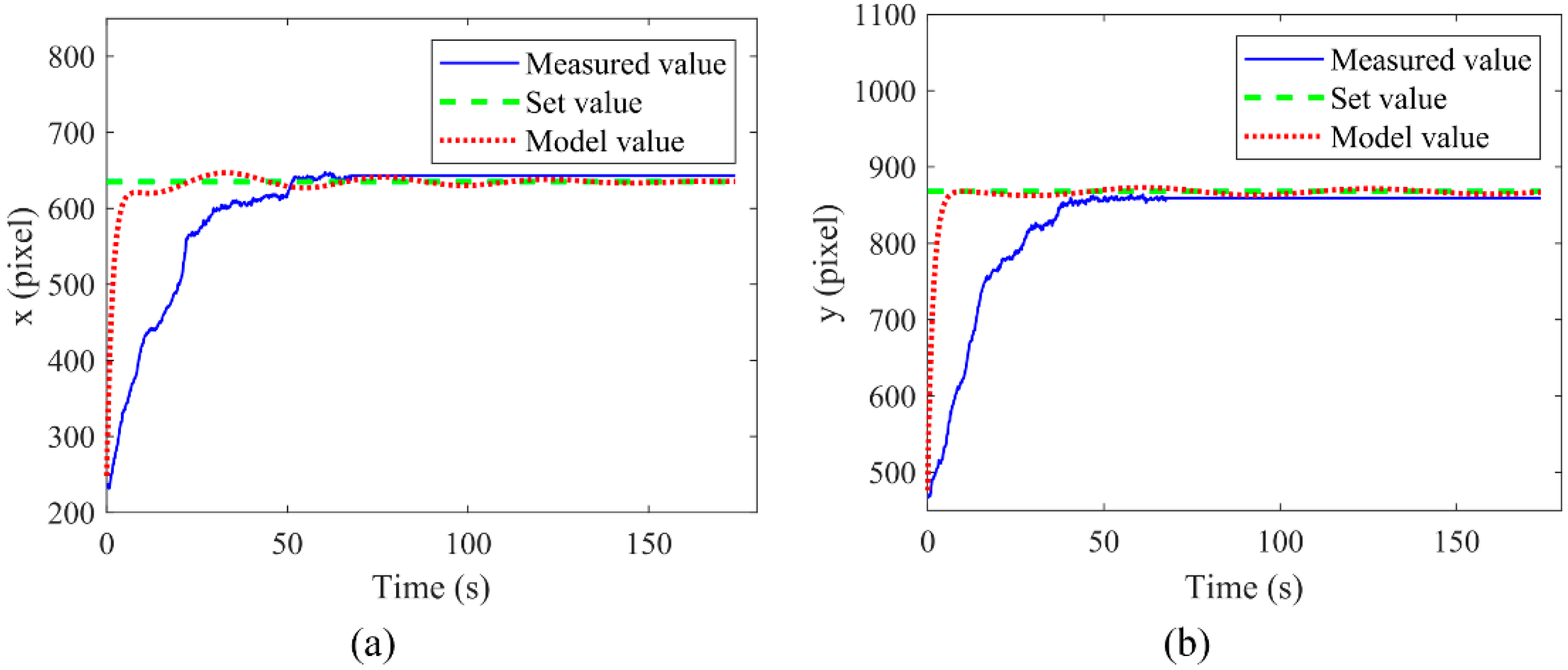
4.1. Experimental Verification
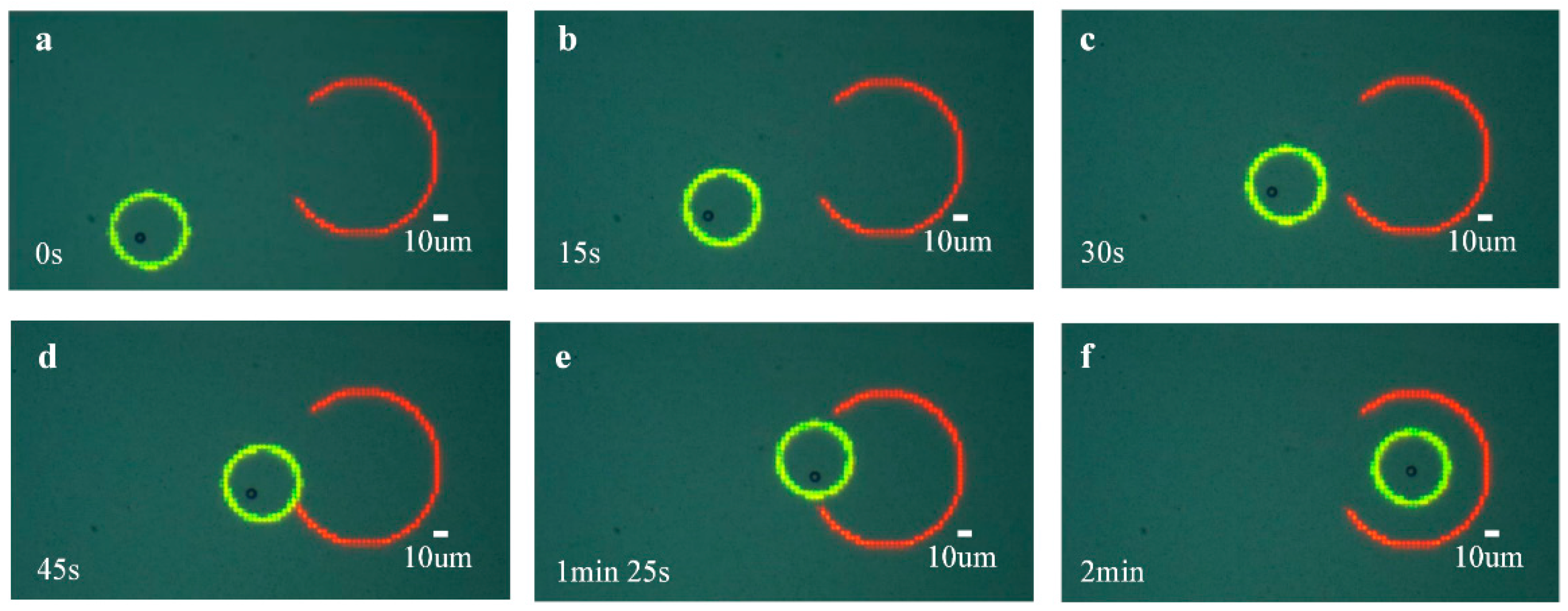
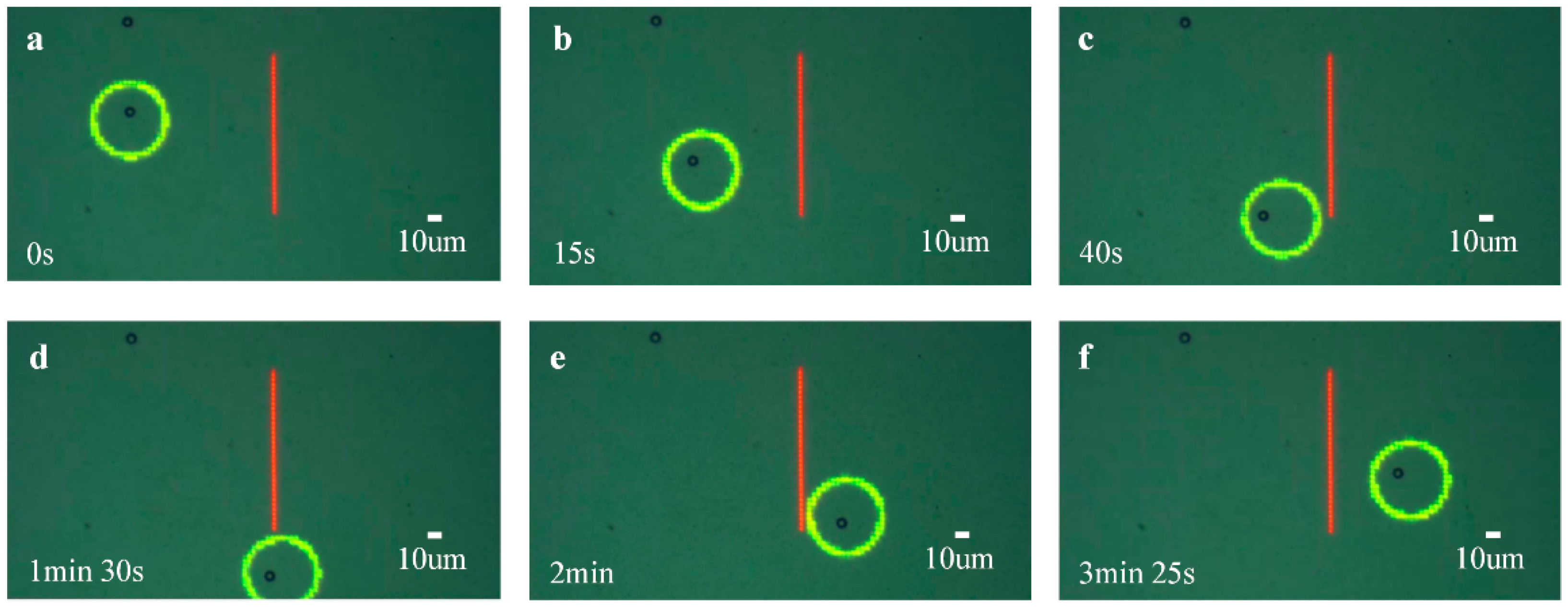
4.2. Accurate Manipulation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hsiao, Y.C.; Wang, C.H.; Lee, W.B.; Lee, G.B. Automatic cell fusion using optically-induced dielectrophoresis and optically-induced localized electric field on a structure-free microfluidic chip. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 12th International Conference on Nano/Micro Engineered and Molecular Systems, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 9–12 April 2017; pp. 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.H.; Lo, H.H.; Lin, C.C.; Weng, K.Y.; Chen, J.C. Optically-induced dielectrophoretic technology for cancer cells identification and concentration. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBS), Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 2415–2418. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, T.K.; Chou, W.P.; Huang, S.B.; Wang, H.M.; Lin, Y.C.; Hsieh, C.H.; Wu, M.H. Application of optically-induced-dielectrophoresis in microfluidic system for purification of circulating tumour cells for gene expression analysis-Cancer cell line model. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiou, P.Y.; Ohta, A.T.; Wu, M.C. Massively parallel manipulation of single cells and microparticles using optical images. Nature 2005, 436, 370–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.-M.; Yu, T.-M.; Huang, H.-P.; Ku, M.-Y.; Hsu, L.; Liu, C.-H. Dynamic manipulation and patterning of microparticles and cells by using TiOPc-based optoelectronic dielectrophoresis. Opt. Lett. 2010, 35, 1959–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.J.; Hsieh, C.H.; Chiu, T.K.; Zhu, Y.X.; Wang, H.M.; Hung, F.C.; Chou, W.P.; Wu, M.H. An optically induced dielectrophoresis (ODEP)-based microfluidic system for the isolation of high-purity CD45neg/EpCAMneg cells from the blood samples of cancer patients-demonstration and initial exploration of the clinical significance of these cells. Micromachines 2018, 9, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Z.; JungLi, W.; Lee, G.B.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, W. Rapid and label-free separation of burkitt’s lymphoma cells from red blood cells by optically-induced electrokinetics. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, M.; Li, G.; Wang, Z.; Ge, Y.; Liu, F. Rapid isolation method of Saccharomyces cerevisiae based on optically induced dielectrophoresis technique for fungal infection diagnosis. Appl. Opt. 2021, 60, 2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Du, M.; Yang, J.; Luan, X.; Liu, L.; Liu, F. Label-free rapid detection of invasive S. cerevisiae infections with optically induced dielectrophoresis-based micromanipulation and graphene transistor. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 14627–14635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Liu, F.; Luan, X.; Li, G. Isolation method of Saccharomyces cerevisiae from red blood cells based on the optically induced dielectrophoresis technique for the rapid detection of fungal infections. Opt. Express 2022, 13, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, S.H.; Huang, S.C.; Lee, G.B. Numerical simulation of optically-induced dielectrophoresis using a voltage-transformation-ratio model. Sensors 2013, 13, 1965–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qu, X.; Dong, L.; Cai, J.; Wang, Z. Manipulation of living cells by optically induced dielectrophoresis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Manipulation, Manufacturing and Measurement on the Nanoscale (3M-NANO), Changchun, China, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 259–262. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.-H.; Lin, M.-W.; Tien, W.-T.; Lai, C.-P.; Weng, K.-Y.; Ko, C.-H.; Lin, C.-C.; Chen, J.-C.; Tiao, K.-T.; Chen, T.-C.; et al. High-purity separation of cancer cells by optically induced dielectrophoresis. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 045002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Buie, C.R. Continuous particle sorting using three dimensional insulator based dielectrophoresis. In Proceedings of the 2014 40th Annual Northeast Bioengineering Conference (NEBEC), Boston, MA, USA, 25–27 April 2014; pp. 31–32. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.; Pyo, J.-W.; Baek, S.H.; Lee, S.W.; Yoon, D.S.; No, K.; Kim, B.-M. Quantitative measurements of absolute dielectrophoretic forces using optical tweezers. Opt. Lett. 2010, 35, 2493–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Li, W.; Elsayed, M.; Tian, P.; Clark, A.W.; Wheeler, A.R.; Neale, S.L. Size-scaling effects for microparticles and cells manipulated by optoelectronic tweezers. Opt. Lett. 2019, 44, 4171–4174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, P.Y.; Hsieh, C.H.; Lin, C.R.; Wu, M.H. The effect of optically induced dielectrophoresis (ODEP)-based cell manipulation in a microfluidic system on the properties of biological cells. Biosensors 2020, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, Y.; Obara, R.; Nakano, M.; Suehiro, J. Concentration of bacteria in high conductive medium using negative dielectrophoresis. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Seville, Spain, 17–19 March 2015; pp. 3336–3340. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Z.; Du, M.; Liu, F.; Li, G. Label-free rapid isolation of saccharomyces cerevisiae with optically induced dielectrophoresis-based automatic micromanipulation. Biomed. Microdevices 2021, 23, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, C.; Liang, S.; Wang, F.; Cao, Y.; Ji, Y.; Lina, J.; Song, L.; Feng, L. Non-contact Massively Parallel Manipulation of Micro-objects by Optoelectronic Tweezers*. In Proceedings of the 2021 WRC Symposium on Advanced Robotics and Automation (WRC SARA), Beijing, China, 11 September 2021; pp. 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Yi, H.; Ni, Z. Frequency-dependent behaviors of individual microscopic particles in an optically induced dielectrophoresis device. Biomicrofluidics 2010, 4, 013202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, L.; Shi, X.; Zhou, T.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Joo, S. A full-scale computational study on the electrodynamics of a rigid particle in an optically induced dielectrophoresis chip. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2020, 34, 2050233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Chen, C.Y.; Chu, P.Y.; Zhu, Y.X.; Hsieh, C.H.; Lu, J.J.; Wu, M.H. Application of an optically induced dielectrophoresis (ODEP)-based microfluidic system for the detection and isolation of bacteria with heterogeneity of antibiotic susceptibility. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2020, 307, 127540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, A.T.; Chiou, P.Y.; Han, T.H.; Liao, J.C.; Bhardwaj, U.; McCabe, E.R.B.; Yu, F.; Sun, R.; Wu, M.C. Dynamic cell and microparticle control via optoelectronic tweezers. J. Microelectromech. Sys. 2007, 16, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chu, P.Y.; Liao, C.J.; Hsieh, C.H.; Wang, H.M.; Chou, W.P.; Chen, P.H.; Wu, M.H. Utilization of optically induced dielectrophoresis in a microfluidic system for sorting and isolation of cells with varied degree of viability: Demonstration of the sorting and isolation of drug-treated cancer cells with various degrees of anti-cancer drug resistance gene expression. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2019, 283, 621–631. [Google Scholar]
- Witte, C.; Reboud, J.; Cooper, J.M.; Neale, S.L.J. Channel integrated optoelectronic tweezer chip for microfluidic particle manipulation. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2020, 30, 045004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Ding, Z.; Wang, M.; Zhao, Z.; Xie, S.; Liu, F. Accurate Micromanipulation of Optically Induced Dielectrophoresis Based on a Data-Driven Kinematic Model. Micromachines 2022, 13, 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13070985
Li G, Ding Z, Wang M, Zhao Z, Xie S, Liu F. Accurate Micromanipulation of Optically Induced Dielectrophoresis Based on a Data-Driven Kinematic Model. Micromachines. 2022; 13(7):985. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13070985
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Gongxin, Zhanqiao Ding, Mindong Wang, Zhonggai Zhao, Shuangxi Xie, and Fei Liu. 2022. "Accurate Micromanipulation of Optically Induced Dielectrophoresis Based on a Data-Driven Kinematic Model" Micromachines 13, no. 7: 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13070985
APA StyleLi, G., Ding, Z., Wang, M., Zhao, Z., Xie, S., & Liu, F. (2022). Accurate Micromanipulation of Optically Induced Dielectrophoresis Based on a Data-Driven Kinematic Model. Micromachines, 13(7), 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13070985





