A Soft Robot Driven by a Spring-Rolling Dielectric Elastomer Actuator with Two Bristles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Design and Fabrication of SRDE and the Robot
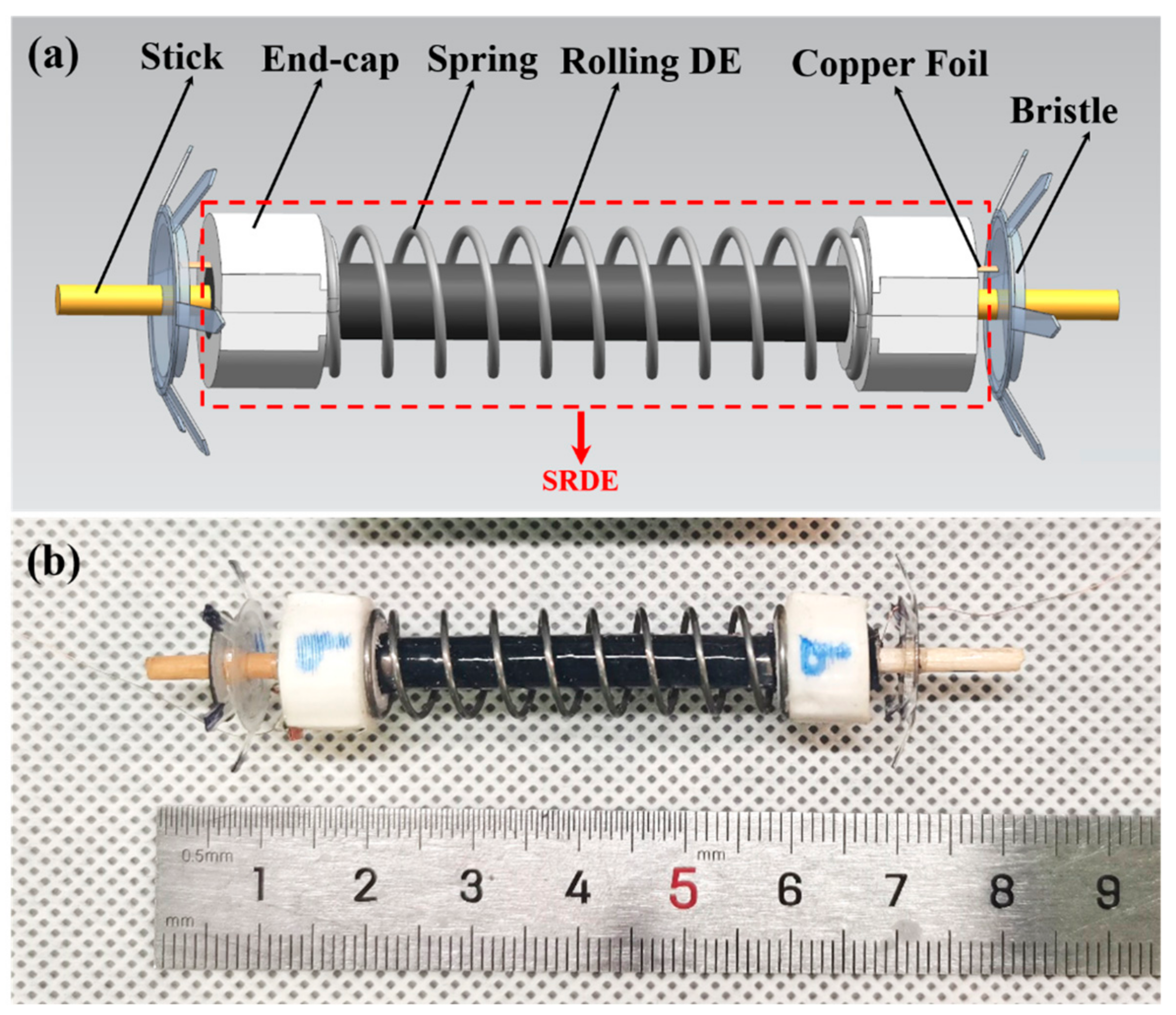
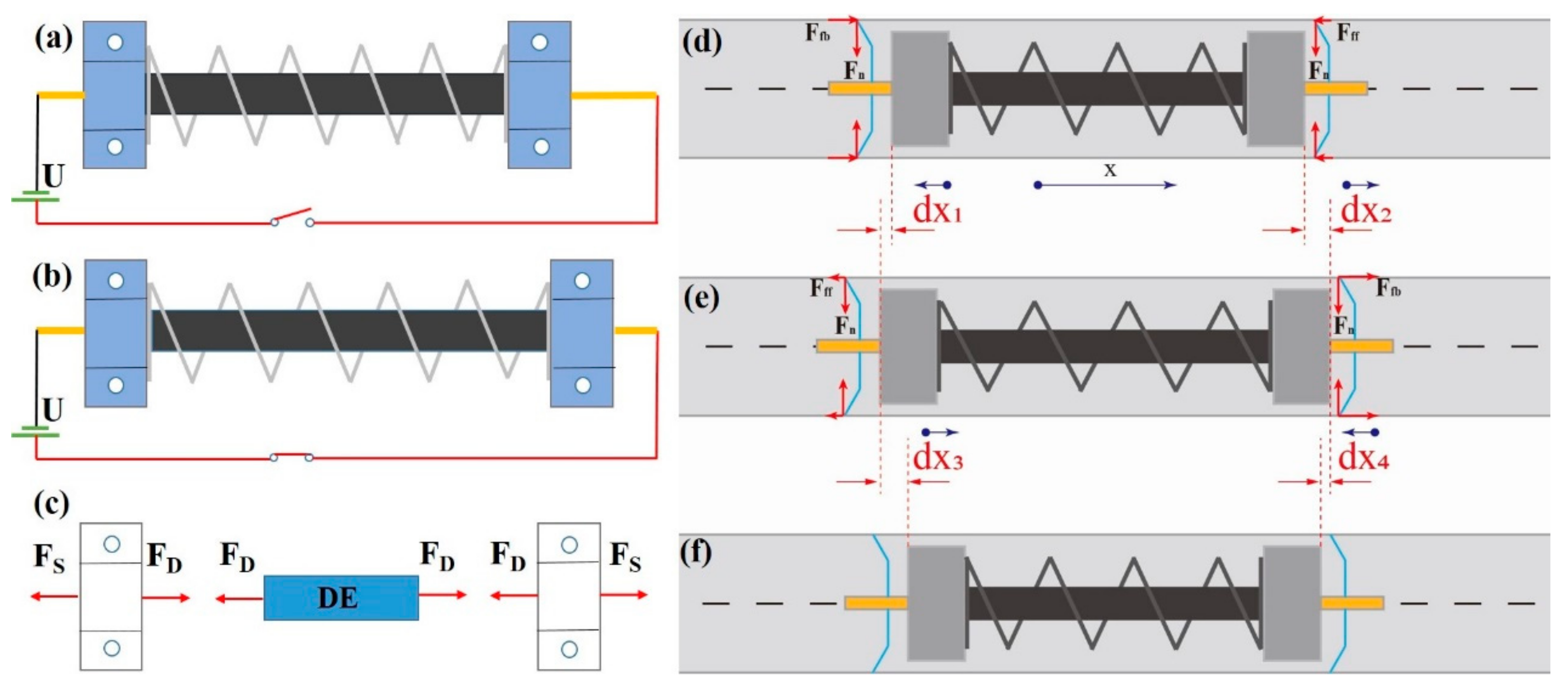
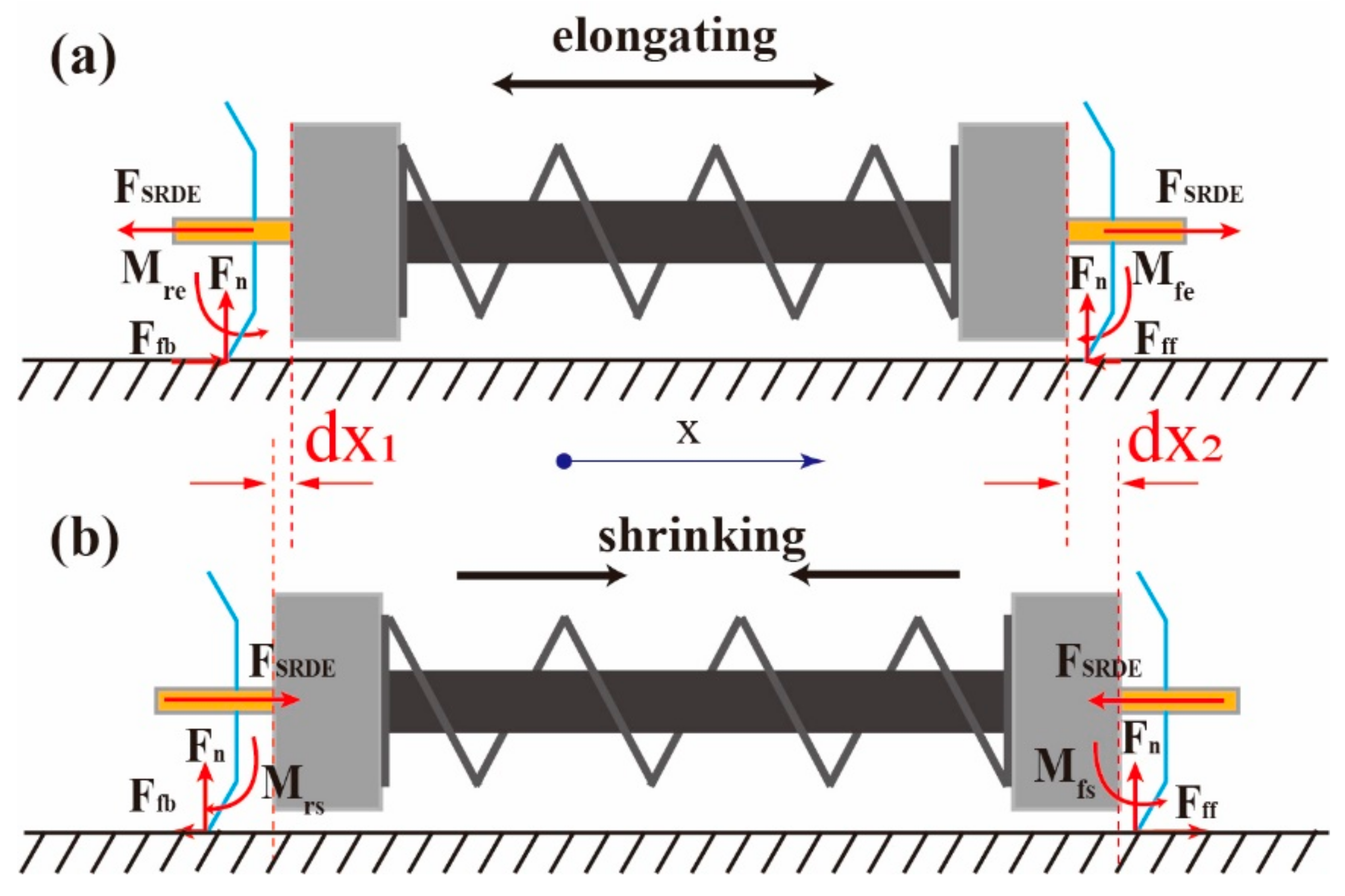
2.1. Design and Principle of SRDE and the Robot
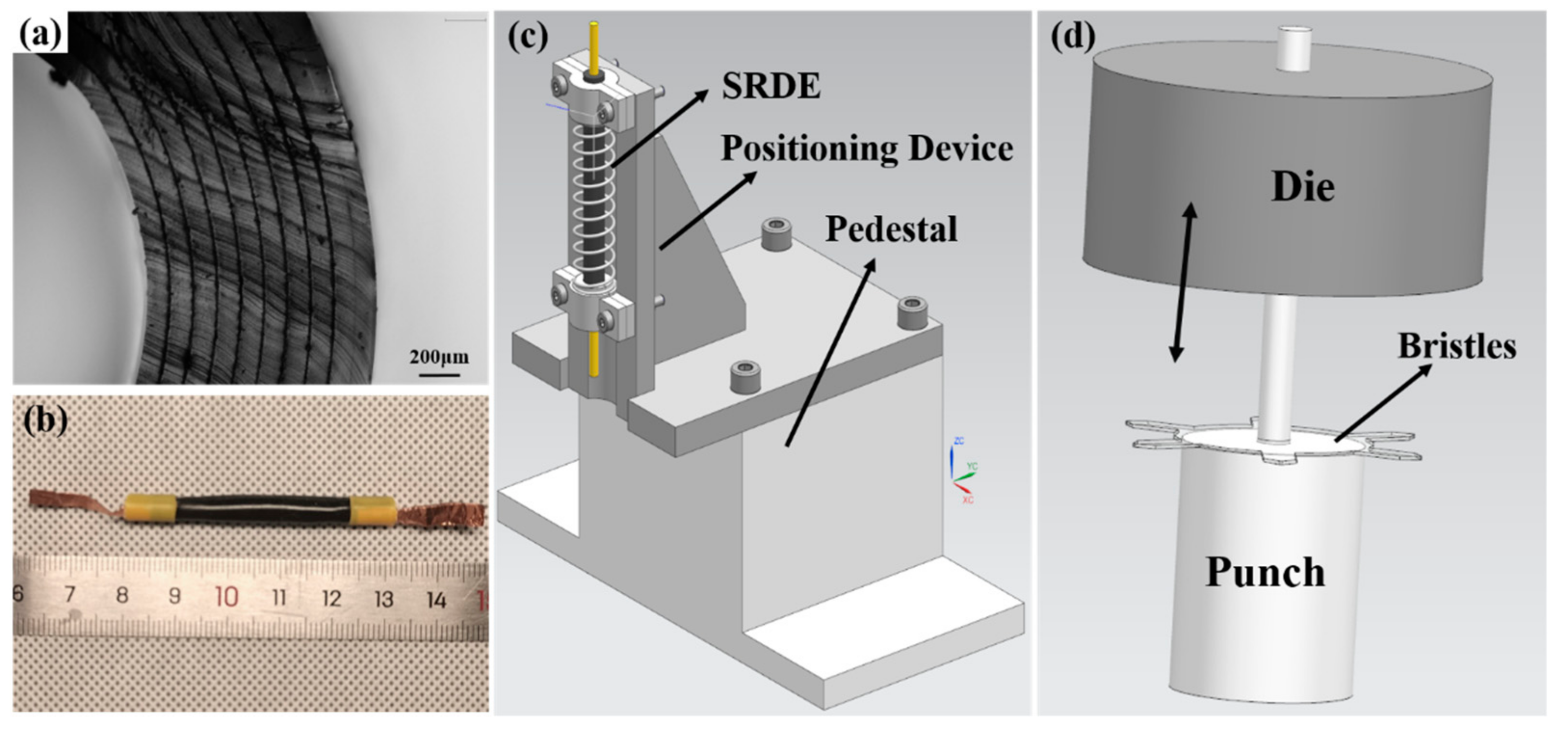
2.2. The Fabrication Process
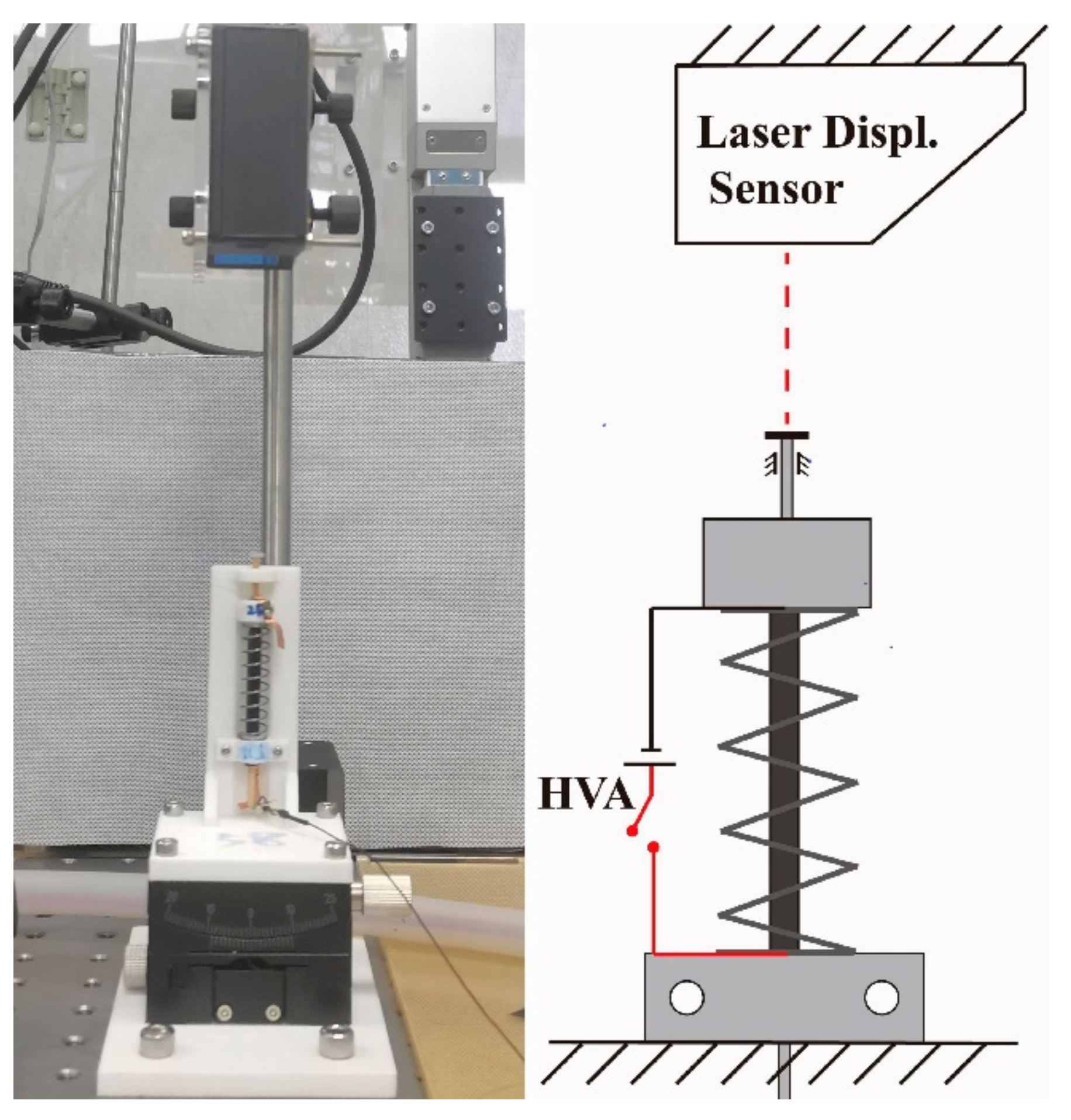
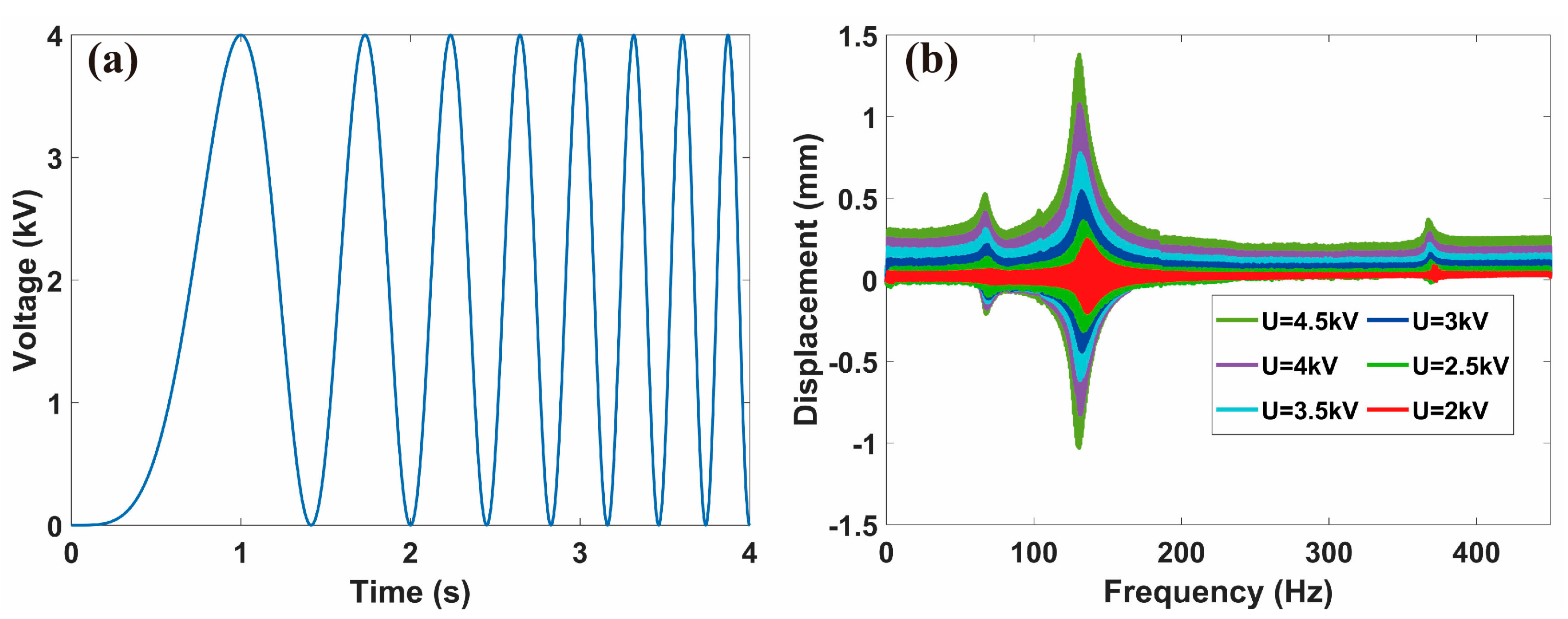
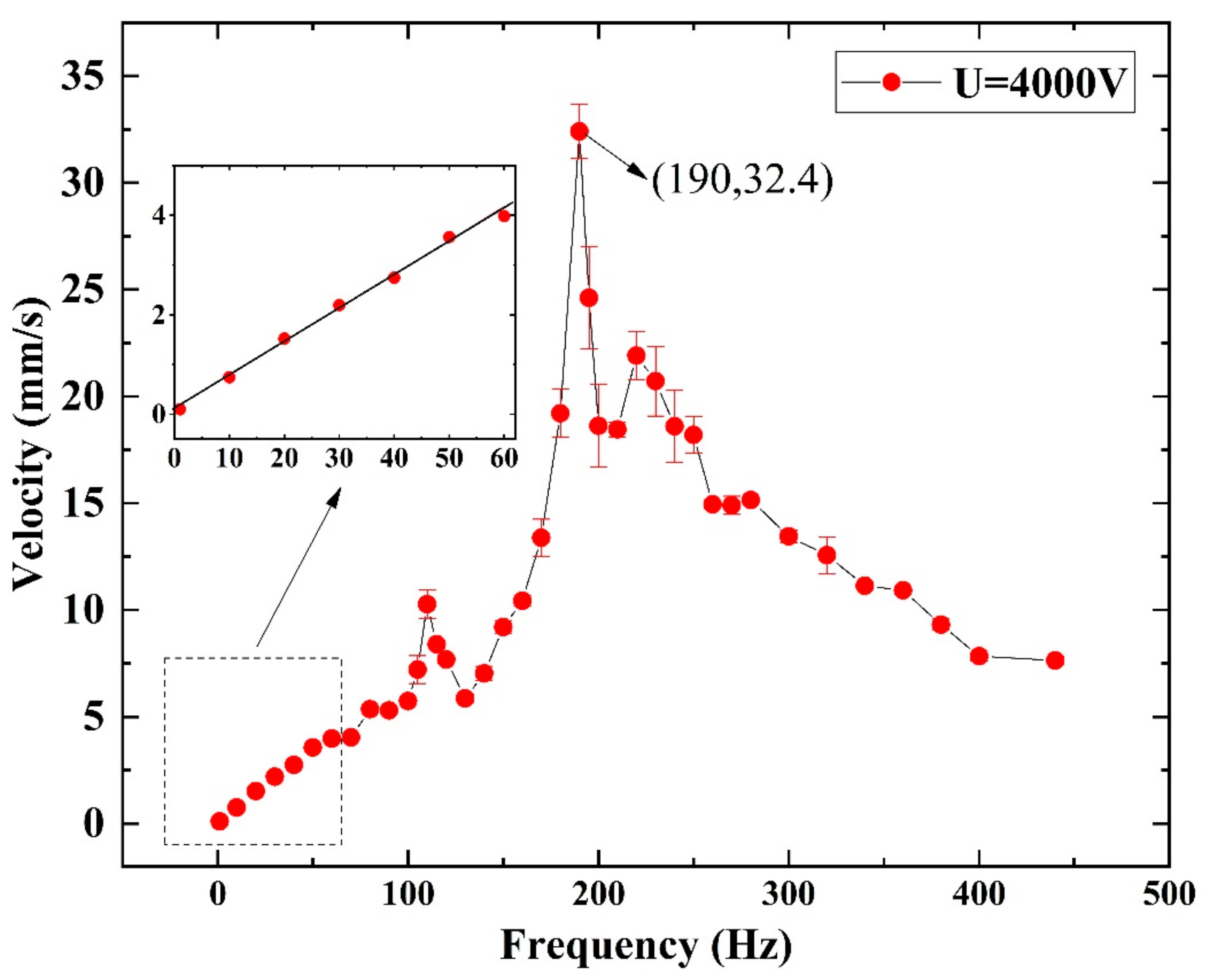
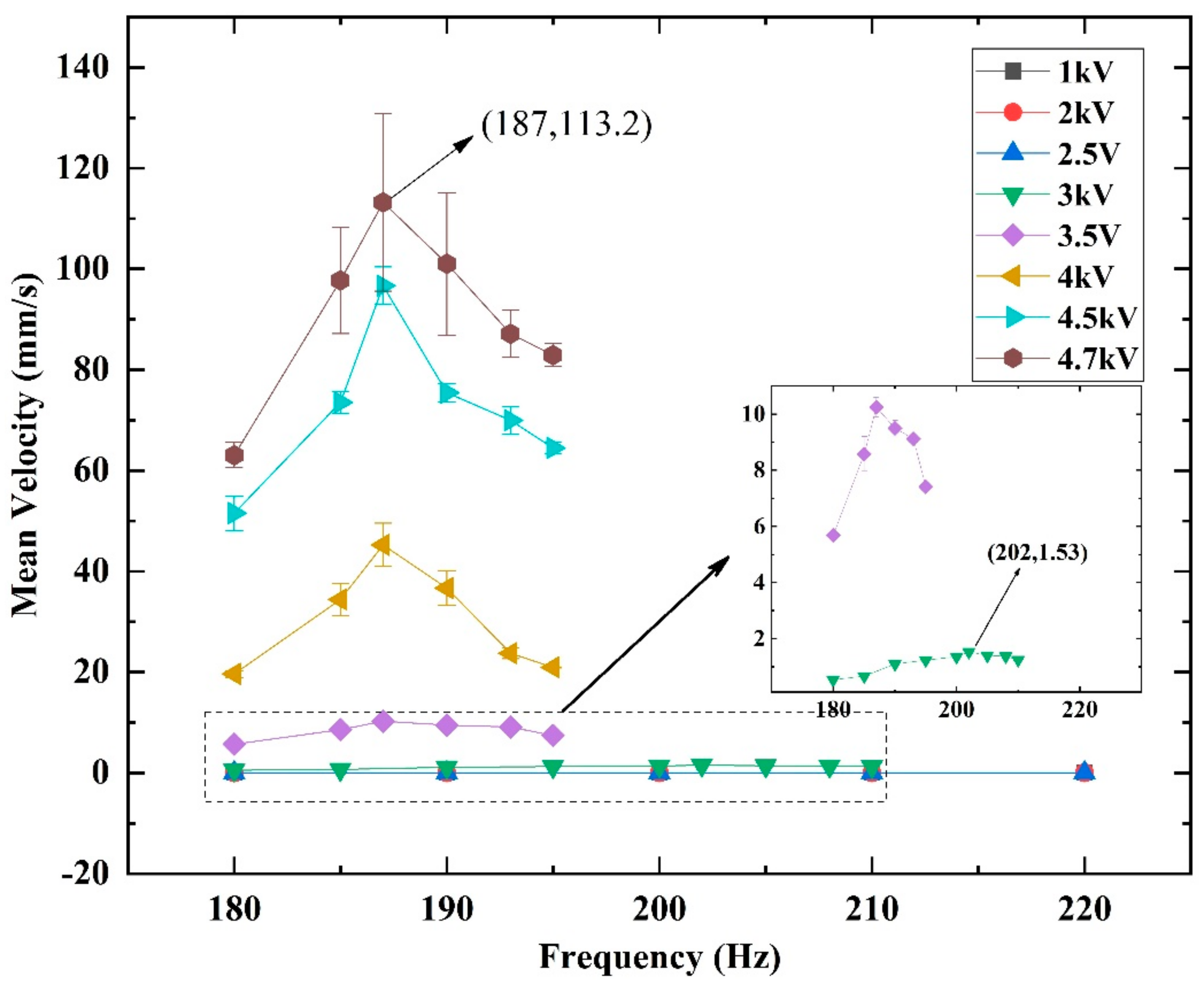
3. Dynamic Characterization of the SRDE
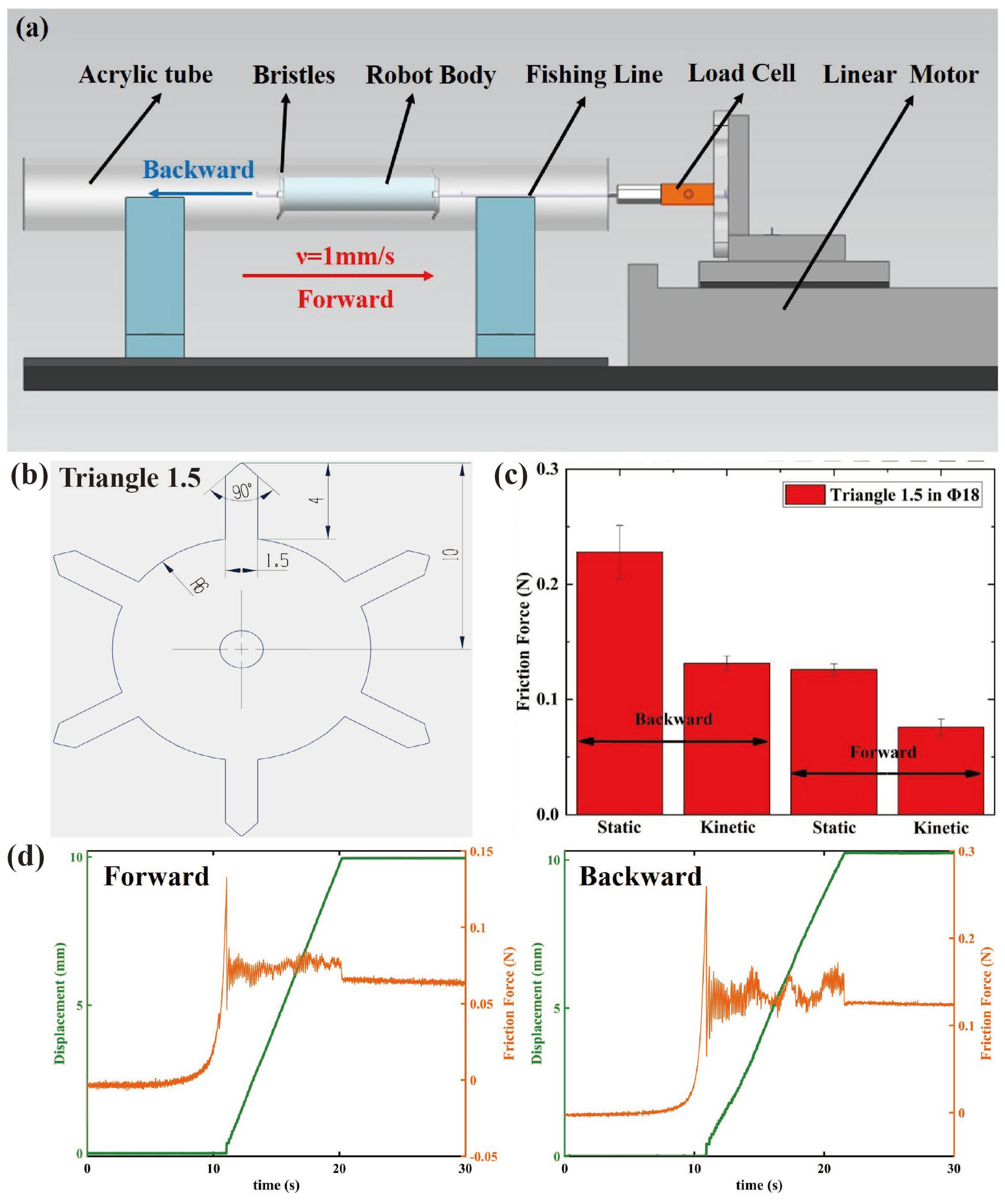
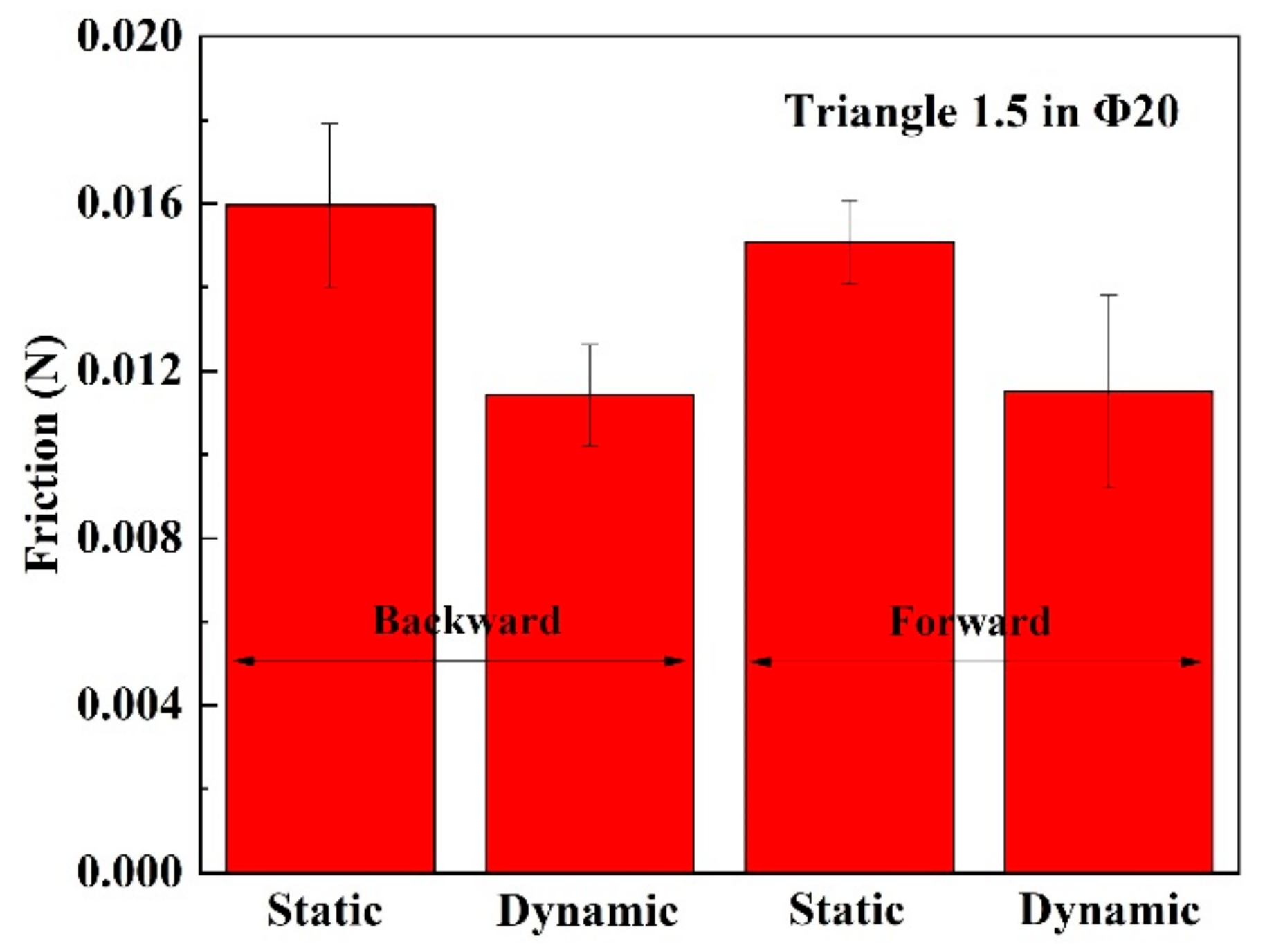
4. The Friction Test of Bristles
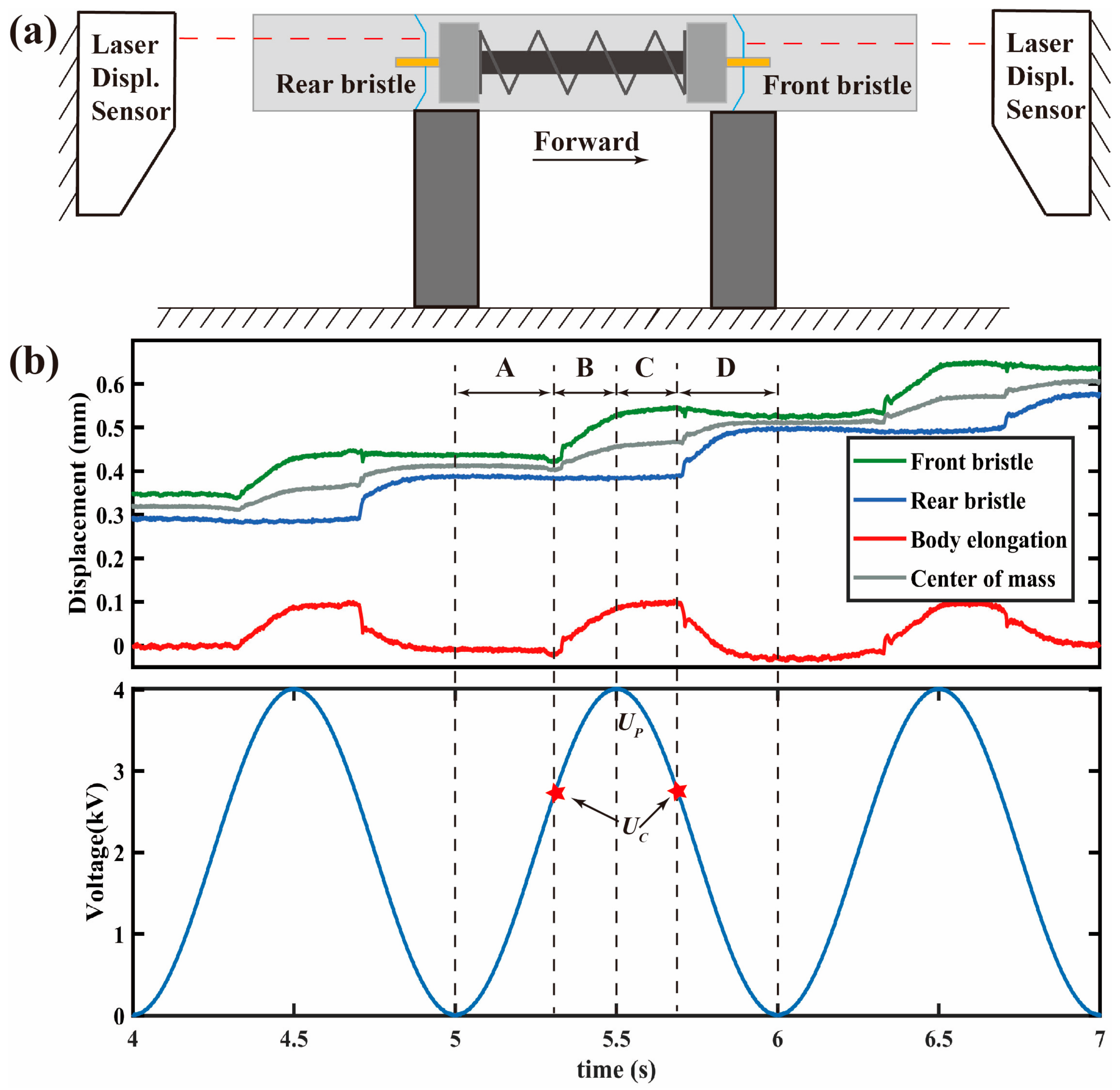
5. Performance Test of the Crawling Robot
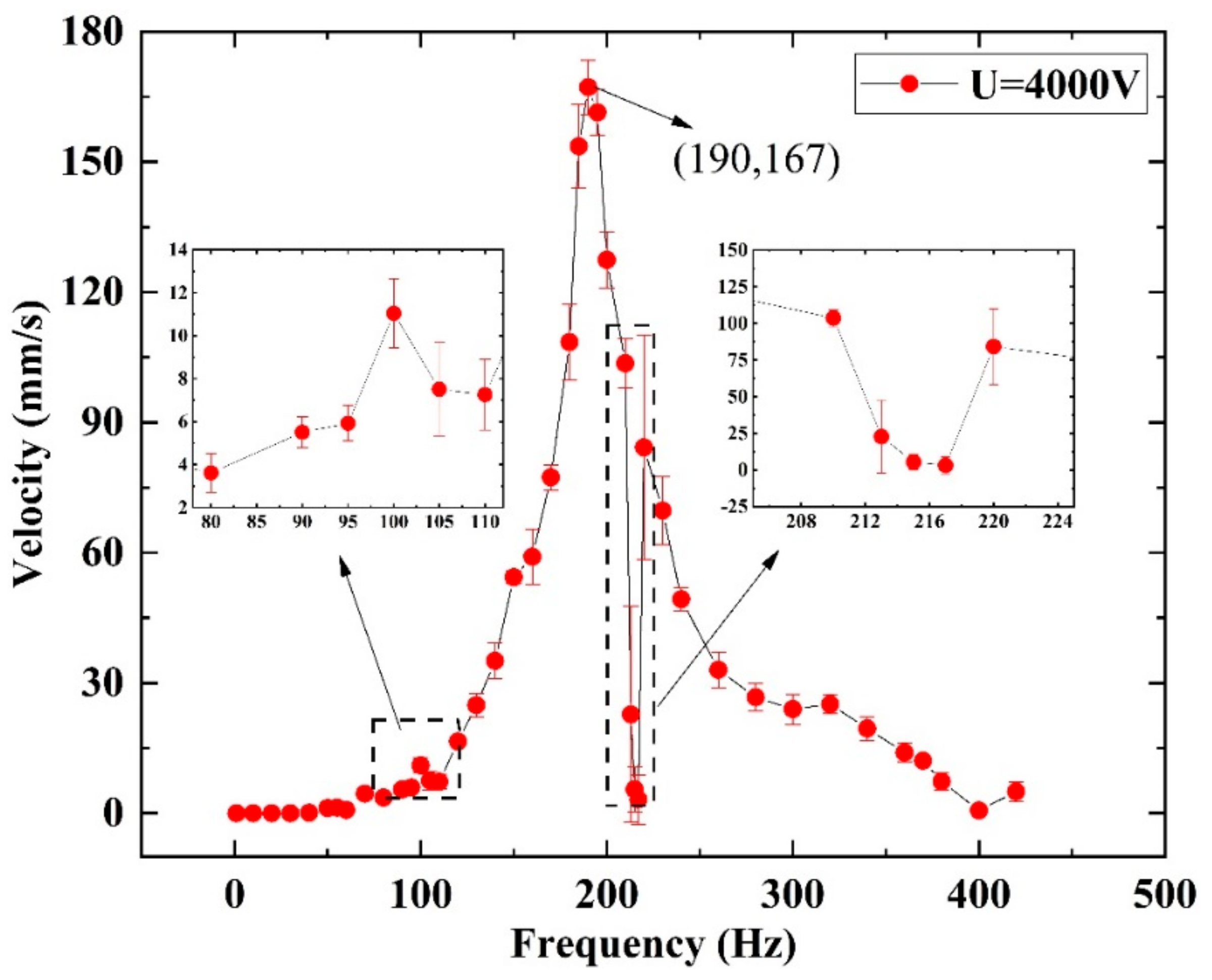
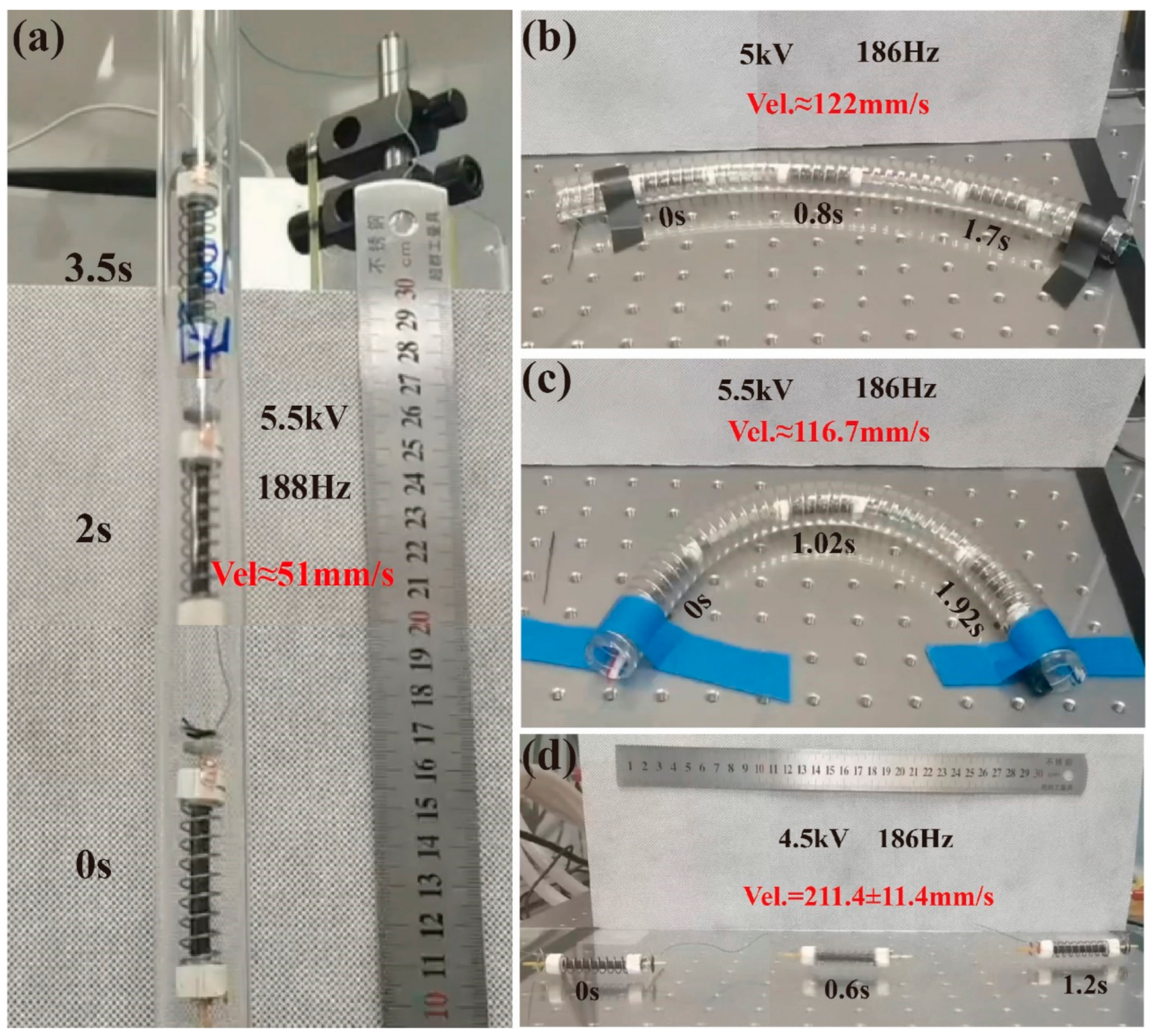
5.1. In Horizontal Acrylic Pipe with 18 mm Inner Diameter
5.2. In Horizontal Acrylic Pipe with 20 mm Inner Diameter
5.3. Further Study in Other Environments
6. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, C.; Yang, X.; Chen, W. Flexible Actuators for Soft Robotics. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2019, 2, 1900077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campbell, S. The Robotics Revolution Will Be Soft: Soft Robotics Proliferate-Along with Their Sources of Inspiration. IEEE Pulse 2018, 9, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafsanjani, A.; Zhang, Y.R.; Liu, B.Y.; Rubinstein, S.M.; Bertoldi, K. Kirigami skins make a simple soft actuator crawl. Sci. Robot. 2018, 3, eaar7555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seok, S.; Onal, C.D.; Cho, K.-J.; Wood, R.J.; Rus, D.; Kim, S. Meshworm: A Peristaltic Soft Robot With Antagonistic Nickel Titanium Coil Actuators. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2013, 18, 1485–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zou, Z.; Mao, G.; Yang, X.; Liang, Y.; Li, C.; Qu, S.; Suo, Z.; Yang, W. Agile and Resilient Insect-Scale Robot. Soft Robot. 2019, 6, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, A.T.; Hinitt, A.D.; Wang, P. Soft segmented inchworm robot with dielectric elastomer muscles. In Proceedings of the Electroactive Polymer Actuators and Devices (EAPAD); SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2014; p. 90562L. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.Y.; Liao, W.H. A Snake Robot Using Shape Memory Alloys. Int. Conf. Robot. Biomim. 2004, 6, 601–605. [Google Scholar]
- Onal, C.D.; Rus, D. Autonomous undulatory serpentine locomotion utilizing body dynamics of a fluidic soft robot. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2013, 8, 026003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calisti, M.; Giorelli, M.; Levy, G.; Mazzolai, B.; Hochner, B.; Laschi, C.; Dario, P. An octopus-bioinspired solution to movement and manipulation for soft robots. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2011, 6, 036002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Godage, I.S.; Nanayakkara, T.; Caldwell, D.G. Locomotion with Continuum Limbs. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vilamoura-Algarve, Portugal, 7–12 October 2012; pp. 293–298. [Google Scholar]
- Villanueva, A.; Smith, C.; Priya, S. A biomimetic robotic jellyfish (Robojelly) actuated by shape memory alloy composite actuators. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2011, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.; Srinivasa, A.R.; Reddy, J.N. Design of Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) Actuators; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Duduta, M.; Berlinger, F.; Nagpal, R.; Clarke, D.R.; Wood, R.J.; Temel, F.Z. Tunable Multi-Modal Locomotion in Soft Dielectric Elastomer Robots. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 3868–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, G.; Schiller, D.; Danninger, D.; Hailegnaw, B.; Hartmann, F.; Stockinger, T.; Drack, M.; Arnold, N.; Kaltenbrunner, M. Ultrafast small-scale soft electromagnetic robots. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, G.; Zou, J.; Zhao, R.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, X. Soft wall-climbing robots. Sci. Robot. 2018, 3, eaat2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Yamamoto, A. Analyses and Solutions for the Buckling of Thin and Flexible Electrostatic Inchworm Climbing Robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2017, 33, 889–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.K.; Wen, Z.J.; Sun, L.N. An in-pipe micro robot actuated by piezoelectric bimorphs. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2009, 54, 2134–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martel, S. Fundamental Principles and Issues of High-speed Piezoactuated Three-legged Motion for Miniature Robots Designed for Nanometer-scale Operations. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2016, 24, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.S.; Ainla, A.; Yang, D.; Harburg, D.; Whitesides, G.M. A Soft Tube-Climbing Robot. Soft Robot. 2018, 5, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Du, B.; Jiang, S.; Shao, Q.; Dong, X.; Liu, X.J.; Zhao, H. A pipeline inspection robot for navigating tubular environments in the sub-centimeter scale. Sci. Robot. 2022, 7, eabm8597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, H.; Mao, J.; Chirarattananon, P.; Helbling, E.F.; Hyun, N.P.; Clarke, D.R.; Wood, R.J. Controlled flight of a microrobot powered by soft artificial muscles. Nature 2019, 575, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, W.; Zou, H.; Peng, Z.; Meng, G. A Fast Rolling Soft Robot Driven by Dielectric Elastomer. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2018, 23, 1630–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-B.; Zhang, W.-M.; Zou, H.-X.; Peng, Z.-K.; Meng, G. Multisegment annular dielectric elastomer actuators for soft robots. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27, 115024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Atab, N.; Mishra, R.B.; Al-Modaf, F.; Joharji, L.; Alsharif, A.A.; Alamoudi, H.; Diaz, M.; Qaiser, N.; Hussain, M.M. Soft Actuators for Soft Robotic Applications: A Review. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 2000128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sideris, E.A.; de Lange, H.C. Pumps operated by solid-state electromechanical smart material actuators—A review. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 307, 111915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlrine, R.; Kornbluh, R.; Pei, Q.; Joseph, J. High-speed electrically actuated elastomers with strain greater than 100%. Science 2000, 287, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Chen, L.; Hill, T.L.; Wang, L.; Gao, X. Exploiting Bistability for High-Performance Dielectric Elastomer Resonators. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2022, 27, 5994–6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Gao, X.; Conn, A.T. A compliantly coupled dielectric elastomer actuator using magnetic repulsion. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 114, 011904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, C.J.; Hill, T.L.; Conn, A.T.; Li, B.; Gao, X. Nonlinear Dynamics of a Magnetically Coupled Dielectric Elastomer Actuator. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2019, 12, 044033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.; Cao, C.J.; Guo, J.L.; Conn, A. Elastic Electroadhesion with Rapid Release by Integrated Resonant Vibration. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chi, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Hong, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yin, J. Bistable and Multistable Actuators for Soft Robots: Structures, Materials, and Functionalities. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2110384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digumarti, K.M.; Cao, C.; Guo, J.; Conn, A.T.; Rossiter, J. Multi-Directional Crawling Robot with Soft Actuators and Electroadhesive Grippers. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), Livorno, Italy, 24–28 April 2018; pp. 303–308. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.; Li, B.; Fang, H.; Li, Z.; Chen, H. A speedy, amphibian, robotic cube: Resonance actuation by a dielectric elastomer. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 270, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Diteesawat, R.S.; Rossiter, J.; Conn, A.T. A Reconfigurable Crawling Robot Driven by Electroactive Artificial Muscle. In Proceedings of the 2019 2nd IEEE International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 14–18 April 2019; pp. 840–845. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, K.; Koo, J.C.; Nam, J.D.; Lee, Y.K.; Choi, H.R. Artificial annelid robot driven by soft actuators. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2007, 2, S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pei, Q.; Rosenthal, M.; Stanford, S.; Prahlad, H.; Pelrine, R. Multiple-degrees-of-freedom electroelastomer roll actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2004, 13, N86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Liu, F.; Ma, Z.; Li, C.; Zhou, J. Soft mobile robots driven by foldable dielectric elastomer actuators. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 120, 084901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, X.; Liu, X.; Cacucciolo, V.; Imboden, M.; Civet, Y.; El Haitami, A.; Cantin, S.; Perriard, Y.; Shea, H. An autonomous untethered fast soft robotic insect driven by low-voltage dielectric elastomer actuators. Sci. Robot. 2019, 4, eaaz6451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Gu, H. A Bristle-Based Pipeline Robot for Ill-Constraint Pipes. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2008, 13, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, X.-T.; Calderon, A.A.; Rigo, A.; Ge, J.Z.; Perez-Arancibia, N.O. SMALLBug: A 30-mg Crawling Robot Driven by a High-Frequency Flexible SMA Microactuator. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 6796–6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunze, J.; Prechtl, J.; Bruch, D.; Fasolt, B.; Nalbach, S.; Motzki, P.; Seelecke, S.; Rizzello, G. Design, Manufacturing, and Characterization of Thin, Core-Free, Rolled Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. Actuators 2021, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.C.; Hussain, A.M.; Duduta, M.; Vogt, D.M.; Wood, R.J.; Clarke, D.R. Compact Dielectric Elastomer Linear Actuators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1804328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Hill, T.L.; Conn, A.T. On the nonlinear dynamics of a circular dielectric elastomer oscillator. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 075020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Chen, L.; Duan, W.; Hill, T.L.; Li, B.; Chen, G.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Gao, X. On the mechanical power output comparisons of cone dielectric elastomer actuators. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2021, 26, 3151–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Composite | C Powder | RT625 | Ecoflex 0030 | Isopropanol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (wt. %) | 3.1% | 41% | 6.2% | 49.7% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, Y.; Wu, X.; Xue, J.; Chen, X.; Cao, C.; Gao, X. A Soft Robot Driven by a Spring-Rolling Dielectric Elastomer Actuator with Two Bristles. Micromachines 2023, 14, 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14030618
Du Y, Wu X, Xue J, Chen X, Cao C, Gao X. A Soft Robot Driven by a Spring-Rolling Dielectric Elastomer Actuator with Two Bristles. Micromachines. 2023; 14(3):618. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14030618
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Yangyang, Xiaojun Wu, Jiasheng Xue, Xingyu Chen, Chongjing Cao, and Xing Gao. 2023. "A Soft Robot Driven by a Spring-Rolling Dielectric Elastomer Actuator with Two Bristles" Micromachines 14, no. 3: 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14030618








