Amine-Impregnated Dendritic Mesoporous Silica for the Adsorption of Formaldehyde
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Dendritic Mesoporous Silica (DMS)
2.3. SBA-15 (Santa Barbara Amorphous, SBA-15)
2.4. Amine Impregnation Method
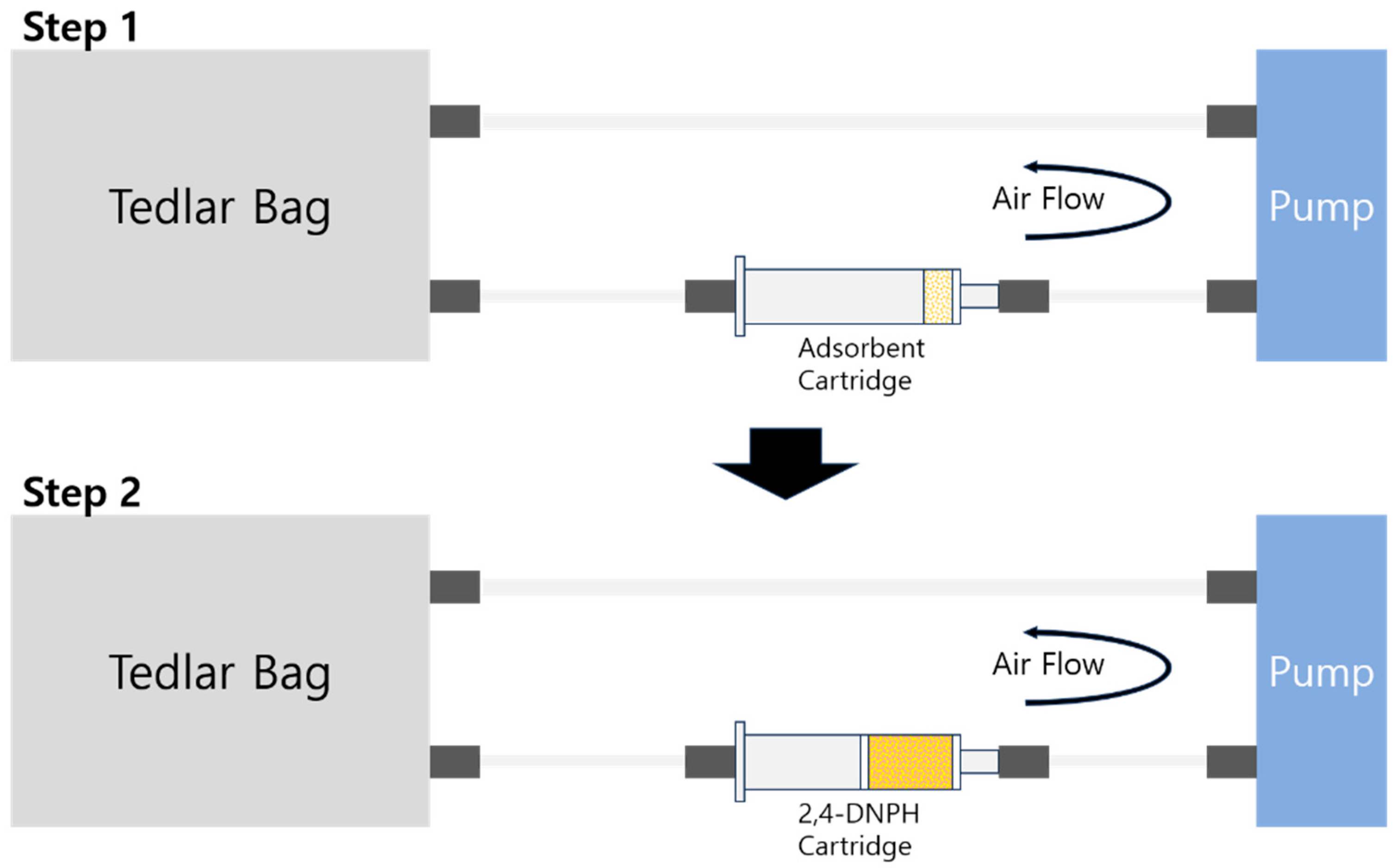
2.5. Formaldehyde Adsorption
2.6. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. WHO Guidelines for Indoor Air Quality: Selected Pollutants; WHO Regional Office for Europe: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010; pp. 103–142. ISBN 978-92-890-0213-4. [Google Scholar]
- Soman, A.; Qiu, Y.; Chan Li, Q. HPLC-UV Method Development and Validation for the Determination of Low Level Formaldehyde in a Drug Substance. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2008, 46, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, B.; Kucukoglu, K.; Asci, A.; Albayrak, M. Determination of formaldehyde in human tissue through derivatization with 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine by square wave polarography method. Int. J. Adv. Chem. Eng. Biol. Sci. 2016, 3, 4–9. [Google Scholar]
- EPA. Compendium of Methods for the Determination of Toxic Organic Compounds in Ambient Air; Compendium Method TO-11A; EPA Office of Research and Development: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1999.
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. NIOSH, Manual of Analytical Methods; Formaldehyde: Method 2016, Issue 2; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, Division of Physical Sciences and Engineering: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1994; pp. 1–7. ISBN 978-01-6045-338-0.
- Lee, K.J.; Miyawaki, J.; Shiratori, N.; Yoon, S.-H.; Jang, J. Toward an effective adsorbent for polar pollutants: Formaldehyde adsorption by activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 260, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahed, M.; Jafari, D.; Esfandyari, M. Adsorption of formaldehyde from aqueous solution using activated carbon prepared from Hibiscus rosa-sinensis. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 102, 2979–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Study on the correlation between pore morphology of porous calcium silicate and high-capacity formaldehyde adsorption. Environ. Technol. 2021, 42, 2021–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wen, B.; Fan, B.; Zhang, H. Study on adsorption mechanism of silicate adsorbents with different morphologies and pore structures towards formaldehyde in water. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 599, 124887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portela, R.; Jansson, I.; Suárez, S.; Villarroel, M.; Sánchez, B.; Avila, P. Natural silicate-TiO2 hybrids for photocatalytic oxidation of formaldehyde in gas phase. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 310, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Wang, L.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xu, S.; Dong, X.; Gao, X.; Ma, R.; Meng, X.; Xiao, F.-S. Hydrophobic Zeolite Containing Titania Particles as Wettability-Selective Catalyst for Formaldehyde Removal. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 5250–5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellat, J.-P.; Weber, G.; Bezverkhyy, I.; Lamonier, J.-F. Selective adsorption of formaldehyde and water vapors in NaY and NaX zeolites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 288, 109563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, C.-J.; Yoo, M.-J.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, K.-H. High-performance materials for effective sorptive removal of formaldehyde in air. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 366, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Lee, J.-T.; Bae, J.Y. Facile Mesoporous Hollow Silica Synthesis for Formaldehyde Adsorption. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, V.; Panda, D.; Singh, S.K. Direct Air Capture of CO2 over Amine-Modified Hierarchical Silica. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 3800–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Gong, Y.; Sun, Y. Amine-impregnated polymeric resin with high CO2 adsorption capacity for biogas upgrading. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.T.; Sakwa-Novak, M.A.; Pang, S.H.; Sujan, A.R.; Ping, E.W.; Jones, C.W. Aminopolymer-Impregnated Hierarchical Silica Structures: Unexpected Equivalent CO2 Uptake under Simulated Air Capture and Flue Gas Capture Conditions. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 5229–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, S.; Su, H.; Li, D.; Gu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Wang, S.; Wang, S. Low-cost preferential different amine grafted silica spheres adsorbents for DAC CO2 removal. J. Energy Chem. 2022, 75, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.; Chejanovsky, I.; Suckeveriene, R.Y. Grafting of Poly(ethylene imine) to Silica Nanoparticles for Odor Removal from Recycled Materials. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almomen, A.; El-Toni, A.M.; Badran, M.; Alhowyan, A.; Abul Kalam, M.; Alshamsan, A.; Alkholief, M. The Design of Anionic Surfactant-Based Amino-Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles and their Application in Transdermal Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafqat, S.S.; Khan, A.A.; Zafar, M.N.; Alhaji, M.H.; Sanaullah, K.; Shafqat, S.R.; Murtaza, S.; Pang, S.C. Development of amino-functionalized silica nanoparticles for efficient and rapid removal of COD from pre-treated palm oil effluent. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoi, T.; Yoshitake, H.; Yamada, T.; Kubota, Y.; Tatsumi, T. Amino-functionalized mesoporous silica synthesized by an anionic surfactant templating route. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 1125–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, L.; Li, S.; Liu, C.; He, H. The Capture and Catalytic Conversion of CO2 by Dendritic Mesoporous Silica-Based Nanoparticles. Energy Environ. Mater. 2023, e12593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, S.; Row, K.H.; Ahn, W.-S. Amine–silica composites for CO2 capture: A short review. J. Energy Chem. 2017, 26, 868–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Na, J.; Konarova, M.; Wakihara, T.; Yamauchi, Y.; Salomon, C.; Gawande, M.B. Functional Mesoporous Silica Nanomaterials for Catalysis and Environmental Applications. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2020, 93, 1459–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Shen, D.; Luo, K.H. A critical review on VOCs adsorption by different porous materials: Species, mechanisms and modification methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 122102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardakhti, M.; Jafari, T.; Tobin, Z.; Dutta, B.; Moharreri, E.; Shemshaki, N.S.; Suib, S.; Srivastava, R. Trends in Solid Adsorbent Materials Development for CO2 Capture. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 34533–34559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borcănescu, S.; Popa, A.; Verdeș, O.; Suba, M. Functionalized Ordered Mesoporous MCM-48 Silica: Synthesis, Characterization and Adsorbent for CO2 Capture. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajumobi, O.; Wang, B.; Farinmade, A.; He, J.; Valla, J.A.; John, V.T. Design of Nanostraws in Amine-Functionalized MCM-41 for Improved Adsorption Capacity in Carbon Capture. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 12079–12088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Ye, Q.; Wang, L.; Meng, F.; Dai, H. Polyethyleneimine-modified layered double hydroxide/SBA-15 composites: A novel kind of highly efficient CO2 adsorbents. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 229, 106660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, Q.; Chen, L.; Fan, W.; Liu, Y.; He, X.; Dan, H.; Zhu, L.; Ding, Y.; Duan, T. Facile synthesis of novel Bi0-SBA-15 adsorbents by an improved impregnation reduction method for highly efficient capture of iodine gas. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Pang, J.; Liu, Z. Dendritic Mesoporous Silica Nanospheres: Toward the Ultimate Minimum Particle Size for Ultraefficient Liquid Chromatographic Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 22970–22977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, P.; Peng, B.; Shan, B.-Q.; Yang, T.-Q.; Zhang, K. Comprehensive understanding of the synthesis and formation mechanism of dendritic mesoporous silica nanospheres. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 1792–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Qiao, S.Z. Dendritic Silica Particles with Center-Radial Pore Channels: Promising Platforms for Catalysis and Biomedical Applications. Small 2015, 11, 392–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, V.; Sharma, S. An overview of ordered mesoporous material SBA-15: Synthesis, functionalization and application in oxidation reactions. J. Porous Mater. 2017, 24, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Cao, J.; Xia, Y.; Zhao, L. Improvement of adsorbent materials for CO2 capture by amine functionalized mesoporous silica with worm-hole framework structure. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 306, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Huo, Q.; Feng, J.; Chmelka, B.F.; Stucky, G.D. Nonionic Triblock and Star Diblock Copolymer and Oligomeric Surfactant Syntheses of Highly Ordered, Hydrothermally Stable, Mesoporous Silica Structures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 6024–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.H.; Fu, C.-C.; Chen, Z.-H.; Tran, T.T.V.; Liu, S.-H.; Juang, R.-S. Enhanced and selective adsorption of urea and creatinine on amine-functionalized mesoporous silica SBA-15 via hydrogen bonding. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 311, 110733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhao, P.; Hao, L.; Xu, Y. Amine-modified SBA-15(P): A promising adsorbent for CO2 capture. J. CO2 Util. 2018, 24, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashtian, K.; Zare-Dorabei, R. Synthesis and characterization of functionalized mesoprous SBA-15 decorated with Fe3O4 nanoparticles for removal of Ce(III) ions from aqueous solution: ICP–OES detection and central composite design optimization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 494, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, X.; Cai, W.; Chen, A. Preparation of three-dimensional dendritic-like mesoporous silica particles and their pore size-dependent polishing behavior and mechanism. J. Porous Mater. 2019, 26, 1869–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirra, S.; Siliveri, S.; Adepu, A.K.; Goskula, S.; Gujjula, S.R.; Narayanan, V. Pd-KIT-6: Synthesis of a novel three-dimensional mesoporous catalyst and studies on its enhanced catalytic applications. J. Porous Mater. 2019, 26, 1667–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Liu, M. Preparation of mesoporous yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) and YSZ–NiO using a triblock copolymer as surfactant. J. Mater. Chem. 2000, 10, 2603–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Z.; Bae, J.Y.; Kevan, L. Photoionization of N-alkylphenothiazines in titanosilicate mesoporous TiSBA-15 molecular sieves. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2001, 48, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Z.; Bae, J.Y.; Kevan, L. Vanadosilicate mesoporous SBA-15 molecular sieves incorporated with N-alkylphenothiazines. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 3202–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musić, S.; Filipović-Vinceković, N.; Sekovanić, L. Precipitation of amorphous SiO2 particles and their properties. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 28, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, K.; Bein, T. Talented Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B. Organic Nitrogen Compounds, Part I: Introduction. Spectroscopy 2019, 34, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, B.C. Organic nitrogen compounds II: Primary amines. Spectroscopy 2019, 34, 22–25. [Google Scholar]








| Adsorbent | Substrate | Amount of the Impregnated TEPA (g/1 g of Substrate) | After Impregnation (TEPA + Substrate, g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DMS | Dendritic mesoporous silica | 0 | 1 |
| DAI-0.5 g | 0.5 | 1.49 | |
| DAI-1.5 g | 1.5 | 2.49 | |
| DAI-2.5 g | 2.5 | 3.46 | |
| SBA-15 | SBA-15 | 0 | 1 |
| SAI-0.5 g | 0.5 | 1.5 | |
| SAI-1.5 | 1.5 | 2.47 |
| Multipoint BET (m2/g) | Total Pore Volume (cc/g) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DMS | 544.90 | 2.23 | 17.00 |
| SBA-15 | 624.98 | 0.91 | 6.41 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.M.; Kang, M.; Kim, J.-S.; Bae, J.Y. Amine-Impregnated Dendritic Mesoporous Silica for the Adsorption of Formaldehyde. Micromachines 2024, 15, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15010030
Lee JM, Kang M, Kim J-S, Bae JY. Amine-Impregnated Dendritic Mesoporous Silica for the Adsorption of Formaldehyde. Micromachines. 2024; 15(1):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15010030
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Ji Myeong, Misun Kang, June-Seo Kim, and Jae Young Bae. 2024. "Amine-Impregnated Dendritic Mesoporous Silica for the Adsorption of Formaldehyde" Micromachines 15, no. 1: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15010030
APA StyleLee, J. M., Kang, M., Kim, J.-S., & Bae, J. Y. (2024). Amine-Impregnated Dendritic Mesoporous Silica for the Adsorption of Formaldehyde. Micromachines, 15(1), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15010030







