Determination of the Minimum Uncut Chip Thickness of Ti-6Al-4V Titanium Alloy Based on Dead Metal Zone
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Simulations
2.1. Numerical Simulation Condition Setting
2.2. Material Properties and Intrinsic Modeling
2.3. Tool–Workpiece Friction Model
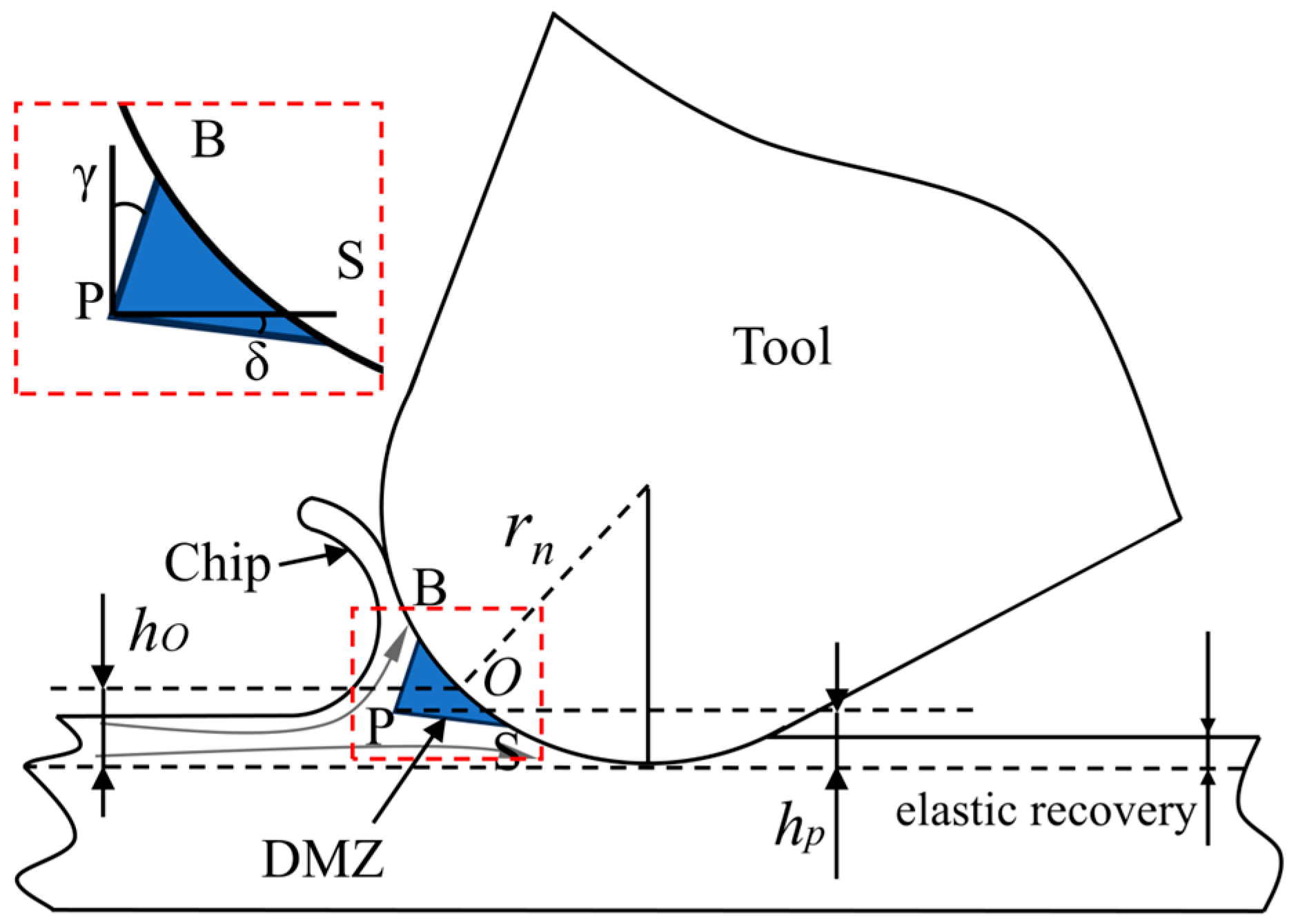
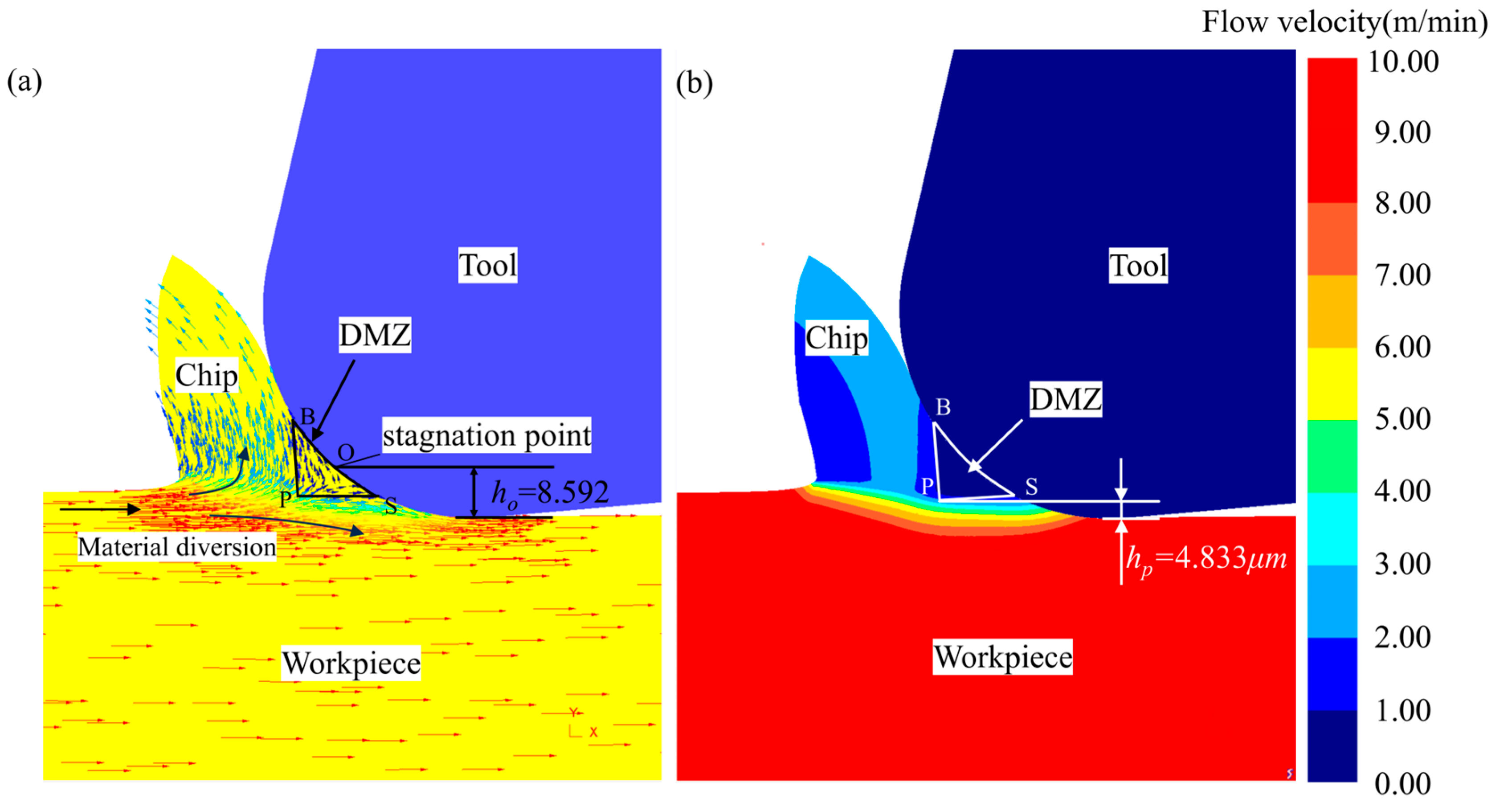
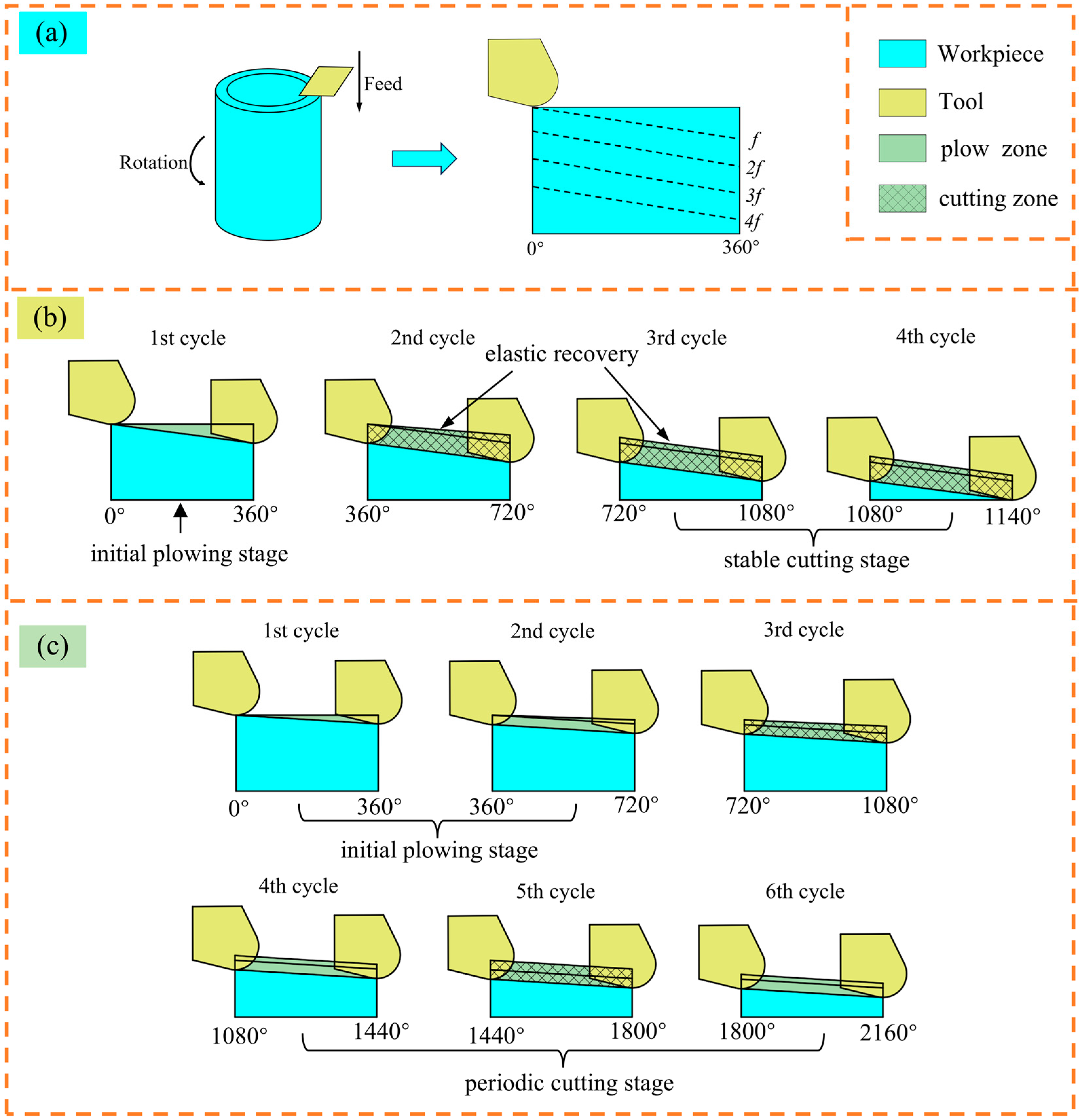
2.4. DMZ and MUCT Analysis
3. Experiment Validation
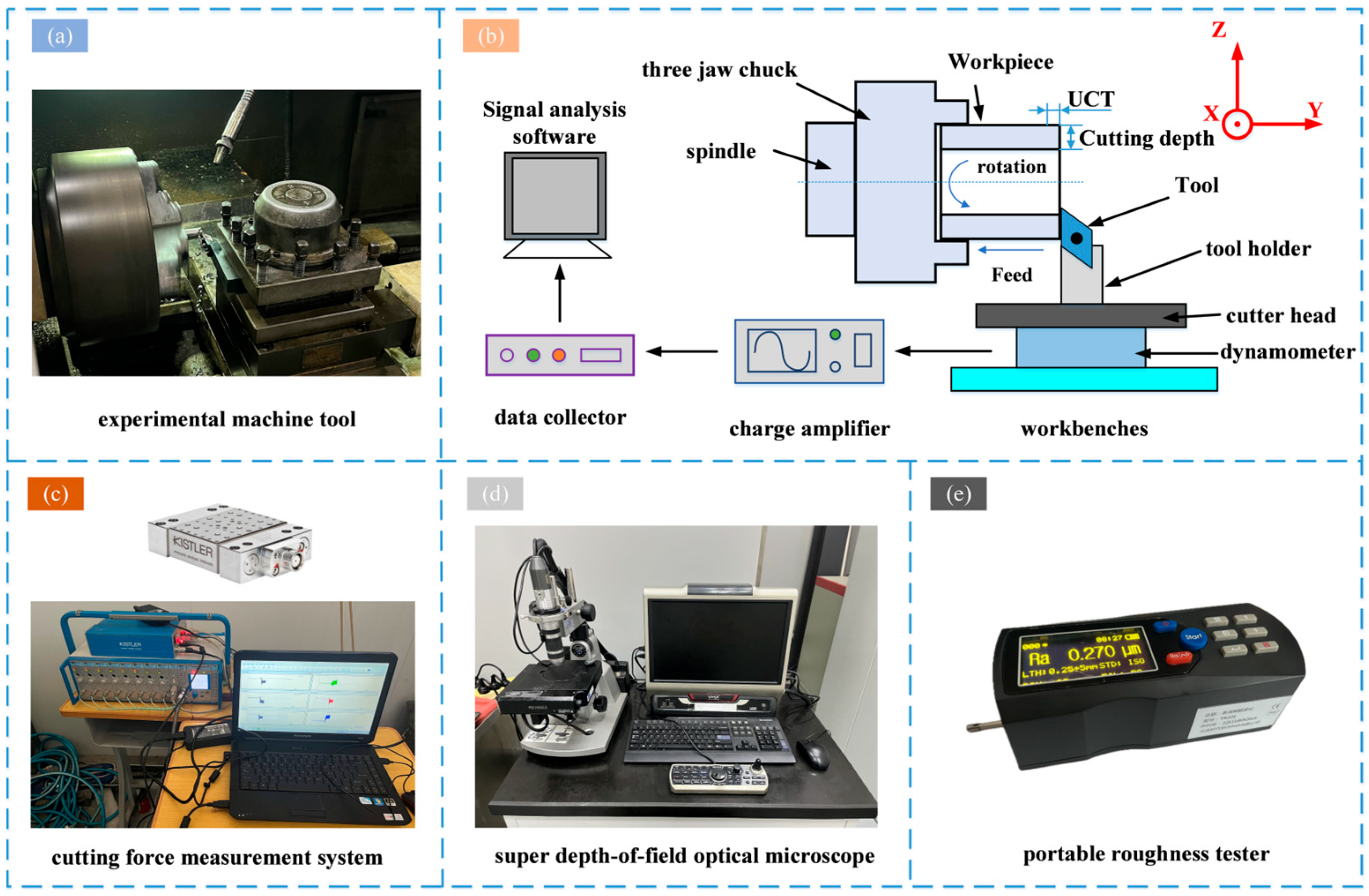
3.1. Experimental Setup
3.2. Comparative Analysis of Cutting Forces
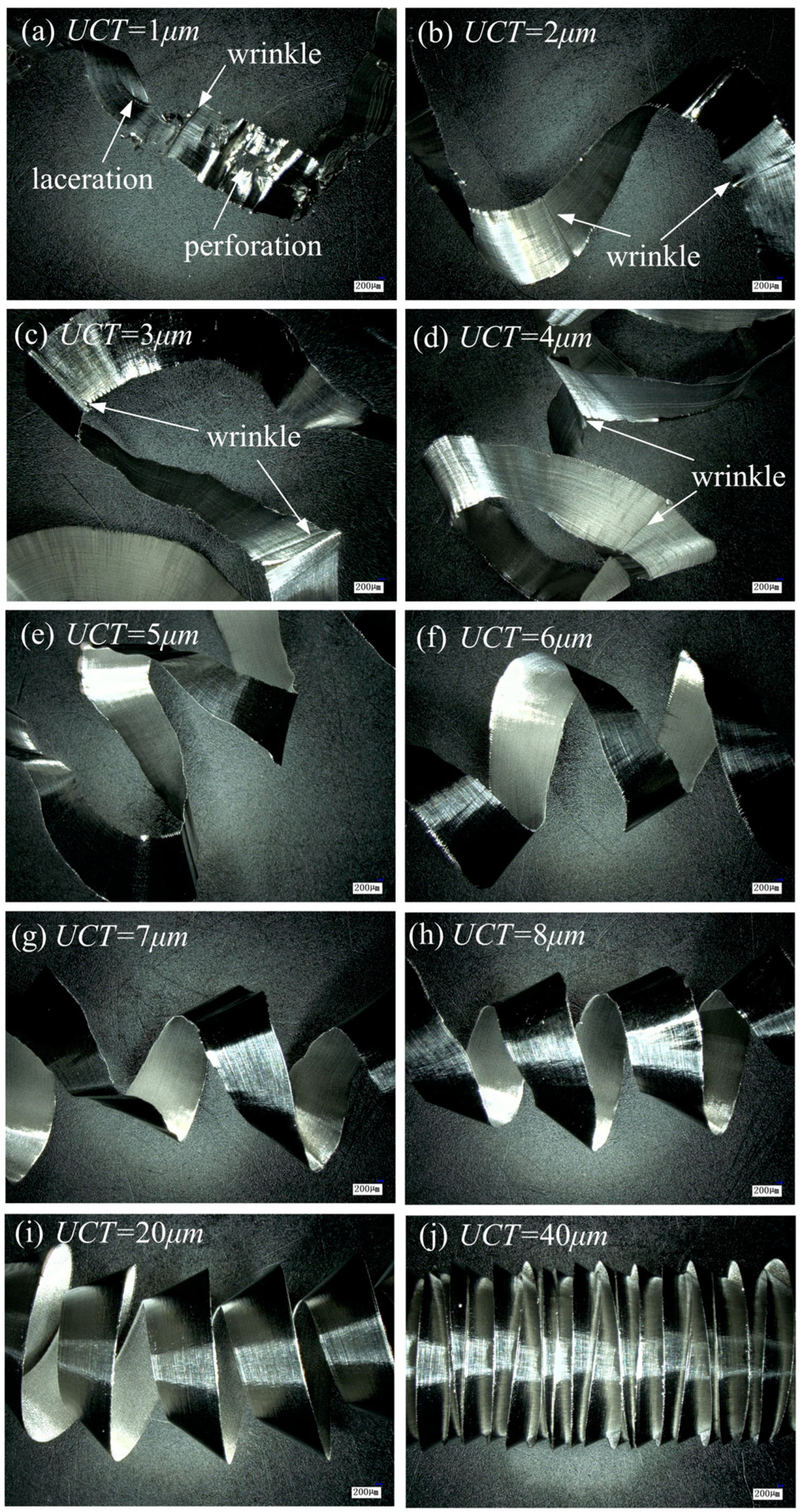
3.3. Chip-Based MUCT Analysis
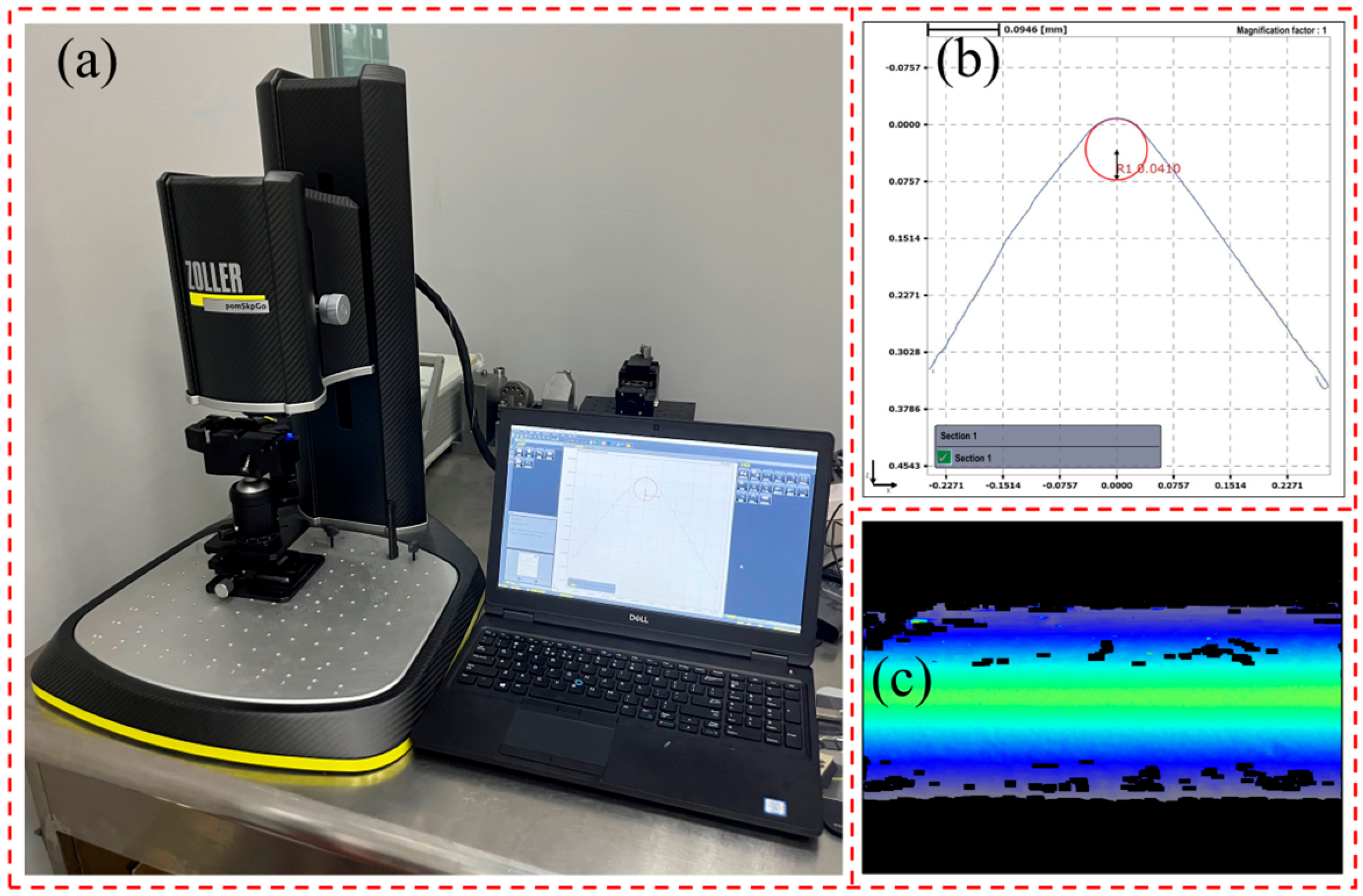
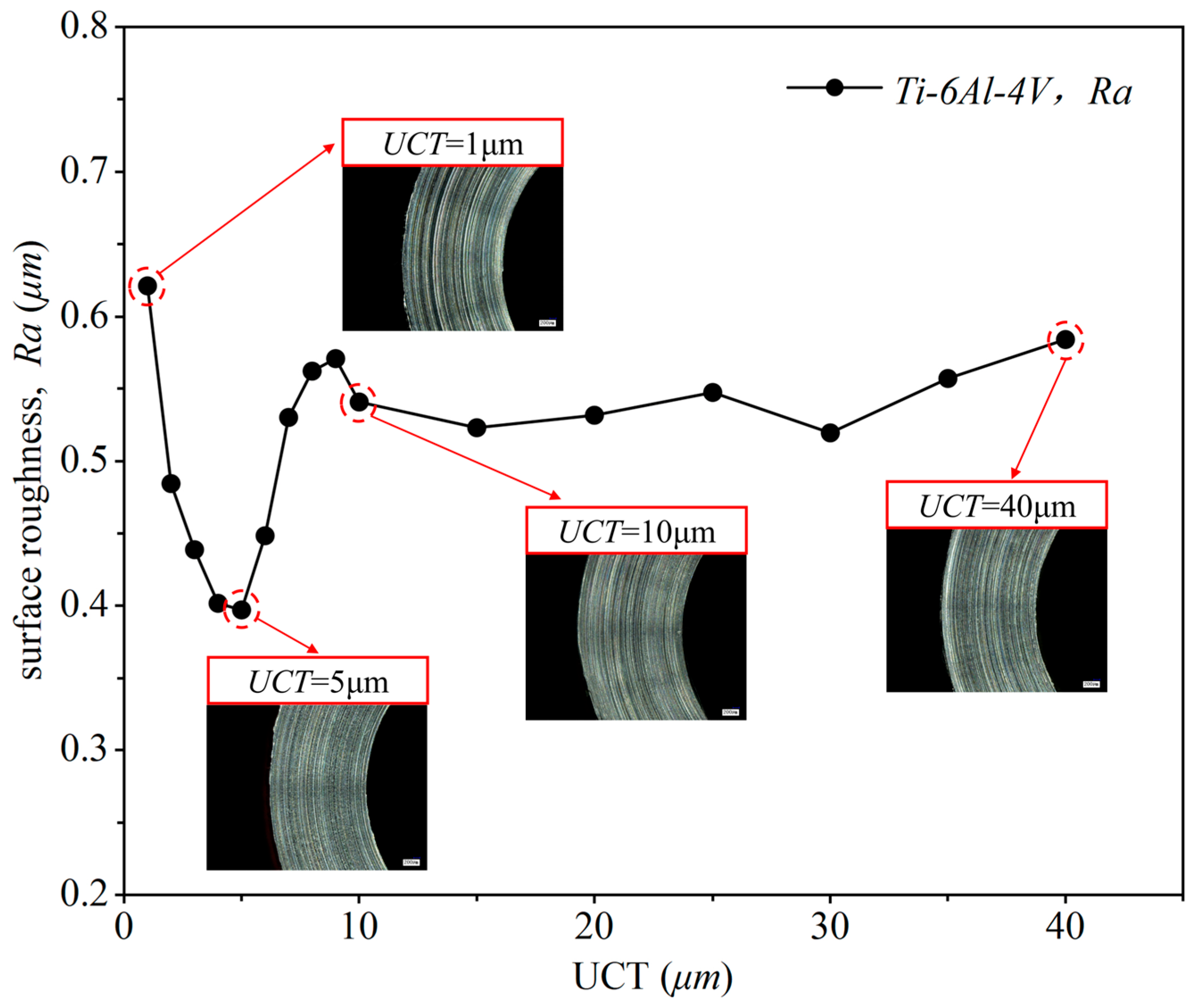
3.4. MUCT Analysis Based on Surface Quality
4. Results and Discussion
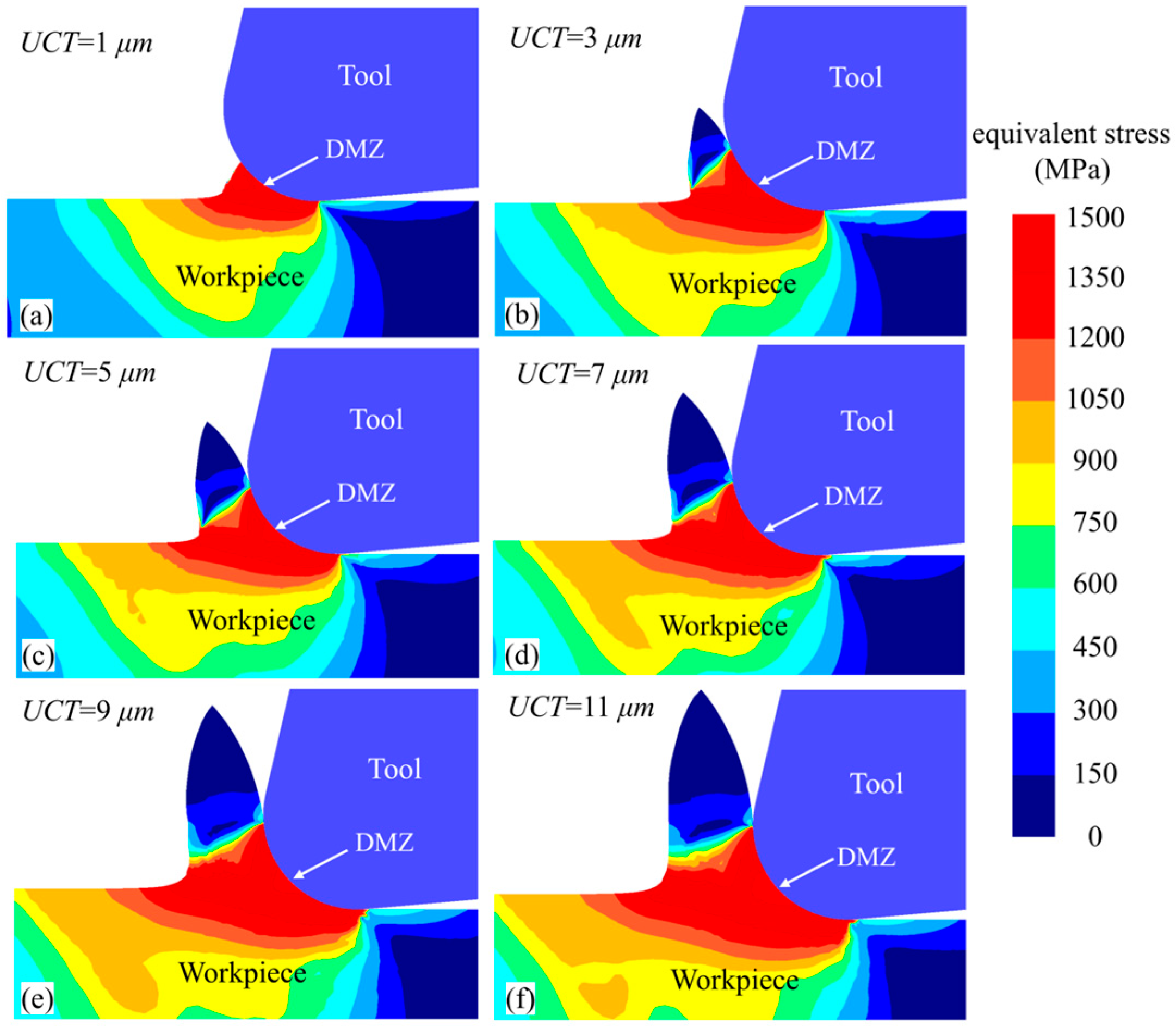
4.1. Effect of UCT on Equivalent Stress and Equivalent Strain Rate
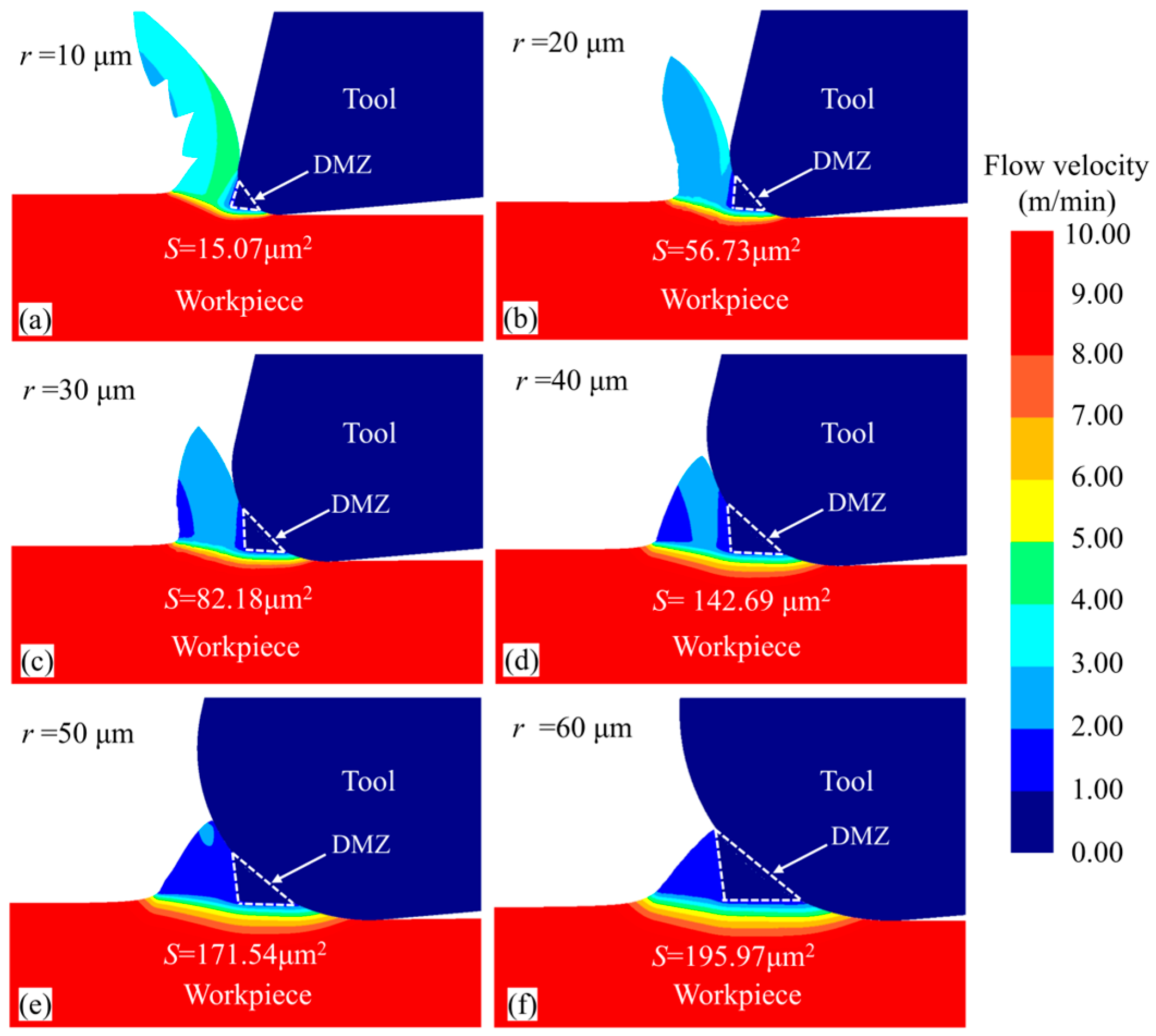
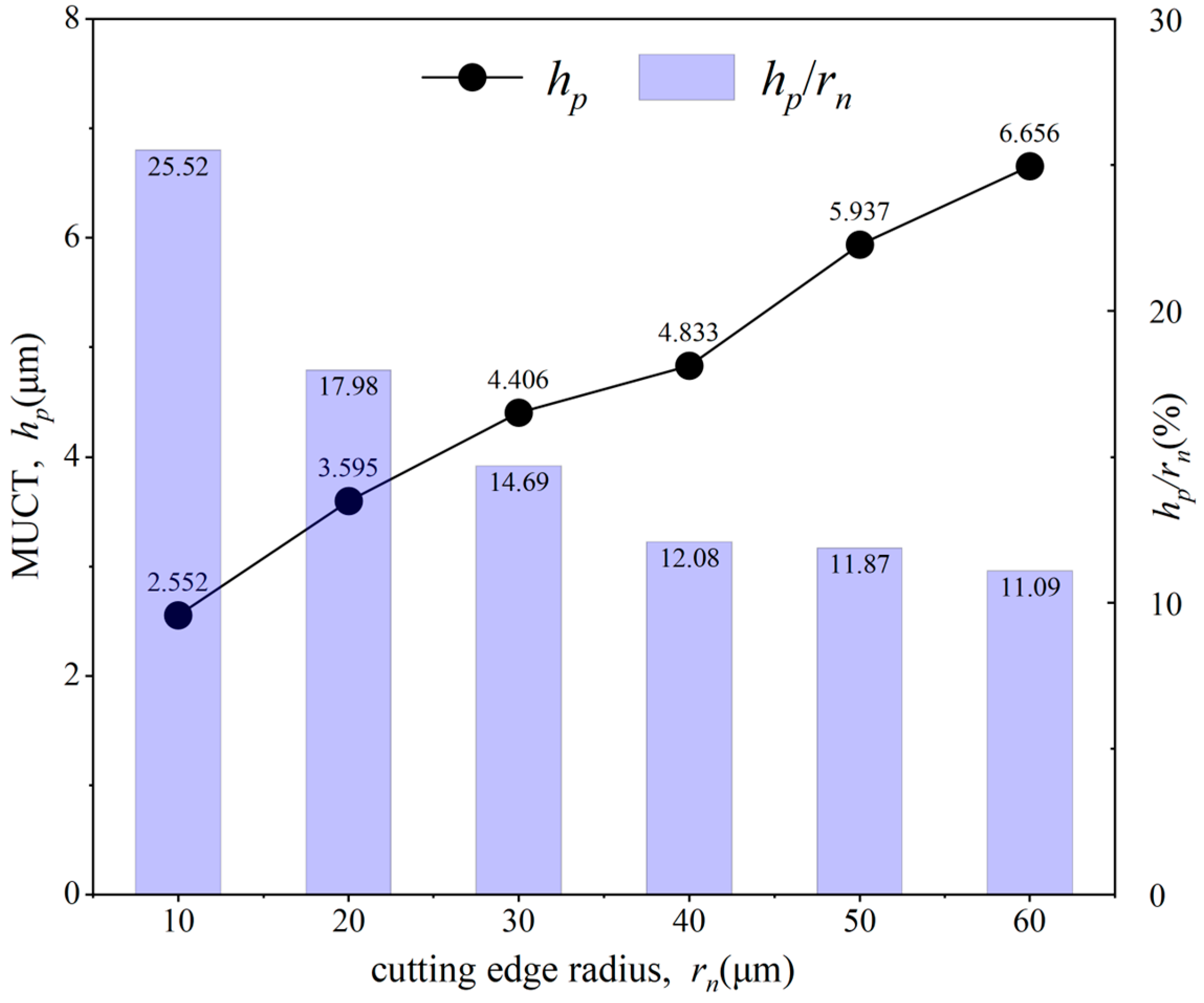
4.2. Effect of Tool Cutting Edge Radius on MUCT
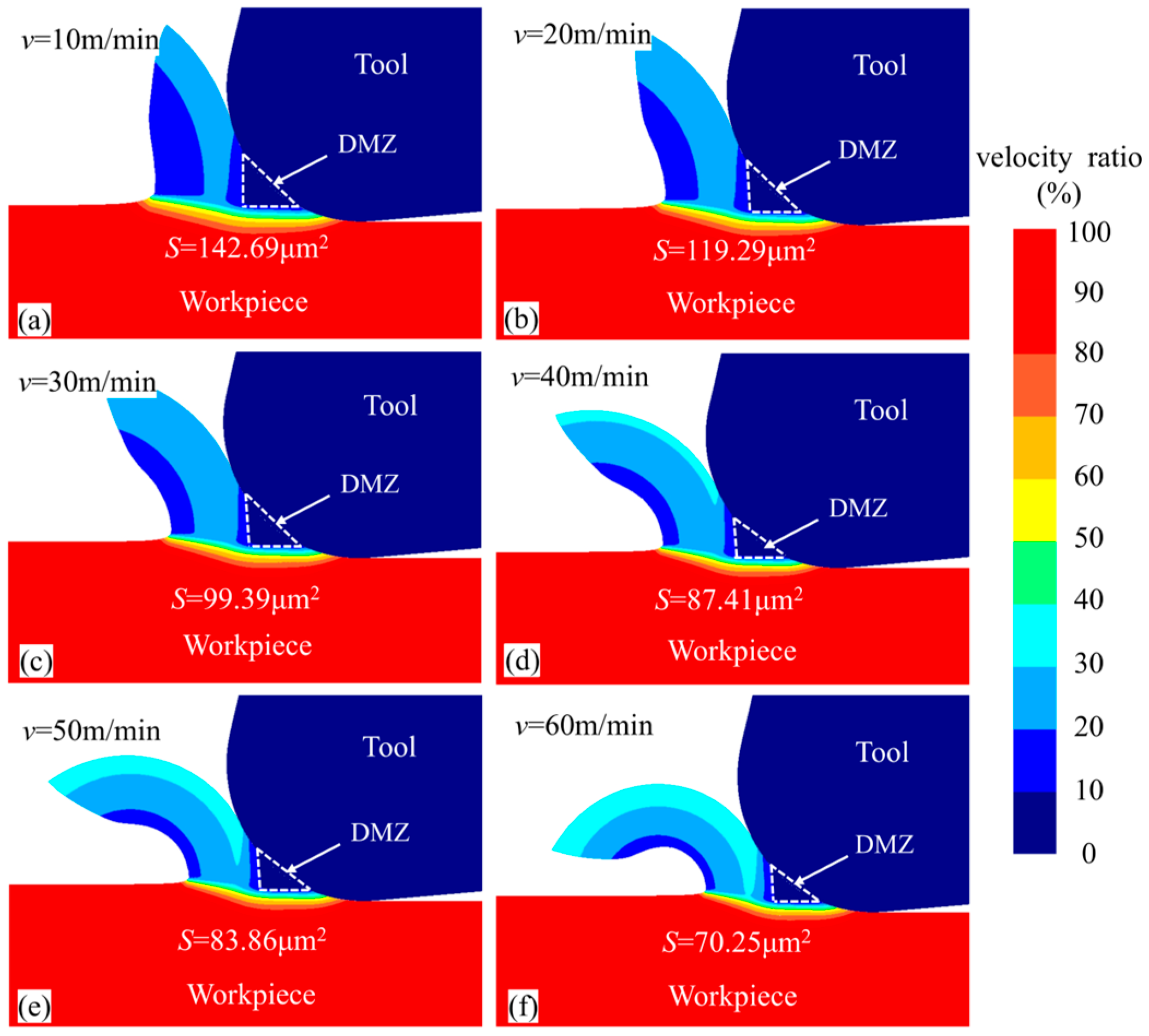
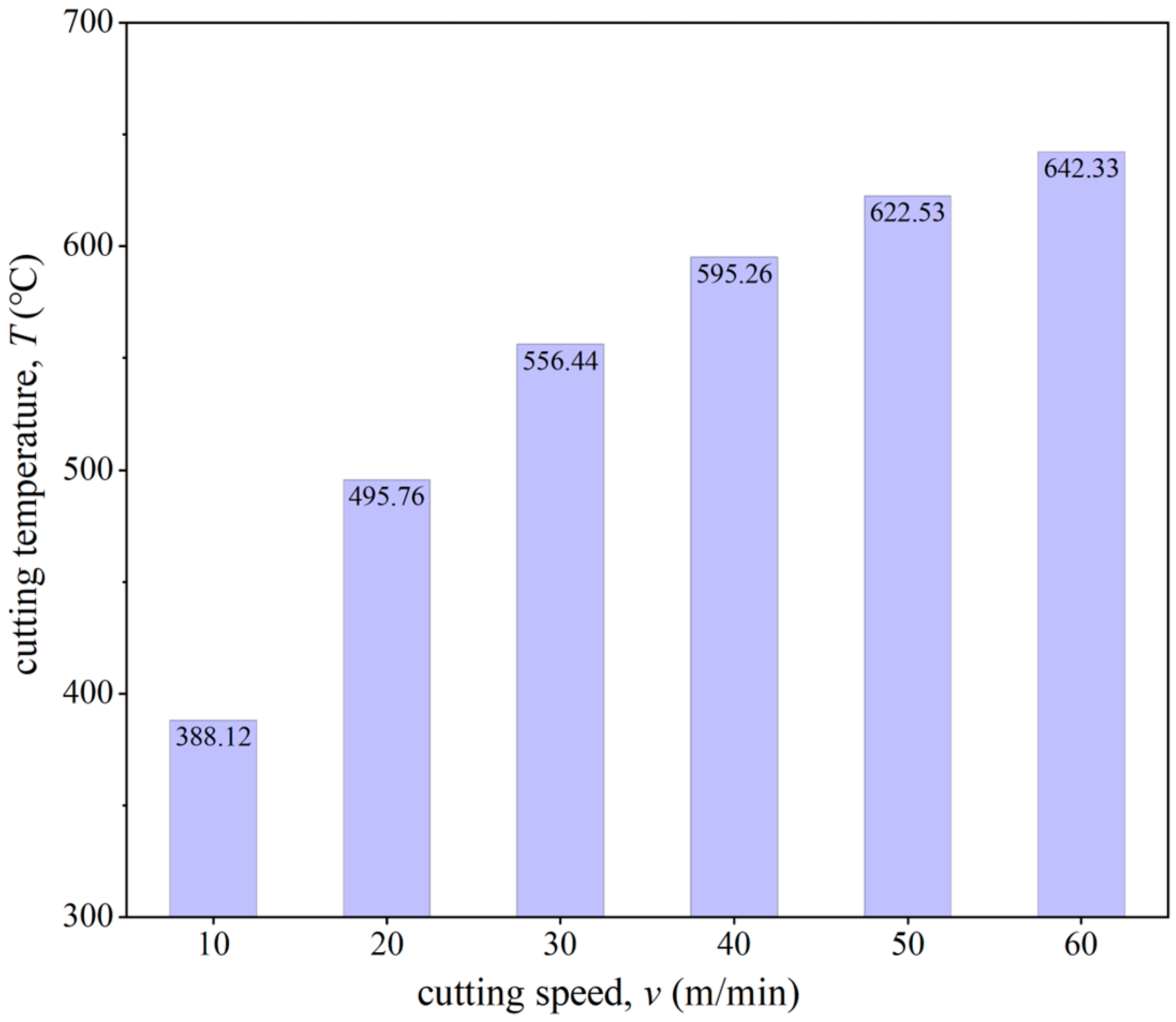
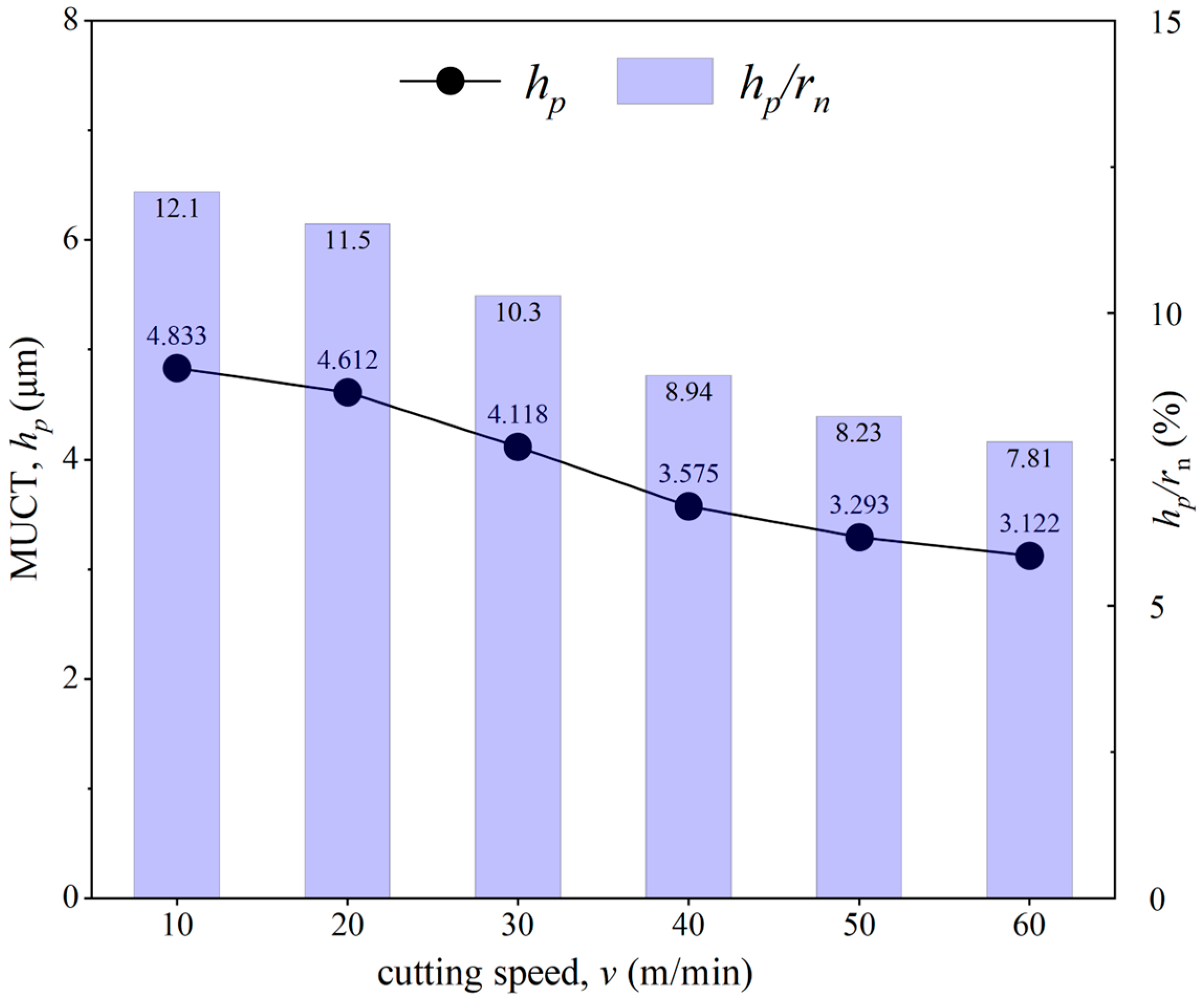
4.3. Effect of Cutting Speed on MUCT
5. Conclusions
- The proposed method of determining the MUCT by DMZ is reliable. The simulation results are in good agreement with the experimental results, and the relative error of cutting force ranges from 2.16% to 10.59%, and the relative error of the MUCT is about 3.34%.
- The equivalent stress and equivalent strain rate at the DMZ boundary are both high, which can be regarded as the boundary of the micro-cutting plastic deformation zone. The UCT only affects the formation speed of the DMZ, with minimal impact on the position and geometry of the DMZ.
- The tool cutting edge radius significantly influences both the DMZ and MUCT. As the tool cutting edge radius increases, the DMZ area and MUCT increase as well. Furthermore, the hp/rn value varies with the tool’s cutting edge radius rather than remaining constant, decreasing as the cutting edge radius increases.
- Cutting speed has a certain impact on the MUCT; as the cutting speed increases, the temperature in the cutting deformation zone rises, leading to a decrease in both the MUCT and hp/rn.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nan, H.; Xie, C.M.; Zhao, J.Q. Development and application of titanium alloy casting technology in China. China Foundry 2005, 2, 239–245. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Kong, B.; Wei, S.; Zang, J.; Li, A. Simulation Study on Residual Stress Distribution of Machined Surface Layer in Two-Step Cutting of Titanium Alloy. Materials 2024, 17, 4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohara, J.; Fang, F.Z. Advances in micro cutting tool design and fabrication. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2019, 1, 032003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Schmittdiel, M.C.; Degertekin, F.L.; Kurfess, T.R. Scanning Grating Microinterferometer for MEMS Metrology. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2004, 126, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowski, S. Estimation of Minimum Uncut Chip Thickness during Precision and Micro-Machining Processes of Various Materials-A Critical Review. Materials 2022, 15, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storch, B.; Zawada-Tomkiewicz, A. Distribution of unit forces on the tool edge rounding in the case of finishing turning. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 60, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.M.; Lim, H.S.; Ahn, J.H. Effects of the friction coefficient on the minimum cutting thickness in micro cutting. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2005, 45, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przestacki, D.; Chwalczuk, T.; Wojciechowski, S. The study on minimum uncut chip thickness and cutting forces during laser-assisted turning of WC/NiCr clad layers. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 91, 3887–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowski, S. Mechanical Problems of Precise Milling with Monolithic Tools; Publishing House of Poznan University of Technology: Poznan, Poland, 2018; ISBN 978-83-7775-511-2. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Liu, L.; Du, M.; Shen, J.; Jiang, F.; Li, Y.; Lin, Y. Experimental study on the minimum undeformed chip thickness based on effective rake angle in micro milling. Micromachines 2020, 11, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Jin, Z.; Guo, D. Modelling the effects of tool edge radius on micro machining based on smooth particle hydrodynamics simulation method. Int. J. Mach. Mach. Mater. 2014, 16, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhuang, K.; Pu, D. A novel finite element investigation of cutting force in orthogonal cutting considering plough mechanism with rounded edge tool. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 108, 3323–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, Y.; Ruan, B.; Liang, Z.; Wang, X. Modeling of the minimum cutting thickness in micro cutting with consideration of the friction around the cutting zone. Front. Mech. Eng. 2020, 15, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Ni, J.; He, L.H.; Zhu, Z.F.; Luo, B.K.; Liao, J.D. Numerical Cutting Simulation and Experimental Investigations on Determining the Minimum Uncut Chip Thickness of PTFE. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2024, 25, 2003–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Rahman, M.; Kumar, A.S. Chip perforation and ‘burnishing-like’ finishing of Al alloy in precision machining. Precis. Eng. 2017, 50, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, H.; Sadeghi, M.H.; Budak, E. Determination of minimum uncut chip thickness under various machining conditions during micro-milling of Ti-6Al-4V. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 95, 1617–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Câmara, M.A.; Abrão, A.M.; Rubio, J.C.C.; Godoy, G.C.D.; Cordeiro, B.S. Determination of the critical undeformed chip thickness in micromilling by means of the acoustic emission signal. Precis. Eng. 2016, 46, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Wang, D.Z. Investigations of tangential ultrasonic vibration turning of Ti6Al4V using finite element method. Int. J. Mater. Form. 2019, 12, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Wang, D.Z.; Gao, Y.Y. The investigation of mechanism of serrated chip formation under different cutting speeds. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 82, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Zhang, L. Investigation on grinding force and machining quality during rotary ultrasonic grinding deep-small hole of fluorophlogopite ceramics. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 104, 2815–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, S.; Wallén, P. A new classification system for dead zones in metal cutting. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 1988, 28, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.; Wen, D.Y.; Ma, Y.C.; Zhang, W.H. On material separation and cutting force prediction in micro milling through involving the effect of dead metal zone. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2019, 146, 103452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsharhanaei, A.; Rebaioli, L.; Parenti, P.; Annoni, M. Finite element modeling of micro-orthogonal cutting process with dead metal cap. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part. B-J. Eng. Manuf. 2018, 232, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhuang, K.; Zhou, J.; Ding, H. On the Steady-State Workpiece Flow Mechanism and Force Prediction Considering Piled-Up Effect and Dead Metal Zone Formation. ASME J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2021, 143, 041009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Z.H.; Shi, L.; Yin, J.; Jiang, S.L.; Zhang, S.F.; Yu; Liu, Y. Research on cutting force of extrusion cutting process based on material flow characteristics. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 122, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, S.; Altan, E. A slip-line approach to the machining with rounded-edge tool. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 63, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesuer, D.R. Experiment Investigations of Material Models for Ti-6Al-4V Titanium and 2024-T3 Aluminum. Tech. Rep. 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Aydın, M.; Koklu, U. Identification and modeling of cutting forces in ball-end milling based on two different finite element models with arbitrary Lagrangian Eulerian technique. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 92, 1465–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Outeiro, J.C.; Mabrouki, T. On the selection of Johnson-Cook constitutive model parameters for Ti-6Al-4V using three types of numerical models of orthogonal cutting. Procedia CIRP 2015, 31, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorev NN, Inter-relationship between shear processes occurring along toolface and shear plane in metal cutting. Int. Res. Prod. Eng. 1963, 49, 143–152.
- Woon, K.S.; Rahman, M.; Neo, K.S.; Liu, K. The effect of tool edge radius on the contact phenomenon of tool-based micromachining. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2008, 48, 1395–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, A.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Miao, Y.; Liu, G. Study on variable parameter helical milling of TC4 titanium alloy tube. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2023, 24, 1947–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellappan, S.; Ahmed, A.; Rahman, M.A. Experimental investigation on extrinsic size effect in micro-orthogonal cutting of commercial aluminium alloy. Precis. Eng. 2024, 88, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opoz, T.T.; Chen, X. Experimental investigation of material removal mechanism in single grit grinding. Int. J. Mach. Tool. Manuf. 2012, 63, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldorf, D.J.; Devor, R.E.; Kapoor, S.G. A slip-line field for ploughing during orthogonal cutting. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 1998, 120, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekian, M.; Mostofa, M.G.; Park, S.S.; Jun, M.B.G. Modeling of minimum uncut chip thickness in micro machining of aluminum. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2012, 212, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| J-C | A (MPa) | B (MPa) | C | n | m |
| 1098 | 1092 | 0.014 | 0.93 | 1.1 | |
| Damage | d1 | d2 | d3 | d4 | d5 |
| −0.09 | 0.27 | −0.5 | 0.014 | 3.87 |
| Temperature (K) | 300 | 373 | 473 | 573 | 673 | 773 |
| Thermal conductivity (w/(m⸱K)) | 6.8 | 7.4 | 8.7 | 9.8 | 10.3 | 11.8 |
| Specific heat (J/(Kg/K)) | 611 | 624 | 653 | 674 | 691 | 703 |
| Density ρ (kg/m3) | Modulus of Elasticity E (GPa) | Poisson’s Ratio μ | Coefficient of Linear Expansion (10−6 K−1) | Inelastic Thermal Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4430 | 110 | 0.33 | 9 | 0.9 |
| Cutting Parameters | Digital |
|---|---|
| Cutting speed | 10 m/min |
| Spindle speed | 200 r/min |
| Cutting depth | 3 mm |
| Uncut chip thickness (UCT) | 1–40 μm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Y.; Huang, W.; Liu, Y.; Duan, P.; Wang, Y. Determination of the Minimum Uncut Chip Thickness of Ti-6Al-4V Titanium Alloy Based on Dead Metal Zone. Micromachines 2024, 15, 1458. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15121458
Zheng Y, Huang W, Liu Y, Duan P, Wang Y. Determination of the Minimum Uncut Chip Thickness of Ti-6Al-4V Titanium Alloy Based on Dead Metal Zone. Micromachines. 2024; 15(12):1458. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15121458
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Yaohui, Wentao Huang, Yangyang Liu, Pengchao Duan, and Yingxiao Wang. 2024. "Determination of the Minimum Uncut Chip Thickness of Ti-6Al-4V Titanium Alloy Based on Dead Metal Zone" Micromachines 15, no. 12: 1458. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15121458
APA StyleZheng, Y., Huang, W., Liu, Y., Duan, P., & Wang, Y. (2024). Determination of the Minimum Uncut Chip Thickness of Ti-6Al-4V Titanium Alloy Based on Dead Metal Zone. Micromachines, 15(12), 1458. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15121458





