Instant Candida albicans Detection Using Ultra-Stable Aptamer Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Aptamer Selection
2.2. Vaginal Fluid Simulant
2.3. Fungal Culture and Reagents
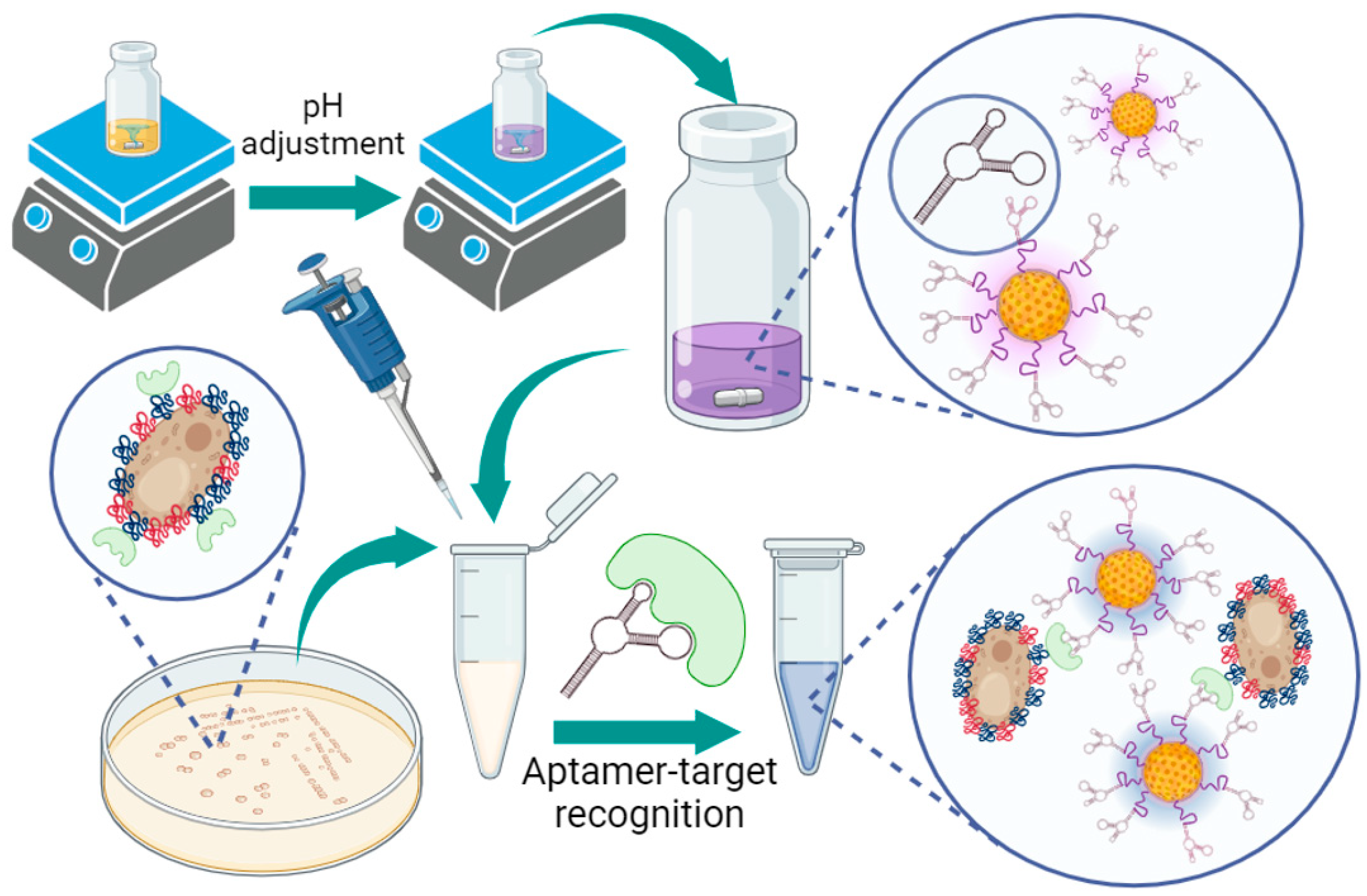
2.4. Gold Nanoparticle Synthesis
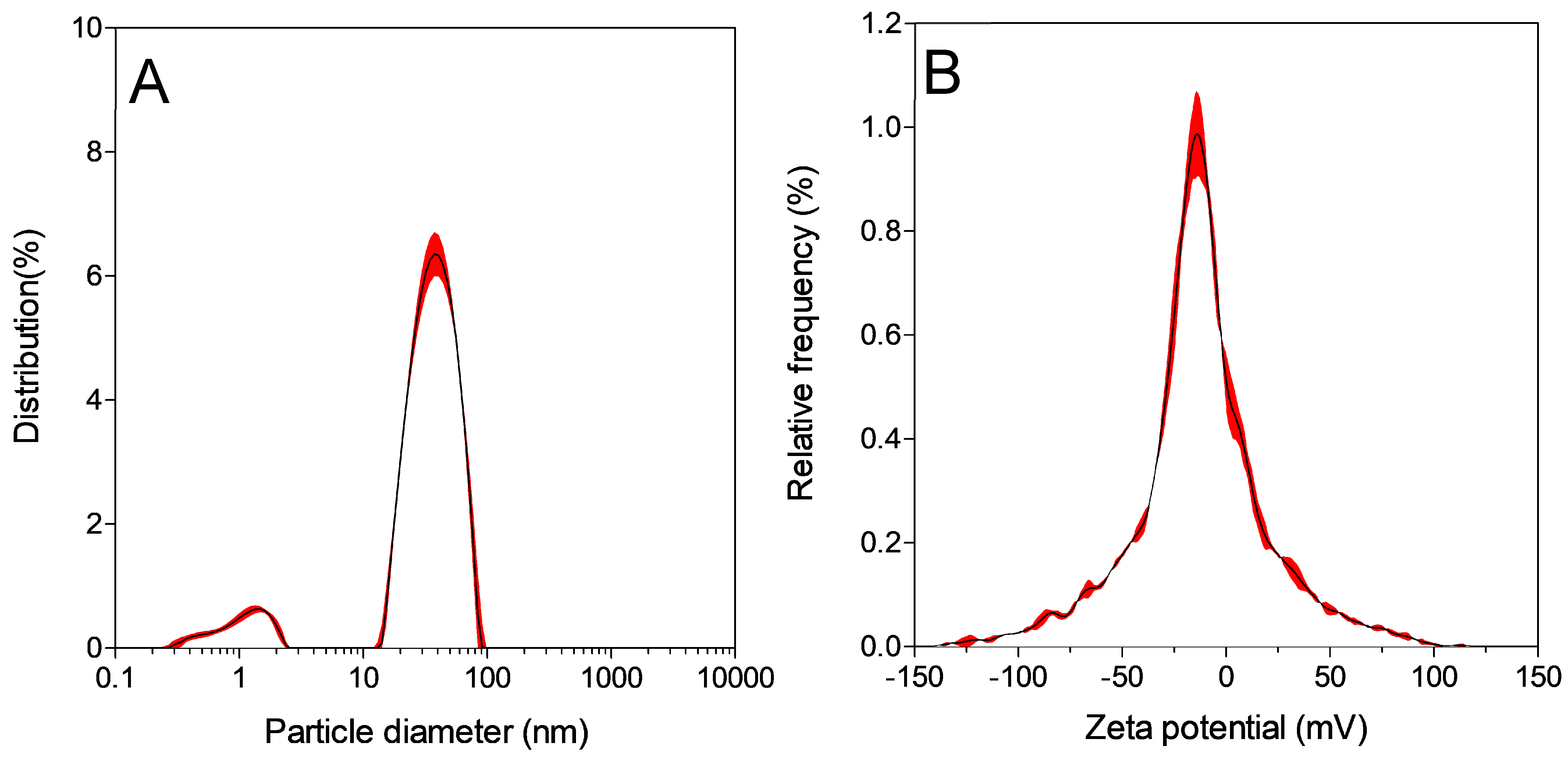
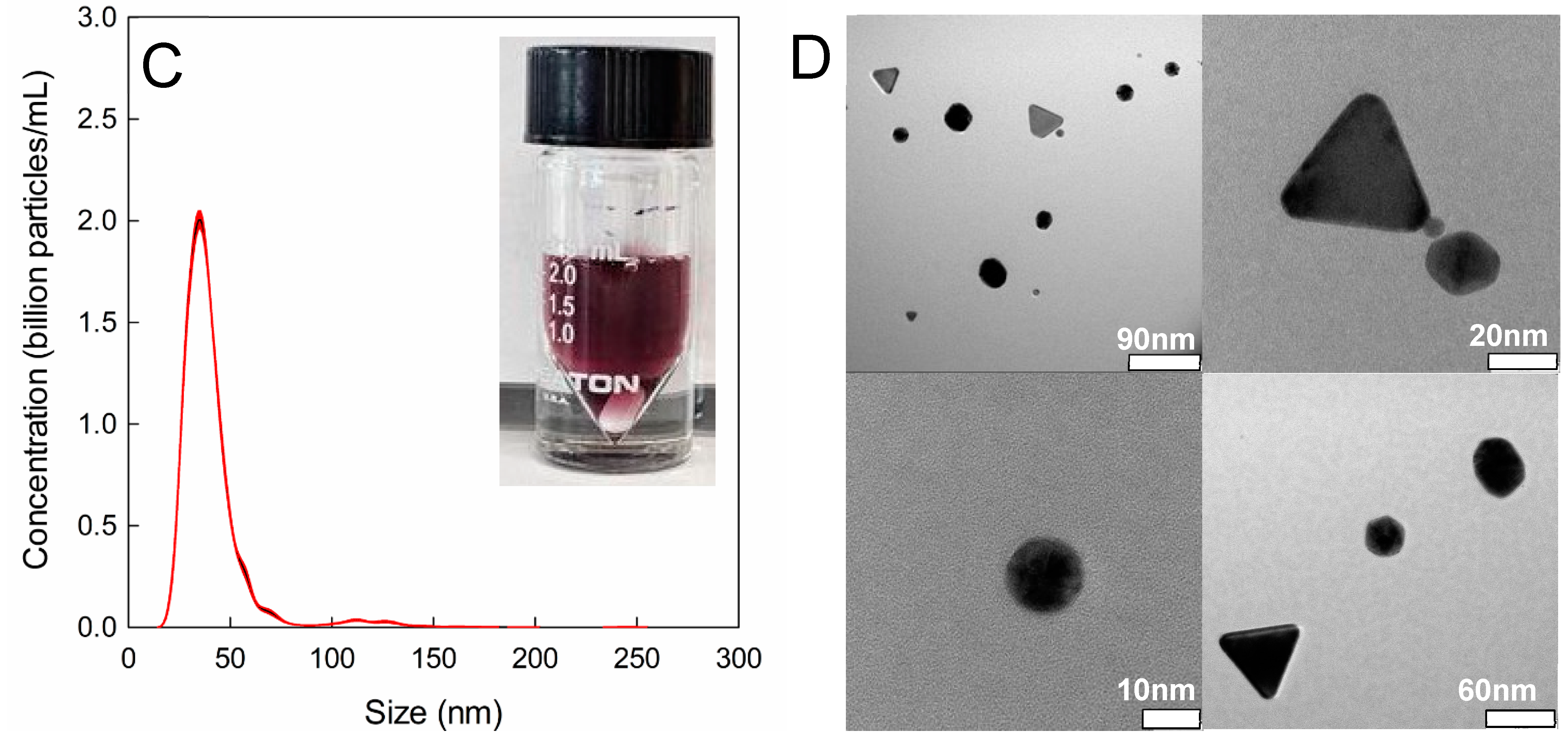
2.5. Nanoparticle Characterization
2.6. pH and Temperature Dependence
2.7. Hydrodynamic Particle Size and Zeta Potential Measurement Using Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
2.8. Mean Particle Size and Concentration with Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
2.9. Particle Shape Analysis viaTransmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.10. Selection of Reagents/Fungal Samples for Platform Specificity Testing
2.11. Image Processing
3. Results and Discussion
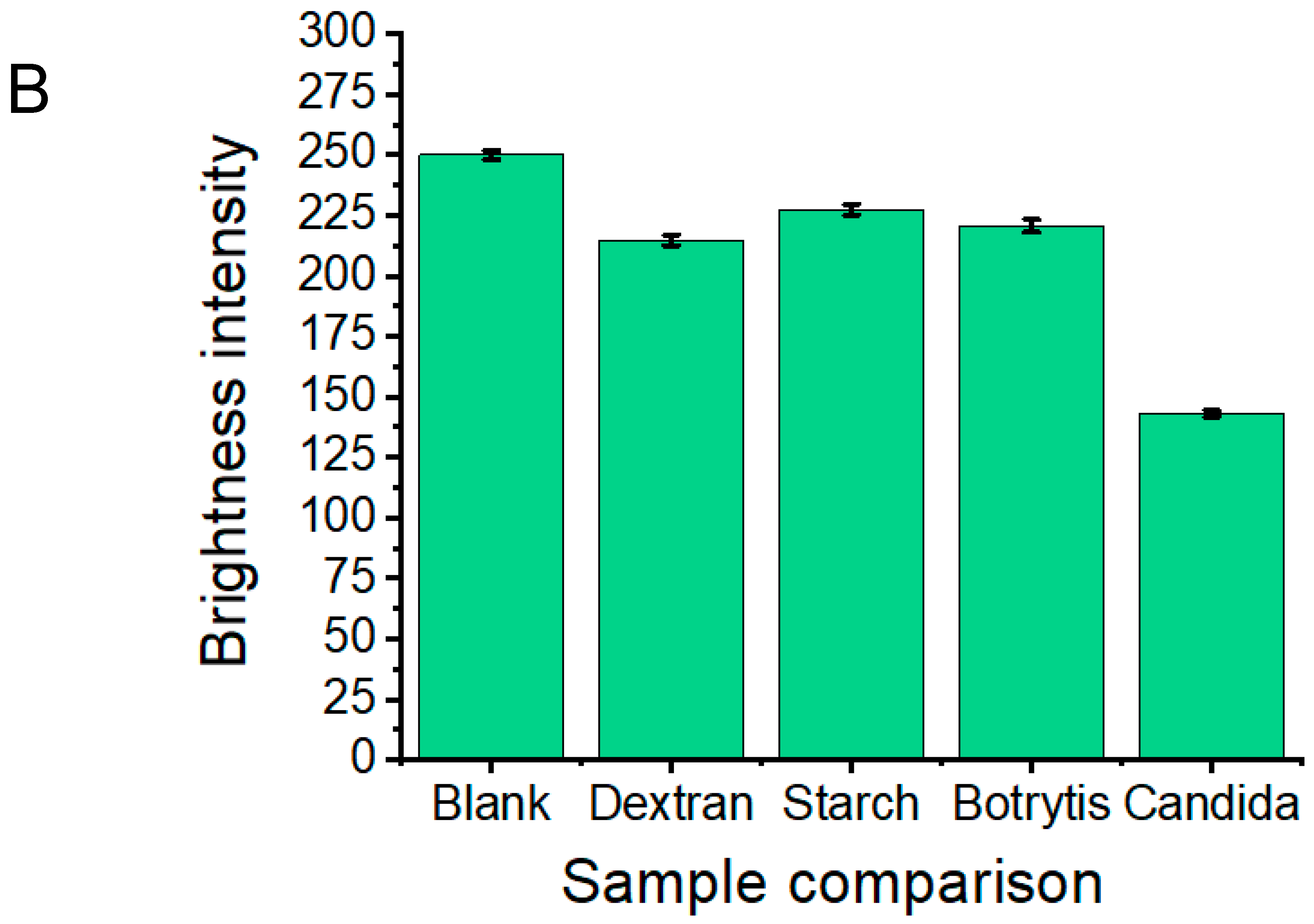
3.1. Proof-of-Concept and Specificity Testing
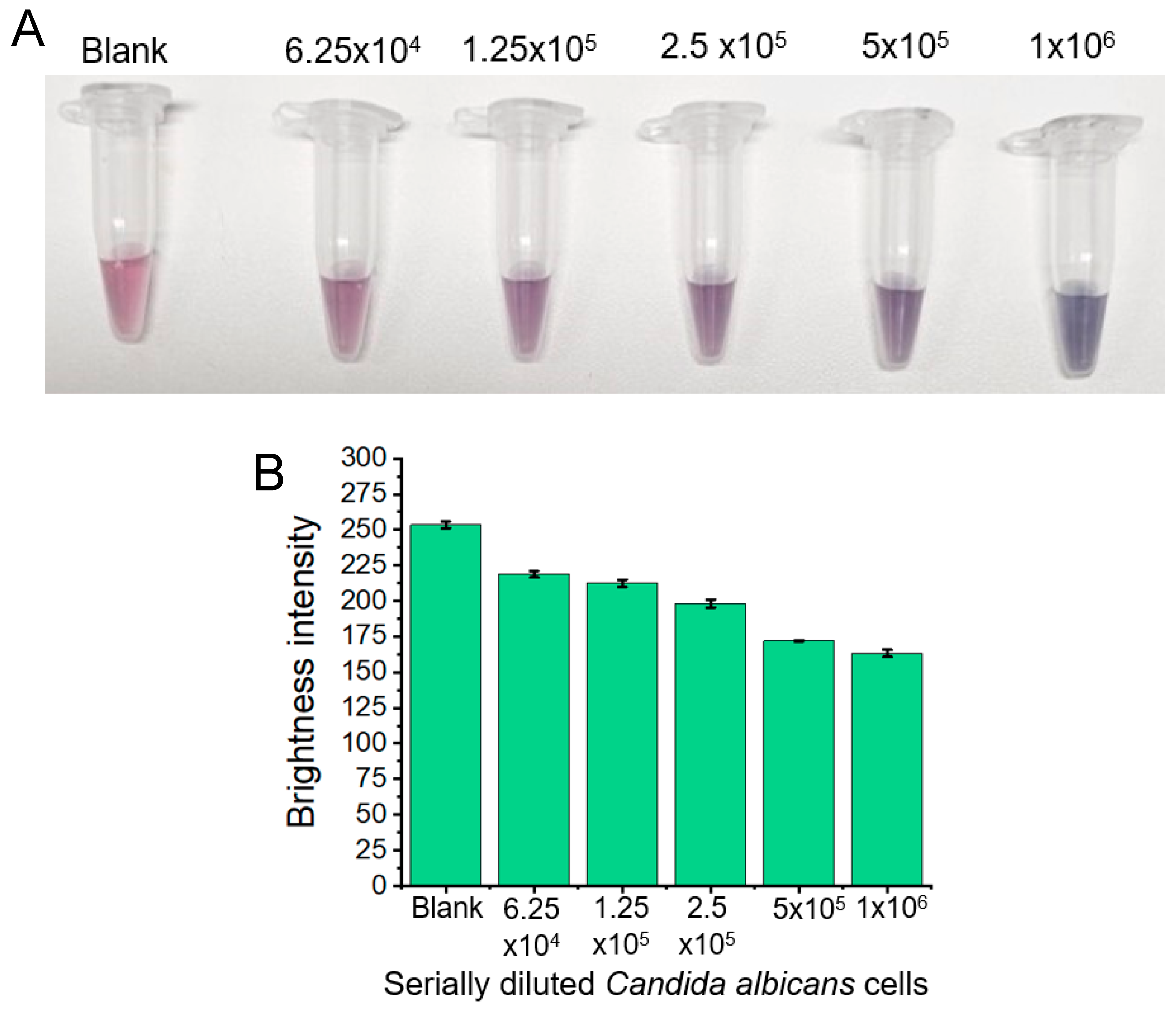
3.2. SemiQuantitative Candida albicans Yeast Cell Detection via OD600
4. Conclusions and Future Direction
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Superti, F.; De Seta, F. Warding Off Recurrent Yeast and Bacterial Vaginal Infections: Lactoferrin and Lactobacilli. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denning, D.W.; Kneale, M.; Sobel, J.D.; Rautemaa-Richardson, R. Global burden of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis: A systematic review. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, e339–e347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojang, E.; Ghuman, H.; Kumwenda, P.; Hall, R.A. Immune Sensing of Candida albicans. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Kakkar, V.; Bhushan, I. Crosstalk between Vaginal Microbiome and Female Health: A review. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 136, 103696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pericolini, E.; Perito, S.; Castagnoli, A.; Gabrielli, E.; Mencacci, A.; Blasi, E.; Vecchiarelli, A.; Wheeler, R.T. Epitope unmasking in vulvovaginal candidiasis is associated with hyphal growth and neutrophilic infiltration. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldewijns, S.; Sillen, M.; Palmans, I.; Vandecruys, P.; Van Dijck, P.; Demuyser, L. The Role of Fatty Acid Metabolites in Vaginal Health and Disease: Application to Candidiasis. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 705779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, N.; Singh, J.; Kaur, M. Microbiota in vaginal health and pathogenesis of recurrent vulvovaginal infections: A critical review. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2020, 19, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talapko, J.; Juzbašić, M.; Matijević, T.; Pustijanac, E.; Bekić, S.; Kotris, I.; Škrlec, I. Candida albicans—The Virulence Factors and Clinical Manifestations of Infection. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Khan, Z. Invasive candidiasis: A review of nonculture-based laboratory diagnostic methods. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 30, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Herrera, J.; Ortiz-Castellanos, L. Cell wall glucans of fungi. A review. Cell Surf. 2019, 5, 100022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Yang, M.; Li, J.; Bi, X.; Li, G.; Xu, J.; Xie, S.; Dong, Y.; Li, D.; Du, Y. The enhancing antifungal effect of AD1 aptamer-functionalized amphotericin B-loaded PLGA-PEG nanoparticles with a low-frequency and low-intensity ultrasound exposure on C. albicans biofilm through targeted effect. NanoImpact 2021, 21, 100275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, H.; Xue, X.; Luo, M.; Liu, H.; Xue, Z. Recent advances in the development of colorimetric analysis and testing based on aggregation-induced nanozymes. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaumpluk, P.; Plubcharoensook, P.; Prasongsuk, S. Rapid detection of aflatoxigenic Aspergillus sp. in herbal specimens by a simple, bendable, paper-based lab-on-a-chip. Biotechnol. J. 2016, 11, 768–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumani, F.; Gómez, S.; Rodrigues, C.; Barros-Velázquez, J.; Garrido-Maestu, A.; Prado, M. Development and evaluation of a real-time fluorescence, and naked-eye colorimetric, loop-mediated isothermal amplification-based method for the rapid detection of spoilage fungi in fruit preparations. Food Control 2022, 135, 108784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.H.; Ahn, G.R.; Lee, B.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Song, M.; Chung, W.-J. Engineered M13 bacteriophage-enhanced colorimetric detection of allergenic fungi. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 393, 134244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, R.K.; Carvalhal, R.F.; Stach-Machado, D.R.; Kubota, L.T. Surface plasmon resonance immunosensor for early diagnosis of Asian rust on soybean leaves. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2483–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, M.; Ray, A.; Dash, S.; Mishra, A.; Achary, K.G.; Nayak, S.; Singh, S. Fungal disease detection in plants: Traditional assays, novel diagnostic techniques and biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 708–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.I.; Jang, S.C.; Chung, J.; Choi, W.-K.; Hong, C.; Ahn, G.R.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, B.Y.; Chung, W.-J. Colorimetric allergenic fungal spore detection using peptide-modified gold nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 327, 128894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, F.; Duan, Y.; Kang, W.; Chen, Q.; Xue, Z. Early detection of wheat Aspergillus infection based on nanocomposite colorimetric sensor and multivariable models. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 351, 130910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojinrin, T.; Conde, J.; Liu, K.; Curtin, J.; Byrne, H.J.; Cui, D.; Tian, F. Plasmonic gold nanoparticles for detection of fungi and human cutaneous fungal infections. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 4647–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, F.; Wang, T.; Iradukunda, L.; Zhan, J. A gold nanoparticle-based lateral flow biosensor for sensitive visual detection of the potato late blight pathogen, Phytophthora infestans. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1036, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.L.; Hua, Y.; Guan, Q.; Yuan, C.H. Improved detection of deeply invasive candidiasis with DNA aptamers specific binding to (1→3)-β-d-glucans from Candida albicans. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 35, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Kulabhusan, P.; Hussain, B.; Yüce, M. Current Perspectives on Aptamers as Diagnostic Tools and Therapeutic Agents. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, S.; Obubuafo, A.; Soper, S.A.; Spivak, D.A. Surface immobilization methods for aptamer diagnostic applications. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 390, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.; Lee, C.-H.; Joo, S.-W.; Lee, K. Kinetics of gold nanoparticle aggregation: Experiments and modeling. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 318, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkevich, J.; Stevenson, P.C.; Hillier, J. A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 1951, 11, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirkey, A.; Babu, P.J. Synthesis and characterization of citrate-capped gold nanoparticles and their application in selective detection of creatinine (A kidney biomarker). Sens. Int. 2024, 5, 100252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonavane, G.; Tomoda, K.; Sano, A.; Ohshima, H.; Terada, H.; Makino, K. In vitro permeation of gold nanoparticles through rat skin and rat intestine: Effect of particle size. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2008, 65, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Chen, Z.; Jing, X.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Y.; Ye, J.; Chu, Q. Tween 20-capped gold nanoparticles for selective extraction of free low-molecular-weight thiols in saliva followed by capillary electrophoresis with contactless conductivity detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2021, 1176, 122756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, Y.-C.; Ke, C.-Y.; Yu, C.-J.; Lu, C.-Y.; Tseng, W.-L. Combined Tween 20-Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles and Reduced Graphite Oxide–Fe3O4 Nanoparticle Composites for Rapid and Efficient Removal of Mercury Species from a Complex Matrix. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 17437–17445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Yuan, H.; Xu, A.; Wang, J.; Wu, L. Rapid Synthesis of Stable and Functional Conjugates of DNA/Gold Nanoparticles Mediated by Tween 80. Langmuir 2011, 27, 13629–13634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Qin, G.; Raveendran, P.; Ikushima, Y. Facile “Green” Synthesis, Characterization, and Catalytic Function of β-d-Glucose-Stabilized Au Nanocrystals. Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, D.H.; Katz, D.F. A vaginal fluid simulant. Contraception 1999, 59, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, A.; Muñoz, M.; Rotstein, B.H.; Suuronen, E.J.; Alarcon, E.I. A low cost and open access system for rapid synthesis of large volumes of gold and silver nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, F.R.W.; Cesca, K.; Valério, A.; de Oliveira, D.; Hotza, D. Colorimetric detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by aptamer-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanh, N.T.K.; Rosenzweig, Z. Development of an Aggregation-Based Immunoassay for Anti-Protein A Using Gold Nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 1624–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Montes, E. Dextran: Sources, Structures, and Properties. Polysaccharides 2021, 2, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Liu, Z.; Sun, D.D. Highly water soluble and recovered dextran coated Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for brackish water desalination. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 81, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tester, R.F.; Karkalas, J.; Qi, X. Starch—Composition, fine structure and architecture. J. Cereal Sci. 2004, 39, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Oirdi, M.; Abd Elrahman, T.; Rigano, L.; El Hadrami, A.; Rodríguez, M.; Daayf, F.; Vojnov, A.; Bouarab, K. Botrytis cinerea Manipulates the Antagonistic Effects between Immune Pathways to Promote Disease Development in Tomato. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 2405–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-ad, N.L.; Bar-Nun, N.; Mayer, A.M. The possible function of the glucan sheath of Botrytis cinerea: Effects on the distribution of enzyme activities. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 199, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, S.; Nazari, Z. A review on gold nanoparticles aggregation and its applications. J. Chem. Rev. 2020, 2, 228–242. [Google Scholar]
- Gulati, M.; Lohse, M.B.; Ennis, C.L.; Gonzalez, R.E.; Perry, A.M.; Bapat, P.; Arevalo, A.V.; Rodriguez, D.L.; Nobile, C.J. In Vitro Culturing and Screening of Candida albicans Biofilms. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2018, 50, e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Clack, K.; Sallam, M.; Muyldermans, S.; Sambasivam, P.; Nguyen, C.M.; Nguyen, N.-T. Instant Candida albicans Detection Using Ultra-Stable Aptamer Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles. Micromachines 2024, 15, 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15020216
Clack K, Sallam M, Muyldermans S, Sambasivam P, Nguyen CM, Nguyen N-T. Instant Candida albicans Detection Using Ultra-Stable Aptamer Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles. Micromachines. 2024; 15(2):216. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15020216
Chicago/Turabian StyleClack, Kimberley, Mohamed Sallam, Serge Muyldermans, Prabhakaran Sambasivam, Cong Minh Nguyen, and Nam-Trung Nguyen. 2024. "Instant Candida albicans Detection Using Ultra-Stable Aptamer Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles" Micromachines 15, no. 2: 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15020216
APA StyleClack, K., Sallam, M., Muyldermans, S., Sambasivam, P., Nguyen, C. M., & Nguyen, N.-T. (2024). Instant Candida albicans Detection Using Ultra-Stable Aptamer Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles. Micromachines, 15(2), 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15020216










