Resonance Modes of Water Drops Pinned to a Vibrating Rectangular Post
Abstract
1. Introduction
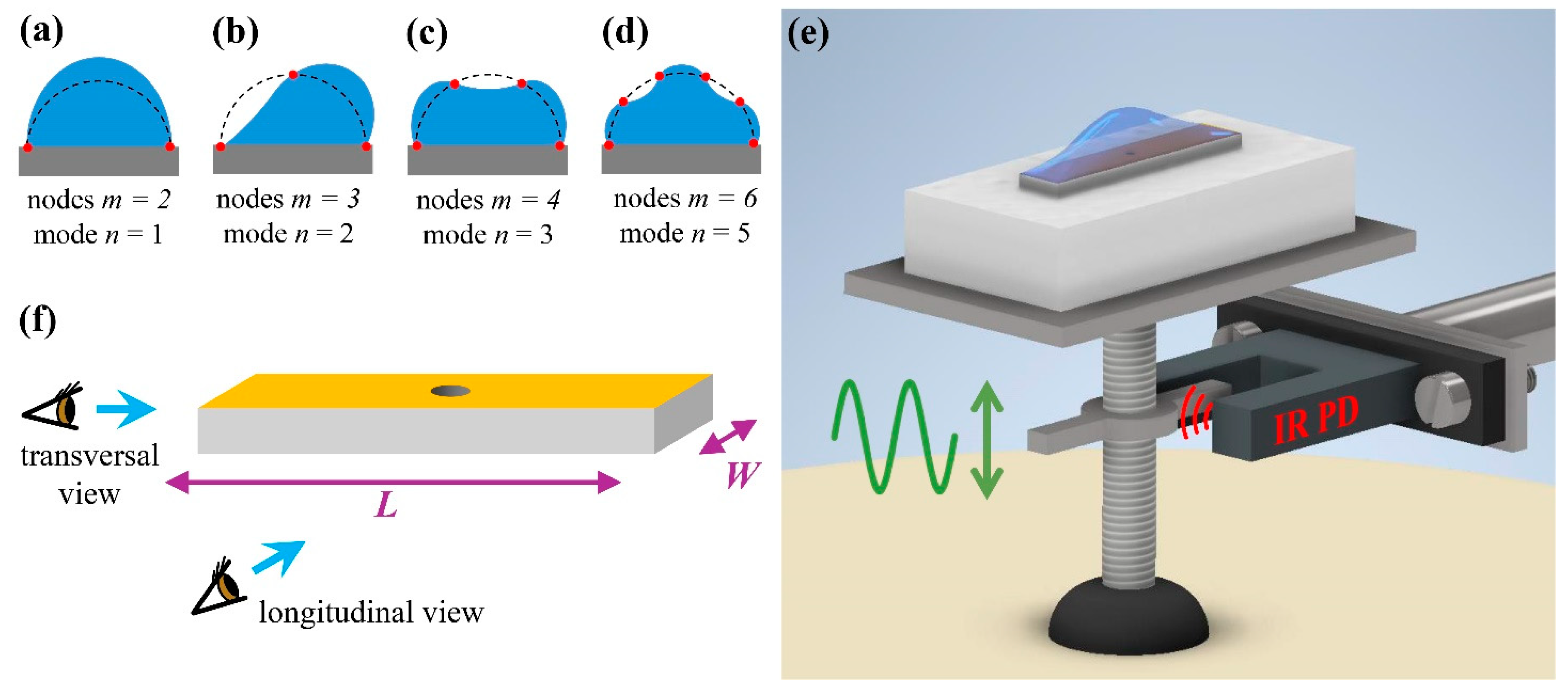
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Optofluidic Setup
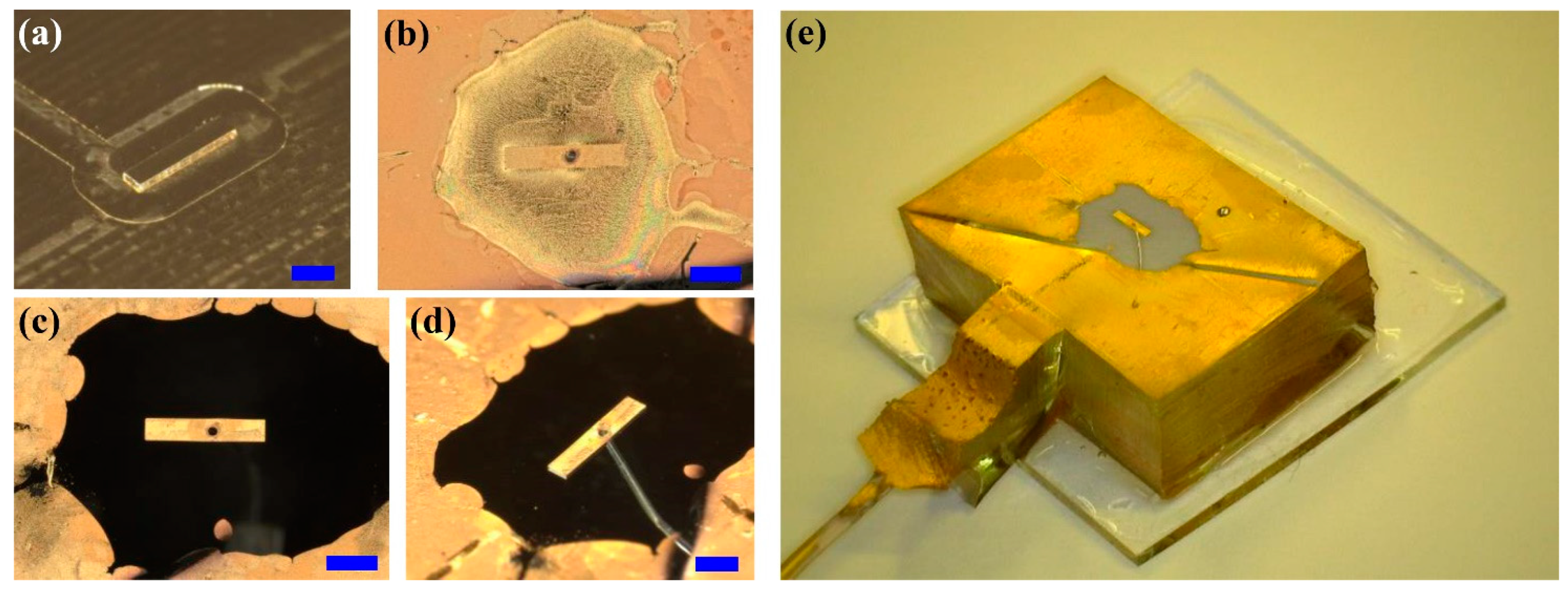
2.2. Fabrication of the Rectangular Posts
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Gennes, P.G.; Brochard-Wyart, F.; Quéré, D. Capillarity and Wetting Phenomena: Drops, Bubbles, Pearls, Waves; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, K.H.; Xiao, R.; Wang, E.N. Uni-directional liquid spreading on asymmetric nanostructured surfaces. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.Y.; Johnson, L.M.; López, G.P. Anisotropic wetting surfaces with one-dimesional and directional structures: Fabrication approaches, wetting properties and potential applications. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1287–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semprebon, C.; Varagnolo, S.; Filippi, D.; Perlini, L.; Pierno, M.; Brinkmann, M.; Mistura, G. Deviation of sliding drops at a chemical step. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 8268–8273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.X.; Chen, F.Z.; Tian, Y.L.; Zhang, D.W.; Lian, Z.X.; Cao, M.Y. Programmable droplet transport on multi-bioinspired slippery surface with tridirectionally anisotropic wettability. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 449, 137831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, M.J.; Sekeroglu, K.; Demirel, M.C. Bioinspired directional surfaces for adhesion, wetting, and transport. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 2223–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gau, H.; Herminghaus, S.; Lenz, P.; Lipowsky, R. Liquid morphologies on structured surfaces: From microchannels to microchips. Science 1999, 283, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.S.; Yao, X.; Jiang, L. Recent developments in bio-inspired special wettability. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3240–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; He, B.; Lee, J.H.; Patankar, N.A. Anisotropy in the wetting of rough surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 281, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumaatmaja, H.; Leopoldes, J.; Dupuis, A.; Yeomans, J.M. Drop dynamics on chemically patterned surfaces. Europhys. Lett. 2006, 73, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chung, J.Y.; Youngblood, J.P.; Stafford, C.M. Anisotropic wetting on tunable micro-wrinkled surfaces. Soft Matter 2007, 3, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.Y.; Brueck, S.R.J. Strongly anisotropic wetting on one-dimensional nanopatterned surfaces. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 2819–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semprebon, C.; Mistura, G.; Orlandini, E.; Bissacco, G.; Segato, A.; Yeomans, J.M. Anisotropy of water droplets on single rectangular posts. Langmuir 2009, 25, 5619–5625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semprebon, C.; Herrmann, C.; Liu, B.Y.; Seemann, R.; Brinkmann, M. Shape evolution of droplets growing on linear microgrooves. Langmuir 2018, 34, 10498–10511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, D.; Semprebon, C.; Toth, T.; Locatelli, E.; Pierno, M.; Mistura, G.; Brinkmann, M. Morphological transitions of droplets wetting rectangular domains. Langmuir 2012, 28, 13919–13923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefle, C.; Brinkmann, M.; Bechinger, C.; Leiderer, P.; Lipowsky, R. Morphological wetting transitions at ring-shaped surface domains. Langmuir 2010, 26, 11878–11885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokowicz, M.; Nowicki, W. Morphological transitions of droplets wetting a series of triangular grooves. Langmuir 2016, 32, 7259–7264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauret, A.; Bick, A.D.; Duprat, C.; Stone, H.A. Wetting of crossed fibers: Multiple steady states and symmetry breaking. Europhys. Lett. 2014, 105, 56006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.J.; Shan, L.; Dogruoz, B.; Agonafer, D. Evolution of microdroplet morphology confined on asymmetric micropillar structures. Langmuir 2019, 35, 12264–12275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, P.; Bonato, L.; Delfitto, G.; Pierno, M.; Mistura, G.; Semprebon, C.; Brinkmann, M. Morphological transitions of water channels induced by vertical vibrations. Langmuir 2018, 34, 12882–12888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Chaudhury, A.; Chaudhury, M.K. Lateral vibration of a water drop and its motion on a vibrating surface. Eur. Phys. J. E 2006, 21, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, S.; Chaudhury, M.K. Rectified motion of liquid drops on gradient surfaces induced by vibration. Langmuir 2002, 18, 3404–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noblin, X.; Kofman, R.; Celestini, F. Ratchetlike motion of a shaken drop. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 194504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunet, P.; Eggers, J.; Deegan, R.D. Vibration-induced climbing of drops. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 144501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, P.; Guglielmin, E.; Ferraro, D.; Filippi, D.; Zaltron, A.; Pierno, M.; Mistura, G. Motion of Newtonian drops deposited on liquid-impregnated surfaces induced by vertical vibrations. J. Fluid Mech. 2019, 876, R4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.V.; Nguyen, M.D.; Takahashi, H.; Matsumoto, K.; Shimoyama, I. Viscosity measurement based on the tapping-induced free vibration of sessile droplets using MEMS-based piezoresistive cantilevers. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 3670–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrold, V.C.; Sharp, J.S. Optovibrometry: Tracking changes in the surface tension and viscosity of multicomponent droplets in real-time. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 8790–8797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.T.; Shiea, J.; Shen, S.C. Fabrication of an integrated piezo-electric micro-nebulizer for biochemical sample analysis. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2007, 17, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noblin, X.; Buguin, A.; Brochard-Wyart, F. Vibrations of sessile drops. Eur. Phys. J. Special Topics 2009, 166, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noblin, X.; Buguin, A.; Brochard-Wyart, F. Vibrated sessile drops: Transition between pinned and mobile contact line oscillations. Eur. Phys. J. E 2004, 14, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkes, E.D.; Basaran, O.A. Forced oscillations of pendant (sessile) drops. Phys. Fluids 1997, 9, 1512–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temperton, R.H.; Sharp, J.S. Vibrational modes of elongated sessile liquid droplets. Langmuir 2013, 29, 4737–4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, S.; Chaudhury, M.K.; de Gennes, P.G. Vibration-actuated drop motion on surfaces for batch microfluidic processes. Langmuir 2005, 21, 4240–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landau, L.D.; Lifshitz, E.M. Fluid Mechanics, 2nd ed.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Mettu, S.; Chaudhury, M.K. Vibration spectroscopy of a sessile drop and its contact line. Langmuir 2012, 28, 14100–14106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, J.S. Resonant properties of sessile droplets; contact angle dependence of the resonant frequency and width in glycerol/water mixtures. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, J.S.; Farmer, D.J.; Kelly, J. Contact angle dependence of the resonant frequency of sessile water droplets. Langmuir 2011, 27, 9367–9371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costalonga, M.; Brunet, P. Directional motion of vibrated sessile drops: A quantitative study. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2020, 5, 023601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

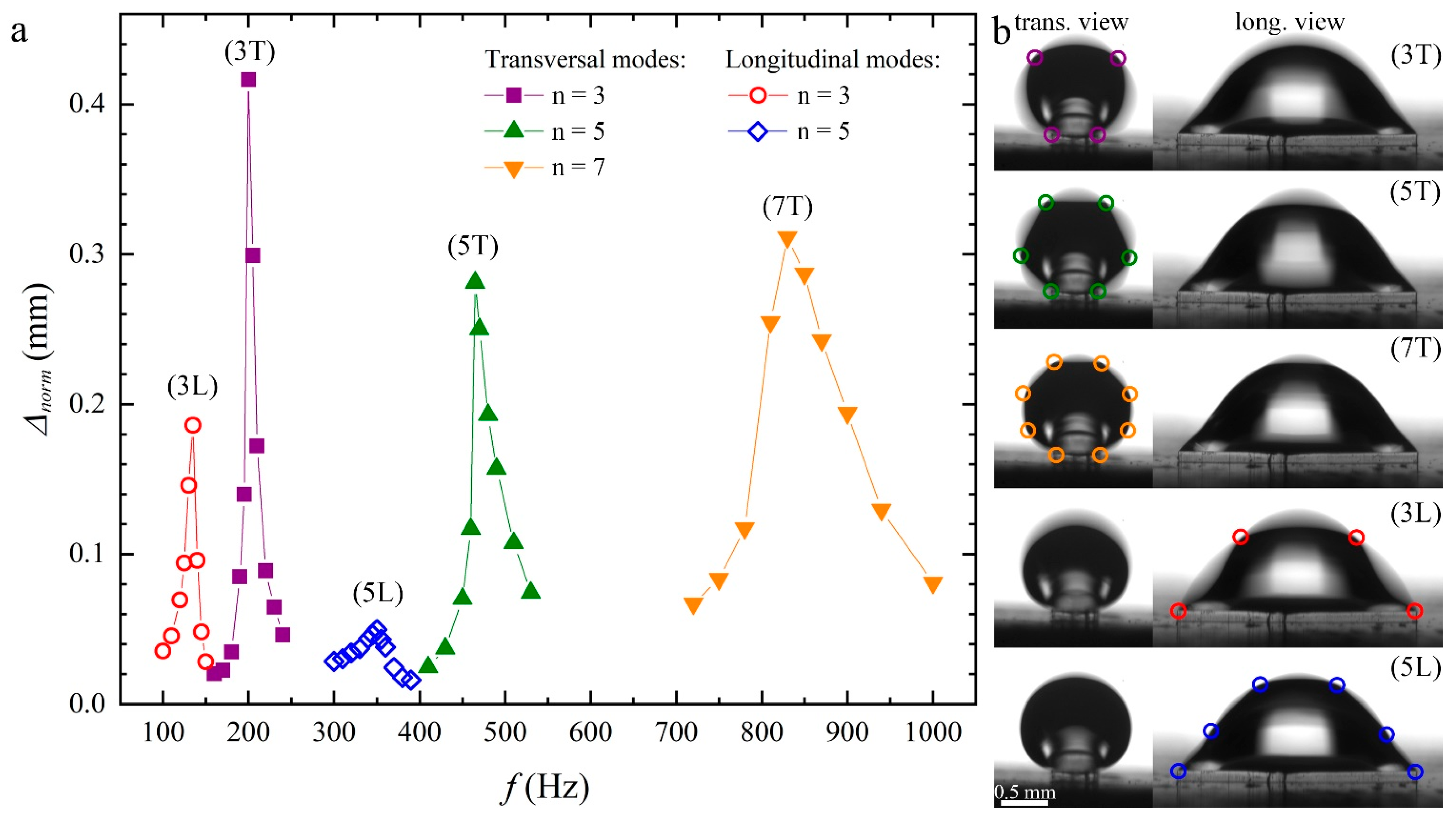
| Mode Number N | Experimental T Mode Frequency fT (Hz) | Theoretical T Mode Frequency fT (Hz) | Experimental L Mode Frequency fL (Hz) | Theoretical L Mode Frequency fL (Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 200 ± 5 | 208 ± 6 | 135 ± 5 | 156 ± 4 |
| 5 | 465 ± 5 | 469 ± 13 | 350 ± 5 | 374 ± 9 |
| 7 | 830 ± 20 | 783 ± 22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sartori, P.; Ferraro, D.; Pierno, M.; Mistura, G. Resonance Modes of Water Drops Pinned to a Vibrating Rectangular Post. Micromachines 2024, 15, 634. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15050634
Sartori P, Ferraro D, Pierno M, Mistura G. Resonance Modes of Water Drops Pinned to a Vibrating Rectangular Post. Micromachines. 2024; 15(5):634. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15050634
Chicago/Turabian StyleSartori, Paolo, Davide Ferraro, Matteo Pierno, and Giampaolo Mistura. 2024. "Resonance Modes of Water Drops Pinned to a Vibrating Rectangular Post" Micromachines 15, no. 5: 634. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15050634
APA StyleSartori, P., Ferraro, D., Pierno, M., & Mistura, G. (2024). Resonance Modes of Water Drops Pinned to a Vibrating Rectangular Post. Micromachines, 15(5), 634. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15050634








