Portable Multi-Layer Capsule-Shaped Triboelectric Generator for Human Motion Energy Harvesting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Fabrication of the CP-TEG
2.2. Electrical Measurements of the CP-TEG
3. Results and Discussion
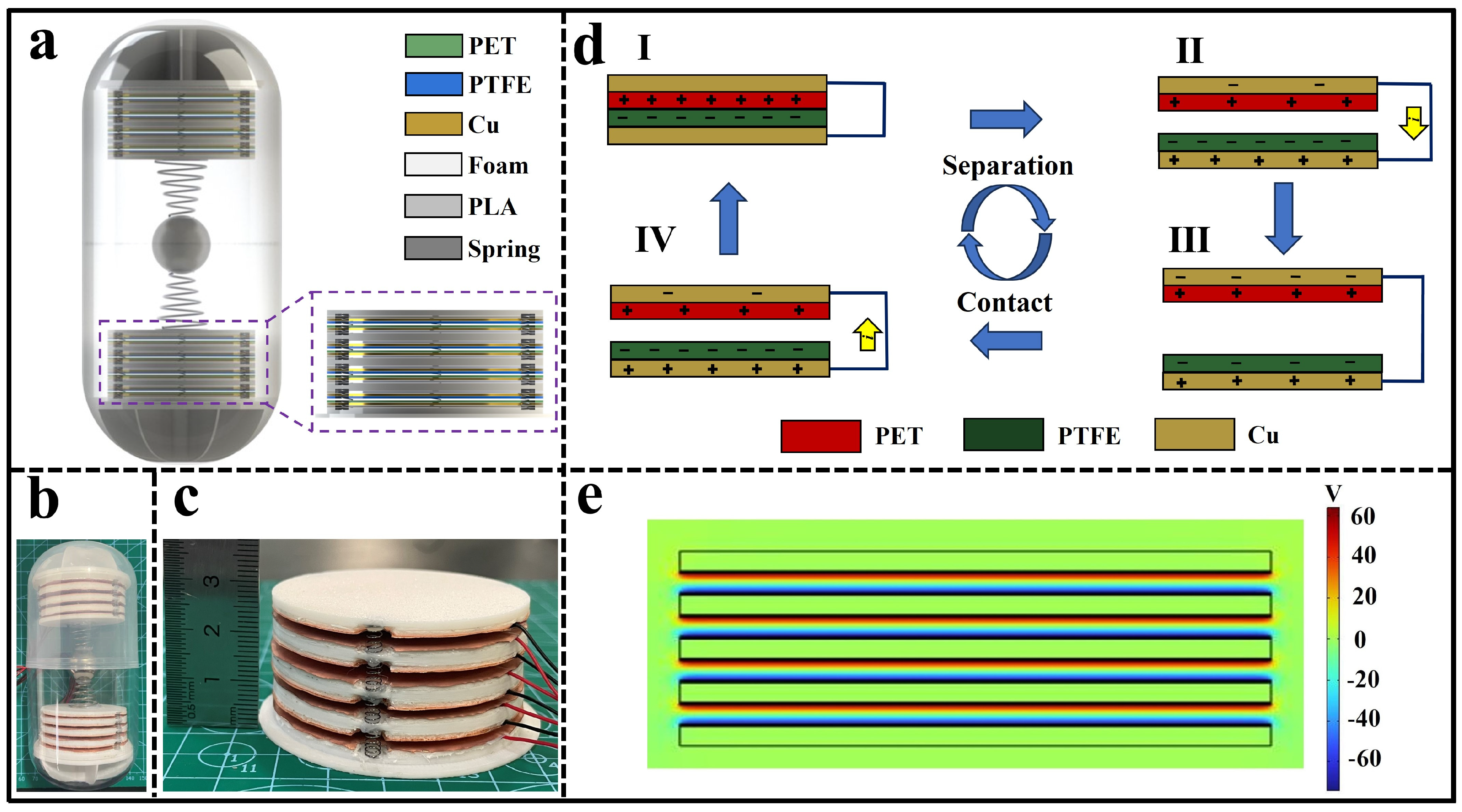
3.1. Structure and Working Principle of the CP-TEG
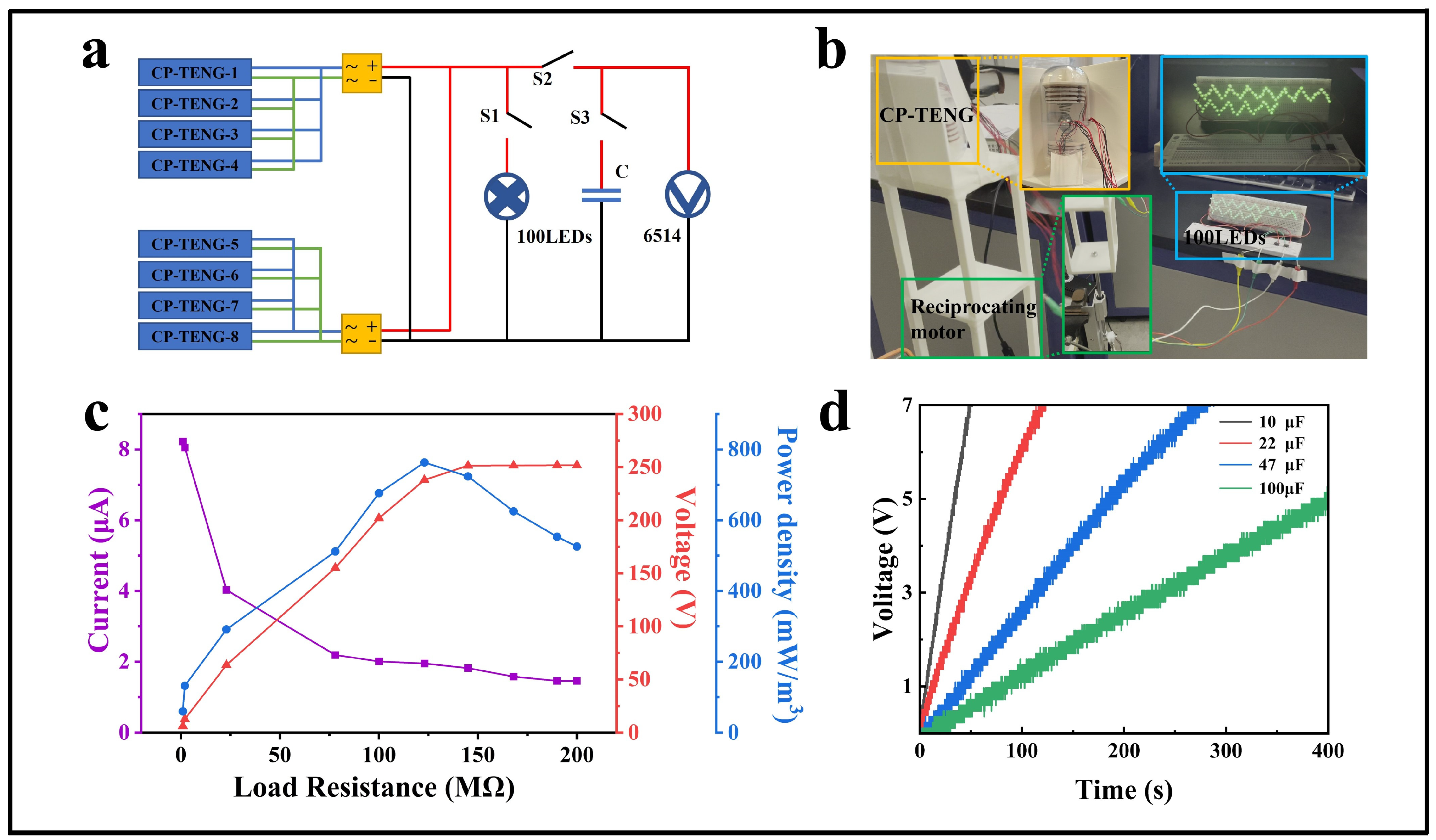
3.2. Performance of the CP-TEG
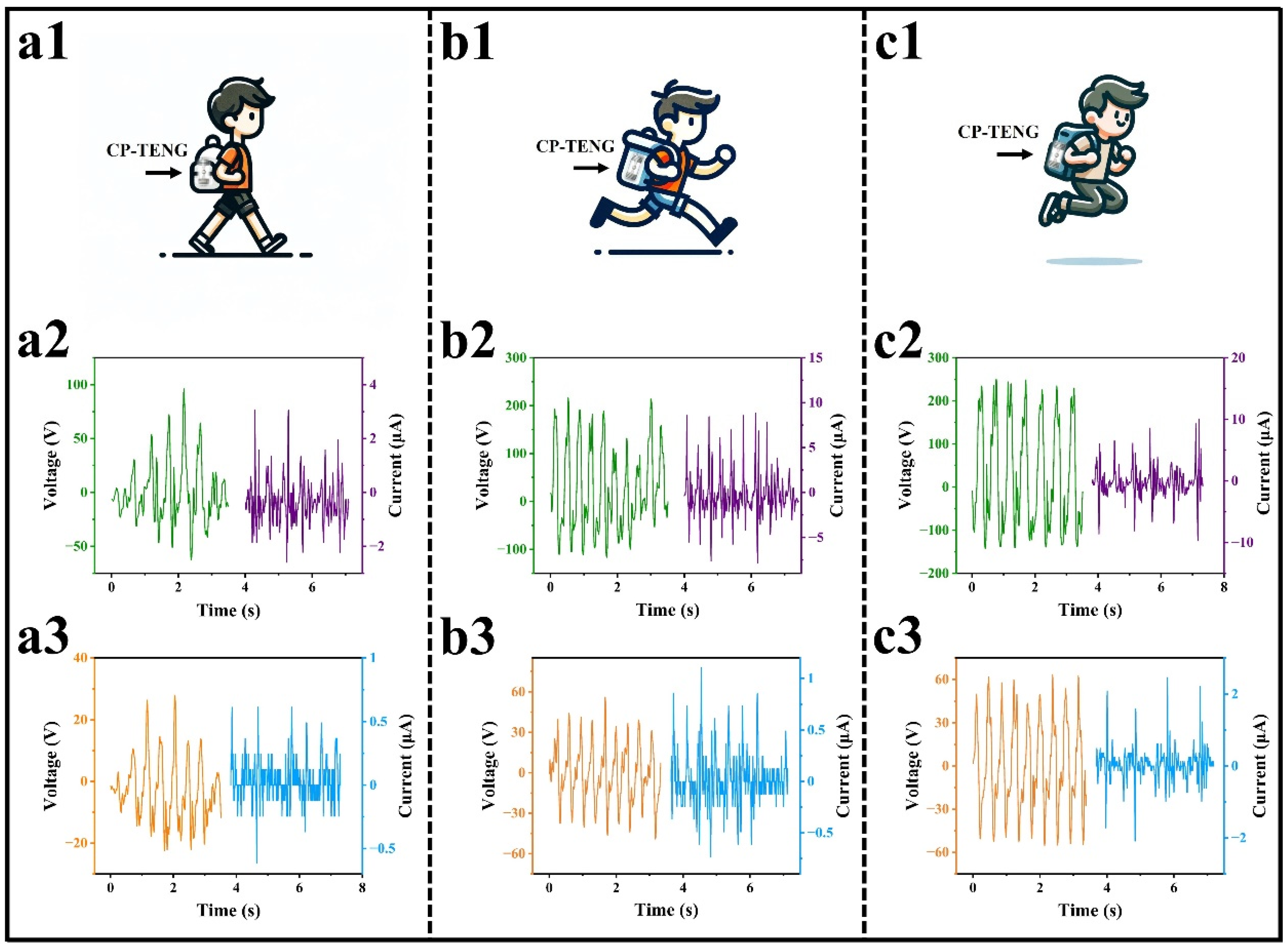
3.3. Portable Applications of CP-TEG
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, F.R.; Tang, W.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible Nanogenerators for Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4283–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Wu, H.; Song, Y.; Miao, L.; Chen, X.; Chen, H.; Su, Z.; Han, M.; Zhang, H. Self-powered digital-analog hybrid electronic skin for noncontact displacement sensing. Nano Energy 2019, 58, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Q.; Wu, J.; Liu, C. Multi-Track Triboelectric Nanogenerator toward Omnidirectional Ocean Wave Energy Harvesting. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2024, 9, 2301824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharjan, P.; Toyabur, R.; Park, J. A human locomotion inspired hybrid nanogenerator for wrist-wearable electronic device and sensor applications. Nano Energy 2018, 46, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Libanori, A.; Xu, J.; Nashalian, A.; Chen, J. Triboelectric Nanogenerator Enabled Smart Shoes for Wearable Electricity Generation. Research 2020, 2020, 7158953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerators as Wearable Power Sources and Self-Powered Sensors. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2023, 10, nwac170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Deng, H.; Wu, H.; Luo, Y.; Deng, Y.; Yuan, H.; Cui, Z.; Tang, J.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, X.; et al. Rotary Wind-driven Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Self-Powered Airflow Temperature Monitoring of Industrial Equipment. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2307382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.; Liu, F.; Chen, J.; Xia, L.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, J.; Dong, K.; Zhang, C.; Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. An epidermal electrode based triboelectric walking energy harvester for wearable wireless sensing applications. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2024, 67, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, Z.; He, W.; Li, G.; Tang, Q.; Guo, H.; Pu, X.; Liu, Y.; Hu, C. High performance floating self-excited sliding triboelectric nanogenerator for micro mechanical energy harvesting. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.; Long, J.; Huang, T.; Xiang, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, J.; Yu, H. Core–Sheath Fiber-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Straight-Arm Sit-up Sensing. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 31427–31435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, K.; Liu, X.; Zhong, S.; Cao, J. Self-powered wireless sensor system for water monitoring based on low-frequency electromagnetic-pendulum energy harvester. Energy 2022, 251, 123883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Cheng, G.; Zi, Y.; Gu, G.; Zhang, B.; Shang, W.; Yang, F.; Yang, J.; Du, Z.; Wang, Z.L. High Energy Storage Efficiency Triboelectric Nanogenerators with Unidirectional Switches and Passive Power Management Circuits. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1805216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, J.; Xu, G.; Fu, J.; Gani, A.B.; Dai, J.; Guan, D.; Tu, Y.; Li, C.; Zi, Y. The Potential Application of the Triboelectric Nanogenerator in the New Type Futuristic Power Grid Intelligent Sensing. EcoMat 2023, 5, e12410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.N.Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Application of Triboelectric Nanogenerator in Fluid Dynamics Sensing: Past and Future. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Liang, X.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Z.L. Advances in Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Blue Energy Harvesting and Marine Environmental Monitoring. Engineering 2023, 33, 204–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin Nazar, A.; Narazaki, Y.; Rayegani, A.; Sardo, F.R. Recent Progress of Triboelectric Nanogenerators as Self-Powered Sensors in Transportation Engineering. Measurement 2022, 203, 112010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Shao, H.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Zhu, M.; Fang, J.; Cheng, T.; Lin, T. A full-textile triboelectric nanogenerator with multisource energy harvesting capability. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 267, 115910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Du, T.; Liu, C.; Hu, Z.; Sun, P.; Xu, M. A Ring-Type Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Rotational Mechanical Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Rotational Speed Sensing. Micromachines 2022, 13, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lee, D.; Ryu, H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, H.; Yoon, H.; Kang, M.; Kwak, S.S.; Kim, S. Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Battery-Free Wireless Sensor System Using Multi-Degree of Freedom Vibration. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2024, 9, 2301427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ren, Z.; Han, M.; Wan, J.; Zhang, H. Hybrid Energy Cells Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerator: From Principle to System. Nano Energy 2020, 75, 104980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.; Yi, H.; Yang, Y.; Chang, H.; Wu, J.; Tang, L.; Yang, Z.; Wang, N.; Hu, L.; Fu, Y.; et al. Origami-inspired electret-based triboelectric generator for biomechanical and ocean wave energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2020, 67, 104197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. Catch Wave Power in Floating Nets. Nature 2017, 542, 159–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, G.; Meng, Q.; Yang, N.; Feng, L.; Wang, F.; Chen, Y.; Wong, C.-P. Superhigh charge density and direct-current output in triboelectric nanogenerators via peak shifting modified charge pumping. Nano Energy 2022, 102, 107637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerators as New Energy Technology for Self-Powered Systems and as Active Mechanical and Chemical Sensors. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 9533–9557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okbaz, A.; Karabiber, A.; Yar, A.; Kınas, Z.; Sarılmaz, A.; Ozel, F. High-performance triboelectric nanogenerator with optimized Al or Ti-embedded silicone tribomaterial. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 252, 115053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liao, S.; Liu, D.; Zhao, R.; Zhou, T.; Yan, W.; Wei, K.; Zou, H.; Zhao, L. Enhanced triboelectric output of PDMS-based composite film with bi-material filling and surface patterning. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2023, 66, 2930–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Han, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C. Fish Scale for Wearable, Self-Powered Teng. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, L.; Wang, A.C.; Han, K.; Jiang, T.; Lai, Q.; Bai, Y.; Tang, W.; Fan, F.R.; et al. Flexible and durable wood-based triboelectric nanogenerators for self-powered sensing in athletic big data analytics. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Park, J.H.; Koo, B.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.L.; Kim, T.W. Capsule Triboelectric Nanogenerators: Toward Optional 3d Integration for High Output and Efficient Energy Harvesting from Broadband-Amplitude Vibrations. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 9947–9957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cao, B.; Yang, C.; Zhang, H.; Fang, L.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z.; He, W.; Wang, P. Broadband and Multi-Cylinder-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Mechanical Energy Harvesting with High Space Utilization. Materials 2023, 16, 3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Yang, P.; Liu, G.; Xu, S.; Yao, H.; Li, W.; Qu, H.; Ding, J.; Li, J.; Wan, L. Flower-like triboelectric nanogenerator for blue energy harvesting with six degrees of freedom. Nano Energy 2022, 93, 106796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhao, T.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.L.; Li, Z.; Pan, X.; Wang, Z.L. High Power Density Tower-Like Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Arbitrary Directional Water Wave Energy. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 1932–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, P.; Aw, K.C.; Jiang, X.; Xin, C.; Guo, H.; Tang, L.; Peng, Y.; Li, Z. Fish gills inspired parallel-cell triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2022, 95, 106976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merces, L.; Ferro, L.M.M.; Thomas, A.; Karnaushenko, D.D.; Luo, Y.; Egunov, A.I.; Zhang, W.; Bandari, V.K.; Lee, Y.; McCaskill, J.S.; et al. Bio-Inspired Dynamically Morphing Microelectronics toward High-Density Energy Applications and Intelligent Biomedical Implants. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, e2313327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Yang, Z.; Choi, J.; Wang, C.; Dai, G.; Yang, J. Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Preventive Health Monitoring. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Han, M.; Song, Y.; Zhang, H. Design, manufacturing and applications of wearable triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2021, 81, 105627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawardhana, K.S.D.; Wanasekara, N.D.; Dharmasena, R.I.G. Towards Truly Wearable Systems: Optimizing and Scaling Up Wearable Triboelectric Nanogenerators. iScience 2020, 23, 101360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, Q.; Ding, Z.; Li, Z.; Zheng, H.; Fu, J.; Diao, C.; Zhang, X.; Tian, J.; Zi, Y. A fully-packaged ship-shaped hybrid nanogenerator for blue energy harvesting toward seawater self-desalination and self-powered positioning. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Raveendran, V.; Chen, J. Wearable Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Biomechanical Energy Harvesting. Nano Energy 2020, 77, 105303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helps, T.; Romero, C.; Taghavi, M.; Conn, A.T.; Rossiter, J. Liquid-amplified zipping actuators for micro-air vehicles with transmission-free flapping. Sci. Robot. 2022, 7, eabi8189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Yong, H.; Moon, H.; Van Duong, Q.; Choi, S.T.; Kim, D.; Lee, S. Hand-Driven Gyroscopic Hybrid Nanogenerator for Recharging Portable Devices. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1801054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Yeh, M.-H.; Liu, G.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Bai, Y.; Feng, L.; Lai, M.; Ho, K.-C.; Guo, H.; et al. Whirligig-inspired triboelectric nanogenerator with ultrahigh specific output as reliable portable instant power supply for personal health monitoring devices. Nano Energy 2018, 47, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Xu, J.; Fang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J. A Hand-Driven Portable Triboelectric Nanogenerator Using Whirligig Spinning Dynamics. Nano Energy 2021, 83, 105845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Han, C.; Feng, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, Z.L.; Wu, Z. Hybrid Triboelectric–Electromagnetic Nanogenerator Based on a Tower Spring for Harvesting Omnidirectional Vibration Energy. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 11577–11585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Name | Specification |
|---|---|
| Capsule Shell | Outer diameter: 70 mm, Height: 147 mm |
| Copper Foil Electrode | Thickness: 60 μm, Radius: 30 mm |
| PTFE Film | Thickness: 50 μm, Radius: 30 mm |
| PET Film | Thickness: 50 μm, Radius: 30 mm |
| Foam | Thickness: 1 mm, Radius: 30 mm |
| PLA Support Plate | Thickness: 1 mm, Radius: 30 mm |
| Spring | Length: 5 mm, Width: 2 mm, Wire diameter: 0.02 mm |
| Steel Ball | Diameter: 22 mm, Weight: 40.5 g |
| Conical Spring | Small outer diameter: 8 mm, Large outer diameter: 16 mm, Length: 20 mm |
| Lateral Support Structures | Diameter: 62 mm, Height: 21 mm |
| Maximum Charge Accumulation Rate | 0.87 μC/s |
| Capacitor Charging Speed | 390 s to charge a 100μF capacitor to 5 V |
| Module Peak Voltage | 250 V |
| Module Peak Current | 7.2 μA |
| Optimal Matching Resistance | 120 MΩ |
| Peak Power Density | 763 mW/m3 |
| Optimal Operating Frequency Range | Greater than 1.5 Hz |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Huo, D.; Su, J.; He, Z. Portable Multi-Layer Capsule-Shaped Triboelectric Generator for Human Motion Energy Harvesting. Micromachines 2024, 15, 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15070852
Yang X, Huo D, Su J, He Z. Portable Multi-Layer Capsule-Shaped Triboelectric Generator for Human Motion Energy Harvesting. Micromachines. 2024; 15(7):852. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15070852
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xinglin, Da Huo, Jianye Su, and Zhouyu He. 2024. "Portable Multi-Layer Capsule-Shaped Triboelectric Generator for Human Motion Energy Harvesting" Micromachines 15, no. 7: 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15070852
APA StyleYang, X., Huo, D., Su, J., & He, Z. (2024). Portable Multi-Layer Capsule-Shaped Triboelectric Generator for Human Motion Energy Harvesting. Micromachines, 15(7), 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15070852






