Silver Nanoparticle-Based Finishing for Leather Antimicrobial and UV Protection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Functionalized Silver Nanoparticles (Ag-F NPs)
2.3. Ag-F NPs Leather-Finishing Agents’ Preparation
2.4. Leather Finishing
2.5. Characterization of Nanoparticles and Leather-Finishing Agents
2.6. Characterization of Leather Properties
2.6.1. Antimicrobial Properties Analysis
2.6.2. Aging Tests
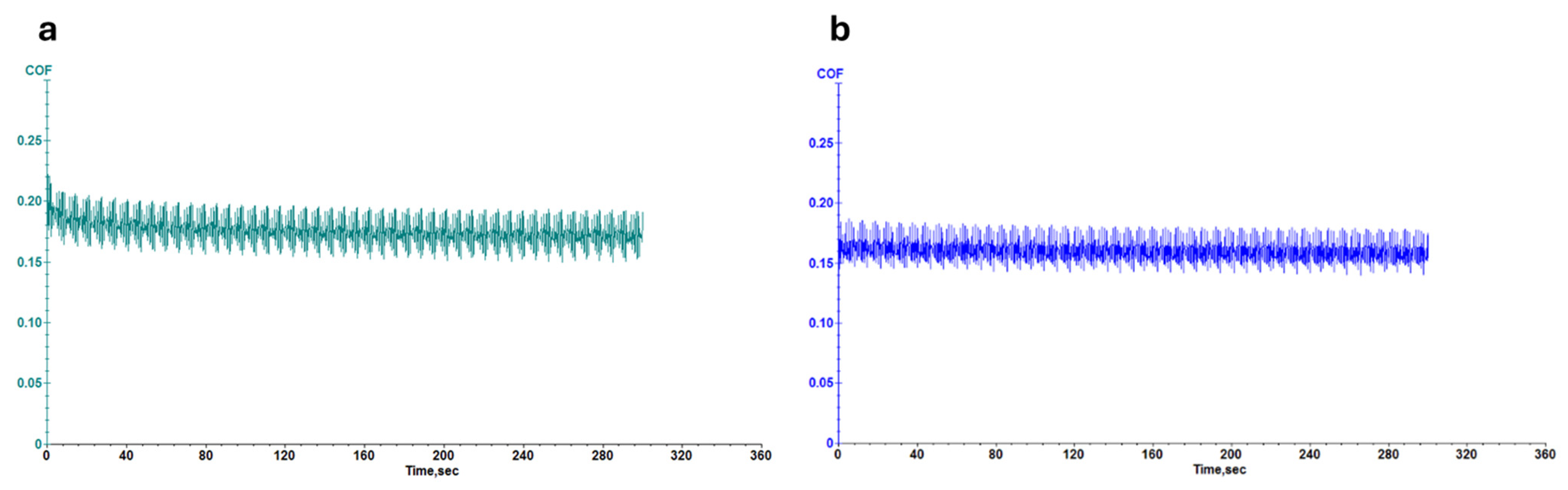
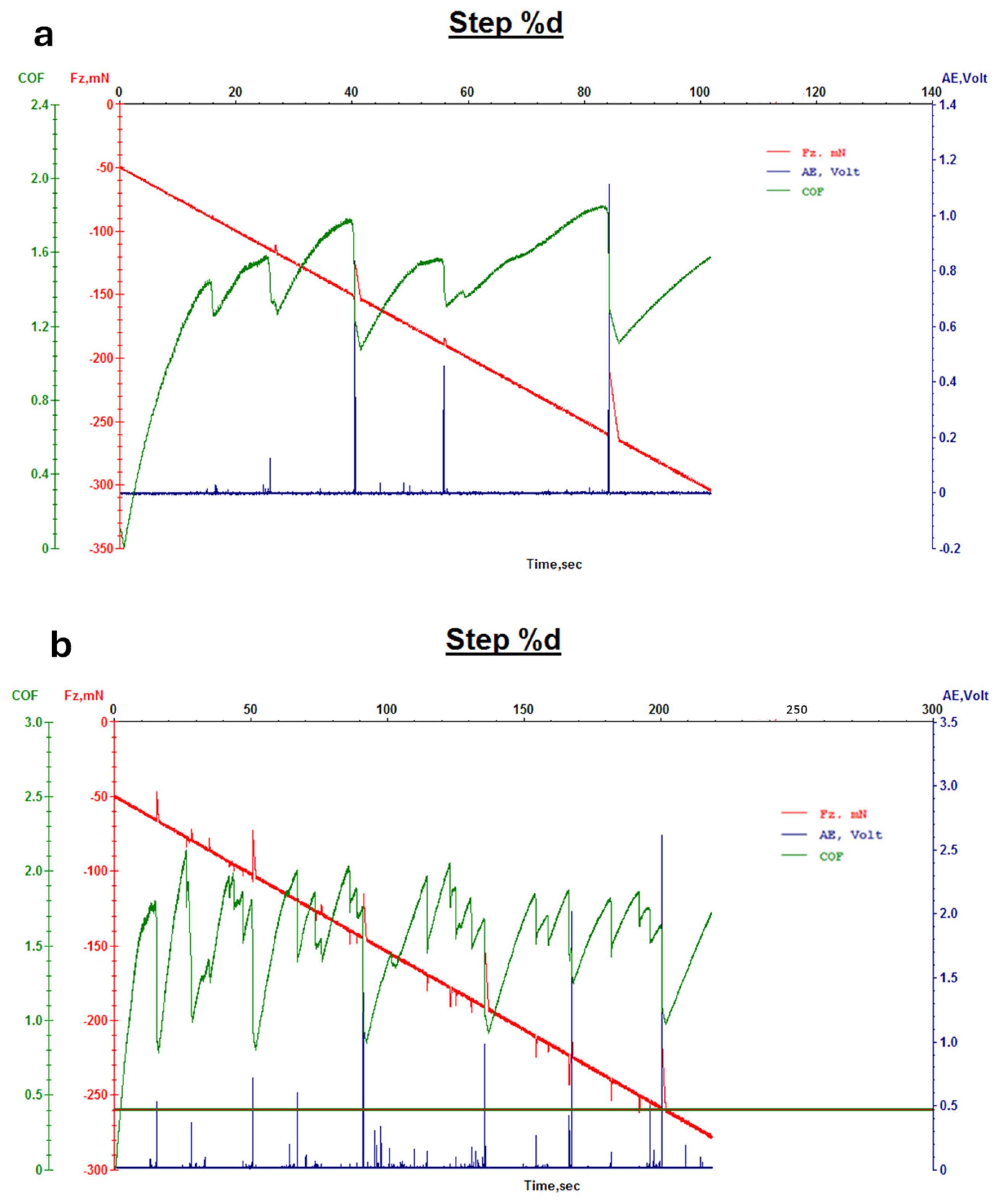
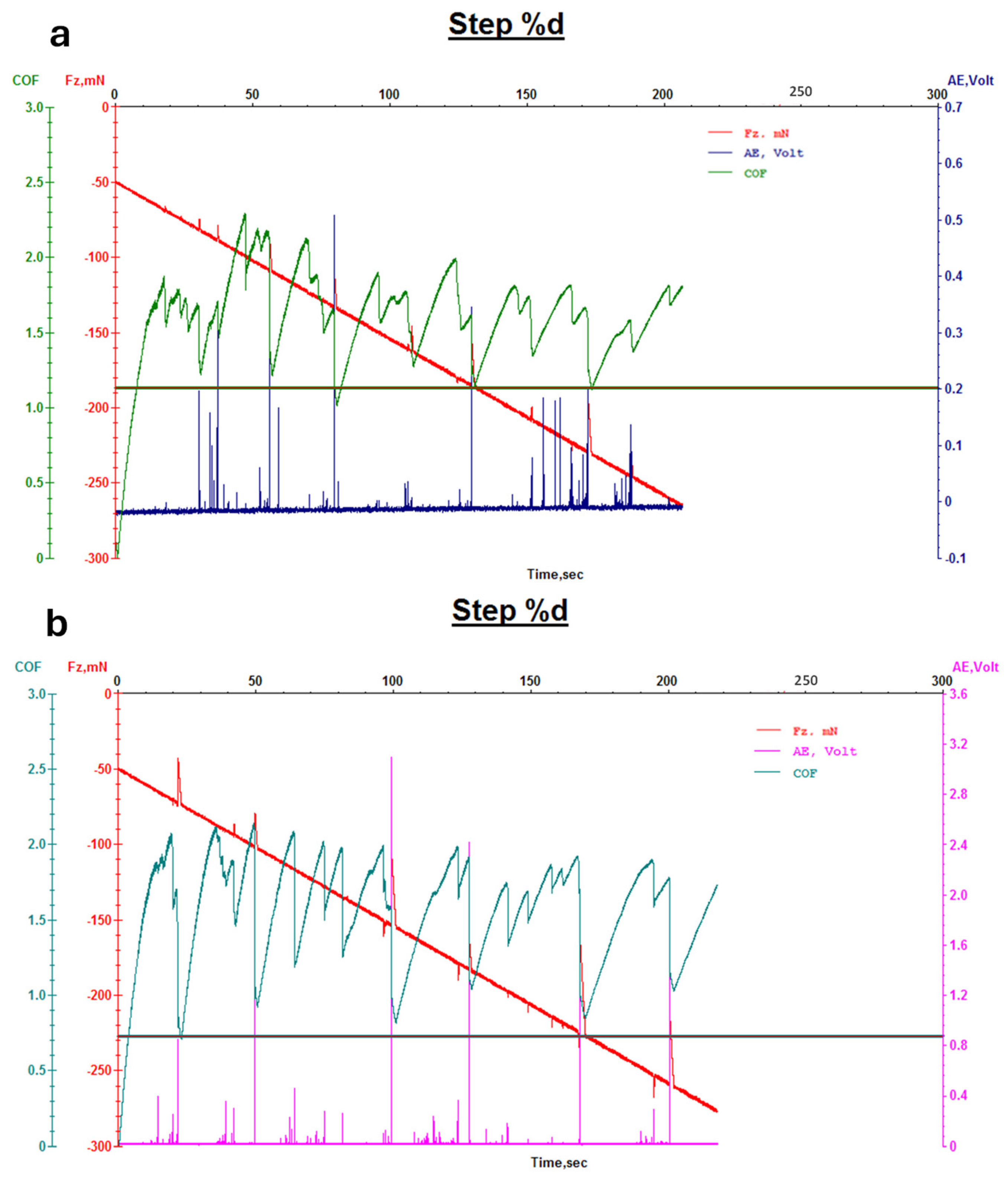
2.6.3. Abrasion Resistance Tests and Wear/Micro-Scratch Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Nanoparticles Characterization
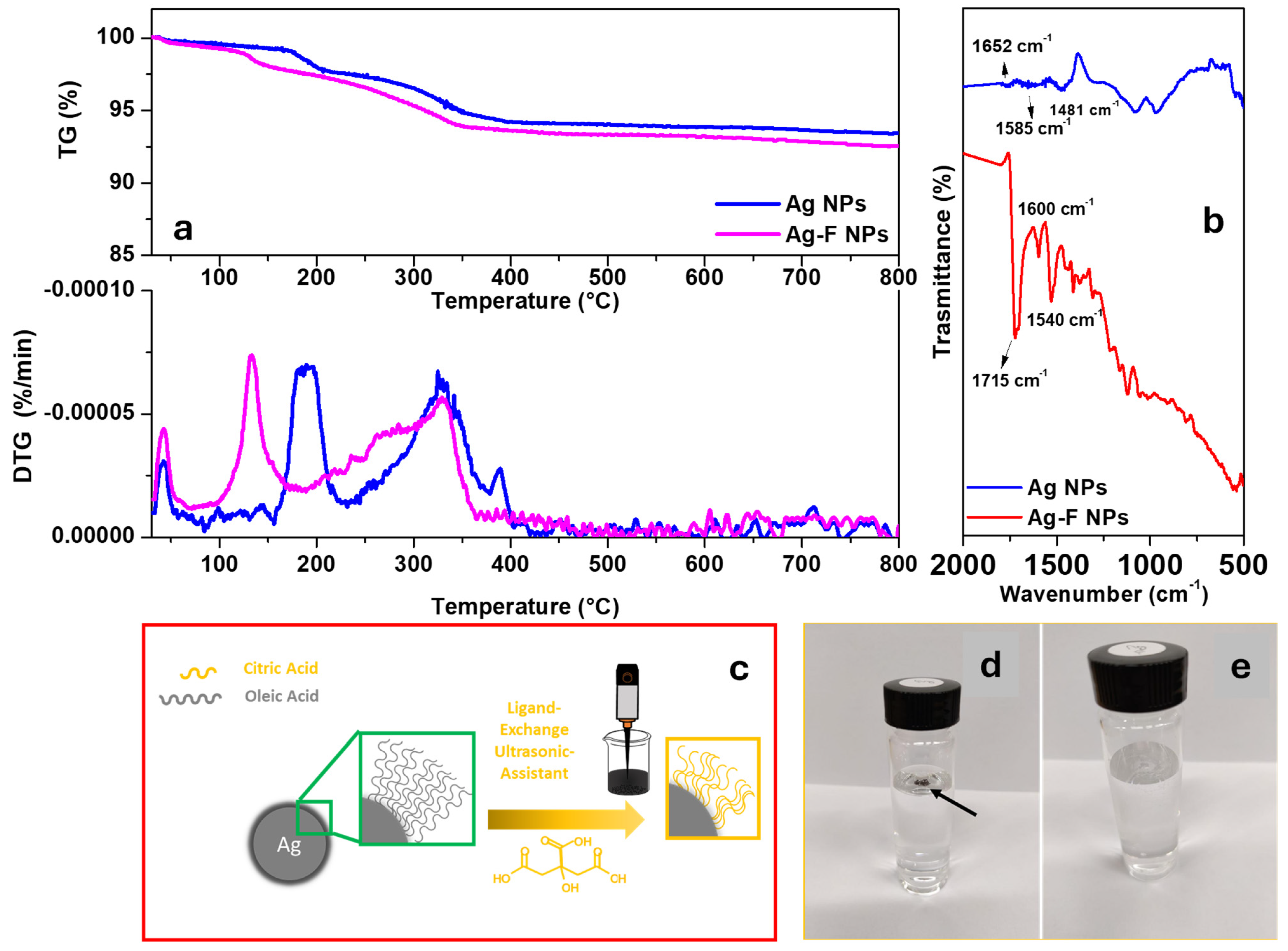
3.1.1. Chemical–Physical Characterization of Nanoparticles
3.1.2. Evaluation of Leather Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nalbat, S.; Onem, E.; Basaran, B.; Yorgancioglu, A.; Yilmaz, I.O. Effect of finishing density on the Physico-Mechanical Properties of leather. J. Soc. Leather Technol. Chem. 2016, 100, 84–89. Available online: https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=6958871 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Shahriar, A.; Zohra, F.; Murad, A.W.; Ahmed, S. Enhancement of Waterproofing Properties of Finished Upper Leather Produced from Bangladeshi Cow Hides. Eur. J. Eng. Technol. Res. 2019, 4, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, P.; Shim, J.; Bang, K.; Oh, B. Gold nanoparticles mediated coloring of fabrics and leather for antibacterial activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 160, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirillo, C.; Iuliano, M.; Scarpa, D.; Gallucci, L.; Florio, C.; Maffei, G.; Loi, A.; Sarno, M. Nanoparticle usage in leather processing: Worker safety and health. ACS Chem. Health Saf. 2024, 31, 276–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Recupido, F.; Lama, G.C.; Oliviero, M.; Verdolotti, L.; Lavorgna, M. Recent advances concerning polyurethane in leather applications: An overview of conventional and greener solutions. Deleted J. 2023, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, M. Ecology of matter and the surface design in the leather fashion industry. J. Text. Sci. Fash. Technol. 2019, 4, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Da Costa AD, S.; Savitri, C.; Ha, S.S.; Wang, P.; Park, K. An injectable, self-assembled multicellular microsphere with the incorporation of fibroblast-derived extracellular matrix for therapeutic angiogenesis. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 113, 110961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Wang, X.; Zheng, M.; Yue, O.; Xie, L.; Zha, S.; Dong, S.; Li, T.; Song, Y.; Huang, M.; et al. Leather for flexible multifunctional bio-based materials: A review. J. Leather Sci. Eng. 2022, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Chua, M.H.; Ong, P.J.; Lee, J.J.C.; Chin, K.L.O.; Wang, S.; Kai, D.; Ji, R.; Kong, J.; Dong, Z.; et al. Recent advances in nanotechnology-based functional coatings for the built environment. Mater. Today Adv. 2022, 15, 100270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Poon, Y.F.; Li, W.; Zhu, H.; Yeap, S.H.; Cao, Y.; Qi, X.; Zhou, C.; Lamrani, M.; Beuerman, R.W.; et al. A polycationic antimicrobial and biocompatible hydrogel with microbe membrane suctioning ability. Nat. Mater. 2010, 10, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.J.; Cai, T.; Neoh, K.; Kang, E.; Dickinson, G.H.; Teo, S.L.; Rittschof, D. Biomimetic anchors for antifouling and antibacterial polymer brushes on stainless steel. Langmuir 2011, 27, 7065–7076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fierro, F.; Iuliano, M.; Cirillo, C.; Florio, C.; Maffei, G.; Loi, A.; Batakliev, T.; Adami, R.; Sarno, M. Multifunctional leather finishing vs. applications, through the addition of well-dispersed flower-like nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.R.; Shakil, M.S.R.; Vorselaars, B.; Rahman, M.; Jawad, I.A.; Ahmed, W. Nanotechnology in Leather Manufacturing. In Micro and Nanomanufacturing Volume II; Jackson, M.J., Ahmed, W., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, H.M.; Attia, R.Z.; Mohamed, O.A.; El-Sayed, N.H.; Ibrahim, S.A. High Bloom Gelatin Strength from White Leather Shavings. Leather Footwear J. 2018, 18, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahim, M.; Shahzaib, A.; Nishat, N.; Jahan, A.; Bhat, T.A.; Inam, A. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles: A Comprehensive review of methods, influencing factors, and applications. JCIS Open 2024, 16, 100125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, H.; Hasanin, M.; Rehan, M. Enhancement of multifunctional properties of leather surface decorated with silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs). J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1234, 130130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owoyemi, H.T.; Adewuyi, B.O.; Oladele, I.O.; Falana, S.O.; Oyegunna, S.A.; Ajileye, J.O. Silver nanoparticles reinforced polyethersulfone composite for sustainable application. Discov. Polym. 2024, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehan, M.; Mashaly, H.M.; Mowafi, S.; Abou El-Kheir, A.; Emam, H.E. Multi-functional textile design using in-situ Ag NPs incorporation into natural fabric matrix. Dyes Pigments 2015, 118, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Emam, H.E.; Rehan, M.; Mashaly, H.M.; Ahmed, H.B. Large scaled strategy for natural/synthetic fabrics functionalization via immediate assembly of AgNPs. Dyes Pigments 2016, 133, 173–183. [Google Scholar]
- Rehan, M.; Barhoum, A.; Van Assche, G.; Dufresne, A.; Gätjen, L.; Wilken, R. Towards multifunctional cellulosic fabric: UV photo-reduction and in-situ synthesis of silver nanoparticles into cellulose fabrics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 877–886. [Google Scholar]
- Mowafi, S.; Kafafy, H.; Arafa, A.; Haggag, K.; Rehan, M. Facile and environmental benign in situ synthesis of silver nanoparticles for multifunctionalization of wool fibers. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 29054–29069. [Google Scholar]
- Rehan, M.; Elshemy, N.S.; Haggag, K.; Montaser, A.; Ibrahim, G.E. Phytochemicals and volatile compounds of peanut red skin extract: Simultaneous coloration and in situ synthesis of silver nanoparticles for multifunctional viscose fibers. Cellulose 2020, 27, 9893–9912. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, S.; Elsayed, H.; Hasnein, M. Biodegradable, antimicrobial and antioxidant biofilm for active packaging based on extracted gelatin and lignocelluloses biowastes. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 472–482. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, S. Biodegradable package films of poly (L-lactic) acid/extracted gelatin blend from white leather fibers. Egypt. J. Chem. 2020, 63, 7–8. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, I.P.; Amaral, J.S.; Pinto, V.; Ferreira, M.J.; Barreiro, M.F. Development of chitosan-based antimicrobial leather coating. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 1229–1235. [Google Scholar]
- Arciola, C.R.; Campoccia, D.; Speziale, P.; Montanaro, L.; Costerton, J.W. Biofilm formation in staphylococcus implant infections. A review of molecular mechanisms and implications for biofilm-resistant materials. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 5967–5982. [Google Scholar]
- Campoccia, D.; Montanaro, L.; Arciola, C.R. A review of the biomaterials technologies for infection-resistant surfaces. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 8533–8554. [Google Scholar]
- Knetsch, M.L.W.; Koole, L.H. New strategies in the development of antimicrobial coatings: The example of increasing usage of silver and silver nanoparticles. Polymers 2011, 3, 340–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzello, L.; Pompa, P.P. Nanosilver-based antibacterial drugs and devices: Mechanisms, methodological drawbacks, and guidelines. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 1501–1518. [Google Scholar]
- Goli, K.K.; Gera, N.; Liu, X.; Rao, B.M.; Rojas, O.J.; Genzer, J. Generation and properties of antibacterial coatings based on electrostatic attachment of silver nanoparticles to protein-coated polypropylene fibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 5298–5306. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.; Ma, B.; Pan, T.; Chen, S.; Sun, J. Silver-nanoparticle-colored cotton fabrics with tunable colors and durable antibacterial and self-healing superhydrophobic properties. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 569–576. [Google Scholar]
- Sarno, M.; Iuliano, M. Highly active and stable Fe3O4/Au nanoparticles supporting lipase catalyst for biodiesel production from waste tomato. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 474, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarno, M.; Iuliano, M. Active biocatalyst for biodiesel production from spent coffee ground. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 266, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iuliano, M.; Cirillo, C.; Fierro, F.; Florio, C.; Maffei, G.; Loi, A.; Batakliev, T.; Adami, R.; Sarno, M. Titania nanoparticles finishing for smart leather surface. Prog. Org. Coat. 2024, 192, 108457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarno, M.; Casa, M. Green and one-step synthesis for Ag/graphene hybrid supercapacitor with remarkable performance. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2018, 120, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNI EN ISO 105-B02:2014; Colour Fastness to Light—Test Method: Xenon Arc Fading Lamp Test. UNI (Ente Nazionale Italiano di Unificazione): Milan, Italy, 2014.
- SAE J2412; Laboratory Lightfastness Test Method for Automotive Interiors. SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2004.
- ISO 17076-1:2012; Leather—Physical and Mechanical Tests—Determination of Abrasion Resistance—Part 1: Taber Method. ISO (International Organization for Standardization): Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- ISO 17076-2:2011; Leather—Physical and Mechanical Tests—Determination of Abrasion Resistance—Part 2: Martindale Method. ISO (International Organization for Standardization): Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- Iuliano, M.; Cirillo, C.; Astorga, E.N.; Sarno, M. A new nanocomposite as adsorbent and catalyst for enhanced removal of methylene blue. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 51, 104582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarno, M.; Iuliano, M.; Viscusi, G.; Zarli, A.; Ciambelli, P. A Nickel/Palladium/Ruthenium-Graphene based nanocatalyst for selective catalytic hydrogenation of vegetable oils. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 170, 113815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hole, P.; Sillence, K.; Hannell, C.; Maguire, C.M.; Roesslein, M.; Suarez, G.; Capracotta, S.; Magdolenova, Z.; Horev-Azaria, L.; Dybowska, A.; et al. Interlaboratory comparison of size measurements on nanoparticles using nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA). J. Nanoparticle Res. 2013, 15, 2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipe, V.; Hawe, A.; Jiskoot, W. Critical evaluation of Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) by NanoSight for the measurement of nanoparticles and protein aggregates. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 796–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachurski, D.; Schuldner, M.; Nguyen, P.; Malz, A.; Reiners, K.S.; Grenzi, P.C.; Babatz, F.; Schauss, A.C.; Hansen, H.P.; Hallek, M.; et al. Extracellular vesicle measurements with nanoparticle tracking analysis—An accuracy and repeatability comparison between NanoSight NS300 and ZetaView. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1596016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rujitanaroj, P.O.; Pimpha, N.; Supaphol, P. Wound-dressing materials with antibacterial activity from electrospun gelatin fiber mats containing silver nanoparticles. Polymer 2008, 49, 4723–4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcão, L.; Araújo, M.E.M. Application of ATR–FTIR spectroscopy to the analysis of tannins in historic leathers: The case study of the upholstery from the 19th century Portuguese Royal Train. Vib. Spectrosc. 2014, 74, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zuo, D.; Tan, C. Construction of C/ZnO/BiOI photocatalyst for enhanced degradation of carbaryl: Characterization, performance and mechanism. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 911, 165023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, P.; Li, M.; Lin, C.; Wang, Y. Z-scheme silver-based p-n junction of AgFeO2-modified Ag3VO4 with enhanced photocatalytic performance. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 918, 165771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Jana, T.K.; Chatterjee, K. Silica supported TiO2 nanostructures for highly efficient photocatalytic application under visible light irradiation. Mater. Res. Bull. 2016, 76, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Silva, Y.D.J.; Toledano-Ayala, M.; Gallardo-Hernández, S.; Godínez, L.A.; Méndez-López, A. Investigation of TiO2 deposit on SiO2 films: Synthesis, characterization, and efficiency for the photocatalytic discoloration of methylene blue in aqueous solution. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FCA 50444; Interior Trim Materials—Performance Requirements. Fiat Chrysler Automobiles (FCA): Auburn Hills, MI, USA, 2014.
- O’Donnell, A.; Dweib, M.; Wool, R. Natural fiber composites with plant oil-based resin. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 64, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukahori, Y.; Liang, H.; Busfield, J. Criteria for crack initiation during rubber abrasion. Wear 2008, 265, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtzen, D.A.; Reid, A.H., Jr. TiO2 Pigments Resistant to Discoloration in the Presence of Polymer Additives. U.S. Patent No. 4,999,055, 12 March 1991. [Google Scholar]

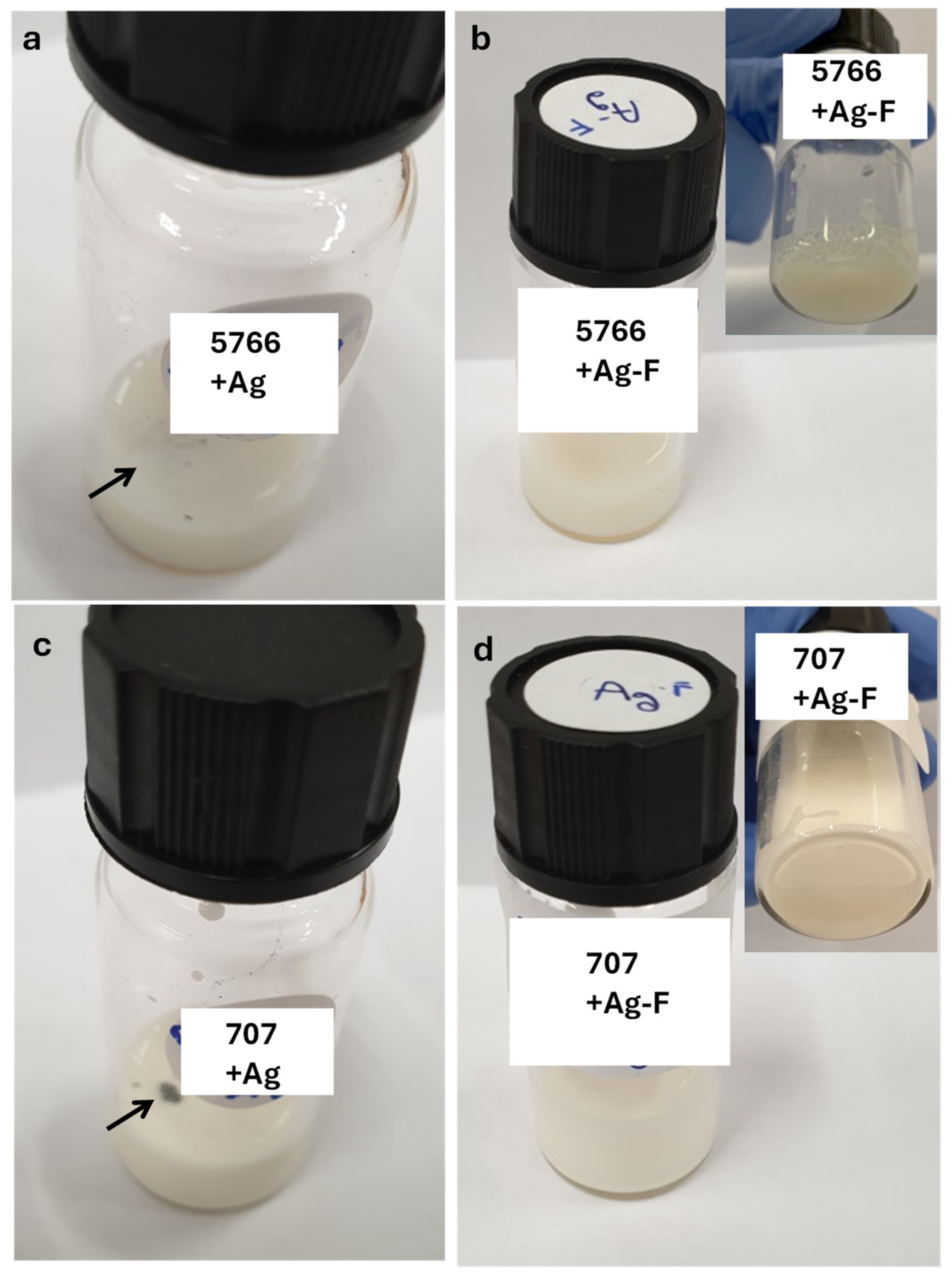



| Sample | CFU/mL MALT | CFU/mL TTC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | |
| Leather with 707 finishing | // | <102 | 103 | <102 | <102 | 102 |
| Leather with 707+Ag finishing | // | // | <102 | // | <102 | <102 |
| Leather with 5766 finishing | // | 103 | 103 | <105 | 105 | 106 |
| Leather with 5766+Ag finishing | // | // | <102 | // | // | <102 |
| Leather Sample | Exposure Time |
|---|---|
| Leather with 707 finishing |  |
| Leather with 707+Ag finishing |  |
| Leather with 5766 finishing |  |
| Leather with 5766+Ag finishing |  |
| Control Sample | Sample Ag-F NPs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | Test Method | Requirements | U.M. | Results | Results |
| To artificial light 225 KJ/m2 | SAEJ 2412 (acc. MS-JK 4000) | ∆E ≤ 3.0 (for closed saloon car) | ∆E | 1.02 | 0.91 |
| Report ∆H, ∆C and L, a, b data | ∆H ∆C ∆L ∆a ∆b | ∆H: 0.24 ∆C: 0.13 ∆L: 0.98 ∆a: 0.04 ∆b: 0.27 | ∆H: 0.01 ∆C: 0.07 ∆L: 0.90 ∆a: 0.00 ∆b: 0.07 | ||
| To artificial light 601 KJ/m2 | SAEJ 2412 (acc. MS-JK 4000) | TBR | ∆E | 1.03 | 0.93 |
| Report ∆H, ∆C and L, a, b data | ∆H ∆C ∆L ∆a ∆b | ∆H: 0.48 ∆C: 0.42 ∆L: 0.81 ∆a: 0.09 ∆b: 0.63 | ∆H: 0.01 ∆C: 0.09 ∆L: 0.79 ∆a: 0.02 ∆b: 0.08 |
| Control Sample | Sample Ag-F NPs | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | Test Method | Requirements | Results | Results |
| To rub with alcohol | FCA 50444 [51] | TILL END OF LIFE ≥3 bleeding on cloth | Beginning break 10 CYCLES | Beginning break 70 CYCLES |
| Martindale ball plate | DIN EN ISO 17076-2 | TILL END OF LIFE | Beginning break 1500 CYCLES | Beginning break 3000 CYCLES |
| TABER TEST_CS-10, 10 N | ISO 17076-1 | TILL END OF LIFE Slight traces of abrasion are permitted. Not permissible: cracks in the finish such that the crust leather surface is visible | Beginning break 1000 CYCLES | Beginning break 2000 CYCLES |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cirillo, C.; Iuliano, M.; Fierro, F.; Florio, C.; Maffei, G.; Loi, A.; Batakliev, T.; Sarno, M. Silver Nanoparticle-Based Finishing for Leather Antimicrobial and UV Protection. Micromachines 2025, 16, 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040376
Cirillo C, Iuliano M, Fierro F, Florio C, Maffei G, Loi A, Batakliev T, Sarno M. Silver Nanoparticle-Based Finishing for Leather Antimicrobial and UV Protection. Micromachines. 2025; 16(4):376. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040376
Chicago/Turabian StyleCirillo, Claudia, Mariagrazia Iuliano, Francesca Fierro, Claudia Florio, Gaetano Maffei, Andrea Loi, Todor Batakliev, and Maria Sarno. 2025. "Silver Nanoparticle-Based Finishing for Leather Antimicrobial and UV Protection" Micromachines 16, no. 4: 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040376
APA StyleCirillo, C., Iuliano, M., Fierro, F., Florio, C., Maffei, G., Loi, A., Batakliev, T., & Sarno, M. (2025). Silver Nanoparticle-Based Finishing for Leather Antimicrobial and UV Protection. Micromachines, 16(4), 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040376








