A New and Improved Sliding Mode Control Design Based on a Grey Linear Regression Model and Its Application in Pure Sine Wave Inverters for Photovoltaic Energy Conversion Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
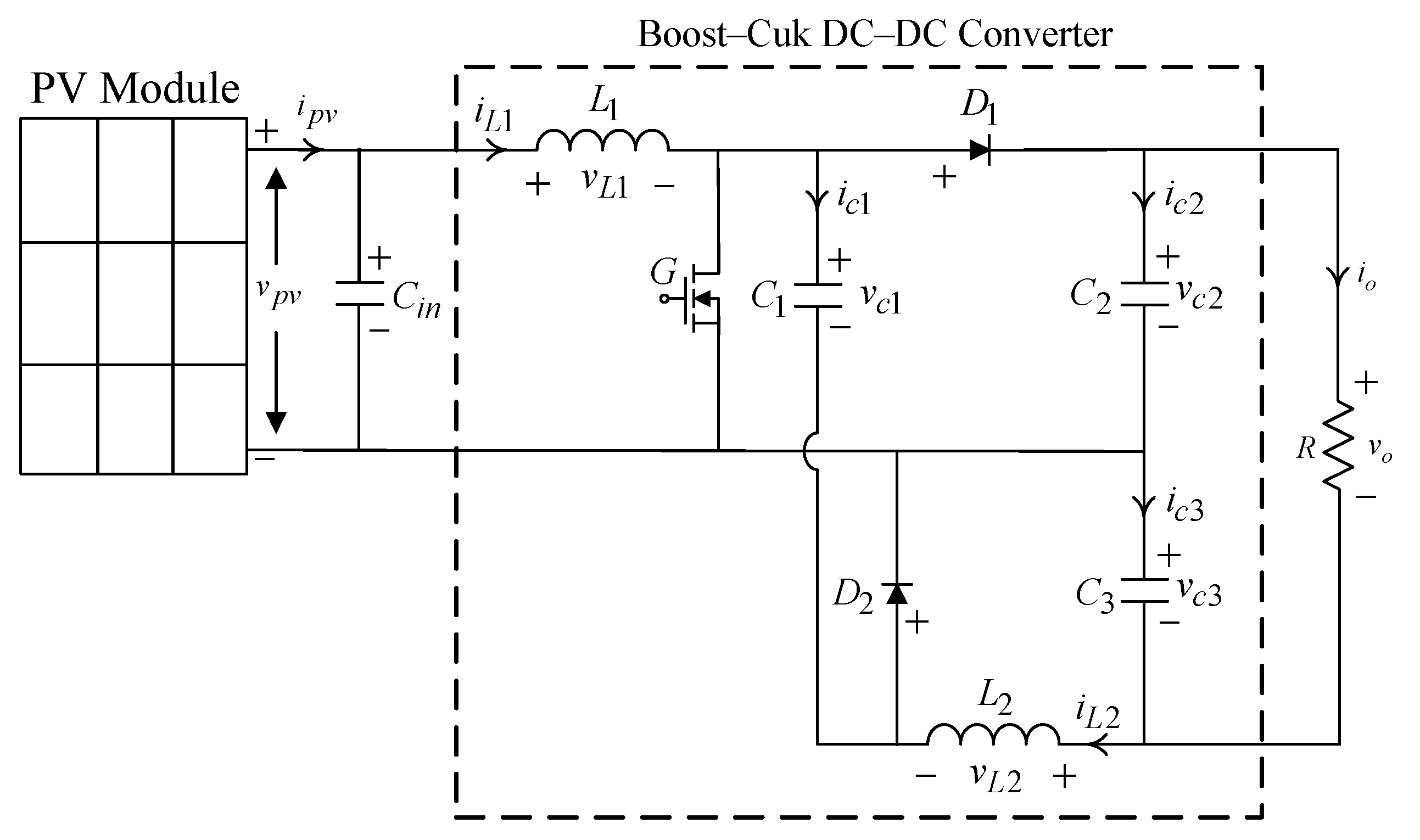
2. System Description
3. Control Design
- Step 1:
- The original data sequence (which represents output voltage values) must be represented as follows:
- Step 2:
- One way to express the accumulated generating operation (AGO) can be expressed as follows:
- Step 3:
- The following findings can be obtained by using to create a first-order differential grey model:
- Step 4:
- The inverse accumulated generating operation (IAGO) can be used to calculate the expected output at :
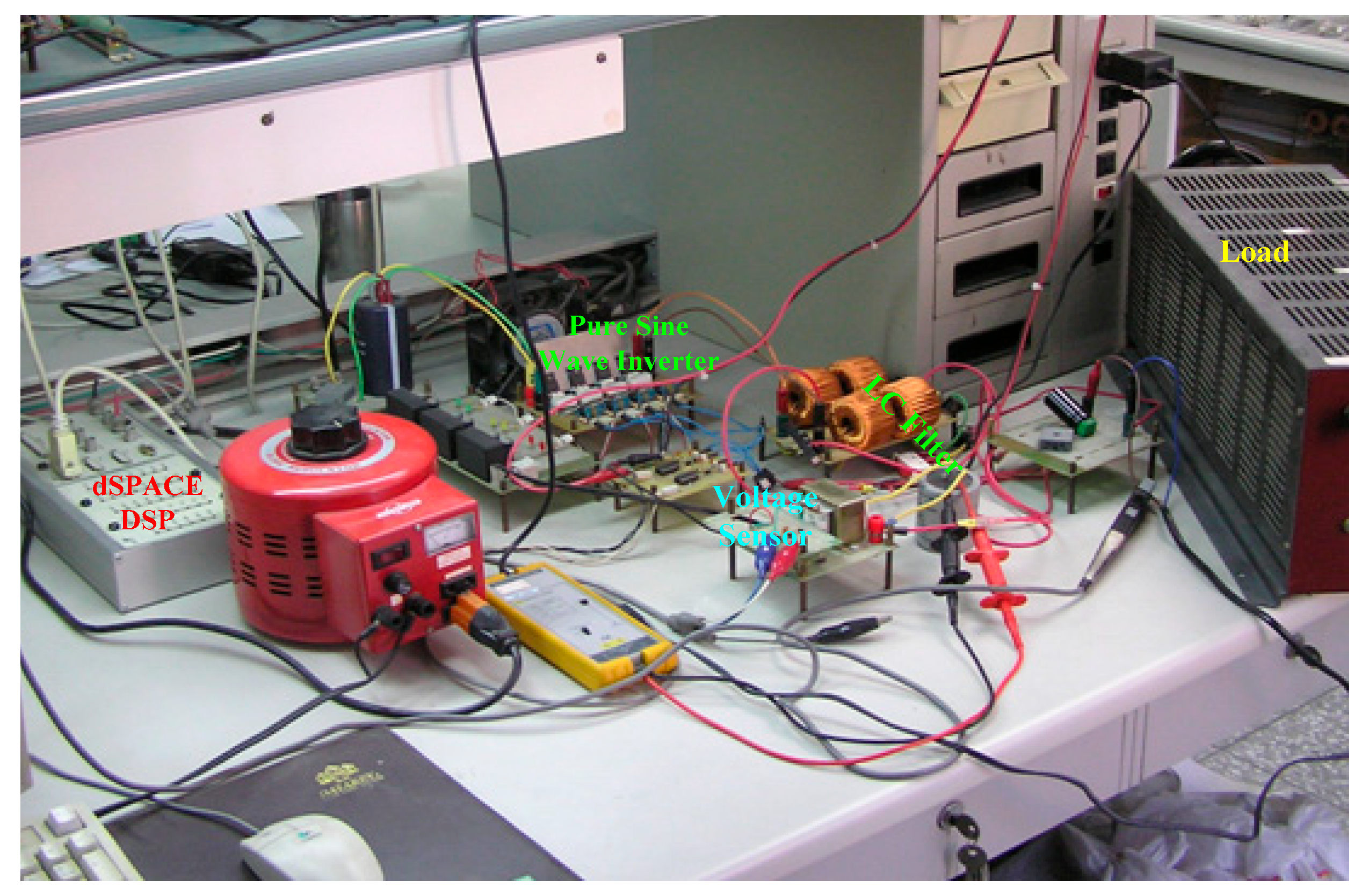
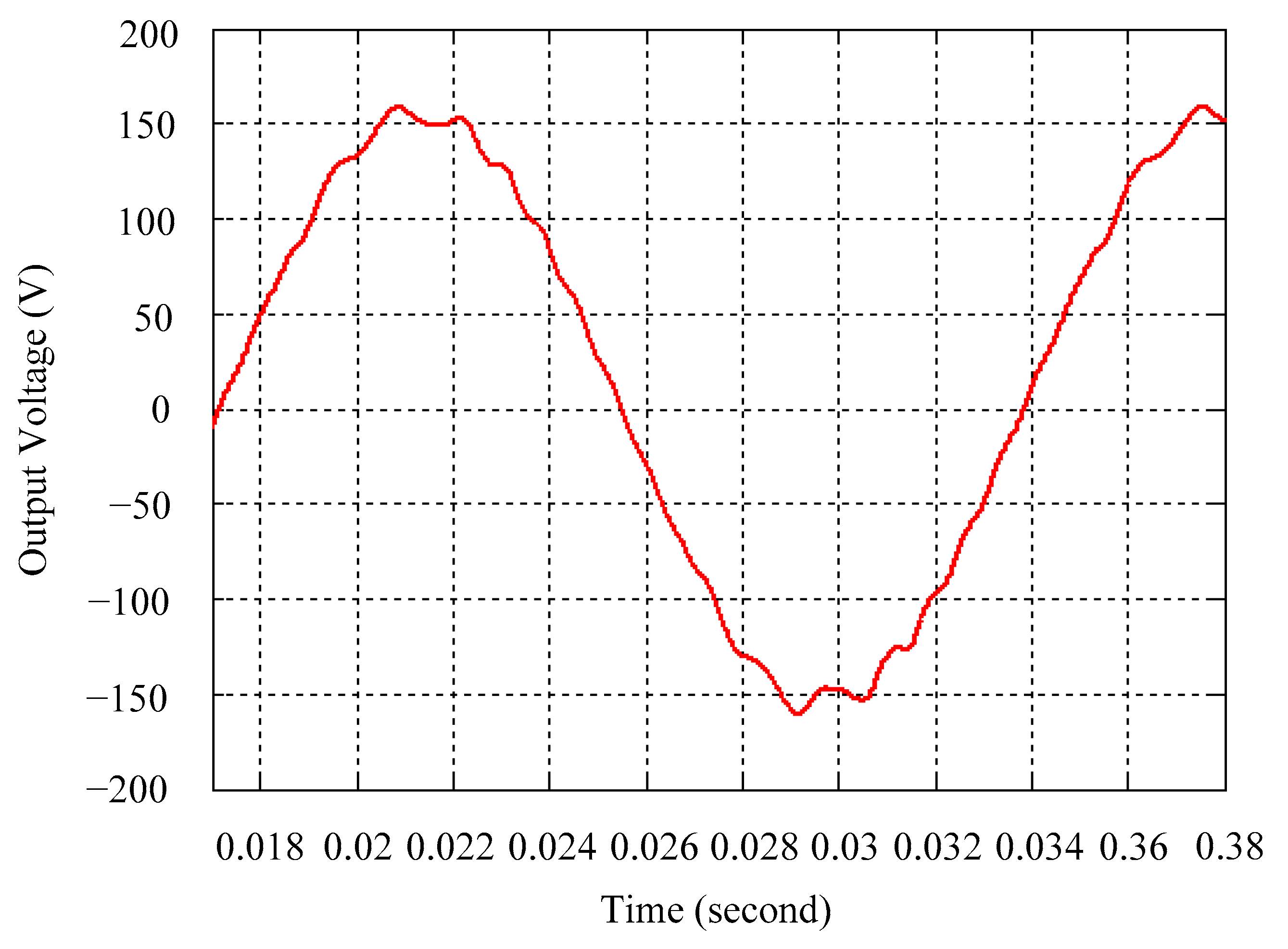
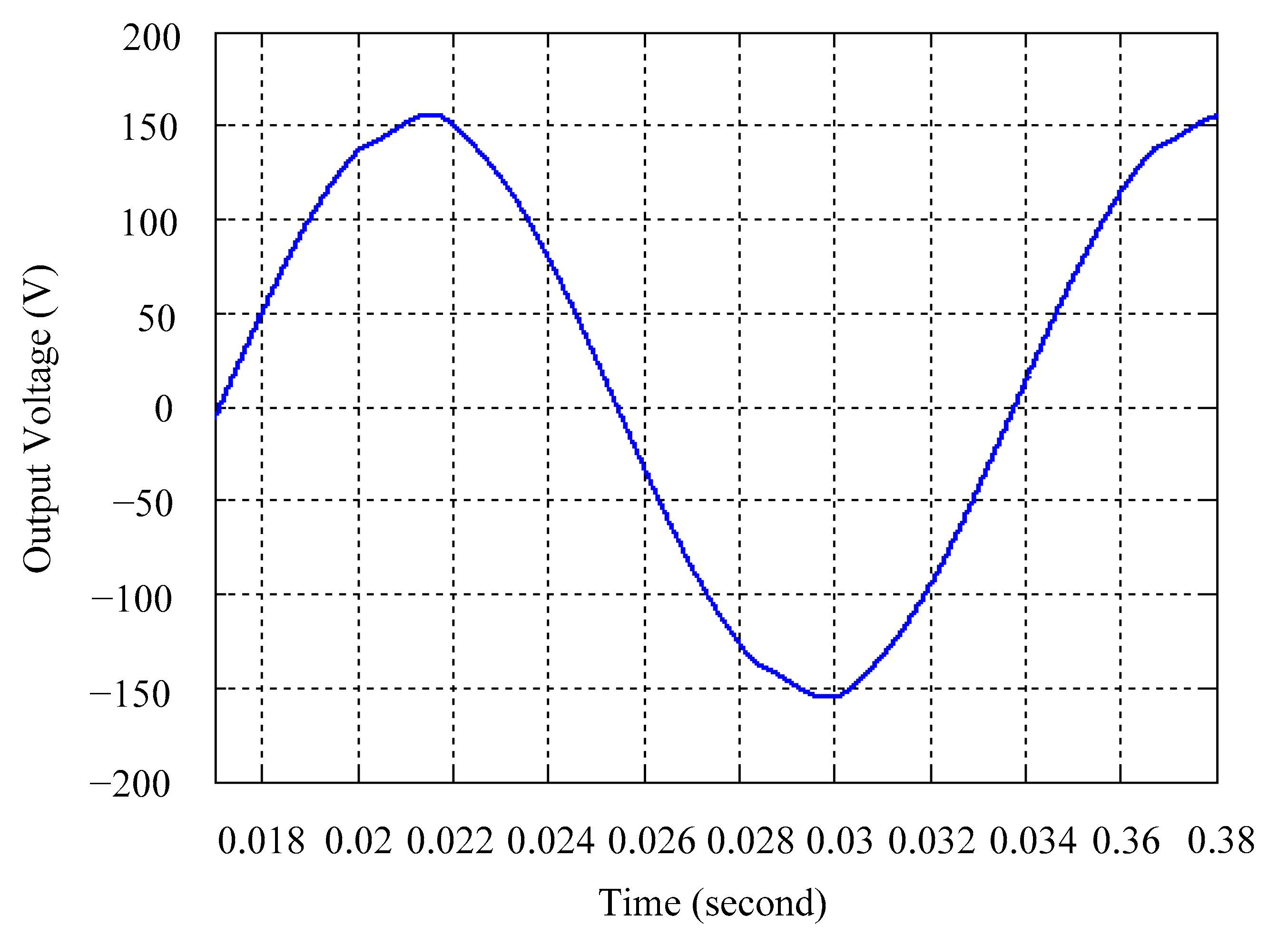
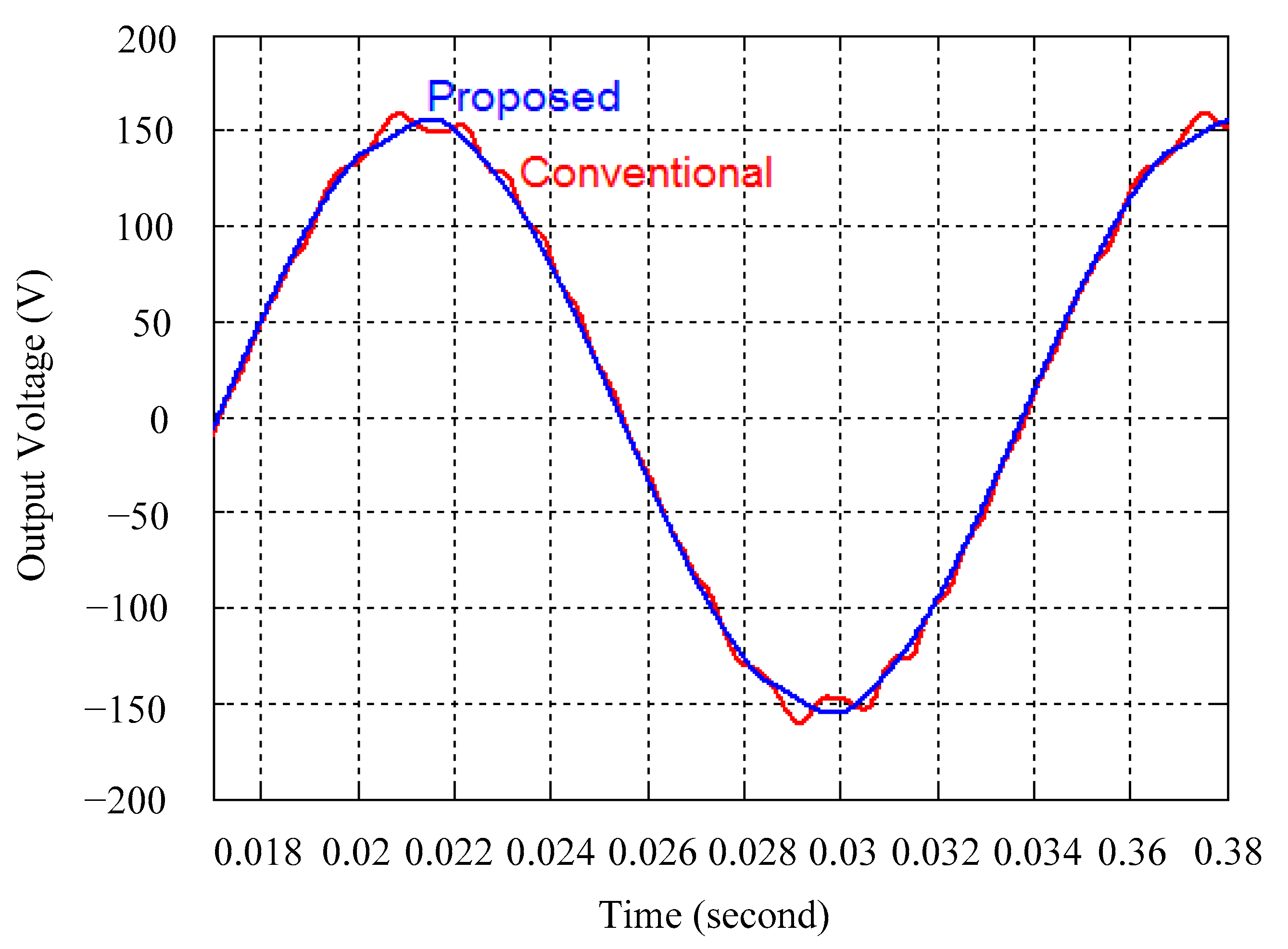
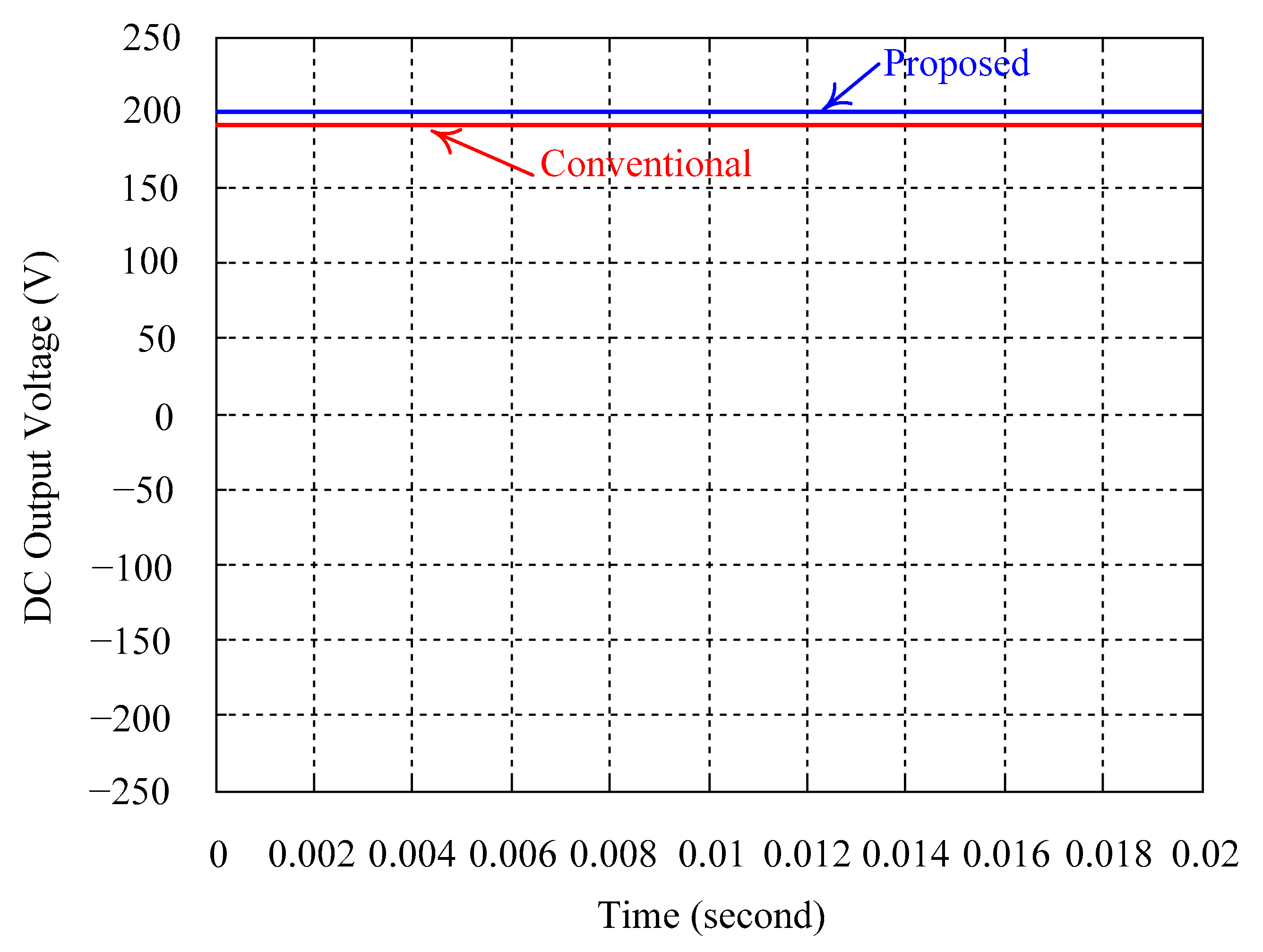
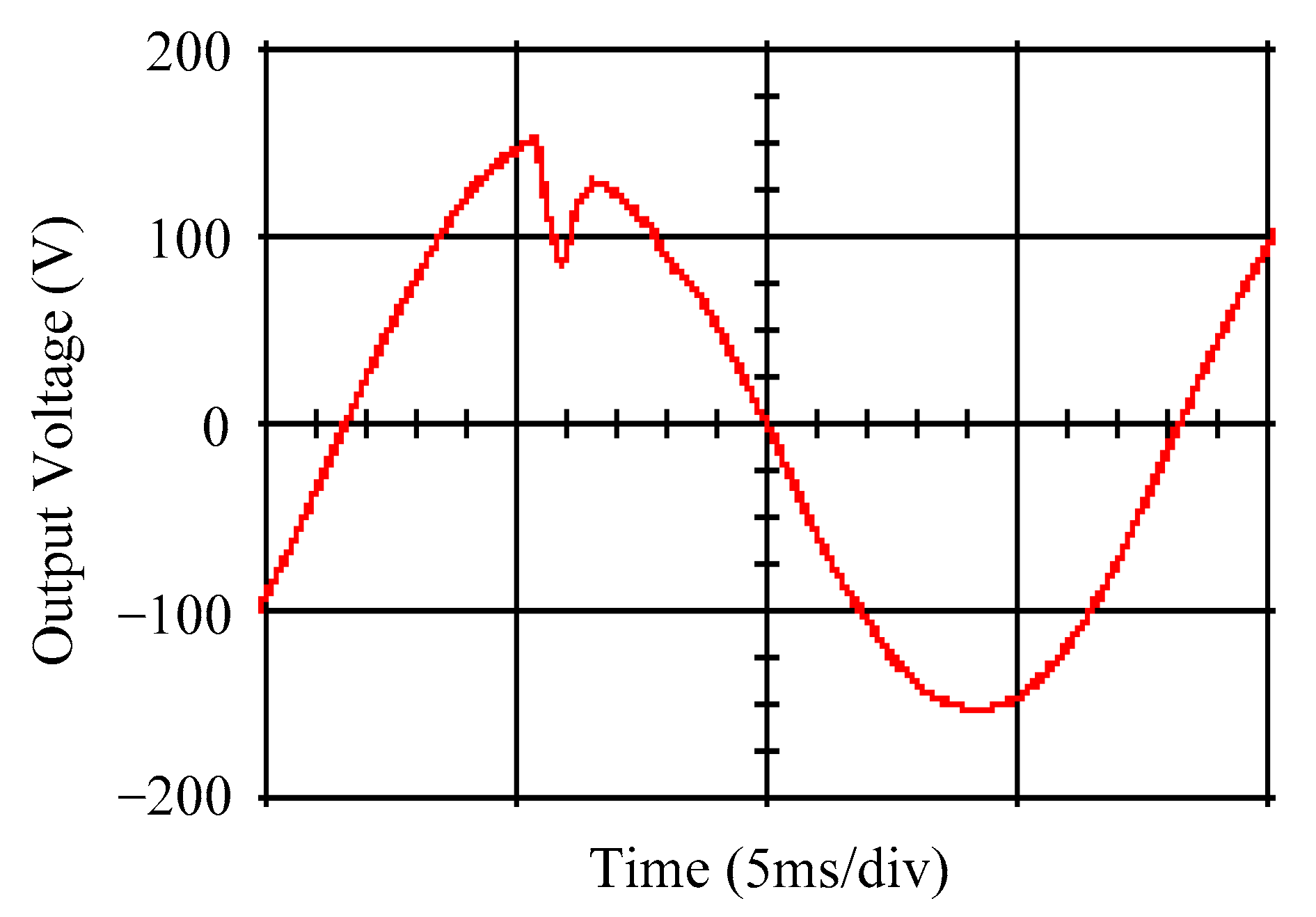
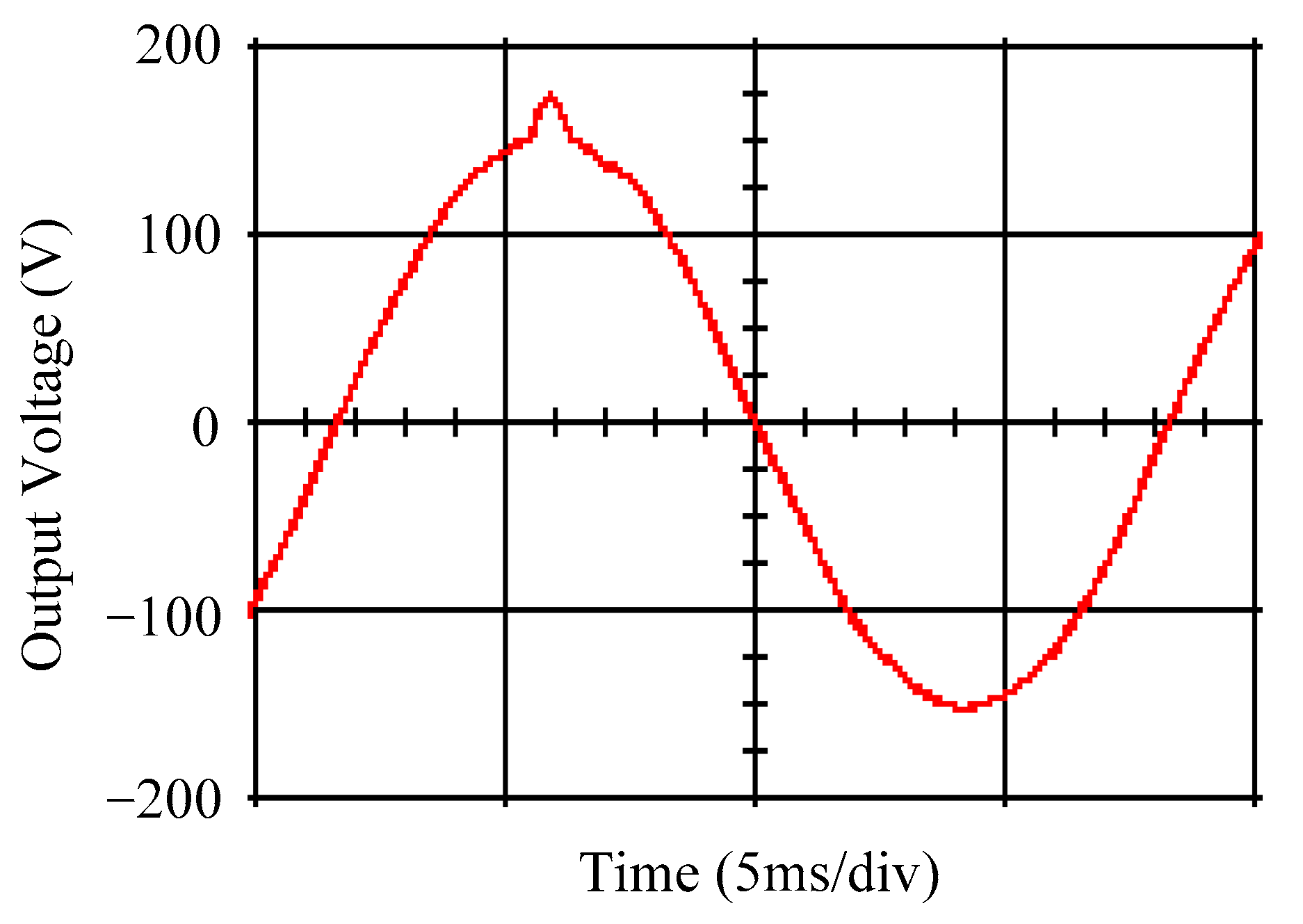
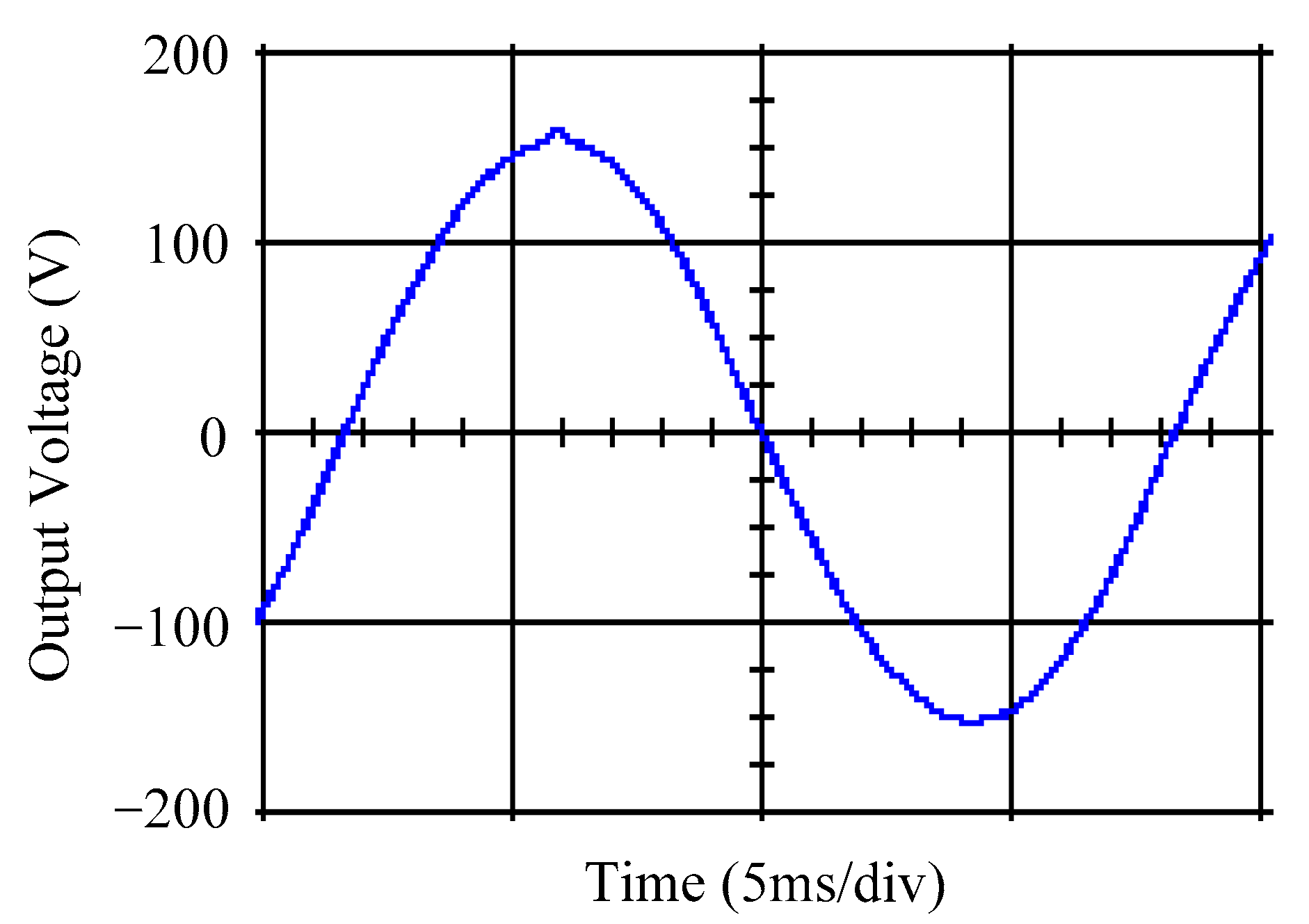
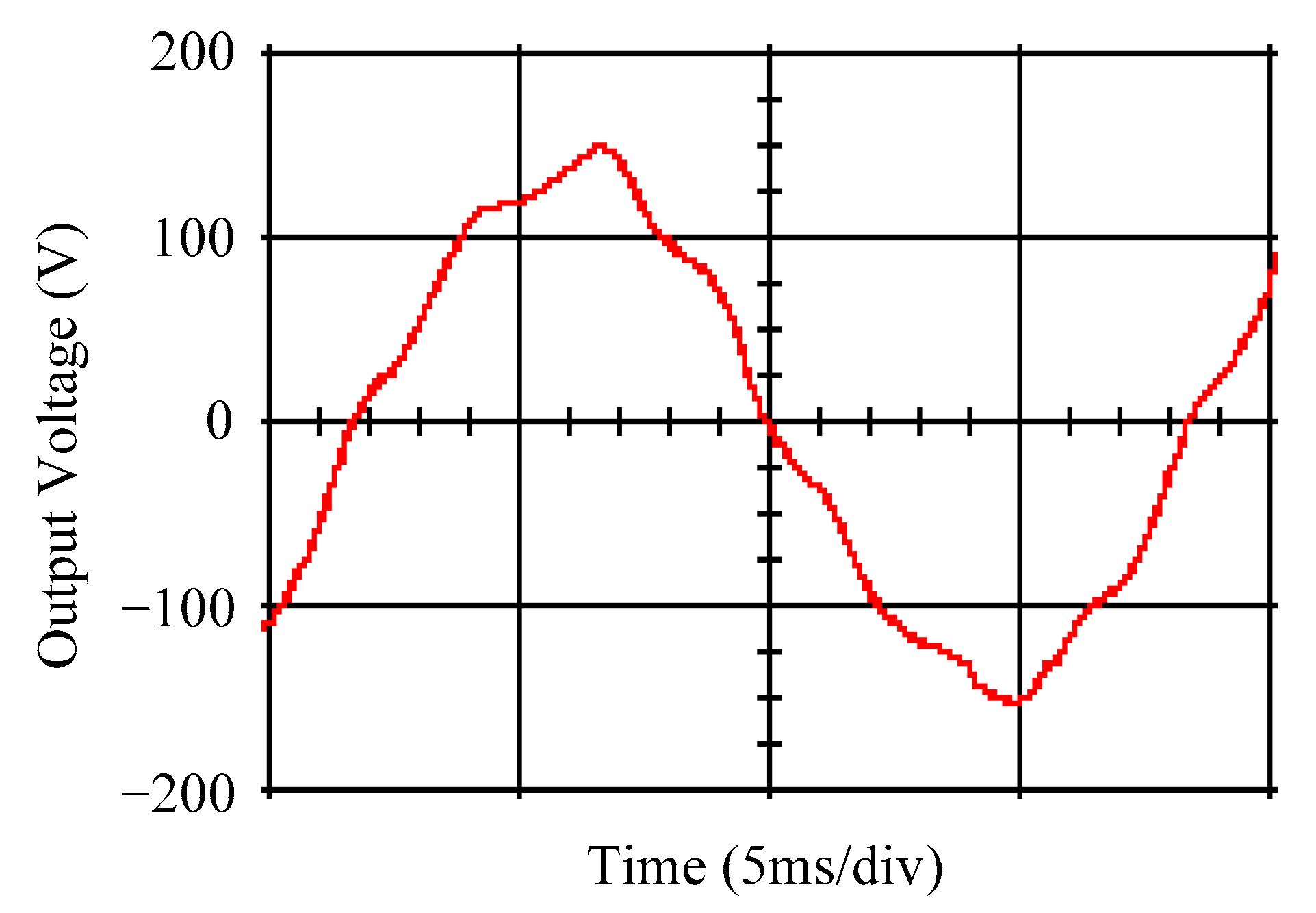
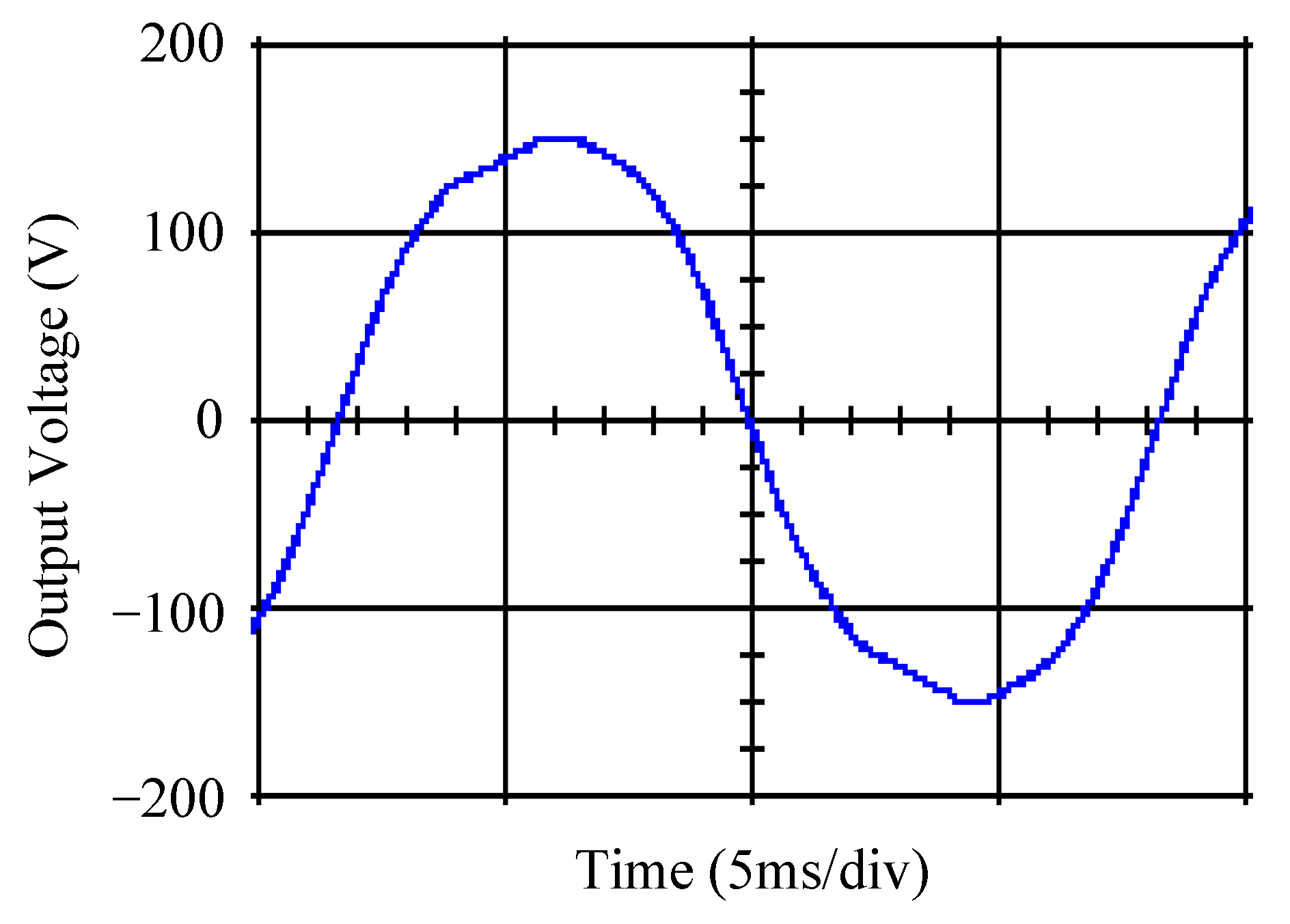
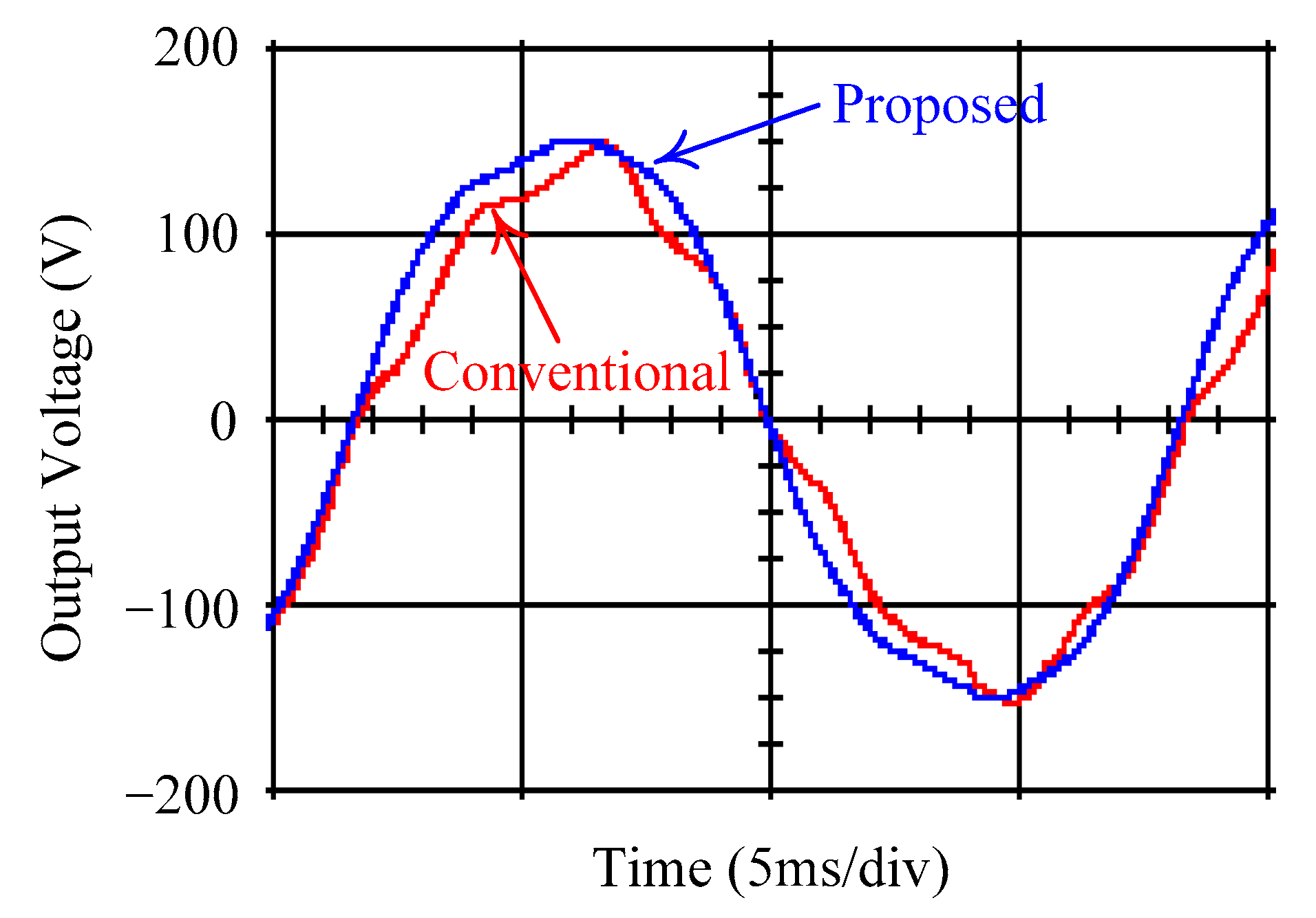
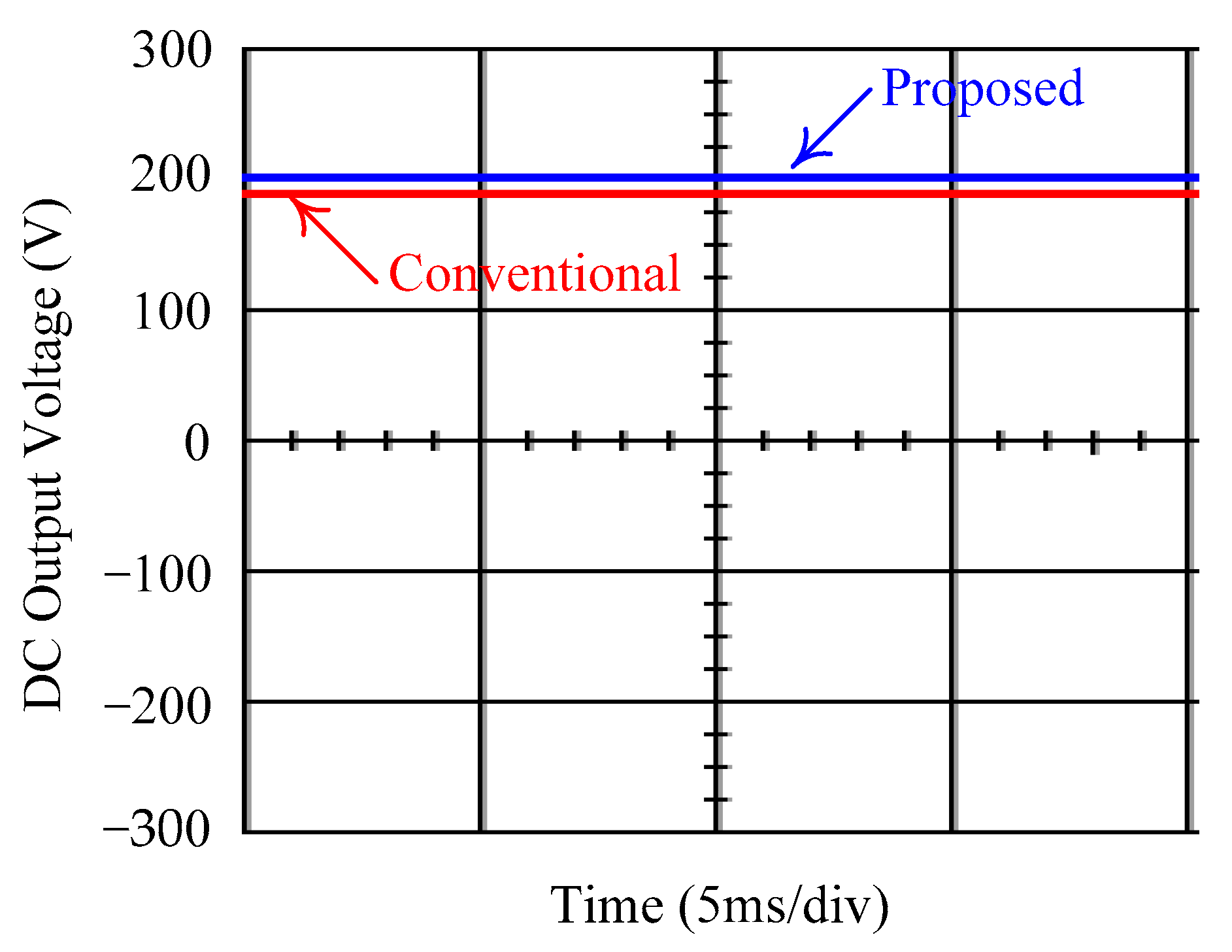
4. Simulation and Experimental Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lobos, F.R.; Bim, E.; Torres, J.P. Power Electronics for Solar and Wind Energy Conversion Systems; Academic Press: London, UK, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Hatti, M. Renewable Energy for Smart and Sustainable Cities; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Victoria, M. Fundamentals of Solar Cells and Photovoltaic Systems Engineering; Academic Press: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.; Ashirvad, M.; Babu, Y.N. An Integrated Boost-Sepic-Ćuk DC-DC Converter with High Voltage Ratio and Reduced Input Current Ripple. Energy Procedia 2017, 117, 984–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, V.F.; Foito, D.; Baptista, F.R.B.; Silva, J.F. A Photovoltaic Generator System with a DC/DC Converter Based on an Integrated Boost-Ćuk Topology. Sol. Energy 2016, 135, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadeesh, I.; Indragandhi, V. Solar Photo Voltaic Based Hybrid CUK, SEPIC, ZETA Converters for Microgrid Applications. e-Prime-Adv. Electr. Eng. Electron. Energy 2023, 6, 100364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubii, C.; El Kafazi, I.; Bannari, R.; El Bhiri, B. A Comparative Study Between Optimization Algorithms of MPPT Algorithms (P&O and In-cremental Conductance Method). In Digital Technologies and Applications, Proceedings of the International Conference on Digital Technologies and Applications, ICDTA 2023, Fez, Morocco, 27–28 January 2023; Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 668, pp. 612–621. [Google Scholar]
- Andrasto, T.; Primadiyono, Y.; Hidayat, S.; Sandyawan, B.; Fauzi, A.R.; Azis, M.K. Incremental Conductance Method in Maximum Power Point Tracking. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1381, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samman, F.A.; Rahmansyah, A.A. Iterative Decremented Step-Size Scanning-Based MPPT Algorithms for Photovoltaic Systems. In Proceedings of the 2017 9th International Conference on Information Technology and Electrical Engineering (ICITEE), Phuket, Thailand, 12–13 October 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Vaidyanathan, S.; Lien, C.H. Applications of Sliding Mode Control in Science and Engineering; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.X.; Gao, Y.B.; Yin, Y.F.; Wang, J.H.; Luo, W.S.; Sun, G.H. Sliding Mode Control Methodology in the Applications of Industrial Power Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Moghaddam, R.K.; Rabbani, M. Methods of Developing Sliding Mode Controllers: Design and Matlab Simulations; Wiley-IEEE Press: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Do, T.A.; Pham, Q.H.; Giap, V.N.; Nguyen, Q.D.; Vu, P. Homogeneous Disturbance Observer Based on Sliding Mode Observer and Controller for T-Type Inverter. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2024, 19, 1671–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Luo, A.; Wang, H.J.; Chen, Y.D.; Li, M.S.; Huang, Y. Adaptive Sliding-Mode Voltage Control for Inverter Operating in Islanded Mode in Microgrid. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2015, 66, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Shen, J. Disturbance Observer and Adaptive Control for Disturbance Rejection of Quadrotor: A Survey. Actuators 2024, 13, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.Y.; Ahn, H.K.; Park, J.; You, K.H. A Modified Exponential Reaching Law for Sliding Mode Control and Its Applications. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2024, 34, 9783–9796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.Y.; Chen, S.Y. Piecewise Fast Multi-Power Reaching Law: Basis for Sliding Mode Control Algorithm. Meas. Control 2020, 53, 1929–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, C.B.; Guo, P.H. Global Terminal Sliding Mode Control with the Quick Reaching Law and Its Application. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 49793–49800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroon, F.; Aamir, M.; Waqar, A. Second-Order Rotating Sliding Mode Control with Composite Reaching Law for Two Level Single Phase Voltage Source Inverters. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 60177–60188. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.H.; Liu, S.Y.; Jiang, S.J.; Zhao, Z.N.; Wang, N.; Liang, X.Y.; Zhang, M.H. A Sliding Mode Control Method Based on Improved Reaching Law for Superbuck Converter in Photovoltaic System. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 574–585. [Google Scholar]
- Benabderrahman, H.E.; Taleb, R.; Helaimi, M.; Chabni, F. Validation of Three Level Solar Inverter Based on Tabu Search Algorithm. In Renewable Energy for Smart and Sustainable Cities: Artificial Intelligence in Renewable Energetic Systems 2, Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Renewable Energetic Systems, Tipaza, Algeria, 24–26 November 2018; Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 62, pp. 429–436. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy, S.; Ergun, H.; Hertem, D.V. A Greedy Algorithm for Optimizing Offshore Wind Transmission Topologies. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2022, 37, 2113–2121. [Google Scholar]
- Musiał, K.; Kotowska, J.; Górnicka, D.; Burduk, A. Tabu Search and Greedy Algorithm Adaptation to Logistic Task. In Computer Information Systems and Industrial Management: 16th IFIP TC8 International Conference, CISIM 2017, Bialystok, Poland, 16–18 June 2017; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 10244, pp. 39–49. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.F.; Yang, Y.J.; Forrest, J.Y. Grey Systems Analysis: Methods, Models and Applications; Springer: Singapore, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.X.; Lin, Y. Review paper: A Briefing to Grey Systems Theory. J. Syst. Sci. Inf. 2014, 2, 178–192. [Google Scholar]
- Tsaur, R.C. Forecasting Analysis by Using Fuzzy Grey Regression Model for Solving Limited Time Series Data. Soft Comput. 2008, 12, 1105–1113. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, X.; Lu, Y. Grey Linear Regression Model and Its Application. Kybernetes 2012, 41, 622–632. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.L.; Li, Z.W.; Song, K.; Guan, D.J.; Zhang, N.; Ye, P.; Li, D.D.; Man, L.K.; Xu, X.L. Forecast and Analysis of Regional Energy Demand Based on Grey Linear Regression Forecast Model. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 645, 012047. [Google Scholar]
- Karthikeyan, M.; Elavarasu, R.; Ramesh, P.; Bharatiraja, C.; Sanjeevikumar, P.; Mihet-Popa, L.; Mitolo, M. A Hybridization of Cuk and Boost Converter Using Single Switch with Higher Voltage Gain Compatibility. Energies 2020, 13, 2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Babu, N.R.; Prabhu, K.R. Analysis of integrated Boost-Cuk high voltage gain DC-DC converter with RBFN MPPT for solar PV application. In Proceedings of the 2017 Innovations in Power and Advanced Computing Technologies (i-PACT), Vellore, India, 21–22 April 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Badawi, A.; Ali, H.; Elzein, I.M.; Zyoud, A.; Abu-Hudrouss, A. Highly Efficient Pure Sine Wave Inverter Using Microcontroller for Photovoltaic Applications. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Symposium on Networks, Computers and Communications (ISNCC), Doha, Qatar, 23–26 October 2023; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Haider, R.; Alam, R.; Yousuf, N.B.; Salim, K.M. Design and Construction of Single Phase Pure Ssine Wave Inverter for Photovoltaic Application. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Informatics, Electronics & Vision (ICIEV), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 18–19 May 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Lademakhi, N.Y.; Shiri, R.; Korayem, A.H. Superiority of Finite Time SDRE and Non-singular Terminal SMC Controller for n-DOF Manipulators. In Proceedings of the 6th RSI International Conference on Robotics and Mechatronics (IcRoM 2018), Tehran, Iran, 23–25 October 2018; pp. 315–321. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.Y.; Guo, G.; Zhang, B. Non-singular Terminal Sliding Mode Heading Control of Surface Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2017 36th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Dalian, China, 26–28 July 2017; pp. 634–638. [Google Scholar]
- IEEE Standard 1159—2019; IEEE Recommended Practice for Monitoring Electric Power Quality. IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019.
- Jung, S.L.; Tzou, Y.Y. Discrete Sliding-Mode Control of a PWM Inverter for Sinusoidal Output Waveform Synthesis with Optimal Sliding Curve. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 1996, 11, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, T.L.; Chen, J.S. UPS inverter Design Using Discrete-Time Sliding Mode Control Scheme. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2002, 49, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Chern, T.L.; Chang, J.; Chen, C.H.; Su, H.T. Microprocessor-Based Modified Integral Discrete Variable-Structure Control for UPS. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1999, 46, 340–347. [Google Scholar]
- IEEE Standard 519—2014; IEEE Recommended Practice and Requirements for Harmonic Control in Electric Power Systems. IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014.
- Zhou, M.H.; Su, H.Y.; Zhou, H.Y.; Wang, L.K.; Liu, Y.; Yu, H.F. Full-Order Terminal Sliding-Mode Control for Soft Open Point. Energies 2023, 15, 4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, B.K.; Mahmud, M.A.; Tousi, B.; Mohammad, F.K. A Step-By-Step Full-Order Sliding Mode Controller Design for Standalone Inverter-Interfaced Cleaner Renewable Energy Sources. Clean. Energy Syst. 2023, 6, 100080. [Google Scholar]
- Sapnken, F.E.; Kibong, M.T.; Tamba, J.G. A Novel Prediction Approach Using Wavelet Transform and Grey Multivariate Convolution Model. MethodsX 2023, 11, 102259. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Deng, Y.; Yuan, H. Forecasting the Natural Gas Supply and Consumption in China Using a Novel Grey Wavelet Support Vector Regressor. Systems 2023, 11, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Cai, G.; Meng, K.; Shen, Z. Application of Grey Feed Forward Back Propagation-Neural Network Model Based on Wavelet Denoising to Predict the Residual Settlement of Goafs. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0281471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| System Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| DC-link voltage () | 200 V |
| Sine wave output voltage () | 110 Vrms |
| Frequency of sine wave output voltage | 60 Hz |
| Filter inductor () | 0.2 mH |
| Filter capacitor () | 20 μF |
| Resistive load () | 12 ohm |
| Switching frequency | 30 kHz |
| Control Parameters | |
| , , , , , and . | |
| Conventional SMC | |||
| Simulations | Abrupt load increasing | Abrupt load removing | Rectified loading |
| Voltage sag | Voltage swell | THD | |
| 69.93 V | 16.14 V | 17.19% | |
| Proposed strategy | |||
| Simulations | Abrupt load increasing | Abrupt load removing | Rectified loading |
| Voltage sag | Voltage swell | THD | |
| 7.96 V | 2.23 V | 0.46% | |
| Conventional SMC | |||
| Experiments | Abrupt load increasing | Abrupt load removing | Rectified loading |
| Voltage sag | Voltage swell | THD | |
| 67.98 V | 19.43 V | 20.54% | |
| Proposed strategy | |||
| Experiments | Abrupt load increasing | Abrupt load removing | Rectified loading |
| Voltage sag | Voltage swell | THD | |
| 10.85 V | 4.42 V | 0.53% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, E.-C.; Sun, Y.-J.; Cheng, C.-A. A New and Improved Sliding Mode Control Design Based on a Grey Linear Regression Model and Its Application in Pure Sine Wave Inverters for Photovoltaic Energy Conversion Systems. Micromachines 2025, 16, 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040377
Chang E-C, Sun Y-J, Cheng C-A. A New and Improved Sliding Mode Control Design Based on a Grey Linear Regression Model and Its Application in Pure Sine Wave Inverters for Photovoltaic Energy Conversion Systems. Micromachines. 2025; 16(4):377. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040377
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, En-Chih, Yeong-Jeu Sun, and Chun-An Cheng. 2025. "A New and Improved Sliding Mode Control Design Based on a Grey Linear Regression Model and Its Application in Pure Sine Wave Inverters for Photovoltaic Energy Conversion Systems" Micromachines 16, no. 4: 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040377
APA StyleChang, E.-C., Sun, Y.-J., & Cheng, C.-A. (2025). A New and Improved Sliding Mode Control Design Based on a Grey Linear Regression Model and Its Application in Pure Sine Wave Inverters for Photovoltaic Energy Conversion Systems. Micromachines, 16(4), 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040377








